Abstract
The most common resistance mechanism to carbapenems is the production of carbapenemases. In 2021, the Pan American Health Organization warned of the emergence and increase in new carbapenemase combinations in Enterobacterales in Latin America. In this study, we characterized four Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates harboring blaKPC and blaNDM from an outbreak during the COVID-19 pandemic in a Brazilian hospital. We assessed their plasmids’ transference ability, fitness effects, and relative copy number in different hosts. The K. pneumoniae BHKPC93 and BHKPC104 strains were selected for whole genome sequencing (WGS) based on their pulsed-field gel electrophoresis profile. The WGS revealed that both isolates belong to ST11, and 20 resistance genes were identified in each isolate, including blaKPC-2 and blaNDM-1. The blaKPC gene was present on a ~56 Kbp IncN plasmid and the blaNDM-1 gene on a ~102 Kbp IncC plasmid, along with five other resistance genes. Although the blaNDM plasmid contained genes for conjugational transfer, only the blaKPC plasmid conjugated to E. coli J53, without apparent fitness effects. The minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of meropenem/imipenem against BHKPC93 and BHKPC104 were 128/64 and 256/128 mg/L, respectively. Although the meropenem and imipenem MICs against E. coli J53 transconjugants carrying the blaKPC gene were 2 mg/L, this was a substantial increment in the MIC relative to the original J53 strain. The blaKPC plasmid copy number was higher in K. pneumoniae BHKPC93 and BHKPC104 than in E. coli and higher than that of the blaNDM plasmids. In conclusion, two ST11 K. pneumoniae isolates that were part of a hospital outbreak co-harbored blaKPC-2 and blaNDM-1. The blaKPC-harboring IncN plasmid has been circulating in this hospital since at least 2015, and its high copy number might have contributed to the conjugative transfer of this particular plasmid to an E. coli host. The observation that the blaKPC-containing plasmid had a lower copy number in this E. coli strain may explain why this plasmid did not confer phenotypic resistance against meropenem and imipenem.
1. Introduction
Carbapenems are a powerful group of broad-spectrum β-lactam antibiotics, which are often the antibiotics of last resort against multidrug-resistant bacterial infections [1,2,3]. The increased use of carbapenems because of the lack of treatment alternatives has triggered the selection of resistance to these antibiotics among an increasing number of pathogens, mainly due to the production of carbapenemases [2,4,5,6].
Carbapenemases are divided into two main types: metallo-β-lactamases (Class B), containing zinc in the enzyme’s active site, and serine β-lactamases (Classes A, C, and D), containing serine in the active site [7]. These enzymes have the highest degradation spectrum/potential among the β-lactamases, which are able to hydrolyze practically all β-lactams [2,8,9,10]. Although carbapenemase-encoding genes were first identified only on the chromosome; many are now transposon/plasmid-mediated, increasing the potential of horizontal transmission [11,12,13].
Currently, Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase (KPC) is the most clinically significant serine carbapenemase in most countries in the world, and due to the fact of its rapid international spread, KPC threatens global public health [4,11,14]. In Brazil, reports indicate KPC as the main carbapenemase, with a prevalence of more than 76% among carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales, while the New Delhi metallo-carbapenemase (NDM) is found at lower frequency and prevalence [15,16,17]. Since its first identification in Brazil, in 2013, NDM-producing bacteria have been considered Brazil’s next public health threat [17,18,19].
Latin America has seen the emergence and rise of novel combinations of carbapenemases in Enterobacterales, as well as the presence of carbapenemases that had not been previously described, according to a warning issued by the Pan American Health Organization. Argentina, Uruguay, Ecuador, Guatemala, and Paraguay identified isolates co-producing KPC and NDM with increasing rates between 2020 and 2021 compared to previous years, mainly in K. pneumoniae [20].
According to data from South and Midwest Brazil, the number of isolates co-producing NDM and KPC increased by almost six times during the COVID-19 pandemic, and they were detected mainly in the Klebsiella pneumoniae complex (59.5%), followed by Pseudomonas aeruginosa (12.9%) and Serratia marcescens (8.8%) [21]. The increase in KPC/NDM co-producers during the COVID-19 pandemic represents a worrying scenario for public health in Latin America [21,22,23]. In Brazil, ceftazidime–avibactam (CAZ-AVI) and aztreonam (ATM) are available to treat infections caused by KPC-producer and NDM-producer bacteria, respectively. However, these drugs alone are inefficient at treating infections with KPC/NDM co-producers. Some cases in the literature have shown the synergism and efficacy of treating infections using the combination of CAZ-AVI and ATM against serine- and metallo-β-lactamase co-producing Enterobacterales and P. aeruginosa [24,25]. A promising drug in these cases would be cefiderocol (CFDC), a novel siderophore cephalosporin, with activity against carbapenem-resistant bacteria, including multidrug-resistant (MDR) Enterobacterales and nonfermenters, due to the fact of its distinct penetration mechanism, which uses active iron transporters, and its stability against carbapenemases [26,27,28]. CFDC showed high activity against MBL-producing isolates and some dual-carbapenemases producers, such as KPC + VIM, NDM + OXA-48-like, and VIM + OXA-48-like [29,30]. However, evidence of activity against KPC/NDM co-producers is limited [29].
In this study, we molecularly characterized four clinical isolates from an outbreak of KPC/NDM co-producer K. pneumoniae, which started during the COVID-19 pandemic in a teaching hospital in Belo Horizonte, MG, Brazil. In addition, we sequenced two isolates and compared the identified blaKPC-carrying plasmid to the plasmids of a previous KPC producer isolate from the same hospital. Finally, we attempted to shed light on why the blaKPC gene is usually more frequent in K. pneumoniae by studying the conjugation efficiency of the blaKPC-containing and blaNDM-containing plasmid to E. coli and assessing their copy number in both species.
2. Results
2.1. A Multidrug-Resistant K. pneumoniae ST11 Clone Spread during the COVID-19 Pandemic
In October 2020, a Brazilian teaching hospital (in Belo Horizonte/MG) detected the first KPC/NDM co-producer K. pneumoniae, which led to a molecular investigation of four isolates. According to the susceptibility profile, the four isolates involved in the outbreak are resistant to multiple antibiotics, and among all antibiotics that were tested, three of the four isolates were only susceptible to amikacin (Table 1). Isolate BHKPC107b was also susceptible to gentamicin.

Table 1.
General data and susceptibility profile of the isolates.
DNA macro-restriction followed by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis revealed the existence of one pulsotype, showing the clonal dissemination of KPC and NDM co-producer K. pneumoniae from the Brazilian hospital. The BHKPC93 strain had two differences, an additional band and the lack of another one, resulting in 95% genetic similarity, and was considered a closely related subtype (Figure 1). Therefore, BHKPC93 and BHKPC104, as representative isolates of two clonal types, were selected for whole genome sequencing (WGS) using Illumina and Nanopore technologies.

Figure 1.
High genetic similarity of the four KPC and NDM co-producer isolates observed after XbaI digestion, pulsed-field gel electrophoresis, and analysis using Bionumerics software v. 7.1. The running direction of the gel was from left to right.
The nanopore mean coverage for BHKPC93 and BHKPC104 was 19×, and the Illumina’s were 134× and 106×, respectively.
