Clinical Resistant Strains of Enterococci and Their Correlation to Reduced Susceptibility to Biocides: Phenotypic and Genotypic Analysis of Macrolides, Lincosamides, and Streptogramins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
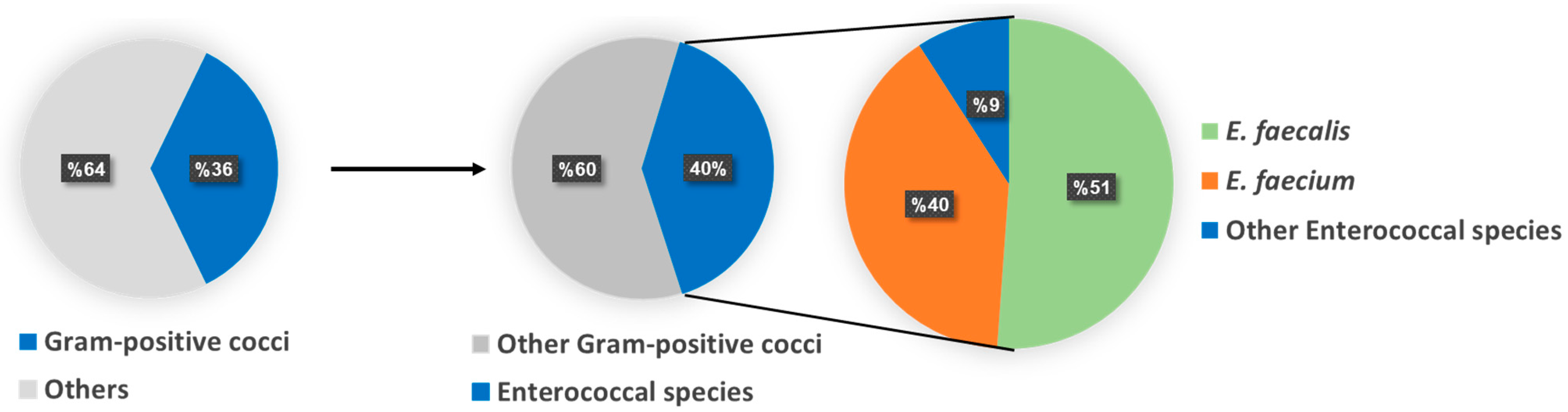
2.1. Isolation and Identification of Enterococci spp.
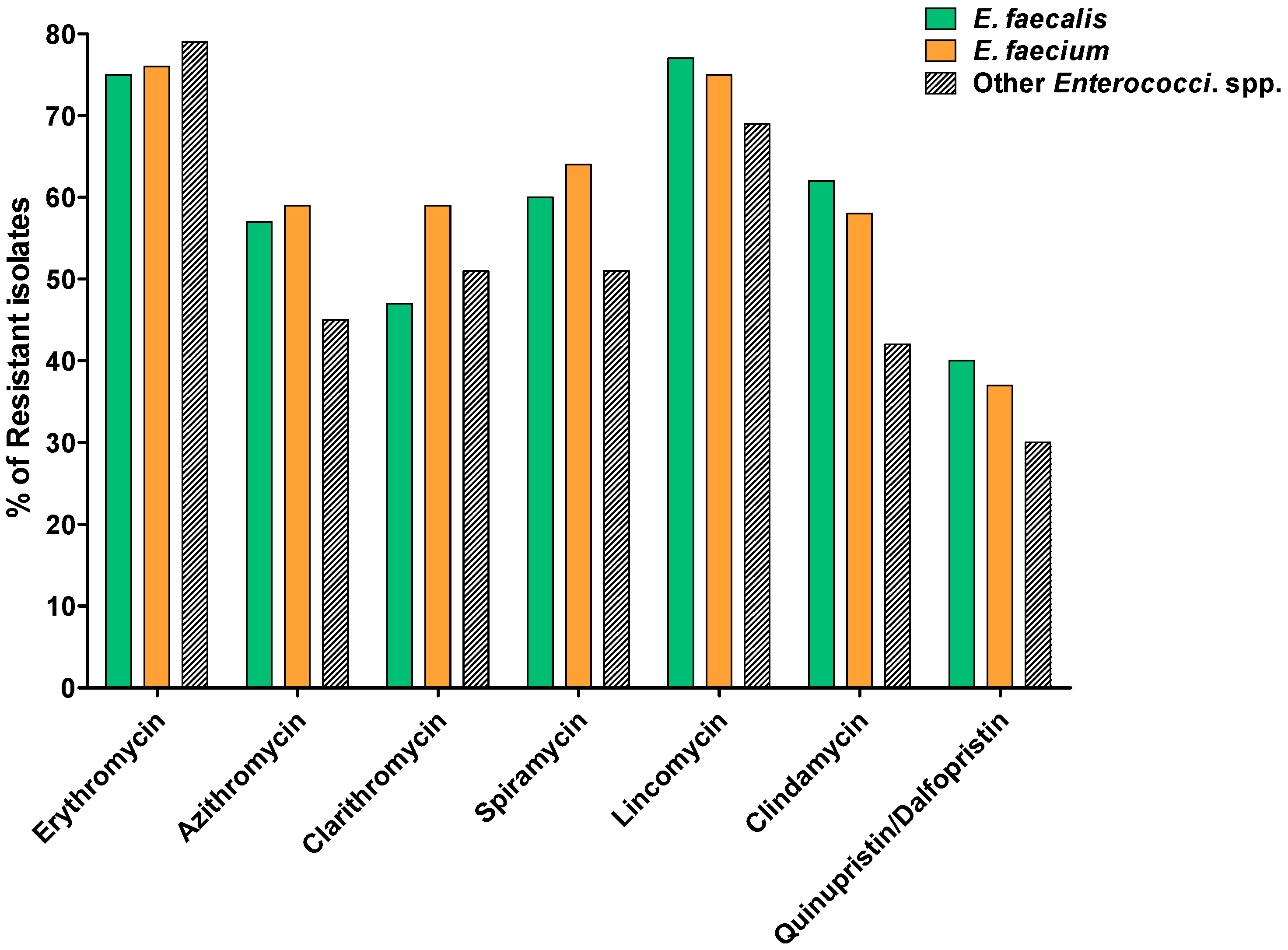
2.2. Susceptibility to MLS
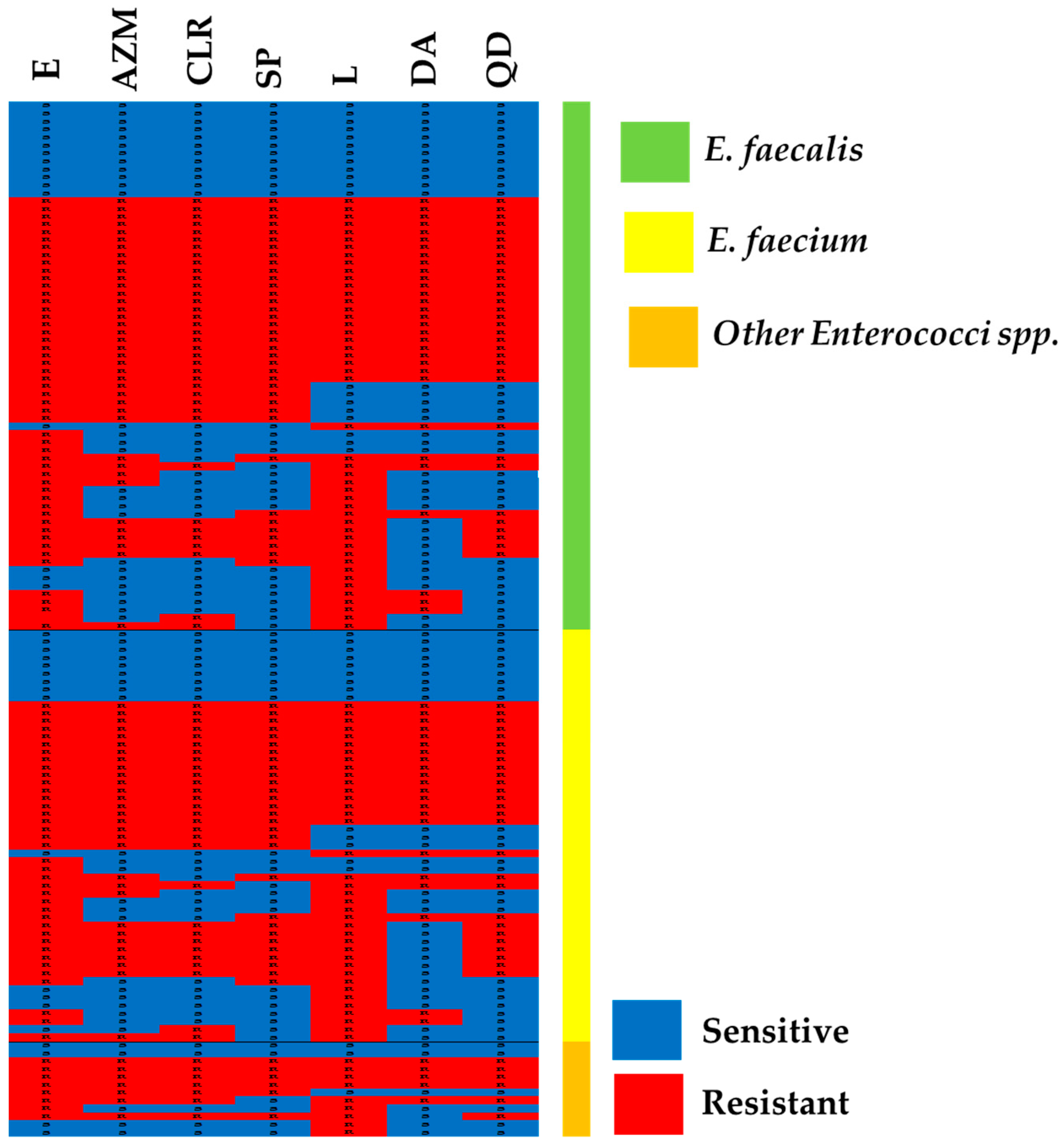
2.3. MLS Resistance Phenotypes
2.4. MLS Resistance Genotypes
2.5. The Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations (MICs) of MLS and Biocides
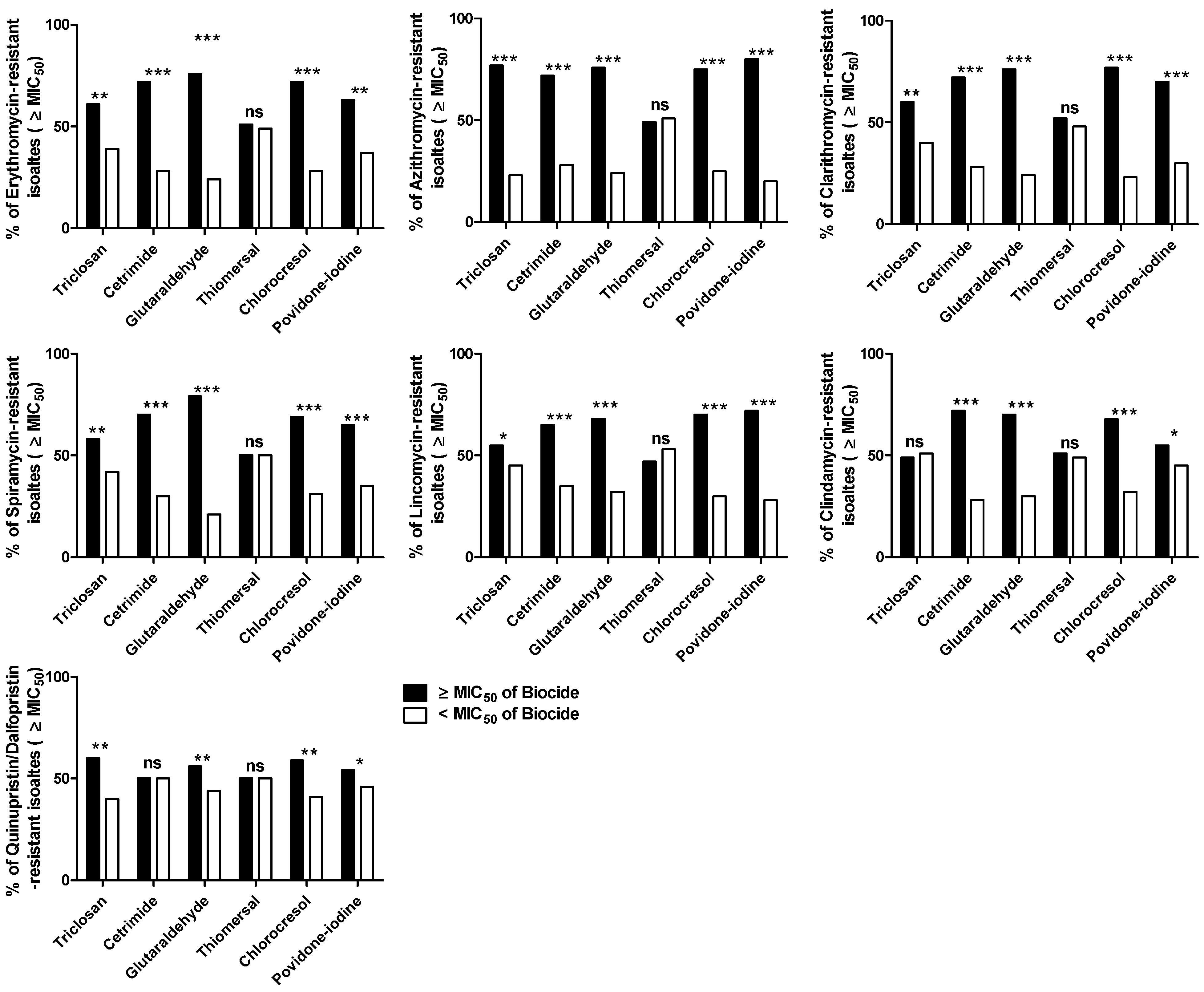
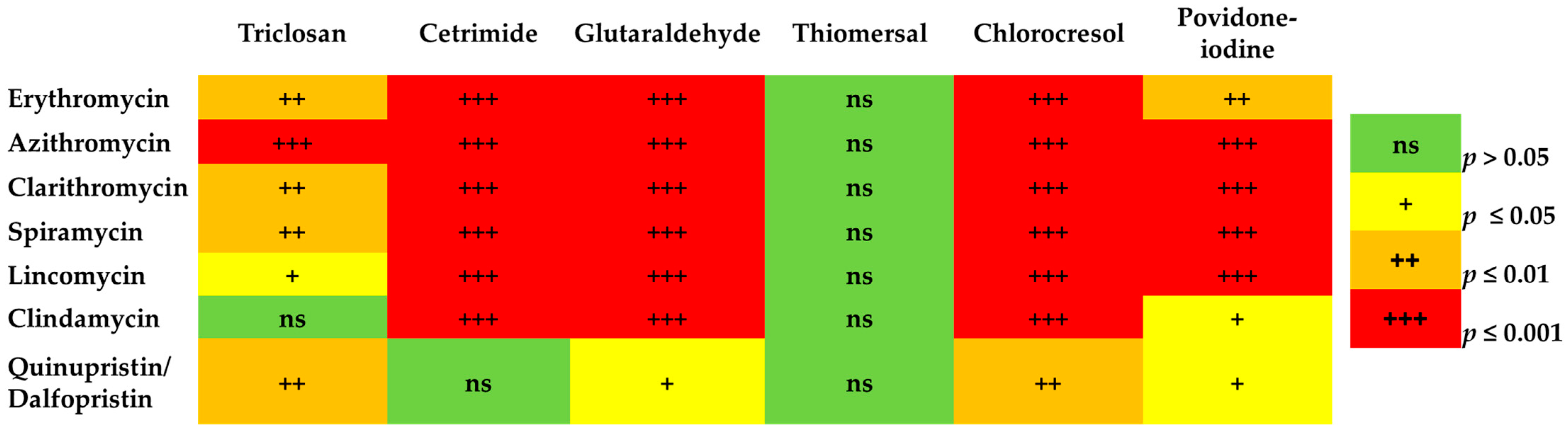
The Correlation between MLS Resistance and Reduced Susceptibility to Biocides
2.6. The Distribution of Resistant MLS Genes in the Resistant Isolates with MIC ≥ MIC50
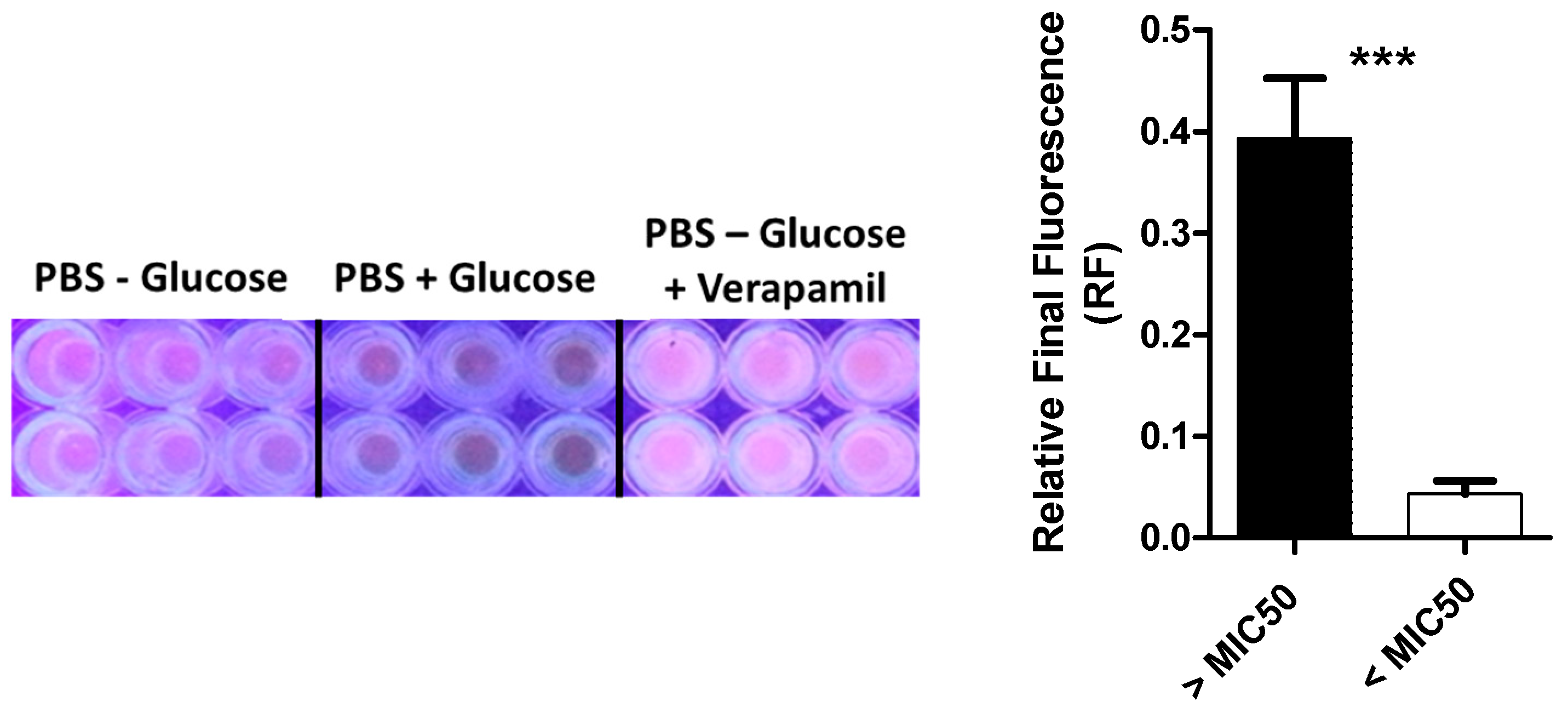
2.7. Efflux Assay in MLS Resistant Isolates
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Microorganisms
4.2. Identification of Enterococcus spp.
4.3. Determination of Antibiotic Susceptibility and MICs of Isolates
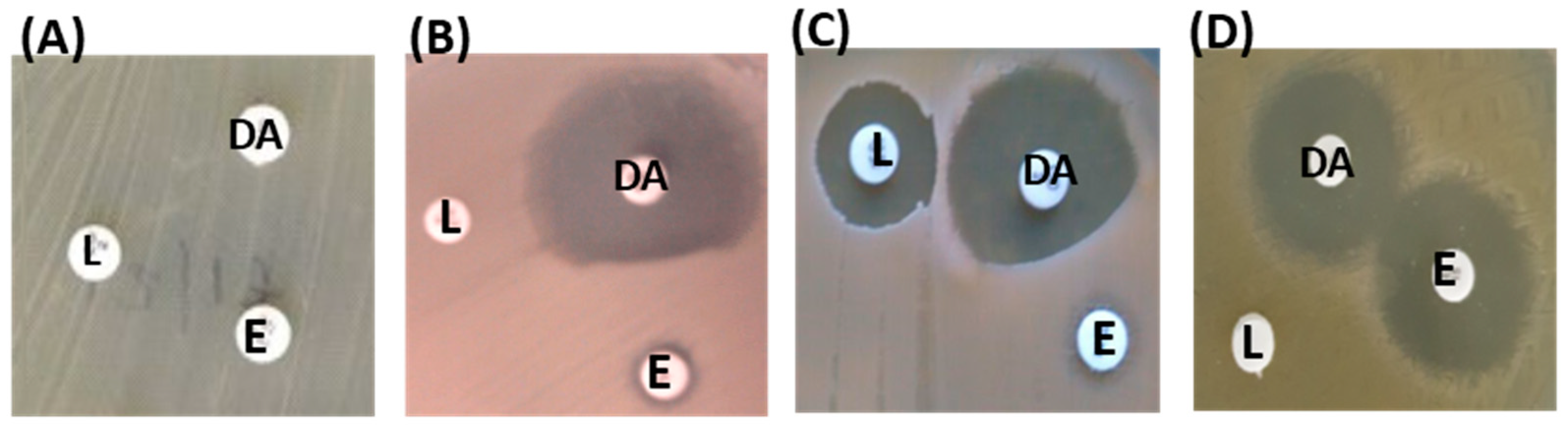
4.4. Determination of MLS Resistance Phenotypes by Triple Disk Diffusion Test
4.5. PCR Detection of MLS Resistance Genes
4.6. Evaluation of the Efflux in MLS Resistant Isolates with Higher MIC to Biocide
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Semedo-Lemsaddek, T.; Barreto-Crespo, M.T.; Tenreiro, R. Occurrence of putative pathogenicity islands in enterococci from distinct species and of differing origins. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7271–7274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monstein, H.J.; Quednau, M.; Samuelsson, A.; Ahrne, S.; Isaksson, B.; Jonasson, J. Division of the genus Enterococcus into species groups using PCR-based molecular typing methods. Microbiology 1998, 144 Pt 5, 1171–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi, Y.; Hasani, A.; Ghotaslou, R.; Naghili, B.; Aghazadeh, M.; Milani, M.; Bazmany, A. Virulence and antimicrobial resistance in enterococci isolated from urinary tract infections. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 3, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirschner, C.; Maquelin, K.; Pina, P.; Ngo Thi, N.A.; Choo-Smith, L.P.; Sockalingum, G.D.; Sandt, C.; Ami, D.; Orsini, F.; Doglia, S.M.; et al. Classification and identification of enterococci: A comparative phenotypic, genotypic, and vibrational spectroscopic study. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 1763–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, E.; Van Tyne, D.; Gilmore, M.S. Pathogenicity of Enterococci. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, W.A.H.; Abbas, H.A. Evaluation of the role of SsaV Salmonella pathogenicity island-2 dependent type III secretion system components on the virulence behavior of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 16, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elal Mus, T.; Cetinkaya, F.; Cibik, R.; Soyutemiz, G.E.; Simsek, H.; Coplu, N. Pathogenicity determinants and antibiotic resistance profiles of enterococci from foods of animal origin in Turkey. Acta Vet. Hung. 2017, 65, 461–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Y.H.; Jeong, J.H.; Choi, Y.J.; Yun, H.J.; Lee, K.; Shim, M.J.; Kwak, J.H.; Choi, E.C. Heterogeneity of macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B resistance phenotypes in enterococci. