Genomic Epidemiology of C2/H30Rx and C1-M27 Subclades of Escherichia coli ST131 Isolates from Clinical Blood Samples in Hungary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Selection of Isolates for the Study
2.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility
2.3. Molecular Epidemiology
2.3.1. Phylogenetic Analysis of E. coli ST131 Isolates
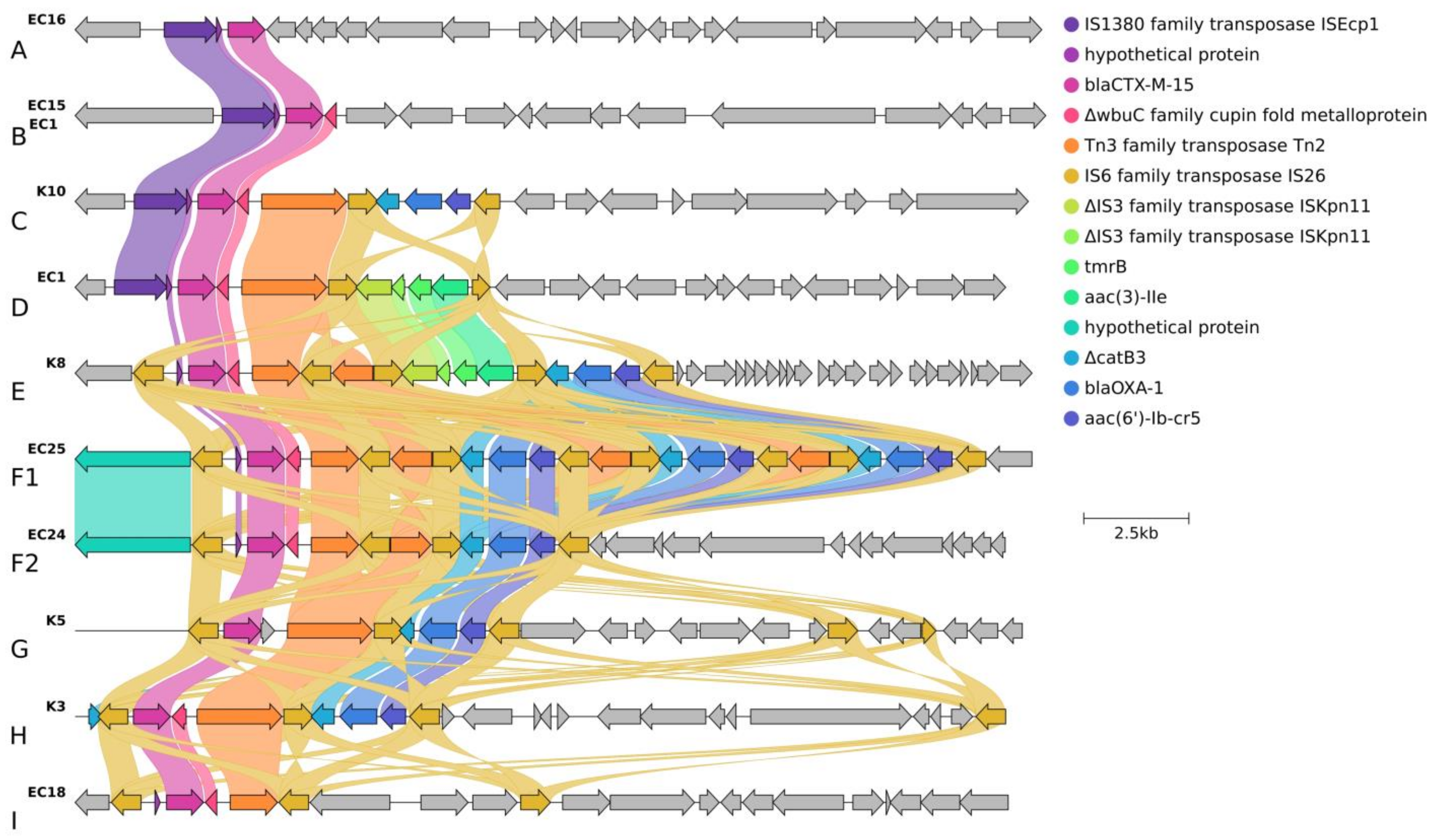
2.3.2. Localization and Genetic Environment of blaCTX-M-15 in the C2/H30Rx Isolates (Group A–I)
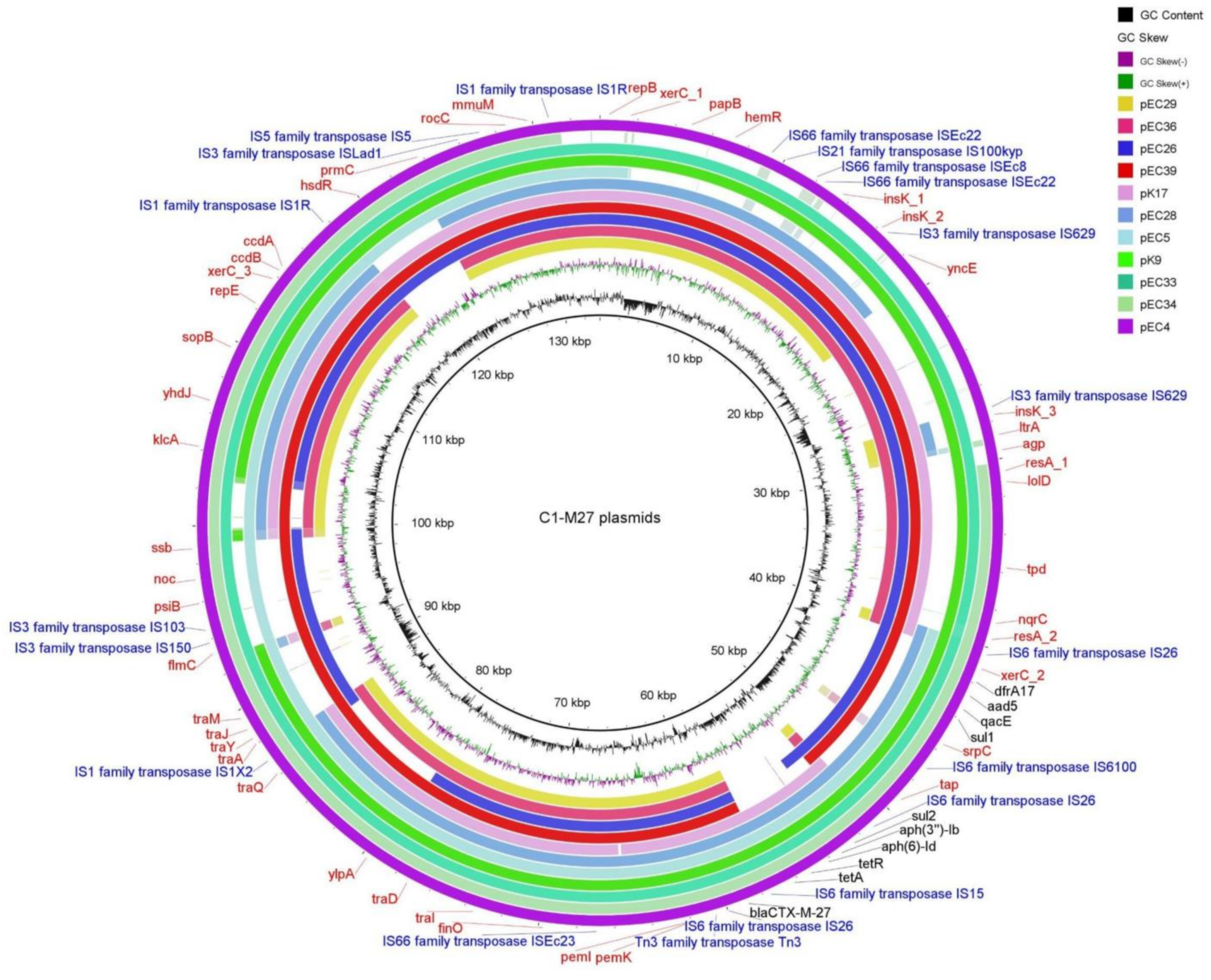
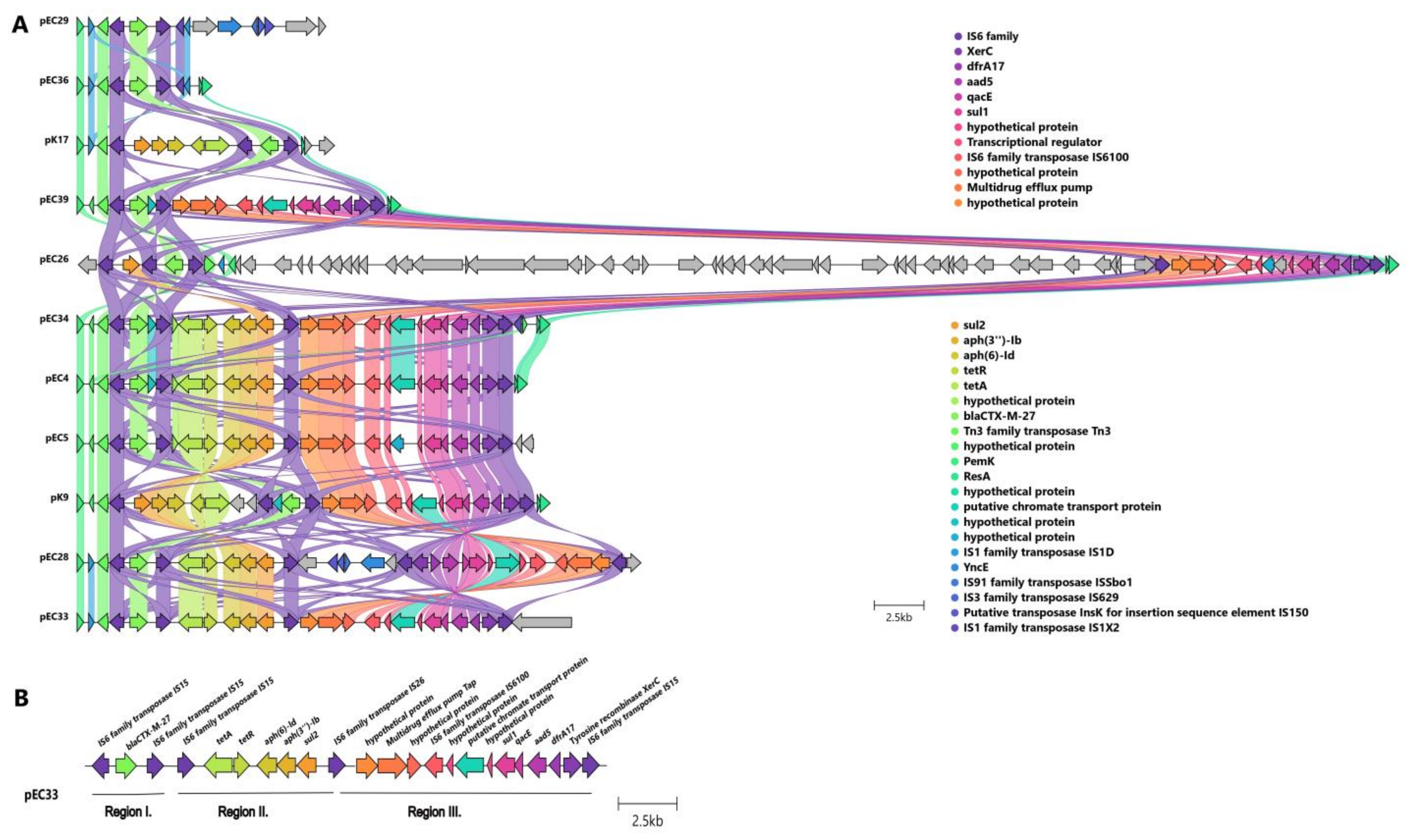
2.3.3. Localization and Genetic Environment of blaCTX-M-27 in the C1-M27 Isolates (Region I–III)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Collection
4.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
4.3. Molecular Characterization
4.3.1. DNA Extraction
4.3.2. Short-Read Sequencing
4.3.3. Long-Read Sequencing and Genome Assembly
4.3.4. Phylogenomic Reconstruction and Clustering of Isolates
4.3.5. Virulence and Antibiotic Resistance Genes Analysis
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Magiorakos, A.-P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassini, A.; Högberg, L.D.; Plachouras, D.; Quattrocchi, A.; Hoxha, A.; Simonsen, G.S.; Colomb-Cotinat, M.; Kretzschmar, M.E.; Devleesschauwer, B.; Cecchini, M.; et al. Attributable Deaths and Disability-Adjusted Life-Years Caused by Infections with Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria in the EU and the European Economic Area in 2015: A Population-Level Modelling Analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petty, N.K.; Ben Zakour, N.L.; Stanton-Cook, M.; Skippington, E.; Totsika, M.; Forde, B.M.; Phan, M.-D.; Gomes Moriel, D.; Peters, K.M.; Davies, M.; et al. Global Dissemination of a Multidrug Resistant Escherichia coli Clone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 5694–5699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, T.J.; Danzeisen, J.L.; Youmans, B.; Case, K.; Llop, K.; Munoz-Aguayo, J.; Flores-Figueroa, C.; Aziz, M.; Stoesser, N.; Sokurenko, E.; et al. Separate F-Type Plasmids Have Shaped the Evolution of the H30 Subclone of Escherichia coli Sequence Type 131. mSphere 2016, 1, e00121-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitout, J.D.D.; Finn, T.J. The Evolutionary Puzzle of Escherichia coli ST131. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 81, 104265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumura, Y.; Pitout, J.D.D.; Gomi, R.; Matsuda, T.; Noguchi, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Peirano, G.; DeVinney, R.; Bradford, P.A.; Motyl, M.R.; et al. Global Escherichia coli Sequence Type 131 Clade with Bla CTX-M-27 Gene. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 1900–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitout, J.D.D.; DeVinney, R. Escherichia coli ST131: A Multidrug-Resistant Clone Primed for Global Domination. F1000Research 2017, 6, Rev-195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathers, A.J.; Peirano, G.; Pitout, J.D.D. The Role of Epidemic Resistance Plasmids and International High-Risk Clones in the Spread of Multidrug-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 565–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, M.; Matsui, M.; Sekizuka, T.; Shima, A.; Segawa, T.; Kuroda, M.; Kawamura, K.; Suzuki, S. Dissemination of IncF Group F1:A2:B20 Plasmid-Harbouring Multidrug-Resistant Escherichia coli ST131 before the Acquisition of BlaCTX-M in Japan. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 23, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitout, J.D.D.; Chen, L. The Significance of Epidemic Plasmids in the Success of Multidrug-Resistant Drug Pandemic Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2023, 12, 1029–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, K.; Tóth, Á.; Kamotsay, K.; Németh, V.; Szabó, D. Population Snapshot of the Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli Invasive Strains Isolated from a Hungarian Hospital. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2022, 21, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirel, L.; Gniadkowski, M.; Nordmann, P. Biochemical Analysis of the Ceftazidime-Hydrolysing Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamse CTX-M-15 and of Its Structurally Related β-Lactamase CTX-M-3. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2002, 50, 1031–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castanheira, M.; Simner, P.J.; Bradford, P.A. Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamases: An Update on Their Characteristics, Epidemiology and Detection. JAC-Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 3, dlab092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnet, R.; Recule, C.; Baraduc, R.; Chanal, C.; Sirot, D.; De Champs, C.; Sirot, J. Effect of D240G Substitution in a Novel ESBL CTX-M-27. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 52, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juhász, E.; Iván, M.; Pintér, E.; Pongrácz, J.; Kristóf, K. Colistin Resistance among Blood Culture Isolates at a Tertiary Care Centre in Hungary. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2017, 11, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, F.; Xu, L.; Ruan, Z.; Luo, Q. Genomic and Transcriptomic Analysis of Colistin-Susceptible and Colistin-Resistant Isolates Identify Two-Component System Evgs/Evga Associated with Colistin Resistance in Escherichia coli. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 2437–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abavisani, M.; Bostanghadiri, N.; Ghahramanpour, H.; Kodori, M.; Akrami, F.; Fathizadeh, H.; Hashemi, A.; Rastegari-Pouyani, M. Colistin Resistance Mechanisms in Gram-Negative Bacteria: A Focus on Escherichia coli. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 76, ovad023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakaria, A.S.; Edward, E.A.; Mohamed, N.M. Genomic Insights into a Colistin-Resistant Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Strain of O23:H4-ST641 Lineage Harboring Mcr-1.1 on a Conjugative IncHI2 Plasmid from Egypt. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, H.; Park, M.; Kang, K.J.; Lim, S.K.; Shin, D.; Ko, K.S. Comparison of Fitness Cost and Virulence in Chromosome- and Plasmid-Mediated Colistin-Resistant Escherichia coli. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, K.J.; Rather, P.N.; Hare, R.S.; Miller, G.H. Molecular Genetics of Aminoglycoside Resistance Genes and Familial Relationships of the Aminoglycoside-Modifying Enzymes. Microbiol. Rev. 1993, 57, 138–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, M.S.; Tolmasky, M.E. Amikacin: Uses, Resistance, and Prospects for Inhibition. Molecules 2017, 22, 2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, M.S.; Tolmasky, M.E. Aminoglycoside Modifying Enzymes. Drug Resist. Updat. 2010, 13, 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robicsek, A.; Strahilevitz, J.; Jacoby, G.A.; Macielag, M.; Abbanat, D.; Chi, H.P.; Bush, K.; Hooper, D.C. Fluoroquinolone-Modifying Enzyme: A New Adaptation of a Common Aminoglycoside Acetyltransferase. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, M.D.; Peters, K.M.; Fraga, L.A.; Wallis, S.C.; Hancock, S.J.; Nhu, N.T.K.; Forde, B.M.; Bauer, M.J.; Paterson, D.L.; Beatson, S.A.; et al. Plasmid-Mediated Ciprofloxacin Resistance Imparts a Selective Advantage on Escherichia coli ST131. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2022, 66, e02146-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, I.; Fukui, N.; Taguchi, M.; Yamauchi, K.; Nakamura, T.; Okano, S.; Yamamoto, Y. Detection of Chromosomal BlaCTX-M-15 in Escherichia coli O25b-B2-ST131 Isolates from the Kinki Region of Japan. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2013, 42, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludden, C.; Decano, A.G.; Jamrozy, D.; Pickard, D.; Morris, D.; Parkhill, J.; Peacock, S.J.; Cormican, M.; Downing, T. Genomic Surveillance of Escherichia coli ST131 Identifies Local Expansion and Serial Replacement of Subclones. Microb. Genom. 2020, 6, e000352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmer, C.J.; Hall, R.M. IS26 Cannot Move Alone. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, 1428–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmer, C.J.; Hall, R.M. An Analysis of the IS6/IS26 Family of Insertion Sequences: Is It a Single Family? Microb. Genom. 2019, 5, e000291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varani, A.; He, S.; Siguier, P.; Ross, K.; Chandler, M. The IS6 Family, a Clinically Important Group of Insertion Sequences Including IS26. Mob. DNA 2021, 12, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipszyc, A.; Szuplewska, M.; Bartosik, D. How Do Transposable Elements Activate Expression of Transcriptionally Silent Antibiotic Resistance Genes? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawa, M.; Furuta, Y.; Mulenga, G.; Mubanga, M.; Mulenga, E.; Zorigt, T.; Kaile, C.; Simbotwe, M.; Paudel, A.; Hang’ombe, B.; et al. Novel Chromosomal Insertions of ISEcp1-Bla CTX-M-15 and Diverse Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in Zambian Clinical Isolates of Enterobacter Cloacae and Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2021, 10, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biggel, M.; Moons, P.; Nguyen, M.N.; Goossens, H.; Van Puyvelde, S. Convergence of Virulence and Antimicrobial Resistance in Increasingly Prevalent Escherichia coli ST131 PapGII+ Sublineages. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awosile, B.B.; Agbaje, M. Genetic Environments of Plasmid-Mediated BlaCTXM-15 Beta-Lactamase Gene in Enterobacteriaceae from Africa. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 12, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shropshire, W.C.; Aitken, S.L.; Pifer, R.; Kim, J.; Bhatti, M.M.; Li, X.; Kalia, A.; Galloway-Penã, J.; Sahasrabhojane, P.; Arias, C.A.; et al. IS26-Mediated Amplification of BlaOXA-1and BlaCTX-M-15 with Concurrent Outer Membrane Porin Disruption Associated with de Novo Carbapenem Resistance in a Recurrent Bacteraemia Cohort. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggel, M.; Xavier, B.B.; Johnson, J.R.; Nielsen, K.L.; Frimodt-Møller, N.; Matheeussen, V.; Goossens, H.; Moons, P.; Van Puyvelde, S. Horizontally Acquired PapGII-Containing Pathogenicity Islands Underlie the Emergence of Invasive Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Lineages. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoesser, N.; Sheppard, A.E.; Pankhurst, L.; de Maio, N.; Moore, C.E.; Sebra, R.; Turner, P.; Anson, L.W.; Kasarskis, A.; Batty, E.M.; et al. Evolutionary History of the Global Emergence of the Escherichia coli Epidemic Clone ST131. MBio 2016, 7, e02162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmud, B.; Wallace, M.A.; Reske, K.A.; Alvarado, K.; Muenks, C.E.; Rasmussen, D.A.; Burnham, C.-A.D.; Lanzas, C.; Dubberke, E.R.; Dantas, G. Epidemiology of Plasmid Lineages Mediating the Spread of Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamases among Clinical Escherichia coli. mSystems 2022, 7, e0051922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, E.-J.; Gwon, B.; Liu, C.; Kim, D.; Won, D.; Park, S.G.; Choi, J.R.; Jeong, S.H. Beneficial Chromosomal Integration of the Genes for CTX-M Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase in Klebsiella Pneumoniae for Stable Propagation. mSystems 2020, 5, 00459-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerquetti, M.; Giufrè, M.; García-Fernández, A.; Accogli, M.; Fortini, D.; Luzzi, I.; Carattoli, A. Ciprofloxacin-Resistant, CTX-M-15-Producing Escherichia coli ST131 Clone in Extraintestinal Infections in Italy. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2010, 16, 1555–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palkovicova, J.; Sukkar, I.; Delafuente, J.; Valcek, A.; Medvecky, M.; Jamborova, I.; Bitar, I.; Phan, M.-D.; San Millan, A.; Dolejska, M. Fitness Effects of Bla CTX-M-15-Harbouring F2:A1:B− Plasmids on Their Native Escherichia coli ST131 H 30Rx Hosts. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2022, 77, 2960–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, N.; Nonogaki, R.; Hayashi, M.; Wachino, J.-I.; Suzuki, M.; Arakawa, Y.; Kawamura, K. Characterization of Bla CTX-M-27/F1:A2:B20 Plasmids Harbored by Escherichia coli Sequence Type 131 Sublineage C1/H 30R Isolates Spreading among Elderly Japanese in Nonacute-Care Settings. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e00202-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasugi, M.; Hatoya, S.; Motooka, D.; Matsumoto, Y.; Shimamura, S.; Tani, H.; Furuya, M.; Mie, K.; Miyake, M.; Nakamura, S.; et al. Whole-Genome Analyses of Extended-Spectrum or AmpC β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli Isolates from Companion Dogs in Japan. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.H.; Wang, J.Y.; Chang, M.X.; Zhao, Q.Y.; Jiang, H.X. A Novel Structure Harboring BlaCTX-M-27 on IncF Plasmids in Escherichia coli Isolated from Swine in China. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherubini, S.; Perilli, M.; Azzini, A.M.; Tacconelli, E.; Maccacaro, L.; Bazaj, A.; Naso, L.; Amicosante, G.; Cascio, G.L.; Piccirilli, A. Resistome and Virulome of Multi-Drug Resistant E. coli ST131 Isolated from Residents of Long-Term Care Facilities in the Northern Italian Region. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondratyeva, K.; Salmon-Divon, M.; Navon-Venezia, S. Meta-Analysis of Pandemic Escherichia coli ST131 Plasmidome Proves Restricted Plasmid-Clade Associations. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’Zali, F.H.; Chanawong, A.; Kerr, K.G.; Birkenhead, D.; Hawkey, P.M. Detection of Extended-Spectrum I-Lactamases in Members of the Family Enterobacteriaceae: Comparison of the MAST DD Test, the Double Disc and the Etest ESBL. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2000, 45, 881–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EUCAST The EUCAST Guideline on Detection of Resistance Mechanisms v 2.0. 2017. Available online: https://www.Eucast.Org/Fileadmin/Src/Media/PDFs/EUCAST_files/Resistance_mechanisms/EUCAST_detection_of_resistance_mechanisms_170711.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- Tóth, Á.; Kocsis, B.; Damjanova, I.; Kristóf, K.; Jánvári, L.; Pászti, J.; Csercsik, R.; Topf, J.; Szabó, D.; Hamar, P.; et al. Fitness Cost Associated with Resistance to Fluoroquinolones Is Diverse across Clones of Klebsiella Pneumoniae and May Select for CTX-M-15 Type Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 33, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumura, Y.; Pitout, J.D.D.; Peirano, G.; DeVinney, R.; Noguchi, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Gomi, R.; Matsuda, T.; Nakano, S.; Nagao, M.; et al. Rapid Identification of Different Escherichia coli Sequence Type 131 Clades. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e00179-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUCAST—The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters. Version 11.0. 2021. Available online: http://www.Eucast.Org (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- Zhou, Z.; Alikhan, N.F.; Mohamed, K.; Fan, Y.; Achtman, M. The EnteroBase User’s Guide, with Case Studies on Salmonella Transmissions, Yersinia Pestis Phylogeny, and Escherichia Core Genomic Diversity. Genome Res. 2020, 30, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Gorrie, C.L.; Holt, K.E. Completing Bacterial Genome Assemblies with Multiplex MinION Sequencing. Microb. Genom. 