Colistin-Resistant Escherichia coli Isolated from Houseflies and Feces of Cattle and Pigs at a Slaughterhouse in Lima, Peru
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.2. Colistin Resistance
2.3. Serotype and Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST)
2.4. Virulence Genes
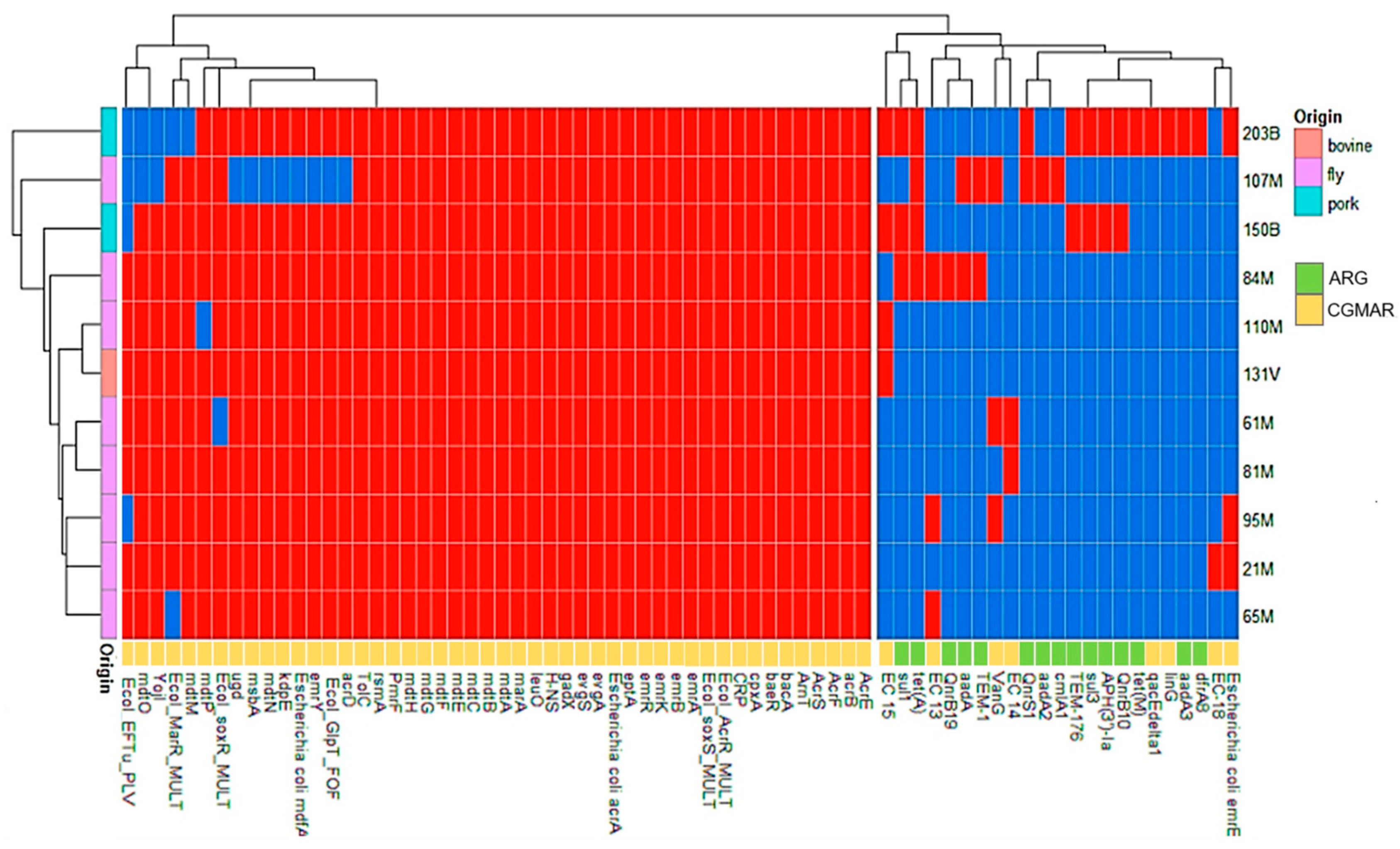
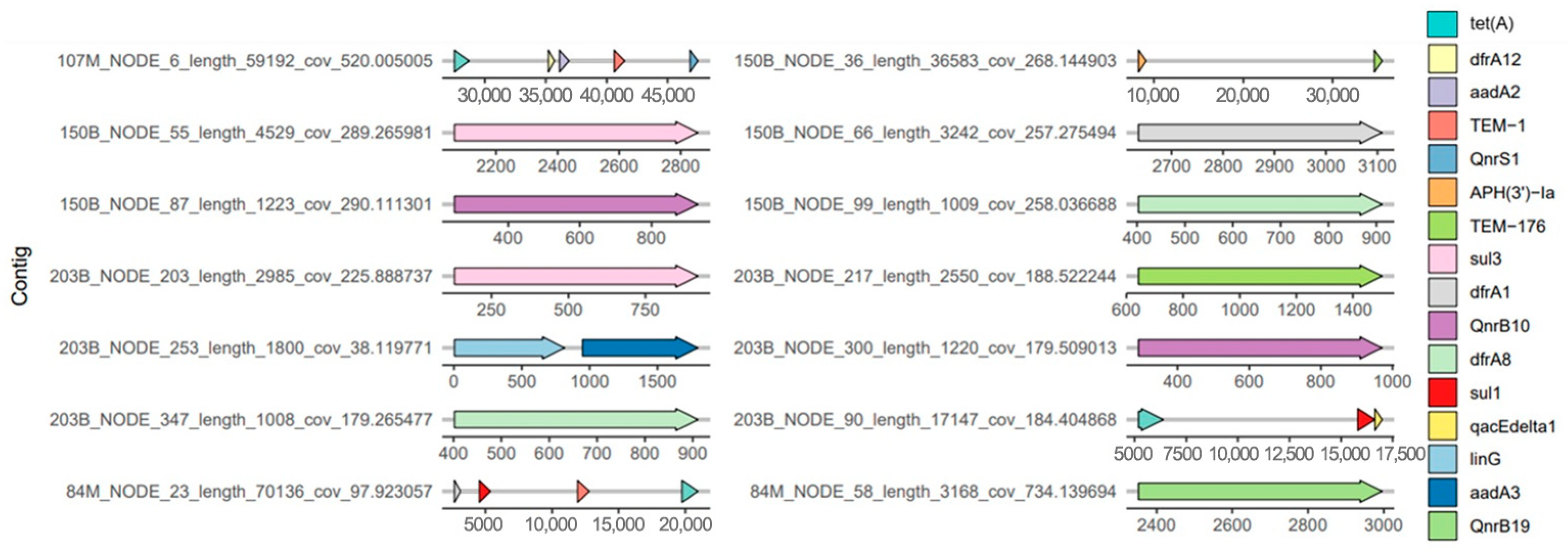
2.5. Antimicrobial Resistance Genes and Chromosomal Gene Mutations Associated with Antimicrobial Resistance
