Genomic Insights into an Environmental Vibrio parahaemolyticus Biofilm Isolate: Deciphering Alternative Resistance Mechanisms and Mobilizable Genetic Elements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
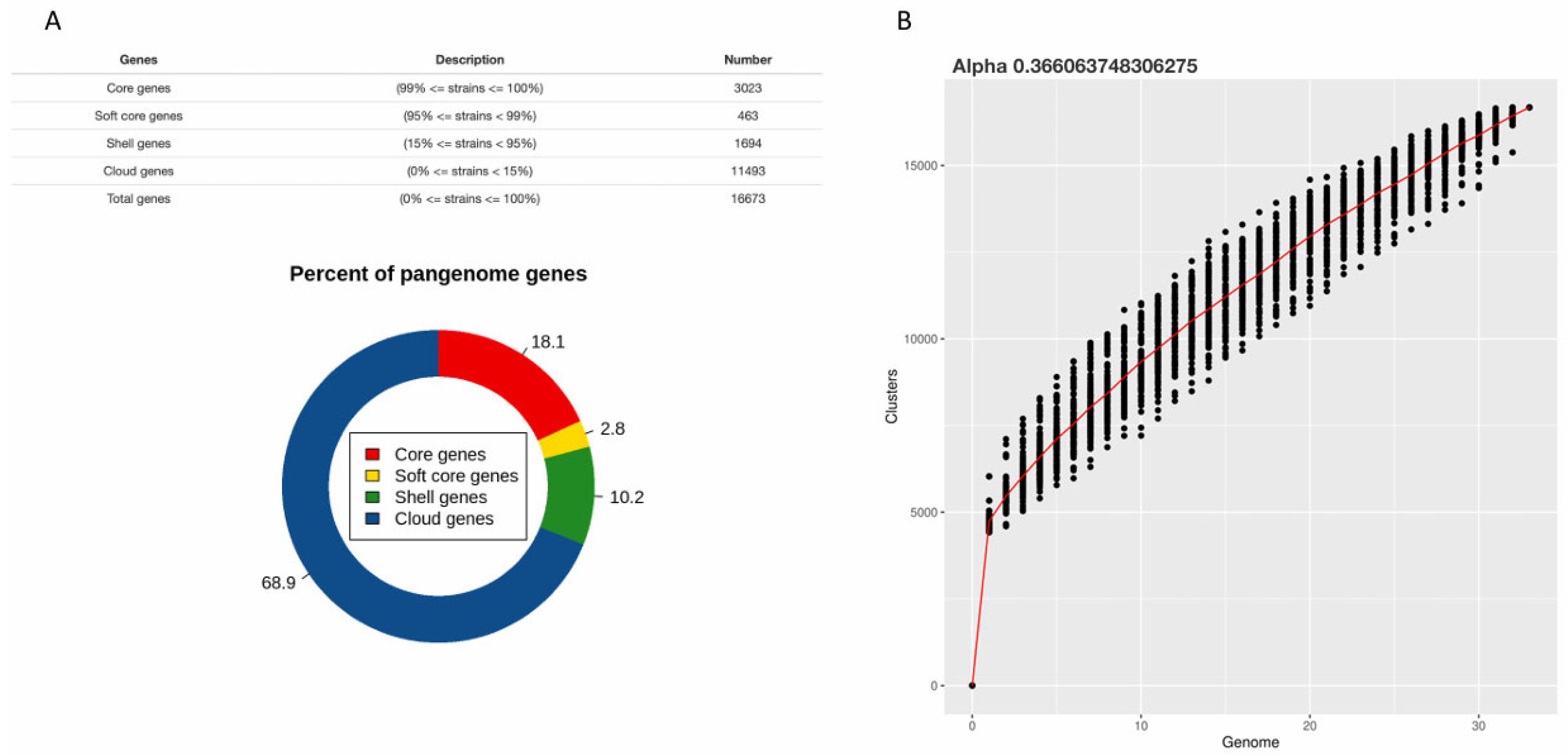
2.1. An Open Pangenome Underpins Extensive Genetic Diversity
2.2. Phylogenetic Analyses Reveal Niche-Driven Evolution
2.3. Strain Vaw-5 Exhibits a Unique Genomic Profile
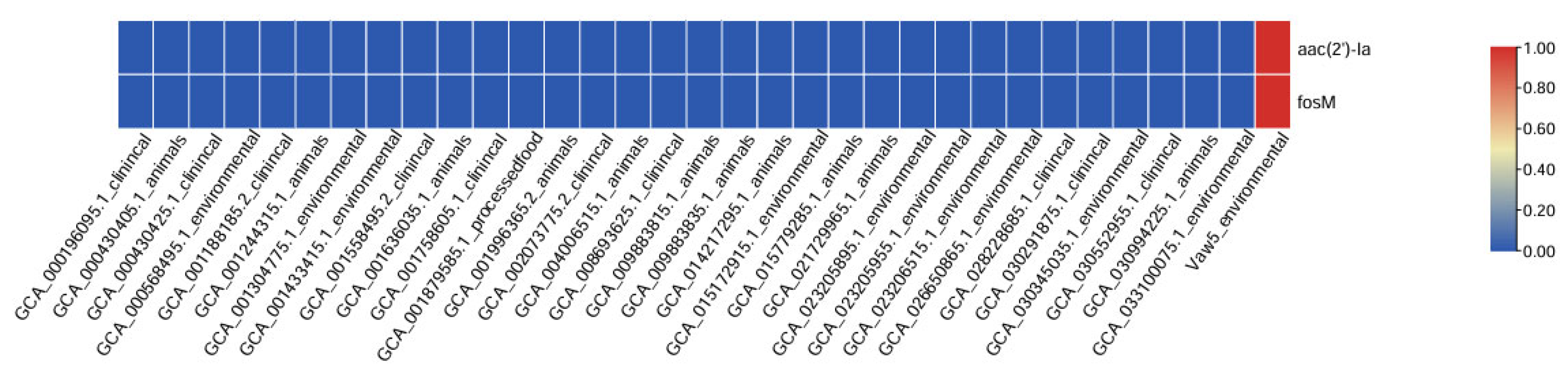
2.4. A Distinct Antibiotic Resistance Gene Profile Highlights Alternative Strategies
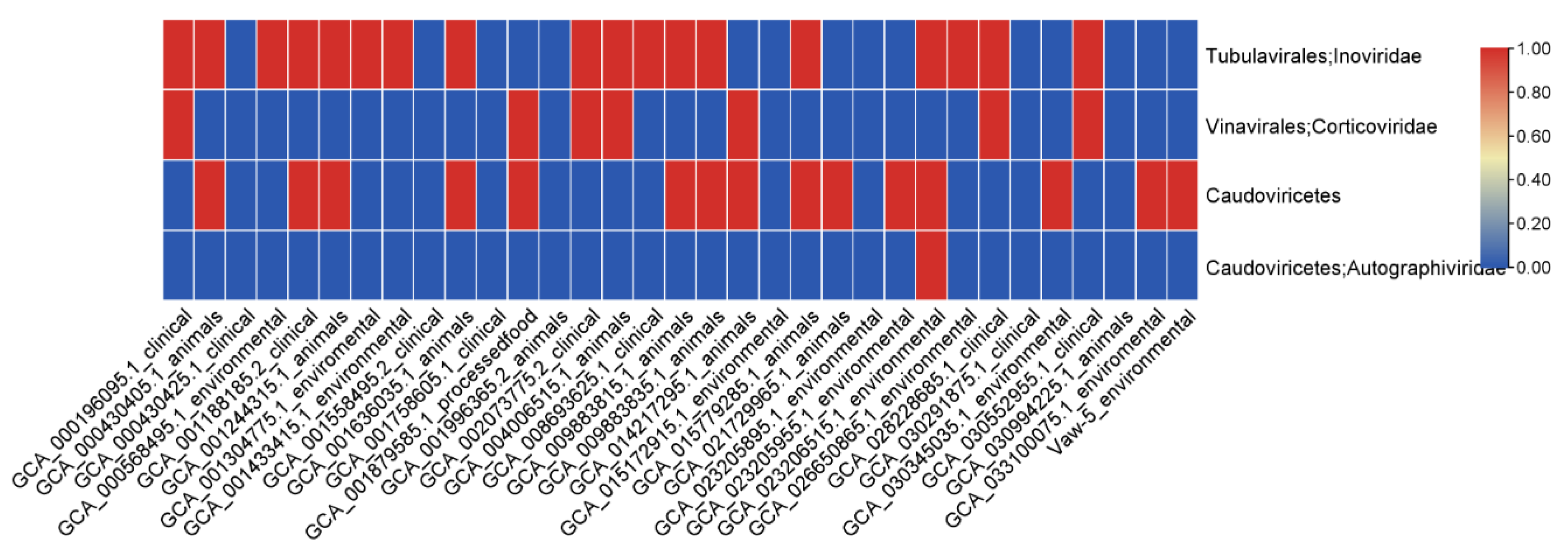
2.5. Mobile Genetic Elements and Genomic Islands Suggest Potential for Antimicrobial Resistance Mobilization
3. Discussion
3.1. Evolutionary Mechanisms and Pangenome Dynamics
3.2. Understanding Adaptation Pathways Using Phylogenetic Analysis
3.3. Distinct Evolutionary Approaches: Clinical Isolates Versus Biofilm Isolate
3.4. Implications of the One Health Concept and Antimicrobial Resistance
3.5. Key Knowledge Gaps and Prospects
3.6. Broader Implications
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Biofilm Sample Collection and Bacterial Isolation
4.2. Genomic DNA Extraction and Quality Control
4.3. Library Preparation, Sequencing, and Primary Data Processing
4.4. Genome Assembly, Quality Assessment, and Contamination Screening
4.5. Comparative Genomic Dataset Curation
4.6. Genome Annotation and Gene Calling
4.7. Pangenome and Phylogenetic Analysis of Genomes and Housekeeping Genes
4.8. Identification of Mobile Genetic Elements (MGEs) and Genomic Islands
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABRicate | A tool for detecting antimicrobial resistance and virulence genes |
| ARGs | Antibiotic Resistance Genes |
| AHPND | Acute Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Disease |
| CRISPR-Cas | Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats and CRISPR-associated proteins |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic Acid |
| GCA | GenBank Assembly Accession prefix |
| HGT | Horizontal Gene Transfer |
| IS | Insertion Sequence |
| MGEs | Mobile Genetic Elements |
| MLST | Multilocus Sequence Typing |
| NCBI | National Center for Biotechnology Information |
| NGS | Next-Generation Sequencing |
| OmpH | Outer Membrane Protein H |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| Prokka | A software tool for prokaryotic genome annotation |
| qnrVC | Quinolone resistance gene variant |
| Refseq | Reference Sequence database |
| ResFinder | A database for antibiotic resistance genes |
| Roary | A pangenome analysis tool |
| ST | Sequence Type |
| TBtools | A bioinformatics software toolkit |
