New Urea Derivatives as Potential Antimicrobial Agents: Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, and Molecular Docking Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
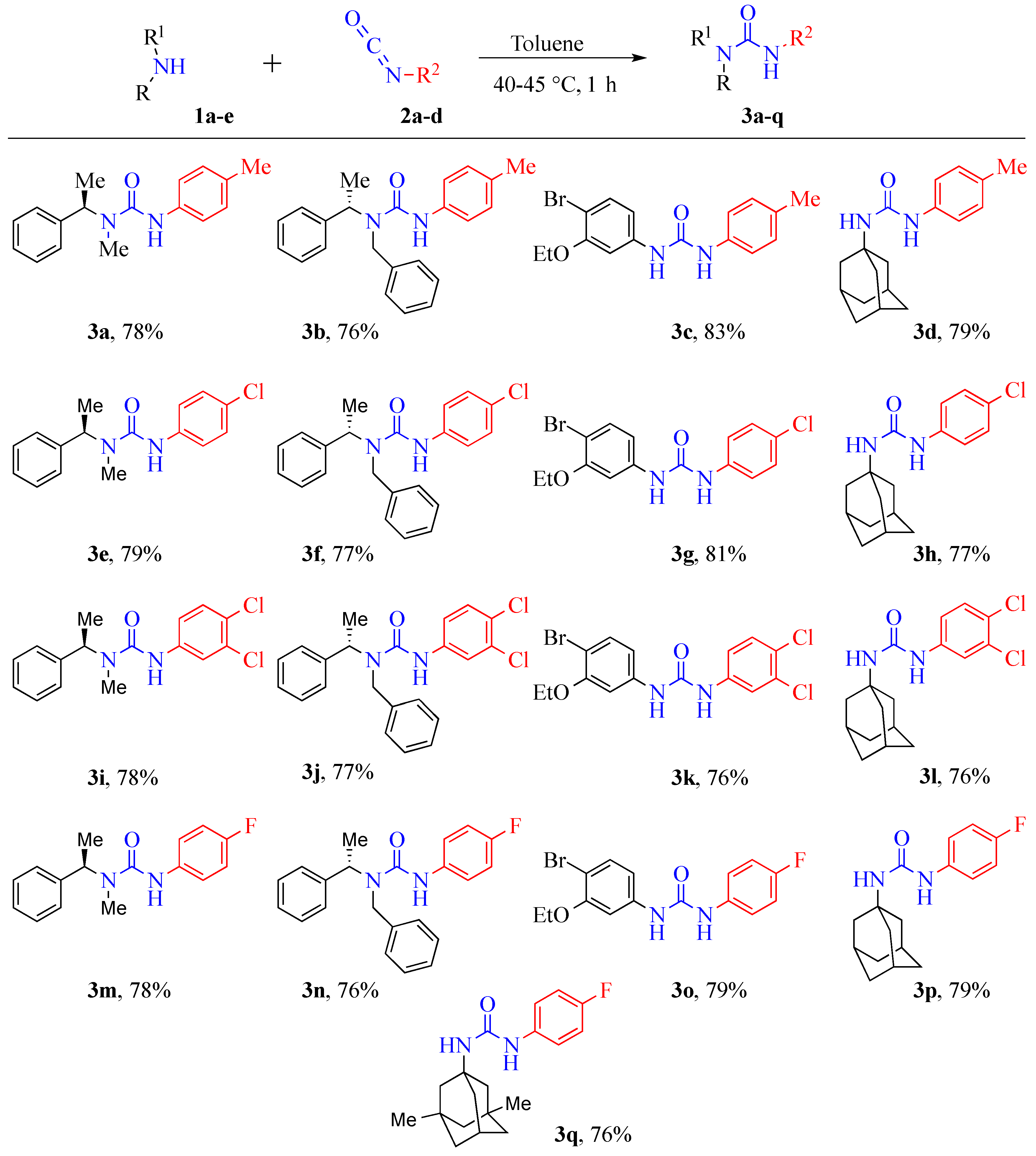
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Spectroscopic Characterization
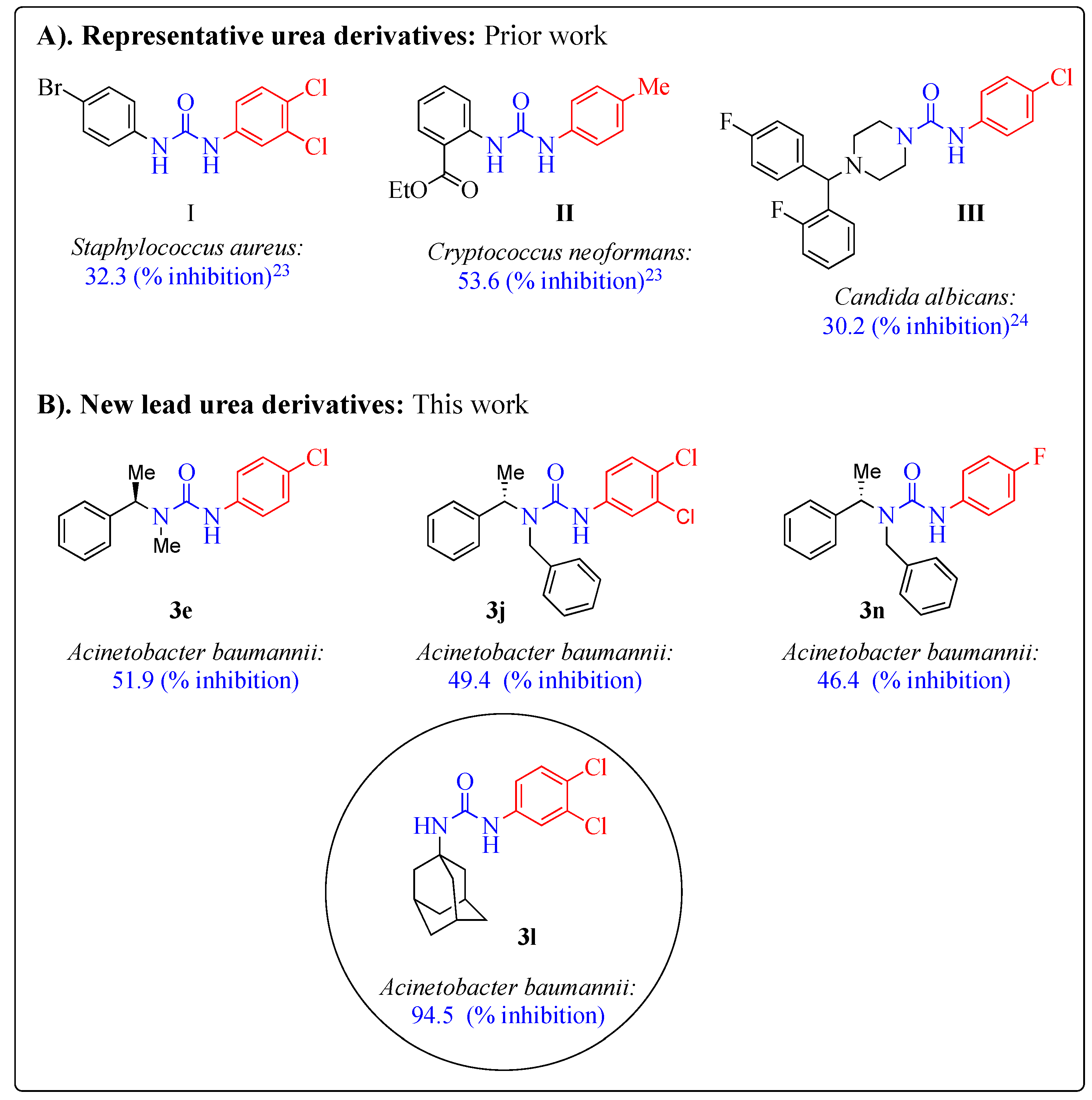
2.3. Antimicrobial Activity
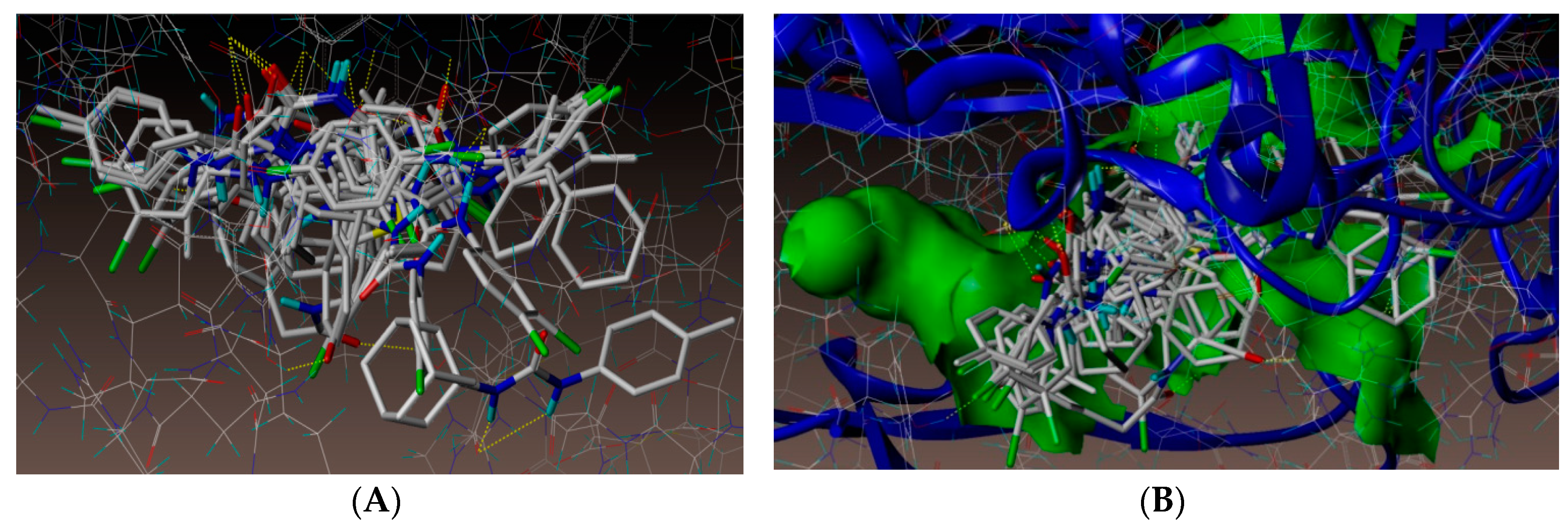
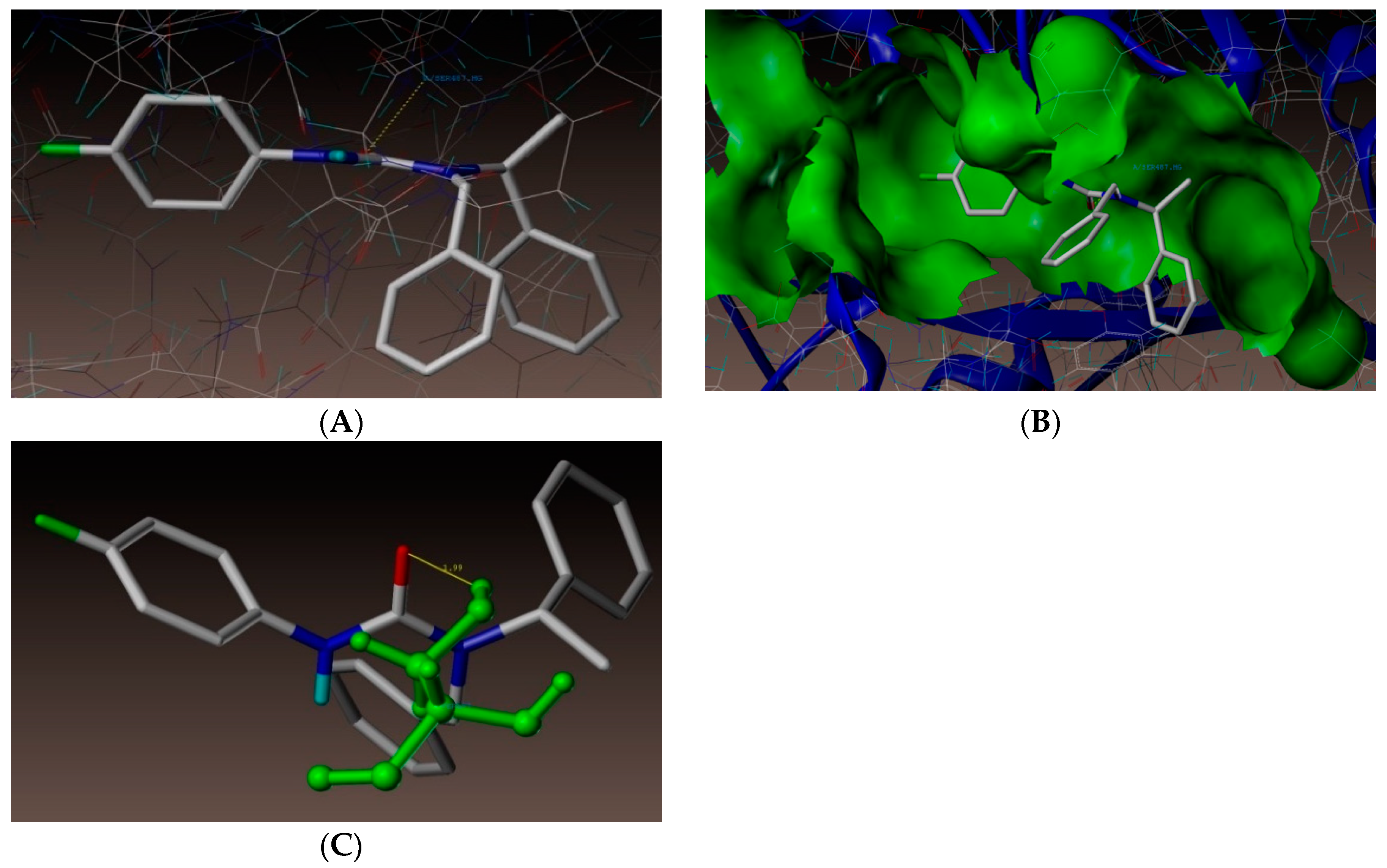
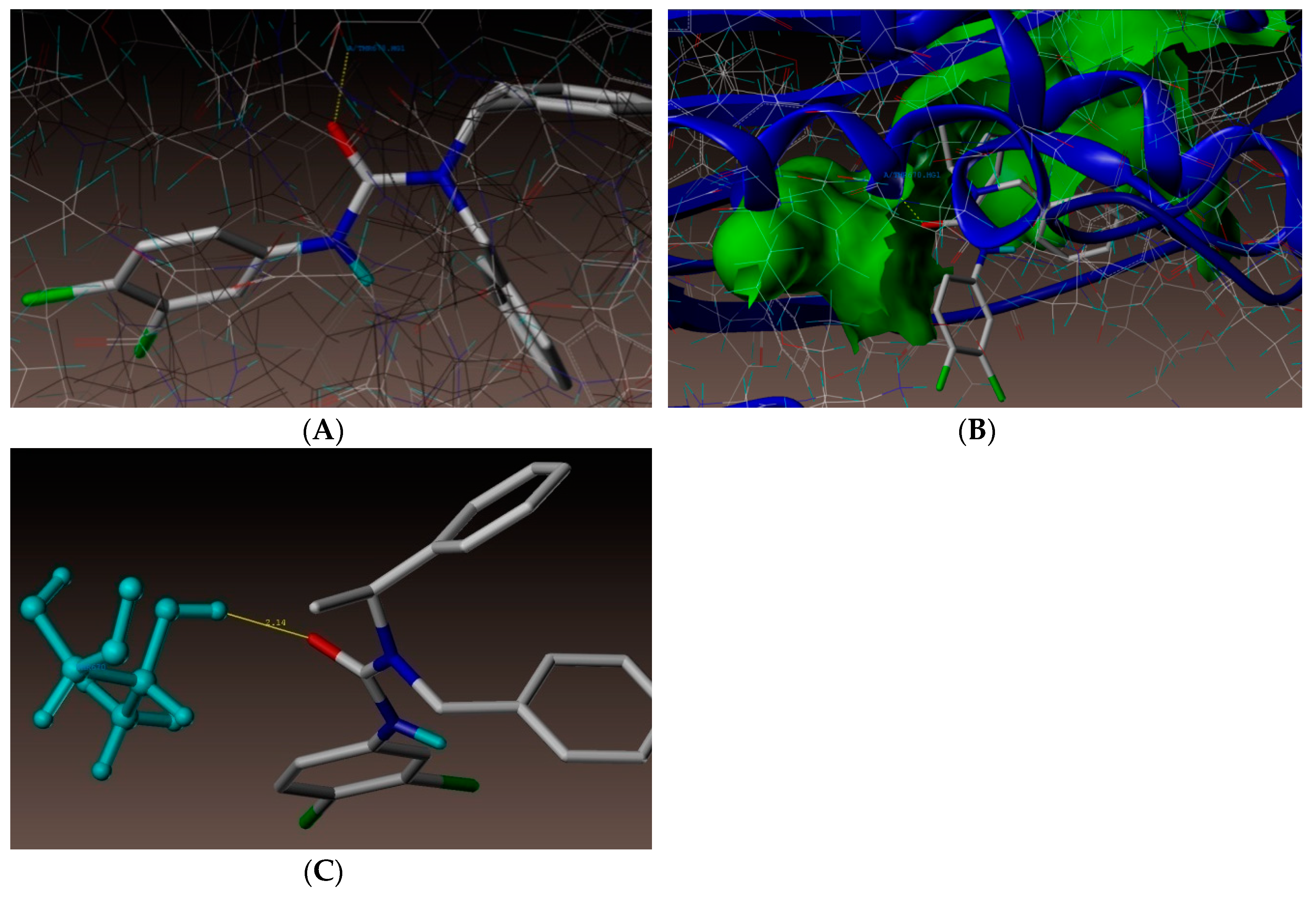
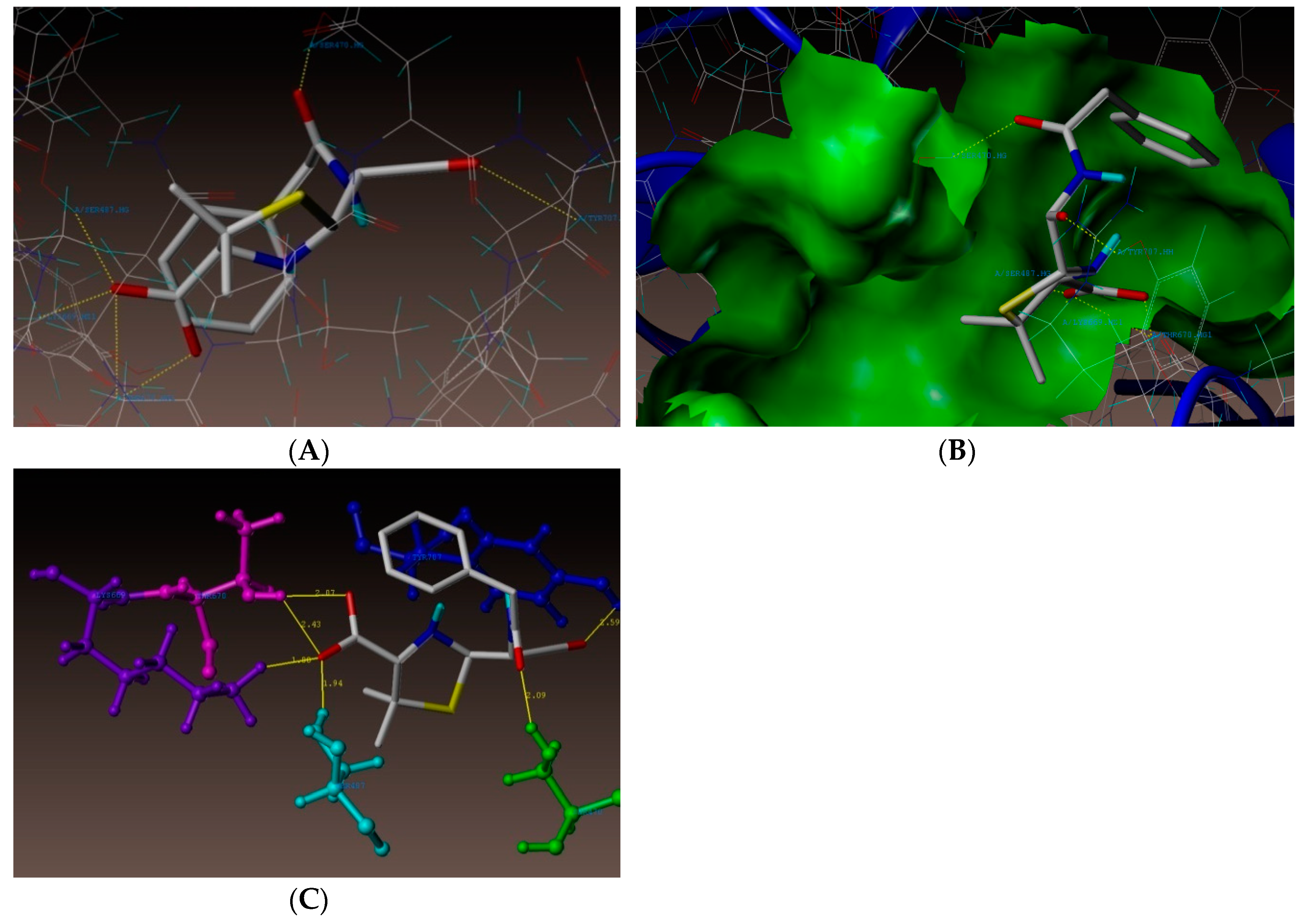
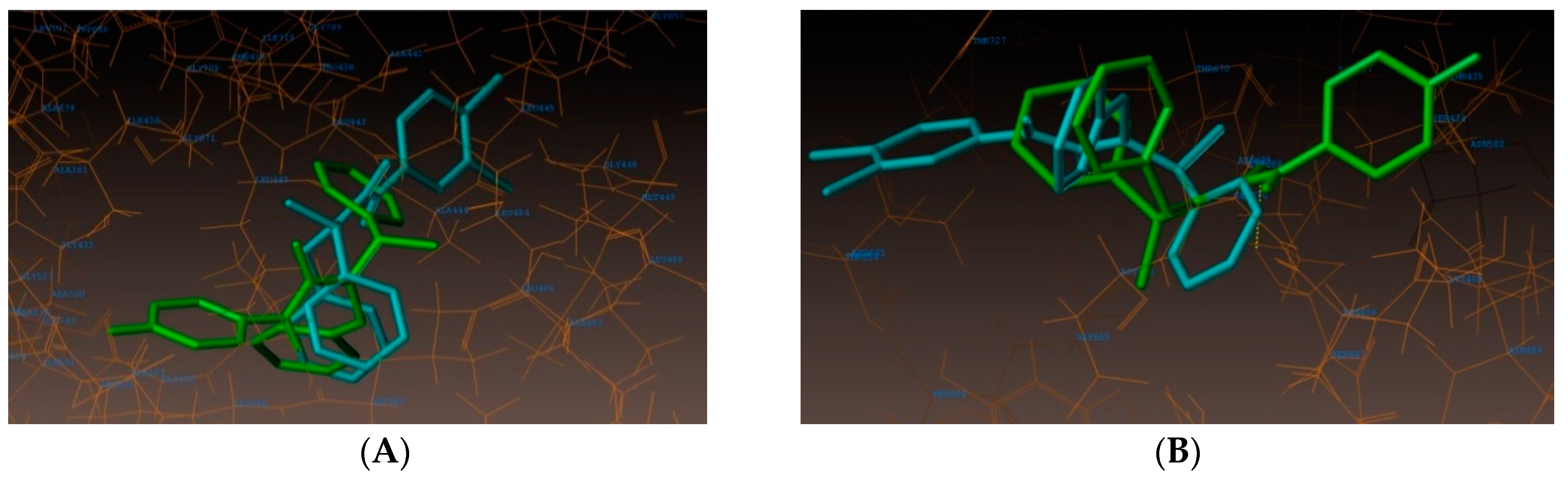
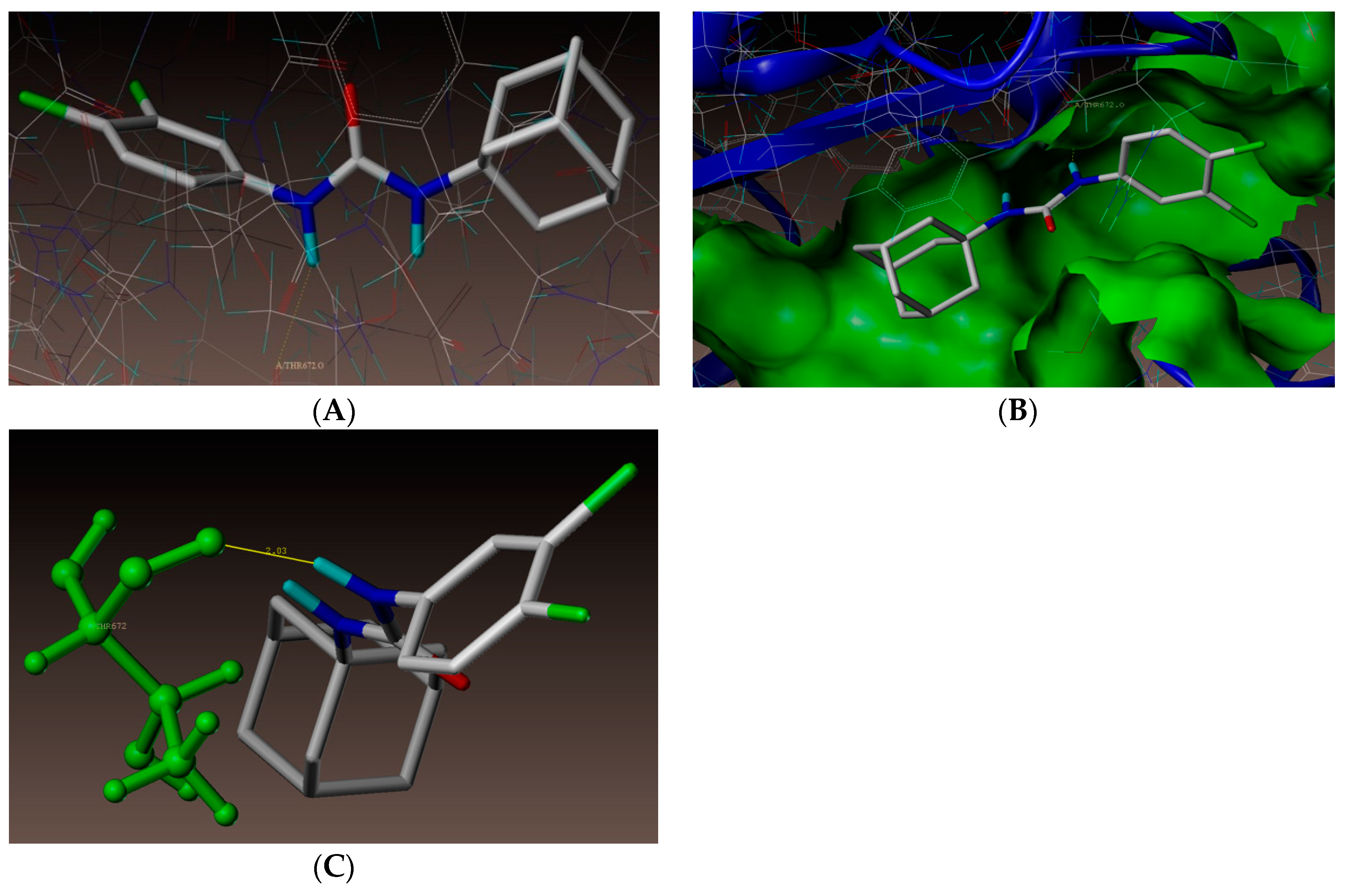
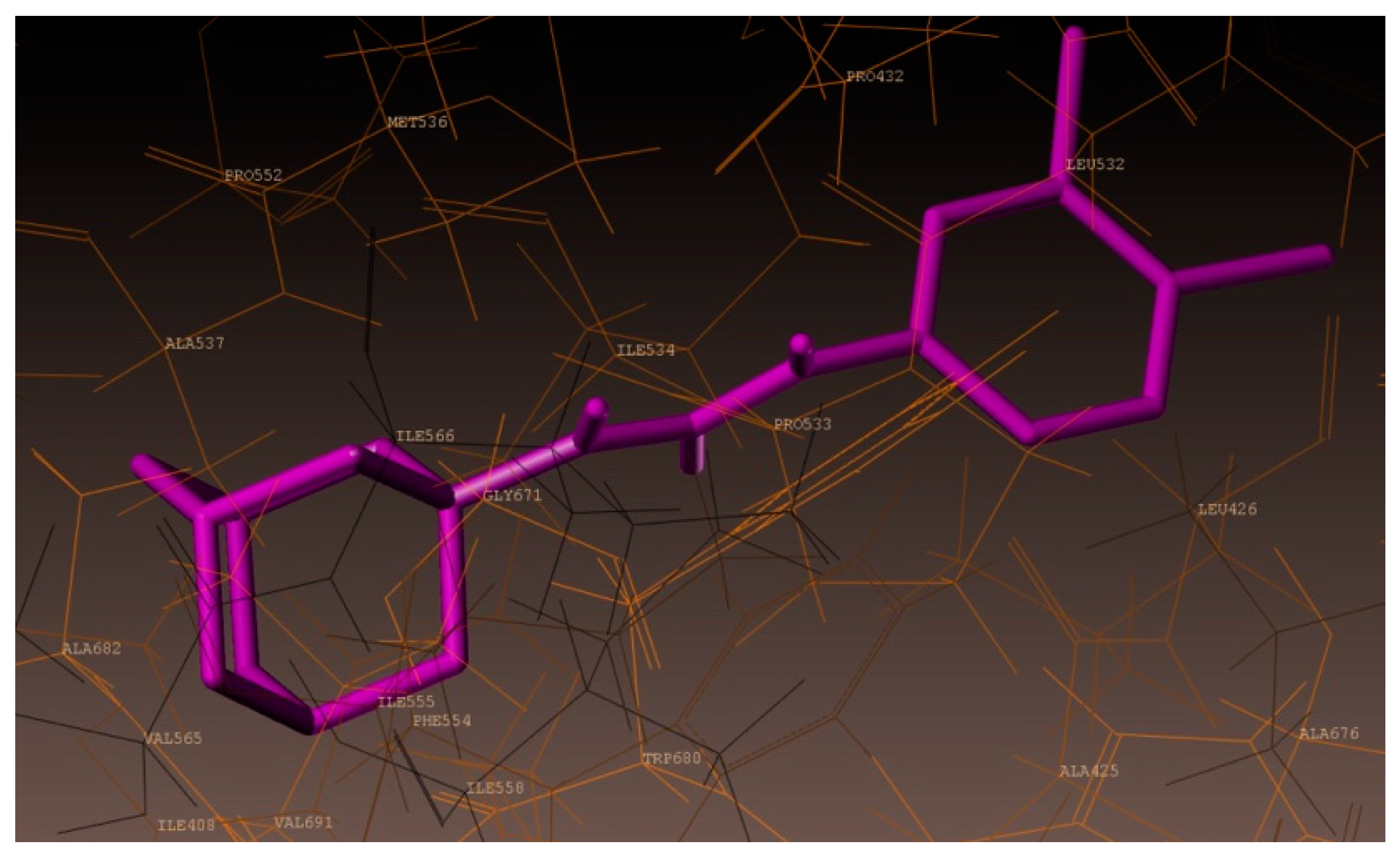
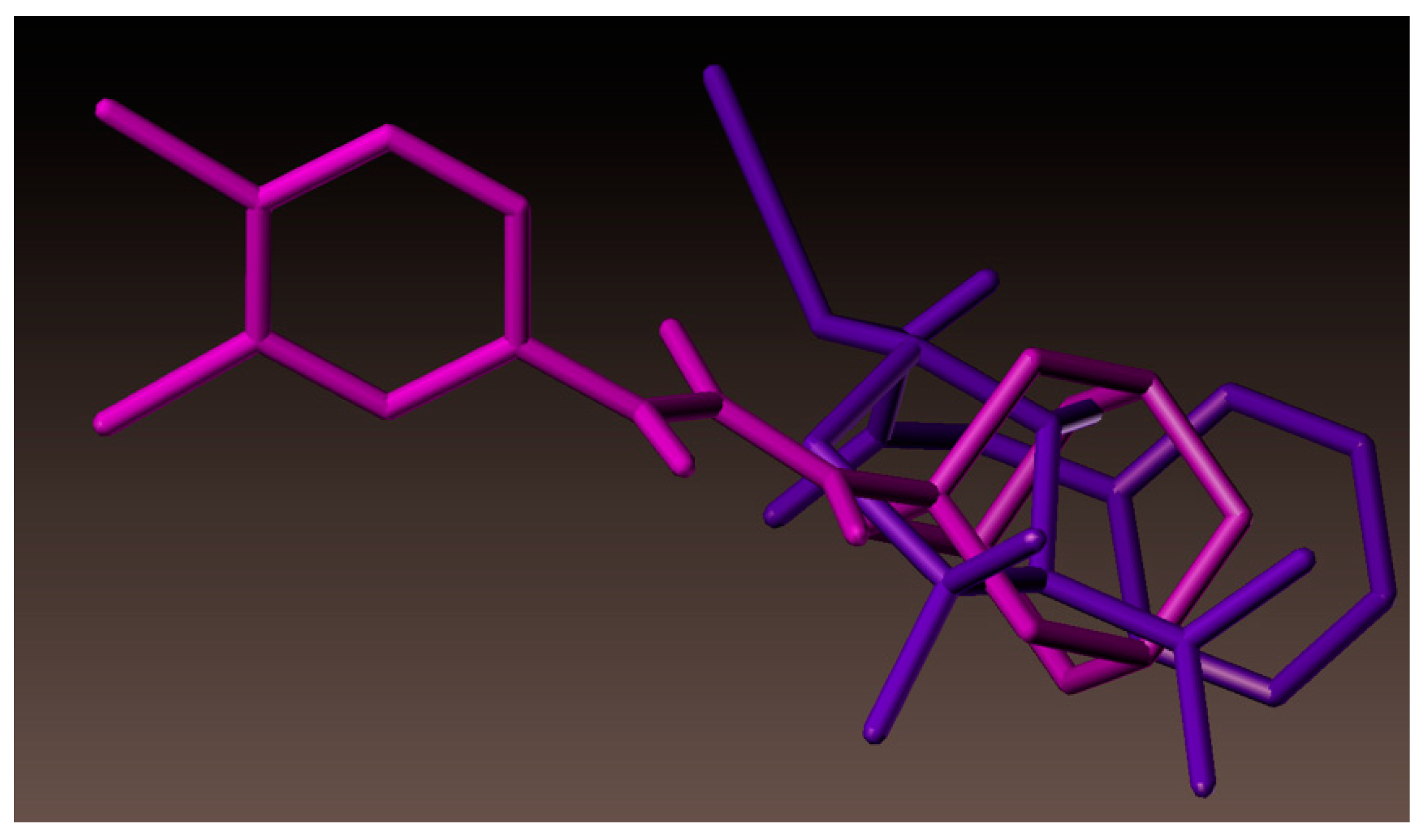
2.4. Molecular Docking Studies
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Consideration
3.2. Syntheses
3.2.1. General Experimental Procedure for the Synthesis of Urea Derivatives
Synthesis of (R)-1-methyl-1-(1-phenylethyl)-3-(p-tolyl)urea (3a)
Synthesis of (S)-1-benzyl-1-(1-phenylethyl)-3-(p-tolyl)urea (3b)
Synthesis of 1-(4-bromo-3-ethoxyphenyl)-3-(p-tolyl)urea (3c)
Synthesis of 1-((3s,5s,7s)-adamantan-1-yl)-3-(p-tolyl)urea (3d)
Synthesis of (R)-3-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-1-(1-phenylethyl)urea (3e)
Synthesis of (S)-1-benzyl-3-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(1-phenylethyl)urea (3f)
Synthesis of 1-(4-bromo-3-ethoxyphenyl)-3-(4-chlorophenyl)urea (3g)
Synthesis of 1-((3S,5S,7S)-adamantan-1-yl)-3-(4-chlorophenyl)urea (3h)
Synthesis of (R)-3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1-methyl-1-(1-phenylethyl)urea (3i)
Synthesis of (S)-1-benzyl-3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1-(1-phenylethyl)urea (3j)