The assembly of the short-read and long-read sequencings of the two isolates, BHKPC93 and BHKPC104, resulted in a closed chromosomal sequence of BHKPC93 and BHKPC104 of 5,749,747 bp and 5,742,965 bp (Figure S1—Supplementary Materials), respectively, and six complete plasmid sequences with sizes ranging between 4.5 kbp and 193 kbp (Figure 2).
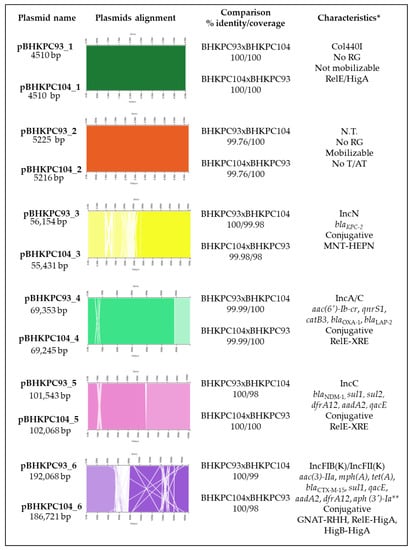
Figure 2.
General information and comparison among the plasmids of the BHKPC93 and BHKPC104 strains. * Characteristics observed: plasmid incompatibility group; resistance genes; conjugation ability; toxin/antitoxin system. No RG, no resistance gene; N.T., non-typeable plasmid; No T/AT, no toxin/antitoxin system detected. ** Resistance gene present only in BHKPC104.
We analyzed the similarity between the isolates BHKPC93 and BHKPC104 based on the gene content. We found that both isolates shared 5425 genes, while only 15 and 11 genes were exclusively found in BHKPC93 and BHKPC104, respectively; this resulted in a Jaccard distance of 0.0046 (Table S2—Supplementary Materials). Moreover, only 13 SNPs were found among shared genome fractions, thus confirming that the isolates were highly related.
The isolates belong to ST11 and harbor the blaKPC-2 and blaNDM-1 genes, plus 18 resistance genes. We found resistance genes to aminoglycosides (aac(6’)-Ib-cr, aac(3)-IIa, aph(3’)-Ia, and aadA2), fosfomycin (fosA), aminocyclitol (aadA2), quinolones (aac(6’)-Ib-cr, oqxA, oqxB, and qnrS1), folate pathway antagonists, such as trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (sul1, sul2, dfrA12, oqxA, and oqxB), tetracycline (tet(A)), β-lactams (blaNDM-1, blaKPC-2, blaSHV-182, blaOXA-1, blaCTX-M-15, and blaLAP-2), quaternary ammonium compounds (oqxA, oqxB, and qacE), amphenicol (catB3, oqxA, and oqxB), and macrolide (mph(A)) (Table S3—Supplementary Materials). The genes fosA, oqxA, oqxB, and blaSHV-182 were located on the chromosome, and the remaining genes were distributed on four plasmids (Figure 2).
In addition, both isolates presented known mutations in the gyrA and parC genes, leading to the amino acid substitutions S83I and S80I, respectively, previously shown to result in ciprofloxacin resistance [31,32].
Next, we explored possible mechanisms of polymyxin resistance in BHKPC93 and BHKPC104. The two isolates did not contain mcr gene family sequences encoding acquired colistin resistance determinants. Additionally, we compared the sequences of the genes mgrB, phoP, phoQ, pmrA, pmrB, pmrC, pmrK, pmrR, qceB, qceC, crrA, and crrB, previously implicated in polymyxin resistance, of BHKPC93 and BHKPC104 with the polymyxin-susceptible ST11 K. pneumoniae AMKP36 strain [33] (genome accession number: SAMN13160271). This comparison did not reveal specific mutations in the two polymyxin-resistant isolates BHKPC93 and BHKPC104.
BHKPC93 and BHKPC104 carried mutations in the ompK36 and ompK37 porin genes that potentially contribute to cephalosporin and carbapenem resistance and can also be involved in polymyxin resistance [34,35].
The string test classified BHKPC93, BHKPC104, BHKPC107a, and BHKPC107b as mucoid. The genome-sequenced strains also have seven virulence factors involved in heat resistance/thermal stress (clpK1), attachment to surfaces (fimH and mrkA), iron acquisition–siderophores genes (fyuA, irp2, and iutA), and serum resistance (traT).
2.2. The K. pneumoniae Isolates Have 16 Resistance Genes Distributed in Four Out of Their Six Plasmids
The BHKPC93 and BHKPC104 complete genome sequencing indicated that these isolates harbor six plasmids ranging from 4510 bp to 192,068 bp, which were very similar between the two strains (Figure 2).
pBHKPC93_1 and pBHKPC104_1 are 100% identical, with 4510 nucleotides (nt) Col440I-type plasmids that are predicted not to be mobilizable and harboring a RelE-like/HigA toxin/antitoxin system.
pBHKPC93_2 and pBHKPC104_2 are non-self-conjugative but mobilizable plasmids that share 99.76% identity. Their incompatibility groups were not identified. In addition to the conjugation system genes, these plasmids harbor DNA methyltransferase, hypothetical protein, and replication initiation protein genes.
pBHKPC93_3 and pBHKPC104_3 are IncN blaKPC-harboring plasmids of 56,154 nt and 55,431 nt, respectively, sharing 99.98% identity.
pBHKPC93_3 is larger than pBHKPC104_3 because it has a duplicated region composed of genes coding for two hypothetical proteins and the cobalamin biosynthesis protein gene (cbiX). In contrast, pBHKPC93_3 lacked the adrA gene that codes for an antirestriction protein, which was present in pBHKPC104_3. These plasmids carried relaxase genes codifying the T4CP and T4SS proteins, classifying them as conjugative plasmids. The blaKPC gene is in a Tn44011b isoform inserted into a gene codifying a phospholipase D family protein in both plasmids (Figures S2 and S3—Supplementary Materials).
pBHKPC93_4 and pBHKPC104_4 are IncA/C-conjugative plasmids of 69,353 nt and 69,245 nt, respectively, carrying five resistance genes and the same toxin/antitoxin system as pBHKPC93_5 and p_BHKPC104_5.
pBHKPC93_5 and pBHKPC104_5 are IncC plasmids harboring blaNDM, which are 102,068 nt and 101,543 nt, respectively. In addition to blaNDM, these plasmids carry five other resistance genes: sul1, sul2, dfrA12, aadA2, and qacE. Although a relaxase gene was not identified using Plascad software, we used the Pfam database and found a gene annotated as a hypothetical protein that matches the MobI codifying gene. We also found genes encoding proteins involved in transfer by conjugation: type IV secretion system protein, TrbG/VirB9 family P-type conjugative transfer protein, conjugal transfer protein TraF, Conjugal transfer protein TraG, Conjugal transfer protein TraH genes. Based on the presence of these genes, these plasmids were classified as conjugative plasmids. The plasmids share 100% identity but 98% coverage due to the absence of an ISKpn18 gene in pBHKPC104_5. A ΔTn125-4 harbors the blaNDM gene with the bleomycin resistance gene (Figures S4 and S5—Supplementary Materials).
The largest plasmids, carrying eight resistance genes, with a complete conjugation system, are pBHKPC93_6 and pBHKPC104_6, with 100% identity and 99/98% coverage. In addition, pBHKPC104_6 has the aph(3’)-Ia gene and lacks the Tn3-like element Tn5403 family transposase gene present in pBHKPC93_6.
