Genotypic and Phenotypic Characterization of Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence in Campylobacter spp. Isolated from Turkeys: Uncovering a Neglected Reservoir in the One Health Context
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation of Campylobacter spp.
2.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibillity Tests Results
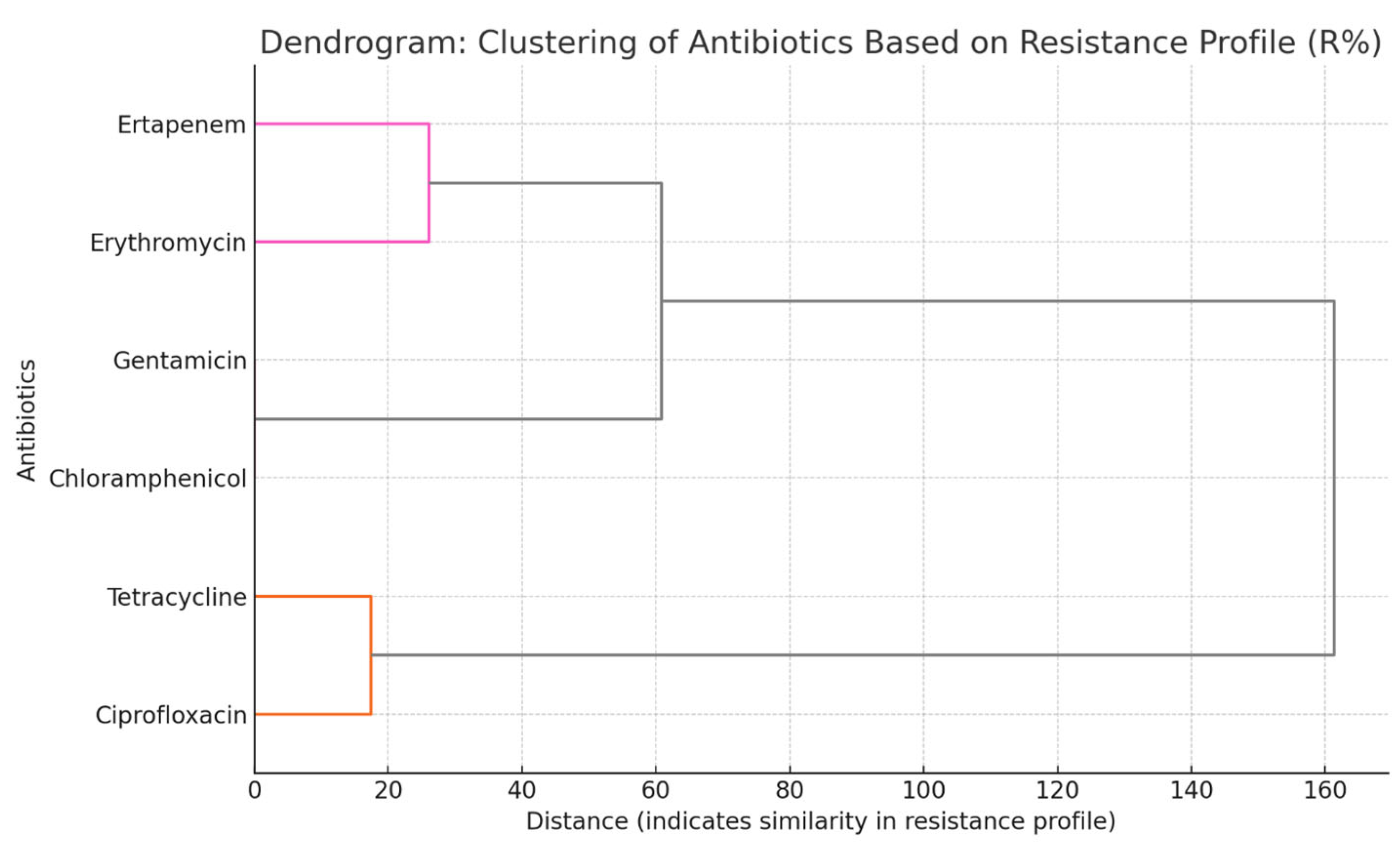
2.3. Correlation and Clustering Analyses of Antimicrobial Resistance in Campylobacter spp. Isolates
2.4. Molecular Analyses
2.5. Statistical Analyses Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design and Samples Collection
4.2. Isolation and Identification of Campylobacter spp.
4.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibiliy Tests
4.4. Molecular Analyses
4.5. Selection of Representative Isolate Subset for Molecular Characterization
4.6. Statistical Analyses
4.7. Bioethics Commission Approval
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ristori, M.V.; Guarrasi, V.; Soda, P.; Petrosillo, N.; Gurrieri, F.; Longo, U.G.; Ciccozzi, M.; Riva, E.; Angeletti, S. Emerging Microorganisms and Infectious Diseases: One Health Approach for Health Shared Vision. Genes 2024, 15, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dafale, N.A.; Srivastava, S.; Purohit, H.J. Zoonosis: An Emerging Link to Antibiotic Resistance Under “One Health Approach”. Indian J. Microbiol. 2020, 60, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, N.; Joji, R.M.; Shahid, M. Evolution and implementation of One Health to control the dissemination of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and resistance genes: A review. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 12, 1065796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sleeman, J.M.; DeLiberto, T.; Nguyen, N. Optimization of human, animal, and environmental health by using the One Health approach. J. Vet. Sci. 2017, 18, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinclair, J.R. Importance of a One Health Approach in Advancing Global Health Security, and the Sustainable Development Goals. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2019, 38, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukari, Z.; Emmanuel, T.; Woodward, J.; Ferguson, R.; Ezughara, M.; Darga, N.; Lopes, B.S. The Global Challenge of Campylobacter: Antimicrobial Resistance and Emerging Intervention Strategies. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2025, 10, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA); European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). The European Union Summary Report on Antimicrobial Resistance in Zoonotic and Indicator Bacteria from Humans, Animals and Food in 2022–2023. EFSA J. 2025, 23, e9237. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, J.; Leite, D.; Fernandes, M.; Mena, C.; Gibbs, P.A.; Teixeira, P. Campylobacter spp. as a foodborne pathogen: A review. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thames, H.T.; Sukumaran, A.T. A Review of Salmonella and Campylobacter in Broiler Meat: Emerging Challenges and Food Safety Measures. Foods 2020, 9, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, S.A.; Morar, A.; Ban-Cucerzan, A.; Imre, K. Last decade mini-review of the scientific progresses in the monitoring of the occurrence and antimicrobial susceptibility profile of poultry origin Campylobacter spp. within the European Union countries. Rev. Rom. Med. Vet. 2022, 32, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Popa, S.A.; Herman, V.; Tîrziu, E.; Morar, A.; Ban-Cucerzan, A.; Imre, M.; Pătrînjan, R.