Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella Species and Their Mobile Genetic Elements from Poultry Farm Environments in Malaysia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Antimicrobial Resistance
2.2. Whole-Genome Sequencing (WGS)
2.3. Sequence Types (STs) and Serovar Prediction
2.4. Antibiotics Resistance Genes (ARGs)
2.5. Chromosomal Point Mutation
2.6. Plasmid Multi-Locus Sequence Typing (pMLST)
2.7. Mobile Genetic Elements (MGEs) and Salmonella Pathogenic Island (SPI)
2.8. Integron
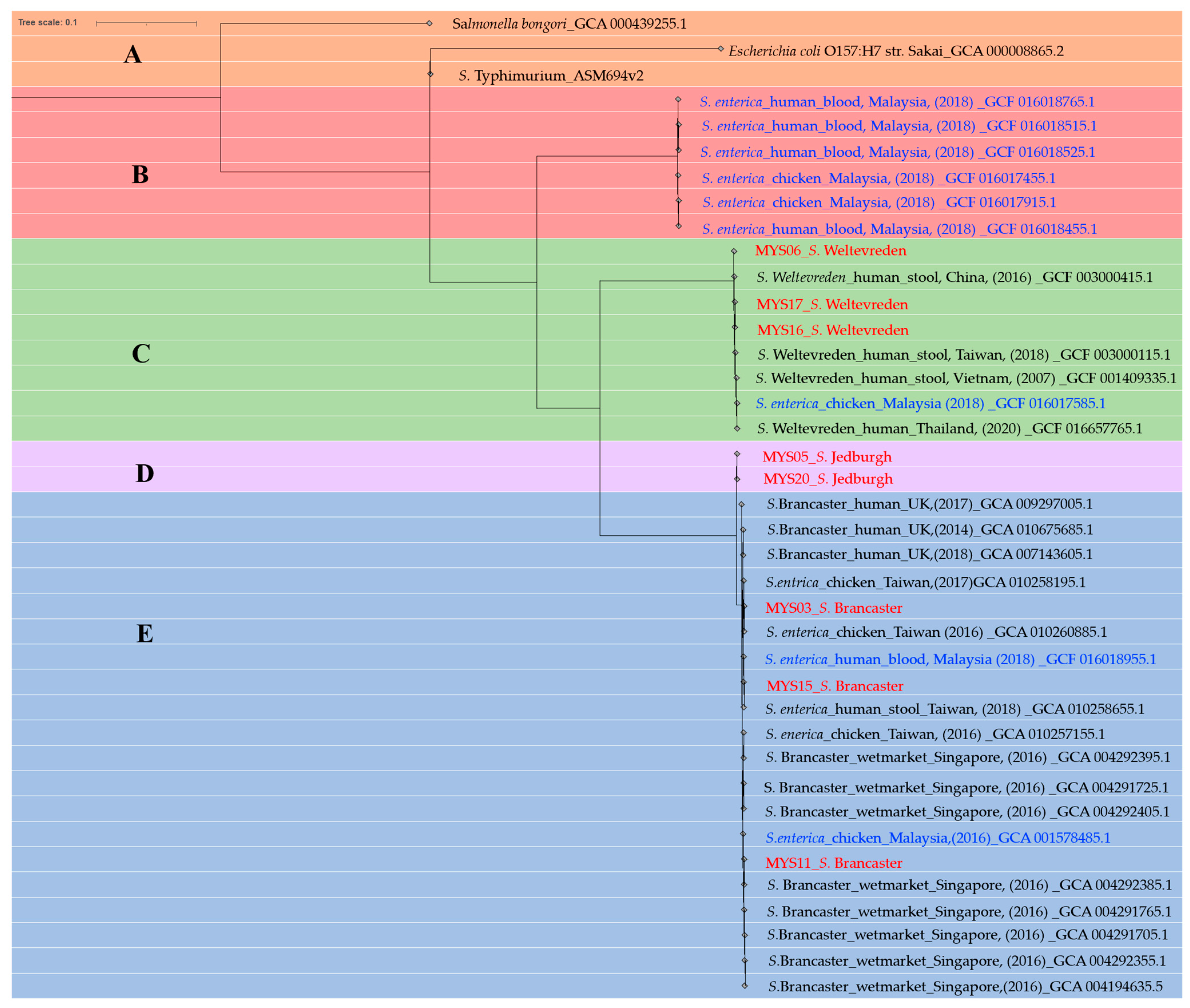
2.9. Phylogenetic Tree
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Location of Sampling
4.2. Enrichment and Isolation of Presumptive Salmonella
4.3. Identification and Susceptibility of Salmonella spp.
4.4. DNA Extraction and Whole Genome Sequencing of Salmonella spp.
4.5. Bioinformatics Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analysis
4.7. Multiple Antibiotic Resistance Index (MAR Index)
5. Conclusions
6. GenBank Accession Numbers
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ashurst, J.V.; Truong, J.; Woodbury, B. Salmonella Typhi. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Giannella, R.A. Salmonella. In Medical Microbiology; Baron, S., Ed.; University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston: Galveston, TX, USA, 1996; Chapter 21; ISBN 978-0-9631172-1-2. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, M.A. Invasive Nontyphoidal Salmonella Disease: Epidemiology, Pathogenesis and Diagnosis. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 24, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanaway, J.D.; Parisi, A.; Sarkar, K.; Blacker, B.F.; Reiner, R.C.; Hay, S.I.; Nixon, M.R.; Dolecek, C.; James, S.L.; Mokdad, A.H.; et al. The Global Burden of Non-Typhoidal Salmonella Invasive Disease: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 1312–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmonella (Non-Typhoidal). Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/salmonella-(non-typhoidal) (accessed on 13 September 2022).
- Salmonella: Causes, Symptoms, Complications, Treatment, and Prevention. Available online: https://www.webmd.com/food-recipes/food-poisoning/what-is-salmonella (accessed on 31 January 2023).
- Dhanoa, A.; Fatt, Q.K. Non-Typhoidal Salmonella Bacteraemia: Epidemiology, Clinical Characteristics and Its’ Association with Severe Immunosuppression. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2009, 8, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, M.A.; Banda, H.T.; Gondwe, M.; Gordon, S.B.; Boeree, M.J.; Walsh, A.L.; Corkill, J.E.; Hart, C.A.; Gilks, C.F.; Molyneux, M.E. Non-Typhoidal Salmonella Bacteraemia among HIV-Infected Malawian Adults: High Mortality and Frequent Recrudescence. AIDS 2002, 16, 1633–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Vargas, R.E.; Herrera-Sánchez, M.P.; Rodríguez-Hernández, R.; Rondón-Barragán, I.S. Antibiotic Resistance in Salmonella spp. Isolated from Poultry: A Global Overview. Vet. World 2020, 13, 2070–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuah, L.-O.; Shamila Syuhada, A.