Synthesis of 1-(4-bromo-3-ethoxyphenyl)-3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)urea (3k)
Synthesis of 1-((3S,5S,7S)-adamantan-1-yl)-3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)urea (3l)
Synthesis of (R)-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-methyl-1-(1-phenylethyl)urea (3m)
Synthesis of (S)-1-benzyl-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(1-phenylethyl)urea (3n)
Synthesis of 1-(4-bromo-3-ethoxyphenyl)-3-(4-fluorophenyl)urea (3o)
Synthesis of 1-((3S,5S,7S)-adamantan-1-yl)-3-(4-fluorophenyl)urea (3p)
Synthesis of 1-((3R,5S,7R)-3,5-dimethyladamantan-1-yl)-3-(4-fluorophenyl)urea (3q)
3.3. Antimicrobial Studies
3.3.1. Antimicrobial Assay
Procedure
Analysis
3.3.2. Antifungal Assay
Procedure
Analysis
3.4. Docking Simulations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Casadevall, A. Fungal Diseases in the 21st century: The near and far horizons. Pathog. Immun. 2018, 3, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, I.M. Coping with antibiotic resistance: The impending crisis. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2010, 36, S1–S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piddock, L.J. The crisis of no new antibiotics—What is the way forward? Lancet Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padiyara, P.; Inoue, H.; Sprenger, M. Global governance mechanisms to address antimicrobial resistance. Infect. Dis. Res. Treat. 2018, 11, 1178633718767887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chattopadhyay, M.K.; Chakraborty, R.; Grossart, H.P.; Reddy, G.S.; Jagannadham, M.V. Antibiotic resistance of bacteria. