Novel p-Hydroxybenzoic Acid Derivative Isolated from Bacopa procumbens and Its Antibacterial Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
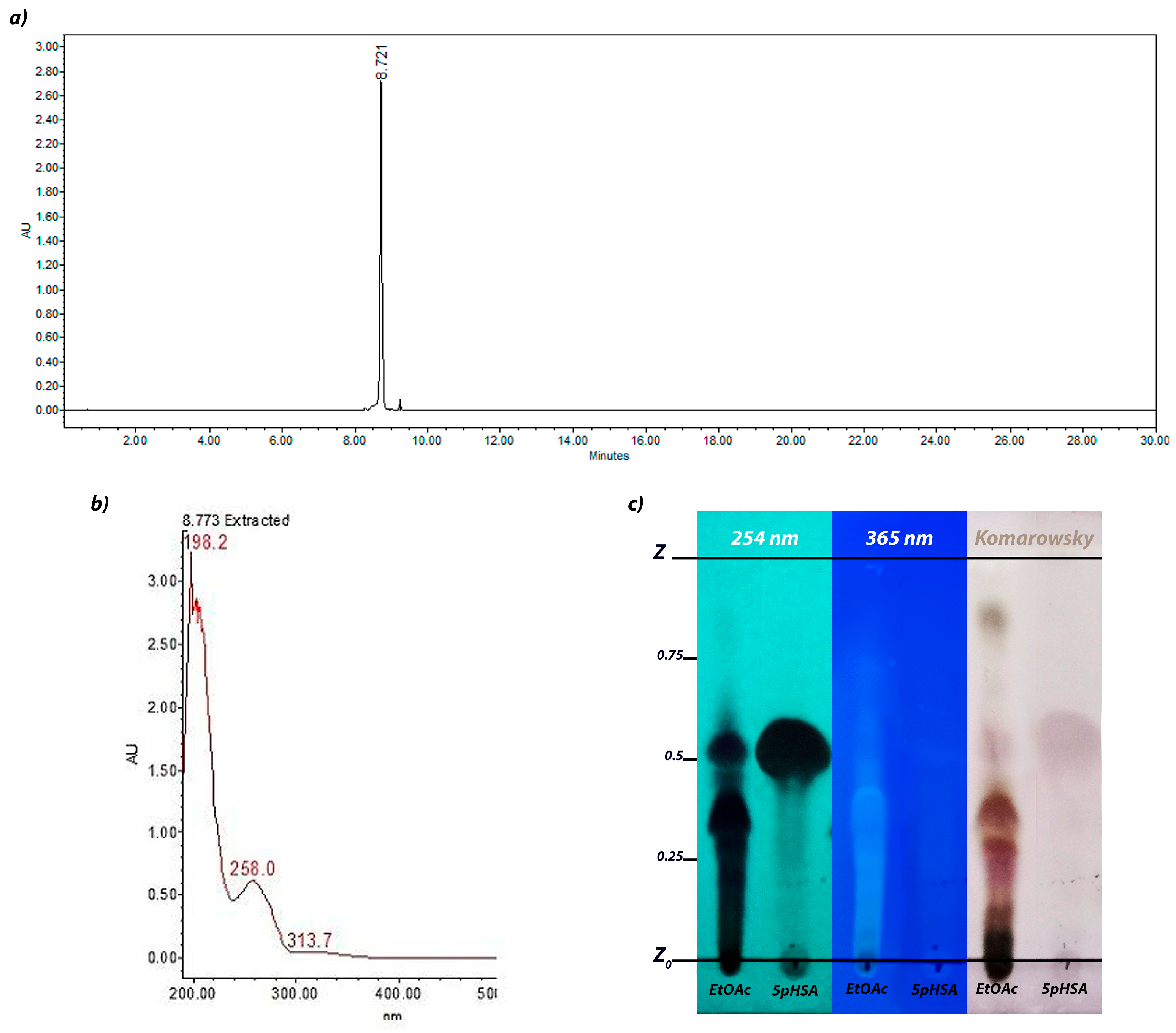
2.1. Ethyl Acetate Fraction Analysis Through HPLC
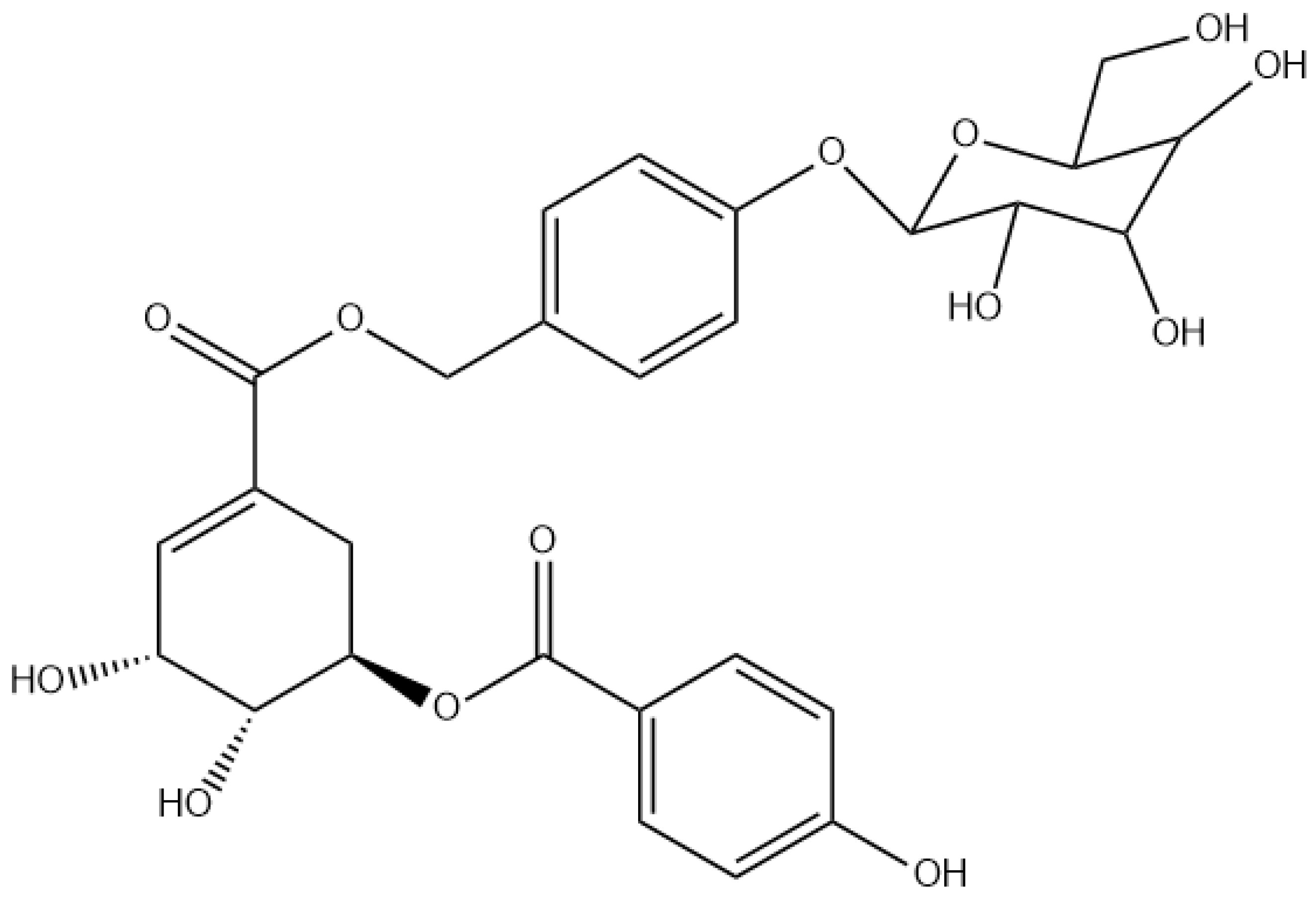
2.2. Structural Elucidation
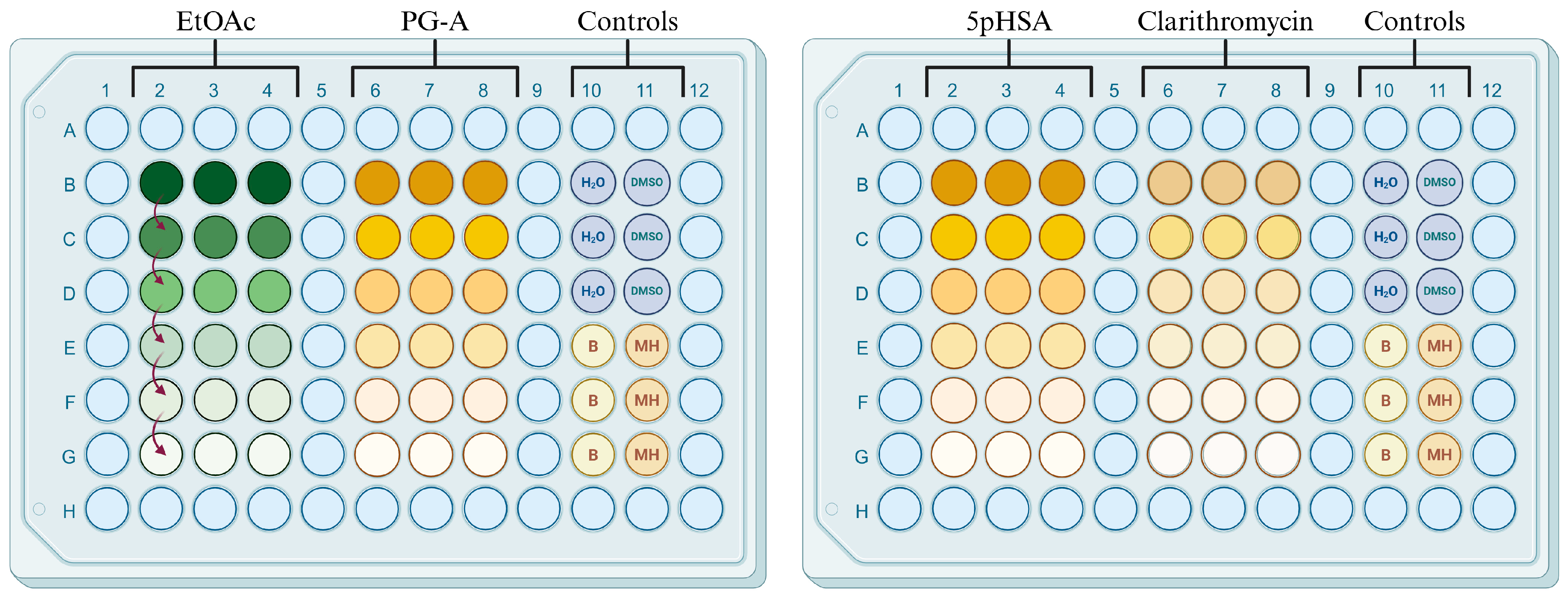
2.3. Antimicrobial Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
4.2. Extraction and Isolation of Ethyl Acetate (EtOAc) Fraction
4.3. Chromatographic Separation and Purification of the Metabolite
4.4. Thin-Layer Chromatography Analysis
4.5. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Analysis
4.6. Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography (UPLC) Analysis
4.7. Antimicrobial Activity
4.7.1. Sample Preparation
4.7.2. Microdilution Assay
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 1H-NMR | Proton nuclear magnetic resonance |
