Abstract
Among the foodborne illnesses, listeriosis has the third highest case mortality rate (20–30% or higher). Emerging drug-resistant strains of Listeria monocytogenes, a causative bacterium of listeriosis, exacerbate the seriousness of this public health concern. Novel anti-Listerial compounds are therefore needed to combat this challenge. In recent years, marine actinobacteria have come to be regarded as a promising source of novel antimicrobials. Hence, our aim was to provide a narrative of the available literature and discuss trends regarding bioprospecting marine actinobacteria for new anti-Listerial compounds. Four databases were searched for the review: Academic Search Ultimate, Google Scholar, ScienceDirect, and South African Thesis and Dissertations. The search was restricted to peer-reviewed full-text manuscripts that discussed marine actinobacteria as a source of antimicrobials and were written in English from 1990 to December 2023. In total, for the past three decades (1990–December 2023), only 23 compounds from marine actinobacteria have been tested for their anti-Listerial potential. Out of the 23 reported compounds, only 2-allyoxyphenol, adipostatins E–G, 4-bromophenol, and ansamycins (seco-geldanamycin B, 4.5-dihydro-17-O-demethylgeldanamycin, and seco-geldanamycin) have been found to possess anti-Listerial activity. Thus, our literature survey reveals the scarcity of published assays testing the anti-Listerial capacity of bioactive compounds sourced from marine actinobacteria during this period.
1. Introduction
Listeria monocytogenes is a major foodborne pathogen that can cause severe listeriosis in humans [1]. Severe listeriosis may be characterized by meningitis, septicaemia, meningoencephalitis in immunocompromised people, invasive infections in newborns and the elderly, fetal malformations, and serious complications in pregnant women (abortion and stillbirth), with a case mortality rate that can range from 20% to 30% [2,3,4,5]. The hospitalization rate of the infection is more than 95% [1]. Although potentially deadly, the disease is relatively rare, with 0.1 to 10 cases per 1 million people annually, depending on the country and area of the world [3]. In contrast to high socio-economic regions of the world, Africa has a comparatively lower prevalence of severe listeriosis, despite the continent generally having a higher burden of foodborne infections [2,5]. Annually, 23,150 illnesses and 5463 deaths result from listeriosis worldwide [2,5]. However, the African continent contributes to 16% of the prevalence [2,5]. Despite this relatively low prevalence, the largest L. monocytogenes outbreak in the world happened in South Africa in 2017–2018, with 1060 reported cases [4,6,7]. The occurrence of an outbreak of this magnitude against the backdrop of a historically low prevalence of the disease in Africa is probably due to specific risk factors, and less awareness of Listeria transmission and risk factors along the food value chain [5].
Drug-resistant strains of Listeria have been documented [8,9], contributing to an escalation in morbidity and mortality rates associated with listeriosis [10]. Consequently, the pursuit of novel anti-Listerial compounds becomes a crucial strategy in addressing this crisis. Nature serves as the primary source of biotechnologically important molecules applicable across diverse fields [11]. Microorganisms, particularly within the Actinobacteria phylum, exhibit a notable proficiency in producing a variety of bioactive compounds due to their unique genetic composition [12,13]. While the extensive bioprospecting of terrestrial actinomycetes has diminished the probability of discovering novel bioactive compounds from this source, the largely unexplored marine environment is promising for identifying new actinomycetes with distinctive bioactive secondary metabolites. This potential is attributed to the harsh physicochemical conditions in the sea, such as high salinity, pressure, and low temperature, which create a conducive environment for the microbial synthesis of structurally and functionally unique molecules [14].
This review aimed to discuss the anti-Listerial compounds obtained from marine actinobacteria from the years 1990 to 2023 in the context of the sources of bioactive compounds, their structures, and antimicrobial activities. Furthermore, the review highlights the challenges and opportunities in the search for new anti-Listerial compounds from marine actinobacteria. Some reviews have summarized the sources, chemical structures, and anti-Listerial activities of bioactive compounds derived from marine actinobacteria [15,16]. In contrast, our review is unique as it focusses on consolidating information specifically and exclusively related to anti-Listerial compounds sourced from marine actinobacteria. By concentrating solely on the reporting of these compounds, our review identifies and emphasizes the gaps and trends observed from 1990 to 2023 in anti-Listerial compounds research. This focused analysis serves to guide future research directions, aiding researchers in pinpointing areas that need deeper exploration.
This literature review was conducted using four databases: Academic Search Ultimate, Google Scholar, ScienceDirect, and South African Thesis and Dissertations. The literature was accessed through the EBSCOhost research platform. The search terms used were “Marine actinomycetes”, “OR”, “actinobacteria”, “AND”, “antimicrobials”, “OR”, “antibiotics”, “OR”, “anti-listerial”, “AND”, “Listeria”.” Individual genera also replaced “actinomycetes” and “actinobacteria” as search terms. Only English-published full-text and peer-reviewed manuscripts were selected for the review. Those manuscripts discussing anti-Listerial compounds obtained from terrestrial actinobacteria or from plant extracts were excluded (Figure 1).
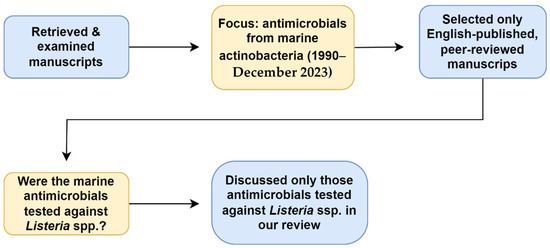
Figure 1.
Relevant data retrieval process.
A limitation of this review is that the literature regarding alternative treatments for listeriosis is outside the scope of our discussion.
2. Background
2.1. Foodborne Listeriosis
Among the foodborne illnesses, listeriosis has the third highest case mortality rate (20–30% or higher) [17]. Thus, listeriosis is a serious public health concern [3,18].
2.1.1. Clinical Features
The clinical signs and symptoms of listeriosis can be differentiated into two categories, namely perinatal (i.e., feto-maternal and neonatal) listeriosis and listeriosis in adults. Perinatal listeriosis involves the infection of the fetus via the placenta. This may lead to abortion, stillbirth, or the baby being born with granulomatosis infantiseptica (a generalized infection) presenting as pyogranulomatous micro-abscesses [18,19,20]. For the mother, the infection may be asymptomatic or may present as a flu-like illness characterized by fatigue, headache, chills, and painful joints and muscles around 2 to 14 days prior to the miscarriage [21,22]. For reasons that are not clear, the mother’s central nervous system (CNS) is rarely infected [20,21,22,23]. In 10–15% of perinatal cases, the aspiration of maternal fluids during delivery may cause late-onset neonatal listeriosis [24,25]. The clinical features may include flu-like symptoms accompanied by meningitis, 1–8 weeks postpartum [24,25].
2.1.2. Listeriosis Outbreaks
Listeriosis was first recognized as a foodborne disease in 1981 [26]. Thereafter, deadly outbreaks of the disease have been recorded worldwide [4,6,27,28,29,30,31,32]. The foods commonly implicated in the outbreaks include ready-to-eat (RTE) foods, unpasteurized milk, dairy products (yogurt, cheese, etc.), raw and unprocessed meats, salads, and fresh produce [3,7,33,34]. However, meat and its products have been responsible for all the major foodborne listeriosis outbreaks worldwide [7]. Table 1 summarizes some of the disease outbreaks associated with various meat types. Between 2017 and 2018, South Africa experienced the largest listeriosis outbreak in the world (Table 1) [4,6,7]. Two hundred and sixteen people (out of 1060 patients that were traced) died, resulting in a case mortality rate of 20.4% [4,31]. Whole-genome sequencing (WGS) was employed to track the source of the outbreak. Ready-to-eat-meat products (mainly polony) were linked to the outbreak [4]. The implicated bacterial strain was confirmed to be L. monocytogenes sequence type (ST) 6 [4]. Consequently, products were recalled from retailers across the country and from 15 importing African countries [35], and litigation was initiated against the RTE meat manufacturing company, leading to financial losses [31]. Therefore, beyond just the impacted customers, the aftermaths of these incidents have wider socioeconomic effects [31].

Table 1.
Selected foodborne listeriosis outbreaks from meat and associated products from 1987 to 2019.
2.1.3. Chemotherapeutic Treatment for Human Listeriosis
The feasible solution for the treatment of listeriosis is antimicrobial chemotherapy [48,49]. Usually, Listeria species are refractory to the lethal effects of many antibiotics. This is because the species are able to live and multiply within the host cells, where they remain hidden from the antibiotics in the extracellular fluid [50]. There are a limited number of antibiotics able to penetrate the host cells and reach the cytosol where the Listeria species normally reside in host cells [19,50]. Therefore, the antibiotic of choice for the treatment of listeriosis must be able to penetrate the host cell in sufficiently high concentrations for it to be efficacious [51,52,53]. Furthermore, the antibiotic must not undergo significant changes in its pH upon penetration into the host cell, as significant changes would hinder its efficacy. In addition, the antibiotic must bind to and block the penicillin-binding protein 3 (PBP 3) of Listeria, which result in a bactericidal effect (PBP 3 is an enzyme that catalyzes the last step of peptidoglycan synthesis) [48,52]. In the case of a pregnant woman, adequate concentrations of the antibiotic must be able to cross the placenta for fetal treatment [22,54]. Thus, the first choice of chemotherapy for treating listeriosis mainly includes the following antibiotics: penicillin G, amoxicillin, and ampicillin [54,55]. These antibiotics penetrate the host cells and exert their bactericidal effects by blocking a number of PBPs [50,52,56]. For synergy, the penicillins are commonly combined with an aminoglycoside, traditionally gentamicin [57]. In the second choice of therapy, trimethoprim is combined with a sulfonamide (e.g., sulfamethoxazole) in co-trimoxazole [56,57,58,59]. Other second-tier therapies include fluoroquinolones, vancomycin, and erythromycin (used in pregnancy) [57]. These second-choice therapies are normally reserved for people who are allergic to penicillin [54,57].
Prior to initiating treatment, it is imperative to conduct an in vitro assessment of the antimicrobial drugs used against the clinical Listeria isolates from a patient [60]. This is because there has been an increase in reports of antimicrobial-resistant L. monocytogenes strains from diverse sources such as meat and meat products [6,7], humans [9,61], animals [9,18,62], and food processing establishments [18,63]. The first strain of L. monocytogenes found to possess acquired antimicrobial resistance was a clinical isolate from France in 1988 [9,64,65]. The strain was multidrug resistant [9,64], resistant to aminoglycosides (erythromycin, and streptomycin), chloramphenicol and tetracyclines [64]. The antimicrobial resistance-encoding genes were found to be conferred by pIP811, a self-transferable 37-Kb plasmid [64]. Antimicrobial resistance has since spread, and is a serious public health challenge [8,9].
2.1.4. Resistance to Quinolones and Fluoroquinolones
Quinolones are a class of antimicrobial compounds that possess a 4-quinolone ring. Nearly all quinolones have a fluorine atom in their structure and are therefore called fluoroqinolones. Members of the quinolones and/or fluoroquinoles family include nalidixic acid, nafloxacin and ciprofloxacin. They exert a bactericidal effect by blocking bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV, thereby inhibiting DNA and RNA syntheses [48,66,67]. However, Listeria spp. that are resistant to this class of antibiotics have been detected in food-producing animals and humans [68,69,70]. The mechanisms by which Listeria spp. resist fluoroquinolones include target gene alterations that include, for example, topoisomerase and gyrase gene mutations in some Listeria species [7,48,71]. These species also resist antibiotics via the overexpression of efflux pumps, namely Lde, MdrL, and FepA [7,72,73,74,75]. The pumps export an antimicrobial agent out of the cytosol and thus minimize its bactericidal or bacteriostatic effects [76,77]. Some Listeria spp. may harbor plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance (PMQR) genes, making them resistant to quinoline [48].