-T.; Imre, K. Public Health Risk of Campylobacter spp. Isolated from Slaughterhouse and Retail Poultry Meat: Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles. Pathogens 2025, 14, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintar, K.D.M.; Christidis, T.; Kate Thomas, M.; Anderson, M.; Nesbitt, A.; Keithlin, J.; Marshall, B.; Pollari, F. A systematic review and meta-Analysis of the Campylobacter spp. Prevalence and concentration in household pets and petting zoo animals for use in exposure assessments. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popa, S.A.; Morar, A.; Ban-Cucerzan, A.; Tîrziu, E.; Herman, V.; Imre, M.; Florea, T.; Morar, D.; Pătrânjan, R.T.; Imre, K. First study on the frequency of isolation and phenotypic antimicrobial resistance profiles of pig- and cattle-origin Campylobacter strains in Romania. Vet. Res. Commun. 2024, 48, 2621–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olvera-Ramírez, A.M.; McEwan, N.R.; Stanley, K.; Nava-Diaz, R.; Aguilar-Tipacamú, G. A systematic review on the role of wildlife as carriers and spreaders of Campylobacter spp. Animals 2023, 13, 1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, S.A.; Herman, V.; Tîrziu, E.; Morar, A.; Ban-Cucerzan, A.; Imre, M.; Pătrânjan, R.T.; Ivan, A.; Gligor, A.; Imre, K. Public health implications of Campylobacter spp. in common pheasants (Phasianus colchicus): A One Health perspective on zoonotic risk and food safety. Rev. Rom. Med. Vet. 2025, 35, 82–88. [Google Scholar]
- Rozynek, E.; Dzierzanowska-Fangrat, K.; Jozwiak, P.; Popowski, J.; Korsak, D.; Dzierzanowska, D. Prevalence of potential virulence markers in Polish Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli isolates obtained from hospitalized children and from chicken carcasses. J. Med. Microbiol. 2005, 54, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepanska, B.; Andrzejewska, M.; Spica, D.; Klawe, J.J. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli isolated from children and environmental sources in urban and suburban areas. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boqvist, S.; Söderqvist, K.; Vågsholm, I. Food safety challenges and One Health within Europe. Acta Vet. Scand. 2018, 60, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gölz, G.; Schielke, A.; Josenhans, C.; Rosner, B.; Löwenstein, A.; Alter, T.; Wieler, L.H.; Kreienbrock, L.; Stark, K.; Suerbaum, S.; et al. Relevance of Campylobacter to public health—The need for a One Health approach. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 304, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie, J.S.; Jeggo, M. The One Health Approach—Why Is It So Important? Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 4, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, M.A.; Al-Amin, M.Y.; Salam, M.T.; Pawar, J.S.; Akhter, N.; Rabaan, A.A.; Alqumber, M.A.A. Antimicrobial Resistance: A Growing Serious Threat for Global Public Health. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, M.U.; Hayat, M.T.; Mukhtar, H.; Imre, K. CRISPR-Cas9 system: A prospective pathway toward combatting antibiotic resistance. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwen, S.A.; Collignon, P.J. Antimicrobial Resistance: A One Health Perspective. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6, 521–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolinger, H.; Kathariou, S. The Current State of Macrolide Resistance in Campylobacter Spp.: Trends and Impacts of Resistance Mechanisms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e00416–e00417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sproston, E.L.; Wimalarathna, H.M.L.; Sheppard, S.K. Trends in fluoroquinolone resistance in Campylobacter. Microb. Genom. 2018, 4, e000198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abukhattab, S.; Taweel, H.; Awad, A.; Crump, L.; Vonaesch, P.; Zinsstag, J.; Hattendorf, J.; Abu-Rmeileh, N.M.E. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Integrated Studies on Salmonella and Campylobacter Prevalence, Serovar, and Phenotyping and Genetic of Antimicrobial Resistance in the Middle East—A One Health Perspective. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahin, O.; Kassem, I.I.; Shen, Z.; Lin, J.; Rajashekara, G.; Sahin, O.; Kassem, A.I.I.; Shen, B.Z.; Lin, A.J.; Rajashekara, C.G.; et al. Campylobacter in Poultry: Ecology and Potential Interventions. Avian Dis. 2015, 59, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertas Onmaz, N.; Demirezen Yilmaz, D.; Imre, K.; Morar, A.; Gungor, C.; Yilmaz, S.; Gundog, D.A.; Dishan, A.; Herman, V.; Gungor, G. Green Synthesis of Gold Nanoflowers Using Rosmarinus officinalis and Helichrysum italicum Extracts: Comparative Studies of Their Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Activities. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plishka, M.; Sargeant, J.M.; Greer, A.L.; Hookey, S.; Winder, C. The prevalence of Campylobacter in live cattle, Turkey, chicken, and swine in the United States and Canada: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2021, 18, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccirillo, A.; Giacomelli, M.; Niero, G.; De Luca, C.; Carraro, L.; Ortali, G.; Mughini-Gras, L. Multilocus Sequence Typing of Campylobacter Jejuni and Campylobacter Coli to Identify Potential Sources of Colonization in Commercial Turkey Farms. Avian Pathol. 2018, 47, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Tang, H.; Wang, Z.; Yin, Y.; Ren, F.; Kong, L.; Jiao, X.; Huang, J. Characterization and Prevalence of Campylobacter spp. from Broiler Chicken Rearing Period to the Slaughtering Process in Eastern China. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinueza-Burgos, C.; Wautier, M.; Martiny, D.; Cisneros, M.; Van Damme, I.; De Zutter, L. Prevalence, Antimicrobial Resistance and Genetic Diversity of Campylobacter coli and Campylobacter jejuni in Ecuadorian Broilers at Slaughter Age. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 2366–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, S.A.; Morar, A.; Ban-Cucerzan, A.; Tîrziu, E.; Herman, V.; Sallam, K.I.; Morar, D.; Acaroz, U.; Imre, M.; Florea, T.; et al. Occurrence of Campylobacter spp. and Phenotypic Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles of Campylobacter jejuni in Slaughtered Broiler Chickens in North-Western Romania. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibanda, N.; McKenna, A.; Richmond, A.; Ricke, S.C.; Callaway, T.; Stratakos, A.C.; Gundogdu, O.; Corcionivoschi, N. A Review of the Effect of Management Practices on Campylobacter Prevalence in Poultry Farms. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Arnedo, I.; Gonzalez-Fandos, E. Prevalence of Campylobacter spp. in poultry in three Spanish farms, a slaughterhouse and a further processing plant. Foods 2019, 8, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, H.; Franklin-Hayes, P.; Koolman, L.; Egan, J.; Gutierrez, M.; Byrne, W.; Golden, O.; Bolton, D.; Reid, P.; Coffey, A. Prevalence and levels of Campylobacter in broiler chicken batches and carcasses in Ireland in 2017–2018. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 372, 109693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beterams, A.; Püning, C.; Wyink, B.; Grosse-Kleimann, J.; Gölz, G.; Schönknecht, A.; Alter, T.; Reich, F. Status quo: Levels of Campylobacter spp. and hygiene indicators in German slaughterhouses for broiler and turkey. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2024, 414, 110610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayed, A.S.; Ibrahim, A.I.; Sobhy, M.M.; Elmahallawy, E.K.; Alsowayeh, N.; Alarjani, K.M.; El-Khadragy, M.F.; Youseef, A.G. Circulation of Thermophilic Campylobacter in Pigeons, Turkeys, and Humans at Live Bird Markets in Egypt. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1150077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomelli, M.; Salata, C.; Martini, M.; Montesissa, C.; Piccirillo, A. Antimicrobial Resistance of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli from Poultry in Italy. Microb. Drug Resist. 2014, 20, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Adawy, H.; Ahmed, M.F.; Hotzel, H.; Tomaso, H.; Tenhagen, B.A.; Hartung, J.; Neubauer, H.; Hafez, H.M. Antimicrobial susceptibilities of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli recovered from organic turkey farms in Germany. Poult. Sci. 2015, 94, 2831–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzeznitzeck, J.; Breves, G.; Rychlik, I.; Hoerr, F.J.; von Altrock, A.; Rath, A.; Rautenschlein, S. The effect of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli colonization on the gut morphology, functional integrity, and microbiota composition of female turkeys. Gut Pathog. 2022, 14, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varga, C.; Guerin, M.T.; Brash, M.L.; Slavic, D.; Boerlin, P.; Susta, L. Antimicrobial Resistance in Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli Isolated from Small Poultry Flocks in Ontario, Canada: A Two-Year Surveillance Study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, S.L.; Carver, D.K.; Siletzky, R.M.; Romine, S.; Morrow, W.E.M.; Kathariou, S. Longitudinal study of prevalence of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli from turkeys and swine grown in close proximity. J. Food Prot. 2008, 71, 1791–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perko-Mäkelä, P.; Isohanni, P.; Katzav, M.; Lund, M.; Hänninen, M.L.; Lyhs, U. A longitudinal study of Campylobacter distribution in a turkey production chain. Acta Vet. Scand. 2009, 51, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kardoğan, Ö.; Müştak, İ.B. Resistance to Antimicrobials of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli Isolated from Turkeys in a Slaughterhouse. Etlik Vet. Mikrobiyol. Derg. 2023, 34, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Food Balance Sheets. FAOSTAT. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/FBS (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Eurostat. Poultry Statistics. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=Poultry_statistics (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- García-Fernández, A.; Dionisi, A.M.; Arena, S.; Iglesias-Torrens, Y.; Carattoli, A.; Luzzi, I. Human Campylobacteriosis in Italy: Emergence of Multi-Drug Resistance to Ciprofloxacin, Tetracycline, and Erythromycin. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, S.; Bakhshi, B.; Najar-Peerayeh, S. Significant contribution of the CmeABC Efflux pump in high-level resistance to ciprofloxacin and tetracycline in Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli clinical isolates. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2021, 20, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medscape. Campylobacteriosis: Medication. Medscape. Available online: https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/213720-medication (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- European Commission. Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2020/1729 of 17 November 2020 on the Monitoring and Reporting of Antimicrobial Resistance in Zoonotic and Commensal Bacteria. Off. J. Eur. Union 2020, L387, 8–21. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:32020D1729 (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- European Reference Laboratory for Antimicrobial Resistance (EURL-AR). CarbaCamp—Establishing MIC Distributions and ECOFFs for Carbapenems in Campylobacter from Animals. Available online: https://www.food.dtu.dk/english/-/media/institutter/foedevareinstituttet/temaer/antibiotikaresistens/eurl-ar/newsletter/704_2023-eurl-ar-newsletter-no17.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- Sougakoff, W.; Papadopoulou, B.; Nordmann, P.; Courvalin, P. Nucleotide Sequence and Distribution of Gene TetO Encoding Tetracycline Resistance in Campylobacter coli. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1987, 44, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avrain, L.; Vernozy-Rozand, C.; Kempf, I. Evidence for natural horizontal transfer of tetO gene between Campylobacter jejuni strains in chickens. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 97, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S.; Zishiri, O.T. Detection and prevalence of antimicrobial resistance genes in Campylobacter spp. isolated from chickens and humans. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2017, 84, e1–e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachoual, R.; Ouabdesselam, S.; Mory, F.; Lascols, C.; Soussy, C.J.; Tankovic, J. Single or Double Mutational Alterations of gyrA Associated with Fluoroquinolone Resistance in Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Microb. Drug Resist. 2001, 7, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Gu, Y.; He, L.; Ran, L.; Xia, S.; Han, X.; Li, H.; Zhou, H.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, J. Molecular typing and antimicrobial susceptibility profiles of Campylobacter jejuni isolates from north China. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 59, 1171–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharbi, M.; Béjaoui, A.; Ben Hamda, C.; Ghedira, K.; Ghram, A.; Maaroufi, A. Distribution of Virulence and Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli Isolated from Broiler Chickens in Tunisia. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2022, 55, 1273–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ocejo, M.; Oporto, B.; Lavín, J.L.; Hurtado, A. Whole genome-based characterisation of antimicrobial resistance and genetic diversity in Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli from ruminants. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, K.; Wołkowicz, T.; Osek, J. Antimicrobial resistance and virulence-associated traits of Campylobacter jejuni isolated from poultry food chain and humans with diarrhea. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysok, B.; Wojtacka, J.; Wiszniewska-Łaszczych, A.; Szteyn, J. Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Properties of Campylobacter Spp. Originating from Domestic Geese in Poland. Animals 2020, 10, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, K.; Wołkowicz, T.; Osek, J. flaA-SVR Based genetic diversity of multiresistant Campylobacter jejuni isolated from chickens and humans. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, D.; Scheutz, F.; Pedersen, K.; Handberg, K.; Madsen, M. PCR detection of seven virulence and toxin genes of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli isolates from Danish pigs and cattle and cytolethal distending toxin production of the isolates. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 94, 1003–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.N.M.; Hotzel, H.; El-Adawy, H.; Tran, H.T.; Le, M.T.H.; Tomaso, H.; Neubauer, H.; Hafez, H.M. Genotyping and antibiotic resistance of thermophilic Campylobacter isolated from chicken and pig meat in Vietnam. Gut Pathog. 