Determination of Drug Efflux Pump Efficiency in Drug-Resistant Bacteria Using MALDI-TOF MS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Efflux Pump Modulator PAβN and CCCP Decrease the IC50 against Drugs and Dyes in E. coli
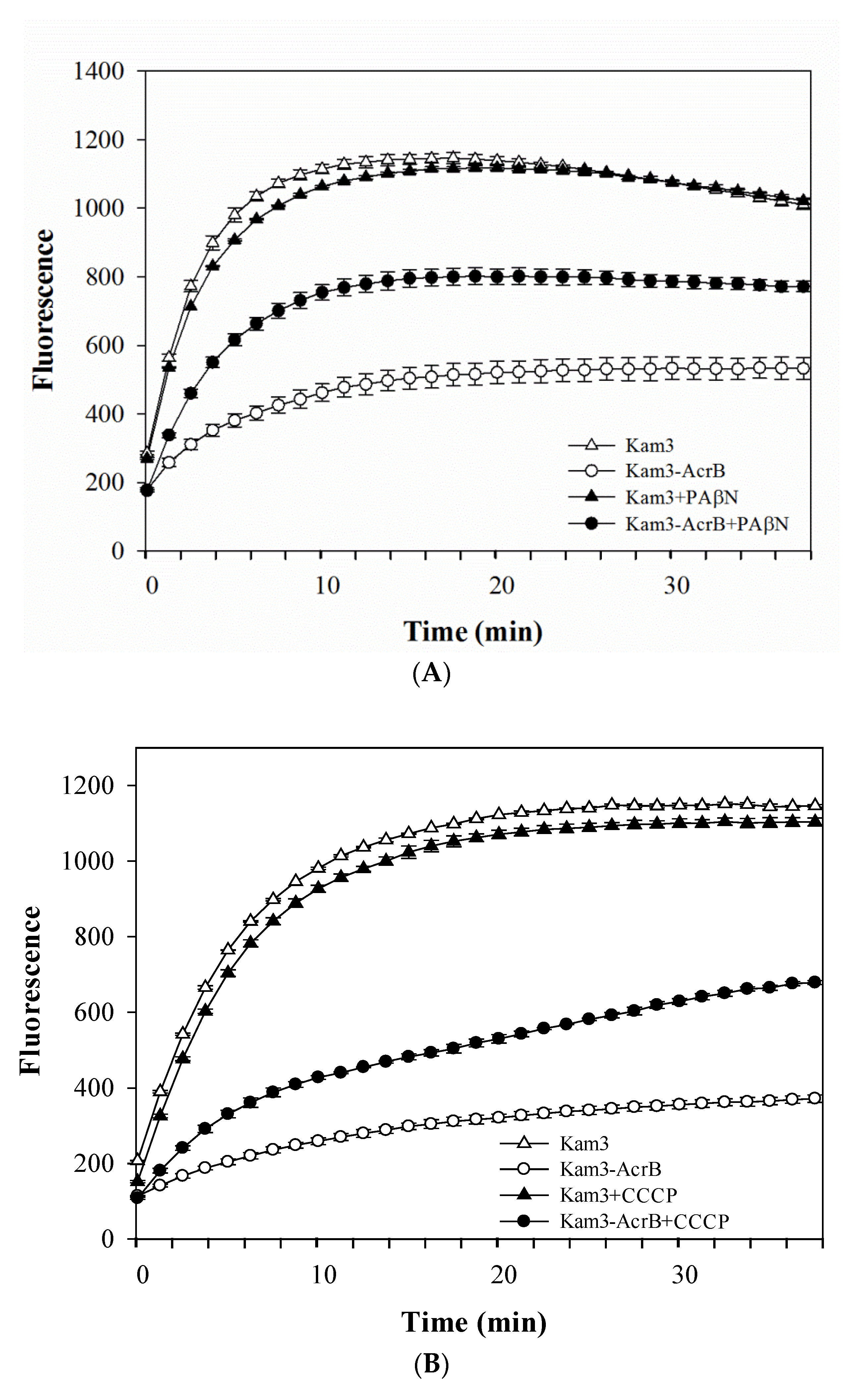
2.2. Dye Accumulation Reduced by Efflux Pump Modulator PAβN and CCCP in E. coli
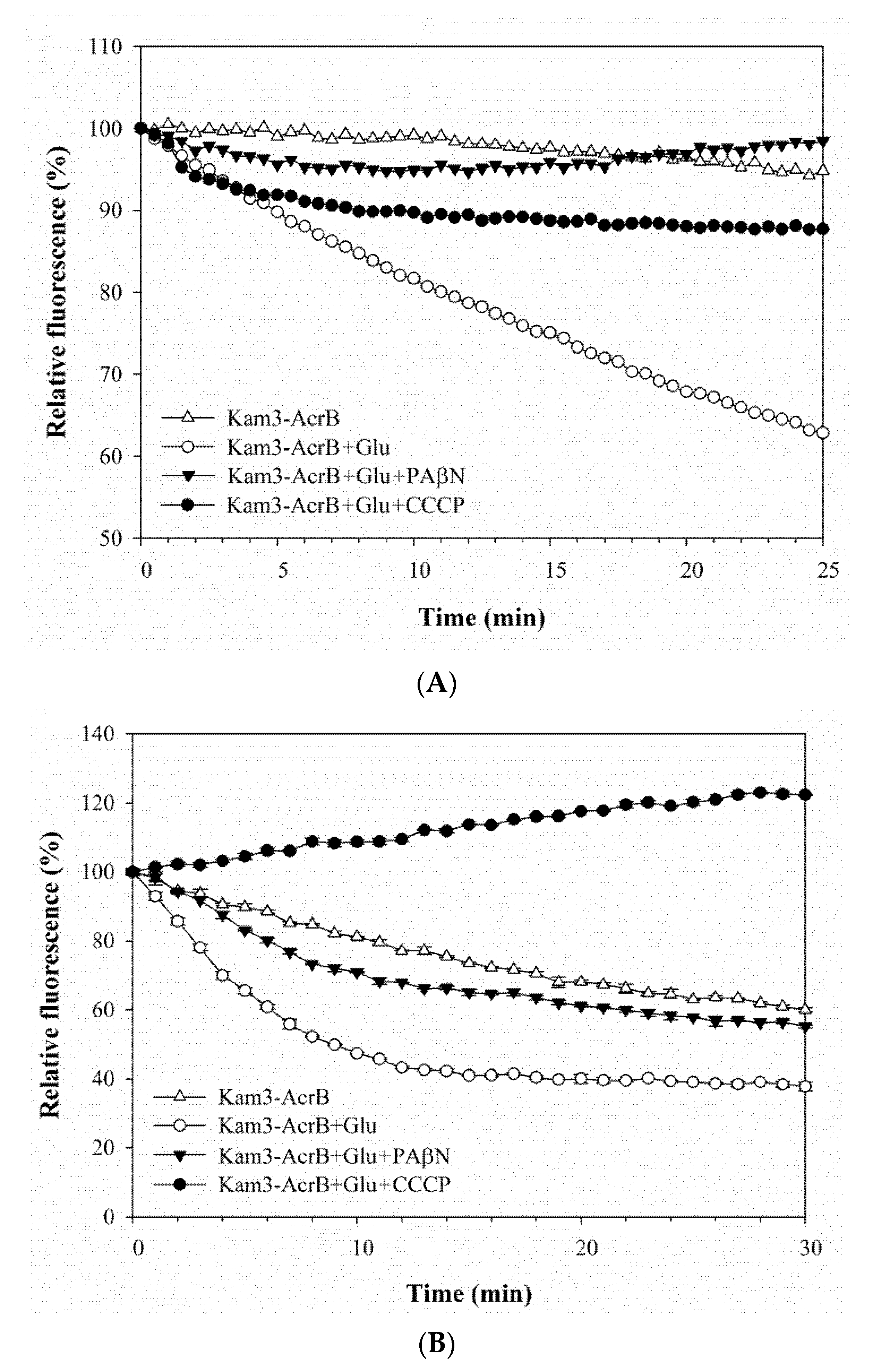
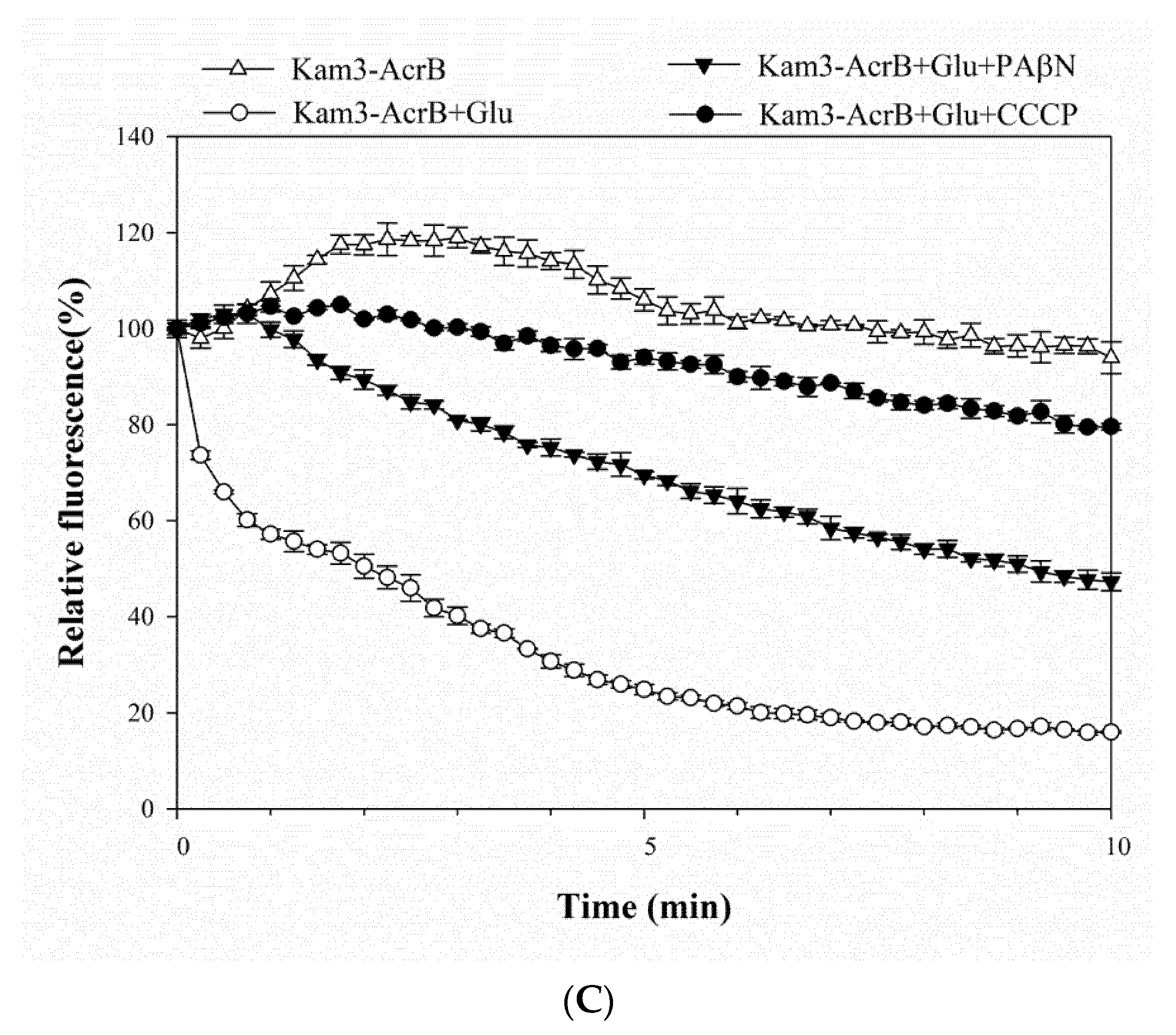
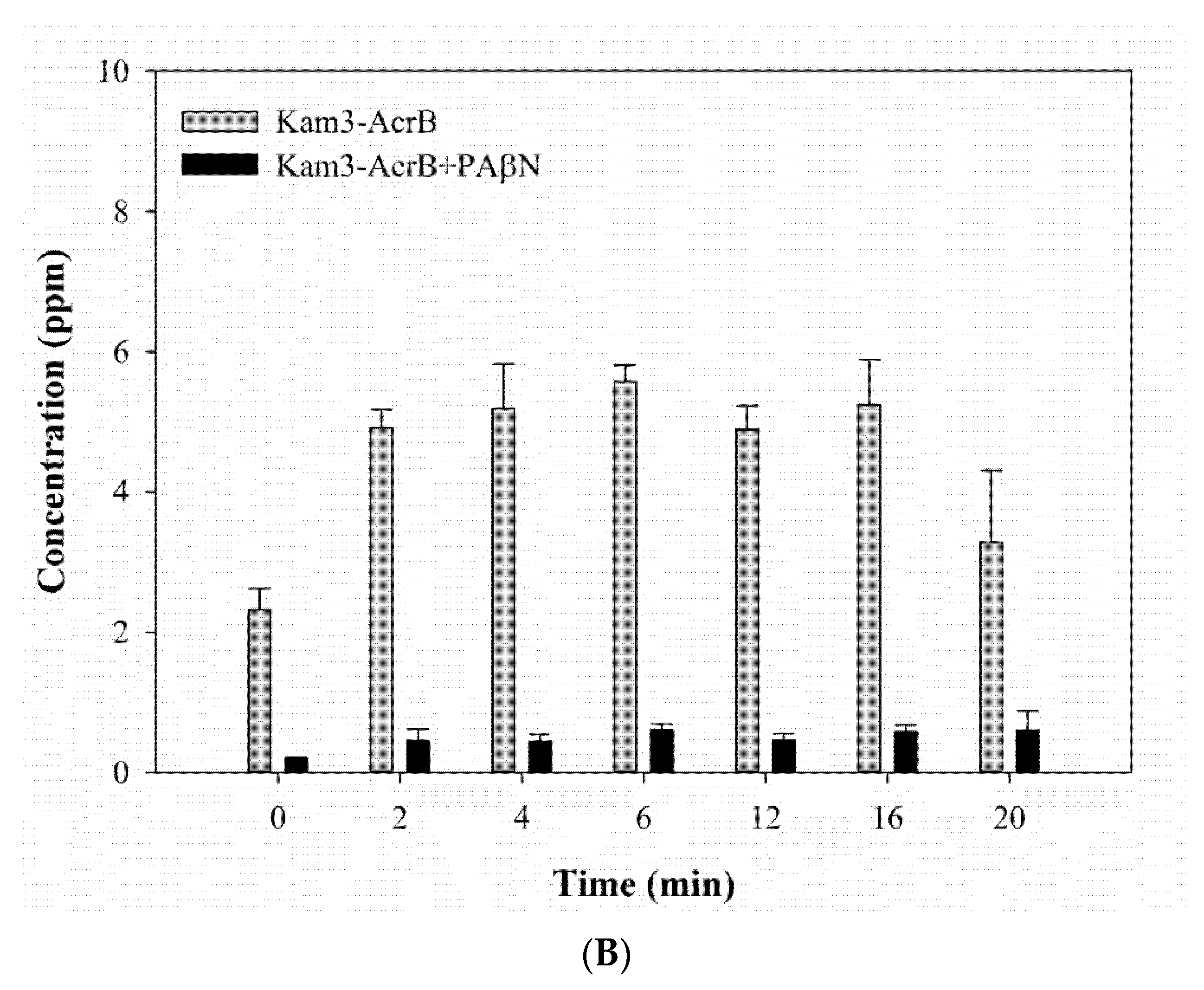
2.3. Pump Efflux Reduced by Efflux Pump Modulator PAβN and CCCP in E. coli
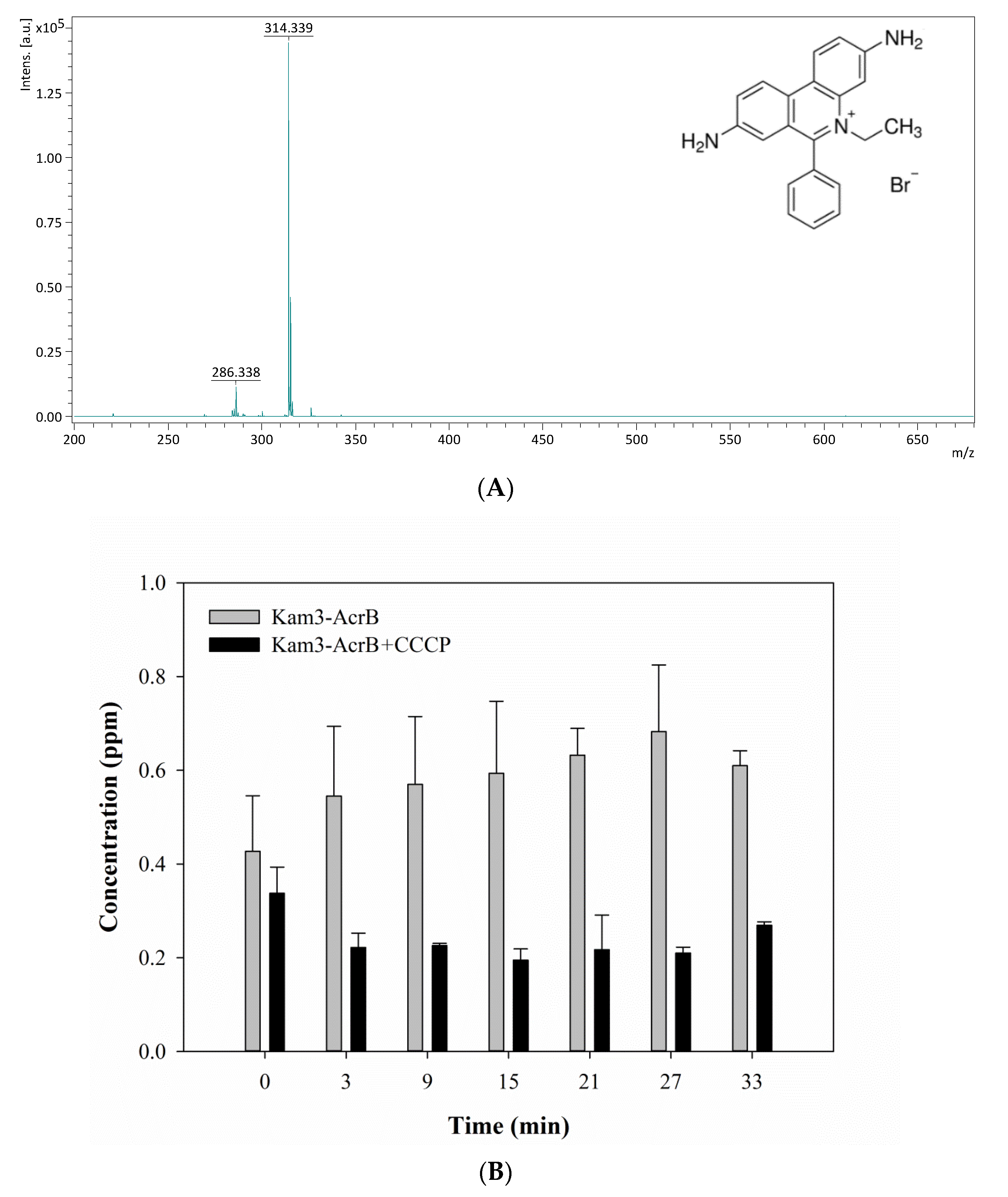
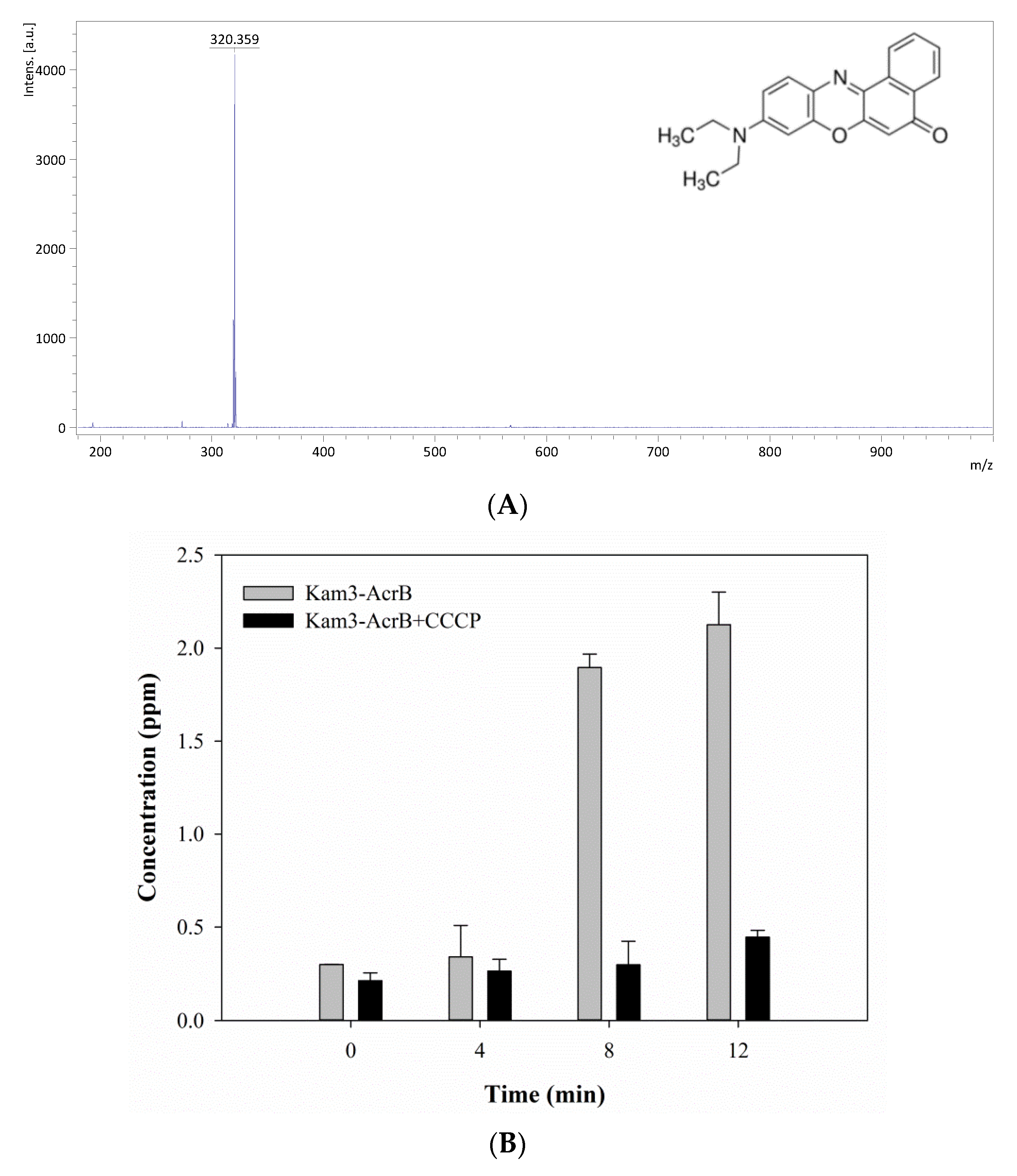
2.4. Measuring the Dye Efflux by Using MALDI-TOF
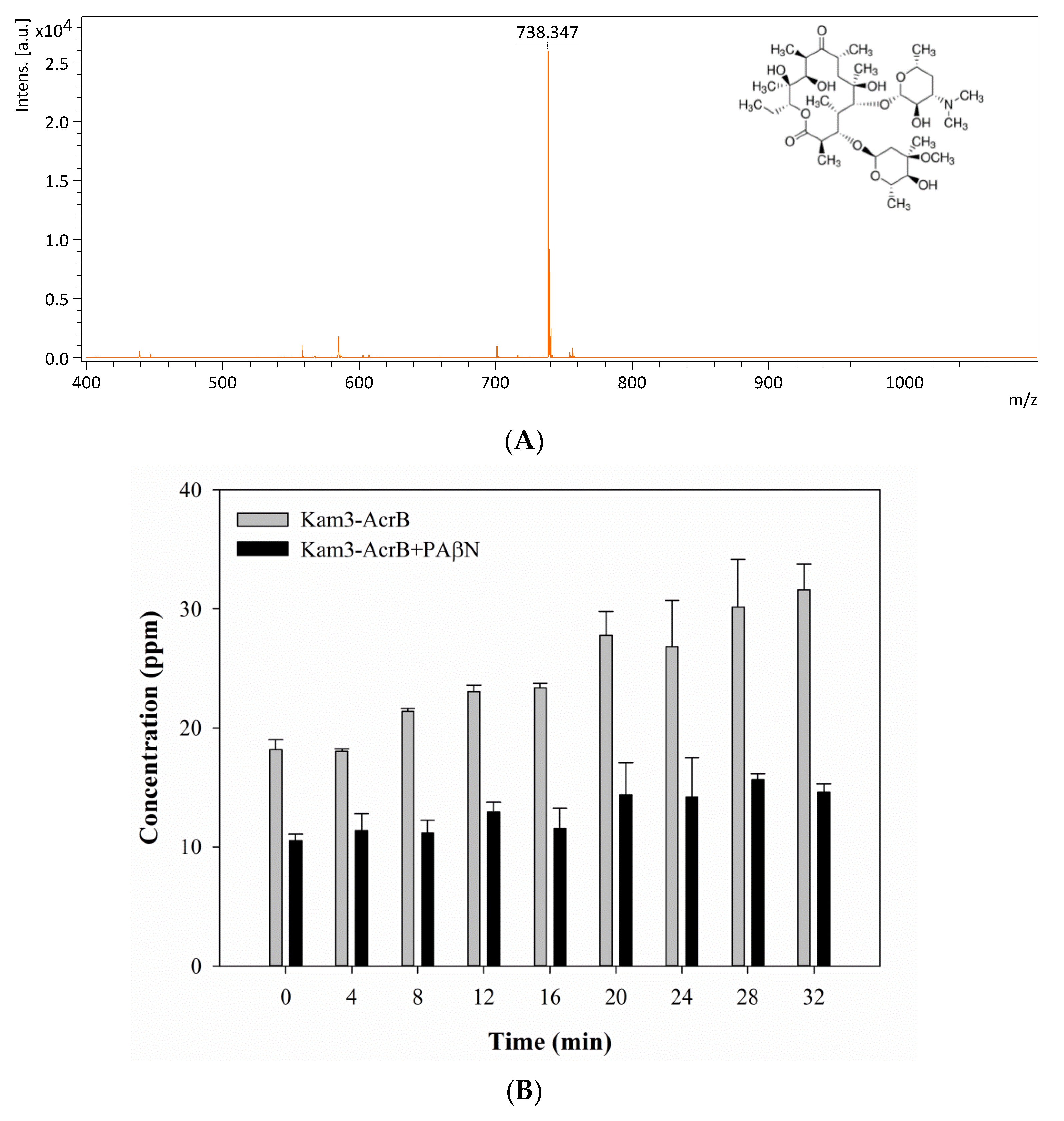
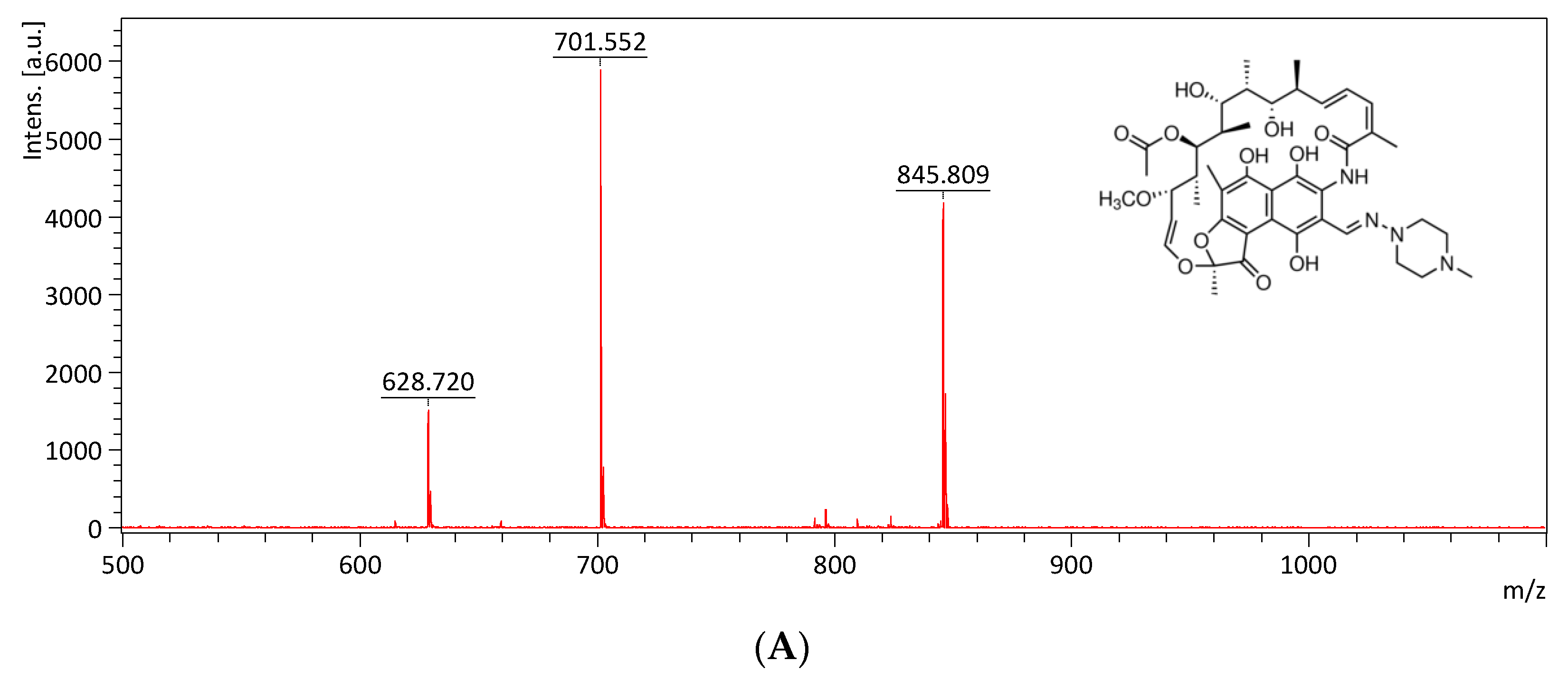
2.5. Monitoring the Drug Efflux by Using MALDI-TOF
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Strains and Plasmids
3.2. Construction of Kam3 Harboring pSYC-acrB Plasmid
3.3. Overexpression, Purification and Identification of Multidrug Transporter AcrB
3.4. Broth Dilution Assay
3.5. Dye Accumulation Assay
3.6. Dye Efflux Assay
3.7. Sample Preparation and Mass Spectrometry Analysis
3.8. Statistics Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, W.J.; Lin, H.J.; Janganan, T.K.; Li, C.Y.; Chin, W.C.; Bavro, V.N.; Lin, H.T.V. ATP-Binding Cassette Transporter VcaM from Vibrio cholerae is Dependent on the Outer Membrane Factor Family for Its Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, D.C.; Johnson, E.; Lewinson, O. ABC transporters: The power to change. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourtesi, C.; Ball, A.R.; Huang, Y.Y.; Jachak, S.M.; Vera, D.M.; Khondkar, P.; Gibbons, S.; Hamblin, M.R.; Tegos, G.P. Microbial efflux systems and inhibitors: Approaches to drug discovery and the challenge of clinical implementation. Open Microbiol. J. 2013, 7, 34–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piddock, L.J.V. Multidrug-resistance efflux pumps-not just for resistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikaido, H. Multidrug efflux pumps of gram-negative bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 5853–5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, J.M.A.; Piddock, L.J.V. How to measure export via bacterial multidrug resistance efflux pumps. Mbio 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Siddiqui, R.; Kazmi, S.U.; Khan, N.A. A simple assay to screen antimicrobial compounds potentiating the activity of current antibiotics. BioMed Res. Int. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otrebska-Machaj, E.; Chevalier, J.; Handzlik, J.; Szymanska, E.; Schabikowski, J.; Boyer, G.; Bolla, J.M.; Kiec-Kononowicz, K.; Pages, J.M.; Alibert, S. Efflux Pump Blockers in Gram-Negative Bacteria: The New Generation of Hydantoin Based-Modulators to Improve Antibiotic Activity. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pumbwe, L.; Piddock, L.J. Identification and molecular characterisation of CmeB, a Campylobacter jejuni multidrug efflux pump. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2002, 206, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baucheron, S.; Imberechts, H.; Chaslus-Dancla, E.; Cloeckaert, A. The AcrB multidrug transporter plays a major role in high-level fluoroquinolone resistance in Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium phage type DT204. Microb. Drug Resist. 2002, 8, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, W.V.; Steinke, P.; Schumacher, A.; Schuster, S.; von Baum, H.; Bohnert, J.A. Effect of 1-(1-naphthylmethyl)-piperazine, a novel putative efflux pump inhibitor, on antimicrobial drug susceptibility in clinical isolates of Escherichia coli. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 57, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomovskaya, O.; Warren, M.S.; Lee, A.; Galazzo, J.; Fronko, R.; Lee, M.; Blais, J.; Cho, D.; Chamberland, S.; Renau, T.; et al. Identification and characterization of inhibitors of multidrug resistance efflux pumps in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Novel agents for combination therapy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaatz, G.W.; Moudgal, V.V.; Seo, S.M.; Kristiansen, J.E. Phenothiazines and thioxanthenes inhibit multidrug efflux pump activity in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, R.; Erwin, A.L. Direct measurement of efflux in Pseudomonas aeruginosa using an environment-sensitive fluorescent dye. Res. Microbiol. 