| 5pHSA | 5-(p-hydroxybenzoyl) shikimic acid |
| 13C-NMR | Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance |
| AMR | Antimicrobial resistance |
| ATCC | American Type Culture Collection |
| CLSI | Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute |
| COSY | Correlation spectroscopy |
| CRAB | Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii |
| CRE | Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales |
| d | Doublet |
| dd | Doublet of doublets |
| ddd | Doublet of doublets of doublets |
| δ | Chemical shift |
| EtOAc | Ethyl acetate |
| ESBL | Extended-spectrum beta-lactamase |
| HMBC | Heteronuclear multiple-bond correlation |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| Hz | Hertz |
| J | Coupling constant |
| MIC | Minimum inhibitory concentration |
| MH | Mueller–Hinton broth |
| MRSA | Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus |
| MRSH | Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus haemolyticus |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazole bromide |
| MS-EI | Electron ionization mass spectrometry |
| nm | Nanometer |
| NMR | Nuclear magnetic resonance |
| PDA | Photodiode array detector |
| PG-A | ProcumGastrodin A |
| ppm | Parts per million |
| Rf | Retention factor |
| TFA | Trifluoroacetic acid |
| TLC | Thin-layer chromatography |
| tR | Retention time |
| TSA | Soy tryptone agar |
| UPLC | Ultra-performance liquid chromatography |
| UV | Ultraviolet radiation |
| UV-Vis | Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy |
References
- CDC. Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States 2019; AR Threats Report; CDC: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2019.