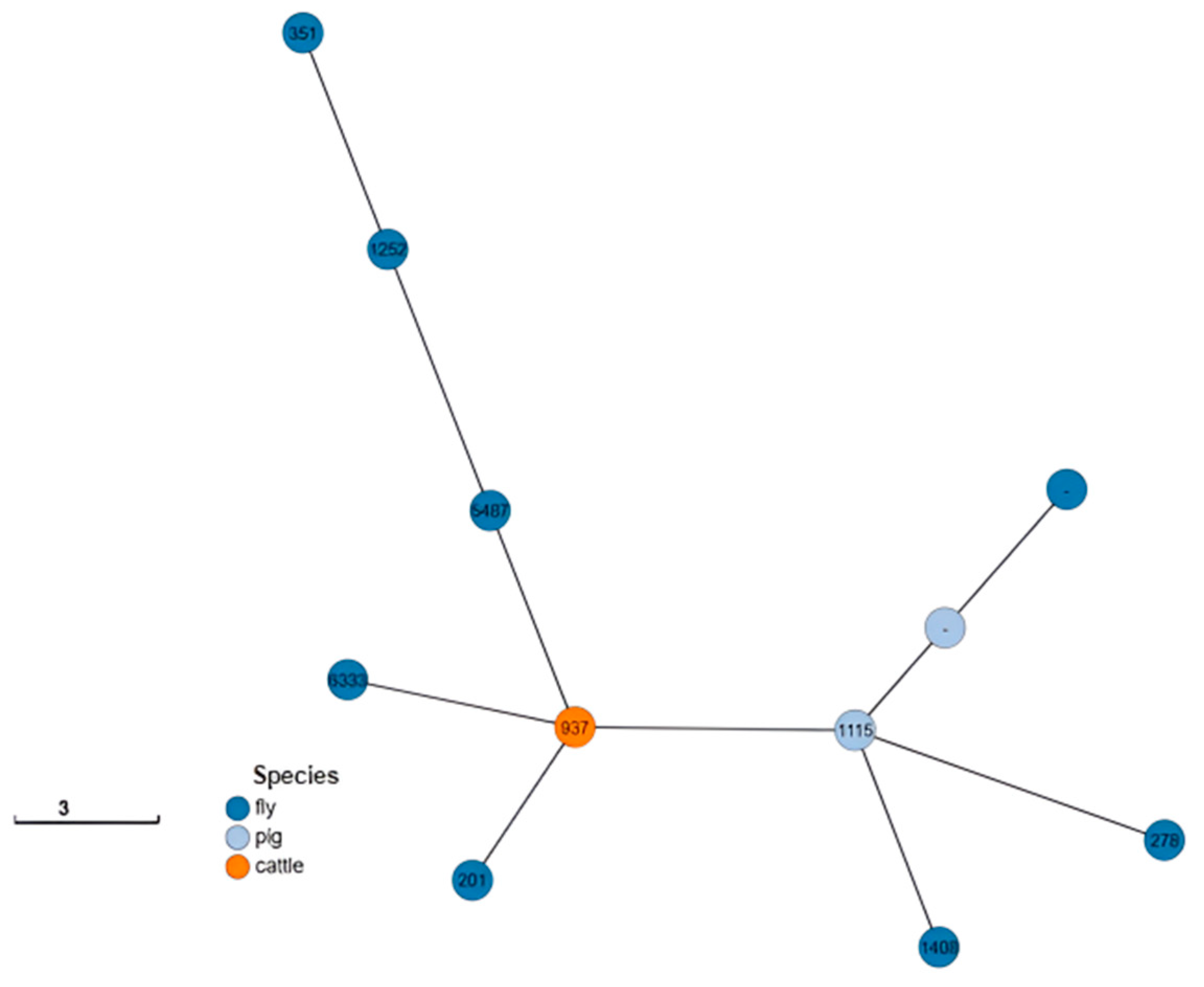
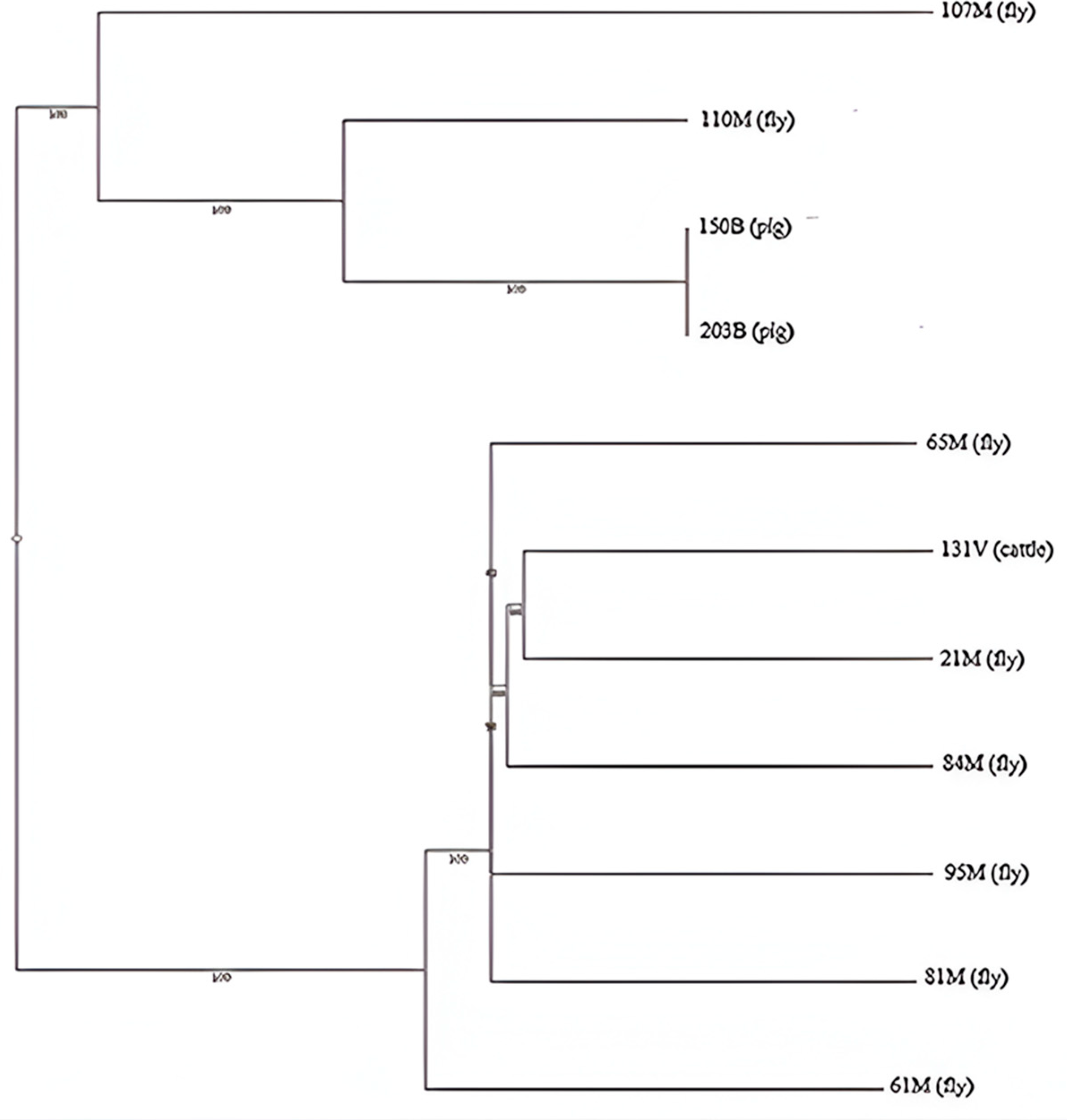
2.6. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Flies Sampling and Escherichia coli Isolation
4.2. Collection of Feces from Pigs and Cattle and Isolation of E. coli
4.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
4.4. Detection of the mcr-1 Gene
4.5. Genome Characterization
4.6. cgMLST Hierarchical Clustering Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Neill, J. Antimicrobial Resistance: Tackling a Crisis for the Health and Wealth of Nations. The Review on Antimicrobial Resistance, Chaired by Jim O’Neill. 2014, pp. 1–20. Available online: https://amr-review.org/sites/default/files/AMR%20Review%20Paper%20-%20Tackling%20a%20crisis%20for%20the%20health%20and%20wealth%20of%20nations_1.pdf (accessed on 3 January 2025).