2015, 166, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, N.; Nishino, K.; Yamaguchi, A. Novel macrolide-specific ABC-type efflux transporter in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 5639–5644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paixao, L.; Rodrigues, L.; Couto, I.; Martins, M.; Fernandes, P.; de Carvalho, C.C.; Monteiro, G.A.; Sansonetty, F.; Amaral, L.; Viveiros, M. Fluorometric determination of ethidium bromide efflux kinetics in Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Eng. 2009, 3, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richmond, G.E.; Chua, K.L.; Piddock, L.J.V. Efflux in Acinetobacter baumannii can be determined by measuring accumulation of H33342 (bis-benzamide). J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 1594–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, R.; Morrison, K.D.; Cho, H.J.; Khuu, T. Importance of real-time assays to distinguish multidrug efflux pump-inhibiting and outer membrane-destabilizing activities in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 2015, 197, 2479–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, D.; Perdigão, J.; Portugal, I.; Pieroni, M.; Silva, P.; Couto, I.; Viveiros, M. Efflux activity differentially modulates the levels of isoniazid and rifampicin resistance among multidrug resistant and monoresistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains. Antibiotics 2018, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coldham, N.G.; Webber, M.; Woodward, M.J.; Piddock, L.J. A 96-well plate fluorescence assay for assessment of cellular permeability and active efflux in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium and Escherichia coli. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 1655–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, A.B.; Corder, A.B.; Ling, V. P-glycoprotein-mediated Hoechst 33342 transport out of the lipid bilayer. Eur. J. Biochem. 1997, 250, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babayan, A.; Nikaido, H. In Pseudomonas aeruginosa ethidium bromide does not induce its own degradation or the assembly of pumps involved in its efflux. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 324, 1065–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howitz, K.T.; Bitterman, K.J.; Cohen, H.Y.; Lamming, D.W.; Lavu, S.; Wood, J.G.; Zipkin, R.E.; Chung, P.; Kisielewski, A.; Zhang, L.L.; et al. Small molecule activators of sirtuins extend Saccharomyces cerevisiae lifespan. Nature 2003, 425, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, A.R.; Ettefagh, K.A.; Todd, D.; Cole, P.S.; Egan, J.M.; Foil, D.H.; Graf, T.N.; Schindler, B.D.; Kaatz, G.W.; Cech, N.B. A mass spectrometry-based assay for improved quantitative measurements of efflux pump inhibition. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrabak, J.; Bitar, I.; Papagiannitsis, C.C. Combination of mass spectrometry and DNA sequencing for detection of antibiotic resistance in diagnostic laboratories. Folia Microbiol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, S.; Nakashima, R.; Yamashita, E.; Yamaguchi, A. Crystal structure of bacterial multidrug efflux transporter AcrB. Nature 2002, 419, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobylka, J.; Kuth, M.S.; Muller, R.T.; Geertsma, E.R.; Pos, K.M. AcrB: A mean, keen, drug efflux machine. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, S.S.; Viveiros, M.; Amaral, L.; Couto, I. Multidrug Efflux Pumps in Staphylococcus aureus: An Update. Open Microbiol. J. 2013, 7, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opperman, T.J.; Nguyen, S. Recent advances toward a molecular mechanism of efflux pump inhibition. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opperman, T.J.; Kwasny, S.M.; Kim, H.S.; Nguyen, S.T.; Houseweart, C.; D’Souza, S.; Walker, G.C.; Peet, N.P.; Nikaido, H.; Bowlin, T.L. Characterization of a novel pyranopyridine inhibitor of the AcrAB efflux pump of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 722–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, S.M.; Ruiz, J.; Mendoza, M.C.; Vila, J. In vitro fluoroquinolone-resistant mutants of Salmonella enterica serotype Enteritidis: Analysis of mechanisms involved in resistance. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2003, 22, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimsey, E.M.; Fais, C.; Marshall, R.L.; Ricci, V.; Ciusa, M.L.; Stone, J.W.; Ivens, A.; Malloci, G.; Ruggerone, P.; Vargiu, A.V.; et al. Chlorpromazine and Amitriptyline Are Substrates and Inhibitors of the AcrB Multidrug Efflux Pump. MBio 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takatsuka, Y.; Chen, C.; Nikaido, H. Mechanism of recognition of compounds of diverse structures by the multidrug efflux pump AcrB of Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 6559–6565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakashima, R.; Sakurai, K.; Yamasaki, S.; Nishino, K.; Yamaguchi, A. Structures of the multidrug exporter AcrB reveal a proximal multisite drug-binding pocket. Nature 2011, 480, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Q.; Wei, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, L.L.; Liu, Z.; Lu, J.; Wan, K. Study of efflux pump gene expression in rifampicin-monoresistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis clinical isolates. J. Antibiot. 2015, 68, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Berg van Saparoea, H.B.; Lubelski, J.; van Merkerk, R.; Mazurkiewicz, P.S.; Driessen, A.J. Proton motive force-dependent Hoechst 33342 transport by the ABC transporter LmrA of Lactococcus lactis. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 16931–16938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Whittle, E.E.; Legood, S.W.; Alav, I.; Dulyayangkul, P.; Overton, T.W.; Blair, J.M.A. Flow cytometric analysis of efflux by dye accumulation. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, A.R.; Evans, D.H.; Lee, J.S.; Pulleyblank, D.E. Review: Ethidium fluorescence assay. Part II. Enzymatic studies and DNA-protein interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979, 7, 571–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosa, G.; Focsaneanu, K.S.; McLean, J.R.; McNamee, J.P.; Scaiano, J.C. Photophysical properties of fluorescent DNA-dyes bound to single- and double-stranded DNA in aqueous buffered solution. Photochem. Photobiol. 