-K.; Mohamad Suhaimi, I.; Farah Hanim, T.; Rusul, G. Genetic Relatedness, Antimicrobial Resistance and Biofilm Formation of Salmonella Isolated from Naturally Contaminated Poultry and Their Processing Environment in Northern Malaysia. Food Res. Int. 2018, 105, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallinga, D.; Smit, L.A.M.; Davis, M.F.; Casey, J.A.; Nachman, K.E. A Review of the Effectiveness of Current US Policies on Antimicrobial Use in Meat and Poultry Production. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2022, 9, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Wei, X.; Yin, J.; Haley, D.R.; Sun, Q.; Lundborg, C.S. Interventions to Optimize the Use of Antibiotics in China: A Scoping Review of Evidence from Humans, Animals, and the Environment from a One Health Perspective. One Health 2022, 14, 100388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales of Veterinary Antimicrobial Agents in 31 European Countries in 2021. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/report/sales-veterinary-antimicrobial-agents-31-european-countries-2021-trends-2010-2021-twelfth-esvac_en.pdf (accessed on 24 May 2023).
- Mulchandani, R.; Wang, Y.; Gilbert, M.; Boeckel, T.P.V. Global Trends in Antimicrobial Use in Food-Producing Animals: 2020 to 2030. PLoS Glob. Public Health 2023, 3, e0001305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanner, S.; Drissner, D.; Walsh, F. Antimicrobial Resistance in Agriculture. mBio 2016, 7, e02227-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, L.S.; Leplae, R.; Summers, A.O.; Toussaint, A. Mobile Genetic Elements: The Agents of Open Source Evolution. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 722–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruden, A.; Larsson, D.G.J.; Amézquita, A.; Collignon, P.; Brandt, K.K.; Graham, D.W.; Lazorchak, J.M.; Suzuki, S.; Silley, P.; Snape, J.R.; et al. Management Options for Reducing the Release of Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance Genes to the Environment. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 878–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argudín, M.A.; Deplano, A.; Meghraoui, A.; Dodémont, M.; Heinrichs, A.; Denis, O.; Nonhoff, C.; Roisin, S. Bacteria from Animals as a Pool of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes. Antibiotics 2017, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, A.; Munusamy, C.; Tan, Y.-C.; Muthuvelu, S.; Hashim, R.; Chien, S.-L.; Wong, M.-K.; Khairuddin, N.A.; Podin, Y.; Lau, P.S.-T.; et al. Invasive Salmonella Infections among Children in Bintulu, Sarawak, Malaysian Borneo: A 6-Year Retrospective Review. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nor Azizah, A.; Fadzilah, M.N.; Mariam, M.; Anis Siham, Z.A.; Ariza, A.; Noor Shafina, M.N.; Anita Kaur, A. Community-Acquired Bacteremia in Paediatrics: Epidemiology, Aetiology and Patterns of Antimicrobial Resistance in a Tertiary Care Centre, Malaysia. Med. J. Malays. 2016, 71, 117–121. [Google Scholar]
- NSAR-2021. Available online: https://imr.nih.gov.my/MyOHAR/index.php/site/archive_rpt (accessed on 17 July 2023).