2.1.5. Resistance to Penicillins and Cephalosporins
Members of the penicillin group include penicillin G, penicillin V, ampicillin, methicillin, and oxacillin, and cephalosporins include the following broad-spectrum antibiotics: cefetamet, cefixime, ceftibuten, ceftazidime, cefdinir, cefpodoxime, cefotaxime, ceftriaxone, and cefuroxime [8,66,78,79]. Both penicillins and cephalosporins contain a β-lactam ring that is essential for their antimicrobial activity, which is the inhibition of bacterial cell wall synthesis [8,48,79]. These antimicrobials generally accomplish this inhibition by binding, through their β-lactam rings, to PBP 3, which inactivates the enzyme [80].
L. monocytogenes strains are naturally resistant to broad-spectrum cephalosporins due to the antimicrobials’ low affinity for the PBB 3 of the bacteria [48,52,80,81]. In contrast, the bacterial strains are generally susceptible to penicillins, except for oxacillin [48]. However, some of the strains eventually become antimicrobial resistant, mainly through horizontal gene transfer, gene mutation, and biofilm formation [52,82,83,84,85]. The acquired antimicrobial resistance may involve various mechanisms [52]. For example, the efflux pump (AnrAB) in L. monocytogenes has been determined to confer resistance to β-lactam antibiotics (oxacillin, ampicillin, cephalosporins, and others) [52]. Another efflux pump (MdrL) makes L. monocytogenes resistant to cefotaxime [86]. According to Luque-Sastre et al. [48] and Srinivasan et al. [87], only the penicillin-binding protein gene (penA) has been linked with L. monocytogenes resistance to penicillin G.
2.1.6. Resistance to Aminoglycosides
Structurally, all aminoglycosides possess a cyclohexane ring and amino sugars [66]. Members of this class of antibiotics include gentamicin, kanamycin, streptomycin, and neomycin [66]. These antibiotics bind to the bacterial 30S ribosomal subunit, thereby blocking protein synthesis [66]. Aminoglycoside-resistant strains have been reported [9,52,53,57,61,87,88]. These strains normally emerge as a result of obtaining plasmid-borne genes and transposons encoding aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes [89]. The enzymes can be classified as follows: acetyltransferase, adenyltransferase, and phosphotransferase [89]. The gene (aad6) coding for 6-N-streptomycin adenylyltransferase (a streptomycin-modifying class of enzymes) has been detected in L. monocytogenes and L. innocua isolates [48,69]. Apart from aad6, no other aminoglycoside resistance genes have been identified to date in Listeria spp. [48,69].
2.1.7. Resistance to Tetracyclines
The tetracycline family includes naturally occurring antibiotics (tetracycline, chlortetracycline, and others) and semi-synthetic antibiotics (minocycline, doxycycline, etc.) [66]. Similar to aminoglycosides, tetracyclines bind to the bacterial 30S ribosomal subunit. This binding prevents the combination of aminoacyl-tRNA molecules with the A site of the ribosome. This family of antibiotics is a broad-spectrum bacteriostatic class [66]. However, the emergence of tetracycline resistance is the most common phenomenon among Listeria species [48,90]. The species obtain most of their resistance-encoding genes from Enterococcus and Streptococcus species through two types of mobile genetic elements: conjugative plasmids and transposons [48]. Usually, the genes [tet (S) and tet (L)] are transported by plasmids, whereas the tet (M) gene is carried by Tn916 (a conjugative transposon) [48,91]. The other tetracycline resistance-encoding genes found in Listeria spp. are tet (A) and tet (K) [48,90]. The genes tet (A), tet (K) and tet (L) code for proton antiporters that facilitate the efflux mechanism, which confers tetracycline resistance only. Meanwhile, the genes [tet (M) and tet (S)] code for ribosome protection proteins that confer resistance to both tetracycline and minocycline [48,90,91].
2.1.8. Resistance to Trimethoprim
Trimethoprim is a broad-spectrum synthetic antibiotic. It inhibits folic acid production by binding to dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR), an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of dihydrofolic acid (DFA) to tetrahydrofolic acid during folic acid production. Due to its structural similarity to DFA (a DHFR substrate), trimethoprim competes with DFA for binding on the active site of the enzyme; consequently, the folic acid synthesis pathway is stopped or hampered [66].
Even though L. monocytogenes is commonly susceptible to trimethoprim [48], cases of resistance against the antibiotic have been published [57,69,92,93]. Usually, the mechanism of resistance against trimethoprim arises through the synthesis of trimethoprim-resistant DHFR in addition to the susceptible enzyme [90,94]. There are two resistance genes in Listeria that facilitate this synthesis: dfrD and dfrG; these are carried by plasmid pIP823 and transposon Tn6198, respectively [48].
2.1.9. Resistance to Chloramphenicol
Initially, Streptomycess venezuelae produced chloramphenicol. However, the chloramphenicol antibiotic is now chemically synthesized. Chloramphenical inhibits peptide elongation by binding to 23S rRNA of the 50S ribosomal subunit. However, this broad-spectrum antibiotic tends to have severe side-effects (e.g., lowering of bone marrow function, which may lead to complications such as aplastic anemia and a low white blood cell count) [66]. Therefore, this antibiotic is only employed when all other antibiotics fail in potentially fatal cases. In Listeria spp., resistance to chloramphenicol is encoded by cat (type A-8) and floR genes. The cat genes code for type A chloramphenicol acetyltransferases (Cat), which are responsible for enzymatic inactivation via the acetylation of the antibiotic [95]. In L. monocytogenes, the floR gene is linked to the export of florfenicol—a fluorinated derivative of chloramphenicol [87].
2.1.10. Resistance to Macrolides
Macrolide antibiotics include members such as erythromycin, clindamycin, and azithromycin. They are broad-spectrum and normally bacteriostatic antibiotics whose mode of action involves inhibiting protein synthesis by binding to the 23S rRNA of the 50S ribosomal subunit [48,66]. Resistance to macrolide is commonly facilitated by rRNA methylases. These enzymes are encoded by erm genes, specifically, erm (A), erm (B), and erm (C) in Listeria spp. The enzymes modify the target site (23S rRNA) by methylating its adenine base, consequently blocking the antibiotic from binding to the site [48,96,97].
2.2. Drivers of Antimicrobial Resistance
Some of the drivers of antimicrobial resistance include the indiscriminate use of antimicrobials in veterinary medicine for prophylaxis, growth promotion, and disease treatment [1,98]. Furthermore, the treatment of listeriosis using antibiotics in humans results in the selection of resistant L. monocytogenes strains [99]. Therefore, the emergence of multi-drug-resistant strains of L. monocytogenes poses a challenge due to potential treatment failure, limited treatment options, extended stays in medical care facilities and even fatalities [10,60,100]. For these reasons, novel anti-Listerial compounds are required.
2.3. Actinobacteria as Potential Sources of Anti-Listerial Compounds
Actinobacteria are known to be prolific producers of novel secondary metabolites with applications in diverse industries including the pharmaceutical industry [101,102]. The phylum Actinobacteria contains gram-positive bacteria with a high G + C content in general (>50 mol%) except Tropheryma whipplei. These bacteria can be filamentous or non-filamentous, and are found both in terrestrial and aquatic environments [103]. They grow via a combination of tip extension and hyphae branching. Their optimum growth conditions include a mesophilic temperature (ranging between 25 and 30 °C) and a pH between 6 and 9. However, some thermophilic strains have been isolated in high temperatures ranging from 50 to 60 °C, and others can grow in acidic conditions (pH 3.5) [104]. Many actinobacteria are of the order Actinomycetales. Members of this order are called actinomycetes. The suborders of Actinomycetales that show significance in bio-prospecting include Streptomycineae, Micromonospineae, Corynebacterineae, and Streptosporangineae [105].
2.3.1. Streptomycineae
The suborder Streptomycineae has a single family, Streptomycetaceae. Family members are often called streptomycetes and play a pivotal role in medicine by producing medicinally important compounds [105]. Among the streptomycetes, the genus Streptomyces produces the majority of the compounds [106]. It has produced 7600 compounds [107]. However, there may still be more undiscovered bioactive compounds. This is because when Streptomyces coelicolor’s genome was analyzed in 2002, genes coding to produce 20 bioactive compounds were discovered, even though the bacterium is known to only produce four antibiotics. Therefore, the challenge of finding other ways of stimulating the expression of the other genes remains [105]. Nonetheless, about 75% of all the bioactive compounds applied in the medical treatment of humans and animals are from Streptomyces spp. [108].
2.3.2. Micromonosporineae
The suborder Micromonosporineae has a single family, Micromonosporaceae, containing four genera: Actinoplanes, Dactylosporangium, Micromonospora, and Pilimela. Collectively, the genera are often called actinoplanetes. They form an elaborate, highly colored, substrate mycelium that lacks aerial hypha. However, commonly raised above the surface of the substrate mycelium are spore-containing-sporangia. The arrangement and morphology of the spores vary among the genera. For instance, in Actinoplanes and Pilimela, several spores are contained in cylindrical, spherical, or irregular sporangia. Meanwhile, for Dactylosporangium, one to six spores are contained in a finger-like sporangia. Micromonospora usually produce single spores, usually in branched sporophores [105].
Actinoplanetes are found in diverse habitats, including the soil, freshwater and sea. These bacteria are a source of bioactive metabolites. The genus Micromonospora is a prolific producer of antimicrobials, second only to the Streptomyces genus [109]. About 8% of the antibiotics used in medicine are from Micromonospora species [110].
2.3.3. Corynebacterineae
The suborder Corynebacterineae has six families: Nocardiaceae, Gordoniaceae, Mycobacteriaceae, Dietziaceae, Tsukamurellaceae and Corynebacteriaceae [105]. In bioprospection, the family Nocardiaceae has shown significance. For example, the two genera (Nocardia and Rhodococcus) belonging to this family contain species capable of producing bioactive compounds [111,112].
The genera Nocardia and Rhodococcus are largely strict aerobes. They are distributed widely in terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, wherein they form substrate hypha that fragment into coccoid fragments and rods. The bacteria also develop aerial mycelium that may form conidia. Most of the bacterial strains are free-living saprophytes. However, some strains of Nocardia (e.g., N. asteroids) can cause nocardiosis, an opportunistic disease in humans and animals [105].
2.3.4. Streptosporangineae
One of the families of the Streptosporangineae suborder is Nocardiopsaceae [113]. The family contains a type genus, Nocardiopsis [114]. The type species of the genus is Nocardiopsis dassonvillei, and IMRU 509 (DSM 43111, ATCC 23218, JCM 7437) is the type strain [114]. Members of the genus are able to prevail under harsh environmental conditions but are generally found in locales with high salt concentrations [115]. Their survival in such conditions is mediated by secreting different and novel bioactive compounds and extracellular enzymes [115]. Thus, the genus is among the biotechnologically important genera of actinobacteria.
2.4. Marine Environment as a Source of Microbes Harbouring Novel Bioactive Metabolites
In the last two decades, the number of newly approved antibiotics has dwindled by 75% [116]. For example, since the year 2000, only 30 novel antibiotics have been issued globally. Of these 30, 16 were synthetic, 2 were natural products, and 12 were natural product derivatives. Forty percent of the 30 antibiotics were from actinomycetes, either as natural products or their derivatives [117]. One of the factors contributing to the decline is the rediscovery of known bioactive compounds from conventional microbial habitats, such as the terrestrial habitat. Terrestrial actinomycetes have been bio-prospected extensively; as a result, 70% of commercial antibiotics are extracted from them. Therefore, the likelihood of finding novel bioactive compounds from terrestrial actinomycetes has decreased [116,118]. Thus, the search for novel bioactive compounds has switched to actinomycetes occupying unexplored or underexploited habitats, such as the marine environment [103].
