Correlation Between Blood Culture Time to Positivity and Vegetation Size in Staphylococcus aureus Infective Endocarditis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical Features
2.2. Vegetation Echocardiographic Characteristics
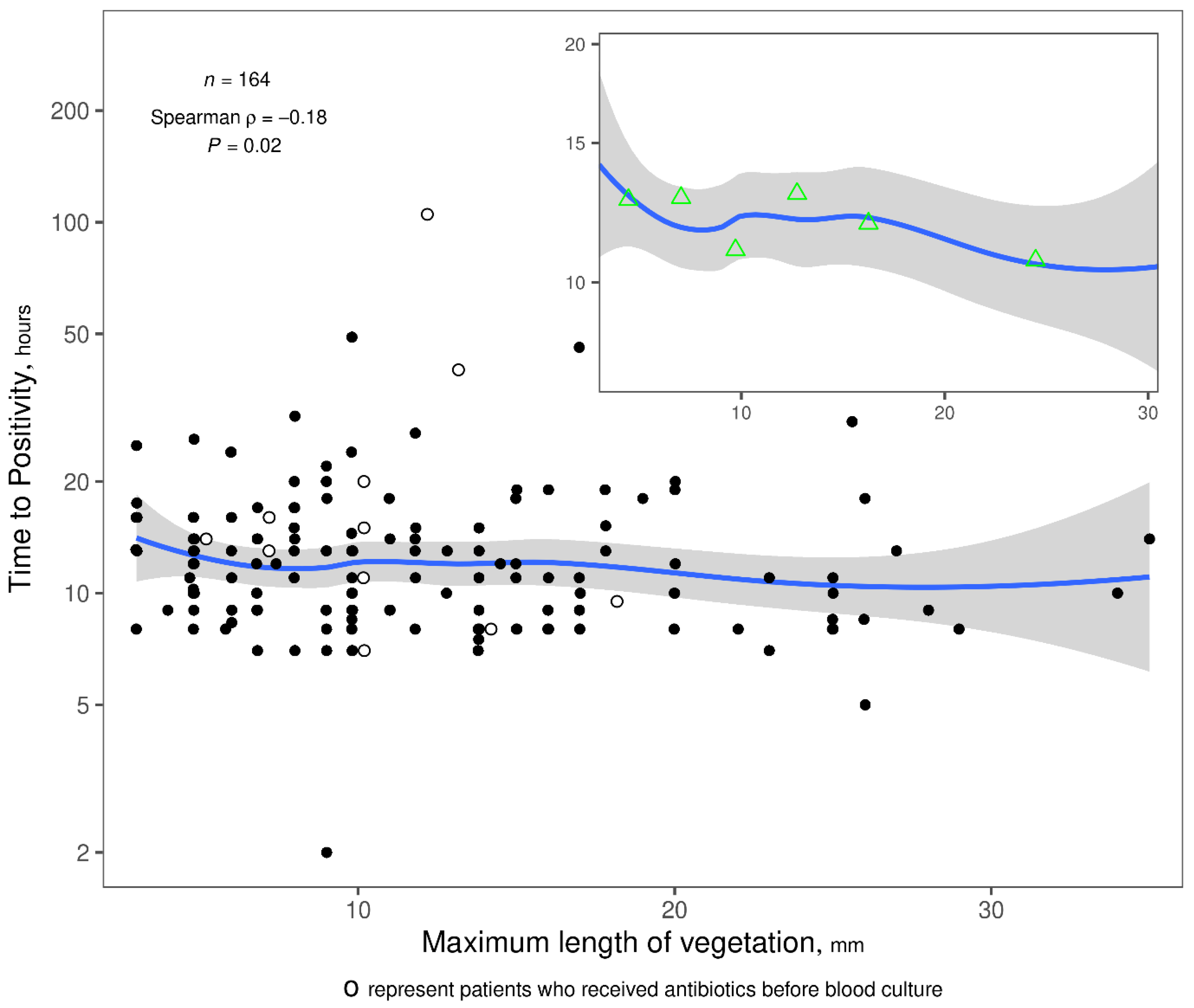
2.3. Correlation Between TTP and Vegetation Length
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Clinical and Microbiologic Data
4.2. Echocardiographic Data
4.3. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Delgado, V.; Marsan, A.N.; de Waha, S.; Bonaros, N.; Brida, M.; Burri, H.; Caselli, S.; Doenst, T.; Ederhy, S.; Erba, P.A.; et al. 2023 ESC Guidelines for the management of endocarditis. Eur. Heart. J. 2023, 44, 3948–4042. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baddour, L.M.; Wilson, W.R.; Bayer, A.S.; Fowler, V.G., Jr.; Tleyjeh, I.M.; Rybak, M.J.; Barsic, B.; Lockhart, P.B.; Gewitz, M.H.; Levison, M.E.; et al. Infective Endocarditis in Adults: Diagnosis, Antimicrobial Therapy, and Management of Complications: A Scientific Statement for Healthcare Professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2015, 132, 1435–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simeon, S.; Le Moing, V.; Tubiana, S.; Duval, X.; Fournier, D.; Lavigne, J.P.; Gustave, C.-A.; Desage, S.; Chirouze, C.; Vandenesch, F.; et al. Time to blood culture positivity: An independent predictor of infective endocarditis and mortality in patients with Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simos, P.A.; Holland, D.J.; Stewart, A.; Isler, B.; Hughes, I.; Price, N.; Henderson, A.; Alcorn, K. Clinical prediction scores and the utility of time to blood culture positivity in stratifying the risk of infective endocarditis in Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2022, 77, 2003–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, F.; Resman, F.; Bergmark, S.; Filiptsev, P.; Nilson, B.; Gilje, P.; Rasmussen, M. Time to blood culture positivity in Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia to determine risk of infective endocarditis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 1345.e7–1345.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatib, R.; Riederer, K.; Saeed, S.; Johnson, L.B.; Fakih, M.G.; Sharma, M.; Tabriz, M.S.; Khosrovaneh, A. Time to positivity in Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: Possible correlation with the source and outcome of infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 41, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddour, L.M.; Christensen, G.D.; Bisno, A.L. Bacterial concentration correlations in experimental endocarditis caused by Staphylococcus epidermidis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1987, 25, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuny, F.; Di Salvo, G.; Belliard, O.; Avierinos, J.F.; Pergola, V.; Rosenberg, V.; Casalta, J.