2.3. A Retrospective Search of blaKPC Plasmids
Some of the bacteria from this hospital had already been sequenced before, and their genomes were deposited in GenBank. Among them, we identified the K. pneumoniae BHKPC49 strain (access number: SAMN32643894), which contained an IncN plasmid carrying blaKPC, which was already circulating in 2015. K. pneumoniae BHKPC49 belongs to ST147 and shares five virulence genes (fimH, mrkA, fyuA, irp2, and iutA) with strains BHKPC93 and BHKPC104, in addition to ccl and nlpI.
BHKPC49 harbors an IncN/IncR plasmid of 134 kbp, carrying blaKPC in Tn4401 and another 9 kbp ColRNAI plasmid. The blaKPC plasmid of BHKPC49 contains the complete sequence of the IncN plasmids pBHKPC104_3 and pBHKPC93_3 and an IncR region harboring another 13 resistance genes: aph(3″)-Ib, aph(6)-Id, aac(3)-IIa, aac(6′)-Ib-cr, qnrS1, dfrA1, sul1, tet(A), blaOXA-1, blaTEM-1B, blaCTX-M-15, qacE, and catB3. The BHKPC49 IncN/IncR plasmid shares the same toxin/antitoxin system (MNT-like/HEPN-like) as pBHKPC104_3 and pBHKPC93_3, and it has two other toxin/antitoxin systems (PIN-like/AbrB-like and Rel-like/Xre-like). The plasmid harboring the blaKPC gene that circulated at the hospital in 2015 might have lost genes over time.
The IncN plasmids pBHKPC93_3 and pBHKPC104_3 also have high similarity (99.96% identity and 100% coverage) with the IncN-pST15 plasmid, which has been circulating in different hosts [36]. We also compared these plasmids with pIncN_C1-94_KPC from Colombia [37], classified as part of an IncN “promiscuous” plasmids group that harbors the blaKPC-2 gene, and our analysis showed 97.7% identity and 81% coverage with pBHKPC93_3 and 99.24% identity and 81% coverage with pBHKPC104_3.
2.4. The Impact of blaKPC Plasmid Presence in E. coli J53
In vitro conjugation assays using strains BHKPC93 and BHKPC104 as donors and E. coli J53 as an acceptor resulted in the transfer of only pBHKPC93_3 and pBHKPC104_3 plasmids with conjugation rates of approximately 2 × 10−5 transconjugants/recipient (Table 2).

Table 2.
Characterization data of blaKPC and blaNDM plasmids.
S1 nuclease/PFGE data confirmed this conjugation, as only one ~50 kbp fragment was present in the E. coli J53 transconjugants originating from the donors BHKPC93 and BHKPC104. Despite the nonidentification of some plasmids using this technique, the presence of the six plasmids was evident from the hybrid assembly, considered a gold standard in this case, in BHKPC93 and BHKPC104 (Figure S6—Supplementary Materials).
The similar doubling times of E. coli J53 and the E. coli J53 transconjugants indicates that the plasmid acquisition did not seem to affect E. coli J53’s fitness in the absence of antibiotics (Table 2), with no statistically significant difference between E. coli J53 and the transconjugants E. coli J53 pBHKPC93 (p = 0.9790) and E. coli J53 pBHKPC104 (p = 0.9494).
The acquisition of pBHKPC93_3 and pBHKPC104_3 carrying the blaKPC gene by E. coli J53 transconjugants resulted in a substantial increase in the meropenem and imipenem MICs. However, according to EUCAST criteria, these transconjugants are still susceptible (Table 2).
The plasmid copy numbers were determined relatively with the values of a housekeeping/one copy chromosomic gene (mdh) and the blaKPC or blaNDM gene. The relative plasmid copy numbers (PCNs) revealed that the PCNs of the blaKPC-containing plasmids in K. pneumoniae were higher than in their E. coli transconjugants (Table 2). In addition, blaKPC-containing plasmids’ PCNs were higher than the blaNDM-containing plasmids’ PCNs in the BHKPC93 and BHKPC104 strains (Table 2).
3. Discussion
Carbapenems are last-resort antibiotics, and their use is increasing due to the difficulty of treating infections caused by multidrug-resistant Enterobacterales. This has led to an increase in carbapenem-resistant clinical isolates, becoming a threat to global public health due to the limited treatment options [38,39]. An even worse scenario occurs when carbapenemases are co-produced, such as KPC and NDM [39].
In Latin America, the first detection of isolates co-producing KPC and NDM was in Enterobacter sp. isolates from September/October 2013 [38,40]. Pereira et al. (2015) described a multidrug-resistant isolate, susceptible to amikacin and polymyxin B, carrying blaKPC associated with Tn4401b in a 50 kb IncN plasmid and blaNDM in a 160 kbp IncA/C plasmid associated to the ΔISAba125 and ble genes. Both genes are associated with mobile genetic elements of worldwide epidemiological importance.
Since its first detection, Argentina, Uruguay, Ecuador, Guatemala, and Paraguay have described isolates co-producing KPC and NDM at increasing rates between 2020 and 2021 [20]. Several studies have described this combination in Brazil since 2015, but so far neither isolates nor plasmids combining the KPC and NDM types of resistance have not been characterized in great detail [13,40,41,42].
In this study, we molecularly investigated a multidrug-resistant K. pneumoniae ST11 clone harboring six plasmids and 20 resistance genes, including blaKPC-2 and blaNDM-1, and characterized the plasmids containing carbapenemases genes.
The carbapenemases genes of this outbreak’s isolates were present in different plasmid groups than those identified in other Latin American countries. The IncA/C-type plasmids carrying blaNDM-1 were previously detected in Enterobacterales isolates in Brazil [40]. The IncA/C plasmids are associated with the dissemination of blaNDM, and these plasmids carrying the carbapenemase gene were isolated from lineages in many countries, such as Brazil, Germany, Romania, Iran, and Pakistan. They are usually larger than pBHKPC93_5 and pBHKPC104_5 and are widely spread [40,43,44,45,46,47,48].
blaKPC-harboring IncN plasmids, such as those identified in BHKPC93 and BHKPC104, were already considered “promiscuous” plasmids and had been detected in Brazil and Latin America in different STs and species, and these isolates had been detected in different hosts (human and dog) [36,37] (Figure S7—Supplementary Materials). Gomez-Simmonds et al. (2022) studied IncN plasmids harboring blaKPC genes from a New York City Medical Centre and suggested evidence for their multispecies horizontal transmission [49]. blaKPC IncN plasmids are widely spread, and they had already been found in isolates from different places, such as Brazil, Colombia, USA, Germany, Italy, and Israel [37,40,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56]. Our analysis shows that a similar IncN plasmid harboring blaKPC was already circulating within the same hospital, in the BHKPC49 strain (access number: SAMN32643894), where BHKPC93 and BHKPC104 were recovered in 2015, as a larger element of K. pneumoniae and which might have lost genes over time.