The marine microbial habitats include sea water and sand, coastal and deep sea sediments, mangrove sediments, and hydrothermal vents [119,120]. These habitats tend to have complex conditions such as low temperatures, salinity, and high pressures [120,121]. Therefore, marine microorganisms may develop novel metabolites (absent in terrestrial microbes) in order to survive in such conditions. As a result, a variety of unique bioactive compounds have been recovered from marine actinomycetes in recent times [119,122].
3. Anti-Listerial Compounds from Marine Actinobacteria
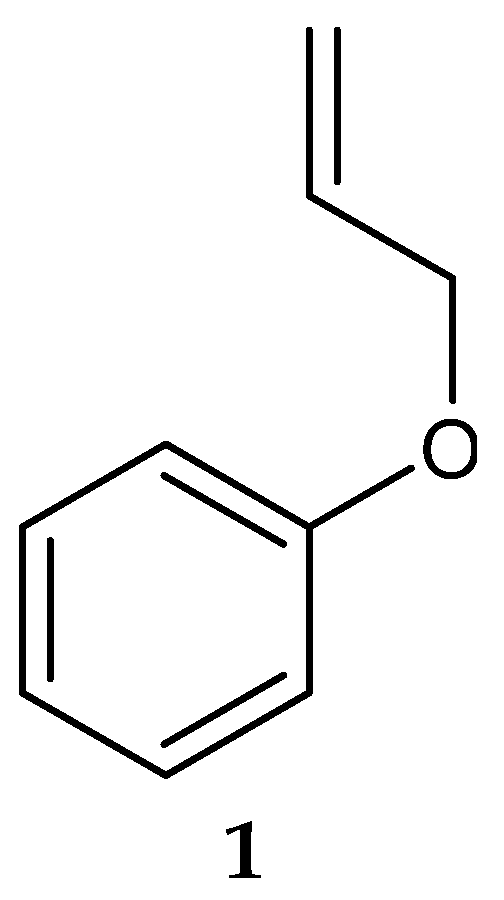
In 2006, Saha et al. [123] isolated a putatively novel Streptomyces MS1/7 from the marine sediments of the Bay of Bengal, India. The actinobacterium produced 2-Allyoxyphenol (1) (Figure 2) (molecular formula: C9H10O2), a synthetic compound obtained as a natural product for the first time by Arumugam et al. [124]. The compound was found to have antimicrobial activity against a panel of 21 bacteria and 3 fungi, with MIC values ranging from 0.2 to 1.75 mg/mL [124]. Specifically, 2-Allyoxyphenol had an MIC value of 0.45 mg/mL against L. monocytogenes MTCC 657, which was determined by the agar dilution method [124].
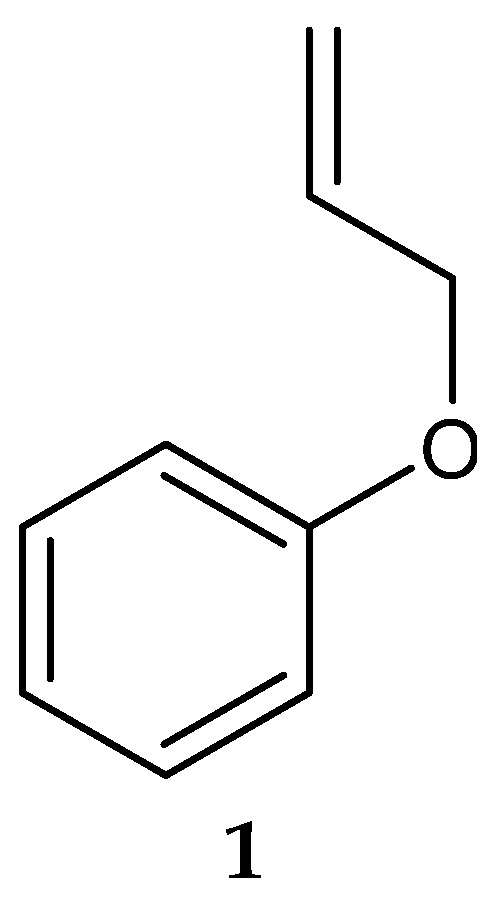
Figure 2.
Structure of 2-Allyoxyphenol (1) [124].
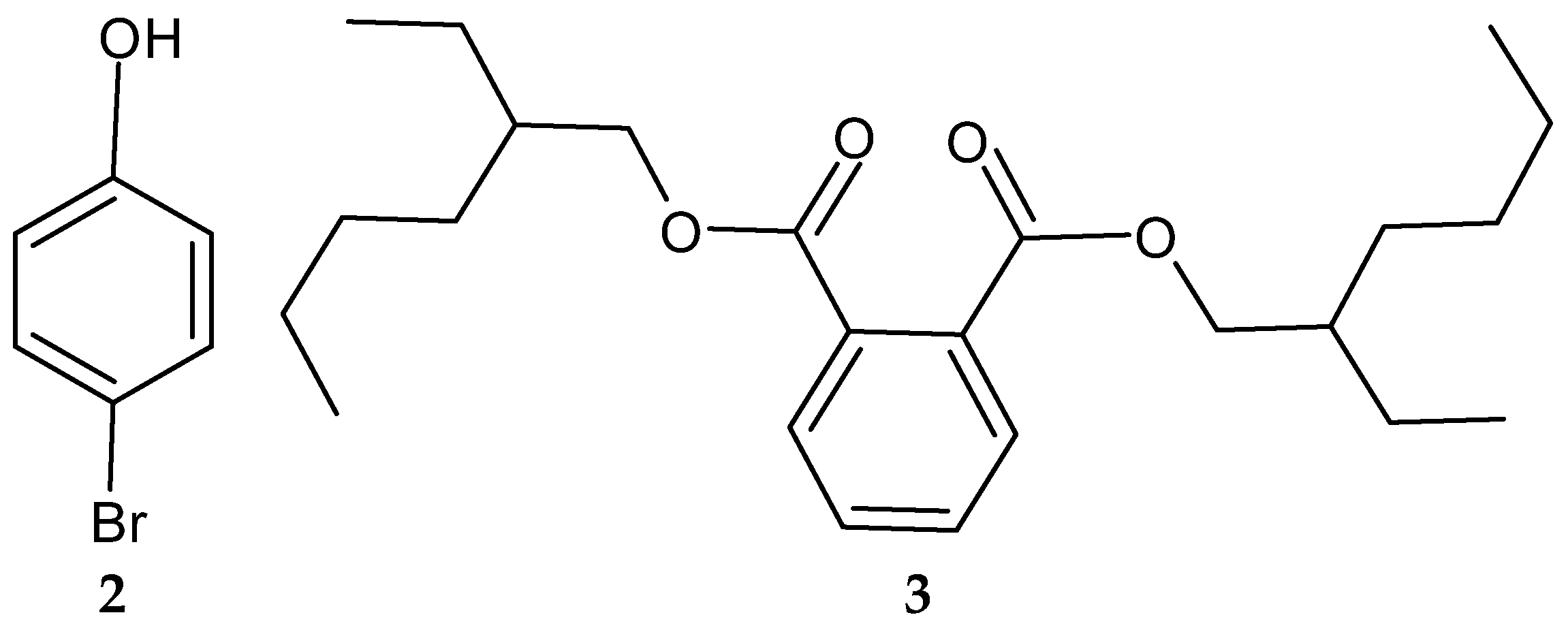
Another study in India reported on the isolation of the rare actinobacterium Nocardiopsis sp. SCA21 from the marine sediment of Havelock Island, the Andaman Islands, and the Nicobar Islands [125]. A bromophenol derivative (4-bromophenol; Figure 2 and Figure 3), and a phthalate ester (Bis (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate; Figure 3, 3) were purified for the first time from the fermentation broth of the genus Nocardiopsis [125]. When tested using the disc diffusion method and the micro-dilution method, respectively, only 4-bromophenol demonstrated activity against L. monocytogenes 13932 (zone of inhibition of 24 ± 0.11 mm and MIC value of 62.5 µg/mL) [125].
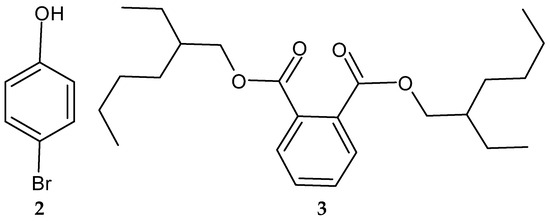
Figure 3.
Structures of compounds 2–3 [125].
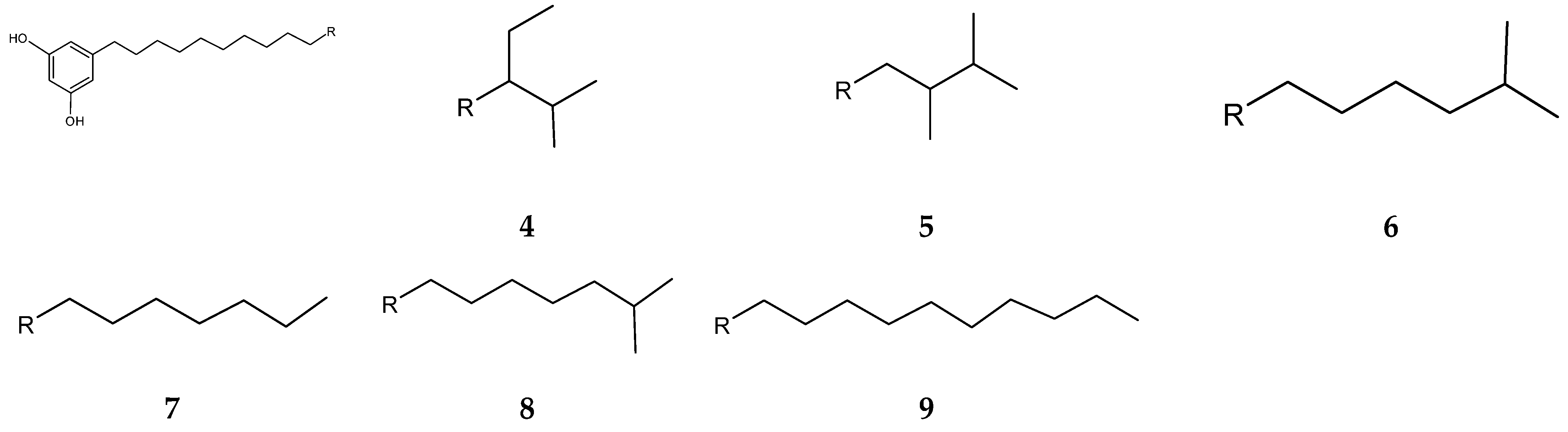
Streptomyces blancoensis 20733 was purified from the marine sediments of San Miguel, Costa Rica, 2020 [126]. Analysis of the bacterium’s extracts led to the isolation of six novel phenolic lipids, adipostatins E–J (4–9) (Figure 4). Adipostatins E–G exhibited antagonistic activity against L. monocytogenes ATCC 19115, with IC50 values of 5.9 µM, 34.2 µM, and 20.3 µM, respectively. Adipostatins H–J showed no activity against the ATCC 19115 strain at the tested concentration [126].
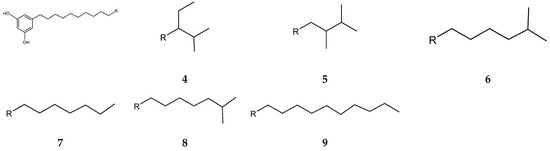
Figure 4.
Structures of adipostatins E–J (4–9) [16,126].
