Effects of Antiseptic Formulations on Oral Microbiota and Related Systemic Diseases: A Scoping Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Objective and PCC Framework
- Population (P): Human subjects, in vitro, and animal models related to oral health;
- Concept (C): Use of antiseptic formulations (e.g., chlorhexidine, essential oils, and cetylpyridinium chloride) and their impact on oral microbiota and systemic health;
- Context (C): Clinical and experimental settings involving oral hygiene and systemic implications.
2.2. Research Question
2.3. Eligibility Criteria
2.4. Information Source and Search Strategy
2.5. Study Selection
2.6. Data Charting and Extraction
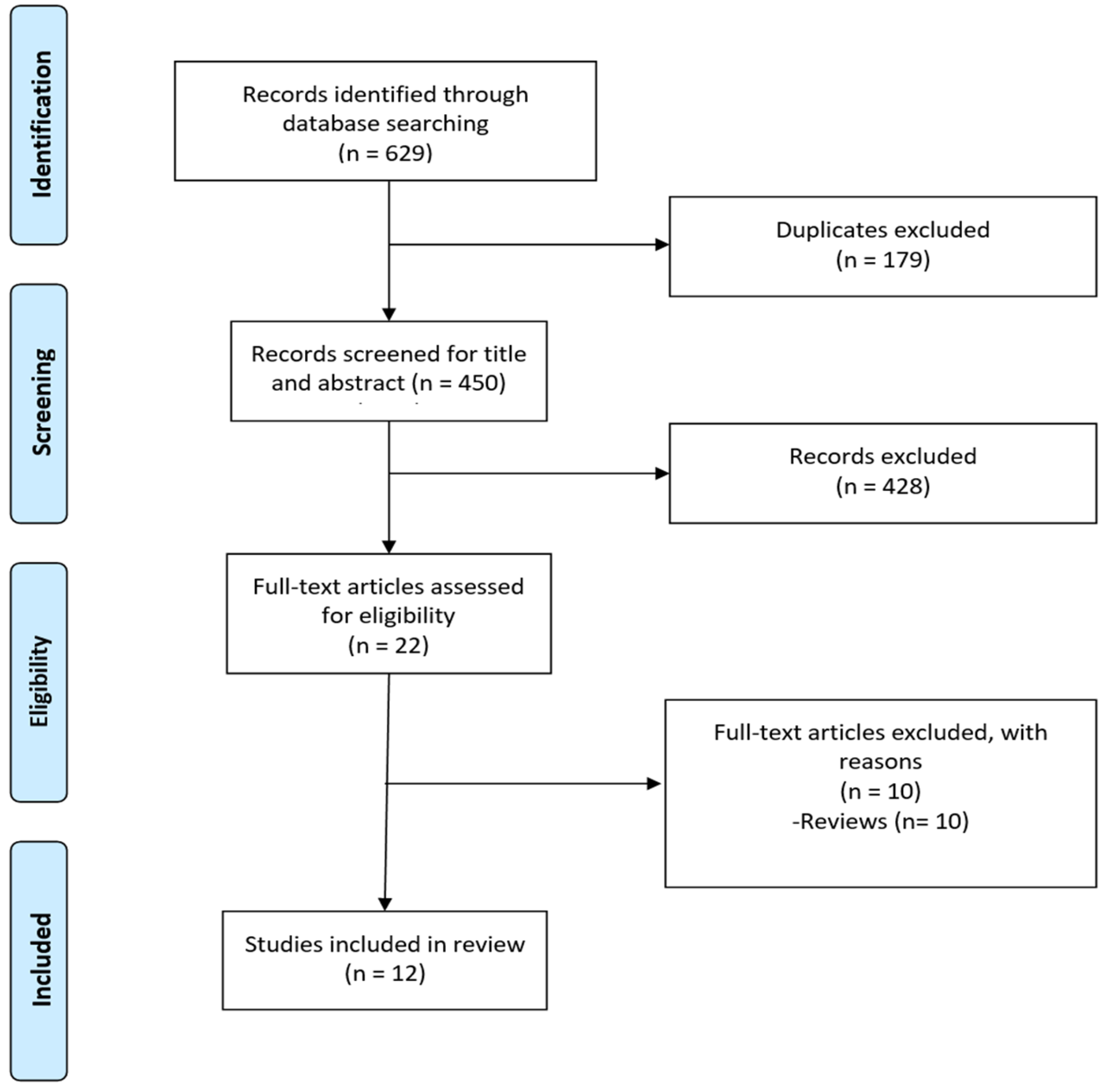
3. Results
3.1. Selection of Sources of Evidence
3.2. Characteristics of Included Studies
3.3. Summary of Findings
4. Discussion
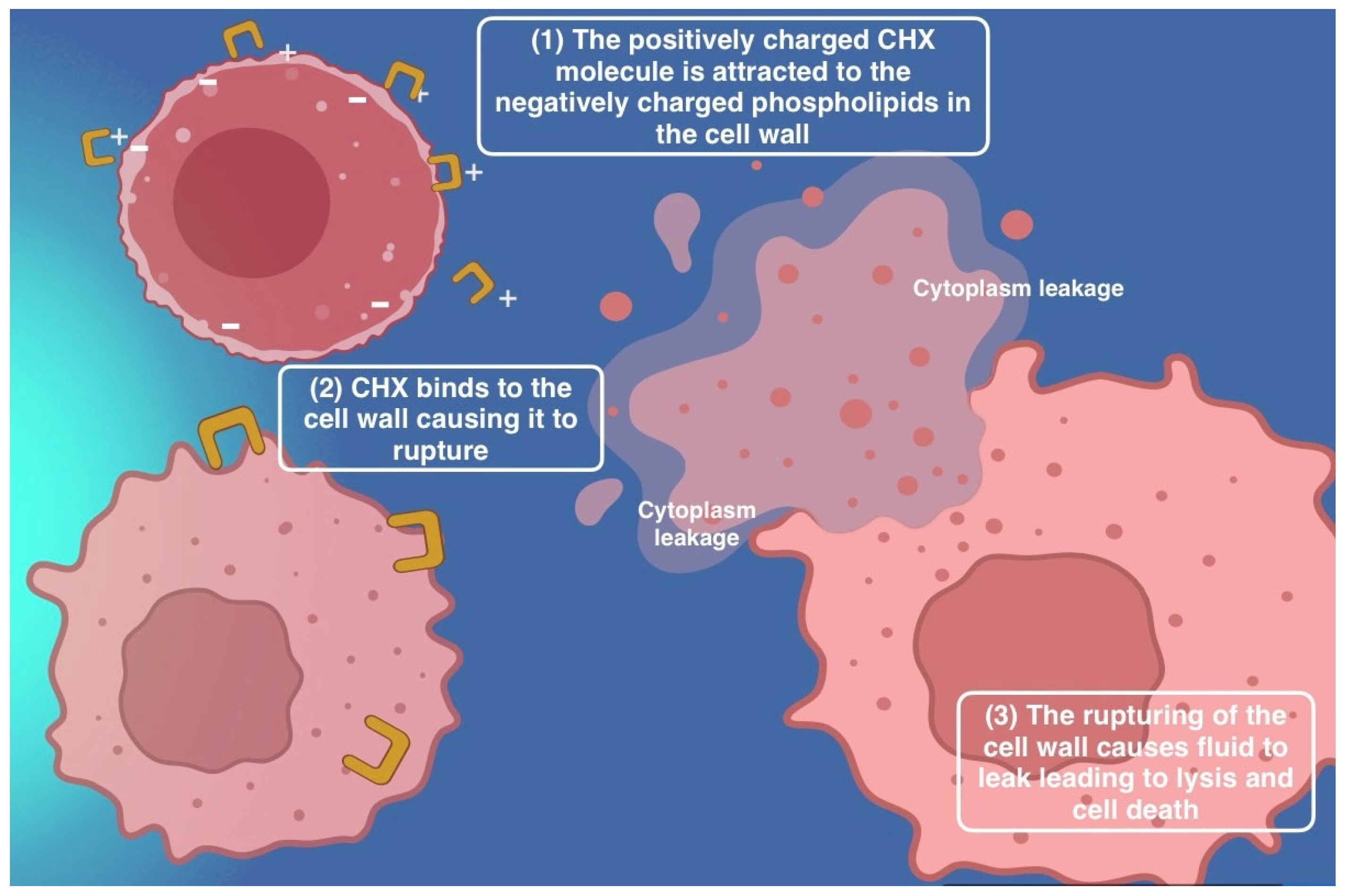
4.1. Antiseptic Formulations: Common Agents, Characteristics, and Microbial Impact
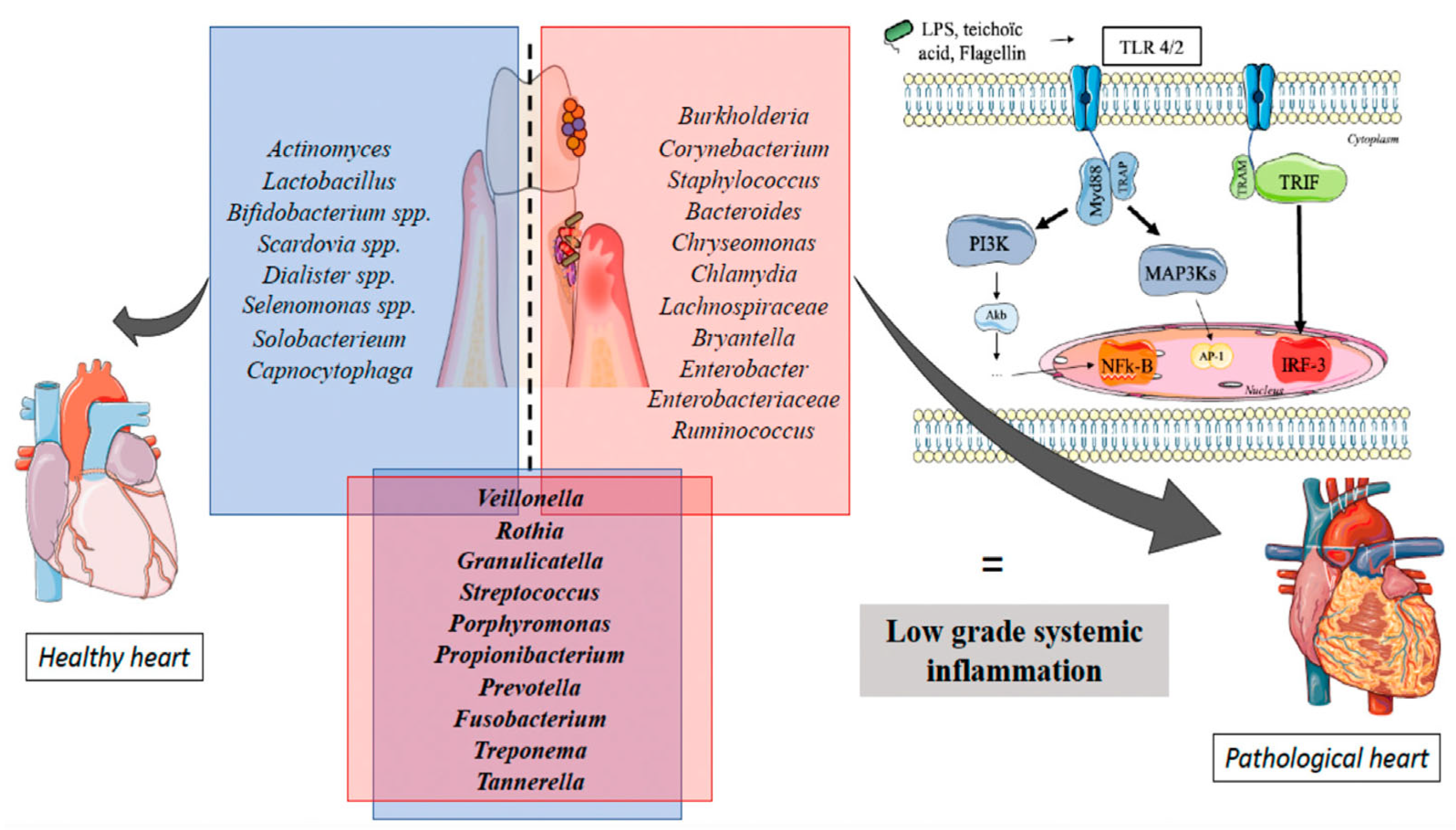
4.2. Systemic Impact of Oral Antiseptics and Related Systemic Diseases
4.3. Alternative Treatments and Future Strategies for Oral Dysbiosis Management
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kilian, M.; Chapple, I.L.C.; Hannig, M.; Marsh, P.D.; Meuric, V.; Pedersen, A.M.; Tonetti, M.S.; Wade, W.G.; Zaura, E. The oral microbiome—An update for oral healthcare professionals. Br. Dent. J. 2016, 221, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekaran, J.J.; Krishnamurthy, H.K.; Bosco, J.; Jayaraman, V.; Krishna, K.; Wang, T.; Bei, K. Oral Microbiome: A Review of Its Impact on Oral and Systemic Health. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Ni, C.; Du, Z.; Yan, F. Human oral microbiota and its modulation for oral health. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 99, 883–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaura, E.; Keijser, B.J.F.; Huse, S.M.; Crielaard, W. Defining the healthy “core microbiome” of oral microbial communities. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deo, P.; Deshmukh, R. Oral microbiome: Unveiling the fundamentals. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. 2019, 23, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Relman, D.A. The human microbiome: Ecosystem resilience and health. Nutr. Rev. 2012, 70, S2–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donohoe, D.R.; Garge, N.; Zhang, X.; Sun, W.; O’Connell, T.M.; Bunger, M.K.; Bultman, S.J. The Microbiome and Butyrate Regulate Energy Metabolism and Autophagy in the Mammalian Colon. Cell Metab. 2011, 13, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, Z.; Teoh, L.; Cieplik, F.; Kumar, P. Mouthwash Effects on the Oral Microbiome: Are They Good, Bad, or Balanced? Int. Dent. J. 2023, 73, S74–S81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Zhi, A.; Lai, P.F.H.; Wang, G.; Xia, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, H.; Lam, J.C.Y.; Tong, C.; Ng, S.C. The oral microbiota—A mechanistic role for systemic diseases. Br. Dent. J. 2018, 224, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.; Minty, M.; Vinel, A.; Canceill, T.; Loubières, P.; Burcelin, R.; Groen, A.K.; Serrano-Villar, S.; Moreno, S.; Sokol, H. Oral Microbiota: A Major Player in the Diagnosis of Systemic Diseases. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosaddad, S.A.; Mahootchi, P.; Safari, S.; Rahimi, H.; Aghili, S.S. Interactions between systemic diseases and oral microbiota shifts in the aging community: A narrative review. J. Basic Microbiol. 2023, 63, 831–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrashdan, M.S.; Leao, J.C.; Doble, A.; McCullough, M.; Porter, S. The Effects of Antimicrobial Mouthwashes on Systemic Disease: What Is the Evidence? Int. Dent. J. 2023, 73, S82–S88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciancio, S.G. Mouthwashes: Rationale for use. Am. J. Dent. 2015, 28, 4A–8A. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Divaris, K.; Moss, K.; Beck, J.D. Biologically informed stratification of periodontal disease holds the key to achieving precision oral health. J. Periodontol. 2020, 91, S50–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haydari, M.; Bardakci, A.G.; Koldsland, O.C.; Aass, A.M.; Sandvik, L.; Preus, H.R. Comparing the effect of 0.06% -, 0.12% and 0.2% Chlorhexidine on plaque, bleeding and side effects in an experimental gingivitis model: A parallel group, double masked randomized clinical trial. BMC Oral Health 2017, 17, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najafi, M.H.; Taheri, M.; Mokhtari, M.R.; Forouzanfar, A.; Farazi, F.; Mirzaee, M.; Ebrahiminik, Z.; Mehrara, R. Comparative study of 0.2% and 0.12% digluconate chlorhexidine mouth rinses on the level of dental staining and gingival indices. Dent. Res. J. 2012, 9, 305–308. [Google Scholar]
- Cousido, M.C.; Tomás Carmona, I.; García-Caballero, L.; Limeres, J.; Álvarez, M.; Diz, P. In vivo substantivity of 0.12% and 0.2% chlorhexidine mouthrinses on salivary bacteria. Clin. Oral Investig. 2010, 14, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, F.; He, T.; Huang, S.; Bo, C.-P.; Li, Z.; Chang, J.-L.; Liu, J.Q.; Charbonneau, D.; Xu, J.; Li, R. Cetylpyridinium chloride mouth rinses alleviate experimental gingivitis by inhibiting dental plaque maturation. Int. J. Oral. Sci. 2016, 8, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Li, X.; Sreenivasan, P.K.; DeVizio, W. A randomized, double-blind clinical study to assess the antimicrobial effects of a cetylpyridinium chloride mouth rinse on dental plaque bacteria. Clin. Ther. 2009, 31, 2540–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rioboo, M.; García, V.; Serrano, J.; O’Connor, A.; Herrera, D.; Sanz, M. Clinical and microbiological efficacy of an antimicrobial mouth rinse containing 0.05% cetylpyridinium chloride in patients with gingivitis. Int. J. Dent. Hyg. 2012, 10, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbach, J.; Ebenezer, S.; Warnke, P.H.; Behrens, E.; Al-Nawas, B. Antimicrobial effect of Australian antibacterial essential oils as alternative to common antiseptic solutions against clinically relevant oral pathogens. Clin. Lab. 2015, 61, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nikolić, M.; Marković, T.; Marković, D.; Glamočlija, J.; Ćirić, A.; Smiljković, M.; Sokovic, M. Antimicrobial activity of three Lamiaceae essential oils against common oral pathogens. Balk. J. Dent. Med. 2016, 20, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsui, T.; Harasawa, R. The effects of essential oil, povidone-iodine, and chlorhexidine mouthwash on salivary nitrate/nitrite and nitrate-reducing bacteria. J. Oral Sci. 2017, 59, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusberti, F.A.; Sampathkumar, P.; Siegrist, B.E.; Lang, N.P. Microbiological and clinical effects of chlorhexidine digluconate and hydrogen peroxide mouthrinses on developing plaque and gingivitis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1988, 15, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, M.S.; Paula, M.S.A.; Cardoso, M.M.; Silva, N.P.; Tavares, L.C.D.; Gomes, T.V.; Porto, D.L.; Aragão, C.F.S.; Fabri, R.L.; Tavares, G.D.; et al. Exploring the antimicrobial efficacy of tea tree essential oil and chitosan against oral pathogens to overcome antimicrobial resistance. Microb. Pathog. 