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 3415–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, P.; Qu, T.; Chen, Y.; Hua, X.; Shi, K.; Yu, Y. Identification of Novel Conjugative Plasmids with Multiple Copies of fosB that Confer High-Level Fosfomycin Resistance to Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, W.A.H.; Rajab, A.A.H.; Abu Lila, A.S.; Abbas, H.A. Anti-diabetics and antimicrobials: Harmony of mutual interplay. World J. Diabetes 2021, 12, 1832–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, C.A.; Reyes, J.; Zuniga, M.; Cortes, L.; Cruz, C.; Rico, C.L.; Panesso, D.; Columbian Antimicrobial Resistance, G. Multicentre surveillance of antimicrobial resistance in enterococci and staphylococci from Colombian hospitals, 2001–2002. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 51, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uttley, A.H.; George, R.C.; Naidoo, J.; Woodford, N.; Johnson, A.P.; Collins, C.H.; Morrison, D.; Gilfillan, A.J.; Fitch, L.E.; Heptonstall, J. High-level vancomycin-resistant enterococci causing hospital infections. Epidemiol. Infect. 1989, 103, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lila, A.S.A.; Rajab, A.A.; Abdallah, M.H.; Rizvi, S.M.D.; Moin, A.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Tabrez, S.; Hegazy, W.A. Biofilm Lifestyle in Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections. Life 2023, 13, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leclercq, R. Mechanisms of resistance to macrolides and lincosamides: Nature of the resistance elements and their clinical implications. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2002, 34, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almalki, A.J.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Taher, E.S.; Mohamed, M.F.A.; Youns, M.; Hegazy, W.A.H.; Al-Mahmoudy, A.M.M. Synthesis, Antimicrobial, Anti-Virulence and Anticancer Evaluation of New 5(4H)-Oxazolone-Based Sulfonamides. Molecules 2022, 27, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agha, K.A.; Abo-Dya, N.E.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Abdel-Aal, E.H.; Hegazy, W.A. Benzotriazole-Mediated Synthesis and Antibacterial Activity of Novel N-Acylcephalexins. Sci. Pharm. 2016, 84, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almalki, A.J.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Elhady, S.S.; Darwish, K.M.; Hegazy, W.A.H. Repurposing & alpha;-Adrenoreceptor Blockers as Promising Anti-Virulence Agents in Gram-Negative Bacteria. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 178. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, M.C. Update on macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin, ketolide, and oxazolidinone resistance genes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 282, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, S.; Shen, J.; Kadlec, K.; Wang, Y.; Brenner Michael, G.; Fessler, A.T.; Vester, B. Lincosamides, Streptogramins, Phenicols, and Pleuromutilins: Mode of Action and Mechanisms of Resistance. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a027037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclercq, R.; Bismuth, R. Classification, structure, pharmacokinetic and mode of action of macrolides, lincosamides and streptogramins. Resistance phenomena. Rev. Prat. 1988, 38, 1005-10. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, M.C. Environmental macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin and tetracycline resistant bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, W.A.H.; Khayat, M.T.