Duration of Neonatal Antibiotic Exposure in Preterm Infants in Association with Health and Developmental Outcomes in Early Childhood
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
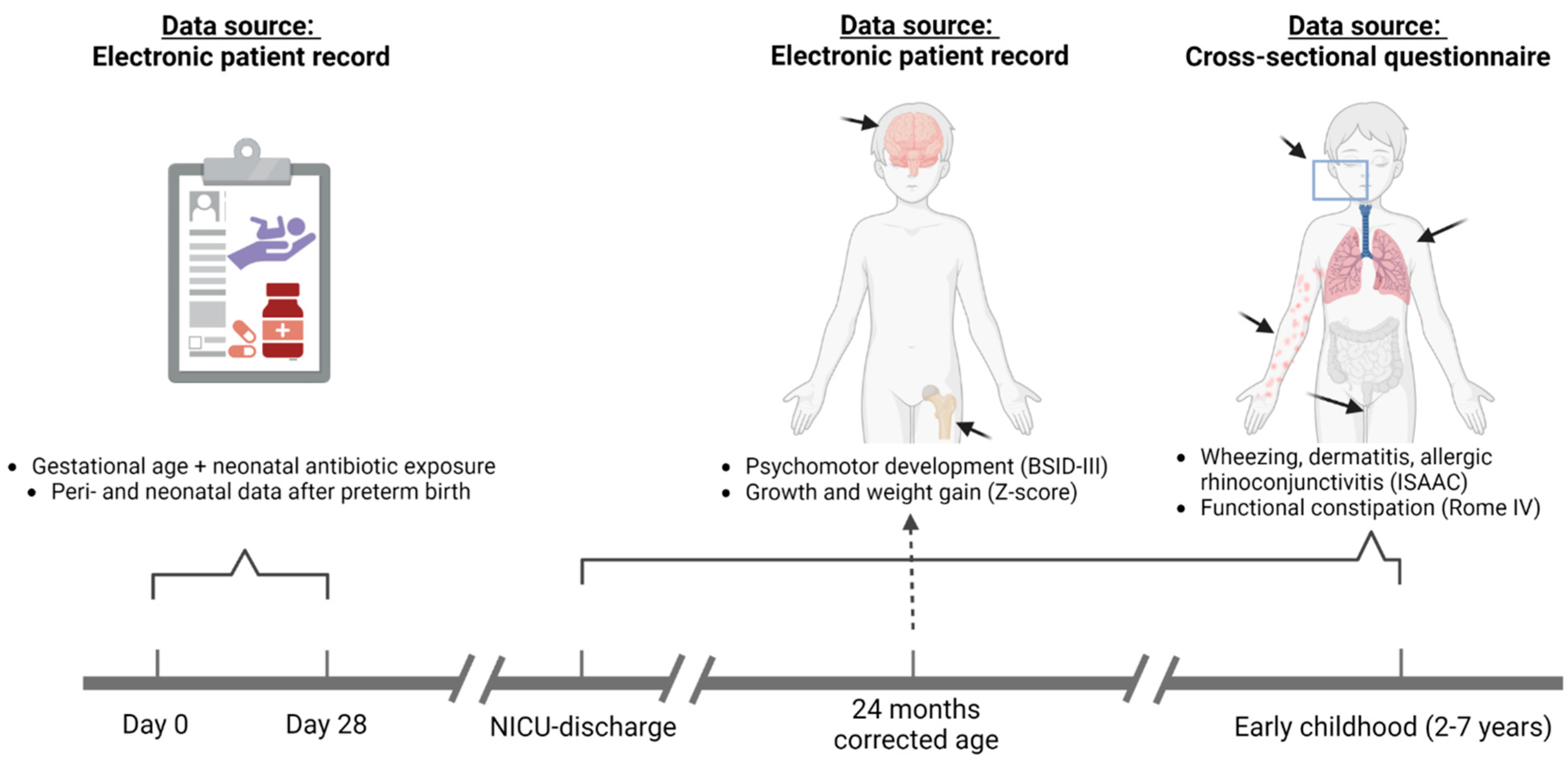
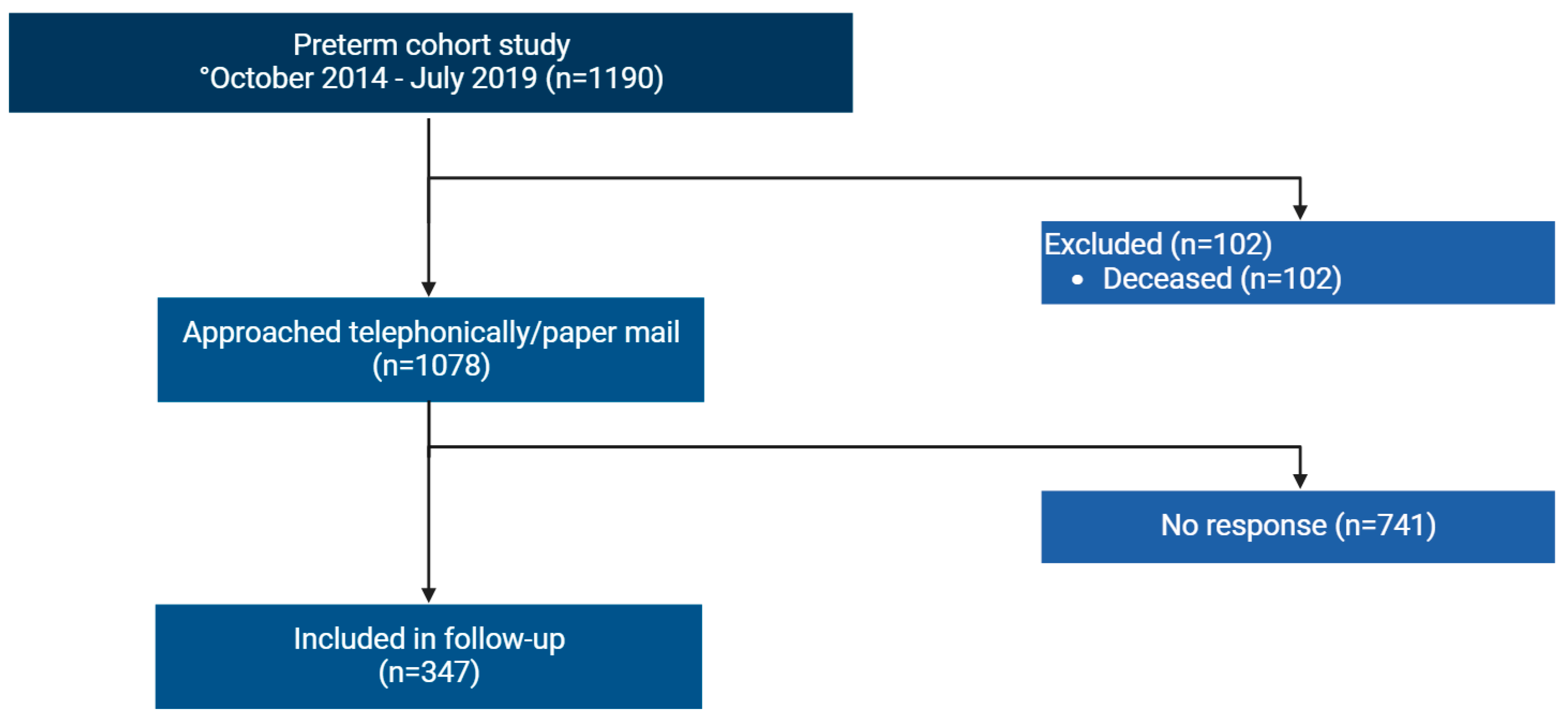
2.1. Design and Subjects
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth and Neurodevelopment at 24 Months’ Corrected Age
3.2. Gastrointestinal Symptoms at Time of Survey
3.3. Respiratory Symptoms in Early Childhood
3.4. Atopic Symptoms in Early Childhood
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Shen, R.L.; Ayede, A.I.; Berrington, J.; Bloomfield, F.H.; Busari, O.O.; Cormack, B.E.; Embleton, N.D.; van Goudoever, J.B.; Greisen, G.; et al. Early Use of Antibiotics Is Associated with a Lower Incidence of Necrotizing Enterocolitis in Preterm, Very Low Birth Weight Infants: The NEOMUNE-NeoNutriNet Cohort Study. J. Pediatr. 2020, 227, 128–134 e122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Zhang, L.; Yan, W.; Li, S.; Han, J.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, Y.; Lee, S.K.; Cao, Y.; Ji, Y.; et al. Antibiotic Use in Neonatal Intensive Care Units in China: A Multicenter Cohort Study. J. Pediatr. 2021, 239, 136–142.e134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Sengupta, S.; Puopolo, K.M. Challenges and opportunities for antibiotic stewardship among preterm infants. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2019, 104, F327–F332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adedeji, W.A. The treasure called antibiotics. Ann. Ib. Postgrad. Med. 2016, 14, 56–57. [Google Scholar]
- Du, W.; Warrier, I.; Tutag Lehr, V.; Salari, V.; Ostrea, E.; Aranda, J.V. Changing Patterns of Drug Utilization in a Neonatal Intensive Care Population. Am. J. Perinatol. 2006, 23, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyman, M.; van Houten, M.A.; Watson, R.L.; Chu, M.; Arp, K.; de Waal, W.J.; Schiering, I.; Plötz, F.B.; Willems, R.J.L.; van Schaik, W.; et al. Effects of early-life antibiotics on the developing infant gut microbiome and resistome: A randomized trial. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppala, V.S.; Meinzen-Derr, J.; Morrow, A.L.; Schibler, K.R. Prolonged Initial Empirical Antibiotic Treatment is Associated with Adverse Outcomes in Premature Infants. J. Pediatr. 2011, 159, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, J.Y.; Roberts, A.; Sherlock, R.; Ojah, C.; Cieslak, Z.; Dunn, M.; Barrington, K.; Yoon, E.W.; Shah, P.S. Duration of Initial Empirical Antibiotic Therapy and Outcomes in Very Low Birth Weight Infants. Pediatrics 2019, 143, e20182286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhar, S.; Petersen, F.C. The Dark Side of Antibiotics: Adverse Effects on the Infant Immune Defense Against Infection. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 544460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, B.B. The contribution of the gut microbiome to neurodevelopment and neuropsychiatric disorders. Pediatr. Res. 2019, 85, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leo, S.; Lazarevic, V.; von Dach, E.; Kaiser, L.; Prendki, V.; Schrenzel, J.; Huttner, B.D.; Huttner, A. Effects of antibiotic duration on the intestinal microbiota and resistome: The PIRATE RESISTANCE project, a cohort study nested within a randomized trial. EBioMedicine 2021, 71, 103566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henrick, B.M.; Rodriguez, L.; Lakshmikanth, T.; Pou, C.; Henckel, E.; Arzoomand, A.; Olin, A.; Wang, J.; Mikes, J.; Tan, Z.; et al. Bifidobacteria-mediated immune system imprinting early in life. Cell 2021, 184, 3884–3898.e3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puopolo, K.M.; Benitz, W.E.; Zaoutis, T.E.; Committee on Fetus and Newborn; Committee On Infectious Diseases; Cummings, J.; Juul, S.; Hand, I.; Eichenwald, E.; Poindexter, B.; et al. Management of Neonates Born at ≤34 6/7 Weeks’ Gestation with Suspected or Proven Early-Onset Bacterial Sepsis. Pediatrics 2018, 142, e20182896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rallis, D.; Giapros, V.; Serbis, A.; Kosmeri, C.; Baltogianni, M. Fighting Antimicrobial Resistance in Neonatal Intensive Care Units: Rational Use of Antibiotics in Neonatal Sepsis. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantey, J.B.; Lopez-Medina, E.; Nguyen, S.; Doern, C.; Garcia, C. Empiric Antibiotics for Serious Bacterial Infection in Young Infants: Opportunities for Stewardship. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2015, 31, 568–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aversa, Z.; Atkinson, E.J.; Schafer, M.J.; Theiler, R.N.; Rocca, W.A.; Blaser, M.J.; LeBrasseur, N.K. Association of Infant Antibiotic Exposure with Childhood Health Outcomes. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2021, 96, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierikx, T.H.; Visser, D.H.; Benninga, M.A.; van Kaam, A.H.L.C.; de Boer, N.K.H.; de Vries, R.; van Limbergen, J.; de Meij, T.G.J. The influence of prenatal and intrapartum antibiotics on intestinal microbiota colonisation in infants: A systematic review. J. Infect. 2020, 81, 190–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, K.; Powell, E.; Cornwell, E.; Simon Kroll, J.; Shaw, A.G. Development of the gut microbiota during early life in premature and term infants. Gut Pathog. 2023, 15, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, H.S.; Liu, Y.; Menkiti, O.R.; Mei, J.; Dai, N.; O’Leary, C.E.; Oliver, P.M.; Kolls, J.K.; Weiser, J.N.; Worthen, G.S. The microbiota regulates neutrophil homeostasis and host resistance to Escherichia coli K1 sepsis in neonatal mice. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Yoo, J.Y.; Valeria Ozorio Dutra, S.; Morgan, K.H.; Groer, M. The Association between Early-Life Gut Microbiota and Long-Term Health and Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patangia, D.V.; Anthony Ryan, C.; Dempsey, E.; Paul Ross, R.; Stanton, C. Impact of antibiotics on the human microbiome and consequences for host health. Microbiologyopen 2022, 11, e1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spees, A.M.; Lopez, C.A.; Kingsbury, D.D.; Winter, S.E.; Bäumler, A.J. Colonization Resistance: Battle of the Bugs or Ménage à Trois with the Host? PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvath, T.D.; Ihekweazu, F.D.; Haidacher, S.J.; Ruan, W.; Engevik, K.A.; Fultz, R.; Hoch, K.M.; Luna, R.A.; Oezguen, N.; Spinler, J.K.; et al. Bacteroides ovatus colonization influences the abundance of intestinal short chain fatty acids and neurotransmitters. iScience 2022, 25, 104158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frati, F.; Salvatori, C.; Incorvaia, C.; Bellucci, A.; Di Cara, G.; Marcucci, F.; Esposito, S. The Role of the Microbiome in Asthma: The Gut(-)Lung Axis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 20, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enaud, R.; Prevel, R.; Ciarlo, E.; Beaufils, F.; Wieers, G.; Guery, B.; Delhaes, L. The Gut-Lung Axis in Health and Respiratory Diseases: A Place for Inter-Organ and Inter-Kingdom Crosstalks. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhoads, J.M.; Collins, J.; Fatheree, N.Y.; Hashmi, S.S.; Taylor, C.M.; Luo, M.; Hoang, T.K.; Gleason, W.A.; Van Arsdall, M.R.; Navarro, F.; et al. Infant Colic Represents Gut Inflammation and Dysbiosis. J. Pediatr. 2018, 203, 55–61.e53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkhout, D.J.C.; Niemarkt, H.J.; Buijck, M.; van Weissenbruch, M.M.; Brinkman, P.; Benninga, M.A.; van Kaam, A.H.; Kramer, B.W.; Andriessen, P.; de Boer, N.K.H.; et al. Detection of Sepsis in Preterm Infants by Fecal Volatile Organic Compounds Analysis: A Proof of Principle Study. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2017, 65, e47–e52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayley, N. Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development, 3rd ed.; Harcourt Assessment Inc.: San Antonio, TX, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Asher, M.I.; Keil, U.; Anderson, H.R.; Beasley, R.; Crane, J.; Martinez, F.; Mitchell, E.A.; Pearce, N.; Sibbald, B.; Stewart, A.W.; et al. International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC): Rationale and methods. Eur. Respir. J. 1995, 8, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansen, H.M.; Lebbink, M.A.; Mul, J.; van Erp, F.C.; van Engelen, M.; de Vries, E.; Prevaes, S.; Le, T.M.; van der Ent, C.K.; Verhagen, L.M. Risk factors for atopic diseases and recurrent respiratory tract infections in children. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2020, 55, 3168–3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benninga, M.A.; Faure, C.; Hyman, P.E.; St James Roberts, I.; Schechter, N.L.; Nurko, S. Childhood Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders: Neonate/Toddler. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1443–1455.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabbers, M.M.; DiLorenzo, C.; Berger, M.Y.; Faure, C.; Langendam, M.W.; Nurko, S.; Staiano, A.; Vandenplas, Y.; Benninga, M.A. Evaluation and treatment of functional constipation in infants and children: Evidence-based recommendations from ESPGHAN and NASPGHAN. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2014, 58, 258–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansson, J.; Kallen, K.; Eklof, E.; Serenius, F.; Aden, U.; Stjernqvist, K. The ability of Bayley-III scores to predict later intelligence in children born extremely preterm. Acta Paediatr. 2021, 110, 3030–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, L.W.; Roberts, G.; Anderson, P.J. Outcomes at Age 2 Years of Infants < 28 Weeks’ Gestational Age Born in Victoria in 2005. J. Pediatr. 2010, 156, 49–53.e41. [Google Scholar]
- Evensen, K.A.; Skranes, J.; Brubakk, A.M.; Vik, T. Predictive value of early motor evaluation in preterm very low birth weight and term small for gestational age children. Early Hum. Dev. 2009, 85, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Beek, P.E.; Rijken, M.; Broeders, L.; Ter Horst, H.J.; Koopman-Esseboom, C.; de Kort, E.; Laarman, C.; Mulder-de Tollenaer, S.M.; Steiner, K.; Swarte, R.M.; et al. Two-year neurodevelopmental outcome in children born extremely preterm: The EPI-DAF study. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2022, 107, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kherkheulidze, M.; Chkhaidze, I.; Kavlashvili, N.; Kandelaki, E.; Adamia, N.; Abelashvili, D.; Tabatadze, T. Evaluation of Developmental Outcomes with Bayley Iii Test in Preterm Infants with Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Georgian Med. News 2018, 279, 67–73. [Google Scholar]
- Bar, S.; Milanaik, R.; Adesman, A. Long-term neurodevelopmental benefits of breastfeeding. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2016, 28, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nay, K.; Jollet, M.; Goustard, B.; Baati, N.; Vernus, B.; Pontones, M.; Lefeuvre-Orfila, L.; Bendavid, C.; Rué, O.; Mariadassou, M.; et al. Gut bacteria are critical for optimal muscle function: A potential link with glucose homeostasis. Am. J. Physiol. -Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 317, E158–E171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslanova, A.; Tarasova, A.; Alexandrova, A.; Novoselova, V.; Shaidullov, I.; Khusnutdinova, D.; Grigoryeva, T.; Yarullina, D.; Yakovleva, O.; Sitdikova, G. Protective Effects of Probiotics on Cognitive and Motor Functions, Anxiety Level, Visceral Sensitivity, Oxidative Stress and Microbiota in Mice with Antibiotic-Induced Dysbiosis. Life 2021, 11, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Cowan, C.S.M.; Sandhu, K.V.; Bastiaanssen, T.F.S.; Boehme, M.; Codagnone, M.G.; Cussotto, S.; Fulling, C.; Golubeva, A.V.; et al. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1877–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luck, B.; Engevik, M.A.; Ganesh, B.P.; Lackey, E.P.; Lin, T.; Balderas, M.; Major, A.; Runge, J.; Luna, R.A.; Sillitoe, R.V.; et al. Bifidobacteria shape host neural circuits during postnatal development by promoting synapse formation and microglial function. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Pu, F.; Peng, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, S.; Wang, S.; Shen, X.; Li, Y.; Cheng, R.; et al. Antibiotic cocktail-induced gut microbiota depletion in different stages could cause host cognitive impairment and emotional disorders in adulthood in different manners. Neurobiol. Dis. 2022, 170, 105757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slykerman, R.F.; Coomarasamy, C.; Wickens, K.; Thompson, J.M.D.; Stanley, T.V.; Barthow, C.; Kang, J.; Crane, J.; Mitchell, E.A. Exposure to antibiotics in the first 24 months of life and neurocognitive outcomes at 11 years of age. Psychopharmacology 2019, 236, 1573–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sewell, E.; Roberts, J.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Association of Infection in Neonates and Long-Term Neurodevelopmental Outcome. Clin. Perinatol. 2021, 48, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, A.; Prescott, S.M.; Dutra, S.; Yoo, J.Y.; Gordon, J.; Shaffer, E.; McSkimming, D.; Groer, M.E. Relationships of the very low birth weight infant microbiome with neurodevelopment at 2 and 4 years of age. Dev. Psychobiol. 2022, 64, e22317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza da Cunha, S.; Santorelli, G.; Pearce, N.; Wright, J.; Oddie, S.; Petherick, E.; Pembrey, L. Evidence for causal associations between prenatal and postnatal antibiotic exposure and asthma in children, England. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2021, 51, 1438–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagano, F.; Conti, M.G.; Boscarino, G.; Pannucci, C.; Dito, L.; Regoli, D.; Di Chiara, M.; Battaglia, G.; Prota, R.; Cinicola, B.; et al. Atopic Manifestations in Children Born Preterm: A Long-Term Observational Study. Children 2021, 8, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinther, J.L.; Ekstrøm, C.T.; Sørensen, T.I.A.; Cederkvist, L.; Lawlor, D.A.; Andersen, A.-M.N. Gestational age and trajectories of body mass index and height from birth through adolescence in the Danish National Birth Cohort. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, E.M.; Poulsen, G.; Field, D.J.; Kurinczuk, J.J.; Wolke, D.; Alfirevic, Z.; Quigley, M.A. Effects of gestational age at birth on health outcomes at 3 and 5 years of age: Population based cohort study. BMJ 2012, 344, e896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeraus, W.H.; Petersen, I.; Gilbert, R. Association between antibiotic prescribing in pregnancy and cerebral palsy or epilepsy in children born at term: A cohort study using the health improvement network. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierrat, V.; Marchand-Martin, L.; Arnaud, C.; Kaminski, M.; Resche-Rigon, M.; Lebeaux, C.; Bodeau-Livinec, F.; Morgan, A.S.; Goffinet, F.; Marret, S.; et al. Neurodevelopmental outcome at 2 years for preterm children born at 22 to 34 weeks’ gestation in France in 2011: EPIPAGE-2 cohort study. BMJ 2017, 358, j3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harsha, S.S.; Archana, B.R. SNAPPE-II (Score for Neonatal Acute Physiology with Perinatal Extension-II) in Predicting Mortality and Morbidity in NICU. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2015, 9, Sc10-2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Asthma Education and Prevention Program. Expert Panel Report 3 (EPR-3): Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma-Summary Report 2007. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 120 (Suppl. S5), S94–S138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, S.J.; Heaton, K.W. Stool form scale as a useful guide to intestinal transit time. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1997, 32, 920–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Initial Cohort (n = 1190) | Follow-Up Cohort (n = 347) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gestational age, weeks + days, mean (SD) | 27 + 4 (1 + 4) | 27 + 5 (1 + 4)) | 0.03 * |
| Gender, female, % | 47% | 45% | 0.67 |
| Delivery mode, cesarean, % | 52% | 48% | 0.23 |
| APGAR score 1 min, median [IQR]) | 6 [4,5,6,7] | 6 [3,4,5,6,7] | 0.93 |
| APGAR score 5 min, median [IQR]) | 8 [6,7,8,9] | 8 [6,7,8,9] | 0.50 |
| Multiplicity (twin or triplet), % | 32% | 27% | 0.02 * |
| Birth weight, gram, mean (SD) | 1025 (271) | 1067 (268) | 0.01 * |
| Birthweight, Z-score, mean (SD) | 0.04 (1.01) | 0.13 (0.99) | 0.16 |
| Late-onset sepsis in first 28 days of life, % | 34% | 27% | 0.02 * |
| Necrotizing enterocolitis, % | 8% | 4% | 0.01 * |
| Mean (SD) or n (%) | Missing Data (N) | |
|---|---|---|
| Infancy | ||
| Duration of neonatal antibiotic exposure (NABE) in the center of birth, days, mean (SD) | 9 (7) | 0 |
| 10 (3) 102 (29) 103 (30) 38 (23) | |
| First gravidity, n (%) | 186 (54) | 0 |
| First parity, n (%) | 228 (66) | 0 |
| Invasive ventilation first 28 d of life, n (%) | 172 (50) | 0 |
| Intraventricular hemorrhage/periventricular leukomalacia grade III-IV, n (%) | 21 (6) | 1 |
| >20% formula milk in first 28 d, n (%) | 61 (21) | 55 |
Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis, sepsis or meningitis, n (%)
| 96 (28) 35 (10) | 0 |
| Exposure to mother’s milk ≥ 6 months | 18 (5) | 8 |
| Moderate to severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia, n (%) | 81 (24) | 7 |
