Bicarinalin Enhances the Antibacterial Activity of Levofloxacin and Clarithromycin Against Helicobacter pylori
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Inhibition Zone Values (Well Diffusion)
2.2. Data of Microdilution Assay
2.3. The Antimicrobial Activity of Bicarinalin and Its Combination with Antibiotics
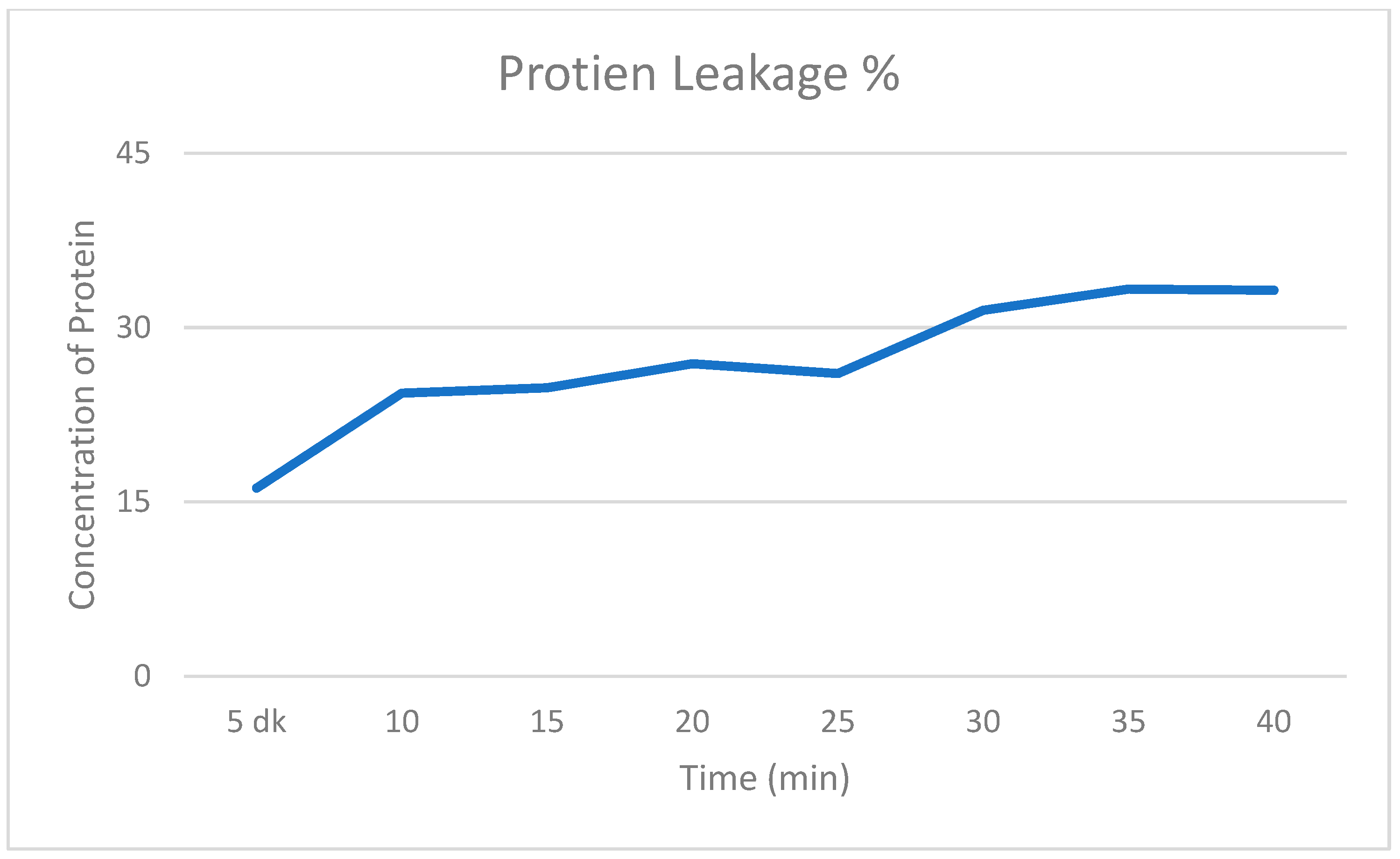
2.4. Intracellular Protein and DNA Leakage Values
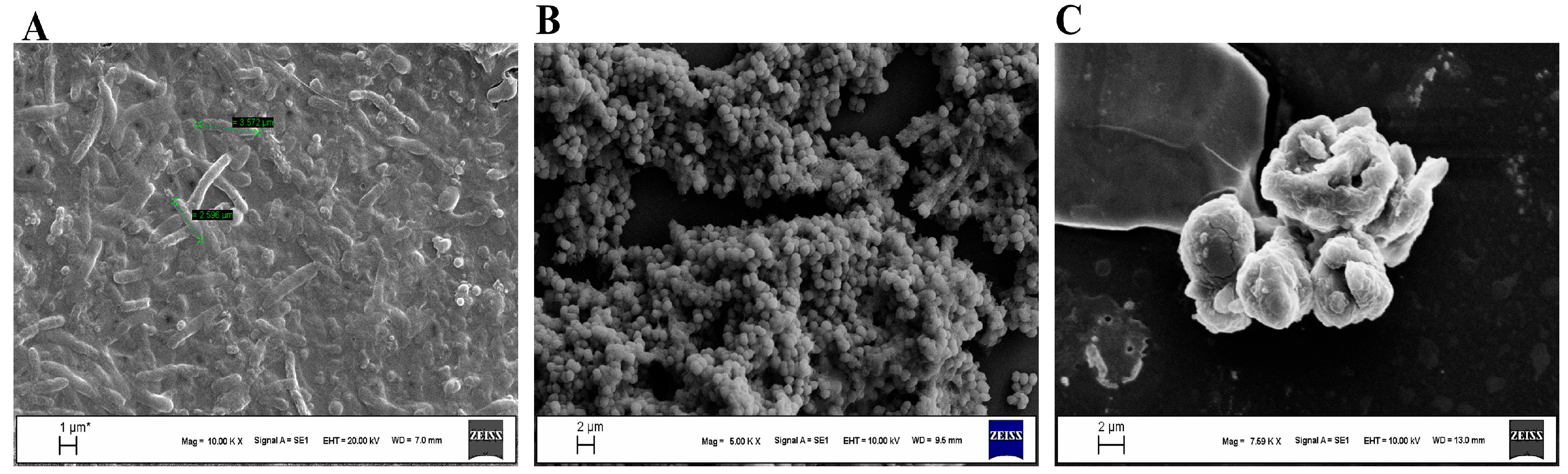
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscope Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. The Synthesis of Bicarinalin
4.2. Bacterial Strains
4.3. Bacterial Isolation and Identification
4.4. Well Diffusion
4.5. Microdilution Assay
4.6. Synergistic Activity of Bicarinalin
4.7. Assessment of Intracellular Protein and DNA Leakage
4.8. SEM Analysis
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kotilea, K.; Bontems, P.; Touati, E. Epidemiology, Diagnosis and risk factors of Helicobacter pylori infection. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1149, 17–33. [Google Scholar]
- Roszczenko-Jasińska, P.; Wojtyś, M.I.; Jagusztyn-Krynicka, E.K. Helicobacter pylori treatment in the post-antibiotics era-searching for new drug targets. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 9891–9905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, H.; Shiotani, A.; Graham, D.Y. Current and future treatment of Helicobacter pylori infections. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1149, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sharndama, H.C.; Mba, I.E. Helicobacter pylori: An up-to-date overview on the virulence and pathogenesis mechanisms. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2022, 53, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mladenova, I. Clinical relevance of Helicobacter pylori infection. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Qian, X.; Liu, X.; Song, Y.; Song, C.; Wu, S.; An, Y.; Yuan, R.; Wang, Y.; Xie, Y. The effect of antibiotic resistance on Helicobacter pylori eradication efficacy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Helicobacter 2020, 25, e12714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbaiomy, R.G.; Luo, X.; Guo, R.; Deng, S.; Du, M.; El-Sappah, A.H.; Bakeer, M.; Azzam, M.M.; Elolimy, A.A.; Madkour, M.; et al. Antibiotic resistance in Helicobacter pylori: A genetic and physiological perspective. Gut Pathog. 2025, 17, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Gonçalves, V.L.; Santos, M.L.C.; Luz, M.S.; Marques, H.S.; de Brito, B.B.; da Silva, F.A.F.; Souza, C.L.; Oliveira, M.V.; de Melo, F.F. From Helicobacter pylori infection to gastric cancer: Current evidence on the immune response. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 13, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Guo, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Gong, Y. The antibiotic resistance of Helicobacter pylori to five antibiotics and influencing factors in an area of China with a high risk of gastric cancer. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terreni, M.; Taccani, M.; Pregnolato, M. New antibiotics for multidrug-resistant bacterial strains: Latest research developments and future perspectives. Molecules 2021, 26, 2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramazi, S.; Mohammadi, N.; Allahverdi, A.; Khalili, E.; Abdolmaleki, P. A review on antimicrobial peptides databases and the computational tools. Database 2022, 2022, baac011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dini, I.; De Biasi, M.G.; Mancusi, A. An overview of the potentialities of antimicrobial peptides derived from natural sources. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talapko, J.; Meštrović, T.; Juzbašić, M.; Tomas, M.; Erić, S.; Horvat Aleksijević, L.; Bekić, S.; Schwarz, D.; Matić, S.; Neuberg, M.; et al. Antimicrobial peptides-mechanisms of action, antimicrobial effects and clinical applications. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, Y.; Kong, Q.; Mou, H.; Yi, H. Antimicrobial peptides: Classification, design, application and research progress in multiple fields. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 582779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mba, I.E.; Nweze, E.I. Antimicrobial peptides therapy: An emerging alternative for treating drug-resistant bacteria. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2022, 95, 445–463. [Google Scholar]
