Abstract
Intensive care units constitute a critical setting for the management of infections. The patients’ fragilities and spread of multidrug-resistant microorganisms lead to relevant difficulties in the patients’ care. Recent epidemiological surveys documented the Gram-negative bacteria supremacy among intensive care unit (ICU) infection aetiologies, accounting for numerous multidrug-resistant isolates. Regarding this specific setting, clinical microbiology support holds a crucial role in the definition of diagnostic algorithms. Eventually, the complete patient evaluation requires integrating local epidemiological knowledge into the best practice and the standardization of antimicrobial stewardship programs. Clinical laboratories usually receive respiratory tract and blood samples from ICU patients, which express a significant predisposition to severe infections. Therefore, conventional or rapid diagnostic workflows should be modified depending on patients’ urgency and preliminary colonization data. Additionally, it is essential to complete each microbiological report with rapid phenotypic minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values and information about resistance markers. Microbiologists also help in the eventual integration of ultimate genome analysis techniques into complicated diagnostic workflows. Herein, we want to emphasize the role of the microbiologist in the decisional process of critical patient management.
1. Introduction
The intensive care units (ICUs) contain a complex variety of microbial communities whose biodiversity and clinical implications are not sufficiently comprehended. Critical hospital wards constitute alarming indoor settings, where microorganisms can easily contaminate surfaces, devices, and healthcare personnel. This condition contributes to reaching a specific setting-related ecosystem due to extensive sanitation protocols, prolonged antimicrobial treatments, and protracted recoveries. Each aspect may select species that can subvert the native microbial communities, developing hypervirulence, resistance patterns, and biofilm formation capability [1,2].
The intrinsic ICU-related ecosystem provides the ideal substrate to generate an unsettling scenario, comprising the persistence of the microorganisms, the difficult-to-treat appearance of the pathogens, and the intense patients’ vulnerability to infections [2]. ICU patients frequently have comorbidities, immunosuppression, and seniority and often experience invasive procedures and external device implantation. On the one hand, these risk factors establish a critical ICU patient’s susceptibility to colonization and possible hospital-acquired infections (HAIs). On the other hand, ICU-related pathogens may express all their virulence or resistance features in these fragile patients.
Specifically, multidrug-resistant (MDR) pathogens hold high morbidity and mortality rates among ICUs [2]. On that premise, it is essential to correctly distinguish between colonization and infection conditions by applying standardized clinical and diagnostic protocols. Clinical microbiology support holds a crucial role in the diagnostic algorithms’ definition to rapidly reach data on identification and antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Eventually, the complete patient evaluation requires integrating local epidemiological knowledge into the best practice and the standardization of antimicrobial stewardship programs.
2. Surveillance and Diagnostic Aspects
The prompt identification of an infection process among ICU patients involves a multiple evaluation. Foremost, it is essential to estimate clinical signs such as pyrexia and tachycardia, which are not specific in this healthcare setting. As a consequence, the clinical approach needs to perform laboratory parameters such as white blood cell count (WBC), C-reactive protein (CRP), procalcitonin (PCT), presepsin, and pro-adrenomedullin. The alteration of these biomarkers allows for the consolidation of the suspected infection, while their normalization may suggest antimicrobial treatment de-escalation. Moreover, biomarkers often show great specificity rates in comparison or in combination to sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) and other clinical scores [3,4,5]. Clinical and laboratory information describes the general condition of the patients, representing the first step to correctly defining a diagnostic microbiological workflow. Clinical microbiologists must help clinicians in distinguishing colonization from infectious conditions. For this purpose, early information about microbiological data results in preventing fatal outcomes and concerning outbreaks. Moreover, microbiological information guides patient management, co-ordinating organization, and infection control procedures.
The ICU settings may involve diversified conditions such as hospital-acquired or community-acquired infections (CAIs), which require clinical microbiologist recognition and reading [6,7]. The most valuable tool in recognizing colonization or infection conditions is the correct planning of surveillance programs. Surveillance may be accomplished through passive protocols, periodically gathering retrospective laboratory data about specific hospital units. On the one hand, this epidemiological research is easy to perform over extended time intervals and does not involve high costs. Furthermore, it collects complete knowledge about isolates, resistance profiles, and effective therapeutical eradications. Therefore, clinicians can manage patients’ conditions, specific aetiology suspicion, and empirical treatment choices by combining single-centre and multi-centre surveillance [6,8]. All this information contributes to settling pragmatic infection control strategies, helping to define active surveillance protocols. The active screening policies strictly depend on the local epidemiology and the features of the most critical hospital units. Patients at high risk of infection or cross-transmission, such as ICU patients, represent the most reliable candidates to apply for an active surveillance program.
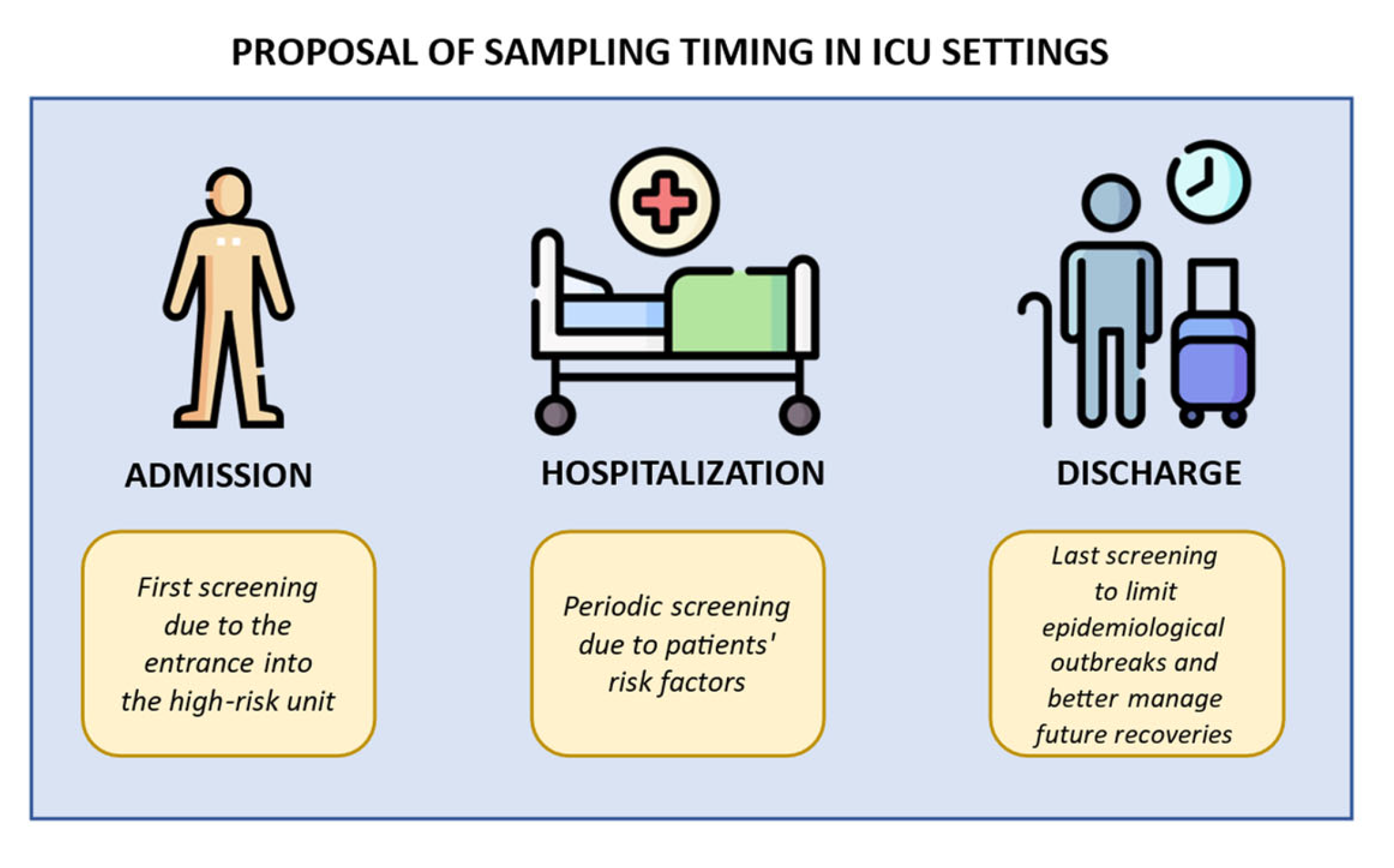
The active surveillance aims to implement standard precautional measures (admission screening), rapidly prevent pathogen transmission within the unit during the recovery (repeated screening), correctly manage possible inter-ward transfers (discharge screening), and finally screen vulnerable patients before invasive procedure (pre-operative screening). Figure 1 illustrates some indications for sampling timing.