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 501658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, J.M.; Webber, M.A.; Baylay, A.J.; Ogbolu, D.O.; Piddock, L.J. Molecular mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schillaci, D.; Spano, V.; Parrino, B.; Carbone, A.; Montalbano, A.; Barraja, P.; Diana, P.; Cirrincione, G.; Cascioferro, S. Pharmaceutical approaches to target antibiotic resistance mechanisms. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 8268–8297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bush, K.; Pucci, M.J. New antimicrobial agents on the horizon. Biochem. Pharm. 2011, 82, 1528–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayana, B.; Ashalatha, B.; Raj, K.; Kumari, N.S. Synthesis of 3-amino-2-methyl/ethyl-5, 6, 7, 8-tetrahydro [1] benzothieno [2, 3-d] pyrimidin-4 (3H)-one and its Schiff bases as possible antimicrobial and non-steroidal antiinflammatory agents. Indian J. Chem. 2006, 45B, 2696–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rahman, A.E.; Bakhite, E.A.; Al-Taifi, E.A. Synthesis and Antimicrobial Activity of New Pyridothienopyrimidines and Pyridothienotriazines. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2002, 49, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayana, B.; Vijaya Raj, K.K.; Ashalatha, B.V.; Kumari, N.S.; Sarojini, B.K. Synthesis of some new 5-(2-substituted-1,3-thiazol-5-yl)-2-hydroxy benzamides and their 2-alkoxy derivatives as possible antifungal agents. Eur. J Med. Chem. 2004, 39, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isloor, A.M.; Kalluraya, B.; Shetty, P. Regioselective reaction: Synthesis, characterization