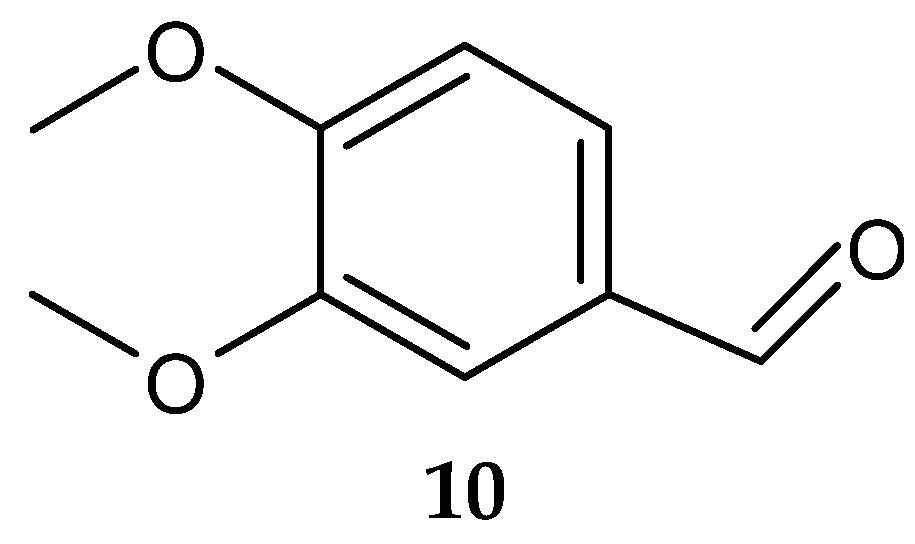
Veratraldehyde (10) (Figure 5) was purified for the first time from the marine actinomycete Streptomyces diastaticus LC360811 (isolated from sediment samples of the Red Sea coast, Egypt) [127]. The compound was active against the tested gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. However, no activity was detected against L. monocytogenes ATCC 35152 [127].
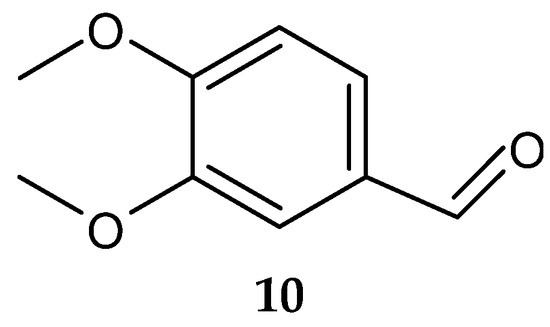
Figure 5.
Structure of veratraldehyde (10) [127].
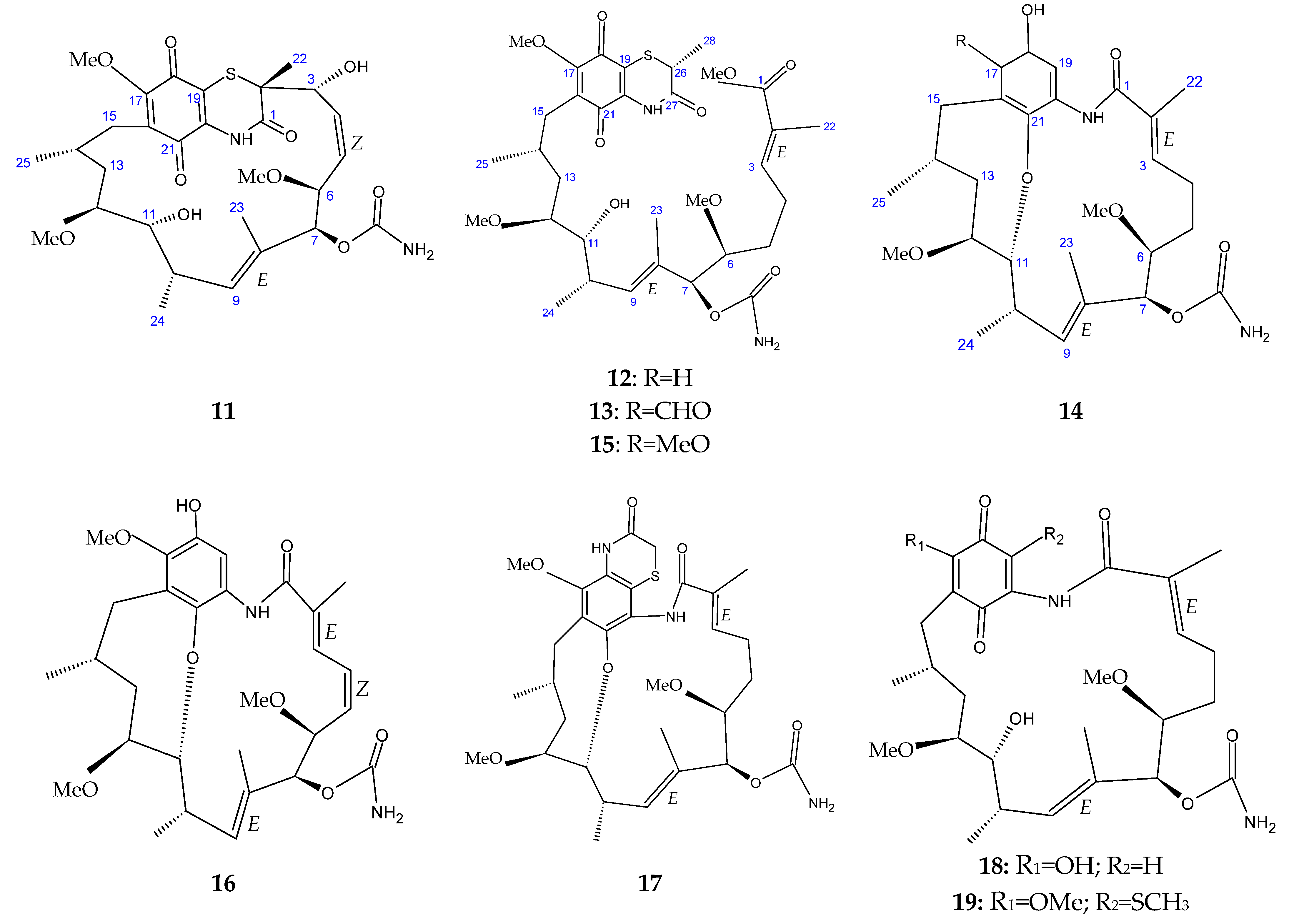
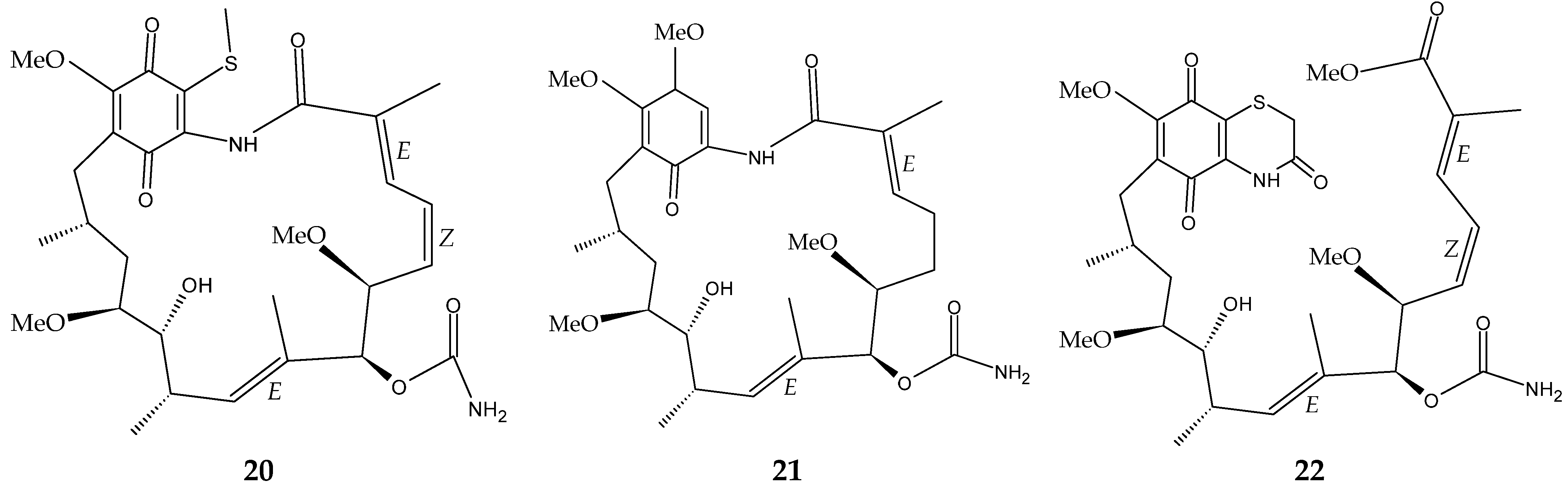
The marine sediment samples collected in July 2021 from Yongzing Island, China, yielded Streptomyces sp. ZYX-F-97 [128]. Four new ansamycin derivatives were then purified from the species’ fermentation (Figure 6) [128]. These are 1,19-epithio-geldanamycin A (11), 17-demethoxylherbimycin H (12), herbimycin M (13), and seco-geldanamycin B (14). Additionally, eight known ansamycin analogues were isolated (Figure 6) [128]: hervimycin H (15), herbimycin I (16), tetracyclic thiazinogeldanamycin (17), 4.5-dihydro-17-O-demethylgeldanamycin (18), 4.5-dihydro-17-S-demethylgeldanamycin (19), 19-S-methylgeldanamycin (20), 18-methylreblastatin (21), and seco-geldanamycin (22). But only compounds 14, 18, and 22 showed remarkable inhibition against L. monocytogenes ATCC 1911, with MIC values of 64 μg/mL, 8 μg/mL, and 16 μg/mL, respectively [128].
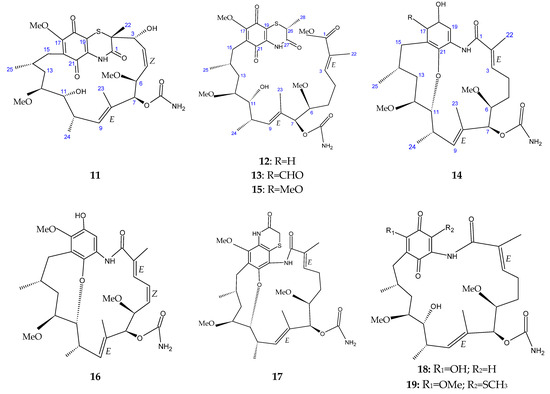
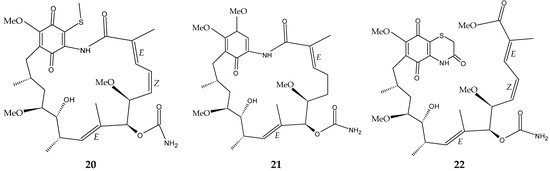
Figure 6.
Structures of ansamycins (11–22) [128].
Another novel antibiotic, a 22-membered macrolide lactam named haneummycin (23) (Figure 7), was purified from Streptomyces sp. KM77-8; this was isolated from marine sediment collected from Tokyo Bay, Japan [129]. The antibiotic was then assayed against Listeria innocua ATCC 33090T and displayed no anti-Listerial activity at the tested concentration [129].
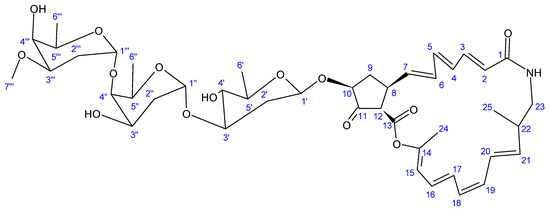
Figure 7.
Structure of haneummycin (23) [129].
In summary, out of the 23 reported compounds, only eight of them possessed anti-Listerial activity. The eight compounds and their wide range of other biological activities are consolidated in Table 2. According to Arumugam et al. [124], the hydroxyl and allyloxy groups of compound 1 were responsible for its antimicrobial and antioxidant activities. Due to the absence of potential carcinogenicity and hemolytic toxicity, the cytotoxicity literature suggests the possible application of compound 1 as a food preservative and oral disinfectant [124].

Table 2.
Anti-Listerial compounds from marine actinobacteria (1990–December 2023).