2001, 73, 585–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Gupta, V.K.; Pathania, R. Efflux pump inhibitors for bacterial pathogens: From bench to bedside. Indian J. Med. Res. 2019, 149, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinana, A.D.; Vargiu, A.V.; May, T.; Nikaido, H. Aminoacyl beta-naphthylamides as substrates and modulators of AcrB multidrug efflux pump. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 1405–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreier, J.; Ruggerone, P. Interaction of antibacterial compounds with RND efflux pumps in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnert, J.A.; Karamian, B.; Nikaido, H. Optimized Nile Red Efflux Assay of AcrAB-TolC Multidrug Efflux System Shows Competition between Substrates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 3770–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucevičius, J.; Lukinavičius, G.; Gerasimaitė, R. The use of hoechst dyes for DNA staining and beyond. Chemosensors 2018, 6, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.L.; Hu, Y.J.; Wang, H.; Yu, B.Q.; Yue, H.L. Molecular Spectroscopy Evidence of Berberine Binding to DNA: Comparative Binding and Thermodynamic Profile of Intercalation. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, J.F.S.; Tintino, S.R.; de Freitas, T.S.; Campina, F.F.; Irwin, R.D.A.; Siqueira-Junior, J.P.; Coutinho, H.D.M.; Cunha, F.A.B. In vitro e in silico evaluation of the inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus efflux pumps by caffeic and gallic acid. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 57, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raherison, S.; Gonzalez, P.; Renaudin, H.; Charron, A.; Bebear, C.; Bebear, C.M. Evidence of active efflux in resistance to ciprofloxacin and to ethidium bromide by Mycoplasma hominis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikaido, H.; Thanassi, D.G. Penetration of lipophilic agents with multiple protonation sites into bacterial cells: Tetracyclines and fluoroquinolones as examples. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1993, 37, 1393–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortimer, P.G.; Piddock, L.J. A comparison of methods used for measuring the accumulation of quinolones by Enterobacteriaceae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1991, 28, 639–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinquin, B.; Maigre, L.; Pinet, E.; Chevalier, J.; Stavenger, R.A.; Mills, S.; Refregiers, M.; Pages, J.M. Microspectrometric insights on the uptake of antibiotics at the single bacterial cell level. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzei, T.; Mini, E.; Novelli, A.; Periti, P. Chemistry and mode of action of macrolides. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1993, 31 (Suppl. SC), 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leclercq, R. Mechanisms of resistance to macrolides and lincosamides: Nature of the resistance elements and their clinical implications. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2002, 34, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, E.A.; Korzheva, N.; Mustaev, A.; Murakami, K.; Nair, S.; Goldfarb, A.; Darst, S.A. Structural mechanism for rifampicin inhibition of bacterial RNA polymerase. Cell 2001, 104, 901–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, E.; Vergalli, J.; Conraux, L.; Taillier, C.; Vassort, A.; Pajovic, J.; Refregiers, M.; Mourez, M.; Pages, J.M. Antibiotics and efflux: Combined spectrofluorimetry and mass spectrometry to evaluate the involvement of concentration and efflux activity in antibiotic intracellular accumulation. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Korzekwa, K.; Elsby, R.; Fenner, K.; Galetin, A.; Lai, Y.; Matsson, P.; Moss, A.; Nagar, S.; Rosania, G.R.; et al. Intracellular Drug Concentrations and Transporters: Measurement, Modeling, and Implications for the Liver. Clin. Pharm. 2013, 94, 126–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, J.J. Principles and applications of liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry in clinical biochemistry. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2009, 30, 19–34. [Google Scholar]