| tdh/trh | Thermostable Direct Hemolysin/TDH-related hemolysin genes |
| Tn5501, Tn5393 | Transposon identifiers |
| TORMES | A pipeline for bacterial genome analysis |
| VFDB | Virulence Factor Database |
| Vaw-5 | Vibrio parahaemolyticus strain name |
References
- Elhadi, N.; Ghenem, L.; Alzahrani, F.; Nishibuchi, M. Vibrio Parahaemolyticus: A review on distribution, pathogenesis, virulence determinants and epidemiology. Saudi J. Med. Med. Sci. 2017, 5, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauge, T.; Mougin, J.; Ells, T.; Midelet, G. Sources and contamination routes of seafood with human pathogenic Vibrio spp.: A Farm-to-Fork approach. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2023, 23, e13283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezzulli, L. Global expansion of Vibrio spp. in hot water. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2022, 15, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndraha, N.; Huang, L.; Wu, V.C.H.; Hsiao, H.-I. Vibrio parahaemolyticus in seafood: Recent progress in understanding influential factors at harvest and food-safety intervention approaches. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2022, 48, 100927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasulkova, R.; Stratev, D. Insights into foodborne Vibrio parahaemolyticus—A review. Food Res. 2024, 8, 190–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, H.; Gurnani, B.; Pippal, B.; Jain, N. Capturing the micro-communities: Insights into biogenesis and architecture of bacterial biofilms. BBA Adv. 2025, 7, 100133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeem, K.; Fatima, S.; Ali, A.; Ubaid, A.; Husain, F.M.; Abid, M. Biochemistry of Bacterial Biofilm: Insights into Antibiotic Resistance Mechanisms and Therapeutic Intervention. Life 2025, 15, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preda, V.G.; Roberts, L.; Săndulescu, O. Biofilms and Their Impact on Human Health. In Handbook of Molecular Biotechnology; Liu, D., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 397–405. [Google Scholar]
- Bajaj, T.; Bhattacharya, S.; Gupta, J. MICROBIAL GENOMICS- the Changing Technological Landscape of Microbiology via NGS. In Microbiology-2.0 Update for a Sustainable Future; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2024; pp. 307–330. [Google Scholar]