- Mazurkiewicz-Pisarek, A.; Baran, J.; Ciach, T. Antimicrobial peptides: Challenging journey to the pharmaceutical, biomedical, and cosmeceutical use. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Tu, Y.; Li, B.; Qu, G.; Li, A.; Peng, X.; Li, S.; Shao, C. Antimicrobial peptide biological activity, delivery systems and clinical translation status and challenges. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 23, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Hao, W.; Wang, X.; Ouyang, J.; Deng, X.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y. Antimicrobial peptides, conventional antibiotics, and their synergistic utility for the treatment of drug-resistant infections. Med. Res. Rev. 2022, 42, 1377–1422. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rifflet, A.; Gavalda, S.; Téné, N.; Orivel, J.; Leprince, J.; Guilhaudis, L.; Génin, E.; Vétillard, A.; Treilhou, M. Identification and characterization of a novel antimicrobial peptide from the venom of the ant Tetramorium bicarinatum. Peptides 2012, 38, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eales, M.G.; Ferrari, E.; Goddard, A.D.; Lancaster, L.; Sanderson, P.; Miller, C. Mechanistic and phenotypic studies of bicarinalin, BP100 and colistin action on Acinetobacter baumannii. Res. Microbiol. 2018, 169, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosaheb, M.; Khan, N.A.; Siddiqui, R. Cockroaches, locusts, and envenomating arthropods: A promising source of antimicrobials. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2018, 21, 873–877. [Google Scholar]
- Téné, N.; Bonnafé, E.; Berger, F.; Rifflet, A.; Guilhaudis, L.; Ségalas-Milazzo, I.; Pipy, B.; Coste, A.; Leprince, J.; Treilhou, M. Biochemical and biophysical combined study of bicarinalin, an ant venom antimicrobial peptide. Peptides 2016, 79, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neshani, A.; Zare, H.; Akbari Eidgahi, M.R.; Hooshyar