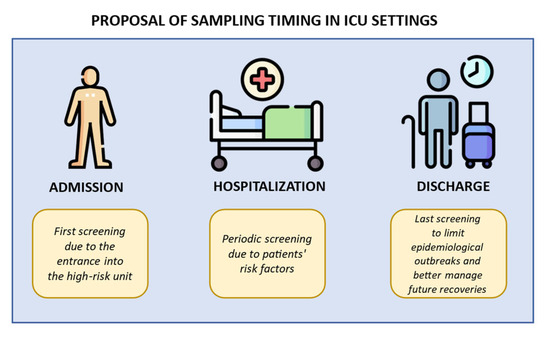
Figure 1.
Indications for sampling timing in ICU settings. Created using image database https://www.flaticon.com (accessed on 7 February 2024). The first step is the admission, when a primary screening is performed before future admittance into a high-risk unit. The second step is the hospitalization, when weekly screenings are performed due to patients’ risk factors (catheters implantations, immunosuppression, or others). The final step is the discharge, when a last screening is performed to better manage the epidemiological outbreak and patients’ future recoveries.
The mentioned screening strategies should be maintained for long-term time intervals within the hospital setting to know the patients’ status. The screening tests can utilize culture-based methods or rapid molecular techniques. A negative result does not exclude the presence of an MDR microorganism below the detection limits of each diagnostic procedure. Positive results should be rapidly provided to clinicians and centre direction to manage eventual contact precautions and enrich epidemiological databases [9]. The gathered information integrates national and international surveillance data about MDR microorganisms into critical healthcare settings [10,11].
3. Epidemiological Details
Several epidemiological surveys documented the Gram-negative bacteria supremacy among ICU infection aetiologies. Specifically, Klebsiella species hold the primate, but Klebsiella pneumoniae detains the highest percentages. Furthermore, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Acinetobacter baumannii could similarly and severely impact ICUs. Among Gram-positive bacteria, Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus species prevail [12,13,14]. Despite this conception, there is no specific and recognized prevalence in mortality and unfavourable outcomes concerning the isolated species. The common risk factors, such as older age or comorbidities, are the basic features for the death rate increase in ICU patients [12,13].
Therefore, a specific bacterial aetiology does not significantly affect the negative outcome rate, and this assumption generally interests the ICUs worldwide.
On the other hand, geographical areas expose country-specific variations in lifestyle, healthcare facilities and accesses, nutritional state, and vaccine or antimicrobial drug availability. Each aspect has a relevant impact on the ICU patient status, even if no data may establish an actual prevalence among all of them [12,13,14,15]. The mentioned premise strictly assumes antimicrobial susceptible microorganisms. Unfortunately, ICUs often notice MDR aetiologies, which dramatically impact patients’ outcomes. The Gram-negative resistance episodes mainly regard third-generation cephalosporins (33.3%) and carbapenems (20.4%) among Enterobacterales. The carbapenem-resistant isolates also belong to P. aeruginosa (30.2%) and A. baumannii (77.7%) [16,17,18]. Moreover, literary data confirm methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus (VRE) as potential ICU mortality causes despite their low prevalence [12,19,20,21].
3.1. Acinetobacter baumannii
Acinetobacter baumannii usually exhibits a lower virulence spectrum, although it has the ability to adhere to surfaces, medical devices, and personnel hands. Moreover, the same species frequently colonizes the patients’ oropharyngeal, cutaneous or gastro-intestinal districts within 48 h of ICU recoveries [22,23]. The opportunity for A. baumannii to develop a biofilm formation increases the chance of resisting the nosocomial environment. Specifically, biofilm-related genes, such as ompA, bap, and blaPER-1, help the microorganism to maintain its persistence [23]. Such bacterial quality largely contributes to the sticking of ICU mechanical ventilators required for acute respiratory failure management among recovered patients. Although these devices improve morbidity rates of the patients, they also correlate with A. baumannii ventilator-associated pneumoniae (VAP) episodes. The COVID-19 pandemic even aggravated A. baumannii-related VAP, extensively contributing to mechanical ventilation requests within ICUs [24,25]. Severe respiratory conditions frequently precede hematic dissemination and systemic infections, complicating therapeutical management due to A. baumannii resistance patterns. For instance, carbapenem-resistance A. baumannii (CRAB) predominates within ICUs, mostly due to blaOXA-23, blaOXA-66, and blaOXA-51 genes [21]. The mentioned resistance markers integrate an extended resistance profile, leading to the A. baumannii insertion into the alert microorganisms’ lists [26].
3.2. Klebsiella pneumoniae
K. pneumoniae accounts for high healthcare-associated infection (HAI) percentages, especially among critically ill patients. The species usually integrates human gut microbiota, even if it can colonize the upper respiratory tract, the hospital environments or the staff. At admission to the ICUs, patients with K. pneumoniae show a concerning chance of developing severe infection due to the same microorganism [27]. This species usually causes acute infectious conditions due to a large virulence spectrum, mainly related to specific plasmid-associated genes. For example, the gene loci iro for salmochelin biosynthesis, and the gene loci iuc for aerobactin synthesis largely contribute to increased siderophore production to face iron-limiting living conditions [28,29].
K. pneumoniae strains present the polysaccharide capsules to evade the patient’s immune response and the lipopolysaccharides to exacerbate the virulence expression against the human host. Furthermore, the rmpA gene regulates the mucoid phenotype, leading to a potential hypermucoviscous K. pneumoniae strain, whose increased capsule production enhances the virulence expression. Additionally, K. pneumoniae can potentially use fimbriae and produce biofilm-related adhesins, increasing at the same time its capability to disseminate or colonize anatomic districts and surfaces [29,30].
K. pneumoniae is also distinguished for complicated susceptibility profiles. Carbapenem resistance due to β-lactamases production and/or membrane permeability alterations is the most relevant phenomenon to notice about this species. Carbapenem-resistant K. pneumoniae (CR-Kp) mainly expresses its pattern through K. pneumoniae carbapenemases (KPC), OXA-48-like enzymes, and metallo-β-lactamases (MBLs), such as Verone-imipenemase (VIM), imipenemase (IMP), and New Delhi metallo-β-lactamases (NDM) [31,32,33]. According to these markers, K. pneumoniae enters the worldwide alert microorganisms’ monitoring programs [10]. Surveillance samples, such as rectal and oropharyngeal swabs, allow for promptly identifying potential MDR strains’ colonization, preventing severe infection spread.
A substantial amount of literary data documented how dissemination episodes strictly depend on previous MDR K. pneumoniae rectal colonization [34,35,36,37]. K. pneumoniae respiratory colonization may involve mechanical ventilation in the VAP generation and the potential subsequent dissemination [38,39]. Several studies highlighted how ICU K. pneumoniae isolates correlate with high-risk clones (HiRiCs), whose features list colonization abilities, epidemicity, nosocomial and/or host persistence, and antimicrobial resistance due to specialized genetic populations [40,41,42].
3.3. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
P. aeruginosa represents the most common aetiological agents among ICU respiratory infections. Its virulence spectrum is the most relevant marker for this species. First, P. aeruginosa has several surface appendages, such as type IV pili and flagella, which allow a promising movement and adhesion capability. Furthermore, outer membrane structures such as lipopolysaccharide and secretion systems (T1SS-T6SS) stimulate the host immune response and produce toxins or biofilm-related compounds such as alginate. The biofilm formation leads to an essential environmental persistence, although with difficult growth conditions. Additionally, the quorum sensing phenomenon modulates biofilm expansion and virulence factor production, regulating bacterial cell-to-cell interactions [43]. Both biofilm and pili potentiate P. aeruginosa capability to adhere to living substrates and medical devices. The quorum sensing regulation leads to regular and specific polysaccharidic bacterial structures, providing an ideal growing environment for P. aeruginosa cells.