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Youns, M.; Mosbah, R.; Soliman, W.E. Repurposing of antidiabetics as Serratia marcescens virulence inhibitors. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2021, 52, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldawsari, M.F.; Khafagy, E.S.; Saqr, A.A.; Alalaiwe, A.; Abbas, H.A.; Shaldam, M.A.; Hegazy, W.A.H.; Goda, R.M. Tackling Virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by the Natural Furanone Sotolon. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnanadhas, D.P.; Marathe, S.A.; Chakravortty, D. Biocides--resistance, cross-resistance mechanisms and assessment. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2013, 22, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, A.D. Antibiotic and biocide resistance in bacteria: Introduction. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 92 (Suppl. S1), 1S–3S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schleifer, K.H.; Kilpper-Bälz, R. Transfer of Streptococcus faecalis and Streptococcus faecium to the genus Enterococcus nom. rev. as Enterococcus faecalis comb. nov. and Enterococcus faecium comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1984, 34, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manero, A.; Blanch, A.R. Identification of Enterococcus spp. with a biochemical key. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 4425–4430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Z.; Nikaido, H. Efflux-mediated drug resistance in bacteria. Drugs 2004, 64, 159–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura-Sato, K.; Wachino, J.; Kondo, T.; Ito, H.; Arakawa, Y. Correlation between reduced susceptibility to disinfectants and multidrug resistance among clinical isolates of Acinetobacter species. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 1975–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spizek, J.; Novotna, J.; Rezanka, T. Lincosamides: Chemical structure, biosynthesis, mechanism of action, resistance, and applications. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 56, 121–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spizek, J.; Rezanka, T. Lincomycin, clindamycin and their applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 64, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, G.; Klare, I.; Witte, W. Molecular analysis of streptogramin resistance in enterococci. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2002, 292, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misic, M.; Kocic, B.; Arsovic, A.; Cukic, J.; Vidanovic, D.; Sekler, M.; Baskic, D. Human enterococcal isolates as reservoirs for macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin and other resistance genes. J. Antibiot. 2022, 75, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thal, L.A.; Zervos, M.J. Occurrence and epidemiology of resistance to virginiamycin and streptogramins. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1999, 43, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershberger, E.; Donabedian, S.; Konstantinou, K.; Zervos, M.J. Quinupristin-dalfopristin resistance in gram-positive bacteria: Mechanism of resistance and epidemiology. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 38, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starosta, A.L.; Karpenko, V.V.; Shishkina, A.V.; Mikolajka, A.; Sumbatyan, N.V.; Schluenzen, F.; Korshunova, G.A.; Bogdanov, A.A.; Wilson, D.N. Interplay between the ribosomal tunnel, nascent chain, and macrolides influences drug inhibition. Chem. Biol. 2010, 17, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunkle, J.A.; Xiong, L.; Mankin, A.S.; Cate, J.H. Structures of the Escherichia coli ribosome with antibiotics bound near the peptidyl transferase center explain spectra of drug action. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 17152–17157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chancey, S.T.; Zahner, D.; Stephens, D.S. Acquired inducible antimicrobial resistance in Gram-positive bacteria. Future Microbiol. 2012, 7, 959–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzyubak, E.; Yap, M.N. The Expression of Antibiotic Resistance Methyltransferase Correlates with mRNA Stability Independently of Ribosome Stalling. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 7178–7188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra-Kumar, S.; Mazzariol, A.; Van Heirstraeten, L.; Lammens, C.; de Rijk, P.; Cornaglia, G.; Goossens, H. Unusual resistance patterns in macrolide-resistant Streptococcus pyogenes harbouring erm(A). J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2009, 63, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.; Shen, J.; Zhang, M.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y. Constitutive and Inducible Expression of the rRNA Methylase Gene erm(B) in Campylobacter. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 6661–6664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Y.H.; Kwon, A.R.; Yoon, J.M.; Yoon, E.J.; Shim, M.J.; Choi, E.C. Molecular analysis of constitutive mutations in ermB and ermA selected in vitro from inducibly MLSB-resistant enterococci. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2008, 31, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novotna, G.; Adamkova, V.; Janata, J.; Melter, O.; Spizek, J. Prevalence of resistance mechanisms against macrolides and lincosamides in methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative staphylococci in the Czech Republic and occurrence of an undefined mechanism of resistance to lincosamides. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 3586–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschi, F.; Kanyo, Z.; Sherer, E.C.; Sutcliffe, J. Macrolide resistance from the ribosome perspective. Curr. Drug Targets Infect. Disord. 2004, 4, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.T.; Hanifah, Y.A.; Yusof, M.; Thong, K.L. ermA, ermC, tetM and tetK are essential for erythromycin and tetracycline resistance among methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from a tertiary hospital in Malaysia. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 30, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.V.; Malathum, K.; Murray, B.E. Disruption of an Enterococcus faecium species-specific gene, a homologue of acquired macrolide resistance genes of staphylococci, is associated with an increase in macrolide susceptibility. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vester, B.; Douthwaite, S. Macrolide resistance conferred by base substitutions in 23S rRNA. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.A.; Kwon, A.R.; Kim, S.K.; Chong, Y.; Lee, K.; Choi, E.C. Prevalence of resistance to macrolide, lincosamide and streptogramin antibiotics in Gram-positive cocci isolated in a Korean hospital. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2002, 49, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktas, Z.; Aridogan, A.; Kayacan, C.B.; Aydin, D. Resistance to macrolide, lincosamide and streptogramin antibiotics in staphylococci isolated in Istanbul, Turkey. J. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, F.J.; Sadurski, R.; Kray, A.; Boos, M.; Geisel, R.; Kohrer, K.; Verhoef, J.; Fluit, A.C. Prevalence of macrolide-resistance genes in Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus faecium isolates from 24 European university hospitals. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2000, 45, 891–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Hamid, M.I.; Sewid, A.H.; Samir, M.; Hegazy, W.A.H.; Bahnass, M.M.; Mosbah, R.A.; Ghaith, D.M.; Khalifa, E.; Ramadan, H.; Alshareef, W.A.; et al. Clonal Diversity and Epidemiological Characteristics of ST239-MRSA Strains. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, Y.H.; Kwon, A.R.; Yoon, E.J.; Shim, M.J.; Choi, E.C. Translational attenuation and mRNA stabilization as mechanisms of erm(B) induction by erythromycin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 1782–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Liu, B.; Klepacki, D.; Gupta, V.; Schulten, K.; Mankin, A.S.; Vazquez-Laslop, N. Nascent peptide assists the ribosome in recognizing chemically distinct small molecules. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenz, S.; Ramu, H.; Gupta, P.; Berninghausen, O.; Beckmann, R.; Vazquez-Laslop, N.; Mankin, A.S.; Wilson, D.N. Molecular basis for erythromycin-dependent ribosome stalling during translation of the ErmBL leader peptide. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Cai, C.; Chen, J.; Cheng, C.; Cheng, G.; Hu, X.; Liu, C. Inducible Expression of both ermB and ermT Conferred High Macrolide Resistance in Streptococcus gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus Isolates in China. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, T.W.; Hung, W.C.; Tsai, J.C.; Lin, Y.T.; Lee, H.; Hsueh, P.R.; Lee, T.F.; Teng, L.J. Novel Structure of Enterococcus faecium-Originated ermB-Positive Tn1546-Like Element in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 6108–6114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, P.; Kannan, K.; Mankin, A.S.; Vazquez-Laslop, N. Regulation of gene expression by macrolide-induced ribosomal frameshifting. Mol. Cell 2013, 52, 629–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, M.; Chettiath, T.; Mankin, A.S. Induction of erm(C) expression by noninducing antibiotics. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 866–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askoura, M.; Almalki, A.J.; Lila, A.S.A.; Almansour, K.; Alshammari, F.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Hegazy, W.A.H. Alteration of Salmonella enterica Virulence and Host Pathogenesis through Targeting sdiA by Using the CRISPR-Cas9 System. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alandiyjany, M.N.; Abdelaziz, A.S.; Abdelfattah-Hassan, A.; Hegazy, W.A.H.; Hassan, A.A.; Elazab, S.T.; Mohamed, E.A.A.; El-Shetry, E.S.; Saleh, A.A.; ElSawy, N.A.; et al. Novel In Vivo Assessment of Antimicrobial Efficacy of Ciprofloxacin Loaded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles against Salmonella typhimurium Infection. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almalki, A.J.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Elhady, S.S.; Hegazy, W.A.H.; Darwish, K.M. Computational and Biological Evaluation of β-Adrenoreceptor Blockers as Promising Bacterial Anti-Virulence Agents. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 110. [Google Scholar]