Chichaklu, A.; Movaqar, A.; Ghazvini, K. Review of antimicrobial peptides with anti-Helicobacter pylori activity. Helicobacter 2019, 24, e12555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel, K.; Lechuga, G.C.; Provance, D.W., Jr.; Morel, C.M.; De Simone, S.G. An update on the therapeutic potential of antimicrobial peptides against Acinetobacter baumannii infections. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzman, J.; Téné, N.; Touchard, A.; Castillo, D.; Belkhelfa, H.; Haddioui-Hbabi, L.; Treilhou, M.; Sauvain, M. Anti-Helicobacter pylori properties of the ant-venom peptide bicarinalin. Toxins 2017, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuding, S.; Gersemann, M.; Hosaka, Y.; Konietzny, S.; Schaefer, C.; Beisner, J.; Wehkamp, J. Gastric antimicrobial peptides fail to eradicate Helicobacter pylori infection due to selective induction and resistance. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.J.; Xu, J.Y.; Wang, X.; Liao, L.J.; Wei, X.; Xie, P.; Huang, Y.Q. Therapeutic effect of demethylated hydroxylated phillygenin derivative on Helicobacter pylori infection. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1071603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moosazadeh Moghaddam, M.; Bolouri, S.; Golmohammadi, R.; Fasihi-Ramandi, M.; Heiat, M.; Mirnejad, R. Targeted delivery of a short antimicrobial peptide (CM11) against Helicobacter pylori gastric infection using concanavalin A-coated chitosan nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2023, 34, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Téné, N.; Roche-Chatain, V.; Rifflet, A.; Bonnafé, E.; Lefranc, B.; Leprince, J.; Treilhou, M. Potent bactericidal effects of bicarinalin against strains of the Enterobacter and Cronobacter genera. Food Control 2014, 42, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri-Araghi, S. Synergistic action of antimicrobial peptides and antibiotics: Current understanding and future directions. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1390765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juretic, D. Antimicrobial peptides of the magainin family: Membrane depolarization studies on E. coli and cytochrome oxidase liposomes. Stud. Biophys. 1990, 138, 79–86. [Google Scholar]