Critical patients often require mechanical ventilation to manage acute respiratory failures, and this need may correlate with P. aeruginosa lower respiratory tract infections due to a frequent previous microorganism mechanical ventilator or pharyngeal tract colonization. According to this, surveillance programs should integrate respiratory sample monitoring to document P. aeruginosa colonization, whose subsequent infection increases mortality rates in fragile patients [43,44]. Moreover, potential resistance patterns complicate P. aeruginosa respiratory infections among ICU patients. Specifically, MBLs or KPC production may lead to carbapenem resistance, along with the most common membrane permeability alterations related to outer membrane protein (Omp) depression or efflux pump overexpression [45,46]. Carbapenem-resistant P. aeruginosa joins nosocomial alert microorganisms within the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) epidemiological reports [10].
3.4. Escherichia coli
Escherichia coli normally integrates into the human gastrointestinal microbiota, as well as K. pneumoniae. Unfortunately, it also represents a facultative pathogen which may cause urinary or systemic infection, disseminating from the native gastrointestinal district. The extra-intestinal migration correlates with virulence factor expression. Numerous compounds as adhesins, toxins, iron acquisition factors, lipopolysaccharides, polysaccharide capsules, and invasins enhance E. coli capability to invade blood and tissues, expressing adherence and persistence [47]. Critical patients, such as immunocompromised hosts, are more predisposed to E. coli dissemination. Therefore, this microorganism frequently causes bacteriemia and sepsis among ICU patients. E. coli may carry extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBL) genes (bla genes), which take place within mobile elements (plasmids) or chromosomal positions. The blaCTX-M genes are the most clinically relevant resistance markers in E. coli, which occasionally carry carbapenem-resistance genes such as blaNDM and blaKPC [48]. Resistant E. coli is included within the ECDC alert microorganisms’ lists, especially due to its capability to transfer resistance genes [10].
3.5. Staphylococcus aureus
S. aureus frequently invades nosocomial settings due to its capability to adhere to different surfaces. This species easily forms biofilm on indwelling medical devices, producing virulence factors to evade the host’s immune response. Specifically, S. aureus produces haemolysins, leucocidins, proteases, enterotoxins, and exfoliative toxins as relevant virulence factors. A regulatory system, the agr system, is a quorum sensing system involved in these factors’ production along with sar, rot, and mgr transcriptional regulators [49]. S. aureus toxins damage host cell membranes, causing cytolytic injuries and cellular function alterations. The toxin production emerges as a relevant feature for severe infectious diseases among ICU patients [50]. Although medical devices often represent the staphylococcal source, fragile patients are frequently prone to opportunistic S. aureus infection. The species may colonize the upper respiratory tract, causing a subsequent lung infection after viral infections or severe immunosuppression. The same conditions may contribute to systemic infections, such as S. aureus bacteriemia and sepsis [51,52].
Resistance patterns complicate S. aureus infection treatment. The methicillin-susceptible S. aureus (MSSA) and the methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) share the same virulence factor spectrum, supporting the importance of promptly identifying resistance markers to really apply an effective therapy [50]. The ECDC surveillance programs included MRSA within alert microorganisms list [10]. S. aureus nasal, pharyngeal, and gut colonization are extremely common in community subjects, but persistent carriers seem to contrast potential S. aureus infections through anti-staphylococcal antibodies. Despite this assumption, the carriers represent a harmful staphylococcal source, especially when they typically attend healthcare settings. All the critical hospital settings need to adequate their infection control protocols to the S. aureus research on rectal and respiratory surveillance samples from potential asymptomatic colonized patients [53,54,55,56,57]. Certainly, epidemiological practices such as hand sanitization and patient isolation support S. aureus eradication in ICUs [58,59]. Antibiotic treatment is still the gold standard for front staphylococcal infection in intensive care patients, especially when MRSA is confirmed [60].
3.6. Enterococcus Species
Enterococcal species account for about 6.1–17.5% of isolated strains from European recovered patients, even if these species initially integrate into the human gut microbiota. These percentages are mainly related to Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium. They frequently cause urinary tract infections, systemic infections, endocarditis, or wound infections after surgical intervention. Furthermore, enterococci may colonize medical devices, causing catheter-related infections [61]. In regard to the virulence spectrum, Enterococcus species produces cytolysins, gelatinases, pore-forming toxins, and aggregation substances, which promote tissue invasion, immune evasion, or cellular damage [62]. Vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) currently represent a fundamental healthcare concern due to an increased mortality rate among ICU patients [63,64,65,66]. Surveillance programs include VRE microbiological research on rectal swabs to prevent invasive diseases according to the ECDC protocols [10].
3.7. Streptococcus pneumoniae
The community-acquired acute bacterial meningitis (CABM) often requires ICU admission due to severe outcomes and high mortality rates. Streptococcus pneumoniae is the most isolated aetiological agent in the case of this condition, which remains fatal in a moderate case percentage (15–33%) despite the diffusion of effective vaccination campaigns [67,68,69,70,71]. Although the possible ICU patient enters with S. pneumoniae meningitis, some patients reach the same units for different acute conditions, developing S. pneumoniae meningitis, bacteriemia, or pneumoniae after an upper tract colonization (nasopharynx) by the same species. The S. pneumoniae capability to cause severe infection depends on the host’s immune conditions and the bacterial virulence pattern [72]. The microorganisms produce a polysaccharide capsule, surface proteins, and the toxin pneumolysin. All these factors contribute to host invasion and damage, but the polysaccharide capsule probably represents the essential pneumococcal virulence feature.
The capsule protects S. pneumoniae from phagocytosis, mucus mechanical removal, and antibiotic exposure [73,74]. Some ECDC periodical reports document the importance of monitoring S. pneumoniae colonization through surveillance programs, considering the dissemination risk [75]. According to the huge aetiological agents’ spectrum, ICU surveillance choices should depend on the suspected microorganisms to detect. Therefore, a reasonable approach may involve multiple sites to sample. Table 1 describes a suggested sampling strategy within ICU settings.

Table 1.
Proposal of a surveillance sampling strategy into ICU settings.
3.8. Clostridioides difficile
ICU patients occasionally suffer from Clostridioides difficile infections. Specifically, the C. difficile infections prevalence among ICU patients accounts for 0.4–4%, slightly impacting on morbidity and mortality rates. An initial colonization (10–20% of ICU patients) may become an infection episode due to patients’ fragilities. Risk factors such as immunosuppression or prolonged broad-spectrum antibiotic treatment should suggest a colonization investigation on stool samples. Culture-based methods, chemiluminescence, or real-time PCR assays may be used to detect C. difficile colonies, antigens or nucleic acid. Molecular methods also allow us to determine the C. difficile ribotype: some hypervirulent strains, such as the O27, severely impact on critically ill patients due to the hyperproduction of toxins [76].
4. Microbiological Diagnostic Procedures
According to several literary data, ICU patients mainly suffer from severe respiratory infections (hospital-acquired infections such as VAP and complicated community-acquired infections also called “CAP”). Urinary tract and bloodstream infections usually reach lower rates in the same patients’ setting. On that premise, the diagnostic microbiology laboratory usually receives respiratory samples from upper or lower tracts, urine, and blood [77].
4.1. Conventional Diagnostic Methods
Regarding respiratory diagnostic procedures, the microscopic analysis still represents an essential starting point. Microscopic results may clarify qualitative information about eventual microorganisms, along with cellular elements evocative of inflammatory processes such as white blood cells (granulocytes) and mucus. Furthermore, the Gram stain verifies respiratory samples’ suitability to subsequent diagnostic phases, excluding invalid specimens according to Bartlett’s criteria. Epithelial squamous cells suggest possible sample contamination through the upper respiratory tract, while granulocytes come out on the side of an acute inflammatory condition. After microscopic validation, respiratory samples such as sputum or broncho-aspirate undergo culture exams on enriched and selective agar media. Lower respiratory tract samples such as bronchoalveolar fluid do not need this validation because their anatomic source is clearer than the upper respiratory tract [78]. Blood samples face a variable incubation period within enriched liquid media, which enter an automated incubator. After being flagged as positive, an extemporary Gram stain is prepared. This investigation may furnish preliminary information about microorganisms’ morphology and type, and early orienting antimicrobial treatments. Consequently, the positive blood samples sustain culture assays through enriched agar media [79].
Urinary samples mainly go through culture exams on enriched and selective agar media, along with a preliminary physical and chemical examination, which support eventual evidence of nitrates, leucocytes, turbidity, or pH significant alterations. With regard to incubation conditions, all the culture plates usually require 18–24 h, which may become 48–72 in the case of fastidious microorganism identification [80].