- World Health Organization (WHO). Antimicrobial Resistance. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antimicrobial-resistance (accessed on 13 April 2025).
- Abushaheen, M.A.; Muzaheed; Fatani, A.J.; Alosaimi, M.; Mansy, W.; George, M.; Acharya, S.; Rathod, S.; Divakar, D.D.; Jhugroo, C.; et al. Antimicrobial Resistance, Mechanisms and Its Clinical Significance. Dis. Mon. 2020, 66, 100971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wang, Z.; Guo, J.; de la Fuente-Nunez, C.; Wang, J.; Han, B.; Tao, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, X. Bacterial Resistance to Antibacterial Agents: Mechanisms, Control Strategies, and Implications for Global Health. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 860, 160461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskandar, K.; Murugaiyan, J.; Halat, D.H.; Hage, S.E.; Chibabhai, V.; Adukkadukkam, S.; Roques, C.; Molinier, L.; Salameh, P.; Van Dongen, M. Antibiotic Discovery and Resistance: The Chase and the Race. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, M.; Ranucci, E.; Romagnoli, P.; Giaccone, V. Antimicrobial Resistance: A Global Emerging Threat to Public Health Systems. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 2857–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). WHO Bacterial Priority Pathogens List; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024; ISBN 978-92-4-009346-1. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, C.J.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance in 2019: A Systematic Analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, G.R.; Swetschinski, L.R.; Weaver, N.D.; Ikuta, K.S.; Mestrovic, T.; Gray, A.P.; Chung, E.; Wool, E.E.; Han, C.; Hayoon, A.G.; et al. The Burden of Antimicrobial Resistance in the Americas in 2019: A Cross-Country Systematic Analysis. Lancet Reg. Health Am. 2023, 25, 100561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rony, M.K.K.; Das Sharmi, P.; Alamgir, H.M. Addressing Antimicrobial Resistance in Low and Middle-Income Countries: Overcoming Challenges and Implementing Effective Strategies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 101896–101902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadri, S.S.; Boucher, H.W.U.S. Efforts to Curb Antibiotic Resistance—Are We Saving Lives? N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 806–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Antibacterial Agents in Clinical and Preclinical Development; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023; ISBN 9789240021303. [Google Scholar]
- Bassetti, M.; Garau, J. Current and Future Perspectives in the Treatment of Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Infections. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, IV23–IV37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, M.; Carrara, E.; Retamar, P.; Tängdén, T.; Bitterman, R.; Bonomo, R.A.; de Waele, J.; Daikos, G.L.; Akova, M.; Harbarth, S.; et al. European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID) Guidelines for the Treatment of Infections Caused by Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacilli (Endorsed by European Society of Intensive Care Medicine). Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2022, 28, 521–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamma, P.D.; Heil, E.L.; Justo, J.A.; Mathers, A.J.; Satlin, M.J.; Bonomo, R.A. Infectious Diseases Society of America 2024 Guidance on the Treatment of Antimicrobial-Resistant Gram-Negative Infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2024, 2024, ciae403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, S.; Newman, D.J.; Colletti, S.L.; Tan, D.S. Cheminformatic Analysis of Natural Product-Based Drugs and Chemical Probes. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2022, 39, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.S.; Weng, J.K. Demystifying Traditional Herbal Medicine with Modern Approaches. Nat. Plants 2017, 3, 17109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, V. Plant-Derived Chemicals: A Source of Inspiration for New Drugs. Plants 2020, 9, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigalunas, M.; Brakmann, S.; Waldmann, H. Chemical Evolution of Natural Product Structure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 3314–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, B.; Dhingra, A.K. Natural Products: A Lead for Drug Discovery and Development. Phyther. Res. 2021, 35, 4660–4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs over the Nearly Four Decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 770–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasim, N.; Sandeep, I.S.; Mohanty, S. Plant-Derived Natural Products for Drug Discovery: Current Approaches and Prospects. Nucleus 2022, 65, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, M.; Ismail, B.B.; He, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Z.; Ding, T.; Ye, X.; Liu, D.; Guo, M. Inhibitory Mechanisms of Promising Antimicrobials from Plant Byproducts: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2023, 22, 2523–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramawat, K.G.; Mérillon, J.M. Natural Products: Phytochemistry, Botany and Metabolism of Alkaloids, Phenolics and Terpenes, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; ISBN 9783642221446. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, M.V.; Pant, S.; Khan, M.A.H.; Shah, A.A.; Siddiqui, S.; Jeridi, M.; Alhamdi, H.W.S.; Ahmad, S. Phytochemicals as Antimicrobials: Prospecting Himalayan Medicinal Plants as Source of Alternate Medicine to Combat Antimicrobial Resistance. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porras, G.; Chassagne, F.; Lyles, J.T.; Marquez, L.; Dettweiler, M.; Salam, A.M.; Samarakoon, T.; Shabih, S.; Farrokhi, D.R.; Quave, C.L. Ethnobotany and the Role of Plant Natural Products in Antibiotic Drug Discovery. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 3495–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobiuc, A.; Pavăl, N.E.; Mangalagiu, I.I.; Gheorghiță, R.; Teliban, G.C.; Amăriucăi-Mantu, D.; Stoleru, V. Future Antimicrobials: Natural and Functionalized Phenolics. Molecules 2023, 28, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Du, C.; Beaman, H.T.; Monroe, M.B.B. Characterization of Phenolic Acid Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Structure–Property Relationships. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tippery, N.P.; Gonzalez-Socoloske, D.; Leliaert, F.; Thompson, T.A.; Scatigna, A.V.; Souza, V.C. Systematics and Biogeography of Bacopa (Plantaginaceae). Plant Syst. Evol. 2024, 310, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyeleke, M.B.; Oni, H.T.; Arokoyo, O.L.; Owoyele, B.V. Therapeutic Effects of Crude Extracts of Bacopa Floribunda on Beta-Amyloid 1-42-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease via Suppression of Dyslipidemia, Systemic Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Male Wistar Rats. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, J.; Utkarsh, K.; Fuloria, S.; Singh, T.; Sekar, M.; Salaria, D.; Rolta, R.; Begum, M.Y.; Gan, S.H.; Rani, N.N.I.M.; et al. Antibacterial Potential of Bacopa Monnieri (L.) Wettst. and Its Bioactive Molecules against Uropathogens—An In Silico Study to Identify Potential Lead Molecule(s) for the Development of New Drugs to Treat Urinary Tract Infections. Molecules 2022, 27, 4971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Sonkar, K.; Singh, V.; Roy, A.; Ghotekar, S. Bacosides: A Pharmaceutically Important Compound. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect. B—Biol. Sci. 2021, 91, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adetuyi, F.O.; Akintimehin, E.S.; Karigidi, K.O. Comparative Analysis of Freshly Harvested and Stored Bacopa Floribunda Leaves: HPLC Phenolic Fingerprinting, Antioxidant and Cholinergic Enzyme Inhibition Properties. Adv. Tradit. Med. 2023, 23, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Cortazar, M.; López-Gayou, V.; Tortoriello, J.; Domínguez-Mendoza, B.E.; Ríos-Cortes, A.M.; Delgado-Macuil, R.; Hernández-Beteta, E.E.; Blé-González, E.A.; Zamilpa, A. Antimicrobial Gastrodin Derivatives Isolated from Bacopa Procumbens. Phytochem. Lett. 2019, 31, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Cuazitl, A.; del Gómez-García, M.C.; Hidalgo-Alegria, O.; Flores, O.M.; Núñez-Gastélum, J.A.; Martínez, E.S.M.; Ríos-Cortés, A.M.; Garcia-Solis, M.; Pérez-Ishiwara, D.G. Characterization of Polyphenolic Compounds from Bacopa Procumbens and Their Effects on Wound-Healing Process. Molecules 2022, 27, 6521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, A.; Kulshreshtha, D.K.; Maurya, R. Chemical Constituents of Bacopa Procumbens. Nat. Prod. Res. 2005, 19, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauffmann, A.C.; Castro, V.S. Phenolic Compounds in Bacterial Inactivation: A Perspective from Brazil. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, A.; Ferreira, C.; Saavedra, M.J.; Simões, M. Antibacterial Activity and Mode of Action of Ferulic and Gallic Acids against Pathogenic Bacteria. Microb. Drug Resist. 