- Khayat, M.T.; Abbas, H.A.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Khayyat, A.N.; Alharbi, M.; Darwish, K.M.; Elhady, S.S.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Safo, M.K.; Hegazy, W.A.H. Anti-Quorum Sensing Activities of Gliptins against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, M.D.; Chan, E.R.; Molyneaux, N.D.; Bonomo, R.A. Genomewide analysis of divergence of antibiotic resistance determinants in closely related isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 3569–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achard, A.; Villers, C.; Pichereau, V.; Leclercq, R. New lnu(C) gene conferring resistance to lincomycin by nucleotidylation in Streptococcus agalactiae UCN36. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 2716–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portillo, A.; Ruiz-Larrea, F.; Zarazaga, M.; Alonso, A.; Martinez, J.L.; Torres, C. Macrolide resistance genes in Enterococcus spp. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 967–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, M.; Endou, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Inoue, M.; Nakajima, Y. A plasmid that encodes three genes for resistance to macrolide antibiotics in Staphylococcus aureus. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1998, 167, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojo, K.K.; Striplin, M.J.; Ulep, C.C.; Close, N.S.; Zittle, J.; Luis, H.; Bernardo, M.; Leitao, J.; Roberts, M.C. Staphylococcus efflux msr(A) gene characterized in Streptococcus, Enterococcus, Corynebacterium, and Pseudomonas isolates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 1089–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lina, G.; Quaglia, A.; Reverdy, M.E.; Leclercq, R.; Vandenesch, F.; Etienne, J. Distribution of genes encoding resistance to macrolides, lincosamides, and streptogramins among staphylococci. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1999, 43, 1062–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iannelli, F.; Santoro, F.; Santagati, M.; Docquier, J.D.; Lazzeri, E.; Pastore, G.; Cassone, M.; Oggioni, M.R.; Rossolini, G.M.; Stefani, S.; et al. Type M Resistance to Macrolides Is Due to a Two-Gene Efflux Transport System of the ATP-Binding Cassette (ABC) Superfamily. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, K. Mechanisms of bacterial biocide and antibiotic resistance. Symp. Ser. 2002, 92 (Suppl. S1), 55S–64S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampf, G. Antibiotic ResistanceCan Be Enhanced in Gram-Positive Species by Some Biocidal Agents Used for Disinfection. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorea, J.G. Low-dose Thimerosal (ethyl-mercury) is still used in infants’ vaccines: Should we be concerned with this form of exposure? J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2018, 49, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paixao, L.; Rodrigues, L.; Couto, I.; Martins, M.; Fernandes, P.; de Carvalho, C.C.; Monteiro, G.A.; Sansonetty, F.; Amaral, L.; Viveiros, M. Fluorometric determination of ethidium bromide efflux kinetics in Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Eng. 2009, 3, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maillard, J.Y. Antimicrobial biocides in the healthcare environment: Efficacy, usage, policies, and perceived problems. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2005, 1, 307–320. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, K.N.; Szumowski, J.D.; Ramakrishnan, L. Verapamil, and its metabolite norverapamil, inhibit macrophage-induced, bacterial efflux pump-mediated tolerance to multiple anti-tubercular drugs. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 210, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capita, R.; Vicente-Velasco, M.; Rodriguez-Melcon, C.; Garcia-Fernandez, C.; Carballo, J.; Alonso-Calleja, C. Effect of low doses of biocides on the antimicrobial resistance and the biofilms of Cronobacter sakazakii and Yersinia enterocolitica. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmer, W.; Stephen, D.; William, M.; Paul, C.; Washington, C. A Color Atlas and Text Book of Diagnostic Microbiology; Lippincott: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Khayyat, A.N.; Abbas, H.A.; Mohamed, M.F.A.; Asfour, H.Z.; Khayat, M.T.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Youns, M.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Abu Lila, A.S.; Safo, M.K.; et al. Not Only Antimicrobial: Metronidazole Mitigates the Virulence of Proteus mirabilis Isolated from Macerated Diabetic Foot Ulcer. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayyat, A.N.; Abbas, H.A.; Khayat, M.T.; Shaldam, M.A.; Askoura, M.; Asfour, H.Z.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Abu Lila, A.S.; Allam, A.N.; Hegazy, W.A.H. Secnidazole Is a Promising Imidazole Mitigator of Serratia marcescens Virulence. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton-Miller, J.M. Calculating MIC50. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1991, 27, 863–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, W.A.H.; Henaway, M. Hepatitis C virus pathogenesis: Serum IL-33 level indicates liver damage. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 9, 1386–1393. [Google Scholar]
- Askoura, M.; Abbas, H.A.; Al Sadoun, H.; Abdulaal, W.H.; Abu Lila, A.S.; Almansour, K.; Alshammari, F.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Hegazy, W.A.H. Elevated Levels of IL-33, IL-17 and IL-25 Indicate the Progression from Chronicity to Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Hepatitis C Virus Patients. Pathogens 2022, 11, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strommenger, B.; Kettlitz, C.; Werner, G.; Witte, W. Multiplex PCR assay for simultaneous detection of nine clinically relevant antibiotic resistance genes in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 4089–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeric, P.E.; Azpiroz, A.; Lopardo, H.; Centron, D. Survey of molecular determinants in Gram-positive cocci isolated from hospital settings in Argentina. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2007, 1, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutcliffe, J.; Grebe, T.; Tait-Kamradt, A.; Wondrack, L. Detection of erythromycin-resistant determinants by PCR. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1996, 40, 2562–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnellmann, C.; Gerber, V.; Rossano, A.; Jaquier, V.; Panchaud, Y.; Doherr, M.G.; Thomann, A.; Straub, R.; Perreten, V. Presence of new mecA and mph(C) variants conferring antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus spp. isolated from the skin of horses before and after clinic admission. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 4444–4454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