Compound 2 had potent antibacterial activity against a panel of test clinical pathogens, with an MIC value ranging from 7.81 to 125 μg/mL [125]. The compound also showed remarkable free radical scavenging potential, with an IC50 value of 187.31 μg/mL against 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl radicals and an IC50 value of 102.22 μg/mL against 2,2′-azinobis (3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) radicals [125]. The iron metal chelating activity of compound 2 was less significant, with an IC50 value of >250 μg/mL. Furthermore, compound 2 exhibited remarkable enzyme inhibitory activities against α-glucosidase and α-amylase [125].
Adipostatins exhibited significant antibacterial activity against gram-positive bacteria through the inhibition of co-enzyme A biosynthesis [126]. None of the adipostatins possessed noticeable inhibition against gram-negative microbes (viz., E. coli, Salmonella enterica, and Shigella flexneri). It was suspected that by inhibiting CoA biosynthesis, the adipostatins might also be affecting the synthesis of peptidoglycans and fatty acids. Consequently, the compounds were more potent against gram-positive bacteria [126].
Similarly, the ansamycins (14, 18, 22) were reported to exhibit significant activity against a panel of gram-positive bacteria [128], but the compounds showed no activity against the gram-negative bacteria (E. coli and Pseudomonas aruginosa) [128].
4. Challenges and Opportunities Associated with Antimicrobials from Marine Actinobacteria
Our literature survey from 1990 to December 2023 reveals the scarcity of published assays testing the anti-Listerial capacity of bioactive compounds purified from marine actinobacteria during this period. For example, only one compound (2-Allyoxyphenol (1)) was tested for antibacterial activity against L. monocytogenes out of the 33 reported antibacterial compounds obtained from marine actinomycetes between 2005 and 2010 in a review by Subramani and Aalbersberg [15]. Furthermore, a review article by Schinke et al. [130] shows that the bioactive compounds derived from marine actinobacteria between 2010 and 2015 were not evaluated for anti-Listerial activity. However, it should be noted that the review only examined bioactive substances with MICs of less than or equal to 20 µg/mL [130]. According to Wang et al. [131], out of the 308 compounds derived from marine actinomycetes from 1990 to 2019, none of them were tested for anti-Listerial activity. Nevertheless, it is not apparent whether this review included studies from the entire year, because in the same year (2019), Siddharth and Rai [125] tested two compounds (4-bromophenol, 2, and bis (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate, 3) against L. monocytogenes 13932 that were isolated from Nocardiopsis sp. SCA21. Likewise, from 1992 to 2020, none of the 127 novel halogenated compounds obtained from marine actinomycetes were examined for their anti-Listerial activities [132]. Only Streptomyces blancoensis strain 20733 was examined for the biosynthesis of new anti-Listerial compounds (4–9) out of more than nine marine streptomycete isolates assessed for the production of novel bioactive compounds in 2020 [16]. A literature review (from 2012 to 2022) by Liang et al. [133] shows that around 62 bioactive secondary metabolites were isolated from marine sponge-associated actinomycetes. Interestingly, according to the observed literature, none of the metabolites were examined for their anti-Listerial potential [133]. During these time periods, it appears that the antimicrobial activity assays used were mostly against microbes such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium (VREF), Bacillus subtilis, Candida species, and others [15,130,134]. This is probably because the World Health Organization considers these bacteria to be the most dangerous group on its list of priority pathogens due to their link to multi-drug resistant nosocomial infections [135].
The research focus for novel anti-Listerial substances appears to be natural antimicrobial agents such as lactoperoxidase, lactoferrin, and lysozyme from animal sources, essential oils and herbal extracts from plant sources, and bacteriocin from microbial sources [136,137,138,139]. These chemicals are primarily being researched for their potential use as natural preservatives to prevent food spoilage and contamination, as L. monocytogenes is a major foodborne pathogen [139,140]. These innovative preservatives would aid in the prevention of L. monocytogenes growth in foods, while new anti-Listerial drug leads derived from marine actinobacteria could be developed and used to treat infected individuals. Thus, both research approaches are valuable.
The majority of the published literature is on preliminary screening assays for anti-Listerial compound production by marine actinobacteria that require further analysis to obtain pure compounds (Table 3 and Table 4). For example, researchers [141,142,143,144] only used the cross-streak method to evaluate the anti-Listerial potential of various marine actinobacteria isolated from marine samples collected between 2013 and 2015 (Table 3). Eythorsdottir et al. [145] employed both the cross-streak and agar well diffusion methods to assess the anti-Listerial activity of marine actinobacterial symbionts recovered from shallow-water hydrothermal vents in Northern Iceland (Table 3). During the years 2016 to 2017, different fish were caught from the offshore waters of Ireland, Iceland, and international waters at depths of 1000 m and 850 m [146]. Arthrobactor sp. APC 3897 was then isolated from the skin of the deep-sea fish and tested for antibacterial activity by colony overlay assays [147]. The isolate showed activity against foodborne L. innocua and L. monocytogenes strains [147].
The in vitro anti-Listerial activities of ethyl acetate crude extracts of Streptomyces cyaneofuscatus isolates were determined by the disc diffusion method (Table 4) [148]. The agar well diffusion method was used to investigate the anti-Listerial capacity of ethyl acetate crude extracts of Nocardiopsis alba isolates (Table 4) [149].
The n-butanol crude extract of Streptomyces sp. Sp1 was evaluated for its anti-Listerial activity by the agar well diffusion method (Table 4) [150]. Ngema et al. [85] employed the 96-well microdilution and in silico molecular docking methods to examine the anti-Listerial potential of Nocardiopsis dassonvillei SOD(B)ST2SA2′s crude extract (Table 4). Such preliminary screening assays are a yet-to-be-tapped potential source of new anti-Listerial compounds, provided they are processed further. However, researchers may stop processing these crude extracts if the dereplication process fails to reveal novel compounds from the extracts [151].

Table 3.
Preliminary assays of marine actinobacterial activity against L. monocytogenes (1990–December 2023).
Table 3.
Preliminary assays of marine actinobacterial activity against L. monocytogenes (1990–December 2023).
| Marine Actinomycete Strain | Year of Isolation | Country | Method Used for Antibacterial Activity Assay | Test Strain | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudonocardia carboxydivorans VO36-3 | 2013 | Chile | Cross-streak method | L. monocytogenes 07PF0776 | [141] |
| Salinoactinospora qingdaoensis VN6-2 | |||||
| Microbacterium profundi VP2-3 | |||||
| Arthrobacter phenanthrenivorans VO30-3 | |||||
| Aeromicrobium alkaliterrae V040-3 | |||||
| Gordonia bronchialis VO29-3 | |||||
| Isoptericola halotolerans VP3-3 | |||||
| Streptomyces janthinus VS4-2 | |||||
| Streptomyces albogriseolus VH47-3 | |||||
| Streptomyces sp. H-KF8 | 2013 | Chile | Cross-streak method | L. monocytogenes 07PF0776 | [144] |
| Streptomyces sp. H-KF8 | 2013 | Chile | Cross-streak method | L. monocytogenes 07PF0776 | [143] |
| Rhodococcus H-CA8F | |||||
| Micrococcus H-CD9b | |||||
| Kocuria H-KB6 | |||||
| Curtobacterium H-ED12 | |||||
| Curtobacterium H-BE10 | |||||
| Corynebacterium H-EH3 | |||||
| Brachybacterium H-CG1 | |||||
| Brachybacterium H-CD1 | |||||
| Arthrobacter H-CA8b | |||||
| Actinomycete 111 | 2013 | Iran | Cross-streak method | L. monocytogenes ATCC 1298 | [142] |
| Actinomycete 112 | |||||
| Actinomycete 115 | |||||
| Actinomycete 117 | |||||
| Actinomycete 127 | |||||
| Actinomycete 131 | |||||
| Actinomycete 135 | |||||
| Actinomycete 141 | |||||
| Actinomycete 275 | |||||
| Tsukamurella strandjordii 101-1518 | 2015 | Northern Iceland | Agar diffusion assay and cross-streak method | L. monocytogenes | [145] |

Table 4.
Anti-Listerial crude extracts from various marine actinobacteria (1990–December 2023).
Table 4.
Anti-Listerial crude extracts from various marine actinobacteria (1990–December 2023).
| Marine Actinomycete Strain | Year of Isolation | Country of Isolation | Crude Extract | Pathogen Target | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Streptomyces cyaneofuscatus M-157 | 2013 | Spain | Ethyl acetate extract | L. monocytogenes 72964 * | [148] |
| Streptomyces cyaneofuscatus M-169 | |||||
| Streptomyces cyaneofuscatus M-192 | |||||
| Streptomyces cyaneofuscatus M-207 | |||||
| Streptomyces cyaneofuscatus M-220 | |||||
| Streptomyces cyaneofuscatus M-231 | |||||
| Streptomyces sp. Sp1 | 2018 | Egypt | n-butanol extract | L. monocytogenes 19115 | [150] |
| Nocardiopsis alba PB-1 | 2020 | India | Ethyl acetate extract | L. monocytogenes ATCC 19112 | [149] |
| Nocardiopsis alba PB-3 | |||||
| N. dassonvillei SOD(B)ST2SA2 | 2021 | South Africa | Chloroform extract | L. monocytogenes KGEO161 | [85] |
| L. monocytogenes ILemanAP345 | |||||
| L. monocytogenes ILemanEO299 | |||||
| L. monocytogenes ILemanER317 | |||||
| L. monocytogenes ILestanBR361 | |||||
| L. monocytogenes ILestanBR363 | |||||
| L. monocytogenes ILestanGP395 | |||||
| L. monocytogenes ILestanGP400 | |||||
| L. monocytogenes ATCC 15313 |
* Cephalosporins-resistant L. monocytogenes.
5. Conclusions
Generally, new compounds from marine actinobacteria have rarely been tested for their anti-Listerial potential during the past three decades (1990–December 2023). Many countries have not conducted or published any research on the new anti-Listerial compounds purified from marine actinobacteria during this period. However, Costa Rica, Egypt, Japan, China, and India published data on 23 compounds from marine actinobacteria that were tested for their anti-Listerial potential. Eleven of the compounds (adipostatins E–J, ansamycins [11,12,13,14], and haneummycin) were novel. The other compounds (4-bromophenol and bis (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate) were purified for the first time from the genus Nocardiopsis. Similarily, veratraldehyde was extracted for the first time from a marine actinomycete. Moreover, a synthetic compound (2-Allyoxyphenol) was obtained as a natural product for the first time. Out of the 23 reported compounds, only 2-allyoxyphenol, adipostatins E–G, 4-bromophenol, and ansamycins (14, 18, and 22) were found to possess anti-Listerial activity. Considering the zoonotic nature of L. monocytogenes, the relatively high case fatality rate of listeriosis, the development and spread of antimicrobial resistance, and the unique nature of secondary metabolites from marine actinobacteria compared to their terrestrial counterparts, it is paramount to expand bioprospecting studies of bioactive compounds from marine actinobacteria, particularly from underexplored ocean environments on the African continent.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.M. and S.S.N.; validation, E.M. and S.S.N.; writing—original draft preparation, S.S.N.; writing—review and editing, E.M.; supervision, E.M.; project administration, E.M.; funding acquisition, E.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Red Meat Research and Development Trust South Africa, and Department of Trade, Industry, and Competition grant number THRIP/22/30/11/2017 and E.M. is the recipient and Principal Investigator. S.S.N. acknowledges The Moses Kotane Institute (MKI) Research Fund (2022) and The FoodBev SETA Bursary (2023).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by the University of Zululand’s Research Ethics Committee (UZREC 171110-030 PGD 2021/26).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the University of Zululand for their provision of library resources that were instrumental in the literature research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Matle, I.; Mbatha, K.R.; Lentsoane, O.; Magwedere, K.; Morey, L.; Madoroba, E. Occurrence, serotypes, and characteristics of Listeria monocytogenes in meat and meat products in South Africa between 2014 and 2016. J. Food Saf. 2019, 39, e12629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Noordhout, C.M.; Devleesschauwer, B.; Angulo, F.J.; Verbeke, G.; Haagsma, J.; Kirk, M.; Havelaar, A.; Speybroeck, N. The global burden of listeriosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/listeriosis (accessed on 13 February 2024).