In the conditions analyzed in this study, the copy numbers of the blaKPC plasmids in BHKPC93 and BHKPC104 were 11-fold and 4-fold higher than the plasmids containing blaNDM, which may have contributed to the fact that only the blaKPC plasmids were conjugated to E. coli J53. According to EUCAST, E. coli J53 transconjugants are susceptible to these carbapenems, even though they are carbapenemase producers, which could contribute to a “silent” dissemination of the antimicrobial resistance gene. The lower copy numbers of the blaKPC plasmids in the E. coli J53 transconjugants could explain the lower MIC values compared with K. pneumoniae BHKPC93 and BHKPC104. According to other studies, different plasmids in a bacterial cell can interact and improve fitness, replication, and gene horizontal transference [57,58]. The strains examined in this study harbor six plasmids, five of which carry toxin–antitoxin (T/A) systems, presumably contributing to their maintenance in bacteria. The small plasmids pBHKPC93_1 and pBHKPC104_1, carrying only a T/A system, could be advantageous, because they could allow cells to exchange plasmids without affecting viability. Studies show the association of a toxin family with different antitoxin families, suggesting that the TA system families’ concept is not adequate, opening the possibility that known toxin genes might be associated with genes representing novel antitoxins and vice versa [59,60,61]. The antitoxin HigA, encoded by these small plasmids, may complement antitoxins of plasmids with the same T/A system that could be lost, such as pBHKPC93_6 and pBHKPC104_6, which are larger and more costly to the cell. Only two plasmids, 1 and 2, were not considered self-conjugative. Plasmid 2, considered mobilizable, probably needs to share conjugative proteins codified by the plasmids in the cell to transfer. Despite the potential of being mobilized, only one plasmid was conjugated to E. coli J53. The PCN of the blaKPC-harboring plasmid were 11-fold and 9-fold higher in K. pneumoniae than in E. coli. So, in addition to the presence of other resistance genes, including β-lactamases, and mutation in porin-coding genes in K. pneumoniae, the interaction among different plasmids might play a role in the difference in the PCNs and carbapenem’s susceptibility in E. coli and K. pneumoniae, which deserves further investigation.
This study’s limitations include the lack of an analysis of the first isolates co-producing KPC/NDM found in the hospital because they were not stored. In addition, we could neither sequence the whole genome of all four isolates initially selected for the study nor the plasmids transferred to E. coli J53. We only checked the transconjugant E. coli plasmid sizes by S1 nuclease assay. Another limitation of this study is that with this method, we were unable to see whether the smaller plasmids were conjugated. Both plasmids, ~4.5 kb and ~5.2 kb, had no resistance genes, and the effect of their presence will be further analyzed by our group.
In conclusion, an extensively multidrug-resistant K. pneumoniae ST11 clone, co-producing KPC and NDM, caused the outbreak in a Brazilian teaching hospital during the COVID-19 pandemic. The blaKPC-harboring IncN plasmid shares a high identity with other plasmids from Latin America and was already circulating in 2015 as a larger element in the same hospital via the BHKPC49 strain (access number: SAMN32643894). The blaKPC plasmid’s high copy number might have contributed to the conjugation of this gene to E. coli. E. coli’s susceptibility to meropenem and imipenem might be due to the fact of this species’ low copy number of the blaKPC -harboring plasmid.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Isolates
From October 2020 to January 2021, the hospital investigated 45 meropenem-resistant isolates, among which 30 were KPC producers, 6 NDM producers, and 6 KPC/NDM co-producers (Camila da Mata and Edna Leite, personal communication). Only four out of 6 KPC/NDM co-producers isolated from three patients were stored and included in this study: K. pneumoniae strains BHKPC93, BHKPC104, BHKPC107a, and BHKPC107b.
In addition, the hospital provided the isolate K. pneumoniae BHKPC49 from 2015, which has the blaKPC-2 gene and belongs to the hospital’s bacteria collection, which was already sequenced. We included BHKPC49 in this study to perform whole genome sequencing (WGS) and, therefore, characterize and compare the blaKPC environment and plasmids to the outbreak isolates’ plasmids. All bacteria isolates were registered at SISGen under the number A6594DF.
4.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test
The susceptibility profiles of all clinical isolates were determined using the Vitek-2 (Biomerieux, Marcy-l’Étoile, France) and CLSI 2020 recommendations by the hospital laboratory, except for meropenem, imipenem, colistin, polymyxin B, and tigecycline for which the minimal inhibitory concentrations (MICs) were determined at the LEMiMo/University of São Paulo, along with the transconjugant strains, using the microdilution method according to the ISO 20776-1 and EUCAST recommendations.
4.3. Genomic DNA Extractions
For polymerase chain reactions (PCRs), the bacteria were inoculated in brain heart infusion (BHI) broth (Kasvi, Parana, Brazil), and the cells were lysed with the mechanical lysis method using glass beads [62]. Nucleic acids were purified by precipitation in isopropanol, rehydrated in ultrapure water, and treated with RNase. The extracted DNA was quantified in a NanoDrop ND 2000c (Thermofisher, Waltham, MA, USA) and stored at −20 °C.
For the genome sequencing, bacterial DNA was extracted according to the manufacturer’s instructions using the Wizard Genomic DNA Purification Kit (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). The extracted DNA was quantified using a NanoDrop ND 2000c and stored at 4 °C.
4.4. blaKPC and blaNDM Genes and Tn4401 Detection
The blaKPC and blaNDM genes were detected individually using PCR with primers described by Poirel et al. (2011) [63,64]. The amplification of Tn4401 was performed using the primer pairs described by Naas et al. (2008) (Table S1—Supplementary Materials) [64].
According to the manufacturer’s instructions, the reactions were prepared using Taq DNA polymerase, recombinant (Thermo Scientific, Vilnius, Lithuania). The PCRs were performed for 35 cycles at 95 °C for 30 s, 55 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 60 s. The PCR products were verified with 1% agarose gel electrophoresis at 90 V for 40 min (PowerPac™ HC High-Current Power Supply, Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA).
4.5. Detection of the Clonality and Plasmid Sizes
The clonality and plasmid sizes were detected after XbaI and S1-nuclease restriction, respectively, followed by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE). Two milliliters of overnight cultures adjusted for OD600nm 1 were used to separate and wash the cells. Agarose plugs were made with 400 µL of cell suspension, 40 µL of proteinase K (10 mg/mL), and 400 µL of 1.25% Seakem Gold Agarose (Lonza, Basel, Switzerland). The immobilized cells in the plugs were lysed using 50 mM Tris-HCl pH8, 50 mM EDTA pH8, 1% Sarcosil, and 50 µL of proteinase K (10 mg/mL) for 2 h at 55 °C. The plugs were then washed with Tris-EDTA buffer and ultrapure water.
According to the manufacturer’s instructions, 5 × 5 mm plug fragments were digested with XbaI or S1-nuclease and submitted to electrophoresis in 1% Seakem Gold Agarose (Lonza, Basel, Switzerland). XbaI-PFGE gel’s run conditions: 6 V gradient, 19 h, 6.76 s initial switch time, and 35.35 s final switch time using the CHEF Mapper system (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). A Lambda DNA Ladder (48.5 KB–1 MB) (Lonza, Basel, Switzerland) was used as the molecular weight standard. S1-nuclease PFGE gel’s run conditions: 6 V gradient, 15 h, 1 s initial switch time, and 18 s final switch time. Low Range PFG Marker (New England Biolabs, Ipswich, MA, USA) was used as the molecular weight standard.
The gels were dyed with SYBR Safe DNA Gel Stain (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) for 60 min and revealed using the ChemiDoc MP Imaging System (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). The PFGE gel image was analyzed using Bionumerics software v. 7.1 (Applied Maths, Sint-Martens-Latem, Belgium) to determine the genetic similarity among the isolates.