2017, 3, e000132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmogorov, M.; Yuan, J.; Lin, Y.; Pevzner, P.A. Assembly of Long, Error-Prone Reads Using Repeat Graphs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Gorrie, C.L.; Holt, K.E. Unicycler: Resolving Bacterial Genome Assemblies from Short and Long Sequencing Reads. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and Accurate Long-Read Alignment with Burrows-Wheeler Transform. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, B.J.; Abeel, T.; Shea, T.; Priest, M.; Abouelliel, A.; Sakthikumar, S.; Cuomo, C.A.; Zeng, Q.; Wortman, J.; Young, S.K.; et al. Pilon: An Integrated Tool for Comprehensive Microbial Variant Detection and Genome Assembly Improvement. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikheenko, A.; Prjibelski, A.; Saveliev, V.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A. Versatile Genome Assembly Evaluation with QUAST-LG. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i142–i150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid Prokaryotic Genome Annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilchrist, C.L.M.; Chooi, Y.H. Clinker & Clustermap.Js: Automatic Generation of Gene Cluster Comparison Figures. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 2473–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carattoli, A.; Zankari, E.; Garciá-Fernández, A.; Larsen, M.V.; Lund, O.; Villa, L.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Hasman, H. In Silico Detection and Typing of Plasmids Using Plasmidfinder and Plasmid Multilocus Sequence Typing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, M.H.K.; Bortolaia, V.; Tansirichaiya, S.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Roberts, A.P.; Petersen, T.N. Detection of Mobile Genetic Elements Associated with Antibiotic Resistance in Salmonella Enterica Using a Newly Developed Web Tool: MobileElementFinder. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alikhan, N.F.; Petty, N.K.; Ben Zakour, N.L.; Beatson, S.A. BLAST Ring Image Generator (BRIG): Simple Prokaryote Genome Comparisons. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonkin-Hill, G.; MacAlasdair, N.; Ruis, C.; Weimann, A.; Horesh, G.; Lees, J.A.; Gladstone, R.A.; Lo, S.; Beaudoin, C.; Floto, R.A.; et al. Producing Polished Prokaryotic Pangenomes with the Panaroo Pipeline. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; Von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R.; Teeling, E. IQ-TREE 2: New Models and Efficient Methods for Phylogenetic Inference in the Genomic Era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonkin-Hill, G.; Lees, J.A.; Bentley, S.D.; Frost, S.D.W.; Corander, J. Fast Hierarchical Bayesian Analysis of Population Structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 5539–5549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Willems, R.J.L.; Top, J.; van Schaik, W.; Leavis, H.; Bonten, M.; Sirén, J.; Hanage, W.P.; Corander, J. Restricted Gene Flow among Hospital Subpopulations of Enterococcus Faecium. MBio 2012, 3, e00151-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Smith, D.K.; Zhu, H.; Guan, Y.; Lam, T.T.Y. Ggtree: An R Package for Visualization and Annotation of Phylogenetic Trees with Their Covariates and Other Associated Data. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2017, 8, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schliep, K.P. Phangorn: Phylogenetic Analysis in R. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 592–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (ITOL) v5: An Online Tool for Phylogenetic Tree Display and Annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolaia, V.; Kaas, R.S.; Ruppe, E.; Roberts, M.C.; Schwarz, S.; Cattoir, V.; Philippon, A.; Allesoe, R.L.; Rebelo, A.R.; Florensa, A.F.; et al. ResFinder 4.0 for Predictions of Phenotypes from Genotypes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 3491–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zankari, E.; Allesøe, R.; Joensen, K.G.; Cavaco, L.M.; Lund, O.; Aarestrup, F.M. PointFinder: A Novel Web Tool for WGS-Based Detection of Antimicrobial Resistance Associated with Chromosomal Point Mutations in Bacterial Pathogens. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 2764–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and Applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joensen, K.G.; Scheutz, F.; Lund, O.; Hasman, H.; Kaas, R.S.; Nielsen, E.M.; Aarestrup, F.M. Real-Time Whole-Genome Sequencing for Routine Typing, Surveillance, and Outbreak Detection of Verotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 1501–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zheng, D.; Liu, B.; Yang, J.; Jin, Q. VFDB 2016: Hierarchical and Refined Dataset for Big Data Analysis—10 Years On. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D694–D697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, J.; Mora, A.; Mamani, R.; López, C.; Blanco, M.; Dahbi, G.; Herrera, A.; Marzoa, J.; Fernández, V.; De La Cruz, F.; et al. Four Main Virotypes among Extended-Spectrum-β-Lactamase-Producing Isolates of Escherichia coli O25b:H4-B2-ST131: Bacterial, Epidemiological, and Clinical Characteristics. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 3358–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Antimicrobial Agent | C2/H30Rx | C1-M27 | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R% (n = 30) | MIC50 (n = 30) | MIC90 (n = 30) | R% (n = 33) | MIC50 (n = 33) | MIC90 (n = 33) | ||
| FOS | 0 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 1 |
| ETP | 0 | 0.0625 | 0.125 | 0 | 0.016 | 0.0625 | 1 |
| CZA | 0 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0 | 0.125 | 0.25 | 1 |
| CAZ | 83.9 | 16 | 64 | 15.6 | 4 | 8 | <0.001 * |
| CRO | 100 | 256 | 256 | 100 | 128 | 256 | 1 |
| COL | 0 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 6.3 | 0.25 | 1 | 0.5 |
| TGC | 0 | ND | ND | 0 | ND | ND | 1 |
| AK | 40 | ND | ND | 6.1 | ND | ND | <0.01 * |
| TM | 66.7 | ND | ND | 3.0 | ND | ND | <0.001 * |
| GM | 40 | ND | ND | 0 | ND | ND | <0.001 * |
| MEM | 0 | ND | ND | 0 | ND | ND | 1 |
| IMI | 0 | ND | ND | 0 | ND | ND | 1 |
| CIP | 100 | ND | ND | 100 | ND | ND | 1 |