- Prevalence of Salmonella spp. in Chicken and Beef from Retail Outlets in Malaysia—ProQuest. Available online: https://www.proquest.com/openview/3d23c28c1b96152778329066346a58ac/1?pq-origsite=gscholar&cbl=816390 (accessed on 24 May 2023).
- Haslinda, W.H.; Tang, J.Y.H.; Tuan Zainazor, T.C. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Non-Typhoidal Salmonella (NTS) from Salad Vegetables at Farms and Retail Markets in Terengganu, Malaysia. Food Res. 2022, 6, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den Bakker, H.C.; Allard, M.W.; Bopp, D.; Brown, E.W.; Fontana, J.; Iqbal, Z.; Kinney, A.; Limberger, R.; Musser, K.A.; Shudt, M.; et al. Rapid Whole-Genome Sequencing for Surveillance of Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. J. 2014, 20, 1306–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, N.; Feng, Y.; Pan, Y.; Huang, H.; Liu, Y.; Xue, C.; Zhu, B.; Hu, Y. Genomic Characterization of Salmonella enterica Isolates from Retail Meat in Beijing, China. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 636332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiorakos, A.-P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-Resistant, Extensively Drug-Resistant and Pandrug-Resistant Bacteria: An International Expert Proposal for Interim Standard Definitions for Acquired Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitanand, M.P.; Kadam, T.A.; Gyananath, G.; Totewad, N.D.; Balhal, D.K. Multiple Antibiotic Resistance Indexing of Coliforms to Identify High Risk Contamination Sites in Aquatic Environment. Indian J. Microbiol. 2010, 50, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afunwa, R.A.; Ezeanyinka, J.; Afunwa, E.C.; Udeh, A.S.; Oli, A.N.; Unachukwu, M. Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Index of Gram-Negative Bacteria from Bird Droppings in Two Commercial Poultries in Enugu, Nigeria. Open J. Med. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, C.E.; Kruczkiewicz, P.; Laing, C.R.; Lingohr, E.J.; Gannon, V.P.J.; Nash, J.H.E.; Taboada, E.N. The Salmonella In Silico Typing Resource (SISTR): An Open Web-Accessible Tool for Rapidly Typing and Subtyping Draft Salmonella Genome Assemblies. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; den Bakker, H.C.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Dinsmore, B.A.; Lane, C.; Lauer, A.C.; Fields, P.I.; Deng, X. SeqSero2: Rapid and Improved Salmonella Serotype Determination Using Whole-Genome Sequencing Data. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e01746-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Minor, L.; Popoff, M.Y. Designation of Salmonella enterica sp. Nov., Nom. Rev., as the Type and Only Species of the Genus Salmonella: Request for an Opinion. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1987, 37, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.K.; Padmanabhan, B.R.; Diene, S.M.; Lopez-Rojas, R.; Kempf, M.; Landraud, L.; Rolain, J.-M. ARG-ANNOT, a New Bioinformatic Tool To Discover Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Bacterial Genomes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolaia, V.; Kaas, R.S.; Ruppe, E.; Roberts, M.C.; Schwarz, S.; Cattoir, V.; Philippon, A.; Allesoe, R.L.; Rebelo, A.R.; Florensa, A.F.; et al. ResFinder 4.0 for Predictions of Phenotypes from Genotypes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 3491–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, J.; Pons, M.J.; Mosquito, S.; Ochoa, T.J.; Sáenz, Y. Characterization of Escherichia coli D7111 producing the β-LACTAMASE TEM-176. Rev. Peru. Med. Exp. Salud Publica 2021, 38, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamma, P.D.; Doi, Y.; Bonomo, R.A.; Johnson, J.K.; Simner, P.J. Antibacterial Resistance Leadership Group A Primer on AmpC β-Lactamases: Necessary Knowledge for an Increasingly Multidrug-Resistant World. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 69, 1446–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akinyemi, K.; Iwalokun, B.A.; Oyefolu, A.O.B.; Fakorede, C. Occurrence of Extended-Spectrum and AmpC β-Lactamases in Multiple Drug Resistant Salmonella Isolates from Clinical Samples in Lagos, Nigeria. Infect. Drug. Resist. 2017, 10, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazel, D. Integrons: Agents of Bacterial Evolution. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pightling, A.W.; Pettengill, J.B.; Luo, Y.; Baugher, J.D.; Rand, H.; Strain, E. Interpreting Whole-Genome Sequence Analyses of Foodborne Bacteria for Regulatory Applications and Outbreak Investigations. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.Y.; Elmi, S.A.; Simons, D.; Elton, L.; Haider, N.; Khan, M.A.; Othman, I.; Zumla, A.; McCoy, D.; Kock, R. Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns and Risk Factors Associated with Salmonella spp. Isolates from Poultry Farms in the East Coast of Peninsular Malaysia: A Cross-Sectional Study. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidaullah, H.; Abirami, N.; Shamila-Syuhada, A.K.; Chuah, L.-O.; Nurul, H.; Tan, T.P.; Abidin, F.W.Z.; Rusul, G. Prevalence of Salmonella in Poultry Processing Environments in Wet Markets in Penang and Perlis, Malaysia. Vet. World 2017, 10, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abatcha, M.G.; Effarizah, M.E.; Rusul, G. Prevalence, antimicrobial resistance, resistance genes and class 1 integrons of Salmonella serovars in leafy vegetables, chicken carcasses and related processing environments in Malaysian fresh food markets. Food Control 2018, 91, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.; Wei Hoong, L.; Lai Siong, Y.; Mustapha, Z.; CW Zalati, C.S.; Aklilu, E.; Mohamad, M.; Kamaruzzaman, N.F. Prevalence of Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) Salmonella spp. and Escherichia coli Isolated from Broilers in the East Coast of Peninsular Malaysia. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trongjit, S.; Angkititrakul, S.; Tuttle, R.E.; Poungseree, J.; Padungtod, P.; Chuanchuen, R. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance in Salmonella enterica Isolated from Broiler Chickens, Pigs and Meat Products in Thailand–Cambodia Border Provinces. Microbiol. Immunol. 2017, 61, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwe, Y.H.; Tang, V.C.Y.; Aung, K.T.; Gutiérrez, R.A.; Ng, L.C.; Yuk, H.-G. Prevalence, Sequence Types, Antibiotic Resistance and, GyrA Mutations of Salmonella Isolated from Retail Fresh Chicken Meat in Singapore. Food Control 2018, 90, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, Y.T.; Nguyen, T.T.; To, P.B.; Pham, D.X.; Le, H.T.H.; Thi, G.N.; Alali, W.Q.; Walls, I.; Doyle, M.P. Quantification, Serovars, and Antibiotic Resistance of Salmonella Isolated from Retail Raw Chicken Meat in Vietnam. J. Food Prot. 2014, 77, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jajere, S.M.; Hassan, L.; Abdul Aziz, S.; Zakaria, Z.; Abu, J.; Nordin, F.; Faiz, N.M. Salmonella in Native “Village” Chickens (Gallus Domesticus): Prevalence and Risk Factors from Farms in South-Central Peninsular Malaysia. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 5961–5970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aung, K.T.; Khor, W.C.; Octavia, S.; Ye, A.; Leo, J.; Chan, P.P.; Lim, G.; Wong, W.K.; Tan, B.Z.Y.; Schlundt, J.; et al. Distribution of Salmonella Serovars in Humans, Foods, Farm Animals and Environment, Companion and Wildlife Animals in Singapore. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trung, N.V.; Carrique-Mas, J.J.; Nghia, N.H.; Tu, L.T.P.; Mai, H.H.; Tuyen, H.T.; Campbell, J.; Nhung, N.T.; Nhung, H.N.; Minh, P.V.; et al. Non-Typhoidal Salmonella Colonization in Chickens and Humans in the Mekong Delta of Vietnam. Zoonoses Public Health 2017, 64, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thong, K.L.; Goh, Y.L.; Radu, S.; Noorzaleha, S.; Yasin, R.; Koh, Y.T.; Lim, V.K.E.; Rusul, G.; Puthucheary, S.D. Genetic Diversity of Clinical and Environmental Strains of Salmonella enterica Serotype Weltevreden Isolated in Malaysia. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 2498–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thong, K.L.; Ngoi, S.T.; Chai, L.C.; Teh, C.S.J. Quinolone Resistance Mechanisms Among Salmonella enterica in Malaysia. Microb. Drug. Resist. 2016, 22, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thong, K.L. Surveillance and Subtyping of Salmonella spp. in Malaysia. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bangtrakulnonth, A.; Pornreongwong, S.; Pulsrikarn, C.; Sawanpanyalert, P.; Hendriksen, R.S.; Wong, D.M.A.L.F.; Aarestrup, F.M. Salmonella Serovars from Humans and Other Sources in Thailand, 1993–2002. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Gao, Y.; Ye, C.; Yang, L.; Wang, T.; Chang, W. Prevalence and Characteristics of Salmonella Isolated from Free-Range Chickens in Shandong Province, China. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, e8183931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Gao, S.; Chang, Y.; Su, M.; Xie, Y.; Sun, S. Occurrence and Characterization of Salmonella Isolated from Large-Scale Breeder Farms in Shandong Province, China. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, e8159567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, J.; Shao, X.; Huang, P.; Zha, J.; Ye, Y. Occurrence and Antimicrobial Resistance of Salmonella Isolated from Retail Meats in Anhui, China. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 4701–4710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.K.; Nguyen, L.T.; Chau, T.T.H.; Nguyen, T.T.; Tran, B.N.; Taniguchi, T.; Hayashidani, H.; Ly, K.T.L. Prevalence and Antibiotic Resistance of Salmonella Isolated from Poultry and Its Environment in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Vet. World 2021, 14, 3216–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkenany, R.M.; Eladl, A.H.; El-Shafei, R.A. Genetic Characterisation of Class 1 Integrons among Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella Serotypes in Broiler Chicken Farms. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2018, 14, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belachew, T.; Mulusew, E.; Tolosa, Y.; Asefa, Z.; Negussie, H.; Sori, T. Prevalence and Antimicrobial-Susceptibility Profiles of Salmonella in Smallhold Broiler Supply Chains in Central Ethiopia. IDR 2021, 14, 4047–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, Z.; Hassan, L.; Ahmad, N.; Husin, S.A.; Ali, R.M.; Sharif, Z.; Sohaimi, N.M.; Garba, B. Discerning the Antimicrobial Resistance, Virulence, and Phylogenetic Relatedness of Salmonella Isolates Across the Human, Poultry, and Food Materials Sources in Malaysia. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 652642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, L.; Zhao, J.; Gan, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Cui, S.; Xia, S.; Hu, Y.; Yan, S.; Wang, J.; et al. Emergence and Diversity of Salmonella enterica Serovar Indiana Isolates with Concurrent Resistance to Ciprofloxacin and Cefotaxime from Patients and Food-Producing Animals in China. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 3365–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, M.B.; Hossain, S.M.B.; Hasan, M.; Alam, M.N.; Debnath, M.; Begum, R.; Roy, S.; Harun-Al-Rashid, A.; Chowdhury, M.S.R.; Rahman, M.M.; et al. Multidrug Antimicrobial Resistance and Molecular Detection of Mcr-1 Gene in Salmonella Species Isolated from Chicken. Animals 2021, 11, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, P.; Nandy, S.; Bharadwaj, R.; Niyogi, S.K.; Dutta, S. Salmonella Enterica Serovar Weltevreden ST1500 Associated Foodborne Outbreak in Pune, India. Indian. J. Med. Res. 2015, 141, 239–241. [Google Scholar]
- Hounmanou, Y.M.G.; Dalsgaard, A.; Sopacua, T.F.; Uddin, G.M.N.; Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Hendriksen, R.S.; Olsen, J.E.; Larsen, M.H. Molecular Characteristics and Zoonotic Potential of Salmonella Weltevreden From Cultured Shrimp and Tilapia in Vietnam and China. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Peng, Z.; Chen, K.; Zhan, Z.; Shen, H.; Feng, S.; Gou, H.; Qu, X.; Ziemann, M.; Layton, D.S.; et al. Genomic Characterization of Salmonella enterica Serovar Weltevreden Associated with Human Diarrhea. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e03542-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassali, M.A.; Yann, H.R.; Verma, A.K.; Hussain, R.; Sivaraman, S. Antibiotic Use in Food Animals: Malaysia Overview; Universiti Sains Malaysia: Gelugor, Malaysia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Veterinary Dept Will Ban Six Antibiotics on Livestock on Aug 31. Available online: https://www.thesundaily.my/local/veterinary-dept-will-ban-six-antibiotics-on-livestock-on-aug-31-XL1926743 (accessed on 29 September 2022).