2013, 19, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinowska, M.; Gołebiewska, E.; Swiderski, G.; Meczynska-Wielgosz, S.; Lewandowska, H.; Pietryczuk, A.; Cudowski, A.; Astel, A.; Swisłocka, R.; Samsonowicz, M.; et al. Plant-Derived and Dietary Hydroxybenzoic Acids—A Comprehensive Study of Structural, Anti-/Pro-Oxidant, Lipophilic, Antimicrobial, and Cytotoxic Activity in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 Cell Lines. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wu, D.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Li, G.; Wang, L.; Li, J. Structure-Activity Relationships of Antimicrobial Phenolic Derivatives from Phyllanthus Emblica against Streptomyces Scabies. Food Biosci. 2024, 58, 103709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, F.M.; Couto, J.A.; Figueiredo, A.R.; Tóth, I.V.; Rangel, A.O.S.S.; Hogg, T.A. Cell Membrane Damage Induced by Phenolic Acids on Wine Lactic Acid Bacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 135, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouarab-Chibane, L.; Forquet, V.; Lantéri, P.; Clément, Y.; Léonard-Akkari, L.; Oulahal, N.; Degraeve, P.; Bordes, C. Antibacterial Properties of Polyphenols: Characterization and QSAR (Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship) Models. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Křen, V.; Řezanka, T. Sweet Antibiotics—The Role of Glycosidic Residues in Antibiotic and Antitumor Activity and Their Randomization. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 32, 858–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, M.K.; Mustafa, Y.F.; Oglah, M.K. Antitumor, Antioxidant, and Antibacterial Activities of Glycosyl-Conjugated Compounds: A Review. Syst. Rev. Pharm. 2020, 11, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, R.; Zelikin, A.N. Chemical (Neo)Glycosylation of Biological Drugs. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 171, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipolla, L.; Arajo, A.C.; Bini, D.; Gabrielli, L.; Russo, L.; Shaikh, N. Discovery and Design of Carbohydrate-Based Therapeutics. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2010, 5, 721–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Barros Rates, A.; Cesarino, I. Pour Some Sugar on Me: The Diverse Functions of Phenylpropanoid Glycosylation. J. Plant Physiol. 2023, 291, 154138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, M.; Ferreira, I.F.R.; Dias, J.; Teixeira, V.; Martins, A.; Pintado, M. A Review on Antimicrobial Activity of Mushroom (Basidiomycetes) Extracts and Isolated Compounds. Planta Med. 2012, 78, 1707–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuete, V.; Nana, F.; Ngameni, B.; Mbaveng, A.T.; Keumedjio, F.; Ngadjui, B.T. Antimicrobial Activity of the Crude Extract, Fractions and Compounds from Stem Bark of Ficus Ovata (Moraceae). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 124, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically, 11th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2018; ISBN 1562388363. [Google Scholar]
- Wiegand, I.; Hilpert, K.; Hancock, R.E.W. Agar and Broth Dilution Methods to Determine the Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) of Antimicrobial Substances. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