2024, 196, 107006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehghani, M.; Abtahi, M.; Hasanzadeh, N.; Farahzad, Z.; Noori, M.; Noori, M. Effect of Propolis mouthwash on plaque and gingival indices over fixed orthodontic patients. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2019, 11, e244–e249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darveau, R.P.; Tanner, A.; Page, R.C. The microbial challenge in periodontitis. Periodontol. 2000 1997, 14, 12–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teles, R.; Teles, F.; Frias-Lopez, J.; Paster, B.; Haffajee, A. Lessons learned and unlearned in periodontal microbiology. Periodontol. 2000 2013, 62, 95–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Chang, M.; Martin, J.; Mitreva, M.; Lux, R.; Klokkevold, P.; Sodergren, E.; Weinstock, G.M.; Haake, S.K.; Li, H. Dynamic Changes in the Subgingival Microbiome and Their Potential for Diagnosis and Prognosis of Periodontitis. mBio 2015, 6, e01926-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabdoub, S.M.; Ganesan, S.M.; Kumar, P.S. Comparative metagenomics reveals taxonomically idiosyncratic yet functionally congruent communities in periodontitis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Z.; Yang, L.; Hu, Y.; Huang, R. Oral microbiota dysbiosis accelerates the development and onset of mucositis and oral ulcers. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1061032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, C.; Song, Z. The Oral Microbiota: Community Composition, Influencing Factors, Pathogenesis, and Interventions. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 895537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wylie, K.M.; Mihindukulasuriya, K.A.; Zhou, Y.; Sodergren, E.; Storch, G.A.; Weinstock, G.M. Metagenomic analysis of double-stranded DNA viruses in healthy adults. BMC Biol. 2014, 12, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, J.L.; Mark Welch, J.L.; Kauffman, K.M.; McLean, J.S.; He, X. The oral microbiome: Diversity, biogeography and human health. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Huang, Y.; Huang, M.; Wang, M.; Ming, Y.; Chen, W.; Tang, Z.; Jia, B. From nitrate to NO: Potential effects of nitrate-reducing bacteria on systemic health and disease. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Wang, P.; Gao, W. Microbial dysbiosis in periodontitis and peri-implantitis: Pathogenesis, immune responses, and therapeutic. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2025, 15, 1517154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-H.; Chen, H.-M.; Yang, S.-F.; Liang, C.; Peng, C.-Y.; Lin, F.-M.; Lee, J.-C.; Chen, C.-Y.; Yang, S.-Y.; Huang, C.-C.; et al. Bacterial alterations in salivary microbiota and their association in oral cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Martin, I.; Doolittle-Hall, J. FRF Teles Exploring the microbiome of healthy and diseased peri-implant sites using Illumina sequencing. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44, 1274–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaka, S.; Sotozono, M.; Ohkura, N.; Noiri, Y. Evidence on the Use of Mouthwash for the Control of Supragingival Biofilm and Its Potential Adverse Effects. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basic, A.; Dahlén, G. Microbial metabolites in the pathogenesis of periodontal diseases: A narrative review. Front. Oral Health 2023, 4, 1210200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzigiannidou, I.; Teughels, W.; Van de Wiele, T.; Boon, N. Oral biofilms exposure to chlorhexidine results in altered microbial composition and metabolic profile. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2020, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costalonga, M.; Herzberg, M.C. The oral microbiome and the immunobiology of periodontal disease and caries. Immunol. Lett. 2014, 162, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.L.; Morton, J.T.; Dinis, M.; Alvarez, R.; Tran, N.C.; Knight, R.; Edlund, A. Deep metagenomics examines the oral microbiome during dental caries, revealing novel taxa and co-occurrences with host molecules. Genome Res. 2021, 31, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Xie, T.; Li, S.; Qiao, X.; Lu, Y.; Feng, Y. Analysis of oral microbial dysbiosis associated with early childhood caries. BMC Oral Health 2021, 21, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abusleme, L.; Dupuy, A.K.; Dutzan, N.; Silva, N.; Burleson, J.A.; Strausbaugh, L.D.; Gamonal, J.; Diaz, P.I. The subgingival microbiome in health and periodontitis and its relationship with community biomass and inflammation. ISME J. 2013, 7, 1016–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galimanas, V.; Hall, M.W.; Singh, N.; Lynch, M.D.J.; Goldberg, M.; Tenenbaum, H.; Cvitkovitch, D.G.; Neufeld, J.D.; Senadheera, D.B. Bacterial community composition of chronic periodontitis and novel oral sampling sites for detecting disease indicators. Microbiome 2014, 2, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weatherly, L.M.; Gosse, J.A. Triclosan exposure, transformation, and human health effects. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B 2017, 20, 447–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, H.J.; Zhang, C.P. The oral microbiota may have influence on oral cancer. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolini, M.; Ranjan, A.; Thompson, A.; Diaz, P.I.; Sobue, T.; Maas, K.; Dongari-Bagtzoglou, A. Candida albicans induces mucosal bacterial dysbiosis that promotes invasive infection. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yue, H.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Shen, J.; Hailili, G.; Sun, Z.; Zhou, X.; Pu, Y.; Song, H.; et al. Oral Microbiota Linking Associations of Dietary Factors with Recurrent Oral Ulcer. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.W.; Wang, X. Mobile Microbiome. J. Dent. Res. 2013, 92, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, O.; Spor, A.; Felin, J.; Fåk, F.; Stombaugh, J.; Tremaroli, V.; Behre, C.J.; Knight, R.; Fagerberg, B.; Ley, R.E. Human oral, gut, and plaque microbiota in patients with atherosclerosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4592–4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Hiergeist, A.; Auer, D.L.; Scholz, K.J.; Muehler, D.; Hiller, K.-A.; Maisch, T.; Buchalla, W.; Hellwig, E.; Gessner, A.; et al. Ecological Effects of Daily Antiseptic Treatment on Microbial Composition of Saliva-Grown Microcosm Biofilms and Selection of Resistant Phenotypes. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 934525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Auer, D.L.; Buchalla, W.; Hiller, K.-A.; Maisch, T.; Hellwig, E.; Al-Ahmad, A.; Cieplik, F. Cetylpyridinium Chloride: Mechanism of Action, Antimicrobial Efficacy in Biofilms, and Potential Risks of Resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e00576-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, J.; Escribano, M.; Roldán, S.; Martín, C.; Herrera, D. Efficacy of adjunctive anti-plaque chemical agents in managing gingivitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2015, 42, S106–S138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido, L.; Lyra, P.; Rodrigues, J.; Viana, J.; Mendes, J.J.; Barroso, H. Revisiting Oral Antiseptics, Microorganism Targets and Effectiveness. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tartaglia, G.M.; Tadakamadla, S.K.; Connelly, S.T.; Sforza, C.; Martín, C. Adverse events associated with home use of mouthrinses: A systematic review. Ther. Adv. Drug Saf. 2019, 10, 2042098619854881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, M.; Herrera, D.; Kebschull, M.; Chapple, I.; Jepsen, S.; Berglundh, T.; Sculean, A.; Tonetti, M.S. Treatment of stage I–III periodontitis—The EFP S3 level clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2020, 47, 4–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, D.; Matesanz, P.; Martín, C.; Oud, V.; Feres, M.; Teughels, W. Adjunctive effect of locally delivered antimicrobials in periodontitis therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2020, 47, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartaglia, G.M.; Kumar, S.; Fornari, C.D.; Corti, E.; Connelly, S.T. Mouthwashes in the 21st century: A narrative review about active molecules and effectiveness on the periodontal outcomes. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2017, 14, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezovska, A.; Meiller, A.; Marinesco, S.; Nedellec, Y.; Giroud, F.; Gross, A.J.; Cosnier, S. Chlorhexidine digluconate exerts bactericidal activity vs Gram positive Staphylococci with bioelectrocatalytic compatibility: High level disinfection for implantable biofuel cells. Bioelectrochemistry 2023, 152, 108435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppolo Deus, F.; Ouanounou, A. Chlorhexidine in Dentistry: Pharmacology, Uses, and Adverse Effects. Int. Dent. J. 2022, 72, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raszewski, Z.; Nowakowska-Toporowska, A.; Weżgowiec, J.; Nowakowska, D. Design and characteristics of new experimental chlorhexidine dental gels with anti-staining properties. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2019, 28, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huyck, C.L. The Effect of Cetylpyridinium Chloride on the Bacterial Growth in the Oral Cavity. J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. (Sci. ed.) 1945, 34, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouhan, S.; Sharma, K.; Guleria, S. Antimicrobial Activity of Some Essential Oils—Present Status and Future Perspectives. Medicines 2017, 4, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakkali, F.; Averbeck, S.; Averbeck, D.; Idaomar, M. Biological effects of essential oils—A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 446–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneyama, A.; Shimizu, M.; Tabata, M.; Yashiro, J.; Takata, T.; Hikida, M. In vitro Short-Time Killing Activity of Povidone-Iodine (Isodine® Gargle) in the Presence of Oral Organic Matter. Dermatology 2006, 212, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuse, Y.; Ito, Y.; Yamaguchi, M.; Tsukada, N. High Ingestion Rate of Iodine from Povidone-Iodine Mouthwash. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 3902–3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi ADe Ferreira, D.C.A.; Silva RABda Queiroz AMde Silva LABda Nelson-Filho, P. Antimicrobial Activity of Toothpastes Containing Natural Extracts, Chlorhexidine or Triclosan. Braz. Dent. J. 2014, 25, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, W.G.; Addy, M. Antibacterial Activity of Some Triclosan-Containing Toothpastes and Their Ingredients. J. Periodontol. 1992, 63, 280–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyganowska-Swiatkowska, M.; Kotwicka, M.; Urbaniak, P.; Nowak, A.; Skrzypczak-Jankun, E.; Jankun, J. Clinical implications of the growth-suppressive effects of chlorhexidine at low and high concentrations on human gingival fibroblasts and changes in morphology. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 37, 1594–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Hu, T.; Cheng, R.; Cai, H. The efficacy of mouthwashes on oral microorganisms and gingivitis in patients undergoing orthodontic treatment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariotti, A.J.; Rumpf, D.A.H. Chlorhexidine-Induced Changes to Human Gingival Fibroblast Collagen and Non-Collagen Protein Production. J. Periodontol. 1999, 70, 1443–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pucher, J.J.; Daniel, C. The Effects of Chlorhexidine Digluconate on Human Fibroblasts In Vitro. J. Periodontol. 1992, 63, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.X.; Werner, J.; Kirsch, T.; Zuckerman, J.D.; Virk, M.S. Cytotoxicity evaluation of chlorhexidine gluconate on human fibroblasts, myoblasts, and osteoblasts. J. Bone Jt. Infect. 2018, 3, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannelli, M.; Chellini, F.; Margheri, M.; Tonelli, P.; Tani, A. Effect of chlorhexidine digluconate on different cell types: A molecular and ultrastructural investigation. Toxicol. Vitr. 2008, 22, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartsch, S.; Kohnert, E.; Kreutz, C.; Woelber, J.P.; Anderson, A.; Burkhardt, A.