- Abd El-Aziz, N.K.; Tartor, Y.H.; Gharieb, R.M.A.; Erfan, A.M.; Khalifa, E.; Said, M.A.; Ammar, A.M.; Samir, M. Extensive Drug-Resistant Salmonella enterica Isolated From Poultry and Humans: Prevalence and Molecular Determinants Behind the Co-Resistance to Ciprofloxacin and Tigecycline. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.J.; Bielak, E.M.; Fortini, D.; Hansen, L.H.; Hasman, H.; Debroy, C.; Nolan, L.K.; Carattoli, A. Expansion of the IncX Plasmid Family for Improved Identification and Typing of Novel Plasmids in Drug-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Plasmid 2012, 68, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassis-Chikhani, N.; Frangeul, L.; Drieux, L.; Sengelin, C.; Jarlier, V.; Brisse, S.; Arlet, G.; Decré, D. Complete Nucleotide Sequence of the First KPC-2- and SHV-12-Encoding IncX Plasmid, PKpS90, from Klebsiella Pneumoniae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 618–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobiasova, H.; Dolejska, M. Prevalence and Diversity of IncX Plasmids Carrying Fluoroquinolone and β-Lactam Resistance Genes in Escherichia Coli Originating from Diverse Sources and Geographical Areas. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 2118–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basic Principles of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy—ClinicalKey. Available online: https://www.clinicalkey.com/#!/content/book/3-s2.0-B9780702074486000512 (accessed on 3 February 2023).
- Lou, L.; Zhang, P.; Piao, R.; Wang, Y. Salmonella Pathogenicity Island 1 (SPI-1) and Its Complex Regulatory Network. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, R.; Wang, L.; Ogunremi, D. Virulence Determinants of Non-Typhoidal Salmonellae; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; ISBN 978-1-83880-188-5. [Google Scholar]
- Pepper, I.L.; Gerba, C.P. Environmental Sample Collection and Processing. In Environmental Microbiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 157–175. ISBN 978-0-12-394626-3. [Google Scholar]
- Clesceri, L.S.; Greenberg, A.E.; Eaton, A.D.; Association, A.P.H.; Franson, M.A.H.; Association, A.W.W.; Federation, W.E. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1998; ISBN 978-0-87553-235-6. [Google Scholar]
- Blasco, M.d.; Esteve, C.; Alcaide, E. Multiresistant Waterborne Pathogens Isolated from Water Reservoirs and Cooling Systems. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 105, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 6579-1:2017; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Detection, Enumeration and Serotyping of Salmonella—Part 1: Detection of Salmonella spp. Slovenski Inštitut za Standardizacijo: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2017.
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A Flexible Trimmer for Illumina Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Gorrie, C.L.; Holt, K.E. Unicycler: Resolving Bacterial Genome Assemblies from Short and Long Sequencing Reads. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A New Genome Assembly Algorithm and Its Applications to Single-Cell Sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid Prokaryotic Genome Annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carattoli, A.; Zankari, E.; García-Fernández, A.; Voldby Larsen, M.; Lund, O.; Villa, L.; Møller Aarestrup, F.; Hasman, H. In Silico Detection and Typing of Plasmids Using PlasmidFinder and Plasmid Multilocus Sequence Typing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galata, V.; Fehlmann, T.; Backes, C.; Keller, A. PLSDB: A Resource of Complete Bacterial Plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D195–D202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolley, K.A.; Bray, J.E.; Maiden, M.C.J. Open-Access Bacterial Population Genomics: BIGSdb Software, the PubMLST.Org Website and Their Applications. Wellcome Open. Res. 2018, 3, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, M.H.K.; Bortolaia, V.; Tansirichaiya, S.