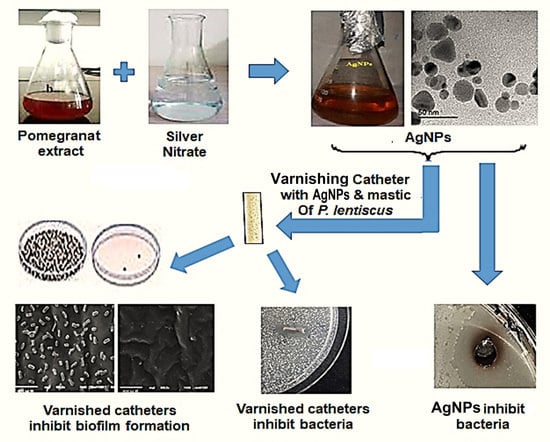
Combating Bacterial Biofilm Formation in Urinary Catheter by Green Silver Nanoparticle
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Media and Chemicals
4.2. Preparation of AgNPs
4.3. Characterisation of AgNPs
4.4. Bacterial Strains
4.5. Antibacterial Effect of Silver Nanoparticles by Agar Well Diffusion Method
4.6. Coating of the Catheter with Silver Nanoparticles
4.7. Agar Diffusion Test for the Bacterial Inhibitory Effect of Coated Catheters
4.8. Viable Count Evaluation of the Inhibitory Effect of AgNPs-Coated Catheters
4.9. Scanning Electron Microscope Analysis
4.10. Quantitate Determination of Silver Ions Released from Catheters
4.11. Statistical Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Das, R.N.; Chandrashekhar, T.S.; Joshi, H.S.; Gurung, M.; Shrestha, N.; Shivananda, P.G. Frequency and susceptibility profile of pathogens causing urinary tract infections at a tertiary care hospital in western nepal. Singap. Med. J. 2006, 47, 281–285. [Google Scholar]
- Behrooozi, A.; Rahbar, M.; Jalil, V. A survey on epidemiology of urinary tract infections and resistance pattern of uropathogens in an iranian 1000-bed tertiary care hospital. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2010, 4, 753–756. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, F.; Malik, S.; Ahmed, J. Antibiotic susceptibility pattern and esbl prevalence in nosocomial escherichia coli from urinary tract infections in pakistan. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 8, 3921–3926. [Google Scholar]
- Tedja, R.; Wentink, J.; O’Horo, J.C.; Thompson, R.; Sampathkumar, P. Catheter-associated urinary tract infections in intensive care unit patients. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2015, 36, 1330–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranz, J.; Schmidt, S.; Wagenlehner, F.; Schneidewind, L. Catheter-associated urinary tract infections in adult patients: Preventive strategies and treatment options. Dtsch. Ärztebl. Int. 2020, 117, 83. [Google Scholar]
- Stickler, D.J. Bacterial biofilms and the encrustation of urethral catheters. Biofouling 1996, 9, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleksy-Wawrzyniak, M.; Junka, A.; Brożyna, M.; Paweł, M.; Kwiek, B.; Nowak, M.; Mączyńska, B.; Bartoszewicz, M. The in vitro ability of klebsiella pneumoniae to form biofilm and the potential of various compounds to eradicate it from urinary catheters. Pathogens 2021, 11, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.A.; Albetran, H.M.; Alheshibri, M.H.; Timoumi, A.; Algarou, N.A.; Akhtar, S.; Slimani, Y.; Almessiere, M.A.; Alahmari, F.S.; Baykal, A. Synthesis of electrospun tio2 nanofibers and characterization of their antibacterial and antibiofilm potential against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahuman, H.B.H.; Dhandapani, R.; Palanivel, V.; Thangavelu, S.; Paramasivam, R.; Muthupandian, S. Bioengineered phytomolecules-capped silver nanoparticles using carissa carandas leaf extract to embed on to urinary catheter to combat uti pathogens. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.; Prasad, S.; Egan, M. Treating utis in reproductive-age women—proceed with caution. J. Fam. Pract. 2010, 59, 220. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Shi, H.; Yu, H.; Yan, S.; Luan, S. The recent advances in surface antibacterial strategies for biomedical catheters. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 4095–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunney, M.M.; Jones, D.S.; Gorman, S.P. Biofilm and Biofilm-Related Encrustation of Urinary Tract Devices. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1999; Volume 310, pp. 558–566. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, P.S.; Costerton, J.W. Antibiotic resistance of bacteria in biofilms. Lancet 2001, 358, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachem, R.; Reitzel, R.; Borne, A.; Jiang, Y.; Tinkey, P.; Uthamanthil, R.; Chandra, J.; Ghannoum, M.; Raad, I. Novel antiseptic urinary catheters for prevention of urinary tract infections: Correlation of in vivo and in vitro test results. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 5145–5149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regev-Shoshani, G.; Ko, M.; Miller, C.; Av-Gay, Y. Slow Release of Nitric Oxide from charged catheters and its effect on biofilm formation by escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.K.; Deshmukh, S.; Ingle, A.; Gade, A.K. Silver nanoparticles: The powerful nanoweapon against multidrug-resistant bacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 112, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.J. A new silver dressing for wounds with delayed healing. Wounds 2006, 2, 70. [Google Scholar]