After the required incubation period, features such as microbial quantity, purity, and morphology are analysed. Specifically, the microbial count is essential to certify microbial aetiology and an ongoing infection process at urinary and respiratory sites. Only significant microbial counts match with the suspicion of an infection and its related clinical conditions. Otherwise, blood samples are processed independently from microbial quantification due to their sterile anatomic source. All the polymicrobial results need to be evaluated as possible contaminations according to the related clinical evidence [81]. Significant microbial growths sustain antimicrobial susceptibility testing, which is usually performed through automated turbidimetric and colourimetric technologies. Its result may require a supplementary 24 h interval, accounting for about 72 h of definitive turn-around time (TAT). Polymicrobial growth, fastidious microorganisms, and extended resistance patterns may prolong this interval. The susceptibility profile evaluation provides the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values, which is crucial in planning patients’ targeted therapies [82].
4.2. Rapid Diagnostic Methods
On the one hand, the conventional methods are reliable, but they require prolonged processing periods. On the other hand, the recent technological advance proposes several identification and susceptibility testing rapid techniques for a significant TAT reduction. Regarding the identification processes, the matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time of flight (MALDI-TOF) and magnetic resonance methods became predominant in the case of positive blood samples [83,84,85]. Additionally, either the nested-PCR or the real-time multiplex PCR is usually integrated into syndromic panels to rapidly identify microbial nucleic acids directly from respiratory specimens, cerebrospinal fluid, and blood within 45–90 min. These molecular technologies often have a restricted identification spectrum but furnish preliminary information about specific resistance markers [86,87,88].
One of the advantages of using the respiratory syndromic panel is the chance to provide an accessory quantitative information about the hypothesized microbial count. Specifically, the molecular technology furnishes a microbial quantification as genomic copies/mL (bin), which does not have the same relevance as a culture microbial count due to the possible presence of non-vital genomic fragments. Quantitative molecular information should integrate culture microbial count to validate a microbiological diagnosis [89,90,91]. ICU patients often require fast susceptibility diagnostic protocols due to possible systemic infections. Therefore, the European Committee for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) proposed a rapid antibiotic susceptibility test (RAST) through the disk diffusion method on agar plates [92,93]. Despite its level of standardization, this method requires strict quality controls and high personnel expertise. On the contrary, automated susceptibility testing is possible through automated time-lapse microscopy or volatile organic compound detection within about 7 h [94,95,96,97]. Additionally, microfluidic systems and mass spectrometry can analyse susceptibility profiles through peak intensity and bacterial growth evaluation [98].
All the abovementioned advanced technologies furnish a preliminary phenotypic susceptibility profile, whose advantage is the reporting of MIC values. However, preliminary results should be confirmed through conventional methods to complete the antimicrobial drugs’ spectrum. Interestingly, the rapid phenotypic antibiogram can be forwarded to laboratory personnel and clinicians through phone call or by mailing to “smart reporting” system. This option may significantly reduce TAT for critical patients. Finally, rapid susceptibility testing methods always integrate antimicrobial stewardship programs, which help for managing infection control and antimicrobial treatment in the ICU [99,100]. Ultimately, recent technologies offer the opportunity to generate a concentrated microbial suspension from a positive blood sample within 30 min. The obtained suspension can be used to rapidly obtain identification from MALDI-TOF and susceptibility profile from the colourimetric technique. The mentioned progress could constitute the last frontier in terms of rapid diagnostic methods, resulting in an untimely and complete microbiological report within 24 h from the positivity of the blood sample [101,102,103].
Proteins involved in resistance mechanisms of MDR bacteria may represent an ideal target for lateral flow assays (LFAs). These disposables have been developed to detect resistance enzymes of typical aetiological agents in ICUs, such as E. coli, A. baumannii, P. aeruginosa, S. aureus, and E. faecium. LFAs demonstrated high sensitivity and specificity rates, while also allowing for the possibility to detect the antigens directly from biological samples [104].
4.3. The Potential Role of Whole-Genome Sequencing
ICU critical patients may occasionally require ultimate diagnostic frontiers. Published data documented that the conventional pathogens detection is impossible in about 60% of pneumoniae cases and 30% of sepsis episodes within ICU settings [105,106,107]. This condition often leads to empirical treatments which are not targeted and underestimate harmful resistance profiles. Metagenomics tools provide a unique opportunity to characterize and quantify microorganisms from biological samples, so whole-genome sequencing (WGS) is currently under review as a diagnostic complementary tool. High sensitivity and specificity rates emerged from the completed studies.
Briefly, a nucleic acid extraction is followed by library construction, nucleic acid fragmentation, and amplification processes. The workflow requires 6 h to several days, depending on the applied protocol (long-read or short-read technologies) and personnel training [105]. False negative results are possible due to the impossibility of standardizing extraction and purification protocols directly from biological samples. Furthermore, accurate bioinformatic software and expertise are essential to complete the interpretation process. This concept is related to the extended information quantity that emerges from a sequencing analysis, which can gather data about multiple microorganisms on the same sample (false positive results). Public databases are usually consulted to obtain sequencing data about pathogen identifications, virulence factors, and resistance genes [105,106].
Different studies tested the WGS as an advanced diagnostic technique, comparing its accuracy to gold standards such as culture assays and real-time PCR protocols. Clinical samples like cerebrospinal fluid, respiratory secretions (tracheal aspirate, bronchoalveolar lavage), and blood were included in the experimental protocols. Unfortunately, some genome coverage limitations emerged about low-diffused resistance genes and less common microbial species. Moreover, the lack of infrastructure and sufficient economic support lead to WGS underutilization in ICUs. Data hypothesize a gradual genome sequencing inclusion into ICU diagnostic workflows after implementations in clinical trials, databases, and personnel-specific training about advanced technologies [105,106,107].
Recent publications suggest the WGS as a potential AST method (WGS-AST) due to the capability to furnish accurate resistance predictions. Furthermore, data about the virulence genes may be highlighted through the same technology. Similar information should be integrated with local epidemiological data and known resistance phenotypes. Despite the absence of solid evidence about this application, the WGS may become an interesting challenge in rapidly providing resistance marker detection [107]. Certainly, these conclusions may emphasize the cruciality of performing genomic analysis and document eventual epidemiological changes of MDR clones.
5. Antimicrobial Stewardship Programs in Intensive Care Settings
Antimicrobial consumption is one of the most relevant concerns in ICU settings, mostly due to empirical broad-spectrum treatments on critical patients. Such fragile subjects and their severe infections made the antimicrobial stewardship (AMS) programs’ formation essential [108,109]. These programs aim to monitor antimicrobial use and dosage, optimize possible microorganisms’ elimination, and reduce treatment duration, impacting patients’ management and recovery costs. The mentioned aims require a multidisciplinary committee consisting of microbiologists, epidemiologists, pharmacologists, infectious disease specialists, and other targeted clinicians [109]. The ultimate AMS goal is to minimize and contain antimicrobial resistance in critical settings. Statistics document that about 60% of ICU patients come from other hospital wards, claiming the importance of applying the same AMS strategies to all healthcare units. According to the AMS program application, rapid pathogen identification is essential for the early administration of targeted therapies and for avoiding broad-spectrum antibiotic use. Additionally, all the targeted therapies need to be administered depending on the patient’s physiological conditions and the drug’s pharmacological features. Finally, the antimicrobial treatment should be monitored through specific biomarkers and clinical parameters to prevent unnecessary prolonged regimens [108].
The AMS strategies require frequent educational programs for all the involved healthcare personnel with a standardized consensus document about all the aims and protocols. In conclusion, economic and logistic support are vital to plan and reach the AMS goals [108,109]. For instance, clinicians may promptly identify the urgency of an ICU patient’s condition through laboratory biomarkers, imaging, symptoms, and clinical scores. The suspicion of infection should be followed by the request of a fast-track protocol.