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Roberts, A.P.; Petersen, T.N. Detection of Mobile Genetic Elements Associated with Antibiotic Resistance in Salmonella enterica Using a Newly Developed Web Tool: MobileElementFinder. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cury, J.; Jové, T.; Touchon, M.; Néron, B.; Rocha, E.P. Identification and Analysis of Integrons and Cassette Arrays in Bacterial Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 4539–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Néron, B.; Littner, E.; Haudiquet, M.; Perrin, A.; Cury, J.; Rocha, E.P.C. IntegronFinder 2.0: Identification and Analysis of Integrons across Bacteria, with a Focus on Antibiotic Resistance in Klebsiella. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roer, L.; Hendriksen, R.S.; Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Lukjancenko, O.; Kaas, R.S.; Hasman, H.; Aarestrup, F.M. Is the Evolution of Salmonella enterica Subsp. Enterica Linked to Restriction-Modification Systems? mSystems 2016, 1, e00009-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaas, R.S.; Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Lund, O. Solving the Problem of Comparing Whole Bacterial Genomes across Different Sequencing Platforms. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (ITOL) v5: An Online Tool for Phylogenetic Tree Display and Annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Antimicrobial Class | Antimicrobial | Salmonella Species | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R/24 | R (%) | I (%) | S (%) | ||
| Beta-Lactams: Penicillin | Ampicillin | 15 | 62.5 | 0 | 37.5 |
| Amoxicillin/Clavulanic Acid | 0 | 0 | 4.2 | 95.8 | |
| Ampicillin/Sulbactam | 12 | 50 | 12.5 | 37.5 | |
| Piperacillin/Tazobactam | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | |
| Beta-Lactams: Cephalosporins 1st Generation | Cefazolin | 23 | 95.8 | 4.2 | 0 |
| 2nd Generation Cephalosporins | Cefuroxime | 23 | 95.8 | 4.2 | 0 |
| Cefoxitin | 23 | 95.8 | 4.2 | 0 | |
| 3rd Generation Cephalosporins | Cefotaxime | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| Ceftazidime | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | |
| Ceftriaxone | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | |
| 4th Generation Cephalosporins | Cefepime | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| Carbapenems | Meropenem | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| Monobactams | Aztreonam | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| Aminoglycosides | Amikacin | 23 | 95.8 | 4.2 | 0 |
| Gentamicin | 23 | 95.8 | 4.2 | 0 | |
| Fluroquinolone | Ciprofloxacin | 8 | 33.3 | 16.7 | 50 |
| Nitrofuran | Nitrofurantoin | 1 | 4.2 | 12.5 | 83.3 |
| Folate biosynthesis pathway inhibitors | Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole | 3 | 12.5 | 0 | 87.5 |
| Number of Antimicrobial | AMR Phenotype | Salmonella spp. (n = 24) | MAR Index | MDR Organism |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9 | AMP/SAM/CF/CXM/FOX/AMK/GEN/CIP/SXT | 1 E | 0.52 | 66.7% |
| 8 | AMP/SAM/CF/CXM/FOX/AMK/GEN/CIP | 3 E, 4 S | 0.47 | |
| 7 | AMP/CF/CXM/FOX/AMK/GEN/CIP | 2 S | 0.42 | |
| AMP/SAM/CF/CXM/FOX/AMK/GEN | 2 S | |||
| AMP/CF/CXM/FOX/AMK/GEN/SXT | 2 S | |||
| 6 | AMP/CF/CXM//FOX/AMK/GEN | 1 S | 0.37 | |
| CF/CXM/FOX/AMK/GEN/CIP | 1 E | |||
| 5 | CF/CXM/FOX/AMK/GEN | 3 E, 4 S | 0.32 | |
| 1 | NIT | 1 E | 0.05 |
| Number of Isolates | STs and Serovar | Group | Subspecies | O Antigens | Flagellar (H) Antigens | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phase 1 | Phase 2 | |||||
| 2 | S. Jedburgh ST 2133 | E1 (O:3,10) | I | 3,10 | z29 | - |
| 3 | S. Weltevreden ST 365 | E1 (O:3,10) | I | 3,{10},{15} | r | z6 |
| 3 | S. Brancaster ST 2133 | B (O:4) | I | 1,4,12,27 | z29 | - |