| Palivizumab administration, n (%) | 261 (88) | 49 |
| Childhood | ||
| Age at questionnaire, years, mean (SD) | 4.6 (0.9) | 0 |
| Weight at ca. 24 months’ CA, mean (SD) | 11.9 (1.6) | 45 |
| Stature at ca. 24 months’ CA, mean (SD) | 86.7 (4.6) | 50 |
| Ever received medical feeding at home (oral or tube), n (%) | 18 (5) | 8 |
| Weekly fastfood or ready-made food, n (%) | 47 (14) | 18 |
| Family history | ||
| Maternal education, university level, n (%) | 182 (55) | 18 |
| Ethnicity mother, non-Dutch/Belgian, n (%) | 62 (19) | 16 |
| Ethnicity father, non-Dutch/Belgian, n (%) | 51 (15) | 14 |
| Both parents’ mother tongue other than Dutch, n (%) | 34 (10) | 13 |
| At least monthly exposure to nicotine smoke, n (%) | 12 (5) | 96 |
| Atopic disease parents or siblings, n (%) | 150 (44) | 7 |
| Neonatal Antibiotic Exposure (per 5 Days) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) or n (%) | Odds Ratio or Regression Coefficient [95%CI] | p-Value | Confounders in the Multivariate Regression Analysis | Missing Data (N) | |
| Growth and development | |||||
| Weight Z-score at ca. 24 months’ CA, mean (SD) | −0.47 (1.06) | −0.11 [−0.20–−0.02] Adj: 0.08 [−0.17–0.02] | 0.01 * 0.10 | Gestational age | 69 |
| Stature Z-score at ca. 24 months’ CA, mean (SD) | 0.14 (1.01) | 0.003 [−0.08–0.09] Adj: NA | 0.22 NA | / | 71 |
| BSID-III Cognitive or Motor score < 90 | 78 (28) | 1.23 [1.02–1.48] Adj: 1.88 [1.05–3.35] | 0.03 * 0.23 | Invasive ventilation (<28 days’ age) | 67 |
| BSID-III cognitive score, mean (SD) | 101 (13) | −0.40 [−1.61–0.80] Adj:NA | 0.51 NA | / | 84 |
| BSID-III cognitive score < 90, n (%) | 52 (17) | 1.00 [0.80–1.24] Adj: 0.90 [0.71–1.15] | 0.99 0.40 | / | 42 |
| BSID-III overall motor score, mean (SD) | 102 (14) | −1.31 [−2.68–0.07] Adj: 0.28 [−0.04–0.60] | 0.06 0.09 | Time until discharge from neonatal intensive care unit | 134 |
| BSID-III overall motor score < 90, n (%) | 63 (22) | 1.32 [1.09–1.61] Adj: 1.22 [0.98–1.52] | 0.005 * 0.08 | Gestational age, invasive ventilation (<28 days’ age) | 58 |
| BSID-III fine motor score < 8, n (%) | 37 (12) | 1.16 [0.91–1.47] Adj: 1.09 [0.84–1.41] | 0.24 0.52 | Gestational age | 47 |
| BSID-III gross motor score < 8, n (%) | 82 (31) | 1.28 [1.06–1.54] Adj: 1.21 [1.00–1.46] | 0.01 * 0.04 * | Gestational age | 71 |
| Gastrointestinal symptoms | |||||
| Pediatric constipation, n (%) | 47 (14) | 1.08 [0.87–1.33] Adj: 1.06 [0.84–1.34] | 0.48 0.61 | Invasive ventilation (<28 days’ age) | 18 |
| Use of antacid medication, n (%) | 13 (4) | 1.14 [0.78–1.67] Adj: NA | 0.50 NA | / | 7 |
| Respiratory symptoms | |||||
| Sought medical attention due to LRT a, n (%) | 114 (34) | 1.12 [0.96–1.32] Adj: 0.94 [0.78–1.13] | 0.15 0.52 | Gestational age, invasive ventilation (<28 days’ age) | 8 |
| Hospitalization due to acute LRT a diseasec, n (%) | 64 (19) | 1.01 [0.83–1.23] Adj: NA | 0.92 NA | / | 7 |
| Ear-nose-throat surgery, n (%) | 65 (19) | 1.11 [0.91–1.34] Adj: NA | 0.30 NA | / | 7 |