-P.; Gouvernet, J.; Derumeaux, G.; Iarussi, D.; et al. Risk of embolism and death in infective endocarditis: Prognostic value of echocardiography: A prospective multicenter study. Circulation 2005, 112, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Gregson, D.B.; Ross, T.; Laupland, K.B. Time to blood culture positivity in Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: Association with 30-day mortality. J. Infect. 2010, 61, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.B.; Lu, C.C.; Wen, Z.K.; Yang, J.R.; Li, J.J.; Lu, C.C. Impact of Vegetation Length on Clinical Complications During Surgical Intervention and Long-Term Survival in Infective Endocarditis. Am. J. Cardiol. 2023, 201, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohananey, D.; Mohadjer, A.; Pettersson, G.; Navia, J.; Gordon, S.; Shrestha, N.; Grimm, R.A.; Rodriguez, L.L.; Griffin, B.P.; Desai, M.Y.; et al. Association of Vegetation Size with Embolic Risk in Patients with Infective Endocarditis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Intern. Med. 2018, 178, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubert, S.; Thuny, F.; Resseguier, N.; Giorgi, R.; Tribouilloy, C.; Le Dolley, Y.; Casalta, J.-P.; Riberi, A.; Chevalier, F.; Rusinaru, D.; et al. Prediction of symptomatic embolism in infective endocarditis: Construction and validation of a risk calculator in a multicenter cohort. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 1384–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, A.; Tan, C.; Daneman, N.; Hansen, M.S.; Habib, G.; Salaun, E.; Lavoute, C.; Hubert, S.; Adhikari, N.K.J. Clinical and echocardiographic predictors of embolism in infective endocarditis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Palraj, B.R.; Baddour, L.M.; Hess, E.P.; Steckelberg, J.M.; Wilson, W.R.; Lahr, B.D.; Sohail, M.R. Predicting Risk of Endocarditis Using a Clinical Tool (PREDICT): Scoring System to Guide Use of Echocardiography in the Management of Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 61, 18–28. [Google Scholar]
- Abu Saleh, O.; Fida, M.; Asbury, K.; Narichania, A.; Sotello, D.; Bosch, W.; Vikram, H.R.; Palraj, R.; Lahr, B.; Baddour, L.M.; et al. Prospective Validation of PREDICT and Its Impact on the Transesophageal Echocardiography Use in Management of Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e1745–e1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubiana, S.; Duval, X.; Alla, F.; Selton-Suty, C.; Tattevin, P.; Delahaye, F.; Piroth, L.; Chirouze, C.; Lavigne, J.P.; Erpelding, M.L.; et al. The VIRSTA score, a prediction score to estimate risk of infective endocarditis and determine priority for echocardiography in patients with Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. J. Infect. 2016, 72, 544–553. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen, R.V.; Høst, U.; Arpi, M.; Hassager, C.; Johansen, H.K.; Korup, E.; Schønheyder, H.C.; Berning, J.; Gill, S.; Flemming, S.; et al. Prevalence of infective endocarditis in patients with Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia: The value of screening with echocardiography. Eur. J. Echocardiogr. 2011, 12, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.M.; Sorabella, R.A.; Vasan, S.; Grbic, M.; Lambert, D.; Prasad, R.; Wang, C.; Kurlansky, P.; Borger, M.A.; Gordon, R.; et al. Influence of Staphylococcus aureus on Outcomes after Valvular Surgery for Infective Endocarditis. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2017, 12, 57. [Google Scholar]
- Santos-Patarroyo, S.D.; Quintero-Martinez, J.A.; Lahr, B.D.; Chesdachai, S.; DeSimone, D.C.; Villarraga, H.R.; Michelena, H.I.; Baddour, L.M. Comprehensive Assessment of the Risk of Symptomatic Embolism in Patients with Infective Endocarditis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2025, 23, e036648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.S.; Sexton, D.J.; Mick, N.; Nettles, R.; Fowler, V.G.; Ryan, T., Jr.; Bashore, T.; Corey, G.R. Proposed modifications to the Duke criteria for the diagnosis of infective endocarditis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2000, 30, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comba, I.Y.; Go, J.R.; Vaillant, J.; O’Horo, J.C.; Stevens, R.W.; Palraj, R.; Abu Saleh, O. Sequential Time to Positivity as a Prognostic Indicator in Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2024, 11, ofae173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Feature | Overall (N = 164) |
|---|---|
| Age, years | 61.6 (42.1–71.8) |
| Male gender | 62.8% (103) |
| Race | |
| White | 87.8% (144) |
| Black/African American | 4.9% (8) |
| American Indian/Alaska Native | 1.8% (3) |
| Other | 5.5% (9) |
| Injection drug use | 13.4% (22) |
| Mitral valve prolapse | 4.3% (7) |
| Bicuspid aortic valve | 7.9% (13) |
| Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy | 1.8% (3) |
| Prosthetic valve | 20.1% (33) |
| Cardiac implantable electronic device | 22.0% (36) |
| Heart failure | 44.5% (73) |
| Chronic kidney disease | 40.2% (66) |
| Myocardial infarction | 26.8% (44) |
| Hypertension | 53.7% (88) |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | 17.1% (28) |
| HIV | 4.3% (7) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 50.0% (82) |
| Atrial fibrillation | 20.7% (34) |
| Moderate/severe liver disease | 9.1% (15) |
| Metastatic solid tumor | 0.0% (0) |
| Other tumors | 16.5% (27) |
| Charlson Comorbidity Index | 3 (1–6) |
| Definite IE | 92.1% (151) |
| Native valve IE | 76.2% (125) |
| Prosthetic valve IE | 17.1% (28) |
| Device-related IE | 16.5% (27) |
| Surgery for IE | 23.8% (39) |
| Side of IE | |
| Left | 70.1% (115) |
| Right | 28.0% (46) |
| Bilateral | 1.8% (3) |
| Time to positivity, hours | 11.0 (9.0–14.6) |