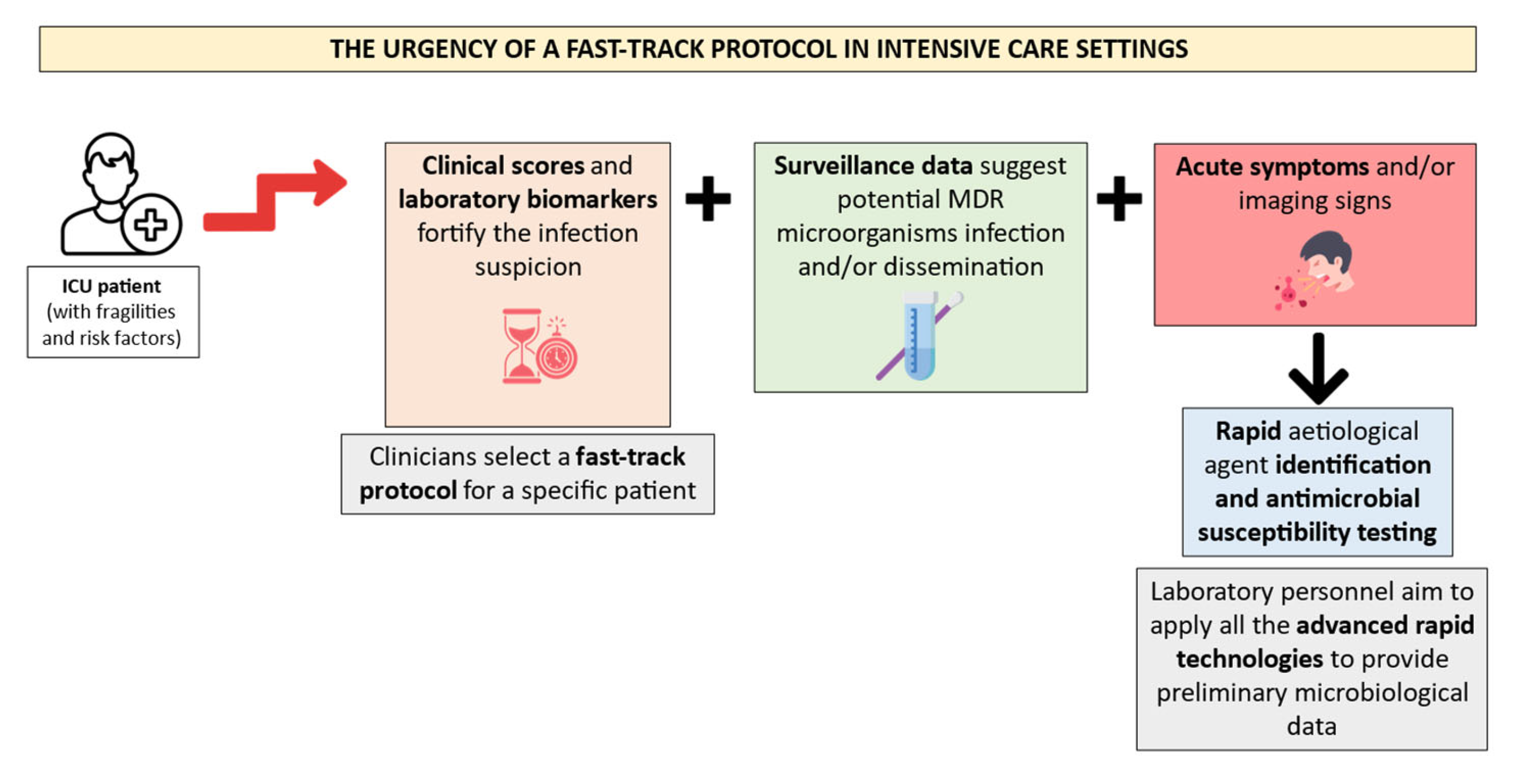
Consequently, the laboratory personnel must apply all the rapid technologies to satisfy these requirements. Figure 2 illustrates a suggested fast-track protocol application for ICU patients’ microbiological diagnosis management.
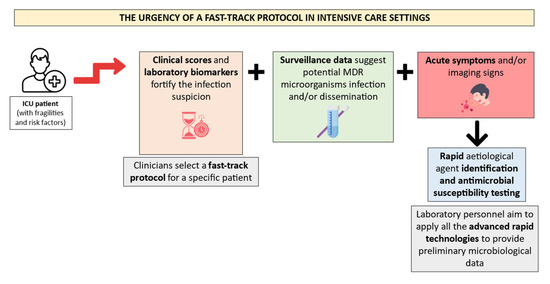
Figure 2.
Proposal of a diagnostic workflow organization in ICU patients. Created using image database https://www.flaticon.com (accessed on 14 February 2024). The ICU patients must hold several risk factors and fragilities to require a fast-track protocol after the suspicion of a severe infection. This suspicion is often fortified by clinical scores and laboratory biomarkers, along with MDR colonization data and acute symptoms. Rapid identification and antimicrobial susceptibility testing technologies should be applied by the laboratory personnel in the abovementioned episodes.
6. Conclusions
Intensive care patients represent a concerning healthcare category due to their fragilities and infection predisposition. The clinical microbiologist has the responsibility of providing early and continuous support to clinicians in managing ICU patients. An essential role is to prevent infections by monitoring the patients during their recovery. For this reason, surveillance programs must be encouraged as the prior infection control strategy in the analysed patient setting. Avoiding infections is the key to reducing critical patients’ fatal outcomes. At the same time, once an infection has occurred, it is vital to promptly provide a concrete plan for patient intervention. As a result, rapid identification results and preliminary susceptibility data become the key to succeed in managing the patient and limiting possible extended outbreaks.
All these phases require punctual communication between the clinicians and the laboratory personnel about the patient’s conditions and microbiological evidence. This kind of approach allows the microbiologist to certify the real urgency in rapidly processing a clinical sample instead of applying conventional protocols.
The microbiological report should include all the information that helps clinicians to apply the best clinical practice. In relation to this assumption, a complete report must contain data about identification, phenotypic susceptibility profile, eventual microbial count, resistance markers typing, and indications of the adopted guidelines.
The application of a complete and rapid microbiological protocol is fundamental both for surveillance samples and the specimen collection of a suspected infection. On one hand, a real-time surveillance activation allows for better and faster infection control procedures. On the other hand, a colonization knowledge provides essential information in the case of sudden signs for infection among ICU patients.
The ICU patient always suffers from time-dependent clinical conditions; thus, clinicians should be prepared to provide rapid management and respond to diagnostic requests. On the other hand, clinical microbiologists must satisfy such a critical condition by applying all the available rapid technologies. In conclusion, the ICU patient has inspired technological diagnostic improvements due to the severity of infection and the need for a time-saving diagnosis. In our opinion, the ICU setting could represent a forefront to encourage further studies on advanced diagnostic tools, whose performances will become more essential in the future to rapidly define a microbiological diagnosis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.S.; methodology, M.C., G.M. and S.S.; investigation, M.C. and G.M.; data curation M.C. and G.M.; writing—original draft preparation, M.C. and G.M.; writing—review and editing, M.C. and G.M.; supervision, S.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partially supported by EU funding with the MUR PNRR Extended Partnership Initiative of Emerging Infection Disease Project no. PE 00000007 INF-ACT.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ribeiro, L.F.; Lopes, E.M.; Kishi, L.T.; Ribeiro, L.F.C.; Menegueti, M.G.; Gaspar, G.G.; Silva-Rocha, R.; Guazzaroni, M.E. Microbial Community Profiling in Intensive Care Units Expose Limitations in Current Sanitary Standards. Front. Public. Health 2019, 7, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ture, Z.; Güner, R.; Alp, E. Antimicrobial stewardship in the intensive care unit. J. Intensive Med. 2022, 3, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heffernan, A.J.; Denny, K.J. Host Diagnostic Biomarkers of Infection in the ICU: Where Are We and Where Are We Going? Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2021, 23, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelshafey, E.E.; Nasa, P.; Elgohary, A.E.; Khalil, M.F.; Rashwan, M.A.; Ghezala, H.B.; Tayar, A.A. Role of Presepsin for the Diagnosis of Sepsis and ICU Mortality: A Prospective Controlled Study. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 25, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, T.; Kuriyama, N.; Suzuki, Y.; Saito, S.; Tanaka, R.; Iwao, M.; Tanaka, M.; Maki, T.; Itoh, H.; Ihara, M.; et al. Mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin is a novel biomarker for arterial stiffness as the criterion for vascular failure in a cross-sectional study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 305, Erratum in Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schouten, J.; De Angelis, G.; De Waele, J.J. A microbiologist consultant should attend daily ICU rounds. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 372–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Princess, I.; Vadala, R. Clinical Microbiology in the Intensive Care Unit: Time for Intensivists to Rejuvenate this Lost Art. Indian. J. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 25, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollef, M.H.; Shorr, A.F.; Bassetti, M.; Timsit, J.F.; Micek, S.T.; Michelson, A.P.; Garnacho-Montero, J. Timing of antibiotic therapy in the ICU. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sy, C.L.; Chen, P.Y.; Cheng, C.W.; Huang, L.J.; Wang, C.H.; Chang, T.H.; Chang, Y.C.; Chang, C.J.; Hii, I.M.; Hsu, Y.L.; et al. Recommendations and guidelines for the treatment of infections due to multidrug resistant organisms. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2022, 55, 359–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, M.E.; Domínguez, M.A.; Ezpeleta, C.; Padilla, B.; Ramírez de Arellano, E.; Martínez-Martínez, L. Cultivos de vigilancia epidemiológica de bacterias resistentes a los antimicrobianos de interés nosocomial [Epidemiological surveillance cultures in antimicrobial-resistant bacteria causing nosocomial infection]. Enfermedades Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2008, 26, 220–229. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/antimicrobial-resistance/surveillance-and-disease-data (accessed on 18 January 2024).