- Carhuaricra-Huaman, D.; Setubal, J.C. Step-by-Step Bacterial Genome Comparison. In Comparative Genomics; Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 107–134. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, M.; Gao, Q.; Yan, R.; Liu, L.; Wang, L.; Wen, B.; Wen, C. Comparative Genomic Analysis of Shrimp-Pathogenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus LC and Intraspecific Strains with Emphasis on Virulent Factors of Mobile Genetic Elements. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Yang, C.; Qiu, H.; Wang, H.; Yang, R.; Falush, D. The landscape of coadaptation in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. eLife 2020, 9, e54136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Liu, H.; Habimana, O. High risk of Vibrio pathogen and antibiotic resistance transfer in live seafood wet markets of Shantou, China. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2025, 432, 111098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuda, M.; Shintani, M. Microbial evolution through horizontal gene transfer by mobile genetic elements. Microb. Biotechnol. 2024, 17, e14408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A.; Roy, V.; Dutta, P.; Adhikary, S.; Saha, B.K.; Saha, J. Genomic Islands in Bacterial Genome Evolution and Speciation. In Microbial Genomic Islands in Adaptation and Pathogenicity; Springer: Singapore, 2023; pp. 83–109. [Google Scholar]
- Cabello, F.C.; Godfrey, H.P.; Tomova, A.; Ivanova, L.; Dölz, H.; Millanao, A.; Buschmann, A.H. Antimicrobial use in aquaculture re-examined: Its relevance to antimicrobial resistance and to animal and human health. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 1917–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.W.; Mah, T.-F. Molecular mechanisms of biofilm-based antibiotic resistance and tolerance in pathogenic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 276–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, K.; Varani, A.M.; Snesrud, E.; Huang, H.; Alvarenga, D.O.; Zhang, J.; Wu, C.; McGann, P.; Chandler, M. TnCentral: A Prokaryotic Transposable Element Database and Web Portal for Transposon Analysis. mBio 2021, 12, e0206021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco–Monsreal, J.; Serralta–Peraza, L.E.d.S.; Flores–Abuxapqui, J.J.; Sánchez–Uluac, M.S. Vibrio parahaemolyticus in fish and shellfish of animal origin from establishments in the port of Chicxulub, Yucatan, Mexico. Biomed. Transl. Sci. 2022, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.-W. A foodborne outbreak of gastroenteritis caused by Vibrio parahaemolyticus associated with cross-contamination from squid in Korea. Epidemiol. Health 2018, 40, e2018056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seelman, S.L.; Whitney, B.M.; Stokes, E.K.; Elliot, E.L.; Griswold, T.; Patel, K.; Bloodgood, S.; Jones, J.L.; Cripe, J.; Cornell, J.; et al. An Outbreak Investigation of Vibrio parahaemolyticus Infections in the United States Linked to Crabmeat Imported from Venezuela: 2018. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2023, 20, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Lei, T.; Jiang, F.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, M.; Xue, L.; Wu, S.; Ye, Q.; et al. Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of Vibrio parahaemolyticus Isolated From Clinical and Food Sources. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 708795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmieder, R.; Edwards, R. Quality control and preprocessing of metagenomic datasets. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 863–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quijada, N.M.; Rodríguez-Lázaro, D.; Eiros, J.M.; Hernández, M. TORMES: An automated pipeline for whole bacterial genome analysis. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 4207–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prjibelski, A.; Antipov, D.; Meleshko, D.; Lapidus, A.; Korobeynikov, A. Using SPAdes De Novo Assembler. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2020, 70, e102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, D.E.; Lu, J.; Langmead, B. Improved metagenomic analysis with Kraken 2. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikheenko, A.; Saveliev, V.; Hirsch, P.; Gurevich, A. WebQUAST: Online evaluation of genome assemblies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W601–W606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, D.H.; Imelfort, M.; Skennerton, C.T.; Hugenholtz, P.; Tyson, G.W. CheckM: Assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates, single cells, and metagenomes. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simão, F.A.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Ioannidis, P.; Kriventseva, E.V.; Zdobnov, E.M. BUSCO: Assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness with single-copy orthologs. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3210–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, A.P.; Roux, S.; Schulz, F.; Babinski, M.; Xu, Y.; Hu, B.; Chain, P.S.G.; Nayfach, S.; Kyrpides, N.C. Identification of mobile genetic elements with geNomad. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024, 42, 1303–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florensa, A.F.; Kaas, R.S.; Clausen, P.; Aytan-Aktug, D.; Aarestrup, F.M. ResFinder—An open online resource for identification of antimicrobial resistance genes in next-generation sequencing data and prediction of phenotypes from genotypes. Microb. Genom. 