| Time to positivity by side of IE | |
| Left Side IE | 11.0 (8.1–15.1) |
| Right Side IE | 11.0 (9.0–14.1) |
| Antibiotics before blood culture | 6.7% (11) |
| Feature | Overall (N = 164) |
|---|---|
| Length of vegetation, mm | 10 (7–15) |
| >10 mm | 57.9% (95) |
| Width of vegetation, mm | 6 (4–10) |
| Area of vegetation, mm2 | 62 (25–126) |
| Location of vegetation | |
| Aortic | 30.5% (50) |
| Mitral | 40.9% (67) |
| Tricuspid | 18.9% (31) |
| Right atrium/ventricle | 7.9% (13) |
| Number of vegetations | |
| Median (IQR) | 1 (1–1) |
| 1 | 79.9% (131) |
| 2 | 14.0% (33) |
| 3 or more | 6.1% (10) |
| Multiple vegetation | 20.1% (33) |
| Mobility | |
| None | 12.8% (21) |
| Low | 30.5% (50) |
| Moderate | 34.8% (57) |
| High | 22.0% (36) |
| Predictor | β (95% CI) | p |
|---|---|---|
| Vegetation length † | −0.36 (−0.69, −0.02) | 0.037 |
| Age † | −0.02 (−0.54, 0.50) | 0.945 |
| Location of vegetation | 0.873 | |
| Aortic (reference) | 0.00 | |
| Mitral | 0.17 (−0.49, 0.83) | |
| Right-Sided | 0.15 (−0.66, 0.96) | |
| IE Type: Native valve | −0.29 (−1.04, 0.46) | 0.447 |
| Regurgitation/stenosis for infected valve: Severe | 0.32 (−0.42, 1.06) | 0.402 |
| IV drug user | −0.22 (−1.19, 0.76) | 0.662 |
| Antibiotics before blood culture | 0.81 (−0.34, 1.96) | 0.166 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santos-Patarroyo, S.D.; Quintero-Martinez, J.A.; Lahr, B.D.; Chesdachai, S.; Abu Saleh, O.; Michelena, H.I.; Villarraga, H.R.; DeSimone, D.C.; Baddour, L.M. Correlation Between Blood Culture Time to Positivity and Vegetation Size in Staphylococcus aureus Infective Endocarditis. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050456
Santos-Patarroyo SD, Quintero-Martinez JA, Lahr BD, Chesdachai S, Abu Saleh O, Michelena HI, Villarraga HR, DeSimone DC, Baddour LM. Correlation Between Blood Culture Time to Positivity and Vegetation Size in Staphylococcus aureus Infective Endocarditis. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(5):456. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050456
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantos-Patarroyo, Sebastian D., Juan A. Quintero-Martinez, Brian D. Lahr, Supavit Chesdachai, Omar Abu Saleh, Hector I. Michelena, Hector R. Villarraga, Daniel C. DeSimone, and Larry M. Baddour. 2025. "Correlation Between Blood Culture Time to Positivity and Vegetation Size in Staphylococcus aureus Infective Endocarditis" Antibiotics 14, no. 5: 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050456
APA StyleSantos-Patarroyo, S. D., Quintero-Martinez, J. A., Lahr, B. D., Chesdachai, S., Abu Saleh, O., Michelena, H. I., Villarraga, H. R., DeSimone, D. C., & Baddour, L. M. (2025). Correlation Between Blood Culture Time to Positivity and Vegetation Size in Staphylococcus aureus Infective Endocarditis. Antibiotics, 14(5), 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050456