-S.; Hellwig, E.; Buchalla, W.; Hiller, K.A.; Krueger, P.R.; et al. Chlorhexidine digluconate mouthwash alters the oral microbial composition and affects the prevalence of antimicrobial resistance genes. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1429692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eley, B.M. Antibacterial agents in the control of supragingival plaque—A review. Br. Dent. J. 1999, 186, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Kumar, K. Importance of Chlorhexidine in Maintaining Periodontal Health. Int. J. Dent. Res. 2016, 1, 31–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkvoll, P.; Rølla, G.; Svendsen, A.K. Interaction between chlorhexidine digluconate and sodium lauryl sulfate in vivo. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1989, 16, 593–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolahi, J.; Soolari, A. Rinsing with chlorhexidine gluconate solution after brushing and flossing teeth: A systematic review of effectiveness. Quintessence Int. 2006, 37, 605–612. [Google Scholar]
- Poppolo Deus, F.; Ouanounou, A. Mouthwashes and their use in dentistry: A review. Oral Health 2021, 1, 22–34. [Google Scholar]
- Gerba, C.P. Quaternary Ammonium Biocides: Efficacy in Application. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Weijden, F.A.; Van der Sluijs, E.; Ciancio, S.G.; Slot, D.E. Can Chemical Mouthwash Agents Achieve Plaque/Gingivitis Control? Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 59, 799–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinković, J.; Rakašević, D.; Nemoda, M.; Nikolić, B.; Marković, T.; Matijević, S.; Markovic, D. EO-based mouthwashes: Is there something that should be known? Balk. J. Dent. Med. 2023, 27, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaka, S.; Ohsumi, T.; Noiri, Y. Evidence-based strategy for dental biofilms: Current evidence of mouthwashes on dental biofilm and gingivitis. Jpn. Dent. Sci. Rev. 2019, 55, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duane, B.; Yap, T.; Neelakantan, P.; Anthonappa, R.; Bescos, R.; McGrath, C.; McCullough, M.; Brookes, Z. Mouthwashes: Alternatives and Future Directions. Int. Dent. J. 2023, 73, S89–S97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radu, C.-M.; Radu, C.C.; Bochiș, S.-A.; Arbănași, E.M.; Lucan, A.I.; Murvai, V.R.; Zaha, D.C. Revisiting the Therapeutic Effects of Essential Oils on the Oral Microbiome. Pharmacy 2023, 11, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagalingam, J.; Feliciano, R.; Hah, J.H.; Labib, H.; Le, T.A.; Lin, J.-C. Practical use of povidone-iodine antiseptic in the maintenance of oral health and in the prevention and treatment of common oropharyngeal infections. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2015, 69, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniz, F.W.M.G.; Cavagni, J.; Langa, G.P.J.; Stewart, B.; Malheiros, Z.; Rösing, C.K. A Systematic Review of the Effect of Oral Rinsing with H2O2 on Clinical and Microbiological Parameters Related to Plaque, Gingivitis, and Microbes. Int. J. Dent. 2020, 2020, 8841722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, G.; Russell, A.D. Antiseptics and Disinfectants: Activity, Action, and Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 12, 147–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etemadi, S.; Barhaghi, M.H.S.; Leylabadlo, H.E.; Memar, M.Y.; Mohammadi, A.B.; Ghotaslou, R. The synergistic effect of turmeric aqueous extract and chitosan against multidrug-resistant bacteria. New Microbes New Infect. 2021, 41, 100861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Zorrilla, S.; Blanco Carrión, A.; García García, A.; Galindo Moreno, P.; Marichalar Mendía, X.; Seoane Prado, R.; Estévez, A.J.P. Effect of antiseptic gels in the microbiologic colonization of the suture threads after oral surgery. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andres, Y.; Giraud, L.; Gerente, C.; Le Cloirec, P. Antibacterial Effects of Chitosan Powder: Mechanisms of Action. Environ. Technol. 2007, 28, 1357–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmingsen, L.M.; Škalko-Basnet, N.; Jøraholmen, M.W. The Expanded Role of Chitosan in Localized Antimicrobial Therapy. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasanth, M. Antimicrobial efficacy of different toothpastes and mouthrinses: An in vitro study. Dent. Res. J. 2011, 8, 85–94. [Google Scholar]
- Maksymowicz, M.; Machowiec, P.; Ręka, G.; Korzeniowska, A.; Leszczyk, P.; Piecewicz-Szczęsna, H. Mechanism of action of triclosan as an endocrine-disrupting chemical with its impact on human health—Literature review. J. Pre-Clin. Clin. Res. 2021, 15, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.C.; Mariana, M.; Cairrao, E. Triclosan and Its Consequences on the Reproductive, Cardiovascular and Thyroid Levels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruszkiewicz, J.A.; Li, S.; Rodriguez, M.B.; Aschner, M. Is Triclosan a neurotoxic agent? J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B 2017, 20, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinicropi, M.S.; Iacopetta, D.; Ceramella, J.; Catalano, A.; Mariconda, A.; Pellegrino, M.; Saturnino, C.; Longo, P.; Aquaro, S. Triclosan: A Small Molecule with Controversial Roles. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halboub, E.; Al-Maweri, S.A.; Al-Wesabi, M.; Al-Kamel, A.; Shamala, A.; Al-Sharani, A.; Koppolu, P. Efficacy of propolis-based mouthwashes on dental plaque and gingival inflammation: A systematic review. BMC Oral Health 2020, 20, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, M.A.; Khabeer, A.; Faridi, M.A.; Makhdoom, G. Effectiveness of propolis in maintaining oral health: A scoping review. Can. J. Dent. Hyg. 2021, 55, 167–176. [Google Scholar]