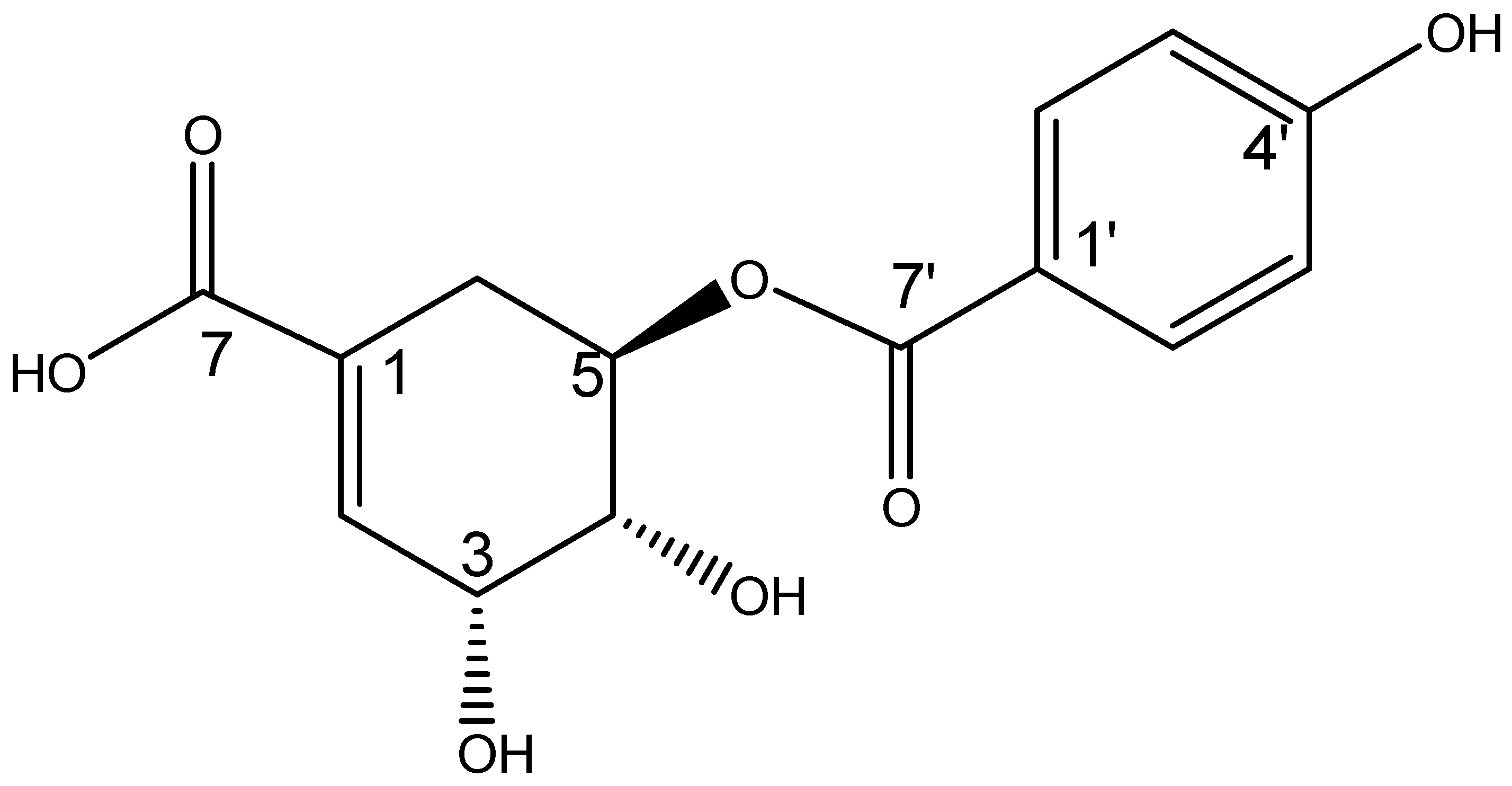
| Position | J (Hz) | |
|---|---|---|
| δH (ppm) | δC (ppm) | |
| 1 | - | 130.7 |
| 2 | 6.87 (1H, d, 3.2) | 138.5 |
| 3 | 4.44 (1H, dd, 3.5, 3.5) | 67.4 |
| 4 | 3.97 (1H, dd, 4.3, 7.5) | 69.9 |
| 5 | 5.34 (1H, ddd, 5.3, 7.5, 12.5) | 71.6 |
| 6A | 2.89 (1H, dd, 5, 18.2) | 29.2 |
| 6B | 2.38 (1H, dd, 5,18.2) | |
| 7 | - | 170.1 |
| p-hydroxybenzoyl | ||
| 1′ | - | 122.1 |
| 2′ | 7.87 (1H, d, 8.6) | 132.8 |
| 3′ | 6.82 (1H, d, 8.9) | 116.1 |
| 4′ | - | 163.6 |
| 5′ | 6.82 (1H, d, 8.9) | 116.1 |
| 6′ | 7.87 (1H, d, 8.6) | 132.8 |
| 7′ | - | 167.5 |
| Number | Strain | MIC (µg/mL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EtOAc | PG-A | 5pHSA | Clarithromycin | ||
| 1 | Staphylococcus aureus | 125 | 50 | >100 | <0.125 |
| 2 | Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) | 250 | >100 | >100 | <0.125 |
| 3 | Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus haemolyticus (MRSH) | 250 | 50 | 100 | >4 |
| 4 | ESBL-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae | 125 | >100 | >100 | <0.125 |
| 5 | Escherichia coli | 500 | 100 | 100 | >4 |
| Number | Strain |
|---|---|
| 1 | Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 29213) |
| 2 | Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) (ATCC 43300) |
| 3 | Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus haemolyticus (MRSH) (derived from ATCC 29970) |
| 4 | Extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae (ATCC 700603) |
| 5 | Escherichia coli (ATCC 25922) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vargas-Anaya, E.; Zamilpa, A.; González-Cortazar, M.; Domínguez-Mendoza, B.E.; Pérez-García, M.D.; Rosas Morales, M.; Ríos Cortés, A.M.; López Gayou, V. Novel p-Hydroxybenzoic Acid Derivative Isolated from Bacopa procumbens and Its Antibacterial Activity. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14060591
Vargas-Anaya E, Zamilpa A, González-Cortazar M, Domínguez-Mendoza BE, Pérez-García MD, Rosas Morales M, Ríos Cortés AM, López Gayou V. Novel p-Hydroxybenzoic Acid Derivative Isolated from Bacopa procumbens and Its Antibacterial Activity. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(6):591. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14060591
Chicago/Turabian StyleVargas-Anaya, Elizabeth, Alejandro Zamilpa, Manasés González-Cortazar, Blanca Eda Domínguez-Mendoza, Ma. Dolores Pérez-García, Minerva Rosas Morales, Ada María Ríos Cortés, and Valentin López Gayou. 2025. "Novel p-Hydroxybenzoic Acid Derivative Isolated from Bacopa procumbens and Its Antibacterial Activity" Antibiotics 14, no. 6: 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14060591
APA StyleVargas-Anaya, E., Zamilpa, A., González-Cortazar, M., Domínguez-Mendoza, B. E., Pérez-García, M. D., Rosas Morales, M., Ríos Cortés, A. M., & López Gayou, V. (2025). Novel p-Hydroxybenzoic Acid Derivative Isolated from Bacopa procumbens and Its Antibacterial Activity. Antibiotics, 14(6), 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14060591