and pharmacological studies of some new Mannich bases derived from 1,2,4-triazoles. Eur. J Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 3784–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, S.; Claffey, J.; Deally, A.; Hogan, M.; Gleeson, B.; Menéndez Méndez, L.M.; Müller-Bunz, H.; Paradisi, F.; Tacke, M. Synthesis, cytotoxicity and antibacterial studies of p-methoxybenzyl-substituted and benzyl-substituted N-heterocyclic carbene-silver complexes. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 1020–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.; Deally, A.; Gleeson, B.; Muller-Bunz, H.; Paradisi, F.; Tacke, M. Novel benzyl-substituted N-heterocyclic carbene-silver acetate complexes: Synthesis, cytotoxicity and antibacterial studies. Metallomics 2011, 3, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, S.A.; Patil, S.A.; Patil, R. Medicinal applications of (benz)imidazole- and indole-based macrocycles. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2017, 89, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, S.A.; Patil, S.A.; Patil, R.; Keri, R.S.; Budagumpi, S.; Balakrishna, G.R.; Tacke, M. N-heterocyclic carbene metal complexes as bio-organometallic antimicrobial and anticancer drugs. Future Med. Chem. 2015, 7, 1305–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, V.; Barragan, E.; Patil, S.A.; Patil, S.A.; Bugarin, A. Direct synthesis and antimicrobial evaluation of structurally complex chalcones. Chem. Sel. 2016, 1, 3647–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahini, C.R.; Achar, G.; Budagumpi, S.; Müller–Bunz, H.; Tacke, M.; Patil, S.A. Benzoxazole and dioxolane substituted benzimidazole–based N –heterocyclic carbene–silver(I) complexes: Synthesis, structural characterization and in vitro antimicrobial activity. J. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 868, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahini, C.R.; Achar, G.; Budagumpi, S.; Tacke, M.; Patil, S.A. Non-symmetrically p-nitrobenzyl-substituted N-heterocyclic carbene-silver(I) complexes as metallopharmaceutical agents. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2017, 31, e3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahini, C.R.; Achar, G.; Budagumpi, S.; Tacke, M.; Patil, S.A. Synthesis, structural investigation and antibacterial studies of non–symmetrically p–nitrobenzyl substituted benzimidazole N–heterocyclic carbene–silver(I) complexes. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2017, 466, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharkey, M.; O’Gara, J.; Gordon, S.; Hackenberg, F.; Healy, C.; Paradisi, F.; Patil, S.; Schaible, B.; Tacke, M. Investigations into the antibacterial activity of the silver-based antibiotic drug candidate SBC3. Antibiotics 2012, 1, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanya Prasad, T.V.; Shahini, C.R.; Patil, S.A.; Huang, X.; Bugarin, A.; Patil, S.A. Non-symmetrically p-nitrobenzyl- and p-cyanobenzyl-substituted N-heterocyclic carbene-silver(I) complexes: Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial studies. J. Coord. Chem. 2017, 70, 600–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, M.; Noonikara-Poyil, A.; Joshi, S.D.; Patil, S.A.; Patil, S.A.; Bugarin, A. Synthesis, molecular docking studies, and antimicrobial evaluation of new structurally diverse ureas. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 87, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, M.; Noonikara-Poyil, A.; Joshi, S.D.; Patil, S.A.; Patil, S.A.; Bugarin, A. Design, synthesis, and molecular docking study of new piperazine derivative as potential antimicrobial agents. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 92, 103217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, W.L.; Grunert, R.R.; Haff, R.F.; McGahen, J.W.; Neumayer, E.M.; Paulshock, M.; Watts, J.C.; Wood, T.R.; Hermann, E.C.; Hoffmann, C.E. Antiviral activity of 1-adamantanamine (amantadie). Science 1964, 144, 862–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolin, R.; Reichman, R.C.; Madore, H.P.; Maynard, R.; Linton, P.N.; Webber-Jones, J. A controlled trial of amantadine and rimantadine in the prophylaxis of influenza A infection. N. Eng. J. Med. 1982, 307, 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Obando, D.; Liao, V.; Lifa, T.; Codd, R. The many faces of the adamantyl group in drug design. Eur. J Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 1949–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanka, L.; Iqbal, K.; Schreiner, P.R. The Lipophilic Bullet Hits the Targets: Medicinal Chemistry of Adamantane Derivatives. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 3516–3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahameethunisa, A.R.; Hopper, W. Antibacterial activity of Artemisia nilagirica leaf extracts against clinical and phytopathogenic bacteria. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2010, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balouiri, M.; Sadiki, M.; Ibnsouda, S.K. Methods for in vitro evaluating antimicrobial activity: A review. J. Pharm. Anal. 2016, 6, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, L.; Ebsworth-Mojica, K.; DiDone, L.; Li, S.G.; Freundlich, J.S.; Connell, N.; Dunman, P.M.; Krysan, D.J. A High throughput screening assay for anti-mycobacterial small molecules based on adenylate kinase release as a reporter of cell lysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greis, K.D.; Zhou, S.; Siehnel, R.; Klanke, C.; Curnow, A.; Howard, J.; Layh-Schmitt, G. Development and validation of a whole-cell inhibition assay for bacterial methionine aminopeptidase by surface-enhanced laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 3428–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasrin, F.; Bulbul, I.; Begum, Y. In vitro antimicrobial and cytotoxicity screening of n-hexane, chloroform and ethyl acetate extracts of Lablab purpureus (L.) leaves. Agric. Biol. J. North Am. 2012, 3, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, I.A.; Elliott, A.G.; Kavanagh, A.M.; Zuegg, J.; Blaskovich, M.A.T.; Cooper, M.A. Contribution of amphipathicity and hydrophobicity to the antimicrobial activity and cytotoxicity of β-hairpin peptides. ACS Infect. Dis. 2016, 2, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasteiger, J.; Marsili, M. Iterative partial equalization of orbital electronegativity—a rapid access to atomic charges. Tetrahedron 1980, 36, 3219–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripos International. Sybyl-X 2.0, Tripos International: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2012.