| Subclade | Cluster Type | Cluster-Specific Virulence Gene | Localization of blaCTX-M | IS Element Linked to blaCTX-M | Copy of blaCTX-M | Genetic Environment of blaCTX-M | Additional Antibiotic Resistance Genes | Corresponding Isolate (s) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Categorization of the Genetic Environment of blaCTX-M | 1st Segment | 2nd Segment | 3rd Segment | 4th Segment | ||||||||
| C1-M27 | A | traT, senB, mcbA, pic | plasmid | IS6 family | 1 | Regions I | blaCTX-M-27 | - | - | - | - | EC29, EC36 |
| Regions I–II | tetA-aph(6)-Id-aph(3″)-Ib-sul2 | - | - | K17 | ||||||||
| Regions I–III | dfrA17- aadA5-qacEΔ1-sul1-mph(A) | - | - | EC39, EC26 | ||||||||
| Regions I–II–III | tetA-aph(6)-Id-aph(3″)-Ib-sul2 | dfrA17- aadA5-qacEΔ1-sul1-mph(A) | - | EC4, EC5, EC28, EC33, EC34, K9 | ||||||||
| C2/H30Rx | B | astA, east1 | chromosomal | ISEcp1 | 2 | Group B, D | blaCTX-M-15 | tmrB-aac(3)-Iia | - | - | qnrB19, sul2, aph(6)-Id, aph(3″)-Ib | EC1, EC2, EC3, EC7 |
| C | - | 1 | Group C | ΔcatB3-blaoxa-1-aac(6′)-Ib-cr5 | - | - | - | K10 | ||||
| D | hyl, cnf1 | IS26 | Group I | - | - | - | EC10, EC18 | |||||
| Group F2 | ΔcatB3-blaoxa-1-aac(6′)-Ib-cr5 | - | - | EC24, EC22 | ||||||||
| Group F1 | ΔcatB3-blaoxa-1-aac(6′)-Ib-cr5 | ΔcatB3-blaoxa-1-aac(6′)-Ib-cr5 | ΔcatB3-blaoxa-1-aac(6′)-Ib-cr5 | EC25 | ||||||||
| Group E | tmrB-aac(3)-Iia | ΔcatB3-blaoxa-1-aac(6′)-Ib-cr5 | - | K4, K6, K8, EC19 | ||||||||
| E | - | ISEcp1 | 3 | Group B | - | - | - | EC15 | ||||
| nfaE, daaA-F, afa operon, draA-D | 1 | Group A | - | - | - | EC16 | ||||||
| F | IS26 | Group I | - | - | - | K7 | ||||||
| chromosomal | Group G | ΔcatB3-blaoxa-1-aac(6′)-Ib-cr5 | - | - | K5 | |||||||
| plasmid | Group H | ΔcatB3-blaoxa-1-aac(6′)-Ib-cr5 | - | - | K3 | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tóth, K.; Damjanova, I.; Laczkó, L.; Buzgó, L.; Lesinszki, V.; Ungvári, E.; Jánvári, L.; Hanczvikkel, A.; Tóth, Á.; Szabó, D. Genomic Epidemiology of C2/H30Rx and C1-M27 Subclades of Escherichia coli ST131 Isolates from Clinical Blood Samples in Hungary. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13040363
Tóth K, Damjanova I, Laczkó L, Buzgó L, Lesinszki V, Ungvári E, Jánvári L, Hanczvikkel A, Tóth Á, Szabó D. Genomic Epidemiology of C2/H30Rx and C1-M27 Subclades of Escherichia coli ST131 Isolates from Clinical Blood Samples in Hungary. Antibiotics. 2024; 13(4):363. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13040363
Chicago/Turabian StyleTóth, Kinga, Ivelina Damjanova, Levente Laczkó, Lilla Buzgó, Virág Lesinszki, Erika Ungvári, Laura Jánvári, Adrienn Hanczvikkel, Ákos Tóth, and Dóra Szabó. 2024. "Genomic Epidemiology of C2/H30Rx and C1-M27 Subclades of Escherichia coli ST131 Isolates from Clinical Blood Samples in Hungary" Antibiotics 13, no. 4: 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13040363
APA StyleTóth, K., Damjanova, I., Laczkó, L., Buzgó, L., Lesinszki, V., Ungvári, E., Jánvári, L., Hanczvikkel, A., Tóth, Á., & Szabó, D. (2024). Genomic Epidemiology of C2/H30Rx and C1-M27 Subclades of Escherichia coli ST131 Isolates from Clinical Blood Samples in Hungary. Antibiotics, 13(4), 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13040363