2022, 8, 000748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yang, J.; Yu, J.; Yao, Z.; Sun, L.; Shen, Y.; Jin, Q. VFDB: A reference database for bacterial virulence factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, D325–D328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, A.J.; Cummins, C.A.; Hunt, M.; Wong, V.K.; Reuter, S.; Holden, M.T.; Fookes, M.; Falush, D.; Keane, J.A.; Parkhill, J. Roary: Rapid large-scale prokaryote pan genome analysis. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3691–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree 2—Approximately Maximum-Likelihood Trees for Large Alignments. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadfield, J.; Croucher, N.J.; Goater, R.J.; Abudahab, K.; Aanensen, D.M.; Harris, S.R. Phandango: An interactive viewer for bacterial population genomics. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 292–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dereeper, A.; Summo, M.; Meyer, D.F. PanExplorer: A web-based tool for exploratory analysis and visualization of bacterial pan-genomes. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 4412–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siguier, P.; Perochon, J.; Lestrade, L.; Mahillon, J.; Chandler, M. ISfinder: The reference centre for bacterial insertion sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D32–D36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, A.; Soares, M.; Pereira, C.; Leitão, N.; Henriques, I.; Correia, A. INTEGRALL: A database and search engine for integrons, integrases and gene cassettes. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1096–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Chen, H.; He, Y.; et al. TBtools-II: A "one for all, all for one" bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertelli, C.; Laird, M.R.; Williams, K.P.; Simon Fraser University Research Computing Group; Lau, B.Y.; Hoad, G.; Winsor, G.L.; Brinkman, F.S. IslandViewer 4: Expanded prediction of genomic islands for larger-scale datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W30–W35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertelli, C.; Brinkman, F.S.L. Improved genomic island predictions with IslandPath-DIMOB. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 2161–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waack, S.; Keller, O.; Asper, R.; Brodag, T.; Damm, C.; Fricke, W.F.; Surovcik, K.; Meinicke, P.; Merkl, R. Score-based prediction of genomic islands in prokaryotic genomes using hidden Markov models. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Scheme | ST | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GCA_015172915.1_environmental | V. parahaemolyticus | N.A | dnaE(330) | gyrB(268) | recA(202) | dtdS(227) | pntA(4) | pyrC(441) | tnaA(145) |