- Vigneshwaran, N.; Kathe, A.A.; Varadarajan, P.V.; Nachane, R.P.; Balasubramanya, R.H. Functional Finishing of Cotton Fabrics Using Silver Nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2007, 7, 1893–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiano, K.; Pleifer, C.; Engelhardt, K.; Brössner, G.; Lackner, P.; Huck, C.; Lass-Flörl, C.; Obwegeser, A. Silver segregation and bacterial growth of intraventricular catheters impregnated with silver nanoparticles in cerebrospinal fluid drainages. Neurol. Res. 2008, 30, 285–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, W.X.; Lai, Y.X.; Choudhury, M.; Amalraj, F.D. Efficacy of incorporating silver nanoparticles into maxillofacial silicone against staphylococcus aureus, candida albicans, and polymicrobial biofilms. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2021; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansdown, A.; Williams, A. Bacterial resistance to silver in wound care and medical devices. J. Wound Care 2007, 16, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skóra, B.; Krajewska, U.; Nowak, A.; Dziedzic, A.; Barylyak, A.; Kus-Liśkiewicz, M. Noncytotoxic silver nanoparticles as a new antimicrobial strategy. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, T. Availability of ag+ ions having most highly bactericidal activity to suppression by inhibitions of viral and cancerous cell growth. Clin. Res. Immunol. 2018, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, S.A.; Das, S.S.; Khatoon, A.; Ansari, M.T.; Afzal, M.; Hasnain, S.; Nayak, A.K. Bactericidal activity of silver nanoparticles: A mechanistic review. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2020, 3, 756–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qahtani, M.; Safan, A.; Jassim, G.; Abadla, S. Efficacy of anti-microbial catheters in preventing catheter associated urinary tract infections in hospitalized patients: A review on recent updates. J. Infect. Public Health 2019, 12, 760–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roe, D.; Karandikar, B.; Bonn-Savage, N.; Gibbins, B.; Roullet, J.-B. Antimicrobial surface functionalization of plastic catheters by silver nanoparticles. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008, 61, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regev-Shoshani, G.; Ko, M.; Crowe, A.; Av-Gay, Y. Comparative Efficacy of Commercially Available and Emerging Antimicrobial Urinary Catheters Against Bacteriuria Caused by E. coli In Vitro. Urology 2011, 78, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, C.N.; Ho, C.M.; Chen, R.; He, Q.Y.; Yu, W.Y.; Sun, H.; Tam, P.K.; Chiu, J.F.; Che, C.M. Silver nanoparticles: Partial oxidation and antibacterial activities. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 12, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimas, K.S.; Pantazis, P.; Ramanujam, R. Review: Chios mastic gum: A plant-produced resin exhibiting numerous diverse pharmaceutical and biomedical properties. Vivo 2012, 26, 777–785. [Google Scholar]
- Goda, R.M.; Shohayeb, M.M. Use of pistacia lentiscus mastic for sustained-release system of chlorocresol and benzoic acid for in vitro prevention of bacterial colonization of silicon urinary catheter. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 73, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, P.; Locklin, J.; Handa, H. A review of the recent advances in antimicrobial coatings for urinary catheters. Acta Biomater. 2017, 50, 20–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Yuan, X. Antimicrobial strategies for urinary catheters. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2019, 107, 445–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz, C.; Torres, R.; Paredes, D. Synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of antibacterial effect of Ag nanoparticles against Escherichia coli O157:H7 and methicillin- resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 1717–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yoshida, T.; Hatano, T.; Ito, H.; Okuda, T. Structural Diversity and Antimicrobial Activities of Ellagitannins. In Chemistry and Biology of Ellagitannins: An Underestimated Class of Bioactive Plant Polyphenols; World Scientific: Singapore, 2009; pp. 55–93. [Google Scholar]