4.6. Determination of the Mucoid Phenotypes
The mucoid phenotypes were determined using the String test, performed as described elsewhere [65,66]. The isolates’ colonies were grown on BHI and MacConkey Agar (Kasvi, Brazil) plates and touched with an inoculation loop. The loop was lifted, and if a string longer than 5 mm was observed, the strain was classified as hypermucoviscous. Otherwise, the strains were classified as mucoid.
4.7. Genome Sequencing
The genomes were sequenced using the Illumina and Nanopore methods at the University Medical Centre Utrecht, Utrecht (The Netherlands). For the Illumina sequencing, the library was prepared with the Nextera DNA sample preparation kit and Nextera index v2 set D for 96 indexes, and the isolates were sequenced using NextSeq500 2 × 150 bp mid-output (120 M clusters) (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA).
For the Nanopore sequencing, the libraries were prepared using Oxford Nanopore’s Ligation Sequencing Kit and Native Barcoding Expansion Kit, and the isolates were sequenced using the MinION sequencer (Oxford Nanopore Technologies, Oxford, UK).
4.8. Quality Analysis and Genome Assembly
Initial quality analysis of Illumina’s reads was performed using Fastqc (v0.11.9). Trim Galore (v.0.6.6) with the default parameters was applied for adapter removal and quality trimming. The genomes were assembled using Unicycler (v.0.4.8) in the bold mode. The hybrid assemblies’ quality was assessed using BUSCO (v5.1.2).
The assembled BHKPC93, BHKPC104, and BHKPC49 genomes were submitted to the NCBI database for annotation and deposited with the accession numbers SAMN26563515, SAMN26563478, and SAMN32643894, respectively.
The genome sequences were analyzed using Resfinder, MLST, and VirulenceFinder, available at the Center for Genomic Epidemiology (http://www.genomicepidemiology.org/ accessed on 8 March 2023).
4.9. Genomes Similarity Analysis
The number of SNPs among the isolates was determined using the CFSAN pipeline (v. 2.1.1) with the default parameters. For this, the Illumina reads of isolate BHKPC93 were mapped against the assembled genome of BHKPC104.
The genomes were annotated with BAKTA (v1.3.3), and the core and accessory genes were identified using Panaroo (v1.2.10) with the default parameters. The gene content similarity was evaluated by calculating the Jaccard distance between the isolates, as indicated below:
The plasmids sequences were submitted to NCBI BLASTn, and Kablammo software with the default parameters was used to analyze the plasmids’ identity and compare with BHKPC49 (accession number: SAMN32643894), IncN-pST15 plasmids (accession numbers: JABSUB010000003.1, CP004367.2, and KX062091.1) [36,37], and pIncN_C1-94_KPC from Colombia [37].
4.10. Code Availability
The codes to reproduce the bioinformatic analysis of this work are publicly available: gitlab.com/jpaganini/saopaulo_kpn_outbreak.
4.11. Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST)
The STs of the four isolates were determined according to the MLST Pasteur scheme [67]. For BHKPC93 and BHKPC104, the whole genome sequence data were used. For BHKPC107a and BHKPC107b, which were not submitted for WGS, the PCRs were conducted with specific MLST K. pneumoniae primers [67], and the amplicons were sequenced using the Sanger method, carried out on an Applied Biosystems 3130 Genetic Analyzer (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA).
4.12. Plasmids Analysis
The plasmids’ mobilization capacity was determined using Plascad software with default parameters.
The genes of the toxin/antitoxin (T/A) systems were detected using the TA Finder web service (https://bioinfo-mml.sjtu.edu.cn/TADB2/index.php accessed on 8 March 2023) with the default parameters.
4.13. Conjugation Assay
Overnight cultures of the receptor strain E. coli J53 and the donor strains K. pneumoniae BHKPC93 and K. pneumoniae BHKPC104 were adjusted to OD600nm 0.3 in 10 mL lysogeny broth (LB) (Kasvi, Brazil) and incubated at 37 °C until OD600nm 0.7. The conjugation assays were performed in 10 mL of 1:1 (receptor:donor) OD600nm 0.7 cultures, which were incubated at 37 °C for 24 h. Serial dilutions of the co-cultures were spread on LB agar with 125 mg/L azide and LB agar with 4 mg/L imipenem and 125 mg/L azide. After incubation, the isolated E. coli colonies were counted, and the conjugation rate was calculated using (CFUreceptor/mL)/(CFUtransconjugant/mL). The isolated colonies detected on imipenem- and azide-containing LB agar were subjected to PCR to detect the blaKPC and blaNDM genes using the same culture suspension as the templates.
4.14. Determination of the Growth Curve and Doubling Time
The overnight cultures were adjusted to OD600nm 0.05–0.1 in cation-adjusted Mueller Hinton broth ( Becton Dickinson and Company, Sparks, MD, USA), and 200 µL of each were added to each well in a 96-well polystyrene microplate. The OD600nm measurements were taken every 15 min with 5 s of agitation before and after the reading using the SpectraMax M5 spectrophotometer (Molecular Devices, San Jose, CA, USA) at 37 °C for 10 h. The assay was performed in five replicates. The measurements were plotted on a growth curve, and the doubling times were calculated using linear regression of the log-phase. The statistical significance was calculated using the Student’s t-test and ANOVA (p < 0.05).
4.15. Determination of the Plasmid Copy Number
The plasmid copy numbers were determined using qPCR, according to the method described by Woodall, C. A. (2003) [68]. The overnight cultures were adjusted to OD600nm 1 in BHI broth (Kasvi, Parana, Brazil), and the cells were lysed at 98 °C for 10 min, followed by freezing for 10 min at 20 °C. The lysed cultures were diluted at 1:10, and 3 µL were used in each reaction. The primers were designed for the housekeeping genes (malate dehydrogenase (mdh) genes) and blaKPC/blaNDM genes. The qPCR reactions contained 1x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix (ThermoFisher, Waltham, CA, USA), 100 nM of each primer, 3 µL of culture, and ultrapure water qs to 10 µL, and they were conducted using the CFX96 Touch Real-Time PCR Detection System (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) with the following conditions: 3 min at 95 °C, 40 cycles of 10 s at 95 °C, 1 min at 50 °C, and 10 s at 72 °C. All qPCR reactions, including the controls, were performed in experimental triplicates. The primers’ efficiency and specificity were determined using standard and melting curves, with five serial dilutions. The standard curves’ slopes were used to calculate the amplification efficiency [69].
The relative plasmid copy numbers (PCNs) were determined, considering the different amplification efficiencies and Ct values for each amplicon (chromosomic -c and plasmid -p) [69].
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/antibiotics12050926/s1, Table S1: Sequences of primers used in this study; Table S2: Description of the 15 and 11 genes found exclusively in BHKPC93 and BHKPC104; Table S3: Resistance genes found in BHKPC93 and BHKPC104; Figure S1: Scheme of the chromosome comparison using BHKPC104 as a reference and compared with BHKPC93; Figure S2: Scheme of pBHKPC93_3; Figure S3: Scheme of pBHKPC104_3; Figure S4: Scheme of pBHKPC93_5; Figure S5: Scheme of pBHKPC104_5; Figure S6: S1 nuclease PFGE gel of the isolates BHKPC93 (A), BHKPC104 (B), BHKPC107a (C), and BHKPC107b (D) and the transconjugants J53_pBHKPC93_3 (E) and J53_pBHKPC104_3 (F); Figure S7: Scheme of the comparison between pBHKPC93_3 and pBHKPC104_3.