- Smith, A.M.; Tau, N.P.; Smouse, S.L.; Allam, M.; Ismail, A.; Ramalwa, N.R.; Disenyeng, B.; Ngomane, M.; Thomas, J. Outbreak of Listeria monocytogenes in South Africa, 2017–2018: Laboratory activities and experiences associated with whole-genome sequencing analysis of isolates. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2019, 16, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibanda, T.; Ntuli, V.; Neetoo, S.H.; Habib, I.; Njage, P.M.K.; Parry-Hanson Kunadu, A.; Andoh, A.H.; Coorey, R.; Buys, E.M. Listeria monocytogenes at the food–human interface: A review of risk factors influencing transmission and consumer exposure in Africa. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 58, 4114–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaptchouang Tchatchouang, C.-D.; Fri, J.; De Santi, M.; Brandi, G.; Schiavano, G.F.; Amagliani, G.; Ateba, C.N. Listeriosis outbreak in South Africa: A comparative analysis with previously reported cases worldwide. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matle, I.; Mbatha, K.R.; Madoroba, E. A review of Listeria monocytogenes from meat and meat products: Epidemiology, virulence factors, antimicrobial resistance and diagnosis. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2020, 87, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaimat, A.N.; Al-Holy, M.A.; Shahbaz, H.M.; Al-Nabulsi, A.A.; Abu Ghoush, M.H.; Osaili, T.M.; Ayyash, M.M.; Holley, R.A. Emergence of antibiotic resistance in Listeria monocytogenes isolated from food products: A comprehensive review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 1277–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanes, R.M.; Huang, Z. Investigation of antimicrobial resistance genes in Listeria monocytogenes from 2010 through to 2021. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Antimicrobial Resistance. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antimicrobial-resistance#:~:text=As%20a%20result%20of%20drug,severe%20illness%2C%20disability%20and%20death (accessed on 11 March 2024).
- Paul, S.I.; Majumdar, B.C.; Ehsan, R.; Hasan, M.; Baidya, A.; Bakky, M.A.H. Bioprospecting potential of marine microbial natural bioactive compounds. Appl. Biotechnol. Rep. 2021, 8, 96–108. [Google Scholar]
- Van Bergeijk, D.A.; Terlouw, B.R.; Medema, M.H.; van Wezel, G.P. Ecology and genomics of actinobacteria: New concepts for natural product discovery. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 546–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girão, M.; Ribeiro, I.; Carvalho, M.d.F. Actinobacteria from marine environments: A unique source of natural products. In Natural Products from Actinomycetes: Diversity, Ecology and Drug Discovery; Rai, R.V., Bai, J.A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 1–45. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, G.; Suthindhiran, K. Diversity and biotechnological potential of marine actinomycetes from India. Indian J. Microbiol. 2022, 62, 475–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramani, R.; Aalbersberg, W. Marine actinomycetes: An ongoing source of novel bioactive metabolites. Microbiol. Res. 2012, 167, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacey, H.J.; Rutledge, P.J. Recently discovered secondary metabolites from Streptomyces species. Molecules 2022, 27, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Listeria (Listeriosis). Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/listeria/faq.html#:~:text=Yes.,we%20call%20the%20infection%20invasive (accessed on 13 February 2023).
- Vázquez-Boland, J.A.; Kuhn, M.; Berche, P.; Chakraborty, T.; Domínguez-Bernal, G.; Goebel, W.; González-Zorn, B.; Wehland, J.; Kreft, J. Listeria pathogenesis and molecular virulence determinants. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2001, 14, 584–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osek, J.; Wieczorek, K. Listeria monocytogenes—How this pathogen uses its virulence mechanisms to infect the hosts. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos Cela, M.; Medina Martínez, A.J.; Vera Martín, I. Infection of Listeria monocytogenes Associated to the Central Nervous System: Cell Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Risk Factors; Archivos de Medicina Universitaria: Granada, Spain, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Donovan, S. Listeriosis: A rare but deadly disease. Clin. Microbiol. Newsl. 2015, 37, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tao, X.; Liu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, X. An update review on Listeria infection in pregnancy. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 1967–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson-Chen, C. Neurologic infections in pregnancy. In Neurological Diseases and Pregnancy: A Coordinated CARE model for Best Management; Ciafaloni, E., Bushnell, C., Thornburg, L.L., Ciafaloni, E., Thornburg, L.L., Bushnell, C.D., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 95–104. [Google Scholar]
- Farber, J.M.; Peterkin, P.I.; Carter, A.O.; Varughese, P.V.; Ashton, F.E.; Ewan, E.P. Neonatal listeriosis due to cross-infection confirmed by isoenzyme typing and DNA fingerprinting. J. Infect. Dis. 1991, 163, 927–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesini, B.L. Neonatal Listeriosis. Available online: https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/pediatrics/infections-in-neonates/neonatal-listeriosis (accessed on 13 February 2024).
- Schlech III, W.F.; Lavigne, P.M.; Bortolussi, R.A.; Allen, A.C.; Haldane, E.V.; Wort, A.J.; Hightower, A.W.; Johnson, S.E.; King, S.H.; Nicholls, E.S. Epidemic listeriosis–evidence for transmission by food. N. Engl. J. Med. 1983, 308, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, D.W.; Cochi, S.L.; MacDonald, K.L.; Brondum, J.; Hayes, P.S.; Plikaytis, B.D.; Holmes, M.B.; Audurier, A.; Broome, C.V.; Reingold, A.L. Pasteurized milk as a vehicle of infection in an outbreak of listeriosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1985, 312, 404–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büla, C.J.; Bille, J.; Glauser, M.P. An epidemic of food-borne listeriosis in western Switzerland: Description of 57 cases involving adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1995, 20, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadhav, S. Detection, Subtyping and Control of Listeria monocytogenes in Food Processing Environments; Swinburne University of Technology: Hawthorn, VIC, Australia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan, R.L.; Gorris, L.G.; Hayman, M.M.; Jackson, T.C.; Whiting, R.C. A review of Listeria monocytogenes: An update on outbreaks, virulence, dose-response, ecology, and risk assessments. Food Control 2017, 75, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warmate, D.; Onarinde, B.A. Food safety incidents in the red meat industry: A review of foodborne disease outbreaks linked to the consumption of red meat and its products, 1991 to 2021. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 398, 110240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Listeria (Listeriosis)–Listeria Outbreaks. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/listeria/outbreaks/index.html (accessed on 14 February 2024).
- Zhang, Y. Antimicrobial Resistance of Listeria monocytogenes and Enterococcus faecium from Food and Animal Sources; University of Maryland: College Park, MD, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kananub, S.; Lertsakkongkul, P.; Aryatawong, P.; Horhirunkhajohn, W.; Pinniam, N.; Krajanglikit, P.; Sonthong, K.; Kasemsuwan, S. Listeria contamination in milk-processing chain and proficiency in Listeria monocytogenes decontamination of small-scale milk retailers. J. Food Qual. 2024, 2024, 6263938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.; Govender, N.; McCarthy, K.M.; Erasmus, L.K.; Doyle, T.J.; Allam, M.; Ismail, A.; Ramalwa, N.; Sekwadi, P.; Ntshoe, G.; et al. Outbreak of listeriosis in South Africa associated with processed meat. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 632–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mead, P.S.; Dunne, E.F.; Graves, L.; Wiedmann, M.; Patrick, M.; Hunter, S.; Salehi, E.; Mostashari, F.; Craig, A.; Mshar, P.; et al. Nationwide outbreak of listeriosis due to contaminated meat. Epidemiol. Infect. 2006, 134, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichler, J.; Much, P.; Kasper, S.; Fretz, R.; Auer, B.; Kathan, J.; Mann, M.; Huhulescu, S.; Ruppitsch, W.; Pietzka, A. An outbreak of febrile gastroenteritis associated with jellied pork contaminated with Listeria monocytogenes. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2009, 121, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, B.; Larsson, J.T.; Lisby, M.; Müller, L.; Madsen, S.B.; Engberg, J.; Bangsborg, J.; Ethelberg, S.; Kemp, M. Outbreak of listeriosis caused by infected beef meat from a meals-on-wheels delivery in Denmark 2009. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 17, 50–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awofisayo-Okuyelu, A.; Arunachalam, N.; Dallman, T.; Grant, K.; Aird, H.; McLauchlin, J.; Painset, A.; Amar, C. An outbreak of human listeriosis in England between 2010 and 2012 associated with the consumption of pork pies. J. Food Prot. 2016, 79, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, L.; Dupont, P.Y.; Wilson, M.; Rohleder, M.; Gilpin, B. An outbreak of multiple genotypes of Listeria monocytogenes in New Zealand linked to contaminated ready-to-eat meats—A retrospective analysis using whole-genome sequencing. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okpo, E.; Leith, J.; Smith-Palmer, A.; Bell, J.; Parks, D.; Browning, F.; Byers, L.; Corrigan, H.; Webster, D.; Karcher, A.M.; et al. An outbreak of an unusual strain of Listeria monocytogenes infection in North-East Scotland. J. Infect. Public Health 2015, 8, 612–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahl, V.; Sundqvist, L.; Hedenström, I.; Löfdahl, M.; Alm, E.; Ringberg, H.; Lindblad, M.; Wallensten, A.; Thisted Lambertz, S.; Jernberg, C. A nationwide outbreak of listeriosis associated with cold-cuts, Sweden 2013–2014. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2017, 7, 1324232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachmann, R.; Halbedel, S.; Adler, M.; Becker, N.; Allerberger, F.; Holzer, A.; Boone, I.; Falkenhorst, G.; Kleta, S.; Al Dahouk, S. Nationwide outbreak of invasive listeriosis associated with consumption of meat products in health care facilities, Germany, 2014–2019. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 1035.e1–1035.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duranti, A.; Sabbatucci, M.; Blasi, G.; Acciari, V.A.; Ancora, M.; Bella, A.; Busani, L.; Centorame, P.; Cammà, C.; Conti, F. A severe outbreak of listeriosis in central Italy with a rare pulsotype associated with processed pork products. J. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 1351–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurella, C.; Gallina, S.; Ru, G.; Adriano, D.; Bellio, A.; Bianchi, D.M.; Chiavacci, L.; Crescio, M.I.; Croce, M.; D’Errico, V.; et al. Outbreak of febrile gastroenteritis caused by Listeria monocytogenes 1/2a in sliced cold beef ham, Italy, May 2016. Eurosurveillance 2018, 23, 17-00155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Althaus, D.; Jermini, M.; Giannini, P.; Martinetti, G.; Reinholz, D.; Nüesch-Inderbinen, M.; Lehner, A.; Stephan, R. Local outbreak of Listeria monocytogenes serotype 4b sequence type 6 due to contaminated meat pâté. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2017, 14, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control; European Food Safety Authority. Rapid Outbreak Assessment: Multi-Country Outbreak of Listeria monocytogenes Sequence Type 6 Infections Linked to Ready-to-Eat Meat Products. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/rapid-outbreak-assessment-multi-country-outbreak-listeria-monocytogenes-sequence (accessed on 11 February 2024).