| Code | Phenotypic Resistance | Genotypic Resistance | Plasmid and pMLST | Mobile Genetic Elements | Chromosome Mutation | Salmonella Pathogenicity Islands (SPI) |
| MYS03 Effluent ST 2133 S. Brancaster | AMP/SAM/CF/ CXM/FOX/ AMK/GEN/CIP | aac (6′)-Iaa, aph(3′)-Ia qnrS1, dfrA14, tet(A), floR blaTEM-176 | IncX1 Col440I ColRNAI Integron 1 | Contig 18: IncX1- aph (3′)Ia, blaTEM-176, IS102, cn_22462_IS102. MITEEc1, Tn6024, ISEch12 * | gyrA: E438A # gyrB: A295G # parC: N395S # parC: T57S acrB: F28L # acrB: L40P # | 1,3,5, 8,9 |
| MYS05 Soil ST 2133 S. Jedburgh | AMP/SAM/CF/ CXM/FOX/ AMK/GEN/CIP | aac (6′)-Iaa aph (3′)-Ia qnrS1, dfrA14, tet(A), floR blaTEM-176 | IncX1 Integron 1 | Contig 18: IncX1-aph (3′)Ia, blaTEM-176, IS102, cn_22462_IS102. MITEEc1, Tn6024 * | gyrA: E438A # gyrB: A295G # parC: N395S # parC: T57S acrB: F28L # acrB: L40P # | 1,3,5,8, 9,12 |
| MYS06 Effluent ST 365 S. Weltevreden | CF/CXM/ FOX/AMK/GEN | aac (6′)-Iaa | IncFII(S)- S1: A-; B- | ISEcl10, ISEam1, ISSen6, MITEEc1, ISSen1, ISSty2 * | acrB: F28L # acrB: L40P # parC: T57S | 1,3,4,5,6, 9,12,13 |
| MYS11 Soil ST 2133 S. Brancaster | AMP/SAM/CF/ CXM/FOX/ AMK/GEN/CIP | aac (6′)-Iaa, aph (4)-Ia aph (3′)-Ia, aac (3)-IV ant (3″)-Ia, fosA, qnrS1 sul3, tet(A), mph(A), lnu(F), blaTEM-1B aadA17 | IncFIA (HI1)- F: A8; B-, IncHI1A- ST 16, HCM1_259_2 *, IncHI1B(R27), IncN-ST 3,12, Col440I Integron 1 | MITEEc1, ISEch12, Tn6024, Tn5403, ISEc30, IS26 * | gyrA: E438A # gyrB: A295G # parC: N395S # parC: T57S acrB: F28L # acrB: L40P # | 1,3,5, 8,9 |
| MYS15 Soil S. Brancaster ST 2133 | AMP/SAM/CF/ CXM/FOX/ AMK/GEN/CIP | aac (6′)-Iaa aph (3′)-Ia qnrS1, dfrA14, tet(A), floR blaTEM-176 | IncX1, Col156 ColRNAI Integron 1 | Contig 17: IncX1-aph(3′)Ia, blaTEM-176, IS102, cn_22462_IS102. ISEch12, Tn6024, MITEEc1 * | gyrA: E438A # gyrB: A295G # parC: N395S # parC: T57S acrB: F28L # acrB: L40P # | 1,3,5, 8,9 |
| MYS16 Soil ST 365 S. Weltevreden | CF/CXM/FOX/ AMK/GEN/ | aac (6′)-Iaa | IncFII(S)- S1: A-; B- | Contig 33: IncFII(S)- ISEam1. ISSen6, MITEEc1, ISKpn2, ISSen1, ISEcl10 * | acrB: F28L # acrB: L40P # parC: T57S | 3,6,9, 12,13,14 |
| MYS17 Effluent ST 365 S. Weltevreden | CF/CXM/FOX/ AMK/GEN/ | aac (6′)-Iaa | IncFII(S)- S1: A-; B- | Contig 31: IncFII(S)- ISEam1. ISEcl10, ISSty2, ISSen1, MITEEc1, ISSen6 * | acrB: F28L # acrB: L40P # parC: T57S | 3,6,9, 12,13,14 |
| MYS20 Effluent ST 2133 S. Jedburgh | AMP/SAM/CF/ CXM/FOX/ AMK/GEN/CIP | aac (6′)-Iaa aph (3′)-Ia qnrS1, dfrA14, tet(A), floR, blaTEM-176 | IncX1 Integron 1 | Contig 20: IncX1- aph(3′)Ia blaTEM-176, IS102, cn_22462_IS102. Tn6024, MITEEc1 * | gyrA: E438A # gyrB: A295G # parC: N395S # parC: T57S acrB: F28L # acrB: L40P # | 1,3,5, 8,9,12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Syed Abu Thahir, S.; Rajendiran, S.; Shaharudin, R.; Veloo, Y. Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella Species and Their Mobile Genetic Elements from Poultry Farm Environments in Malaysia. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12081330
Syed Abu Thahir S, Rajendiran S, Shaharudin R, Veloo Y. Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella Species and Their Mobile Genetic Elements from Poultry Farm Environments in Malaysia. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(8):1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12081330
Chicago/Turabian StyleSyed Abu Thahir, Syahidiah, Sakshaleni Rajendiran, Rafiza Shaharudin, and Yuvaneswary Veloo. 2023. "Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella Species and Their Mobile Genetic Elements from Poultry Farm Environments in Malaysia" Antibiotics 12, no. 8: 1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12081330
APA StyleSyed Abu Thahir, S., Rajendiran, S., Shaharudin, R., & Veloo, Y. (2023). Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella Species and Their Mobile Genetic Elements from Poultry Farm Environments in Malaysia. Antibiotics, 12(8), 1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12081330