Author Contributions
As the main researcher, C.M.d.S.B. conducted all experimental assays and wrote the manuscript; J.A.P. and R.S.M. performed the genome assembly and analysis; R.J.L.W. and F.L.P. performed the genome sequencing; C.P.S.M.d.M. and E.M.M.L. provided the isolates and their data and performed part of the susceptibility profile determination; I.L.B.C.C., F.L.P. and A.C.S. organized the teams; I.L.B.C.C., as the principal investigator, supervised the experiments and results; guided, administrated, and organized the project; and wrote part of the manuscript. I.L.B.C.C., F.L.P., R.J.L.W., A.C.S. and J.A.P. reviewed the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
C.M.d.S.B. was supported by a fellowship from Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES), finance Code 001, grant numbers: 88882.328750/2019-01 and 88887.600137/2021-00. I.L.B..C. was supported by a fellowship from CNPq Research Productivity Scholar, level 2, grant number: 304325/2021-0, by the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study by the Comissão Nacional de Ética em Pesquisa (CONEP) because the study did not involve human beings.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Rafael Spadaccia Panhota, who conducted the Sanger sequencing for the MLST at the “Sérgio Mascarenhas” Biophysics and Structural Biology Group at IFSC-USP.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kattan, J.N.; Villegas, M.V.; Quinn, J.P. New Developments in Carbapenems. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2008, 14, 1102–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopotsa, K.; Osei Sekyere, J.; Mbelle, N.M. Plasmid Evolution in Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae: A Review. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2019, 1457, 61–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taggar, G.; Rheman, M.A.; Boerlin, P.; Diarra, M.S. Molecular Epidemiology of Carbapenemases in Enterobacteriales from Humans, Animals, Food and the Environment. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Mathema, B.; Chavda, K.D.; DeLeo, F.R.; Bonomo, R.A.; Kreiswirth, B.N. Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella Pneumoniae: Molecular and Genetic Decoding. Trends Microbiol. 2014, 22, 686–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buehrle, D.J.; Shields, R.K.; Clarke, L.G.; Potoski, B.A.; Clancy, C.J.; Hong Nguyen, M. Carbapenem-Resistant Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Bacteremia: Risk Factors for Mortality and Microbiologic Treatment Failure. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e01243-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Echols, R.; Magee, G.; Ferreira, J.C.A.; Morgan, G.; Ariyasu, M.; Sawada, T.; Nagata, T. Prevalence of Carbapenem-Resistant Gram-Negative Infections in the United States Predominated by Acinetobacter Baumannii and Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Open Forum. Infect. Dis. 2017, 4, ofx176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swathi, C.H.; Chikala, R.; Ratnakar, K.S.; Sritharan, V. A Structural, Epidemiological & Genetic Overview of Klebsiella Pneumoniae Carbapenemases (KPCs). Indian J. Med. Res. 2016, 144, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queenan, A.M.; Bush, K. Carbapenemases: The Versatile β-Lactamases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 440–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gniadek, T.J.; Carroll, K.C.; Simner, P.J. Carbapenem-Resistant Non-Glucose-Fermenting Gram-Negative Bacilli: The Missing Piece to the Puzzle. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, L.N.; Lúcia, A.; Darini, C. Bacilos Gram-Negativos Produtores de Beta-Lactamases: Que Bla Bla Bla é Esse? J. Infect. Control 2017, 6, 16–25. [Google Scholar]
- Tzouvelekis, L.S.; Markogiannakis, A.; Psichogiou, M.; Tassios, P.T.; Daikos, G.L. Carbapenemases in Klebsiella Pneumoniae and Other Enterobacteriaceae: An Evolving Crisis of Global Dimensions. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 682–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, J.M.A.; Webber, M.A.; Baylay, A.J.; Ogbolu, D.O.; Piddock, L.J.V. Molecular Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance. Nature Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 13, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivas, R.; Dolabella, S.S.; Barbosa, A.A.T.; Jain, S. Prevalence of Klebsiella Pneumoniae Carbapenemase—And New Delhi Metallo-Beta-Lactamase-Positive K. Pneumoniae in Sergipe, Brazil, and Combination Therapy as a Potential Treatment Option. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2020, 53, e20200064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz-Price, L.S.; Poirel, L.; Bonomo, R.A.; Schwaber, M.J.; Daikos, G.L.; Cormican, M.; Cornaglia, G.; Garau, J.; Gniadkowski, M.; Hayden, M.K.; et al. Clinical Epidemiology of the Global Expansion of Klebsiella Pneumoniae Carbapenemases. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozales, F.P.; Ribeiro, V.B.; Magagnin, C.M.; Pagano, M.; Lutz, L.; Falci, D.R.; Machado, A.; Barth, A.L.; Zavascki, A.P. Emergence of NDM-1-Producing Enterobacteriaceae in Porto Alegre, Brazil. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 25, 79–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampaio, J.L.M.; Gales, A.C. Antimicrobial Resistance in Enterobacteriaceae in Brazil: Focus on β-Lactams and Polymyxins. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2016, 47, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wink, P.L.; Martins, A.S.; Volpato, F.; Zavascki, A.P.; Barth, A.L. Increased Frequency of Bla NDM in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Southern Brazil. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2021, 52, 299–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho-Assef, A.P.D.; Pereira, P.S.; Albano, R.; Berião, G.C.; Chagas, T.; Timm, L.N.; Da Silva, R.C.F.; Falci, D.; Asensi, M.D. Isolation of NDM-Producing Providencia Rettgeri in Brazil. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 2956–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, I.R.; Aires, C.A.M.; Conceição-Neto, O.C.; de Oliveira Santos, I.C.; Ferreira Pereira, N.; Moreno Senna, J.P.; Carvalho-Assef, A.P.D.A.; Asensi, M.D.; Rocha-De-Souza, C.M. Distribution of Clinical NDM-1-Producing Gram-Negative Bacteria in Brazil. Microb. Drug Resist. 2019, 25, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PAHO. Epidemological Alert: Emergence and Increase of New Combinations of Carbapenemases in Enterobacterales in Latin and Caribbean. 22 October 2021. Available online: https://www.paho.org/en/documents/epidemiological-alert-emergence-and-increase-new-combinations-carbapenemases (accessed on 8 March 2023).
- BRASIL.MINISTERIO DA SAUDE. Vigilancia em saúde: Nota técnica n.74/2022-CGLAB/DAEUS/SVS/MS. Available online: https://brcast.org.br/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/SEI_MS-0028220258-Nota-Tecnica-NDM-e-coproducao-carbapenemase.pdf (accessed on 8 March 2023).