| GCA_026650865.1_environmental | V. parahaemolyticus | N.A | dnaE(44) | gyrB(106) | recA(393) | dtdS(126) | pntA(28) | pyrC(268) | tnaA(193) |
| GCA_009883815.1_animals | V. parahaemolyticus | N.A | dnaE(42) | gyrB(134) | recA(99) | dtdS(460) | pntA(26) | pyrC(41) | tnaA(51) |
| GCA_030994225.1_animals | Vibrio | N.A | gyrB(83) | pyrH(36) | recA(62) | atpA(60) | N.D | N.D | N.D |
| GCA_008693625.1_clinical | V. parahaemolyticus | N.A | dnaE(26) | gyrB(16) | recA(56) | dtdS(157) | pntA(4) | pyrC(32) | tnaA(51) |
| GCA_001558495.2_clinical | V. parahaemolyticus | 1 | dnaE(5) | gyrB(52) | recA(27) | dtdS(13) | pntA(17) | pyrC(25) | tnaA(10) |
| GCA_030552955.1_clinical | V. parahaemolyticus | 3 | dnaE(3) | gyrB(4) | recA(19) | dtdS(4) | pntA(29) | pyrC(4) | tnaA(22) |
| GCA_028228685.1_clinical | V. parahaemolyticus | 3 | dnaE(3) | gyrB(4) | recA(19) | dtdS(4) | pntA(29) | pyrC(4) | tnaA(22) |
| GCA_002073775.2_clinical | V. parahaemolyticus | 3 | dnaE(3) | gyrB(4) | recA(19) | dtdS(4) | pntA(29) | pyrC(4) | tnaA(22) |
| GCA_000196095.1_clinical | V. parahaemolyticus | 3 | dnaE(3) | gyrB(4) | recA(19) | dtdS(4) | pntA(29) | pyrC(4) | tnaA(22) |
| GCA_004006515.1_animals | V. parahaemolyticus | 3 | dnaE(3) | gyrB(4) | recA(19) | dtdS(4) | pntA(29) | pyrC(4) | tnaA(22) |
| GCA_000430405.1_animals | V. parahaemolyticus | 23 | dnaE(17) | gyrB(16) | recA(13) | dtdS(36) | pntA(15) | pyrC(31) | tnaA(26) |
| GCA_001188185.2_clinical | V. parahaemolyticus | 36 | dnaE(21) | gyrB(15) | recA(1) | dtdS(23) | pntA(23) | pyrC(21) | tnaA(16) |
| GCA_030291875.1_clinical | V. parahaemolyticus | 224 | dnaE(28) | gyrB(83) | recA(82) | dtdS(117) | pntA(18) | pyrC(69) | tnaA(79) |
| GCA_001879585.1_processedfood | V. parahaemolyticus | 233 | dnaE(109) | gyrB(136) | recA(114) | dtdS(121) | pntA(83) | pyrC(107) | tnaA(83) |
| GCA_015779285.1_animals | V. parahaemolyticus | 413 | dnaE(47) | gyrB(8) | recA(166) | dtdS(19) | pntA(28) | pyrC(46) | tnaA(121) |
| GCA_009883835.1_animals | V. parahaemolyticus | 415 | dnaE(42) | gyrB(134) | recA(99) | dtdS(79) | pntA(26) | pyrC(41) | tnaA(51) |
| GCA_021729965.1_animals | V. parahaemolyticus | 424 | dnaE(170) | gyrB(224) | recA(75) | dtdS(139) | pntA(117) | pyrC(18) | tnaA(124) |
| Vaw-5_environmental | V. parahaemolyticus | 424 | dnaE(170) | gyrB(224) | recA(75) | dtdS(139) | pntA(117) | pyrC(18) | tnaA(124) |
| GCA_000568495.1_environmental | V. parahaemolyticus | 471 | dnaE(175) | gyrB(22) | recA(168) | dtdS(201) | pntA(130) | pyrC(17) | tnaA(73) |
| GCA_030345035.1_environmental | V. parahaemolyticus | 624 | dnaE(3) | gyrB(4) | recA(73) | dtdS(13) | pntA(4) | pyrC(214) | tnaA(33) |
| GCA_023205955.1_environmental | V. parahaemolyticus | 722 | dnaE(26) | gyrB(16) | recA(234) | dtdS(7) | pntA(18) | pyrC(32) | tnaA(7) |