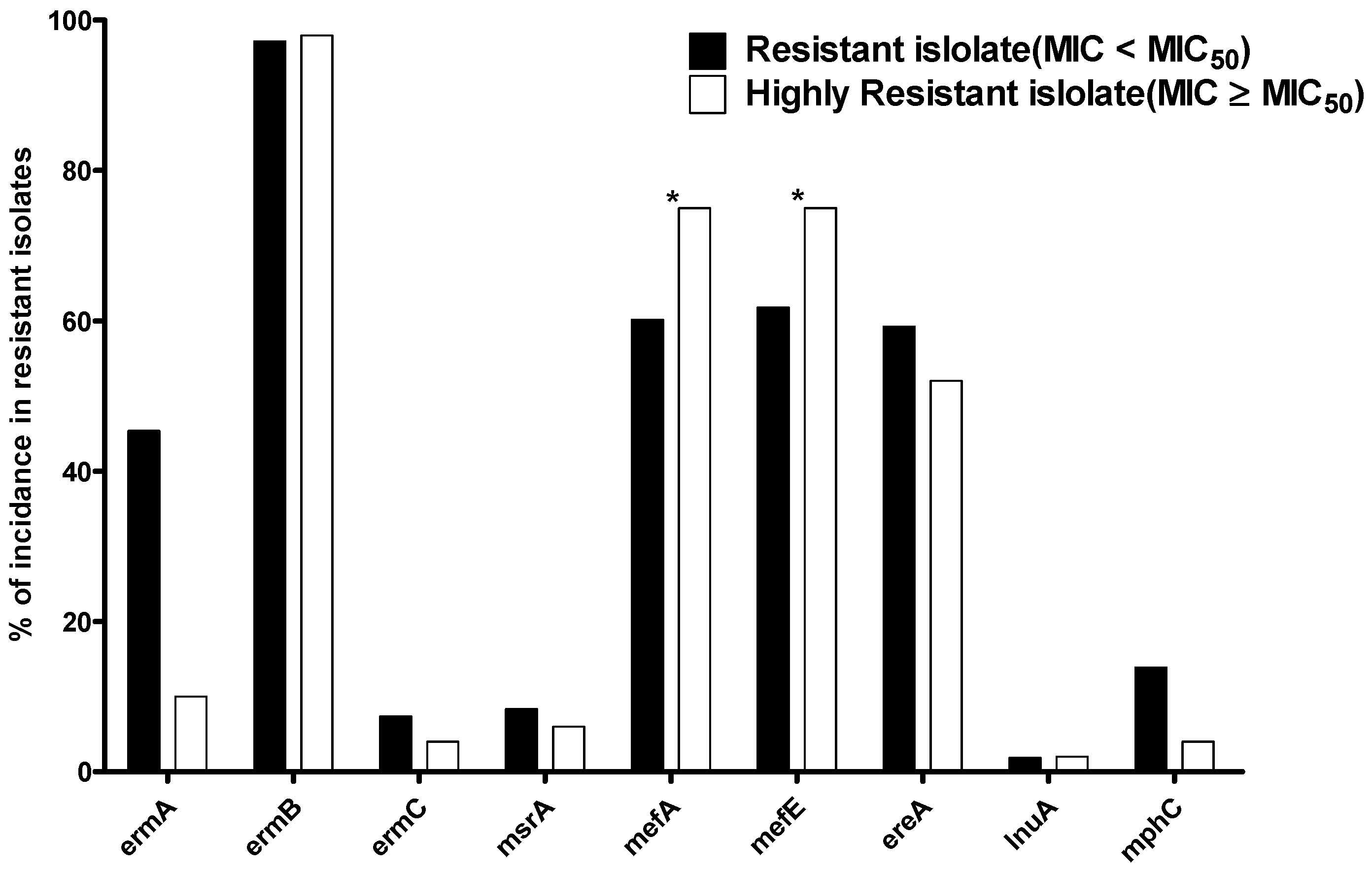
| Test | E. faecalis | E. faecium |
|---|---|---|
| Catalase | − | − |
| Oxidase | − | − |
| Motility | Non-motile | Non-motile |
| Growth in 6.5% NaCl | + | + |
| Growth at 45 °C | + | + |
| Lactose fermentation | + | + |
| Mannitol fermentation | + | + |
| Growth in 0.04% tellurite | + | − |
| Arabinose fermentation | − | + |
| Isolates | Resistance Phenotype | Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cMLS | iMLS | M | L | ||
| E. faecalis | 42 (76.4%) | 2 (3.6%) | 10 (18.2%) | 1 (1.8%) | 55 |
| E. faecium | 34 (79.1%) | 1 (2.3%) | 7 (16.3%) | 1 (2.3%) | 43 |
| Other Enterococci | 7 (70%) | 1 (10%) | 2 (20%) | 0 | 10 |
| Total | 83 (76.8%) | 4 (3.7%) | 19 (17.6%) | 2 (1.9%) | 108 |
| Gene | Primer | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| ermA | F | AAGCGGTAAACCCCTCTGA | [83] |
| R | TTCGCAAATCCCTTCTCAAC | ||
| ermB | F | CTATCTGATTGTTGAAGAAGGATT | [49] |
| R | GTTTACTCTTGGTTTAGGATGAAA | ||
| ermC | F | AATCGTCAATTCCTGCATGT | [83] |
| R | TAATCGTGGAATACGGGTTTG | ||
| msrA | F | TCCAATCATTGCACAAAATC | [49] |
| R | AATTCCCTCTATTTGGTGGT | ||
| mefA | F | CGTAGCATTGGAACAGC | [84] |
| R | TGCCGTAGTACAGCCAT | ||
| mefE | F | CGTAGCATTGGAACAGC | [84] |
| R | TCGAAGCCCCCTAATCTT | ||
| ereA | F | AACACCCTGAACCCAAGGGACG | [85] |
| R | CTTCACATCCGGATTCGCTCGA | ||
| lnuA | F | GGTGGCTGGGGGGTAGATGTATTAACTGG | [68] |
| R | GCTTCTTTTGAAATACATGGTATTTTTCGATC | ||
| mphC | F | ATGACTCGACATAATGAAAT | [86] |
| R | CTACTCTTTCATACCTAACTC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abu Lila, A.S.; Alharby, T.N.; Alanazi, J.; Alanazi, M.; Abdallah, M.H.; Rizvi, S.M.D.; Moin, A.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Tabrez, S.; Al Balushi, A.A.; et al. Clinical Resistant Strains of Enterococci and Their Correlation to Reduced Susceptibility to Biocides: Phenotypic and Genotypic Analysis of Macrolides, Lincosamides, and Streptogramins. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030461
Abu Lila AS, Alharby TN, Alanazi J, Alanazi M, Abdallah MH, Rizvi SMD, Moin A, Khafagy E-S, Tabrez S, Al Balushi AA, et al. Clinical Resistant Strains of Enterococci and Their Correlation to Reduced Susceptibility to Biocides: Phenotypic and Genotypic Analysis of Macrolides, Lincosamides, and Streptogramins. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(3):461. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030461
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbu Lila, Amr Selim, Tareq Nafea Alharby, Jowaher Alanazi, Muteb Alanazi, Marwa H. Abdallah, Syed Mohd Danish Rizvi, Afrasim Moin, El-Sayed Khafagy, Shams Tabrez, Abdullah Ali Al Balushi, and et al. 2023. "Clinical Resistant Strains of Enterococci and Their Correlation to Reduced Susceptibility to Biocides: Phenotypic and Genotypic Analysis of Macrolides, Lincosamides, and Streptogramins" Antibiotics 12, no. 3: 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030461
APA StyleAbu Lila, A. S., Alharby, T. N., Alanazi, J., Alanazi, M., Abdallah, M. H., Rizvi, S. M. D., Moin, A., Khafagy, E.-S., Tabrez, S., Al Balushi, A. A., & Hegazy, W. A. H. (2023). Clinical Resistant Strains of Enterococci and Their Correlation to Reduced Susceptibility to Biocides: Phenotypic and Genotypic Analysis of Macrolides, Lincosamides, and Streptogramins. Antibiotics, 12(3), 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030461