- Fisman, D.; Patrozou, E.; Carmeli, Y.; Perencevich, E.; Tuite, A.R.; Mermel, L.A.; Geographical Variability of Bacteremia Study Group. Geographical variability in the likelihood of bloodstream infections due to gram-negative bacteria: Correlation with proximity to the equator and health care expenditure. PLoS ONE. 2014, 9, e114548, Corrected in PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, J.L.; Sakr, Y.; Singer, M.; Martin-Loeches, I.; Machado, F.R.; Marshall, J.C.; Finfer, S.; Pelosi, P.; Brazzi, L.; Aditianingsih, D.; et al. Prevalence and Outcomes of Infection among Patients in Intensive Care Units in 2017. JAMA 2020, 323, 1478–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakr, Y.; Moreira, C.L.; Rhodes, A.; Ferguson, N.D.; Kleinpell, R.; Pickkers, P.; Kuiper, M.A.; Lipman, J.; Vincent, J.L. Extended Prevalence of Infection in Intensive Care Study Investigators. The impact of hospital and ICU organizational factors on outcome in critically ill patients: Results from the Extended Prevalence of Infection in Intensive Care study. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 43, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouel-Cheron, A.; Swihart, B.J.; Warner, S.; Mathew, L.; Strich, J.R.; Mancera, A.; Follmann, D.; Kadri, S.S. Epidemiology of ICU-Onset Bloodstream Infection: Prevalence, Pathogens, and Risk Factors Among 150, 948 ICU Patients at 85 U.S. Hospitals. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 50, 1725–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalil, A.C.; Klompas, M. Ceftazidime-avibactam versus meropenem for the treatment of nosocomial pneumonia. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 229–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcone, M.; Tiseo, G.; Carbonara, S.; Marino, A.; Di Caprio, G.; Carretta, A.; Mularoni, A.; Mariani, M.F.; Maraolo, A.E.; Scotto, R.; et al. Mortality Attributable to Bloodstream Infections Caused by Different Carbapenem-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacilli: Results From a Nationwide Study in Italy (ALARICO Network). Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 76, 2059–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naimi, T.; Ringwald, P.; Besser, R.; Thompson, S.; Bell, D. Antimicrobial Resistance. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/antimicrobial-resistance (accessed on 2 March 2023).
- Marino, A.; Campanella, E.; Stracquadanio, S.; Calvo, M.; Migliorisi, G.; Nicolosi, A.; Cosentino, F.; Marletta, S.; Spampinato, S.; Prestifilippo, P.; et al. Ceftazidime/Avibactam and Meropenem/Vaborbactam for the Management of Enterobacterales Infections: A Narrative Review, Clinical Considerations, and Expert Opinion. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepape, A.; Jean, A.; De Waele, J.; Friggeri, A.; Savey, A.; Vanhems, P.; Gustin, M.P.; Monnet, D.L.; Garnacho-Montero, J.; Kohlenberg, A. European intensive care physicians’ experience of infections due to antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2020, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/sites/default/files/documents/healthcare-associated-infections-intensive-care-units-annual-epidemiological-report-2019.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Doughty, E.L.; Liu, H.; Moran, R.A.; Hua, X.; Ba, X.; Guo, F.; Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Holmes, M.; van Schaik, W.; et al. Endemicity and diversification of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in an intensive care unit. Lancet Reg. Health–West. Pac. 2023, 37, 100780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.K.; Hospenthal, D.R. Acinetobacter infection in the ICU. Crit. Care Clin. 2008, 24, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.A.F.; Ahmed, F.A.; Elkhateeb, A.F.; Mahmoud, E.E.; Ahmed, M.I.; Ahmed, R.I.; Hosni, A.; Alghamdi, S.; Kabrah, A.; Dablool, A.S.; et al. Virulence Characteristics of Biofilm-Forming Acinetobacter baumannii in Clinical Isolates Using a Galleria mellonella Model. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Yu, T.; Du, R.; Fan, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, B.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1054–1062, Erratum in Lancet 2020, 395, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novović, K.; Kuzmanović Nedeljković, S.; Poledica, M.; Nikolić, G.; Grujić, B.; Jovčić, B.; Kojić, M.; Filipić, B. Virulence potential of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from COVID-19 patients on mechanical ventilation: The first report from Serbia. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1094184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance in Europe 2023—2021 Data. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/sites/default/files/documents/Antimicrobial%20resistance%20surveillance%20in%20Europe%202023%20-%202021%20data.pdf (accessed on 2 February 2024).
- Gorrie, C.L.; Mirceta, M.; Wick, R.R.; Edwards, D.J.; Thomson, N.R.; Strugnell, R.A.; Pratt, N.F.; Garlick, J.S.; Watson, K.M.; Pilcher, D.V.; et al. Gastrointestinal Carriage Is a Major Reservoir of Klebsiella pneumoniae Infection in Intensive Care Patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.W.; Zheng, J.X.; Bai, B.; Xu, G.J.; Lin, F.J.; Chen, Z.; Sun, X.; Qu, D.; Yu, Z.J.; Deng, Q.W. Characteristics of Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: Does low expression of rmpA contribute to the absence of hypervirulence? Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 436–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.A.; Marr, C.M. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00001-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paczosa, M.K.; Mecsas, J. Klebsiella pneumoniae: Going on the Offense with a Strong Defense. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-R.; Lee, J.H.; Park, K.S.; Jeon, J.H.; Kim, Y.B.; Cha, C.-J.; Jeong, B.C.; Lee, S.H. Antimicrobial Resistance of Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: Epidemiology, Hypervirulence-Associated Determinants, and Resistance Mechanisms. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, J.; Aguilar, A.C.; Caicedo, A. Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: Microbiology Key Points for Clinical Practice. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2019, 12, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karampatakis, T.; Antachopoulos, C.; Iosifidis, E.; Tsakris, A.; Roilides, E. Molecular epidemiology of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in Greece. Future Microbiol. 2016, 11, 809–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Ucha, J.C.; Arca-Suárez, J.; Bou, G.; Beceiro, A. New Carbapenemase Inhibitors: Clearing the Way for the β-Lactams. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, M.P.; Oshiro, I.C.; Pierrotti, L.C.; Bonazzi, P.R.; de Oliveira, L.M.; Song, A.T.; Camargo, C.H.; van der Heijden, I.M.; Rossi, F.; Costa, S.F.; et al. Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae Acquired Before Liver Transplantation: Impact on Recipient Outcomes. Transplantation 2017, 101, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConville, T.H.; Sullivan, S.B.; Gomez-Simmonds, A.; Whittier, S.; Uhlemann, A.-C. Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae colonization (CRE) and subsequent risk of infection and 90-day mortality in critically ill patients, an observational study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girmenia, C.; Bertaina, A.; Piciocchi, A.; Perruccio, K.; Algarotti, A.; Busca, A.; Cattaneo, C.; Raiola, A.M.; Guidi, S.; Iori, A.P.; et al. Incidence, Risk Factors and Outcome of Pre-engraftment Gram-Negative Bacteremia After Allogeneic and Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: An Italian Prospective Multicenter Survey. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, 1884–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannella, M.; Trecarichi, E.; De Rosa, F.G.; Del Bono, V.; Bassetti, M.; Lewis, R.; Losito, A.R.; Corcione, S.; Saffioti, C.; Bartoletti, M.; et al. Risk factors for carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae bloodstream infection among rectal carriers: A prospective observational multicentre study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 1357–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Xiao, M.; Hou, R.; Wang, D.; Yang, M.; Chen, M.; Chen, L. Bundles of care for prevention of ventilator-associated pneumonia caused by carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in the ICU. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 3561–3572. [Google Scholar]
