Antibiotic Treatment Induces Long-Lasting Effects on Gut Microbiota and the Enteric Nervous System in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
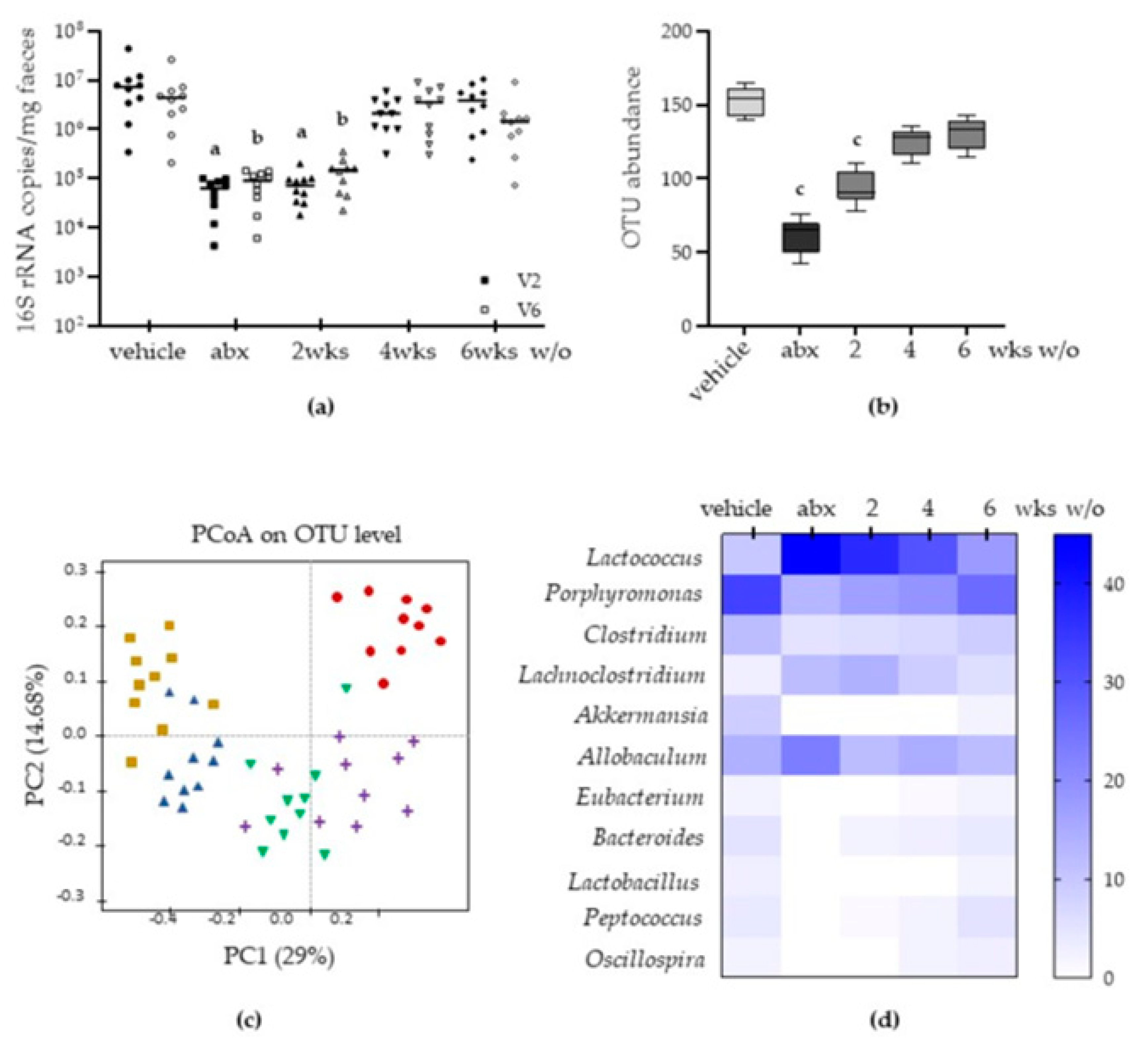
2.1. Antibiotic Treatment Causes Long-Lasting Alterations in Gut Microbiota
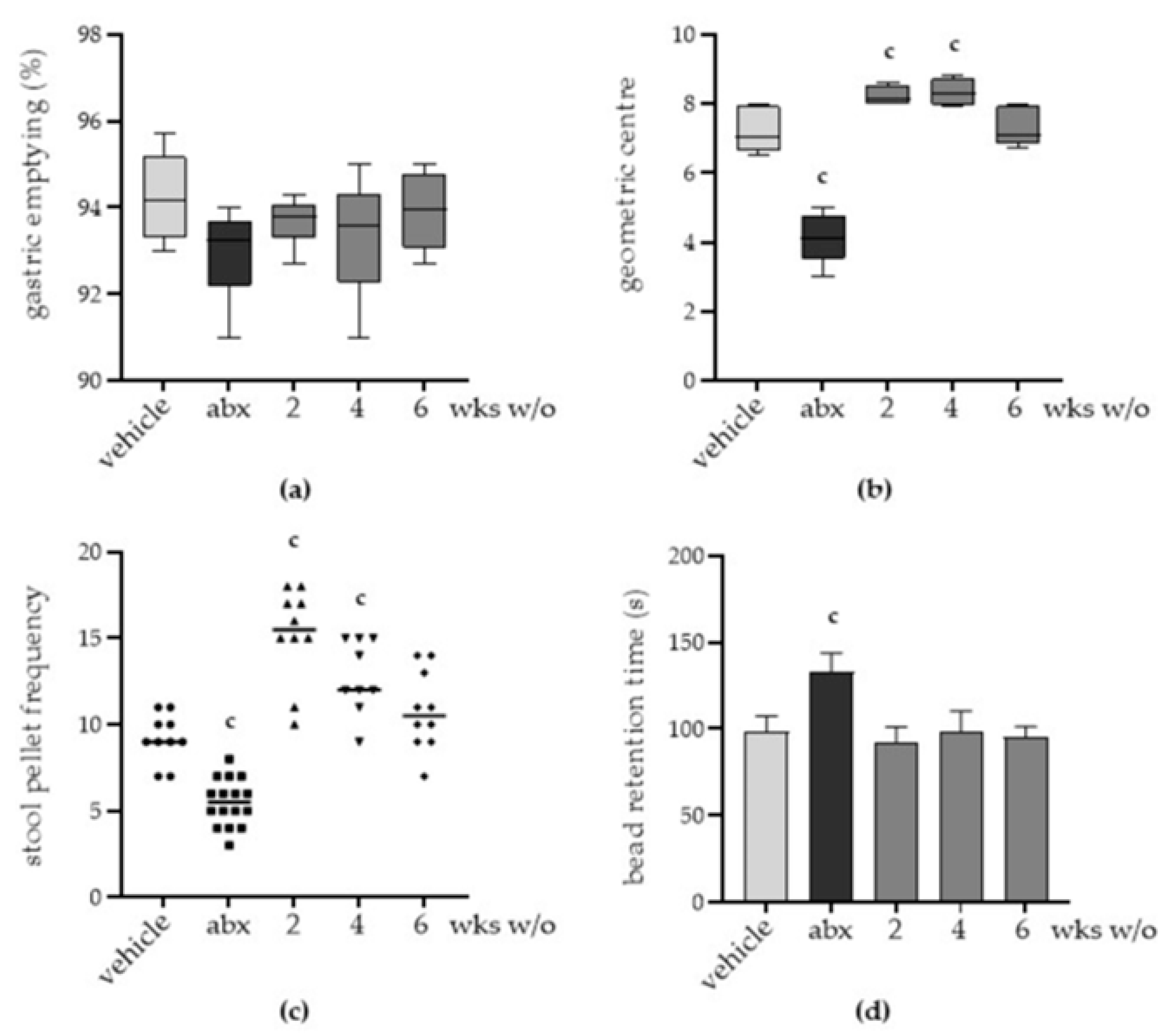
2.2. Antibiotic Treatment Induces Persistent Gut Dysmotility
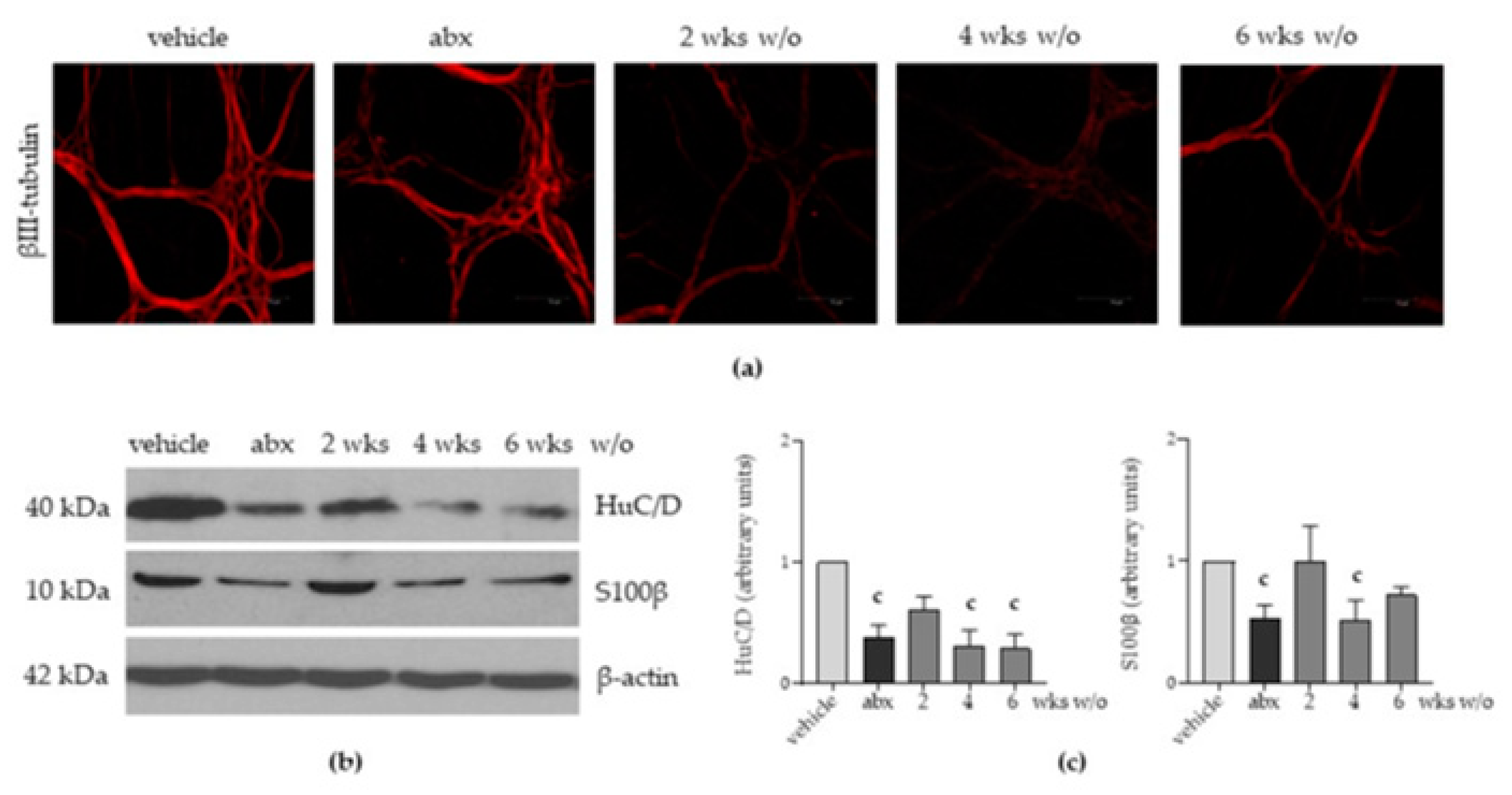
2.3. Antibiotic Administration Induces Structural Alterations in the Enteric Nervous System
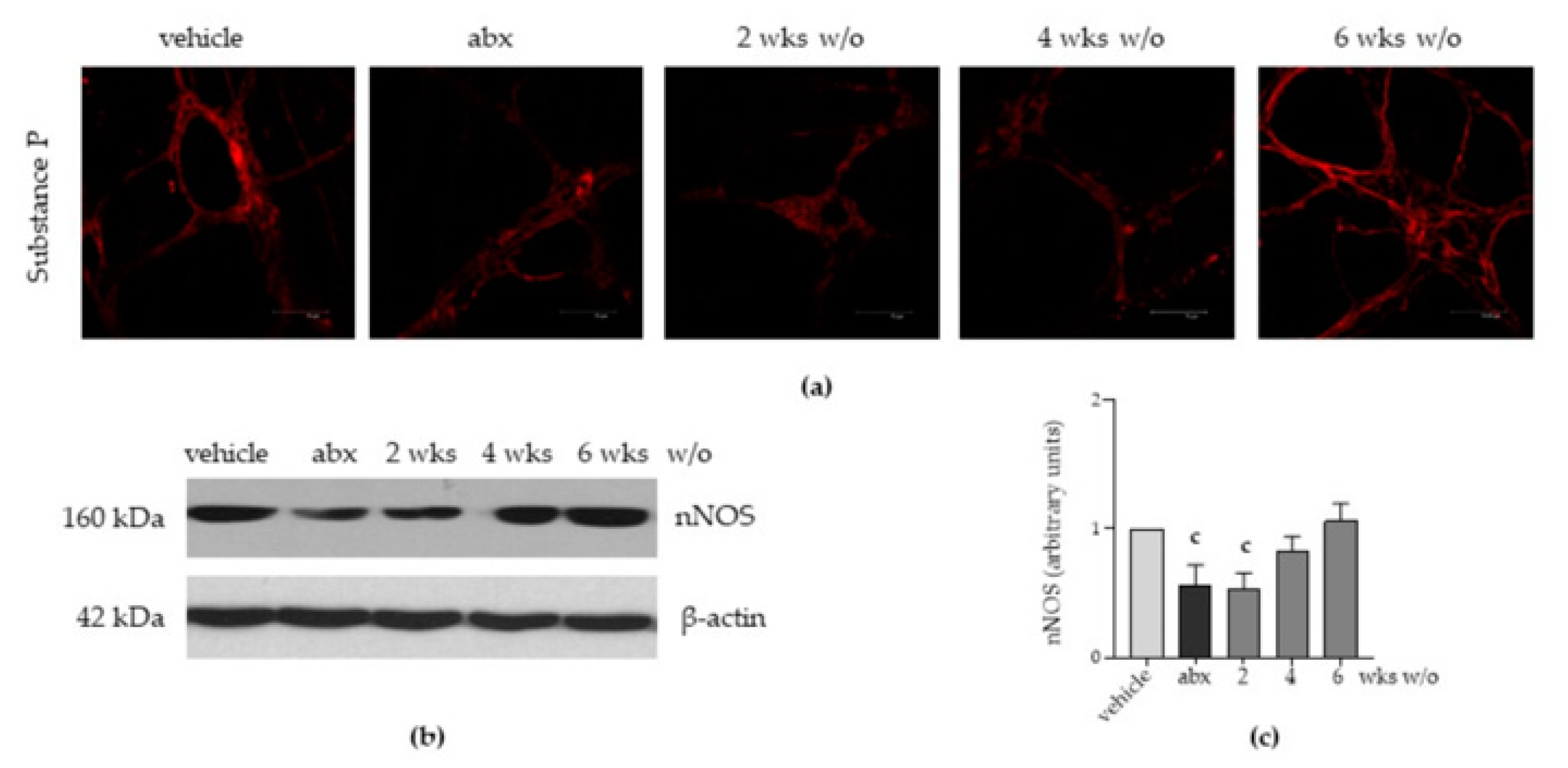
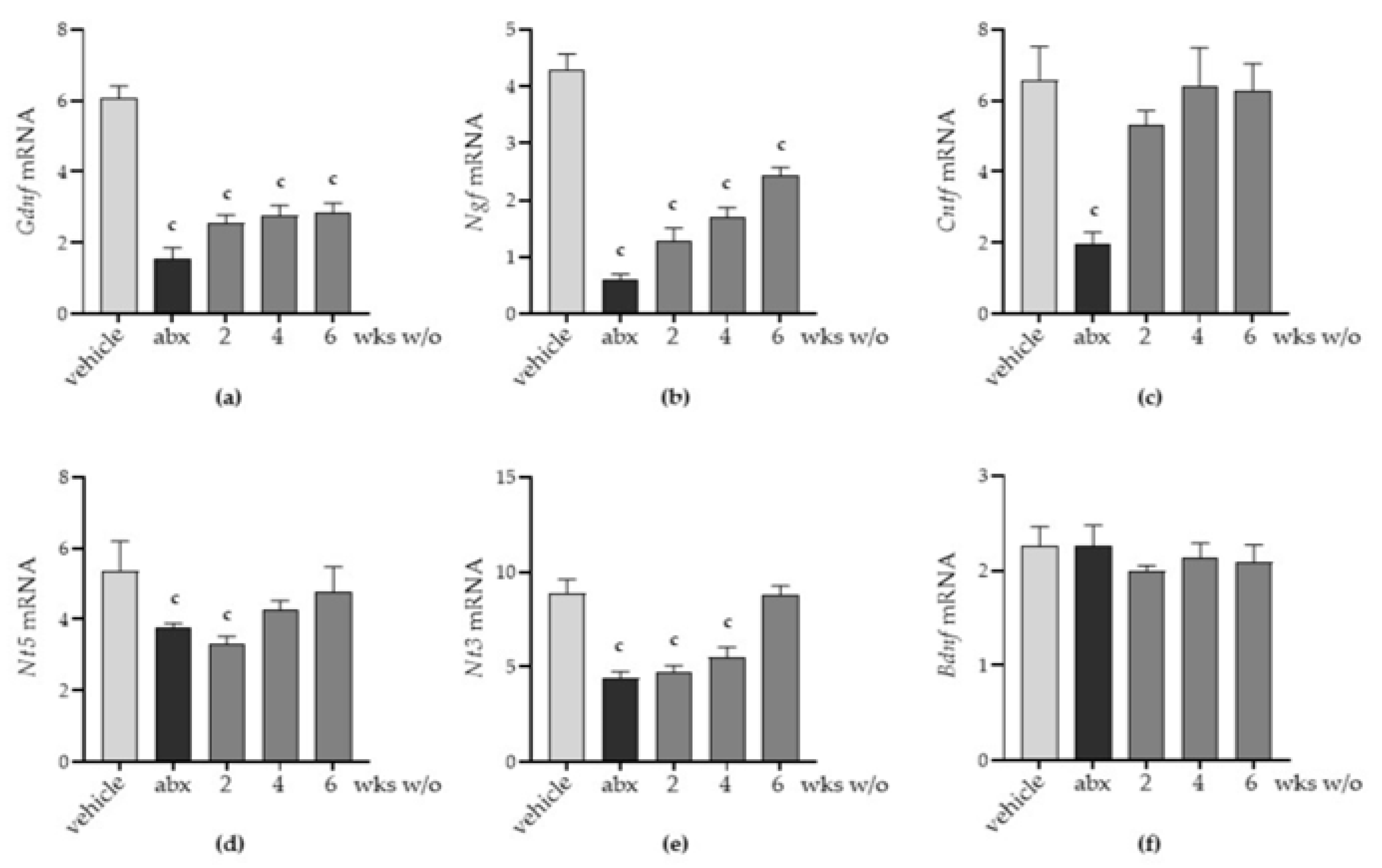
2.4. Antibiotic Alters the Neurochemical Code in the Enteric Nervous System
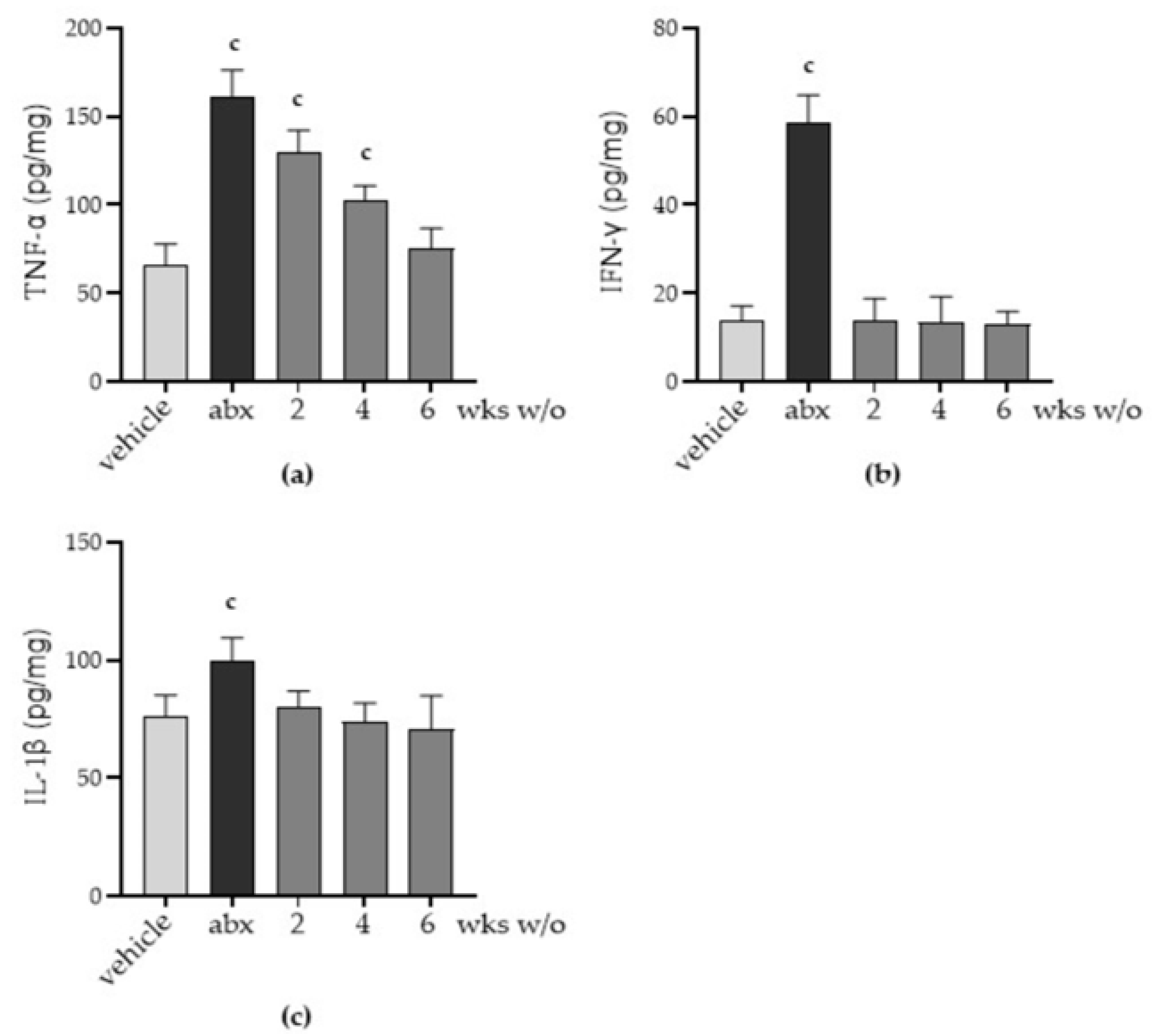
2.5. Antibiotic Administration Triggers Inflammation in the Myenteric Plexus
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
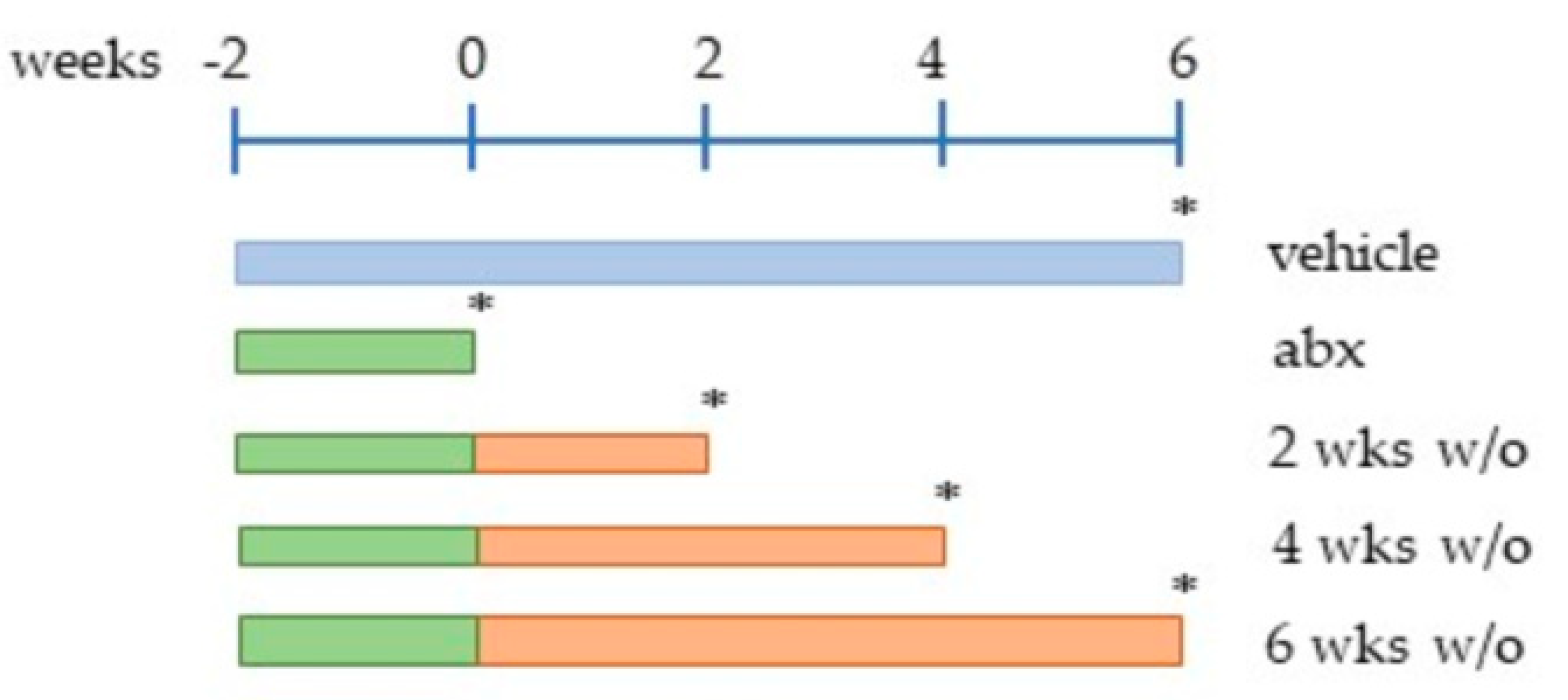
4.1. Mice Treatment
4.2. Microbiota Analysis
4.3. Gastrointestinal Transit
4.4. Colonic Motility
4.5. Histopathological Evaluation
4.6. Whole-Mount Staining
4.7. Immunoblot Analysis
4.8. Inflammatory Cytokine Profile
4.9. RNA Isolation and Quantitative RT-PCR
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berg, G.; Rybakova, D.; Fischer, D.; Cernava, T.; Vergès, M.-C.C.; Charles, T.; Chen, X.; Cocolin, L.; Eversole, K.; Corral, G.H.; et al. Microbiome definition re-visited: Old concepts and new challenges. Microbiome 2020, 8, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferranti, E.P.; Dunbar, S.B.; Dunlop, A.L.; Corwin, E.J. 20 Things You Didn’t Know About the Human Gut Microbiome. J. Cardiovasc. Nurs. 2014, 29, 479–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, N.; Yang, H. Factors affecting the composition of the gut microbiota, and its modulation. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicentini, F.A.; Keenan, C.M.; Wallace, L.E.; Woods, C.; Cavin, J.