- Shakil, S.; Azhar, E.I.; Tabrez, S.; Kamal, M.A.; Jabir, N.R.; Abuzenadah, A.M.; Damanhouri, G.A.; Alam, Q. New Delhi Metallo-β-Lactamase (NDM-1): An Updates. J. Chemother. 2013, 23, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, T.; Nouér, S.A.; Martins, R.C.R.; Neto, L.V.P.; Martins, W.M.B.S.; Barbosa, A.C.N.; Ferreira, A.L.P.; Costa, S.F.; Gales, A.C. Ceftazidime-Avibactam as Salvage Therapy for Infections Caused by Enterobacteriales Coresistant to Carbapenems and Polymyxins. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e00528-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davido, B.; Fellous, L.; Lawrence, C.; Maxime, V.; Rottman, M.; Dinha, A. Ceftazidime-Avibactam and Aztreonam, an Interesting Strategy to Overcome -Lactam Resistance Conferred by Metallo--Lactamases in Enterobacteriaceae and Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e01008-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcone, M.; Daikos, G.L.; Tiseo, G.; Bassoulis, D.; Giordano, C.; Galfo, V.; Leonildi, A.; Tagliaferri, E.; Barnini, S.; Sani, S.; et al. Efficacy of Ceftazidime-Avibactam Plus Aztreonam in Patients with Bloodstream Infections Caused by Metallo-β-Lactamase–Producing Enterobacterales. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72, 1871–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamano, Y.; Yamano, Y. In Vitro Activity of Cefiderocol Against a Broad Range of Clinically Important Gram-Negative Bacteria. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 69, S544–S551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul-Mutakabbir, J.C.; Alosaimy, S.; Morrisette, T.; Kebriaei, R.; Rybak, M.J. Cefiderocol: A Novel Siderophore Cephalosporin against Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Pathogens. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug. Ther. 2020, 40, 1228–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansone, P.; Giaccari, L.G.; Coppolino, F.; Aurilio, C.; Barbarisi, A.; Passavanti, M.B.; Pota, V.; Pace, M.C. Cefiderocol for Carbapenem-Resistant Bacteria: Handle with Care! A Review of the Real-World Evidence. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, G.; Boattini, M.; Comini, S.; Casale, R.; Iannaccone, M.; Cavallo, R.; Costa, C. Occurrence of Multi-Carbapenemases Producers among Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacterales and in Vitro Activity of Combinations Including Cefiderocol, Ceftazidime-Avibactam, Meropenem-Vaborbactam, and Aztreonam in the COVID-19 Era. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2022, 41, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraki, S.; Mavromanolaki, V.E.; Stafylaki, D.; Scoulica, E. In Vitro Activity of Newer β-Lactam/β-Lactamase Inhibitor Combinations, Cefiderocol, Plazomicin and Comparators against Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella Pneumoniae Isolates. J. Chemother. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.J.; Lauderdale, T.L.; Ho, M.; Lo, H.J. The Roles of Mutations in GyrA, ParC, and OmpK35 in Fluoroquinolone Resistance in Klebsiella Pneumoniae. Microb. Drug Resist. 2004, 9, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akya, A.; Lorestani, R.C.; Elahi, A.; Ghadiri, K. The Impact of Mutations in Topoisomerase Genes and the Plasmid-Mediated Quinolone Resistance (PMQR) Determinants on the Resistance to Fluoroquinolones in Klebsiella Pneumoniae. Arch. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 12, 57290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, R.C.; Dabul, A.N.G.; Boralli, C.M.D.S.; Zuvanov, L.; Camargo, I.L.B.D.C. Dissemination of BlaKPC-2 in an NTEKPC by an IncX5 Plasmid. Plasmid 2019, 106, 102446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- al Mana, H.; Sundararaju, S.; Tsui, C.K.M.; Perez-Lopez, A.; Yassine, H.; al Thani, A.; Al-Ansari, K.; Eltai, N.O. Whole-Genome Sequencing for Molecular Characterization of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae Causing Lower Urinary Tract Infection among Pediatric Patients. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özad Düzgün, A. From Turkey: First Report of KPC-3- and CTX-M-27-Producing Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae ST147 Clone Carrying OmpK36 and Ompk37 Porin Mutations. Microb. Drug Resist. 2021, 27, 1265–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellera, F.P.; Fuga, B.; Fontana, H.; Esposito, F.; Cardoso, B.; Konno, S.; Berl, C.; Cappellanes, M.H.; Cortez, M.; Ikeda, M.; et al. Detection of IncN-pST15 One-health Plasmid Harbouring Bla in a Hypermucoviscous Klebsiella Pneumoniae CG258 Isolated from an Infected Dog, Brazil. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rada, A.M.; de la Cadena, E.; Agudelo, C.; Capataz, C.; Orozco, N.; Pallares, C.; Dinh, A.Q.; Panesso, D.; Ríos, R.; Diaz, L.; et al. Dynamics of BlaKPC-2 Dissemination from Non-CG258 Klebsiella Pneumoniae to Other Enterobacterales via IncN Plasmids in an Area of High Endemicity. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e01743-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiles, M.G.; Rocchetti, T.T.; Fehlberg, L.C.; Kusano, E.J.U.; Chebabo, A.; Pereira, R.M.G.; Gales, A.C.; Pignatari, A.C.C. Unusual Association of NDM-1 with KPC-2 and ArmA among Brazilian Enterobacteriaceae Isolates. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2014, 48, 174–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vásquez-Ponce, F.; Dantas, K.; Becerra, J.; Melocco, G.; Esposito, F.; Cardoso, B.; Rodrigues, L.; Lima, K.; de Lima, A.V.; Sellera, F.P.; et al. Detecting KPC-2 and NDM-1 Coexpression in Klebsiella Pneumoniae Complex from Human and Animal Hosts in South America. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0115922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, P.S.; Borghi, M.; Albano, R.M.; Lopes, J.C.O.; Silveira, M.C.; Marques, E.A.; Oliveira, J.C.R.; Asensi, M.D.; Carvalho-Assef, A.P.D.A. Coproduction of NDM-1 and KPC-2 in Enterobacter Hormaechei from Brazil. Microb. Drug Resist. 2015, 21, 234–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firmo, E.F.; Beltrão, E.M.B.; da Silva, F.R.F.; Alves, L.C.; Brayner, F.A.; Veras, D.L.; Lopes, A.C.S. Association of BlaNDM-1 with BlaKPC-2 and Aminoglycoside-Modifying Enzyme Genes among Klebsiella Pneumoniae, Proteus Mirabilis and Serratia Marcescens Clinical Isolates in Brazil. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 21, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, É.M.; Beltrão, E.M.B.; Scavuzzi, A.M.L.; Barros, J.F.; Lopes, A.C.S. High Plasmid Variability, and the Presence of IncFIB, IncQ, IncA/C, IncHI1B, and IncL/M in Clinical Isolates of Klebsiella Pneumoniae with Bla KPC and Bla NDM from Patients at a Public Hospital in Brazil. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2020, 53, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, T.M.; Göttig, S.; Mark, L.; Christ, S.; Kempf, V.A.J.; Wichelhaus, T.A.; Hamprecht, A. Pathogenicity of Pan-Drug-Resistant Serratia Marcescens Harbouring BlaNDM-1. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 70, 1026–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, L.; Guerra, B.; Schmoger, S.; Fischer, J.; Helmuth, R.; Zong, Z.; García-Fernández, A.; Carattoli, A. IncA/C Plasmid Carrying BlaNDM-1, BlaCMY-16, and FosA3 in a Salmonella Enterica Serovar Corvallis Strain Isolated from a Migratory Wild Bird in Germany. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 6597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnár, S.; Flonta, M.M.M.; Almaş, A.; Buzea, M.; Licker, M.; Rus, M.; Földes, A.; Székely, E. Dissemination of NDM-1 Carbapenemase-Producer Providencia Stuartii Strains in Romanian Hospitals: A Multicentre Study. J. Hosp. Infect. 2019, 103, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solgi, H.; Giske, C.G.; Badmasti, F.; Aghamohammad, S.; Havaei, S.A.; Sabeti, S.; Mostafavizadeh, K.; Shahcheraghi, F. Emergence of Carbapenem Resistant Escherichia Coli Isolates Producing BlaNDM and BlaOXA-48-like Carried on IncA/C and IncL/M Plasmids at Two Iranian University Hospitals. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 55, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wailan, A.M.; Sartor, A.L.; Zowawi, H.M.; Perry, J.D.; Paterson, D.L.; Sidjabat, H.E. Genetic Contexts of BlaNDM-1 in Patients Carrying Multiple NDM-Producing Strains. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 7405–7410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qamar, M.U.; Ejaz, H.; Walsh, T.R.; Shah, A.A.; Al Farraj, D.A.; Alkufeidy, R.M.; Alkubaisi, N.A.; Saleem, S.; Jahan, S. Clonal Relatedness and Plasmid Profiling of Extensively Drug-Resistant New Delhi Metallo-β-Lactamase-Producing Klebsiella Pneumoniae Clinical Isolates. Futur. Microbiol. 2021, 16, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Simmonds, A.; Annavajhala, M.K.; Tang, N.; Rozenberg, F.D.; Ahmad, M.; Park, H.; Lopatkin, A.J.; Uhlemann, A.C. Population Structure of BlaKPC-Harbouring IncN Plasmids at a New York City Medical Centre and Evidence for Multi-Species Horizontal Transmission. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2022, 77, 1873–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nascimento, T.; Cantamessa, R.; Melo, L.; Lincopan, N.; Fernandes, M.R.; Cerdeira, L.; Fraga, E.; Dropa, M.; Sato, M.I.Z. International High-Risk Clones of Klebsiella Pneumoniae KPC-2/CC258 and Escherichia Coli CTX-M-15/CC10 in Urban Lake Waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 910–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Chaparro, P.J.; Cerdeira, L.T.; Queiroz, M.G.; De Lima, C.P.S.; Levy, C.E.; Pavez, M.; Lincopan, N.; Gonçalves, E.C.; Mamizuka, E.M.; Sampaio, J.L.M.; et al. Complete Nucleotide Sequences of Two BlaKPC-2-Bearing IncN Plasmids Isolated from Sequence Type 442 Klebsiella Pneumoniae Clinical Strains Four Years Apart. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 2958–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carattoli, A.; Aschbacher, R.; March, A.; Larcher, C.; Livermore, D.M.; Woodford, N. Complete Nucleotide Sequence of the IncN Plasmid PKOX105 Encoding VIM-1, QnrS1 and SHV-12 Proteins in Enterobacteriaceae from Bolzano, Italy Compared with IncN Plasmids Encoding KPC Enzymes in the USA. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 2070–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weingarten, R.A.; Johnson, R.C.; Conlan, S.; Ramsburg, A.M.; Dekker, J.P.; Lau, A.F.; Khil, P.; Odom, R.T.; Deming, C.; Park, M.; et al. Genomic Analysis of Hospital Plumbing Reveals Diverse Reservoir of Bacterial Plasmids Conferring Carbapenem Resistance. mBio 2018, 9, e02011-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweizer, C.; Bischoff, P.; Bender, J.; Kola, A.; Gastmeier, P.; Hummel, M.; Klefisch, F.R.; Schoenrath, F.; Frühauf, A.; Pfeifer, Y. Plasmid-Mediated Transmission of KPC-2 Carbapenemase in Enterobacteriaceae in Critically Ill Patients. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Imirzalioglu, C.; Hain, T.; Kaase, M.; Gatermann, S.; Exner, M.; Mielke, M.; Hauri, A.; Dragneva, Y.; Bill, R.; et al. Complete Nucleotide Sequence of a Citrobacter Freundii Plasmid Carrying KPC-2 in a Unique Genetic Environment. Genome Announc. 2014, 2, e01157-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitar, I.; Caltagirone, M.; Villa, L.; Marchetti, V.M.; Nucleo, E.; Sarti, M.; Migliavacca, R.; Carattoli, A. Interplay among IncA and BlaKPC-Carrying Plasmids in Citrobacter Freundii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e02609-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horne, T.; Orr, V.T.; Hall, J.P. How Do Interactions between Mobile Genetic Elements Affect Horizontal Gene Transfer? Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2023, 73, 102282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gama, J.A.; Zilhão, R.; Dionisio, F. Plasmid Interactions Can Improve Plasmid Persistence in Bacterial Populations. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guglielmini, J.; Van Melderen, L. Bacterial Toxin-Antitoxin Systems. Mob. Genet. Elements 2011, 1, 283–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anantharaman, V.; Aravind, L. New Connections in the Prokaryotic Toxin-Antitoxin Network: Relationship with the Eukaryotic Nonsense-Mediated RNA Decay System. Genome Biol. 2003, 4, R81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leplae, R.; Geeraerts, D.; Hallez, R.; Guglielmini, J.; Drze, P.; Van Melderen, L. Diversity of Bacterial Type II Toxin-Antitoxin Systems: A Comprehensive Search and Functional Analysis of Novel Families. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 5513–5525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzo, I.C.V.; Rehder, A.; Darini, A.L.C. Quantitative Disk Diffusion as a Convenient Method for Determining Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations of Oxacillin for Staphylococci Strains. J. Microbiol. Methods. 2007, 71, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirel, L.; Walsh, T.R.; Cuvillier, V.; Nordmann, P. Multiplex PCR for Detection of Acquired Carbapenemase Genes. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 70, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naas, T.; Cuzon, G.; Villegas, M.V.; Lartigue, M.F.; Quinn, J.P.; Nordmann, P. Genetic Structures at the Origin of Acquisition of the β-Lactamase BlaKPC Gene. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 1257–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuotto, C.; Longo, F.; Pascolini, C.; Donelli, G.; Balice, M.P.; Libori, M.F.; Tiracchia, V.; Salvia, A.; Varaldo, P.E. Biofilm Formation and Antibiotic Resistance in Klebsiella Pneumoniae Urinary Strains. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 123, 1003–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Apolito, D.; Arena, F.; Conte, V.; de Angelis, L.H.; di Mento, G.; Carreca, A.P.; Cuscino, N.; Russelli, G.; Iannolo, G.; Barbera, F.; et al. Phenotypical and Molecular Assessment of the Virulence Potential of KPC-3-Producing Klebsiella Pneumoniae ST392 Clinical Isolates. Microbiol. Res. 2020, 240, 126551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diancourt, L.; Passet, V.; Verhoef, J.; Grimont, P.A.D.; Brisse, S. Multilocus Sequence Typing of Klebsiella Pneumoniae Nosocomial Isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodall, C.A. DNA Transfer by Bacterial Conjugation. Methods Mol. Biol. 2003, 235, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Škulj, M.; Okršlar, V.; Jalen, Š.; Jevševar, S.; Slanc, P.; Štrukelj, B.; Menart, V. Improved Determination of Plasmid Copy Number Using Quantitative Real-Time PCR for Monitoring Fermentation Processes. Microb. Cell Fact. 2008, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).