| GCA_000430425.1_clinical | V. parahaemolyticus | 799 | dnaE(28) | gyrB(4) | recA(82) | dtdS(88) | pntA(63) | pyrC(187) | tnaA(1) |
| GCA_001244315.1_animals | V. parahaemolyticus | 984 | dnaE(49) | gyrB(209) | recA(249) | dtdS(50) | pntA(112) | pyrC(37) | tnaA(23) |
| GCA_033100075.1_environmental | V. parahaemolyticus | 1160 | dnaE(153) | gyrB(191) | recA(70) | dtdS(19) | pntA(6) | pyrC(8) | tnaA(1) |
| GCA_001433415.1_environmental | V. parahaemolyticus | 1628 | dnaE(111) | gyrB(320) | recA(22) | dtdS(34) | pntA(20) | pyrC(21) | tnaA(24) |
| GCA_001636035.1_animals | V. parahaemolyticus | 1629 | dnaE(225) | gyrB(104) | recA(226) | dtdS(201) | pntA(50) | pyrC(250) | tnaA(17) |
| GCA_001304775.1_enviromental | V. parahaemolyticus | 1630 | dnaE(31) | gyrB(106) | recA(135) | dtdS(402) | pntA(37) | pyrC(212) | tnaA(54) |
| GCA_014217295.1_animals | V. parahaemolyticus | 1743 | dnaE(112) | gyrB(8) | recA(61) | dtdS(425) | pntA(26) | pyrC(8) | tnaA(57) |
| GCA_023206515.1_environmental | V. parahaemolyticus | 1750 | dnaE(103) | gyrB(490) | recA(31) | dtdS(169) | pntA(26) | pyrC(401) | tnaA(79) |
| GCA_023205895.1_environmental | V. parahaemolyticus | 1805 | dnaE(47) | gyrB(91) | recA(166) | dtdS(46) | pntA(79) | pyrC(45) | tnaA(26) |
| GCA_001996365.2_animals | V. parahaemolyticus | 1913 | dnaE(363) | gyrB(505) | recA(218) | dtdS(442) | pntA(30) | pyrC(303) | tnaA(26) |
| GCA_001758605.1_clinical | V. parahaemolyticus | 2015 | dnaE(67) | gyrB(522) | recA(31) | dtdS(70) | pntA(47) | pyrC(436) | tnaA(17) |
| Sample | Type | Source | Country | Collection Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GCA_000196095.1_clinical.fna | clinical | Human | Japan | 1996 |
| GCA_000430405.1_animals.fna | animals | Bivalves | USA | 2007 |
| GCA_000430425.1_clinical.fna | clinical | Human | USA | 2006 |
| GCA_000568495.1_environmental.fna | environmental | Sediment | Spain | 2002 |
| GCA_001188185.2_clinical.fna | clinical | Human | USA | 1998 |
| GCA_001244315.1_animals.fna | animals | Fish | South Korea | 2014 |
| GCA_001304775.1_environmental.fna | environmental | Surface | South Korea | 2014 |
| GCA_001433415.1_environmental.fna | environmental | Water | South Korea | 2014 |
| GCA_001558495.2_clinical.fna | clinical | Human | Japan | 1951 |
| GCA_001636035.1_animals.fna | animals | Fish | South Korea | 2015 |
| GCA_001758605.1_clinical.fna | clinical | Human | South Korea | 2014 |
| GCA_001879585.1_processedfood.fna | processed food | Crab | South Korea | Not available |
| GCA_001996365.2_animals.fna | animals | Shrimp | Malaysia | 2016 |
| GCA_002073775.2_clinical.fna | clinical | Human | India | 1996 |