- Alpaslan Yayli, N.; Tunc, S.K.; Degirmenci, B.U.; Dikilitas, A.; Taspinar, M. Comparative Evaluation of the Cytotoxic Effects of Different Oral Antiseptics. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2021, 24, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignatelli, P.; Fabietti, G.; Ricci, A.; Piattelli, A.; Curia, M.C. How Periodontal Disease and Presence of Nitric Oxide Reducing Oral Bacteria Can Affect Blood Pressure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulares, A.; Jdidi, H.; Bragazzi, N.L. Impact of Mouthwash-Induced Oral Microbiome Disruption on Alzheimer’s Disease Risk: A Perspective Review. Int. Dent. J. 2025, 75, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellepola, A.N.B.; Chandy, R.; Khan, Z.U. In vitro Impact of Limited Exposure to Subtherapeutic Concentrations of Chlorhexidine Gluconate on the Adhesion-Associated Attributes of Oral Candida Species. Med. Princ. Pract. 2016, 25, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- do Amaral, G.C.L.S.; Hassan, M.A.; Sloniak, M.C.; Pannuti, C.M.; Romito, G.A.; Villar, C.C. Effects of antimicrobial mouthwashes on the human oral microbiome: Systematic review of controlled clinical trials. Int. J. Dent. Hyg. 2023, 21, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, S.M.; El Samak, M.; El-Baz, L.M.F.; Hanora, A.M.S.; Satyal, P.; Dosoky, N.S. Effects of Mint Oils on the Human Oral Microbiome: A Pilot Study. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verspecht, T.; Rodriguez Herrero, E.; Khodaparast, L.; Khodaparast, L.; Boon, N.; Bernaerts, K.K.; Quirynen, M.; Teughels, W. Development of antiseptic adaptation and cross-adapatation in selected oral pathogens in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshipura, K.; Muñoz-Torres, F.; Fernández-Santiago, J.; Patel, R.P.; Lopez-Candales, A. Over-the-counter mouthwash use, nitric oxide and hypertension risk. Blood Press. 2020, 29, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondonno, C.P.; Liu, A.H.; Croft, K.D.; Considine, M.J.; Puddey, I.B.; Woodman, R.J.; Hodgson, J.M. Antibacterial Mouthwash Blunts Oral Nitrate Reduction and Increases Blood Pressure in Treated Hypertensive Men and Women. Am. J. Hypertens. 2015, 28, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, N.S.; Tribble, G.; Angelov, N. Oral Microbiome and Nitric Oxide: The Missing Link in the Management of Blood Pressure. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2017, 19, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshipura, K.J.; Muñoz-Torres, F.J.; Morou-Bermudez, E.; Patel, R.P. Over-the-counter mouthwash use and risk of pre-diabetes/diabetes. Nitric Oxide 2017, 71, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preshaw, P.M. Mouthwash use and risk of diabetes. Br. Dent. J. 2018, 225, 923–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Joshipura, K.; Ricart, K.; Patel, R.P.; Gower, B.A.; Andriankaja, O.M.; Bermudez, E.M. Association of over-the-counter mouthwash use with markers of nitric oxide metabolism, inflammation, and endothelial function—A cross-sectional study. Front. Oral Health 2025, 6, 1488286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.Z.; Joshipura, K.J.; Habash, F.; Lopez-Candales, A. Dentists and physicians’ practices meet once again: Potential unfavorable clinical effects of frequent mouthwash use. Postgrad. Med. 2021, 133, 123–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugesan, G.S.; Venkat, M.P. The effect of iodine in patients using povidone-iodine mouth wash on thyroid function. Int. J. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 5, 1562–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggers, M. Infectious Disease Management and Control with Povidone Iodine. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2019, 8, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, W.; Pohlabeln, H.; Foraita, R.; Nelis, M.; Lagiou, P.; Lagiou, A.; Bouchardy, C.; Slamova, A.; Schejbalova, M.; Merletti, F. Oral health, dental care and mouthwash associated with upper aerodigestive tract cancer risk in Europe: The ARCAGE study. Oral Oncol. 2014, 50, 616–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceves Argemí, R.; González Navarro, B.; Ochoa García-Seisdedos, P.; Estrugo Devesa, A.; López-López, J. Mouthwash With Alcohol and Oral Carcinogenesis: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Evid. Based Dent. Pract. 2020, 20, 101407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, J.L.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, L.; Ge, L. The role of oral microbiome in respiratory health and diseases. Respir. Med. 2021, 185, 106475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Kaplan, R.C.; Burk, R.D.; Qi, Q. The Oral Microbiota, Microbial Metabolites, and Immuno-Inflammatory Mechanisms in Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lê, S.; Cecchin-Albertoni, C.; Thomas, C.; Kemoun, P.; Minty, M.; Blasco-Baque, V. The Role of Dysbiotic Oral Microbiota in Cardiometabolic Diseases: A Narrative Review. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francisqueti-Ferron, F.V.; Nakandakare-Maia, E.T.; Siqueira, J.S.; Ferron, A.J.T.; Vieira, T.A.; Bazan, S.G.Z.; Corrêa, C.R. The role of gut dysbiosis-associated inflammation in heart failure. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2022, 68, 1120–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannosh, I.; Staletovic, D.; Toljic, B.; Radunovic, M.; Pucar, A.; Matic Petrovic, S.; Grubisa, I.; Lazarevic, M.; Brkic, Z.; Vukcevic, J.K.; et al. The presence of periopathogenic bacteria in subgingival and atherosclerotic plaques—An age related comparative analysis. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2018, 12, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenkein, H.A.; Loos, B.G. Inflammatory mechanisms linking periodontal diseases to cardiovascular diseases. J. Periodontol. 2013, 84, S51–S69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietiäinen, M.; Liljestrand, J.M.; Kopra, E.; Pussinen, P.J. Mediators between oral dysbiosis and cardiovascular diseases. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2018, 126, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Cheng, L.; You, Y.; Tang, C.; Ren, B.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhou, X. Oral microbiota in human systematic diseases. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2022, 14, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozak, M.; Pawlik, A. The Role of the Oral Microbiome in the Development of Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haran, J.P.; Bradley, E.; Zeamer, A.L.; Cincotta, L.; Salive, M.-C.; Dutta, P.; Mutaawe, S.; Anya, O.; Segura, M.M.; Moormann, A.M.; et al. Inflammation-type dysbiosis of the oral microbiome associates with the duration of COVID-19 symptoms and long COVID. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e152346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Zhong, M.-M.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Zhao, J.; Dusenge, M.A.; Feng, Y.; Ye, Q.; Hu, J.; et al. Potential interaction between the oral microbiota and COVID-19: A meta-analysis and bioinformatics prediction. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1193340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, N.; El Karim, I. Periodontitis May Be Associated With Respiratory Diseases Such as Asthma, COPD, and Pneumonia. J. Evid. Based Dent. Pract. 2020, 20, 101498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Mu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, J.; Liang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, W.; et al. Dysbiosis of the Salivary Microbiome Is Associated with Non-smoking Female Lung Cancer and Correlated with Immunocytochemistry Markers. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Shi, F.; Zeng, J.; Bi, J.; Mo, C.; Chai, Y.; Wu, B.; Xu, S. Oral microbiota and respiratory diseases: Advances and perspectives. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2025, 38, e00150-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.; Ren, H.; Guo, H.; Xing, W.; Liu, C.; Ji, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, P.; Du, M. Periodontal infection with Porphyromonas gingivalis induces preterm birth and lower birth weight in rats. Mol. Oral Microbiol. 2018, 33, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, J.; Oh, K.; Yang, H.; Jun, J.; Jin, B.; Paik, D.; Bae, K.H. Oral Health Behaviors, Periodontal Disease, and Pathogens in Preeclampsia: A Case-Control Study in Korea. J. Periodontol. 2011, 82, 1685–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merchant, A.T.; Gupta RDas Akonde, M.; Reynolds, M.; Smith-Warner, S.; Liu, J.; Tarannum, F.; Beck, J.; Mattison, D. Association of Chlorhexidine Use and Scaling and Root Planing With Birth Outcomes in Pregnant Individuals With Periodontitis. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2247632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S. Oral Microbiome and Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes: An Update. Online J. Health Allied Sci. 2022, 21, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Näse, L.; Hatakka, K.; Savilahti, E.; Saxelin, M.; Pönkä, A.; Poussa, T.; Korpela, R.; Meurman, J.H. Effect of Long–Term Consumption of a Probiotic Bacterium, Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, in Milk on Dental Caries and Caries Risk in Children. Caries Res. 2001, 35, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S. Effect of Probiotic Curd on Salivary pH and Streptococcus mutans: A Double Blind Parallel Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, ZC13–ZC16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrique Soares, K.; Firoozi, P.; Maria de Souza, G.; Beatriz Lopes Martins, O.; Gabriel Moreira Falci, S.; Rocha dos Santos, C.R. Efficacy of Probiotics Compared to Chlorhexidine Mouthwash in Improving Periodontal Status: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Dent. 2023, 2023, 4013004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheisary, Z.; Mahmood, R.; Harri Shivanantham, A.; Liu, J.; Lieffers, J.R.L.; Papagerakis, P.; Papagerakis, S. The Clinical, Microbiological, and Immunological Effects of Probiotic Supplementation on Prevention and Treatment of Periodontal Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inchingolo, F.; Inchingolo, A.M.; Malcangi, G.; De Leonardis, N.; Sardano, R.; Pezzolla, C.; Di Cosola, M.; Fiorillo, L.; Cantore, S.; Palmieri, B. The Benefits of Probiotics on Oral Health: Systematic Review of the Literature. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, Z.C.; Villa, M.M.; Durand, H.K.; Jiang, S.; Dallow, E.P.; Petrone, B.L.; Silverman, J.D.; Lin, P.-H.; David, L.A. Microbiota responses to different prebiotics are conserved within individuals and associated with habitual fiber intake. Microbiome 2022, 10, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surana, K.; Ahire, E.D.; Pawar, R.; Khairnar, R.; Mahajan, S.; Kshirsagar, S.; Talele, S.G.; Thombre, N.; Ahire, B.; Keservani, R.K. Oral Health and Prebiotics. In Prebiotics and Probiotics in Disease Regulation and Management; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 291–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slomka, V.; Hernandez-Sanabria, E.; Herrero, E.R.; Zaidel, L.; Bernaerts, K.; Boon, N.; Quirynen, M.; Teughels, W. Nutritional stimulation of commensal oral bacteria suppresses pathogens: The prebiotic concept. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosier, B.T.; Buetas, E.; Moya-Gonzalvez, E.M.; Artacho, A.; Mira, A. Nitrate as a potential prebiotic for the oral microbiome. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magrin, G.L.; Strauss, F.J.; Benfatti, C.A.M.; Maia, L.C.; Gruber, R. Effects of Short-Chain Fatty Acids on Human Oral Epithelial Cells and the Potential Impact on Periodontal Disease: A Systematic Review of In Vitro Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonov, G.E.; Varaeva, Y.R.; Livantsova, E.N.; Starodubova, A.V. The Complicated Relationship of Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Oral Microbiome: A Narrative Review. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homayouni Rad, A.; Pourjafar, H.; Mirzakhani, E. A comprehensive review of the application of probiotics and postbiotics in oral health. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1120995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jastrząb, R.; Graczyk, D.; Siedlecki, P. Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms Influenced by Postbiotics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Tu, H.; Chen, T. Postbiotics in Human Health: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rui, W.; Zhong, S.; Li, X.; Tang, X.; Wang, L.; Yang, J. Evaluating the Role of Postbiotics in the Modulation of Human Oral Microbiota: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetta, H.F.; Ramadan, Y.N.; Rashed, Z.I.; Alharbi, A.A.; Alsharef, S.; Alkindy, T.T.; Alkhamali, A.; Albalawi, A.S.; Battah, B.; Donadu, M.G. Quorum Sensing Inhibitors: An Alternative Strategy to Win the Battle against Multidrug-Resistant (MDR) Bacteria. Molecules 2024, 29, 3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polizzi, A.; Donzella, M.; Nicolosi, G.; Santonocito, S.; Pesce, P.; Isola, G. Drugs for the Quorum Sensing Inhibition of Oral Biofilm: New Frontiers and Insights in the Treatment of Periodontitis. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muras, A.; Mallo, N.; Otero-Casal, P.; Pose-Rodríguez, J.M.; Otero, A. Quorum sensing systems as a new target to prevent biofilm-related oral diseases. Oral Dis. 2022, 28, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czajkowski, R.; Jafra, S. Quenching of acyl-homoserine lactone-dependent quorum sensing by enzymatic disruption of signal molecules. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2009, 56, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompilio, A.; Scocchi, M.; Mangoni, M.L.; Shirooie, S.; Serio, A.; Ferreira Garcia da Costa, Y.; Alves, M.S.; Şeker Karatoprak, G.; Süntar, I.; Khan, H.; et al. Bioactive compounds: A goldmine for defining new strategies against pathogenic bacterial biofilms? Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 49, 117–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostanci, N.; Belibasakis, G.N. Precision periodontal care: From omics discoveries to chairside diagnostics. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2023, 27, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, R.; Pap, B.; Maróti, G.; Vályi, P.; Komlósi, L.; Barta, N.; Strang, O.; Minárovits, J.; Kovács, K.L. Toward Personalized Oral Diagnosis: Distinct Microbiome Clusters in Periodontitis Biofilms. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 747814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belibasakis, G.N.; Bostanci, N.; Marsh, P.D.; Zaura, E. Applications of the oral microbiome in personalized dentistry. Arch. Oral Biol. 2019, 104, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMAScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study (Author, Year) | Aim of the Study | Study Design | Antiseptic Formulation | Outcomes Measured | Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Haydari M. et al., 2017 [15] | To evaluate the effect of antiseptic mouth rinses on plaque and gingivitis. | Double-blinded, randomized controlled trial (RCT) | Chlorhexidine | Reduction in plaque and gingivitis scores. | 0.2% CHX mouthwash showed a statistically significant superior effect in preventing dental plaque compared to the 0.12% and 0.06% solutions. |
| Najafi M. H. et al., 2012 [16] | Assess efficacy of chlorhexidine mouthwashes on gingival indices and level of dental staining. | Randomized controlled trial (RCT) | Chlorhexidine | Significant plaque reduction, gingival, bleeding, and stain index. | Lower concentrations of chlorhexidine are recommended to minimize side effects as higher concentrations do not provide additional benefits in controlling plaque and gingivitis. |
| Cousido M. C. et al, 2010 [17] | To evaluate and compare the in vivo antimicrobial activity of 0.12% and 0.2% chlorhexidine on salivary flora up to 7 h after application. | Experimental, in vivo, comparative study | Chlorhexidine digluconate | Percentage of bacterial vitality in saliva over time using epifluorescence microscopy with SYTO 9/propidium iodide staining. | The 0.2% chlorhexidine mouthrinses showed greater and longer-lasting antimicrobial activity than 0.12%, with double rinsing at 0.2% further reducing bacterial vitality. Concentration influences antimicrobial effectiveness and substantivity. |
| Teng F. et al., 2016 [18] | To investigate how cetylpyridinium chloride (CPC)-containing oral rinses affect supragingival plaque microbiota and gingivitis progression in humans. | Double-blinded, randomized controlled trial (RCT) | Cetylpyridinium chloride | Changes in supragingival plaque microbiota composition, gingival inflammation, and bacterial network connectivity. | CPC rinses slowed gingival inflammation progression by inhibiting gingivitis-associated bacteria, preserved healthy plaque biodiversity, and disrupted bacterial network connectivity. |
| Hu D. et al., 2009 [19] | To compare the effects of a 0.05% cetylpyridinium chloride (CPC) mouth rinse versus a fluoride mouth rinse on anaerobic bacteria in supragingival plaque. | Randomized controlled trial (RCT) | Cetylpyridinium chloride | Reduction in anaerobic bacteria in supragingival plaque | CPC mouth rinse significantly reduced anaerobic bacteria in plaque more than fluoride rinse after both one use and 14 days, with no adverse events reported. |
| Rioboo M. et al., 2012 [20] | To evaluate the effects of a mouth rinse and dentifrice containing 0.05% CPC on plaque and gingivitis in patients with gingivitis. | Double-blind, parallel, randomized clinical trial | Mouth rinse and dentifrice with 0.05% cetylpyridinium chloride | Plaque index, gingival index, patient-based and microbiological variables. | Limited benefit of CPC formulations in reducing plaque and no significant effect on gingivitis as adjuncts to unsupervised oral hygiene. |
| Karbach J. et al., 2015 [21] | To compare the in vitro antibacterial activity of various essential oils versus standard oral antiseptics against oral microorganisms. | In vitro antimicrobial study | Essential oils tested: tea tree oil, eucalyptus oil, lemongrass oil, eucalyptus-based mixture compared with chlorhexidine digluconate, povidone-iodine, and octenidine dihydrochloride | Size of antimicrobial inhibition zones against oral bacteria and Candida species. | Some essential oils, especially lemongrass oil, showed stronger antimicrobial effects than standard antiseptics, suggesting potential for clinical and oral hygiene use. Further research needed on concentrations and application methods. |
| Nikolić M. et al., 2016 [22] | To investigate the chemical composition, antimicrobial activity, and cytotoxicity of commercial essential oils from Hyssopus officinalis, Rosmarinus officinalis, and Salvia officinalis against oral pathogens. | In vitro experimental study | Essential oils from H. officinalis, R. officinalis, and S. officinalis | Chemical composition, antimicrobial activity against oral Candida spp. and bacteria; cytotoxic potential. | All tested essential oils were active against oral pathogens, with S. officinalis oil showing the lowest antimicrobial activity. The oils show promise as natural agents for preventing or treating oral diseases, though careful formulation is needed. |
| Mitsui T. et al., 2017 [23] | To evaluate the effects of different mouthwashes on salivary nitrate/nitrite levels and oral nitrate-reducing bacteria after nitrate intake. | Crossover experimental study | Essential oil mouthwash, povidone-iodine, chlorhexidine, and water (control) | Salivary nitrate/nitrite levels (colorimetric assay) and presence of Veillonella dispar at 0, 1, 5, and 10 h post-treatment. | Chlorhexidine significantly reduced V. dispar presence, suggesting potential inhibition of nitrate-reducing activity with repeated use. Essential oil and povidone-iodine had minimal effects. |