- Naghmouchi, K.; Le Lay, C.; Baah, J.; Drider, D. Antibiotic and antimicrobial peptide combinations: Synergistic inhibition of Pseudomonas fluorescens and antibiotic-resistant variants. Res. Microbiol. 2012, 163, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, M.; Berditsch, M.; Hawecker, J.; Ardakani, M.F.; Gerthsen, D.; Ulrich, A.S. Damage of the bacterial cell envelope by antimicrobial peptides gramicidin S and PGLa as revealed by transmission and scanning electron microscopy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 3132–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayana, J.L.; Huang, H.N.; Wu, C.J.; Chen, J.Y. Efficacy of the antimicrobial peptide TP4 against Helicobacter pylori infection: In vitro membrane perturbation via micellization and in vivo suppression of host immune responses in a mouse model. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 12936–12954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.G.; Kwon, H.C.; Kim, D.H.; Hong, S.J.; Han, S.G. In vitro synergistic antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects of nisin and lactic acid in yogurt against Helicobacter pylori and human gastric cells. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2023, 43, 751–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdivieso-Rivera, F.; Bermúdez-Puga, S.; Proaño-Bolaños, C.; Almeida, J.R. Deciphering the limitations and antibacterial mechanism of cruzioseptins. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2020, 28, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, B.; Edwards-Gayle, C.; Barrett, G. Peptide lipidation and shortening optimises antibacterial, antibiofilm and membranolytic actions of an amphiphilic polylysine-polyphenyalanine octapeptide. Curr. Res. Biotechnol. 2024, 8, 100240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitmire, J.M.; Merrell, D.S. Successful culture techniques for Helicobacter species: General culture techniques for Helicobacter pylori. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 921, 17–27. [Google Scholar]