| Compound (#) | Percentage of Inhibition of Growth [a] | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibacterial Activity | Antifungal Activity | ||||||
| Gram-Positive | Gram-Negative Bacteria | ||||||
| Staphylococcus aureus | Escherichia coli | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Klebsiella pneumoniae | Acinetobacter baumannii | Candida albicans | Cryptococcus neoformans | |
| 3a | −0.1 ± 2.26 | 4 ± 0.98 | −20.65 ± 3.18 | −0.75 ± 2.75 | −88.85 ± 22.82 | 17.45 ± 19.44 | 30.65 ± 2.05 |
| 3b | −29.7 5± 6.29 | 8.15 ± 2.61 | 11.15 ± 15.48 | −7.4 ± 0.70 | −58.1 ± 21.7 | −1.4 ± 0.98 | 10.6 ± 12.58 |
| 3c | 7.6 ± 1.55 | 3.3 ± 0.14 | −2.34 ± 0.05 | 29.35 ± 0.77 | 20.1 ± 3.81 | 5.75 ± 2.19 | −4.4 ± 0.42 |
| 3d | 7.25 ± 0.49 | 5.35 ± 0.91 | 10.95 ± 15.62 | 17.55 ± 0.77 | 11 ± 31.39 | −5.6 ± 0.00 | 2.2 ± 2.96 |
| 3e | 0.45 ± 3.60 | 9.2 ± 0.00 | −5.35 ± 18.17 | −5.55 ± 6.15 | 51.85 ± 12.94 | 2.75 ± 1.34 | −2.35 ± 7.56 |
| 3f | 1.6 ± 0.28 | 3.55 ± 1.48 | −12 ± 6.50 | −4.9 ± 7.91 | 25.9 ± 27.86 | 3.15 ± 2.47 | −3.2 ± 9.47 |
| 3g | −5.8 ± 4.38 | 2.2 ± 5.09 | −3.65 ± 10.53 | 21.25 ± 4.31 | −6.3 ± 33.79 | −4.0 ± 3.67 | −9.85 ± 2.75 |
| 3h | −0.9 ± 0.70 | 9.45 ± 3.18 | 2.3 ± 15.98 | −3.65 ± 1.34 | 13.75 ± 46.31 | 2.2 ± 1.97 | −4.45 ± 6.01 |
| 3i | 12.4 ± 4.24 | 10.15 ± 0.63 | −4.6 ± 15.13 | 11.4 ± 8.62 | 25.15 ± 31.59 | 6.25 ± 0.49 | −6.2 ± 14.00 |
| 3j | −11.05 ± 1.48 | −1.65 ± 4.87 | −17.45 ± 6.29 | 0.95 ± 3.18 | 49.35 ± 49.69 | 13.4 ± 3.81 | −0.8 ± 19.37 |
| 3k | 24.9 ± 1.13 | −0.5 ± 2.40 | −8.5 ± 6.50 | −11.8 ± 0.70 | −97.4 ± 93.76 | 4.45 ± 4.17 | 15.25 ± 1.76 |
| 3l | 13.25 ± 0.49 | −1.2 ± 0.28 | −16.5 ± 0.14 | −16 ± 1.69 | 94.5 ± 17.23 | 3.05 ± 3.32 | 12.05 ± 3.88 |
| 3m | −23.5 ± 3.95 | 11.65 ± 0.07 | −6.15 ± 22.41 | −6.65 ± 1.20 | −16.15 ± 8.27 | 0.35 ± 1.62 | 11.3 ± 7.91 |
| 3n | 7.8 ± 1.69 | 7.9 ± 0.14 | −3.25 ± 6.71 | 2.0 ± 1.13 | 46.35 ± 16.33 | 1.25 ± 3.88 | −3.75 ± 1.06 |
| 3o | 8.35 ± 0.07 | 2.25 ± 1.48 | −5.4 ± 13.43 | −21.5 ± 0.70 | 2.65 ± 33.44 | 0.00 ± 3.39 | −2.6 ± 6.08 |
| 3p | 2.15 ± 9.26 | 5.9 ± 2.26 | −1.65 ± 19.86 | −7.85 ± 2.61 | 14.6 ± 30.97 | 3.45 ± 1.20 | 3.4 ± 3.25 |
| 3q | 7.55 ± 0.35 | 10.45 ± 0.07 | −0.55 ± 16.05 | −5.0 ± 4.24 | 14.9 ± 36.91 | 0.2 ± 3.25 | −3.35 ± 4.73 |
| Compounds | C Score a | Crash Score b | Polar Score c | D Score d | PMF Score e | G Score f | Chem Score g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3UDI_Ligand | 5.12 | −1.73 | 5.34 | −127.811 | −36.763 | −199.315 | −26.957 |
| 3a | 4.91 | −0.99 | 0.43 | −96.944 | 15.031 | −156.919 | −21.467 |
| 3b | 4.98 | −1.67 | 1.04 | −108.502 | −16.998 | −206.677 | −28.934 |
| 3c | 4.86 | −1.63 | 1.11 | −106.679 | −22.362 | −177.149 | −23.114 |
| 3d | 4.75 | −0.50 | 1.38 | −72.791 | 21.318 | −141.071 | −19.363 |
| 3e | 3.58 | −1.22 | 0.00 | −87.507 | 31.814 | −143.787 | −15.604 |
| 3f | 4.73 | −1.53 | 1.05 | −108.037 | −21.206 | −206.699 | −28.745 |
| 3g | 4.17 | −1.30 | 1.09 | −102.700 | −24.068 | −171.270 | −22.764 |
| 3h | 2.91 | −0.47 | 0.00 | −79.382 | −16.486 | −124.882 | −19.191 |
| 3i | 3.44 | −1.36 | 0.82 | −94.042 | −29.559 | −161.576 | −23.494 |
| 3j | 4.96 | −1.62 | 0.91 | −105.444 | −20.461 | −208.403 | −27.100 |
| 3k | 4.37 | −0.95 | 2.27 | −95.562 | −30.750 | −146.048 | −26.797 |
| 3l | 3.61 | −0.56 | 0.97 | −86.268 | −0.930 | −140.976 | −20.941 |
| 3m | 5.19 | −1.60 | 0.73 | −101.453 | 41.298 | −176.730 | −19.940 |
| 3n | 5.19 | −1.94 | 0.08 | −121.156 | 19.866 | −212.017 | −27.491 |
| 3o | 4.43 | −1.30 | 0.99 | −99.796 | −23.667 | −166.866 | −22.226 |
| 3p | 3.48 | −0.92 | 0.09 | −85.783 | 17.463 | −127.721 | −18.822 |
| 3q | 3.46 | −0.66 | 0.00 | −87.632 | 10.207 | −129.574 | −20.064 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Patil, M.; Noonikara-Poyil, A.; Joshi, S.D.; Patil, S.A.; Patil, S.A.; Bugarin, A. New Urea Derivatives as Potential Antimicrobial Agents: Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, and Molecular Docking Studies. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8040178
Patil M, Noonikara-Poyil A, Joshi SD, Patil SA, Patil SA, Bugarin A. New Urea Derivatives as Potential Antimicrobial Agents: Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, and Molecular Docking Studies. Antibiotics. 2019; 8(4):178. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8040178
Chicago/Turabian StylePatil, Mahadev, Anurag Noonikara-Poyil, Shrinivas D. Joshi, Shivaputra A. Patil, Siddappa A. Patil, and Alejandro Bugarin. 2019. "New Urea Derivatives as Potential Antimicrobial Agents: Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, and Molecular Docking Studies" Antibiotics 8, no. 4: 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8040178
APA StylePatil, M., Noonikara-Poyil, A., Joshi, S. D., Patil, S. A., Patil, S. A., & Bugarin, A. (2019). New Urea Derivatives as Potential Antimicrobial Agents: Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, and Molecular Docking Studies. Antibiotics, 8(4), 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8040178