2016, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazão, M.R.; Medeiros, M.I.C.; Duque, S.D.S.; Falcão, J.P. Pathogenic potential and genotypic diversity of Campylobacter jejuni: A neglected food-borne pathogen in Brazil. J. Med. Microbiol. 2017, 66, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, D.; Hannon, S.J.; Townsend, H.G.; Potter, A.; Allan, B.J. Genes coding for virulence determinants of Campylobacter jejuni in human clinical and cattle isolates from Alberta, Canada, and their potential role in colonization of poultry. Int. Microbiol. 2011, 14, 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Bolton, D.J. Campylobacter virulence and survival factors. Food Microbiol. 2016, 48, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara-Tejero, M.; Galán, J.E. CdtA, CdtB, and CdtC Form a Tripartite Complex That Is Required for Cytolethal Distending Toxin Activity. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 4358–4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Findik, A.; Ica, T.; Onuk, E.E.; Percin, D.; Kevenk, T.O.; Ciftci, A. Molecular typing and CDT genes prevalence of Campylobacter jejuni isolates from various sources. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2011, 43, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, S.; Niwa, H.; Itoh, K. Prevalence of 11 pathogenic genes of Campylobacter jejuni by PCR in strains isolated from humans, poultry meat and broiler and bovine faeces. J. Med. Microbiol. 2003, 52, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Meng, J.; Zhao, S.; Singh, R.; Song, W. Adherence to and Invasion of Human Intestinal Epithelial Cells by Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli Isolates from Retail Meat Products. J. Food Prot. 2006, 69, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, T.E.; McVeigh, A.L.; Scott, D.A.; Michielutti, R.E.; Bixby, A.; Carroll, S.A.; Bourgeois, A.L.; Guerry, P. Campylobacter jejunic cytolethal distending toxin mediates release of interleukin-8 from intestinal epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 6535–6541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhuo, Q.; Hong, Y.; Wu, Y.; Gu, Q.; Yuan, D.; Dong, Q.; Shao, J. Correlation between Multilocus Sequence Typing and Antibiotic Resistance, Virulence Potential of Campylobacter jejuni Isolates from Poultry Meat. Foods 2022, 11, 1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koolman, L.; Whyte, P.; Burgess, C.; Bolton, D. Distribution of Virulence-Associated Genes in a Selection of Campylobacter Isolates. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2015, 12, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, R.T.; Nalevaiko, P.C.; Mendonca, E.P.; Borges, L.W.; Fonseca, B.B.; Beletti, M.E.; Rossi, D.A. Campylobacter jejuni strains isolated from chicken meat harbor several virulence factors and represent a potential risk to humans. Food Control 2013, 33, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Park, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.H.; Jung, J.I.; Cho, S.; Ryu, S.; Jeon, B. Comparative Analysis of Aerotolerance, Antibiotic Resistance, and Virulence Gene Prevalence in Campylobacter jejuni Isolates from Retail Raw Chicken and Duck Meat in South Korea. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, K.; Osek, J. Identification of Virulence Genes in Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli Isolates by PCR. Bull. Vet. Inst. Pulawy 2008, 52, 211–216. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 10272-1; Microbiology of the Food Chain–Horizontal Method for Detection and Enumeration of Campylobacter spp.—Part 1: Detection Method. ISO (International Organization for Standardization): Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- EU. Commission implementing decision 2013/652/EU of 12 November 2013 on the monitoring and reporting of antimicrobial resistance in zoonotic and commensal bacteria. Off. J. Eur. Union L 2013, 303, 26–39. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA; ECDC. The European Union Summary Report on Antimicrobial Resistance in Zoonotic and Indicator Bacteria from Humans, Animals and Food in 2019–2020. EFSA J. 2021, 19, 6490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Clark, C.G.; Taylor, T.M.; Pucknell, C.; Barton, C.; Price, L.; Woodward, D.L.; Rodgers, F.G. Colony multiplex PCR assay for identification and differentiation of Campylobacter jejuni, C. coli, C. lari, C. upsaliensis, and C. fetus subsp. fetus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 4744–4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaGier, M.J.; Joseph, L.A.; Passaretti, T.V.; Musser, K.A.; Cirino, N.M. A real-time multiplexed PCR assay for rapid detection and differentiation of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Mol. Cell Probes 2004, 18, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zirnstein, G.; Li, Y.; Swaminathan, B.; Angulo, F. Ciprofloxacin Resistance in Campylobacter jejuni Isolates: Detection of gyrA Resistance Mutations by Mismatch Amplification Mutation Assay PCR and DNA Sequence Analysis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 3276–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Taylor, D.E. Chloramphenicol resistance in Campylobacter coli: Nucleotide sequence, expression, and cloning vector construction. Gene 1990, 94, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Deng, F.; Shen, Z.; Wu, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, J. Emergence of multidrug-resistant Campylobacter species isolates with a horizontally acquired rRNA methylase. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 5405–5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurinčič, M.; Botteldoorn, N.; Herman, L.; Smole Možina, S. Mechanisms of erythromycin resistance of Campylobacter spp. isolated from food; animals and humans. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 120, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olah, P.A.; Doetkott, C.; Fakhr, M.K.; Logue, C.M. Prevalence of the Campylobacter multi-drug efflux pump (CmeABC) in Campylobacter spp. Isolated from freshly processed Turkeys. Food Microbiol. 2006, 23, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeng, A.S.; Rickard, H.; Sexton, M.; Pang, Y.; Peng, H.; Barton, M. Antimicrobial susceptibilities and resistance genes in Campylobacter strains isolated from poultry and pigs in Australia. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 113, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, A.; Korolik, V. Tetracycline resistance of Australian Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli isolates. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2005, 55, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konkel, M.E.; Gray, S.A.; Kim, B.J.; Garvis, S.G.; Yoon, J. Identification of enteropathogens Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli based on the cadF virulence gene and its product. J. Clin Microbiol. 1999, 37, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casabonne, C.; González, A.; Aquili, V.; Subils, T.; Balague, C. Prevalence of Seven Virulence Genes of Campylobacter jejuni Isolated from Patients with Diarrhea in Rosario, Argentina. Int. J. Infect. 2016, 3, e37727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochran, W.G. Sampling Techniques, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1977; ISBN 0-471-16240-X. [Google Scholar]
- Parsons, V.L. Stratified Sampling. In Wiley StatsRef: Statistics Reference Online; Balakrishnan, N., Colton, T., Everitt, B., Piegorsch, W., Ruggeri, F., Teugels, J.L., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