- Shinde, V.V.; Jadhav, P.R.; Kim, J.H.; Patil, P.S. One-step synthesis and characterization of anisotropic silver nanoparticles: Application for enhanced antibacterial activity of natural fabric. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 8393–8401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restrepo, C.V.; Villa, C.C. Monitoring; Management. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles, influence of capping agents, and dependence on size and shape: A review. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2021, 15, 100428. [Google Scholar]
- Devanesan, S.; AlSalhi, M.S.; Balaji, R.V.; Ranjitsingh, A.J.A.; Ahamed, A.; Alfuraydi, A.; AlQahtani, F.Y.; Aleanizy, F.S.; Othman, A.H. Antimicrobial and Cytotoxicity Effects of Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles from Punica granatum Peel Extract. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadzadeh Kakhki, R.; Hedayat, S.; Mohammadzadeh, K. Novel, green and low cost synthesis of ag nanoparticles with superior adsorption and solar based photocatalytic activity. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 8788–8795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Ren, Y.-Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, C. Preparation and antibacterial activities of ag/ag+/ag3+ nanoparticle composites made by pomegranate (punica granatum) rind extract. Results Phys. 2016, 6, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chutrakulwong, F.; Thamaphat, K.; Tantipaibulvut, S.; Limsuwan, P. In Situ Deposition of Green Silver Nanoparticles on Urinary Catheters under Photo-Irradiation for Antibacterial Properties. Processes 2020, 8, 1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, Y.Y.; Rukayadi, Y.; Nor-Khaizura, M.-A.; Kuan, C.H.; Chieng, B.W.; Nishibuchi, M.; Radu, S. In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity of Green Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles Against Selected Gram-negative Foodborne Pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wady, A.F.; Machado, A.L.; Foggi, C.C.; Zamperini, C.A.; Zucolotto, V.; Moffa, E.B.; Vergani, C.E. Effect of a silver nanoparticles solution on staphylococcus aureus and candida spp. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-R.; Xie, X.-B.; Shi, Q.-S.; Duan, S.-S.; Ouyang, Y.-S.; Chen, Y.-B. Antibacterial effect of silver nanoparticles on Staphylococcus aureus. BioMetals 2011, 24, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gould, C.V.; Umscheid, C.A.; Agarwal, R.K.; Kuntz, G.; Pegues, D.A. Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee (HICPAC) Guideline for Prevention of Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infections 2009. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2010, 31, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yassin, M.A.; Elkhooly, T.A.; Elsherbiny, S.M.; Reicha, F.M.; Shokeir, A.A. Facile coating of urinary catheter with bio–inspired antibacterial coating. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wayne, P. Clinical and laboratory standards institute. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Inf. J. 2011, 31, 100–121. [Google Scholar]
- Chaiban, G.; Hanna, H.; Dvorak, T.; Raad, I. A rapid method of impregnating endotracheal tubes and urinary catheters with gendine: A novel antiseptic agent. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2005, 55, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balouiri, M.; Sadiki, M.; Ibnsouda, S.K. Methods for in vitro evaluating antimicrobial activity: A review. J. Pharm. Anal. 2016, 6, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goda, R.M.; El-Baz, A.M.; Khalaf, E.M.; Alharbi, N.K.; Elkhooly, T.A.; Shohayeb, M.M. Combating Bacterial Biofilm Formation in Urinary Catheter by Green Silver Nanoparticle. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11040495
Goda RM, El-Baz AM, Khalaf EM, Alharbi NK, Elkhooly TA, Shohayeb MM. Combating Bacterial Biofilm Formation in Urinary Catheter by Green Silver Nanoparticle. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(4):495. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11040495
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoda, Reham M., Ahmed M. El-Baz, Eman M. Khalaf, Nada K. Alharbi, Tarek A. Elkhooly, and Mohamed M. Shohayeb. 2022. "Combating Bacterial Biofilm Formation in Urinary Catheter by Green Silver Nanoparticle" Antibiotics 11, no. 4: 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11040495
APA StyleGoda, R. M., El-Baz, A. M., Khalaf, E. M., Alharbi, N. K., Elkhooly, T. A., & Shohayeb, M. M. (2022). Combating Bacterial Biofilm Formation in Urinary Catheter by Green Silver Nanoparticle. Antibiotics, 11(4), 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11040495