- Vidal-Cortés, P.; Martin-Loeches, I.; Rodríguez, A.; Bou, G.; Cantón, R.; Diaz, E.; De la Fuente, C.; Torre-Cisneros, J.; Nuvials, F.X.; Salavert, M.; et al. Current Positioning against Severe Infections Due to Klebsiella pneumoniae in Hospitalized Adults. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyres, K.L.; Lam, M.M.C.; Holt, K.E. Population genomics of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 344–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baquero, F.; Coque, T.M. Multilevel population genetics in antibiotic resistance. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 35, 705–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.; Huang, X.; Wang, Q.; Yao, D.; Lu, W. Virulence Factors of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa and Antivirulence Strategies to Combat Its Drug Resistance. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 926758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Estrada, S.; Borgatta, B.; Rello, J. Pseudomonas aeruginosa ventilator-associated pneumonia management. Infect. Drug Resist. 2016, 9, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovagnorio, F.; De Vito, A.; Madeddu, G.; Parisi, S.G.; Geremia, N. Resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A Narrative Review of Antibiogram Interpretation and Emerging Treatments. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachori, P.; Gothalwal, R.; Gandhi, P. Emergence of antibiotic resistance Pseudomonas aeruginosa in intensive care unit; a critical review. Genes. Dis. 2019, 6, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarowska, J.; Futoma-Koloch, B.; Jama-Kmiecik, A.; Frej-Madrzak, M.; Ksiazczyk, M.; Bugla-Ploskonska, G.; Choroszy-Krol, I. Virulence factors, prevalence and potential transmission of extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from different sources: Recent reports. Gut Pathog. 2019, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, R.A.; Baomo, L.; Doughty, E.L.; Guo, Y.; Ba, X.; van Schaik, W.; Zhuo, C.; McNally, A. Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase Genes Traverse the Escherichia coli Populations of Intensive Care Unit Patients, Staff, and Environment. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0507422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oogai, Y.; Matsuo, M.; Hashimoto, M.; Kato, F.; Sugai, M.; Komatsuzawa, H. Expression of virulence factors by Staphylococcus aureus grown in serum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 8097–8105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laabei, M.; Recker, M.; Rudkin, J.K.; Aldeljawi, M.; Gulay, Z.; Sloan, T.J.; Williams, P.; Endres, J.L.; Bayles, K.W.; Fey, P.D.; et al. Predicting the virulence of MRSA from its genome sequence. Genome Res. 2014, 24, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, G.Y.C.; Bae, J.S.; Otto, M. Pathogenicity and virulence of Staphylococcus aureus. Virulence 2021, 12, 547–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampedro, G.R.; Bubeck Wardenburg, J. Staphylococcus aureus in the Intensive Care Unit: Are These Golden Grapes Ripe for a New Approach? J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, S64–S70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulcahy, M.E.; McLoughlin, R.M. Host-Bacterial Crosstalk Determines Staphylococcus aureus Nasal Colonization. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 872–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, R.; Subramani, K.; Thomas, A.N.; Chadwick, P. Nasal carriage of Staphylococcus aureus on admission to intensive care: Incidence and prognostic significance. Intensive Care Med. 2003, 29, 655–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senn, L.; Clerc, O.; Zanetti, G.; Basset, P.; Prod’hom, G.; Gordon, N.C.; Sheppard, A.E.; Crook, D.W.; James, R.; Thorpe, H.A.; et al. The Stealthy Superbug: The Role of Asymptomatic Enteric Carriage in Maintaining a Long-Term Hospital Outbreak of ST228 Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. mBio 2016, 7, e02039-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Belkum, A. Hidden Staphylococcus aureus Carriage: Overrated or Underappreciated? mBio 2016, 7, e00079-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bihan, C.; Zahar, J.R.; Timsit, J.F. Staphylococcus aureus transmission in the intensive care unit: The potential role of the healthcare worker carriage. Ann. Infect. 2017, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muto, C.A.; Jernigan, J.A.; Ostrowsky, B.E.; Richet, H.M.; Jarvis, W.R.; Boyce, J.M.; Farr, B.M. SHEA guideline for preventing nosocomial transmission of multidrug-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2003, 24, 362–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widmer, A.F.; Lakatos, B.; Frei, R. Strict infection control leads to low incidence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infection over 20 years. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2015, 36, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovich, K.J.; Aureden, K.; Ham, D.C.; Harris, A.D.; Hessels, A.J.; Huang, S.S.; Maragakis, L.L.; Milstone, A.M.; Moody, J.; Yokoe, D.; et al. SHEA/IDSA/APIC Practice Recommendation: Strategies to prevent methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus transmission and infection in acute-care hospitals: 2022 Update. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2023, 44, 1039–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraldes, C.; Tavares, L.; Gil, S.; Oliveira, M. Enterococcus Virulence and Resistant Traits Associated with Its Permanence in the Hospital Environment. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillay, S.; Zishiri, O.T.; Adeleke, M.A. Prevalence of virulence genes in Enterococcus species isolated from companion animals and livestock. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2018, 85, e1–e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falgenhauer, L.; Preuser, I.; Imirzalioglu, C.; Falgenhauer, J.; Fritzenwanker, M.; Mack, D.; Best, C.; Heudorf, U.; Chakraborty, T. Changing epidemiology of vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium: Results of a genome-based study at a regional neurological acute hospital with intensive care and early rehabilitation treatment. Infect. Prev. Pract. 2021, 3, 100138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marom, R.; Mandel, D.; Haham, A.; Berger, I.; Ovental, A.; Raskind, C.; Grisaru-Soen, G.; Adler, A.; Lellouche, J.; Schwartz, D.; et al. A silent outbreak of vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium in a neonatal intensive care unit. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2020, 9, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, S.; Shallal, A.; Zervos, M. Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci: Epidemiology, Infection Prevention, and Control. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 35, 953–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bijlsma, M.W.; Brouwer, M.C.; Kasanmoentalib, E.S.; Kloek, A.T.; Lucas, M.J.; Tanck, M.W.; van der Ende, A.; van de Beek, D. Community-acquired bacterial meningitis in adults in the Netherlands, 2006–2014: A prospective cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 339–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auburtin, M.; Wolff, M.; Charpentier, J.; Varon, E.; Le Tulzo, Y.; Girault, C.; Mohammedi, I.; Renard, B.; Mourvillier, B.; Bruneel, F.; et al. Detrimental role of delayed antibiotic administration and penicillin-nonsusceptible strains in adult intensive care unit patients with pneumococcal meningitis: The PNEUMOREA prospective multicenter study. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 34, 2758–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdem, H.; Elaldi, N.; Öztoprak, N.; Sengoz, G.; Ak, O.; Kaya, S.; Inan, A.; Nayman-Alpat, S.; Ulu-Kilic, A.; Pekok, A.U.; et al. Mortality indicators in pneumococcal meningitis: Therapeutic implications. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 19, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Auburtin, M.; Porcher, R.; Bruneel, F.; Scanvic, A.; Trouillet, J.L.; Bédos, J.P.; Regnier, B.; Wolff, M. Pneumococcal meningitis in the intensive care unit: Prognostic factors of clinical outcome in a series of 80 cases. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 713–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Beek, D.; Brouwer, M.; Hasbun, R.; Koedel, U.; Whitney, C.G.; Wijdicks, E. Community-acquired bacterial meningitis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2016, 3, 16074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Cerezuela, M.; Aseginolaza-Lizarazu, M.; Boronat-García, P.; Asensio-Martín, M.J.; Alamán-Laguarda, G.; Álvarez-Lerma, F.; Roa-Alonso, D.; Socias, L.; Vera-Artázcoz, P.; Ramírez-Galleymore, P.; et al. Severe community-acquired Streptococcus pneumoniae bacterial meningitis: Clinical and prognostic picture from the intensive care unit. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiser, J.N.; Ferreira, D.M.; Paton, J.C. Streptococcus pneumoniae: Transmission, colonization and invasion. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.M.; Mitchell, T.J. Streptococcus pneumoniae: Virulence factors and variation. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2010, 16, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquart, M.E. Pathogenicity and virulence of Streptococcus pneumoniae: Cutting to the chase on proteases. Virulence 2021, 12, 766–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prechter, F.; Katzer, K.; Bauer, M.; Stallmach, A. Sleeping with the enemy: Clostridium difficile infection in the intensive care unit. Crit. Care 2017, 21, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/sites/default/files/documents/AER_for_2018_IPD.pdf (accessed on 5 February 2024).