| Origin | Campylobacter spp. | No. of Positive/ No. of Samples | Prevalence, % [95% CI] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Slaughterhouse | C. coli | 63/138 | 45.7 [37.6–54.0] |
| C. jejuni | 75/138 | 54.3 [46.0–62.4] |
| Antimicrobial | Cut Off Values | MIC Breakpoint (µg/mL) | No. of Resistant Isolates/Total Investigated (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Agent | S | R | C. jejuni | C. coli | |
| Fluoroquinolone | Ciprofloxacin | 0.5 | 0.125 | 32 | 70/75 (93.3) | 54/63 (85.7) |
| Amphenicols | Chloramphenicol | 16 | 2 | 64 | 0/75 (0) | 0/63 (0)- |
| Macrolide | Erythromycin | 8 (4) a | 1 | 512 | 14/75(18.7) | 18/63 (28.6) |
| Carbapenem | Ertapenem | 0.5 | 0.125 | 4 | 11/75 (14.7) | 8/63 (12.7) |
| Aminoglycoside | Gentamicin | 2 | 0.25 | 16 | 0/75 (0) | 0/63 (0)- |
| Tetracycline | Tetracycline | 2 (1) a | 0.5 | 64 | 58/75 (77.3) | 59/ 63 (93.7) |
| Gene Function | Determinants | C. jejuni % (p/N) | C. coli % (p/N) | Total % (p/N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resistance | gyrA (Thr-86-Ile mutation) | 90.4 (47/52) | 81.8 (36/44) | 86.5 (83/96) |
| catI | 0 (0/52) | 0 (0/44) | 0 (0/96) | |
| ermB | 100 (14/14) a | 100 (18/18) b | 100 (32/32) | |
| Ery23S (A2075G) | 71.4 (10/14) a | 50.0 (9/18) b | 59.4 (19/32) | |
| cmeB | 90.9 (10/11) c | 75.0 (6/8) d | 84.2 (16/19) | |
| aphA-3 | 0 (0/52) | 0 (0/44) | 0 (0/96) | |
| tetO | 100 (52/52) | 93.2 (41/44) | 96.9 (93/96) | |
| Virulence | cadF | 94.2 (49/52) | 84.1 (37/44) | 89.6 (86/96) |
| cdtA | 96.2 (50/52) | 84.1 (37/44) | 90.6 (87/96) | |
| cdtB | 92.3 (48/52) | 90.9 (40/44) | 91.7 (88/96) | |
| ciaB | 90.4 (47/52) | 88.6 (39/44) | 89.6 (86/96) | |
| flaA | 100 (52/52) | 100 (44/44) | 100 (96/96) | |
| virB11 | 63.5 (33/52) | 47.7 (21/44) | 56.3 (54/96) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Popa, S.A.; Herman, V.; Sallam, K.I.; Tîrziu, E.; Andor, C.; Morar, A.; Imre, M.; Ban-Cucerzan, A.; Pătrînjan, R.-T.; Pocinoc, A.; et al. Genotypic and Phenotypic Characterization of Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence in Campylobacter spp. Isolated from Turkeys: Uncovering a Neglected Reservoir in the One Health Context. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 935. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090935
Popa SA, Herman V, Sallam KI, Tîrziu E, Andor C, Morar A, Imre M, Ban-Cucerzan A, Pătrînjan R-T, Pocinoc A, et al. Genotypic and Phenotypic Characterization of Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence in Campylobacter spp. Isolated from Turkeys: Uncovering a Neglected Reservoir in the One Health Context. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(9):935. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090935
Chicago/Turabian StylePopa, Sebastian Alexandru, Viorel Herman, Khalid Ibrahim Sallam, Emil Tîrziu, Claudiu Andor, Adriana Morar, Mirela Imre, Alexandra Ban-Cucerzan, Răzvan-Tudor Pătrînjan, Alexandra Pocinoc, and et al. 2025. "Genotypic and Phenotypic Characterization of Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence in Campylobacter spp. Isolated from Turkeys: Uncovering a Neglected Reservoir in the One Health Context" Antibiotics 14, no. 9: 935. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090935
APA StylePopa, S. A., Herman, V., Sallam, K. I., Tîrziu, E., Andor, C., Morar, A., Imre, M., Ban-Cucerzan, A., Pătrînjan, R.-T., Pocinoc, A., & Imre, K. (2025). Genotypic and Phenotypic Characterization of Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence in Campylobacter spp. Isolated from Turkeys: Uncovering a Neglected Reservoir in the One Health Context. Antibiotics, 14(9), 935. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090935