-B.; Flockton, A.R.; Macklin, W.B.; Belkind-Gerson, J.; Hirota, S.A.; Sharkey, K.A. Intestinal microbiota shapes gut physiology and regulates enteric neurons and glia. Microbiome 2021, 9, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brun, P.; Giron, M.C.; Qesari, M.; Porzionato, A.; Caputi, V.; Zoppellaro, C.; Banzato, S.; Grillo, A.R.; Spagnol, L.; De Caro, R.; et al. Toll-Like Receptor 2 Regulates Intestinal Inflammation by Controlling Integrity of the Enteric Nervous System. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 1323–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fung, C.; Van den Berghe, P. Functional circuits and signal processing in the enteric nervous system. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 4505–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitha, M.; Reichardt, F.; Tabatabavakili, S.; Nezami, B.G.; Chassaing, B.; Mwangi, S.; Vijay-Kumar, M.; Gewirtz, A.; Srinivasan, S. Intestinal Dysbiosis Contributes to the Delayed Gastrointestinal Transit in High-Fat Diet Fed Mice. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 2, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gershon, M.D. Review article: Serotonin receptors and transporters–roles in normal and abnormal gastrointestinal motility. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 20, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vadder, F.; Grasset, E.; Holm, L.M.; Karsenty, G.; MacPherson, A.J.; Olofsson, L.E.; Bäckhed, F. Gut microbiota regulates maturation of the adult enteric nervous system via enteric serotonin networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 6458–6463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husebye, E.; Hellstrom, P.; Sundler, F.; Chen, J.; Midtvedt, T. Influence of microbial species on small intestinal myoelectric activity and transit in germ-free rats. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2001, 280, G368–G380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manca, C.; Boubertakh, B.; Leblanc, N.; Deschênes, T.; Lacroix, S.; Martin, C.; Houde, A.; Veilleux, A.; Flamand, N.; Muccioli, G.G.; et al. Germ-free mice exhibit profound gut microbiota-dependent alterations of intestinal endocannabinoidome signaling. J. Lipid Res. 2020, 61, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Asmakh, M.; Zadjali, F. Use of Germ-Free Animal Models in Microbiota-Related Research. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 25, 1583–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soret, R.; Chevalier, J.; De Coppet, P.; Poupeau, G.; Derkinderen, P.; Segain, J.P.; Neunlist, M. Short-Chain Fatty Acids Regulate the Enteric Neurons and Control Gastrointestinal Motility in Rats. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 1772–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, A.D.; Wang, X.-Y.; Parsons, S.P.; Khan, W.I.; Huizinga, J.D. Abnormal absorptive colonic motor activity in germ-free mice is rectified by butyrate, an effect possibly mediated by mucosal serotonin. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2018, 315, G896–G907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, J.; Guarner, F.; Fernandez, L.B.; Maruy, A.; Sdepanian, V.L.; Cohen, H. Antibiotics as Major Disruptors of Gut Microbiota. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 572912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palleja, A.; Mikkelsen, K.H.; Forslund, S.K.; Kashani, A.; Allin, K.H.; Nielsen, T.; Hansen, T.H.; Liang, S.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, C.; et al. Recovery of gut microbiota of healthy adults following antibiotic exposure. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 1255–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, E.A.; King, K.Y.; Baldridge, M.T. Mouse Microbiota Models: Comparing Germ-Free Mice and Antibiotics Treatment as Tools for Modifying Gut Bacteria. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, L.Y.; Boonma, P.; Unterweger, P.; Parathan, P.; Haag, A.; Luna, R.A.; Bornstein, J.C.; Savidge, T.C.; Foong, J.P. Neonatal Antibiotics Disrupt Motility and Enteric Neural Circuits in Mouse Colon. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 8, 298–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, S.S.B.; Hung, L.Y.; Wu, Q.; Parathan, P.; Yalcinkaya, N.; Haag, A.; Luna, R.A.; Bornstein, J.C.; Savidge, T.C.; Foong, J.P.P. Neonatal antibiotics have long term sex-dependent effects on the enteric nervous system. J. Physiol. 2022, 600, 4303–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reikvam, D.H.; Erofeev, A.; Sandvik, A.; Grcic, V.; Jahnsen, F.L.; Gaustad, P.; McCoy, K.D.; Macpherson, A.J.; Meza-Zepeda, L.A.; Johansen, F.-E. Depletion of Murine Intestinal Microbiota: Effects on Gut Mucosa and Epithelial Gene Expression. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, P.; Conti, J.; Zatta, V.; Russo, V.; Scarpa, M.; Kotsafti, A.; Porzionato, A.; De Caro, R.; Scarpa, M.; Fassan, M.; et al. Persistent Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 Infection of Enteric Neurons Triggers CD8+ T Cell Response and Gastrointestinal Neuromuscular Dysfunction. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 615350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamma, P.D.; Avdic, E.; Li, D.X.; Dzintars, K.; Cosgrove, S.E. Association of Adverse Events With Antibiotic Use in Hospitalized Patients. JAMA Intern. Med. 2017, 177, 1308–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castagliuolo, I.; Riegler, M.F.; Valenick, L.; LaMont, J.T.; Pothoulakis, C. Saccharomyces boulardii protease inhibits the effects of Clostridium difficile toxins A and B in human colonic mucosa. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fordtran, J.S. Colitis Due to Clostridium Difficile Toxins: Underdiagnosed, Highly Virulent, and Nosocomial. Bayl. Univ. Med. Cent. Proc. 2006, 19, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yassour, M.; Vatanen, T.; Siljander, H.; Hämäläinen, A.-M.; Härkönen, T.; Ryhänen, S.J.; Franzosa, E.A.; Vlamakis, H.; Huttenhower, C.; Gevers, D.; et al. Natural history of the infant gut microbiome and impact of antibiotic treatment on bacterial strain diversity and stability. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 343ra81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Champagne-Jorgensen, K.; Kunze, W.A.; Forsythe, P.; Bienenstock, J.; Neufeld, K.-A.M. Antibiotics and the nervous system: More than just the microbes? Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 77, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minocha, A.; Galligan, J.J. Erythromycin inhibits contractions of nerve-muscle preparations of the guinea pig small intestine. Experiment 1991, 257, 1248–1252. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.C.; Qiao, Y.; Xu, L.; Kacimi, R.; Sun, X.; Giffard, R.G.; Yenari, M.A. Direct protection of cultured neurons from ischemia-like injury by minocycline. Anat. Cell Biol. 2010, 43, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Parkington, H.C.; Hussein, M.; Zhao, J.; Bergen, P.; Rudd, D.; Deane, M.A.; Oberrauch, S.; Cornthwaite-Duncan, L.; et al. Transcriptomic Mapping of Neurotoxicity Pathways in the Rat Brain in Response to Intraventricular Polymyxin B. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 60, 1317–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsson, H.E.; Jernberg, C.; Andersson, A.F.; Sjölund-Karlsson, M.; Jansson, J.K.; Engstrand, L. Short-Term Antibiotic Treatment Has Differing Long-Term Impacts on the Human Throat and Gut Microbiome. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jernberg, C.; Löfmark, S.; Edlund, C.; Jansson, J.K. Long-term impacts of antibiotic exposure on the human intestinal microbiota. Microbiology 2010, 156, 3216–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maloy, K.J.; Powrie, F. Intestinal homeostasis and its breakdown in inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 2011, 474, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, P.; Gobbo, S.; Caputi, V.; Spagnol, L.; Schirato, G.; Pasqualin, M.; Levorato, E.; Palù, G.; Giron, M.C.; Castagliuolo, I. Toll like receptor-2 regulates production of glial-derived neurotrophic factors in murine intestinal smooth muscle cells. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 68, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anitha, M.; Vijay–Kumar, M.; Sitaraman, S.V.; Gewirtz, A.T.; Srinivasan, S. Gut Microbial Products Regulate Murine Gastrointestinal Motility via Toll-Like Receptor 4 Signaling. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 1006–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. Mind-altering microorganisms: The impact of the gut microbiota on brain and behaviour. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piletz, J.E.; Cooper, J.; Chidester, K.; Erson, K.; Melton, S.; Osemeka, A.; Patterson, M.; Strickland, K.; Wan, J.X.; Williams, K. Transepithelial Effect of Probiotics in a Novel Model of Gut Lumen to Nerve Signaling. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janik, R.; Thomason, L.A.; Stanisz, A.M.; Forsythe, P.; Bienenstock, J.; Stanisz, G.J. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy reveals oral Lactobacillus promotion of increases in brain GABA, N-acetyl aspartate and glutamate. Neuroimage 2016, 125, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bercik, P.; Denou, E.; Collins, J.; Jackson, W.; Lu, J.; Jury, J.; Deng, Y.; Blennerhassett, P.; Macri, J.; McCoy, K.D.; et al. The Intestinal Microbiota Affect Central Levels of Brain-Derived Neurotropic Factor and Behavior in Mice. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, L.Y.; Parathan, P.; Boonma, P.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Haag, A.; Luna, R.A.; Bornstein, J.C.; Savidge, T.C.; Foong, J.P.P. Antibiotic exposure postweaning disrupts the neurochemistry and function of enteric neurons mediating colonic motor activity. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2020, 318, G1042–G1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, S.; Ranjha, R.; Paul, J. Neuroimmunomodulation by gut bacteria: Focus on inflammatory bowel diseases. World J. Gastrointest. Pathophysiol. 2021, 12, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Dowd, S.; Sun, Y.; Secor, P.R.; Rhoads, D.D.; Wolcott, B.M.; A James, G.; Wolcott, R.D. Survey of bacterial diversity in chronic wounds using Pyrosequencing, DGGE, and full ribosome shotgun sequencing. BMC Microbiol. 2008, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Target | Sequence |
|---|---|
| 16S V2 region | Fw *: AGYGGCGIACGGGTGAGTAA |
| Rv *: CYIACTGCTGCCTCCCGTAG | |
| 16S V6 region | Fw: AGGATTAGATACCCTGGTA |
| Rv: CRRCACGAGCTGACGAC | |
| Gdnf | Fw: TCAACTGGGGGTCTACG |
| Rv: GCATCTGGGGGTCAACCT | |
| Ngf | Fw: AGTTTTGGCCTGTGGTCGT |
| Rv: GGACATTACGCTATGCACCTC | |
| Cntf | Fw *: GGCCAAGCAAATGTAGCTCTT |
| Rv *: GCCCCTGGGGAACTACTG | |
| Nt5 | Fw: CCCATCCAACATGACCCTA |
| Rv: CAATGAGCTGCATGAGGAGA | |
| Nt3 | Fw: CGACGTCCCTGGAAATAGTC |
| Rv: TGGACATCACCTTGTTCCACC | |
| Bdnf | Fw: GAAGGCTGCAGGGGCATAGCAAA |
| Rv: TACACAGGAAGTGTCTATCCTTATG | |
| Lif | Fw: CGCCTAACATGACAGACTTCCCAT |
| Rv: AGGCCCCTCATGACGTCTATAGTA | |
| Rn18s | Fw: AACTTCTTAGAGGGACAAGTGG |
| Rv: CGGACATCTAAGGGCATCAC |