- Luque-Sastre, L.; Arroyo, C.; Fox, E.M.; McMahon, B.J.; Bai, L.; Li, F.; Fanning, S. Antimicrobial resistance in Listeria species. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6, 237–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarr, M.; Alou, M.T.; Padane, A.; Diouf, F.S.; Beye, M.; Sokhna, C.; Fenollar, F.; Mboup, S.; Raoult, D.; Million, M. A review of the literature of Listeria monocytogenes in Africa highlights breast milk as an overlooked human source. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1213953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hof, H.; Nichterlein, T.; Kretschmar, M. Management of listeriosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1997, 10, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamont, R.F.; Sobel, J.; Mazaki-Tovi, S.; Kusanovic, J.P.; Vaisbuch, E.; Kim, S.K.; Uldbjerg, N.; Romero, R. Listeriosis in human pregnancy: A systematic review. J. Perinat. Med. 2011, 39, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keet, R. Categorization of Listeria monocytogenes from Food, Environmental, and Clinical Origin in the Western Cape (South Africa); Stellenbosch University: Western Cape, South Africa, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Keet, R.; Rip, D. Listeria monocytogenes isolates from Western Cape, South Africa exhibit resistance to multiple antibiotics and contradicts certain global resistance patterns. AIMS Microbiol. 2021, 7, 40–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janakiraman, V. Listeriosis in pregnancy: Diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Rev. Obstet. Gynecol. 2008, 1, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dos Reis, J.O.; Vieira, B.S.; Cunha Neto, A.; Castro, V.S.; Figueiredo, E.E.S. Antimicrobial resistance of Listeria monocytogenes from animal foods to first- and second-line drugs in the treatment of listeriosis from 2008 to 2021: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2022, 2022, 1351983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishihara, Y.; Akazawa, K. Treatment of Listeria monocytogenes bacteremia with oral levofloxacin in an immunocompromised patient. IDCases 2023, 31, e01680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayode, A.J.; Okoh, A.I. Antibiotic resistance profile of Listeria monocytogenes recovered from ready-to-eat foods surveyed in South Africa. J. Food Prot. 2022, 85, 1807–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Rocha, L.S.; Gunathilaka, G.U.; Zhang, Y. Antimicrobial-resistant Listeria species from retail meat in metro Detroit. J. Food Prot. 2012, 75, 2136–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosnowski, M.; Lachtara, B.; Wieczorek, K.; Osek, J. Antimicrobial resistance and genotypic characteristics of Listeria monocytogenes isolated from food in Poland. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 289, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, M.E.; Abd El-Hamid, M.I.; El-Gedawy, A.; Bendary, M.M.; RM, E.L.; Alhomrani, M.; Alamri, A.S.; Alghamdi, S.A.; Arnout, M.; Binjawhar, D.N.; et al. New insights into Listeria monocytogenes antimicrobial resistance, virulence attributes and their prospective correlation. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, M.; Fraccalvieri, R.; Pasquali, F.; Santagada, G.; Latorre, L.M.; Difato, L.M.; Miccolupo, A.; Normanno, G.; Parisi, A. Antimicrobial susceptibility and multilocus sequence typing of Listeria monocytogenes isolated over 11 years from food, humans, and the environment in Italy. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2020, 17, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailu, W.; Helmy, Y.A.; Carney-Knisely, G.; Kauffman, M.; Fraga, D.; Rajashekara, G. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance profiles of foodborne pathogens isolated from dairy cattle and poultry manure amended farms in Northeastern Ohio, the United States. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachtara, B.; Wieczorek, K.; Osek, J. Antimicrobial resistance of Listeria monocytogenes serogroups IIa and IVb from food and food-production environments in Poland. J. Vet. Res. 2023, 67, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poyart-Salmeron, C.; Carlier, C.; Trieu-Cuot, P.; Courtieu, A.L.; Courvalin, P. Transferable plasmid-mediated antibiotic resistance in Listeria monocytogenes. Lancet 1990, 335, 1422–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charpentier, E.; Courvalin, P. Antibiotic resistance in Listeria spp. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1999, 43, 2103–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willey, J.M.; Sherwood, L.M.; Woolverton, C.J. Prescott’s Microbiology, 8th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 832–838. [Google Scholar]
- Millanao, A.R.; Mora, A.Y.; Villagra, N.A.; Bucarey, S.A.; Hidalgo, A.A. Biological effects of quinolones: A family of broad-spectrum antimicrobial agents. Molecules 2021, 26, 7153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyon, S.A.; Berrang, M.E.; Fedorka-Cray, P.J.; Fletcher, D.L.; Meinersmann, R.J. Antimicrobial resistance of Listeria monocytogenes isolated from a poultry further processing plant. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2008, 5, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morvan, A.; Moubareck, C.; Leclercq, A.; Hervé-Bazin, M.; Bremont, S.; Lecuit, M.; Courvalin, P.; Le Monnier, A. Antimicrobial resistance of Listeria monocytogenes strains isolated from humans in France. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 2728–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakaria, A.I.; Sabala, R.F. Potential public health hazards related to consumption of poultry contaminated with antibiotic resistant Listeria monocytogenes in Egypt. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, K.L.; Arnold, C.; Threlfall, E.J. Rapid detection of gyrA and parC mutations in quinolone-resistant Salmonella enterica using Pyrosequencing® technology. J. Microbiol. Methods 2007, 68, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata, M.; Baquero, F.; Perez-Diaz, J. A multidrug efflux transporter in Listeria monocytogenes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2000, 187, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godreuil, S.; Galimand, M.; Gerbaud, G.; Jacquet, C.; Courvalin, P. Efflux pump Lde is associated with fluoroquinolone resistance in Listeria monocytogenes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 704–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verraes, C.; Van Boxstael, S.; Van Meervenne, E.; Van Coillie, E.; Butaye, P.; Catry, B.; De Schaetzen, M.-A.; Van Huffel, X.; Imberechts, H.; Dierick, K. Antimicrobial resistance in the food chain: A review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 2643–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerin, F.; Galimand, M.; Tuambilangana, F.; Courvalin, P.; Cattoir, V. Overexpression of the novel MATE fluoroquinolone efflux pump FepA in Listeria monocytogenes is driven by inactivation of its local repressor FepR. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courvalin, P. Antimicrobial drug resistance: “prediction is very difficult, especially about the future”. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cernicchi, G.; Felicetti, T.; Sabatini, S. Microbial efflux pump inhibitors: A journey around quinoline and indole derivatives. Molecules 2021, 26, 6996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troxler, R.; Von Graevenitz, A.; Funke, G.; Wiedemann, B.; Stock, I. Natural antibiotic susceptibility of Listeria species: L. grayi, L. innocua, L. ivanovii, L. monocytogenes, L. seeligeri and L. welshimeri strains. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2000, 6, 525–535. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, J.; Muraoka, A.; Bedenbaugh, M.; Childress, B.; Pernot, L.; Wiencek, M.; Peterson, Y.K. The chemical relationship among beta-lactam antibiotics and potential impacts on reactivity and decomposition. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 807955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krawczyk-Balska, A.; Markiewicz, Z. The intrinsic cephalosporin resistome of Listeria monocytogenes in the context of stress response, gene regulation, pathogenesis and therapeutics. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 120, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpundu, P.; Muma, J.B.; Mukubesa, A.N.; Kainga, H.; Mudenda, S.; Bumbangi, F.N.; Muleya, W.; Katemangwe, P.; Munyeme, M. Antibiotic resistance patterns of Listeria species isolated from broiler abattoirs in Lusaka, Zambia. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Wintersdorff, C.J.; Penders, J.; Van Niekerk, J.M.; Mills, N.D.; Majumder, S.; Van Alphen, L.B.; Savelkoul, P.H.; Wolffs, P.F. Dissemination of antimicrobial resistance in microbial ecosystems through horizontal gene transfer. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiśniewski, P.; Zakrzewski, A.J.; Zadernowska, A.; Chajęcka-Wierzchowska, W. Antimicrobial resistance and virulence characterization of Listeria monocytogenes strains isolated from food and food processing environments. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelis, C.; Grohmann, E. Horizontal gene transfer of antibiotic resistance genes in biofilms. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngema, S.S.; Khumalo, S.H.; Ojo, M.C.; Pooe, O.J.; Malilehe, T.S.; Basson, A.K.; Madoroba, E. Evaluation of antimicrobial activity by marine Nocardiopsis dassonvillei against foodborne Listeria monocytogenes and Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, K.J.; Wałecka-Zacharska, E.; Chen, J.C.; Katarzyna, K.-P.; Devlieghere, F.; Van Meervenne, E.; Osek, J.; Wieczorek, K.; Bania, J. Listeria monocytogenes–an examination of food chain factors potentially contributing to antimicrobial resistance. Food Microbiol. 2016, 54, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, V.; Nam, H.; Nguyen, L.; Tamilselvam, B.; Murinda, S.; Oliver, S. Prevalence of antimicrobial resistance genes in Listeria monocytogenes isolated from dairy farms. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2005, 2, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, S.O.; Hussien, A.A.; Youseef, A.G.; Younis, W.K.; Mubarak, A.G. Prevalence, antibiotic resistance, and phylogenetic analysis of Listeria monocytogenes isolated from various sources in Egypt: Fish, vegetables, and humans. Iraqi J. Vet. Sci. 2024, 38, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, K.; Rather, P.; Hare, R.; Miller, G. Molecular genetics of aminoglycoside resistance genes and familial relationships of the aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes. Microbiol. Rev. 1993, 57, 138–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moura, A.; Leclercq, A.; Vales, G.; Tessaud-Rita, N.; Bracq-Dieye, H.; Thouvenot, P.; Madec, Y.; Charlier, C.; Lecuit, M. Phenotypic and genotypic antimicrobial resistance of Listeria monocytogenes: An observational study in France. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2024, 37, 100800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lancaster, H.; Roberts, A.P.; Bedi, R.; Wilson, M.; Mullany, P. Characterization of Tn 916 S, a Tn 916-like element containing the tetracycline resistance determinant tet(S). J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 4395–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charpentier, E.; Courvalin, P. Emergence of the trimethoprim resistance gene dfrD in Listeria monocytogenes BM4293. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1997, 41, 1134–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayode, A.J.; Okoh, A.I. Antimicrobial-resistant Listeria monocytogenes in ready-to-eat foods: Implications for food safety and risk assessment. Foods 2023, 12, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huovinen, P.; Sundström, L.; Swedberg, G.; Sköld, O. Trimethoprim and sulfonamide resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1995, 39, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, S.; Kehrenberg, C.; Doublet, B.; Cloeckaert, A. Molecular basis of bacterial resistance to chloramphenicol and florfenicol. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 28, 519–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, M.C.; Facinelli, B.; Giovanetti, E.; Varaldo, P.E. Transferable erythromycin resistance in Listeria spp. isolated from food. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 269–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granier, S.A.; Moubareck, C.; Colaneri, C.; Lemire, A.; Roussel, S.; Dao, T.-T.; Courvalin, P.; Brisabois, A. Antimicrobial resistance of Listeria monocytogenes isolates from food and the environment in France over a 10-year period. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 2788–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, M.P.; Loneragan, G.H.; Scott, H.M.; Singer, R.S. Antimicrobial resistance: Challenges and perspectives. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2013, 12, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostamian, M.; Kooti, S.; Mohammadi, B.; Salimi, Y.; Akya, A. A systematic review and meta-analysis of Listeria monocytogenes isolated from human and non-human sources: The antibiotic susceptibility aspect. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2022, 102, 115634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manyi-Loh, C.E.; Okoh, A.I.; Lues, R. Occurrence and multidrug resistance in strains of Listeria monocytogenes recovered from the anaerobic co-digestion sludge contained in a single stage steel biodigester: Implications for antimicrobial stewardship. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, J.W.-F.; Letchumanan, V.; Tan, L.T.-H.; Ser, H.-L.; Goh, B.-H.; Lee, L.-H. The rising of “modern actinobacteria” era. Prog. Microbes Mol. Biol. 2020, 3, a0000064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, M.L.; Tan, L.T.; Letchumanan, V.; He, Y.W.; Fang, C.M.; Chan, K.G.; Law, J.W.; Lee, L.H. The extremophilic actinobacteria: From microbes to medicine. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, M.M.; Bahamdain, L.A.; Aba, S.A. Unexplored extreme habitats as sources of novel and rare actinomycetes with enzyme and antimicrobial activities. J. Pharm. Biol. Sci. 2019, 14, 45–54. [Google Scholar]