| Wheezing episode in the past 12 months, n (%) | 88 (26) | 1.08 [0.91–1.29] Adj: 0.93 [0.76–1.13] | 0.38 0.46 | Invasive ventilation (<28 days’ age) | 10 |
| Bronchodilation past month, n (%) | 73 (22) | 1.13 [0.94–1.36] 1.00 [0.81–1.23] | 0.21 0.99 | Invasive ventilation (<28 days’ age) | 10 |
| Bronchodilatation (weekly), n (%) | 36 (11) | 1.17 [0.92–1.48] Adj: 1.02 [0.78–1.34] | 0.20 0.88 | Invasive ventilation (<28 days’ age) | 15 |
| Atopic symptoms | |||||
| Suspected food allergies, n (%) | 55 (17) | 1.18 [0.96–1.44] Adj: NA | 0.12 NA | / | 10 |
| Medically confirmed food allergies, n (%) | 9 (3) | 0.69 [0.36–1.31] Adj: NA | 0.25 NA | / | 11 |
| Atopic dermatitis (ever), n (%) | 35 (10) | 0.87 [0.66–1.16] Adj: NA | 0.35 NA | / | 7 |
| Allergic rhinitis or conjunctivitis (past 12 months), n (%) | 43 (14) | 1.03 [0.81–1.30] Adj: NA | 0.82 NA | / | 29 |
| Anti-allergic treatment (current), n (%) | 6 (2) | 1.60 [0.98–2.63] Adj: NA | 0.06 NA | / | 7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deianova, N.; de Boer, N.K.; Aoulad Ahajan, H.; Verbeek, C.; Aarnoudse-Moens, C.S.H.; Leemhuis, A.G.; van Weissenbruch, M.M.; van Kaam, A.H.; Vijbrief, D.C.; Hulzebos, C.V.; et al. Duration of Neonatal Antibiotic Exposure in Preterm Infants in Association with Health and Developmental Outcomes in Early Childhood. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 967. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12060967
Deianova N, de Boer NK, Aoulad Ahajan H, Verbeek C, Aarnoudse-Moens CSH, Leemhuis AG, van Weissenbruch MM, van Kaam AH, Vijbrief DC, Hulzebos CV, et al. Duration of Neonatal Antibiotic Exposure in Preterm Infants in Association with Health and Developmental Outcomes in Early Childhood. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(6):967. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12060967
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeianova, Nancy, Nanne K. de Boer, Hafsa Aoulad Ahajan, Cilla Verbeek, Cornelieke S. H. Aarnoudse-Moens, Aleid G. Leemhuis, Mirjam M. van Weissenbruch, Anton H. van Kaam, Daniel C. Vijbrief, Chris V. Hulzebos, and et al. 2023. "Duration of Neonatal Antibiotic Exposure in Preterm Infants in Association with Health and Developmental Outcomes in Early Childhood" Antibiotics 12, no. 6: 967. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12060967
APA StyleDeianova, N., de Boer, N. K., Aoulad Ahajan, H., Verbeek, C., Aarnoudse-Moens, C. S. H., Leemhuis, A. G., van Weissenbruch, M. M., van Kaam, A. H., Vijbrief, D. C., Hulzebos, C. V., Giezen, A., Cossey, V., de Boode, W. P., de Jonge, W. J., Benninga, M. A., Niemarkt, H. J., & de Meij, T. G. J. (2023). Duration of Neonatal Antibiotic Exposure in Preterm Infants in Association with Health and Developmental Outcomes in Early Childhood. Antibiotics, 12(6), 967. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12060967