| Target (Host) | Clone | Source | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| β-actin (mouse) | AC-15 | Merck | WB |
| βIII-tubulin (rabbit) | polyclonal | Couvance | WM |
| HuC/D (mouse) | 16A11 | Abcam | WB |
| nNOS (rabbit) | polyclonal | Invitrogen | WB |
| Substance P (rabbit) | polyclonal | ImmunoStar | WM |
| S100β (rabbit) | EP1576Y | Millipore | WB |
| anti-mouse IgG | HRP conjugate | Merck | WB |
| anti-rabbit IgG | HRP conjugate | Merck | WB |
| anti-rabbit IgG | Alexa Fluor 555 conjugate | Invitrogen | WM |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bernabè, G.; Shalata, M.E.M.; Zatta, V.; Bellato, M.; Porzionato, A.; Castagliuolo, I.; Brun, P. Antibiotic Treatment Induces Long-Lasting Effects on Gut Microbiota and the Enteric Nervous System in Mice. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1000. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12061000
Bernabè G, Shalata MEM, Zatta V, Bellato M, Porzionato A, Castagliuolo I, Brun P. Antibiotic Treatment Induces Long-Lasting Effects on Gut Microbiota and the Enteric Nervous System in Mice. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(6):1000. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12061000
Chicago/Turabian StyleBernabè, Giulia, Mahmoud Elsayed Mosaad Shalata, Veronica Zatta, Massimo Bellato, Andrea Porzionato, Ignazio Castagliuolo, and Paola Brun. 2023. "Antibiotic Treatment Induces Long-Lasting Effects on Gut Microbiota and the Enteric Nervous System in Mice" Antibiotics 12, no. 6: 1000. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12061000
APA StyleBernabè, G., Shalata, M. E. M., Zatta, V., Bellato, M., Porzionato, A., Castagliuolo, I., & Brun, P. (2023). Antibiotic Treatment Induces Long-Lasting Effects on Gut Microbiota and the Enteric Nervous System in Mice. Antibiotics, 12(6), 1000. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12061000