| GCA_004006515.1_animals.fna | animals | Processed food | China | 2012 |
| GCA_008693625.1_clinical.fna | clinical | Human | USA | Not available |
| GCA_009883815.1_animals.fna | animals | Shrimp | China | 2014 |
| GCA_009883835.1_animals.fna | animals | Shrimp | China | 2014 |
| GCA_014217295.1_animals.fna | animals | Shrimp | China | 2017 |
| GCA_015172915.1_environmental.fna | environmental | Water | South Korea | 2019 |
| GCA_015779285.1_animals.fna | animals | Shrimp | China | 2020 |
| GCA_021729965.1_animals.fna | animals | Shrimp | China | 2017 |
| GCA_023205895.1_environmental.fna | environmental | Water | China | 2019 |
| GCA_023205955.1_environmental.fna | environmental | Water | China | 2018 |
| GCA_023206515.1_environmental.fna | environmental | Water | China | 2018 |
| GCA_026650865.1_environmental.fna | environmental | Water | China | 2020 |
| GCA_028228685.1_clinical.fna | clinical | Human | Thailand | 2021 |
| GCA_030291875.1_clinical.fna | clinical | Human | China | 2015 |
| GCA_030345035.1_environmental.fna | environmental | Water | South Korea | 2022 |
| GCA_030552955.1_clinical.fna | clinical | Human | China | 2009 |
| GCA_030994225.1_animals.fna | animals | Bivalves | Colombia | 2021 |
| GCA_033100075.1_environmental.fna | environmental | Water | China | 2023 |
| Vaw-5_environmental.fna | environmental | Biofilm | China | 2023 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Dong, Y.; Lin, Z.; Habimana, O. Genomic Insights into an Environmental Vibrio parahaemolyticus Biofilm Isolate: Deciphering Alternative Resistance Mechanisms and Mobilizable Genetic Elements. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14101005
Liu H, Dong Y, Lin Z, Habimana O. Genomic Insights into an Environmental Vibrio parahaemolyticus Biofilm Isolate: Deciphering Alternative Resistance Mechanisms and Mobilizable Genetic Elements. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(10):1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14101005
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Huiyu, Yujian Dong, Zhongyang Lin, and Olivier Habimana. 2025. "Genomic Insights into an Environmental Vibrio parahaemolyticus Biofilm Isolate: Deciphering Alternative Resistance Mechanisms and Mobilizable Genetic Elements" Antibiotics 14, no. 10: 1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14101005
APA StyleLiu, H., Dong, Y., Lin, Z., & Habimana, O. (2025). Genomic Insights into an Environmental Vibrio parahaemolyticus Biofilm Isolate: Deciphering Alternative Resistance Mechanisms and Mobilizable Genetic Elements. Antibiotics, 14(10), 1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14101005