- Stehling, E.G.; Calero-Cáceres, W.; Makita, K.; Furlan, J.P.R. Editorial: Livestock and its role in the emergence, spread, and evolution of antimicrobial resistance: Animal-to-human or animal-to-environment transmission. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1270955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhouma, M.; Madec, J.Y.; Laxminarayan, R. Colistin: From the shadows to a One Health approach for addressing antimicrobial resistance. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2023, 61, 106713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirel, L.; Madec, J.Y.; Lupo, A.; Schink, A.K.; Kieffer, N.; Nordmann, P.; Schwarz, S. Antimicrobial Resistance in Escherichia coli. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6, 10-1128/microbiolspec.arba-0026-2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhang, R.; Schwarz, S.; Wu, C.; Shen, J.; Walsh, T.R.; Wang, Y. Farm animals and aquaculture: Significant reservoirs of mobile colistin resistance genes. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 2469–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffatt, J.H.; Harper, M.; Boyce, J.D. Mechanisms of Polymyxin Resistance. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1145, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirel, L.; Jayol, A.; Nordmann, P. Polymyxins: Antibacterial Activity, Susceptibility Testing, and Resistance Mechanisms Encoded by Plasmids or Chromosomes. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 30, 557–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Woo, J.H.; Kim, N.; Kim, M.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Son, J.H.; Moon, D.C.; Lim, S.K.; Shin, M.; Lee, J.C. Characterization of Chromosome-Mediated Colistin Resistance in Escherichia coli Isolates from Livestock in Korea. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 3291–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamel, M.; Rolain, J.M.; Baron, S.A. The History of Colistin Resistance Mechanisms in Bacteria: Progress and Challenges. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.; Walsh, T.R.; Yi, L.X.; Zhang, R.; Spencer, J.; Doi, Y.; Tian, G.; Dong, B.; Huang, X.; et al. Emergence of plasmid-mediated colistin resistance mechanism MCR-1 in animals and human beings in China: A microbiological and molecular biological study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, N.H.; Al-Kadmy, I.M.S.; Taha, B.M.; Hussein, J.D. Mobilized colistin resistance (mcr) genes from 1 to 10: A comprehensive review. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 2897–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.H.; Liu, Y.Y.; Shen, Y.B.; Yang, J.; Walsh, T.R.; Wang, Y.; Shen, J. Plasmid-mediated colistin-resistance genes: Mcr. Trends Microbiol. 2024, 32, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed Ahmed, M.A.E.; Zhong, L.L.; Shen, C.; Yang, Y.; Doi, Y.; Tian, G.B. Colistin and its role in the Era of antibiotic resistance: An extended review (2000–2019). Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 868–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, A.H.; Khare, K.; Saxena, P.; Debnath, P.; Mukhopadhyay, K.; Yadav, D. A Review on Colistin Resistance: An Antibiotic of Last Resort. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Förster, M.; Klimpel, S.; Sievert, K. The house fly (Musca domestica) as a potential vector of metazoan parasites caught in a pig-pen in Germany. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 160, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazari, M.; Mehrabi, T.; Hosseini, S.M.; Alikhani, M.Y. Bacterial Contamination of Adult House Flies (Musca domestica) and Sensitivity of these Bacteria to Various Antibiotics, Captured from Hamadan City, Iran. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2017, 11, DC04–DC07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onwugamba, F.C.; Mellmann, A.; Nwaugo, V.O.; Süselbeck, B.; Schaumburg, F. Antimicrobial resistant and enteropathogenic bacteria in ‘filth flies’: A cross-sectional study from Nigeria. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onwugamba, F.C.; Fitzgerald, J.R.; Rochon, K.; Guardabassi, L.; Alabi, A.; Kühne, S.; Grobusch, M.P.; Schaumburg, F. The role of ‘filth flies’ in the spread of antimicrobial resistance. Travel. Med. Infect. Dis. 2018, 22, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcón-Calle, M.A.; Osorio-Guevara, V.L.; Salas-Asencios, R.; Yareta, J.; Marcos-Carbajal, P.; Rodrigo-Rojas, M.E. Carbapenems and colistin resistance genes isolated in Musca domestica from a garbage dump near a hospital in Lima. Genes resistentes a carbapenémicos y colistina aislados en Musca domestica proveniente de un basural cercano a un hospital de Lima. Rev. Peru. Med. Exp. Salud Publica 2024, 41, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, R.; Izadi, M.; Hafshejani, T.T.; Khamesipour, F. Molecular detection and antimicrobial resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae from house flies (Musca domestica) in kitchens, farms, hospitals and slaughterhouses. J. Infect. Public Health 2016, 9, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ommi, D.; Hemmatinezhad, B.; Hafshejani, T.T.; Khamesipour, F. Incidencia y resistencia antimicrobiana de Campylobacter y Salmonella de moscas domésticas (Musca domestica) en cocinas, granjas, hospitales y mataderos. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 87, 1285–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, B.; Jang, Y.J.; Kim, Y.R.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, W.I.; Han, S.; Kim, S.R.; Ryu, J.G.; Kim, H.J. Virulence profile and antimicrobial resistance of Escherichia coli from flies captured from agricultural environment. J. Food Hyg. Saf. 2017, 32, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odetoyin, B.; Adeola, B.; Olaniran, O. Frequency and Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns of Bacterial Species Isolated from the Body Surface of the Housefly (Musca domestica) in Akure, Ondo State, Nigeria. J. Arthropod Borne Dis. 2020, 14, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Pires, J.; Silvester, R.; Zhao, C.; Song, J.; Criscuolo, N.G.; Gilbert, M.; Bonhoeffer, S.; Laxminarayan, R. Global trends in antimicrobial resistance in animals in low- and middle-income countries. Science 2019, 365, eaaw1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, P. Links between industrial livestock production, disease including zoonoses and antimicrobial resistance. Anim. Res. One Health 2023, 1, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castanon, J.I. History of the use of antibiotic as growth promoters in European poultry feeds. Poult. Sci. 2007, 86, 2466–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huyghebaert, G.; Ducatelle, R.; Van Immerseel, F. An update on alternatives to antimicrobial growth promoters for broilers. Vet. J. 2011, 187, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, C.X.; Tan, L.T.; Ab Mutalib, N.S.; Pusparajah, P.; Goh, B.H.; Chan, K.G.; Letchumanan, V.; Lee, L.H. Unveiling the Impact of Antibiotics and Alternative Methods for Animal Husbandry: A Review. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, R.; Li, C.; Zhao, M.; Wang, H.; Tang, Y. Withdrawal of antibiotic growth promoters in China and its impact on the foodborne pathogen Campylobacter coli of swine origin. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1004725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, R.A.; Arenas, N.E.; Luiza, V.L.; Bermudez, J.A.Z.; Clarke, S.E. Regulations on the Use of Antibiotics in Livestock Production in South America: A Comparative Literature Analysis. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Brower, C.; Gilbert, M.; Grenfell, B.T.; Levin, S.A.; Robinson, T.P.; Teillant, A.; Laxminarayan, R. Global trends in antimicrobial use in food animals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5649–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekagul, A.; Tangcharoensathien, V.; Mills, A.; Rushton, J.; Yeung, S. How antibiotics are used in pig farming: A mixed-methods study of pig farmers, feed mills and veterinarians in Thailand. BMJ Glob. Health 2020, 5, e001918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippitzi, M.; Callens, B.; Pardon, B.; Persoons, D.; Dewulf, J. Antimicrobial use in pigs, broilers and veal calves in Belgium. Vlaams Diergeneeskd. Tijdschrift. 2014, 83, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melgarejo-Touchet, N.; Busignani, S.; Dunjo, P.; Brítez, M.; Weiler, N.; Orrego, V.; Alonzo, M.; Martínez-Mora, M. Resistencia antimicrobiana en Escherichia coli de muestras cecales de bovinos para carne faenados en frigoríficos de la zona del arroyo Mburicao, Asunción-Paraguay. Año 2021. Mem. Inst. Investig. Cienc. Salud 2022, 20, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera González, M.A.; Vásquez Pérez, H.V.; Quilcate-Pairazamán, C.; Bazán-Arce, J.; Cueva-Rodríguez, M. Evaluación de resistencia a antibióticos en muestras de heces de terneros con diarrea en la región Cajamarca, Perú. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Pecu. 2023, 14, 782–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, I.; Roberts, M. Tetracycline antibiotics: Mode of action, applications, molecular biology, and epidemiology of bacterial resistance. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2001, 65, 232–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuda, M.; Shintani, M. Microbial evolution through horizontal gene transfer by mobile genetic elements. Microb. Biotechnol. 2024, 17, e14408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarebout, G.; Nativelle, E.; Leclercq, R. Unusual Inducible Cross Resistance to Macrolides, Lincosamides, and Streptogramins B by Methylase Production in Clinical Isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. Microb. Drug Resist. 2001, 7, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svetlov, M.S.; Syroegin, E.A.; Aleksandrova, E.V.; Atkinson, G.C.; Gregory, S.T.; Mankin, A.S.; Polikanov, Y.S. Structure of Erm-modified 70S ribosome reveals the mechanism of macrolide resistance. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2021, 17, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ríos, C.A.; Morales-Cauti, S.; Vilca, L.M.; Carhuallanqui, A.; Ramos, D. Determinación del perfil de resistencia antibiótica de Salmonella enterica aislada de cerdos faenados en un matadero de Lima, Perú. Rev. Investig. Vet. Perú 2019, 30, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carhuaricra, D.; Duran Gonzales, C.G.; Rodríguez Cueva, C.L.; Ignacion León, Y.; Silvestre Espejo, T.; Marcelo Monge, G.; Rosadio Alcántara, R.H.; Lincopan, N.; Espinoza, L.L.; Maturrano Hernández, L. Occurrence and Genomic Characterization of mcr-1-Harboring Escherichia coli Isolates from Chicken and Pig Farms in Lima, Peru. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertelloni, F.; Bresciani, F.; Cagnoli, G.; Scotti, B.; Lazzerini, L.; Marcucci, M.; Colombani, G.; Bilei, S.; Bossù, T.; De Marchis, M.L.; et al. House Flies (Musca domestica) from Swine and Poultry Farms Carrying Antimicrobial Resistant Enterobacteriaceae and Salmonella. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervelin, V.; Fongaro, G.; Pastore, J.B.; Engel, F.; Reimers, M.A.; Viancelli, A. Enterobacteria associated with houseflies (Musca domestica) as an infection risk indicator in swine production farms. Acta Trop. 2018, 185, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, S.; Sabuj, A.A.M.; Haque, Z.F.; Kafi, M.A.; Rahman, M.T.; Saha, S. Detection of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and their resistance genes from houseflies. Vet. World. 2020, 13, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias-Osores, S. Uso de colistina en el sector pecuario: Necesidad de una prohibición global. Acta Med. Peru. 2020, 37, 114–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.P.; Su, L.; Liu, J.W.; Yao, M.X.; Yuan, G.Y. Study on the association between drug resistance and gene mutations of the active efflux pump acrAB tolC gene and its regulatory genes. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 8228–8236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, M.; Wang, L.P.; Kashif, J.; Memon, J.; Umar, S.; Iqbal, M.F.; Fiaz, M.; Lu, C.P. Genetic characterization of phenicol-resistant Escherichia coli and role of wild-type repressor/regulator gene (acrR) on phenicol resistance. Folia Microbiol. 2018, 63, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; Saralaya, V.; Adhikari, P.; Shenoy, S.; Baliga, S.; Hegde, A. Characterization of Escherichia coli Phylogenetic Groups Associated with Extraintestinal Infections in South Indian Population. Ann. Med. Health Sci. Res. 2015, 5, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewers, C.; de Jong, A.; Prenger-Berninghoff, E.; El Garch, F.; Leidner, U.; Tiwari, S.K.; Semmler, T. Genomic Diversity and Virulence Potential of ESBL- and AmpC-β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli Strains From Healthy Food Animals Across Europe. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 626774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messele, Y.E.; Trott, D.J.; Hasoon, M.F.; Veltman, T.; McMeniman, J.P.; Kidd, S.P.; Djordjevic, S.P.; Petrovski, K.R.; Low, W.Y. Phylogenetic Analysis of Escherichia coli Isolated from Australian Feedlot Cattle in Comparison to Pig Faecal and Poultry/Human Extraintestinal Isolates. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulchandani, R.; Wang, Y.; Gilbert, M.; Van Boeckel, T.P. Global trends in antimicrobial use in food-producing animals: 2020 to 2030. PLoS Glob. Public Health 2023, 3, e0001305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carattoli, A. Resistance Plasmid Families in Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 2227–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Pizzali, M.L.; Venkatesh, A.; Riveros, M.; Cuicapuza, D.; Salmon-Mulanovich, G.; Mäusezahl, D.; Hartinger, S.M. Whole-Genome Characterisation of ESBL-Producing E. coli Isolated from Drinking Water and Dog Faeces from Rural Andean Households in Peru. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Gong, L.; Liu, E.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Liang, J. Characterization of the Disinfectant Resistance Genes qacEΔ1 and cepA in Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2023, 110, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalchuk, S.N.; Arkhipova, A.L.; Bondar, S.V.; Konanov, D.N.; Krivonos, D.V.; Chulkova, P.S.; Ageevets, V.A.; Fedorova, L.S.; Ilina, E.N. A TaqMan real-time PCR assay for detection of qacEΔ1 gene in Gram-negative bacteria. J. Microbiol. Methods 2024, 227, 107054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Fu, J.; Zhao, K.; Yang, S.; Li, C.; Penttinen, P.; Ao, X.; Liu, A.; Hu, K.; Li, J.; et al. Class 1 integron carrying qacEΔ1 gene confers resistance to disinfectant and antibiotics in Salmonella. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 404, 110319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organisation WHO. List of Critically Important Antimicrobials for Human Medicine. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241515528 (accessed on 19 April 2024).
- Olaitan, A.O.; Morand, S.; Rolain, J.M. Mechanisms of polymyxin resistance: Acquired and intrinsic resistance in bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, S.; Hadjadj, L.; Rolain, J.M.; Olaitan, A.O. Molecular mechanisms of polymyxin resistance: Knowns and unknowns. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2016, 48, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeannot, K.; Bolard, A.; Plésiat, P. Resistance to polymyxins in Gram-negative organisms. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 49, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, H.; Park, M.; Kang, K.; Lim, S.K.; Shin, D.; Ko, K.S. Comparison of Fitness Cost and Virulence in Chromosome- and Plasmid-Mediated Colistin-Resistant Escherichia coli. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, C.J.; Alegre, K.O. Clamping down on drugs: The Escherichia coli multidrug efflux protein MdtM. Res. Microbiol. 2018, 169, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holdsworth, S.R.; Law, C.J. Multidrug resistance protein MdtM adds to the repertoire of antiporters involved in alkaline pH homeostasis in Escherichia coli. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.J.; Kim, S.J.; Moon, D.C.; Mechesso, A.F.; Choi, J.H.; Kang, H.Y.; Boby, N.; Yoon, S.S.; Lim, S.K. Antimicrobial Resistance in Escherichia coli Isolates from Healthy Food Animals in South Korea, 2010–2020. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobur, M.A.; Ievy, S.; Haque, Z.F.; Nahar, A.; Zaman, S.B.; Rahman, M.T. Emergence of colistin-resistant Escherichia coli in poultry, house flies, and pond water in Mymensingh, Bangladesh. J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 2019, 6, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gwenzi, W.; Chaukura, N.; Muisa-Zikali, N.; Teta, C.; Musvuugwa, T.; Rzymski, P.; Abia, A.L.K. Insects, Rodents, and Pets as Reservoirs, Vectors, and Sentinels of Antimicrobial Resistance. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skovgård, H.; Nachman, G. Population dynamics of stable flies Stomoxys calcitrans (Diptera: Muscidae) at an organic dairy farm in Denmark based on mark-recapture with destructive sub-sampling. Environ. Entomol. 2012, 41, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, T.H.; Faruque, A.S.; Wu, Y.; Das, S.K.; Hossain, A.; Ahmed, S.; Ahmed, D.; Nasrin, D.; Kotloff, K.L.; Panchilangam, S.; et al. Housefly population density correlates with shigellosis among children in Mirzapur, Bangladesh: A time series analysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stelder, J.J.; Kjær, L.J.; Jensen, L.B.; Boklund, A.E.; Denwood, M.; Carlsen, M.; Bødker, R. Livestock-associated MRSA survival on house flies (Musca domestica) and stable flies (Stomoxys calcitrans) after removal from a Danish pig farm. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzker, W.; Pfeifer, Y.; Wolke, S.; Haselbeck, A.; Leistner, R.; Kola, A.; Gastmeier, P.; Salm, F. Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase (ESBL)-Producing Escherichia coli Isolated from Flies in the Urban Center of Berlin, Germany. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, B. Flies and Disease, 1st ed.; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1971; Volume 1, pp. 856–863. [Google Scholar]
- Pava-Ripoll, M.; Pearson, R.E.; Miller, A.K.; Ziobro, G.C. Detection of foodborne bacterial pathogens from individual filth flies. J. Vis. Exp. 2015, 96, e52372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, T.D.S.; Lara, G.H.B.; Maluta, R.P.; Ribeiro, M.G.; Leite, D.D.S. Carrier flies of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli as potential dissemination agent in dairy farm environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1345–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, W.H. Edwards and Ewing’s Identification of Enterobacteriaceae, 4th ed.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1986; pp. 181–201. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, P.; Weagant, S.D.; Grant, M.A.; Burkhardt, W.; Shellfish, M.; Water, B. BAM: Enumeration of Escherichia coli and the Coliform Bacteria. In Bacteriological Analytical Manual; US Food & Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2002; Volume 13, pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Barlow, R.; McMillan, K.; Mellor, G.; Duffy, L.; Jordan, D.; Abraham, R.; O’Dea, M.; Sahibzada, S.; Abraham, S. Phenotypic and Genotypic Assessment of Antimicrobial Resistance in Escherichia coli from Australian Cattle Populations at Slaughter. J. Food Prot. 2022, 85, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M100; Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 31st ed. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI): Wayne, PA, USA, 2021.