- Arac, E.; Kaya, S.; Parlak, E.; Büyüktuna, S.; Baran, A.; Akgul, F.; Gökler, M.; Aksoz, S.; Sagmak Tartar, A.; Tekin, R.; et al. Evaluation of Infections in Intensive Care Units: A Multicentre Point-Prevalence Study. Mikrobiyoloji Bul. 2019, 53, 364–373. (In Turkish) [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett, J.G.; Dowell, S.F.; Mandell, L.A.; File, T.M., Jr.; Musher, D.M.; Fine, M.J. Practice guidelines for the management of community-acquired pneumonia in adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2000, 31, 347–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ombelet, S.; Barbé, B.; Affolabi, D.; Ronat, J.B.; Lompo, P.; Lunguya, O.; Jacobs, J.; Hardy, L. Best Practices of Blood Cultures in Low- and Middle-Income Countries. Front. Med. 2019, 6, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austin, B. The value of cultures to modern microbiology. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 2017, 110, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornaglia, G.; Courcol, R.; Herrmann, J.L.; Kahlmeter, G.; Lafeuille, H.P.; Vila, J. Europe—An Manual of Clinical Microbiology. Prima Edizione. Basilea: ESCMID. 2012. Available online: https://markterfolg.de/ESCMID/European_Manual_CM_2012/?#page=6 (accessed on 6 February 2024).
- Jin, W.Y.; Jang, S.J.; Lee, M.J.; Park, G.; Kim, M.J.; Kook, J.K.; Kim, D.M.; Moon, D.S.; Park, Y.J. Evaluation of VITEK 2, MicroScan, and Phoenix for identification of clinical isolates and reference strains. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 70, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchida, S.; Umemura, H.; Nakayama, T. Current Status of Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization-Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) in Clinical Diagnostic Microbiology. Molecules 2020, 25, 4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paggi, R.; Cenci, E.; De Socio, G.V.; Belati, A.; Marini, D.; Gili, A.; Camilloni, B.; Mencacci, A. Accuracy and Impact on Patient Management of New Tools for Diagnosis of Sepsis: Experience with the T2 Magnetic Resonance Bacteria Panel. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, G.; Posteraro, B.; De Carolis, E.; Menchinelli, G.; Franceschi, F.; Tumbarello, M.; De Pascale, G.; Spanu, T.; Sanguinetti, M. T2Bacteria magnetic resonance assay for the rapid detection of ESKAPEc pathogens directly in whole blood. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, iv20–iv26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tansarli, G.S.; Chapin, K.C. Diagnostic test accuracy of the BioFire® FilmArray® meningitis/encephalitis panel: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.S.; Tsai, C.L.; Chang, J.; Hsu, T.C.; Lin, S.; Lee, C.C. Multiplex PCR system for the rapid diagnosis of respiratory virus infection: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krifors, A.; Rådberg, G.; Golbob, S.; Omar, Z.; Svensson, C.; Heimer, D.; Carlander, C. The clinical impact of implementing GenMark ePlex blood culture panels for around-the-clock blood culture identification; a prospective observational study. Infect Dis. 2020, 52, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginocchio, C.C.; Garcia-Mondragon, C.; Mauerhofer, B.; Rindlisbacher, C. BioFire® FilmArray® Pneumonia plus Panel as compared to standard of care testing. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 40, 1609–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.N.; Fowler, R.; Balada-Llasat, J.M.; Carroll, A.; Stone, H.; Akerele, O.; Buchan, B.; Windham, S.; Hopp, A.; Ronen, S.; et al. Multicenter Evaluation of the BioFire FilmArray Pneumonia/Pneumonia Plus Panel for Detection and Quantification of Agents of Lower Respiratory Tract Infection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e00128-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webber, D.M.; Wallace, M.A.; Burnham, C.A.D.; Anderson, N.W. Evaluation of the BioFire FilmArray Pneumonia Panel for Detection of Viral and Bacterial Pathogens in Lower Respiratory Tract Specimens in the Setting of a Tertiary Care Academic Medical Center. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e00343-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUCAST. Rapid AST Directly from Blood Culture Bottles. 2022. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/rapid_ast_in_blood_cultures/ (accessed on 5 February 2024).
- Soo, Y.T.; Waled, S.N.M.B.; Ng, S.; Peh, Y.H.; Chew, K.L. Evaluation of EUCAST rapid antimicrobial susceptibility testing (RAST) directly from blood culture bottles. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 39, 993–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungphakorn, W.; Lagerbäck, P.; Nielsen, E.I.; Tängdén, T. Automated time-lapse microscopy a novel method for screening of antibiotic combination effects against multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 778.e7–778.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marschal, M.; Bachmaier, J.; Autenrieth, I.; Oberhettinger, P.; Willmann, M.; Peter, S. Evaluation of the Accelerate Pheno System for Fast Identification and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing from Positive Blood Cultures in Bloodstream Infections Caused by Gram-Negative Pathogens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 2116–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tibbetts, R.; George, S.; Burwell, R.; Rajeev, L.; Rhodes, P.A.; Singh, P.; Samuel, L. Performance of the Reveal Rapid Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing System on Gram-Negative Blood Cultures at a Large Urban Hospital. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2022, 60, e0009822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.P.; Kirby, J.E. Rapid Susceptibility Testing Methods. Clin. Lab. Med. 2019, 39, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migliorisi, G.; Calvo, M.; Collura, A.; Di Bernardo, F.; Perez, M.; Scalia, G.; Stefani, S. The Rapid Phenotypic Susceptibility Testing in Real-Life Experience: How the MIC Values Impact on Sepsis Fast Diagnostic Workflow. Diagnostics 2023, 14, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamy, B.; Sundqvist, M.; Idelevich, E.A.; ESCMID Study Group for Bloodstream Infections, Endocarditis and Sepsis (ESGBIES). Bloodstream infections-Standard and progress in pathogen diagnostics. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak-Weekley, S.M.; Khine, A.A.; Alavie, T.; Fernandez, N.; Pandey, L.; Talebpour, A. 660 Evaluation of Qvella’s FAST-PrepTM Liquid ColonyTM for Early Antimicrobial Sensitivity Testing of Positive Blood Culture by Disk Diffusion Method. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2020, 7, S386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddalena, C.; Giuseppe, M.; Perez, M.; Guido, S.; Stefania, S. Evaluation of the liquid colony for identification and antimicrobial susceptibility testing directly from positive blood cultures. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2023, 22, 78, Erratum in Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2023, 22, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyton, L.P.A.; Langelier, C.R.; Calfee, C.S. Metagenomic Sequencing in the ICU for Precision Diagnosis of Critical Infectious Illnesses. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutal, H.; Moguet, C.; Pommiès, L.; Simon, S.; Naas, T.; Volland, H. The Revolution of Lateral Flow Assay in the Field of AMR Detection. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanford, E.F.; Clark, M.M.; Farnaes, L.; Williams, M.R.; Perry, J.C.; Ingulli, E.G.; Sweeney, N.M.; Doshi, A.; Gold, J.J.; Briggs, B.; et al. Rapid Whole Genome Sequencing Has Clinical Utility in Children in the PICU. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 20, 1007–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, M.A.; Al-Amin, M.Y.; Pawar, J.S.; Akhter, N.; Lucy, I.B. Conventional methods and future trends in antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 30, 103582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satam, H.; Joshi, K.; Mangrolia, U.; Waghoo, S.; Zaidi, G.; Rawool, S.; Thakare, R.P.; Banday, S.; Mishra, A.K.; Das, G.; et al. Next-Generation Sequencing Technology: Current Trends and Advancements. Biology 2023, 12, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortegiani, A.; Antonelli, M.; Falcone, M.; Giarratano, A.; Girardis, M.; Leone, M.; Pea, F.; Stefani, S.; Viaggi, B.; Viale, P. Rationale and clinical application of antimicrobial stewardship principles in the intensive care unit: A multidisciplinary statement. J. Anesth. Analg. Crit. Care 2023, 3, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokrani, D.; Chommeloux, J.; Pineton de Chambrun, M.; Hékimian, G.; Luyt, C.E. Antibiotic stewardship in the ICU: Time to shift into overdrive. Ann. Intensive Care 2023, 13, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).