- Barka, E.A.; Vatsa, P.; Sanchez, L.; Gaveau-Vaillant, N.; Jacquard, C.; Klenk, H.-P.; Clément, C.; Ouhdouch, Y.; van Wezel, G.P. Taxonomy, physiology, and natural products of Actinobacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willey, J.M.; Sandman, K.M.; Wood, D.H. Prescott’s Microbiology, 11th ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 538–545. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Liu, S.; Lu, Q.; Zheng, H.; Osterman, I.A.; Lukyanov, D.A.; Sergiev, P.V.; Dontsova, O.A.; Liu, S.; Ye, J. Studies on antibacterial activity and diversity of cultivable actinobacteria isolated from mangrove soil in Futian and Maoweihai of China. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 3476567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Razek, A.S.; El-Naggar, M.E.; Allam, A.; Morsy, O.M.; Othman, S.I. Microbial natural products in drug discovery. Processes 2020, 8, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacios-Michelena, S.; Aguilar González, C.N.; Alvarez-Perez, O.B.; Rodriguez-Herrera, R.; Chávez-González, M.; Arredondo Valdés, R.; Ascacio Valdés, J.A.; Govea Salas, M.; Ilyina, A. Application of Streptomyces antimicrobial compounds for the control of phytopathogens. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 696518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hifnawy, M.S.; Fouda, M.M.; Sayed, A.M.; Mohammed, R.; Hassan, H.M.; AbouZid, S.F.; Rateb, M.E.; Keller, A.; Adamek, M.; Ziemert, N.; et al. The genus Micromonospora as a model microorganism for bioactive natural product discovery. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 20939–20959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arifuzzaman, M.; Khatun, M.; Rahman, H. Isolation and screening of actinomycetes from Sundarbans soil for antibacterial activity. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 4615–4619. [Google Scholar]
- El-sersy, N.A.; Abou-Elela, G.M. Antagonistic effect of marine Nocardia brasiliensis against the fish pathogen Vibrio damsela: Application of Piackett-Burman experimental design to evaluate factors affecting the production of the antibacterial agent. Int. J. Oceans Oceanogr. 2006, 1, 141–150. [Google Scholar]
- Naragani, K.; Munaganti, R.K.; Mangamuri, U.K.; Vijayalakshmi, M. Optimization of culture conditions for enhanced antimicrobial activity of Rhodococcus erythropolis VLK-12 isolated from South Coast of Andhra Pradesh, India. Br. Microbiol. Res. J. 2014, 4, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stackebrandt, E.; Rainey, F.A.; Ward-Rainey, N.L. Proposal for a new hierarchic classification system, actinobacteria classis nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1997, 47, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhairamkar, S.; Kadam, P.; Anjulal, H.; Joshi, A.; Chaudhari, R.; Bagul, D.; Javdekar, V.; Zinjarde, S. Comprehensive updates on the biological features and metabolic potential of the versatile extremophilic actinomycete Nocardiopsis dassonvillei. Res. Microbiol. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennur, T.; Kumar, A.R.; Zinjarde, S.; Javdekar, V. Nocardiopsis species: Incidence, ecological roles and adaptations. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 174, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.M.; Siddiqui, R.; Khan, N.A. Antimicrobial discovery from natural and unusual sources. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2018, 70, 1287–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramani, R.; Sipkema, D. Marine rare actinomycetes: A promising source of structurally diverse and unique novel natural products. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohseni, M.; Norouzi, H.; Hamedi, J.; Roohi, A. Screening of antibacterial producing actinomycetes from sediments of the Caspian Sea. Int. J. Mol. Cell. Med. 2013, 2, 64. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kamjam, M.; Sivalingam, P.; Deng, Z.; Hong, K. Deep sea actinomycetes and their secondary metabolites. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaradoddi, J.S.; Kontro, M.H.; Ganachari, S.V.; Banapurmath, N.R.; Oli, A.; Katti, A.S.; Sulochana, M. Actinobacteria in marine environments. In Actinobacteria: Ecology, Diversity, Classification and Extensive Applications; Yaradoddi, J.S., Kantro, M.H., Ganachari, S.V., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 21–38. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Xi, L.; Ruan, J.; Huang, Y. Microbacterium marinum sp. nov., isolated from deep-sea water. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 35, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2023, 40, 275–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, M.; Jaisankar, P.; Das, S.; Sarkar, K.K.; Roy, S.; Besra, S.E.; Vedasiromani, J.R.; Ghosh, D.; Sana, B.; Mukherjee, J. Production and purification of a bioactive substance inhibiting multiple drug resistant bacteria and human leukemia cells from a salt-tolerant marine actinobacterium sp. isolated from the Bay of Bengal. Biotechnol. Lett. 2006, 28, 1083–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, M.; Mitra, A.; Jaisankar, P.; Dasgupta, S.; Sen, T.; Gachhui, R.; Kumar Mukhopadhyay, U.; Mukherjee, J. Isolation of an unusual metabolite 2-allyloxyphenol from a marine actinobacterium, its biological activities and applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 86, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddharth, S.; Rai, V.R. Isolation and characterization of bioactive compounds with antibacterial, antioxidant and enzyme inhibitory activities from marine-derived rare actinobacteria, Nocardiopsis sp. SCA21. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 137, 103775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Rodríguez, L.; Schultz, P.J.; Tamayo-Castillo, G.; Dotson, G.D.; Sherman, D.H.; Tripathi, A. Adipostatins E–J, new potent antimicrobials identified as inhibitors of coenzyme-A biosynthesis. Tetrahedron Lett. 2020, 61, 151469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Naggar, M.Y.; Barakat, K.M.; Aly-Eldeen, M.A.; Ghoneim, H.B.; Hamdan, A.M. Veratraldehyde as a food additive produced by the marine isolate Streptomyces diastaticus LC360811. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish 2021, 25, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, K.-X.; Xie, Q.-Y.; Ma, Q.-Y.; Yang, L.; Dai, H.-F.; Zhao, Y.-X.; Hao, Y.-E. Diverse ansamycin derivatives from the marine-derived Streptomyces sp. ZYX-F-97 and their antibacterial activities. Fitoterapia 2024, 173, 105814. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Uemura, M.; Kobayashi, K.; Sato, N.; Nagai, K.; Seki, R.; Kamio, M.; Fukuda, T.; Tsubouchi, T.; Tomoda, H.; Ohshiro, T.; et al. Haneummycin, a new 22-membered macrolide lactam antibiotic, produced by marine-derived Streptomyces sp. KM77-8. J. Antibiot. 2023, 76, 650–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schinke, C.; Martins, T.; Queiroz, S.C.; Melo, I.S.; Reyes, F.G. Antibacterial compounds from marine bacteria, 2010–2015. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1215–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Lu, Y.; Cao, S. Antimicrobial compounds from marine actinomycetes. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2020, 43, 677–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Du, W.; Lu, H.; Lan, J.; Liang, K.; Cao, S. A review: Halogenated compounds from marine Actinomycetes. Molecules 2021, 26, 2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; She, J.; Fu, J.; Wang, J.; Ye, Y.; Yang, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Tao, H. Advances in natural products from the marine-sponge-associated microorganisms with antimicrobial activity in the last decade. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, F.; Pinto, E.; Kijjoa, A.; Pinto, M.; Sousa, E. Targeting antimicrobial drug resistance with marine natural products. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 56, 106005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Prioritization of Pathogens to Guide Discovery, Research and Development of New Antibiotics for Drug-Resistant Bacterial Infections, Including Tuberculosis. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-EMP-IAU-2017.12 (accessed on 16 August 2023).
- Molinos, A.C.; Abriouel, H.; López, R.L.; Omar, N.B.; Valdivia, E.; Gálvez, A. Enhanced bactericidal activity of enterocin AS-48 in combination with essential oils, natural bioactive compounds and chemical preservatives against Listeria monocytogenes in ready-to-eat salad. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 2216–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, B.; Rodríguez, A.; Suárez, E. Antimicrobial peptides produced by bacteria: The bacteriocins. In New Weapons to Control Bacterial Growth; Villa, T.G., Vinas, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 15–38. [Google Scholar]
- Batiha, G.E.-S.; Hussein, D.E.; Algammal, A.M.; George, T.T.; Jeandet, P.; Al-Snafi, A.E.; Tiwari, A.; Pagnossa, J.P.; Lima, C.M.; Thorat, N.D. Application of natural antimicrobials in food preservation: Recent views. Food Control 2021, 126, 108066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorshidian, N.; Khanniri, E.; Yousefi, M. Antibacterial activity of pediocin and pediocin-producing bacteria against Listeria monocytogenes in meat products. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 709959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Nobile, M.A.; Lucera, A.; Conte, A. Food applications of natural antimicrobial compounds. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 28087. [Google Scholar]
- Claverías, F.P.; Undabarrena, A.N.; González, M.; Cámara, B.P. Culturable diversity and antimicrobial activity of actinobacteria from marine sediments in Valparaíso bay, Chile. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 121535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shams, M.; Shahnavaz, B.; Ghazvini, K.; Valinasab, T. Screening of actinomycetes from Lipar area of Oman Sea to investigate the antibacterial compounds. Avicenna J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 2, 23621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Undabarrena, A.; Beltrametti, F.; Claverías, F.P.; Moore, E.R.; Cámara, B. Exploring the diversity and antimicrobial potential of marine actinobacteria from the comau fjord in Northern Patagonia, Chile. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 210381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Undabarrena, A.; Ugalde, J.A.; Seeger, M.; Cámara, B. Genomic data mining of the marine actinobacteria Streptomyces sp. H-KF8 unveils insights into multi-stress related genes and metabolic pathways involved in antimicrobial synthesis. PeerJ 2017, 5, e2912. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eythorsdottir, A.; Omarsdottir, S.; Einarsson, H. Antimicrobial activity of marine bacterial symbionts retrieved from shallow water hydrothermal vents. Mar. Biotechnol. 2016, 18, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, F.W.; Walsh, C.J.; Gomez-Sala, B.; Guijarro-García, E.; Stokes, D.; Jakobsdóttir, K.B.; Kristjánsson, K.; Burns, F.; Cotter, P.D.; Rea, M.C. The microbiome of deep-sea fish reveals new microbial species and a sparsity of antibiotic resistance genes. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1921924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uniacke-Lowe, S.; Collins, F.W.; Hill, C.; Ross, R.P. Bioactivity screening and genomic analysis reveals deep-sea fish microbiome isolates as sources of novel antimicrobials. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmiento-Vizcaíno, A.; González, V.; Braña, A.F.; Palacios, J.J.; Otero, L.; Fernández, J.; Molina, A.; Kulik, A.; Vázquez, F.; Acuña, J.L. Pharmacological potential of phylogenetically diverse actinobacteria isolated from deep-sea coral ecosystems of the submarine Avilés Canyon in the Cantabrian Sea. Microb. Ecol. 2017, 73, 338–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dangar, K.G.; Singh, S.P. Antimicrobial Activities and Antibiotic Resistance of Nocardiopsis alba Isolated from the Saline Habitats of Coastal Gujarat. In Proceedings of the National Conference on Innovations in Biological Sciences (NCIBS), Rajkot, India, 10 January 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Atallah, B.M.; El-Mohsnawy, E.; El-Shouny, W.; Haroun, S. Identification and characterization of different potentially antibacterial compounds from a marine Streptomyces sp. Sp1. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2023, 33, 166–173. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, N.; Khajuria, V.; Gupta, S.; Kumar, C.; Sharma, A.; Lone, N.A.; Paul, S.; Meena, S.R.; Ahmed, Z.; Satti, N.K. Dereplication based strategy for rapid identification and isolation of a novel anti-inflammatory flavonoid by LCMS/MS from Colebrookea oppositifolia. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 30241–30259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).