- Institute of Infectious Diseases. National Administration of Laboratories and Health Institutes “Dr. Carlos, G. Malbrán”. PCR Protocol for the Detection of the Mcr-1 Gene in Gram-Negative Bacilli Isolates. Available online: https://antimicrobianos.com.ar/ATB/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/Detecci%c3%b3n-mcr-1-v1.pdf (accessed on 20 April 2024).
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joensen, K.G.; Tetzschner, A.M.; Iguchi, A.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Scheutz, F. Rapid and Easy In Silico Serotyping of Escherichia coli Isolates by Use of Whole-Genome Sequencing Data. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 2410–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, N.R.; Abram, F.; Brennan, F.; Holmes, A.; Pritchard, L. Easy phylotyping of Escherichia coli via the EzClermont web app and command-line tool. Access Microbiol. 2020, 2, acmi000143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carattoli, A.; Zankari, E.; García-Fernández, A.; Voldby Larsen, M.; Lund, O.; Villa, L.; Møller Aarestrup, F.; Hasman, H. In silico detection and typing of plasmids using PlasmidFinder and plasmid multilocus sequence typing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2024, 58, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, K.; Morooka, N.; Yamamoto, Y.; Fujita, K.; Isono, K.; Choi, S.; Ohtsubo, E.; Baba, T.; Wanner, B.L.; Mori, H.; et al. Highly accurate genome sequences of Escherichia coli K-12 strains MG1655 and W3110. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2006, 2, 2006-0007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xiong, Y.; Rogers, L.; Carter, G.P.; French, N. Genome-by-genome approach for fast bacterial genealogical relationship evaluation. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3025–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Rozewicki, J.; Yamada, K.D. MAFFT online service: Multiple sequence alignment, interactive sequence choice and visualization. Brief. Bioinform. 2018, 20, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, D.; Moulton, V. Neighbor-Net: An agglomerative method for the construction of phylogenetic networks. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2004, 21, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Antibiotics | Cattle (%) n = 150 | Pig (%) n = 150 | Fly (%) n = 150 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lincomycin | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Enrofloxacin | 11.81 | 38.62 | 40.19 |
| Tetracycline | 81.89 | 97.24 | 90.65 |
| Neomycin | 8.66 | 53.1 | 49.53 |
| Ampicillin | 18.9 | 89.66 | 74.77 |
| Amoxicillin | 20.47 | 89.66 | 72.9 |
| Chloramphenicol | 22.05 | 92.41 | 69.16 |
| Nalidixic Acid | 23.62 | 70.34 | 63.55 |
| Sulfatrimethoprim | 16.54 | 77.93 | 63.55 |
| Colistin | 0.79 | 1.38 | 7.48 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 4.72 | 31.72 | 39.25 |
| Nitrofurantoin | 0 | 1.38 | 3.74 |
| Cephalexin | 4.72 | 6.9 | 30.84 |
| Gentamicin | 6.3 | 27.59 | 32.71 |
| Multidrug resistance | 19.68 | 93.73 | 71.96 |
| Antibiotics | Cattle | Pig | Fly | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 131V | 150B | 203B | 21M | 61M | 65M | 81M | 84M | 95M | 107M | 110M | |
| Lincomycin | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R |
| Enrofloxacin | R | R | R | R | S | R | S | S | S | R | S |
| Tetracycline | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R |
| Neomycin | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R |
| Ampicillin | S | R | R | R | S | R | R | R | S | R | S |
| Amoxicillin | S | R | R | S | S | S | S | R | S | R | S |
| Chloramphenicol | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R |
| Nalidixic Acid | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R |
| Sulfatrimethoprim | S | R | R | R | S | S | S | R | S | R | S |
| Ciprofloxacin | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R |
| Nitrofurantoin | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| Cephalexin | S | R | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| Gentamicin | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R |
| Strain | Species | ST | Serotype | Phylogroup | Clonal Complex |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 107M | fly | - | O13 H29 | B1 | - |
| 110M | fly | ST 1408 | O13 H30 | A | - |
| 131V | cattle | ST 937 | O43 H2 | B1 | - |
| 150B | pig | ST 1115 | O102 H40 | A | - |
| 203B | pig | - | O102 H20 | A | - |
| 21M | fly | ST 201 | O3 H19 | B1 | ST469 Cplx |
| 61M | fly | ST 1252 | O13 H11 | B1 | - |
| 65M | fly | ST 6333 | O123 H14 | B1 | - |
| 81M | fly | ST 278 | H7 | B1 | ST278 Cplx |
| 84M | fly | ST 5487 | H25 | B1 | - |
| 95M | fly | ST 351 | O18 H7 | B1 | - |
| Genes | Isolates | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fly | Cattle | Pig | |||||||||
| 107M | 110M | 21M | 61M | 65M | 81M | 84M | 95M | 131V | 150B | 203B | |
| algW | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| aslA | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| cheA | − | − | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | − |
| cheD | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| cheY | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| csgB | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| csgD | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| csgE | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| csgF | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| csgG | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| entA | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| entB | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| entC | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| entD | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| entE | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| entF | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| entS | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| espL1 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| espL4 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| espR1 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| espX1 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| espX4 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| espX5 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| espR4 | + | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| espX6 | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| espY2 | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| espY4 | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| fdeC | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| fepA | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| fepB | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| fepC | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| fepD | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| fepG | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| f17d-A | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | − |
| f17d-C | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | − |
| f17d-D | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | − |
| f17d-G | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | − |
| fes | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| fimA | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| fimB | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| fimC | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| fimD | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| fimE | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| fimF | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| fimG | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| fimH | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| fimI | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| flgD | + | − | + | − | + | + | − | + | + | − | − |
| flgF | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| flgE | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| flgG | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| flgH | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| flgM | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| flgJ | + | + | − | + | − | − | + | − | − | + | + |
| flhA | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| fliG | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| fliI | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| fliM | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| fliN | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| fliP | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| fliC | + | − | − | + | − | − | + | − | + | + | + |
| gmd | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| gspC | − | − | + | + | + | + | + | − | + | + | + |
| gspD | − | − | + | + | + | + | + | − | + | + | + |
| gspE | − | − | + | + | + | + | + | − | + | + | + |
| gspF | − | − | + | + | + | + | + | − | + | + | + |
| gspG | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| gspH | − | − | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| gspI | − | − | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| gspJ | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| gspK | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| gspL | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| gspM | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| gtrA | + | + | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| gtrB | + | + | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| gtrII | + | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| katB | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| ompA | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| sfaF | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| pefC | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| pefD | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| iroB | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − |
| iroC | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − |
| iroD | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − |
| iroE | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − |
| iroN | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − |
| yagV/ecpE | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| yagW/ecpD | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| yagX/ecpC | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| yagY/ecpB | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| yagZ/ecpA | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| ykgK/ecpR | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| irp1 | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| irp2 | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| fyuA | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carhuallanqui, A.; Villafana, L.; Gonzalez-Veliz, R.; Cobo-Díaz, J.F.; Álvarez-Ordoñez, A.; Ramos-Delgado, D.D. Colistin-Resistant Escherichia coli Isolated from Houseflies and Feces of Cattle and Pigs at a Slaughterhouse in Lima, Peru. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 818. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14080818
Carhuallanqui A, Villafana L, Gonzalez-Veliz R, Cobo-Díaz JF, Álvarez-Ordoñez A, Ramos-Delgado DD. Colistin-Resistant Escherichia coli Isolated from Houseflies and Feces of Cattle and Pigs at a Slaughterhouse in Lima, Peru. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(8):818. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14080818
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarhuallanqui, Andrea, Lorena Villafana, Rosa Gonzalez-Veliz, José F. Cobo-Díaz, Avelino Álvarez-Ordoñez, and Daphne Doris Ramos-Delgado. 2025. "Colistin-Resistant Escherichia coli Isolated from Houseflies and Feces of Cattle and Pigs at a Slaughterhouse in Lima, Peru" Antibiotics 14, no. 8: 818. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14080818
APA StyleCarhuallanqui, A., Villafana, L., Gonzalez-Veliz, R., Cobo-Díaz, J. F., Álvarez-Ordoñez, A., & Ramos-Delgado, D. D. (2025). Colistin-Resistant Escherichia coli Isolated from Houseflies and Feces of Cattle and Pigs at a Slaughterhouse in Lima, Peru. Antibiotics, 14(8), 818. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14080818