- Morita, Y.; Kodama, K.; Shiota, S.; Mine, T.; Kataoka, A.; Mizushima, T.; Tsuchiya, T. NorM, a putative multidrug efflux protein, of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and its homolog in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1998, 42, 1778–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.J.; Lin, H.J.; Hsu, P.H.; Lai, M.; Chiu, J.Y.; Lin, H.T.V. Brown and red seaweeds serve as potential efflux pump inhibitors for drug-resistant Escherichia coli. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, R.; Ferrari, A.; Rijnbrand, R.; Erwin, A.L. A Fluorescent Microplate Assay Quantifies Bacterial Efflux and Demonstrates Two Distinct Compound Binding Sites in AcrB. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 2388–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Drugs and Dyes | Kam3-AcrB IC50 (μg/mL) | Kam3-AcrB + PAβN | Kam3-AcrB + CCCP | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 (μg/mL) | MF | IC50 (μg/mL) | MF | ||
| Macrolide | |||||
| Erythromycin | 250 | 31.25 | 8 | 31.25 | 8 |
| Clarithromycin | 87.5 | 21.87 | 4 | 3.5 | 25 |
| Quinolone | |||||
| Norfloxacin | 1.56 | 1.56 | 1 | 0.015 | 100 |
| Tetracycline | |||||
| Tetracycline | 0.39 | 0.16 | 2 | 0.16 | 2 |
| Rifampicin | 1.25 | 0.019 | 64 | 1.25 | 1 |
| Dyes | |||||
| Hoechst 33342 | 15.625 | 7.815 | 2 | 0.488 | 32 |
| Ethidium bromide | 100 | 50 | 2 | 25 | 4 |
| Nile red | >16 | >16 | 1 | >16 | 1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, W.-J.; Lin, H.-J.; Hsu, P.-H.; Lin, H.-T.V. Determination of Drug Efflux Pump Efficiency in Drug-Resistant Bacteria Using MALDI-TOF MS. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9100639
Lu W-J, Lin H-J, Hsu P-H, Lin H-TV. Determination of Drug Efflux Pump Efficiency in Drug-Resistant Bacteria Using MALDI-TOF MS. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(10):639. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9100639
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Wen-Jung, Hsuan-Ju Lin, Pang-Hung Hsu, and Hong-Ting Victor Lin. 2020. "Determination of Drug Efflux Pump Efficiency in Drug-Resistant Bacteria Using MALDI-TOF MS" Antibiotics 9, no. 10: 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9100639
APA StyleLu, W.-J., Lin, H.-J., Hsu, P.-H., & Lin, H.-T. V. (2020). Determination of Drug Efflux Pump Efficiency in Drug-Resistant Bacteria Using MALDI-TOF MS. Antibiotics, 9(10), 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9100639