- Dimri, A.G.; Chaudhary, S.; Singh, D.; Chauhan, A.; Aggarwal, M. Morphological and biochemical characterization of foodborne gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Sci. Arch. 2020, 1, 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Erdoğan Eliuz, E.A. Antibacterial activity and antibacterial mechanism of ethanol extracts of Lentinula edodes (Shiitake) and Agaricus bisporus (button mushroom). Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2022, 32, 1828–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
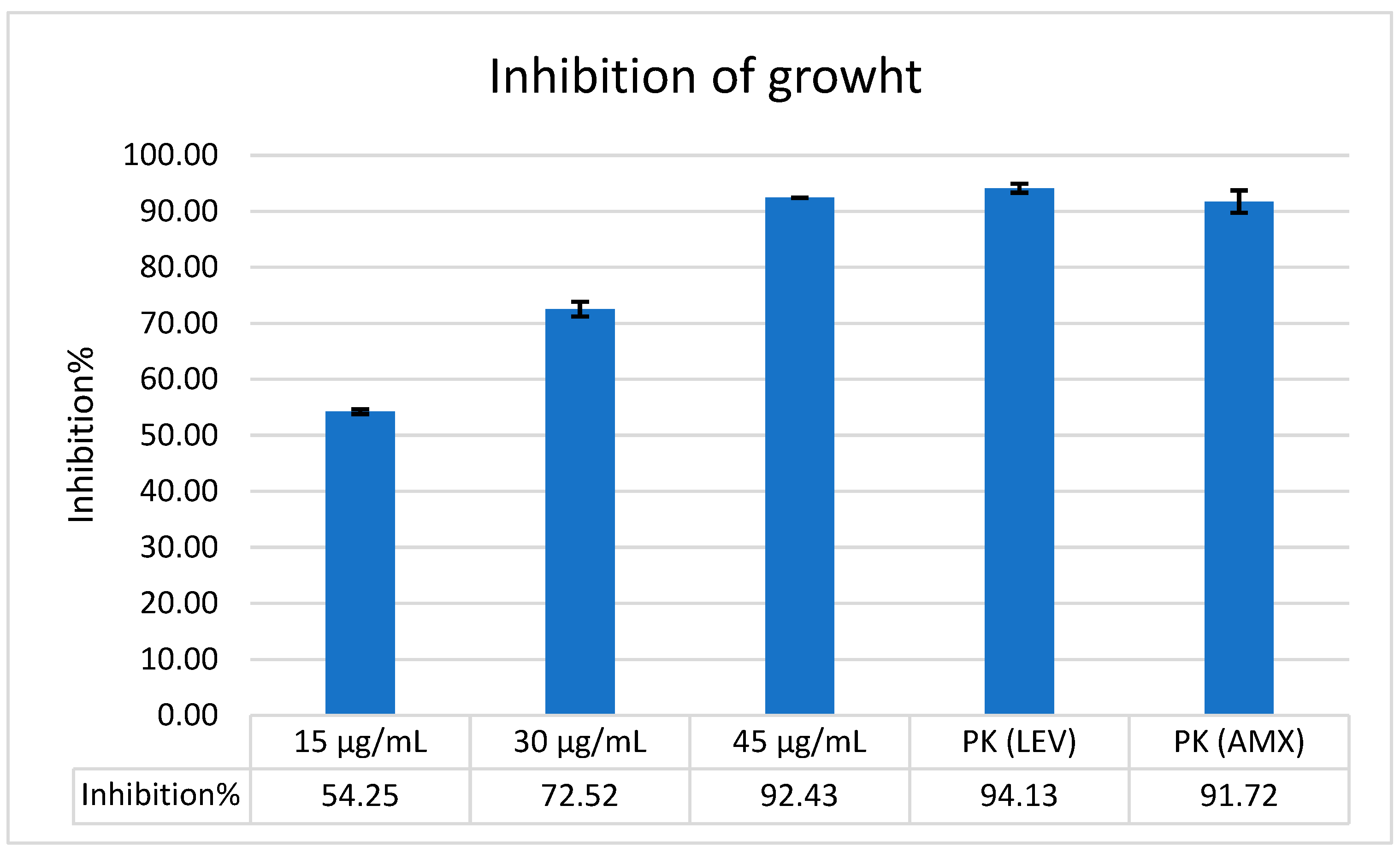

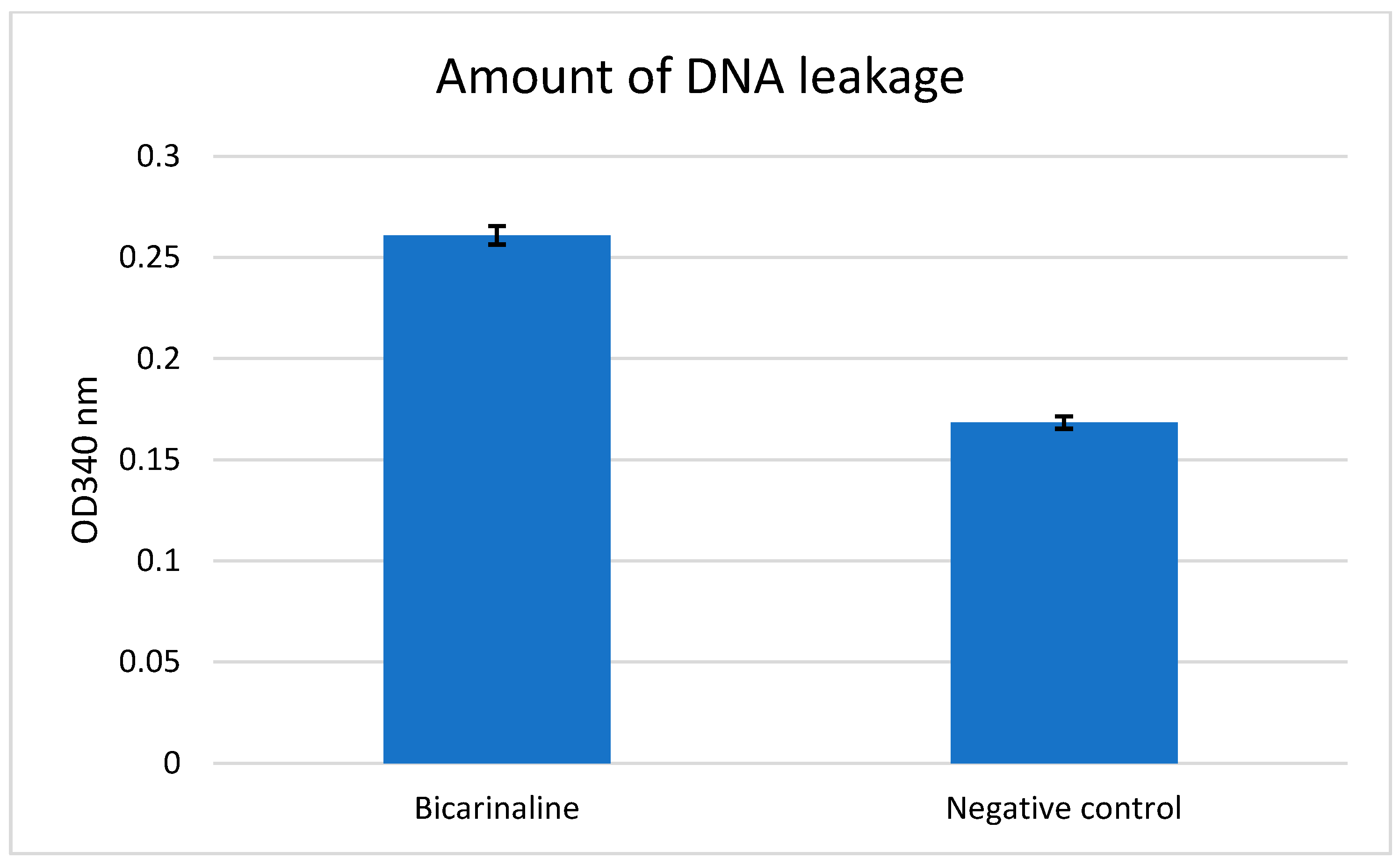

| Concentration of Bicarinalin | 4 μg/mL | 8 μg/mL | 16 μg/mL | 32 μg/mL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibition zone | 7.8 mm | 8.7 mm | 9.7 mm | 18.3 mm |
| Antibiotics/Bicarinalin | Inhibition Zones (in mm) |
|---|---|
| LEV | 14.2 mm |
| CLR | 7.3 mm |
| 15 μg/mL | 11 mm |
| 30 μg/mL | 11 mm |
| 45 μg/mL | 12 mm |
| LEV + Bic | 20 mm |
| CLR + Bic | 16 mm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saleh, I.; Çevik, P.K. Bicarinalin Enhances the Antibacterial Activity of Levofloxacin and Clarithromycin Against Helicobacter pylori. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14101003
Saleh I, Çevik PK. Bicarinalin Enhances the Antibacterial Activity of Levofloxacin and Clarithromycin Against Helicobacter pylori. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(10):1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14101003
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaleh, Iman, and Pınar Küce Çevik. 2025. "Bicarinalin Enhances the Antibacterial Activity of Levofloxacin and Clarithromycin Against Helicobacter pylori" Antibiotics 14, no. 10: 1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14101003
APA StyleSaleh, I., & Çevik, P. K. (2025). Bicarinalin Enhances the Antibacterial Activity of Levofloxacin and Clarithromycin Against Helicobacter pylori. Antibiotics, 14(10), 1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14101003