| Gusberti F. A. et al., 1988 [24] | To compare the clinical and microbiological effects of 0.12% chlorhexidine (CHX) and 1% hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) mouthrinses in an experimental gingivitis model. | Randomized controlled trial | 0.12% chlorhexidine mouthrinse and 1% hydrogen peroxide mouthrinse | Gingivitis incidence, bleeding sites, plaque scores; microbiological composition of supragingival and marginal plaque. | CHX was highly effective in reducing gingivitis, bleeding, and plaque, and significantly reduced a wide range of oral bacteria. H2O2 had minimal clinical or microbiological benefits. |
| Oliveira M. S. et al., 2024 [25] | To evaluate the antimicrobial effects of tea tree oil and chitosan alone, and in combination, against oral pathogens and biofilms, and to assess the chemical composition and cytotoxicity of TTO. | In vitro experimental study | Tea tree oil, chitosan, and their combination | Antimicrobial activity, biofilm inhibition, synergy, chemical composition of TTO, bacterial growth delay, and fibroblast, cytotoxicity. | TTO and CH showed effective antimicrobial and antibiofilm activity against oral pathogens. Their combination was synergistic and non-cytotoxic at tested concentrations, offering a potential natural strategy against antimicrobial resistance. |
| Dehghani M. et al., 2019 [26] | To evaluate and compare the effects of propolis and chlorhexidine mouthwashes on plaque, gingival, and periodontal indices in patients undergoing fixed orthodontic treatment. | Triple-blind, randomized clinical trial | Propolis mouthwash and chlorhexidine mouthwash | Plaque index, gingival index, and Community Periodontal Index measured before and after 3 weeks of mouthwash use. | Both propolis and chlorhexidine mouthwashes significantly improved PI, GI, and CPI. Propolis showed similar effectiveness and may be a suitable alternative to CHX without its side effects. |
| Oral Antiseptics | Most Common Formulations | Spectrum | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chlorhexidine |
Oral rinses, aerosols, and spray formulations (0.12–0.2%) Gels (0.12–1%) Dental varnishes (1%, 10%, 40%) Toothpaste, gels for cleaning teeth, and dental flosses | Broad activity: stronger against Gram-positive bacteria and less effective against Gram-negative bacteria. Also active against fungi and some lipophilic viruses | [61,62,63] |
| Cetylpyridinium chloride | Mouthrinses and toothpaste: 0.05–0.10% | Broad antimicrobial spectrum: most effective against gram-positive pathogens and yeast | [18,54,64] |
| Essential oils | Primarily applied externally (e.g., in mouthwashes) for maximum effectiveness | Broad spectrum of antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral and insecticidal fungi and yeast; in addition, potential to inhibit the growth of drug-resistant microbial strains and antioxidant and anti- inflammatory properties | [65,66] |
| Povidone-Iodine | Local topical solution (7.5%, 10%), spray (5%), Povidone-iodine solution Fe-150 | Broad antibacterial spectrum: Gram-positive and Gram-negative; bacteria spores, fungi, protozoa, and viruses | [67,68] |
| Triclosan | Toothpaste and mouthrinses 0.3% | Broad antimicrobial action against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria and fungi | [69,70] |
| Bacteria | Commensal (Healthy State) | Dysbiosis (Associated Systemic Diseases) |
|---|---|---|
| Porphyromonas gingivalis | Present in low levels in healthy oral microbiota | Strongly associated with CVD, Alzheimer’s disease, and periodontitis |
| Fusobacterium nucleatum | Part of normal oral flora, involved in periodontal health | Linked to CVD, adverse pregnancy outcomes (preterm birth, low birth weight), and colorectal cancer |
| Streptococcus spp. | Predominant in healthy biofilm, help in plaque formation | Overgrowth associated with CVD, diabetes, and periodontal disease |
| Prevotella spp. | Present in low abundance, contribute to balance | Overgrowth associated with periodontal disease, diabetes, and adverse pregnancy outcomes |
| Lactobacillus spp. | Contribute to oral health, maintain pH balance | Overgrowth linked to dental caries, potentially contributing to CVD through inflammation |
| Neisseria spp. | Part of healthy oral microbiota, aid in microbial balance | Dysbiosis may contribute to respiratory infections and periodontal disease |
| Actinomyces spp. | Present in healthy individuals, play a role in homeostasis | Associated with periodontal disease and CVD through inflammation |
| Veillonella spp. | Maintain oral balance in healthy individuals | Dysbiosis linked to periodontal disease, may exacerbate CVD due to inflammatory response |
| Tannerella forsythia | Present in healthy oral microbiome in low abundance | Overgrowth linked to periodontitis, CVD, and Alzheimer’s disease through systemic inflammation |
| Probiotics: Mechanism Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Direct Mechanisms | - Action on plaque formation by competing with bacteria-to-bacteria attachments - Competing with oral microorganisms for substrates available - Production of antimicrobial substances that inhibit oral bacteria - Involvement in the binding of oral microorganisms to proteins [143]. |
| Indirect Mechanisms | - Effect on local immunity and non-immunologic defense mechanisms - Regulation of mucosal permeability - Modulating systemic immune function - Oral colonization by less pathogenic species [143]. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Angjelova, A.; Jovanova, E.; Polizzi, A.; Leonardi, R.; Isola, G. Effects of Antiseptic Formulations on Oral Microbiota and Related Systemic Diseases: A Scoping Review. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 815. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14080815
Angjelova A, Jovanova E, Polizzi A, Leonardi R, Isola G. Effects of Antiseptic Formulations on Oral Microbiota and Related Systemic Diseases: A Scoping Review. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(8):815. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14080815
Chicago/Turabian StyleAngjelova, Angela, Elena Jovanova, Alessandro Polizzi, Rosalia Leonardi, and Gaetano Isola. 2025. "Effects of Antiseptic Formulations on Oral Microbiota and Related Systemic Diseases: A Scoping Review" Antibiotics 14, no. 8: 815. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14080815
APA StyleAngjelova, A., Jovanova, E., Polizzi, A., Leonardi, R., & Isola, G. (2025). Effects of Antiseptic Formulations on Oral Microbiota and Related Systemic Diseases: A Scoping Review. Antibiotics, 14(8), 815. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14080815










