Evaluation of the Correspondence between the Concentration of Antimicrobials Entering Sewage Treatment Plant Influent and the Predicted Concentration of Antimicrobials Using Annual Sales, Shipping, and Prescriptions Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microbes and Reagents
2.2. Sampling
| Antimicrobials | Molecular Formula | Molecular Mass (g/mol) | Structure | Excretion Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ampicillin (APL) | C16H19N3O4S | 349.4 |  | 71 [46] |
| Cefdinir (CDN) | C14H13N5O5S2 | 395.4 |  | 31 [47] |
| Cefpodoxime proxetil (CPXP) | C21H27N5O9S2 | 557.6 | 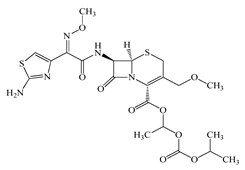 | 50 [48] |
| Ciprofloxacin (CFX) | C17H18FN3O3 | 331.3 | 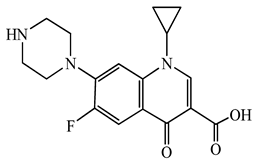 | 50 [49] |
| Clarithromycin (CTM) | C38H69NO13 | 748.0 |  | 24 [50] |
| Doxycycline (DCL) | C22H24N2O8 | 444.4 |  | 80 [51] |
| Levofloxacin (LFX) | C18H20FN3O4 | 361.4 | 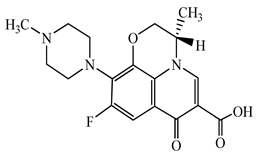 | 83 [52] |
| Minocycline (MCL) | C23H27N3O7 | 457.5 | 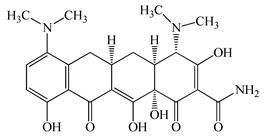 | 36 [51] |
| Tetracycline (TCL) | C22H24N2O8 | 444.4 | 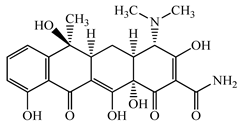 | 60 [53] |
| Vancomycin (VMC) | C66H75Cl2N9O24 | 1449.3 | 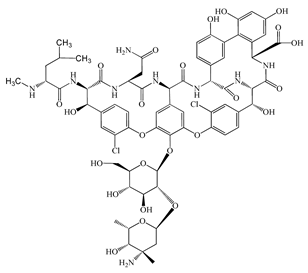 | 85 [54] |
2.3. Analytical Procedures for Antimicrobials
2.4. Method Validation
2.5. Prediction of the Concentration of Antimicrobials in the Targeted STP Influent
3. Results and Discussion
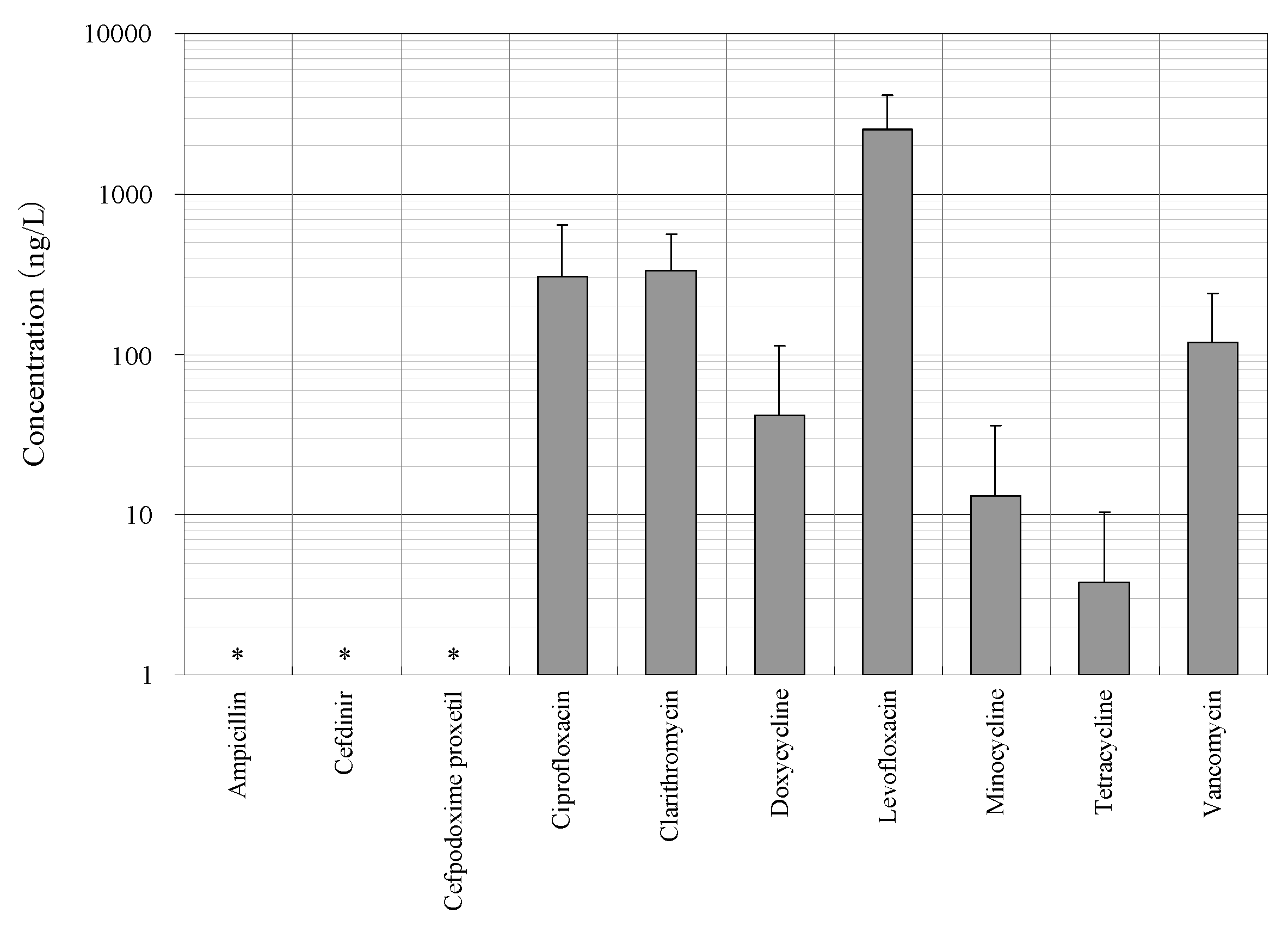
3.1. Distribution of Concentrations of Antimicrobials in the STP Influent
3.2. Prediction of Annual Concentrations of Targeted Antimicrobials in the STP Influent
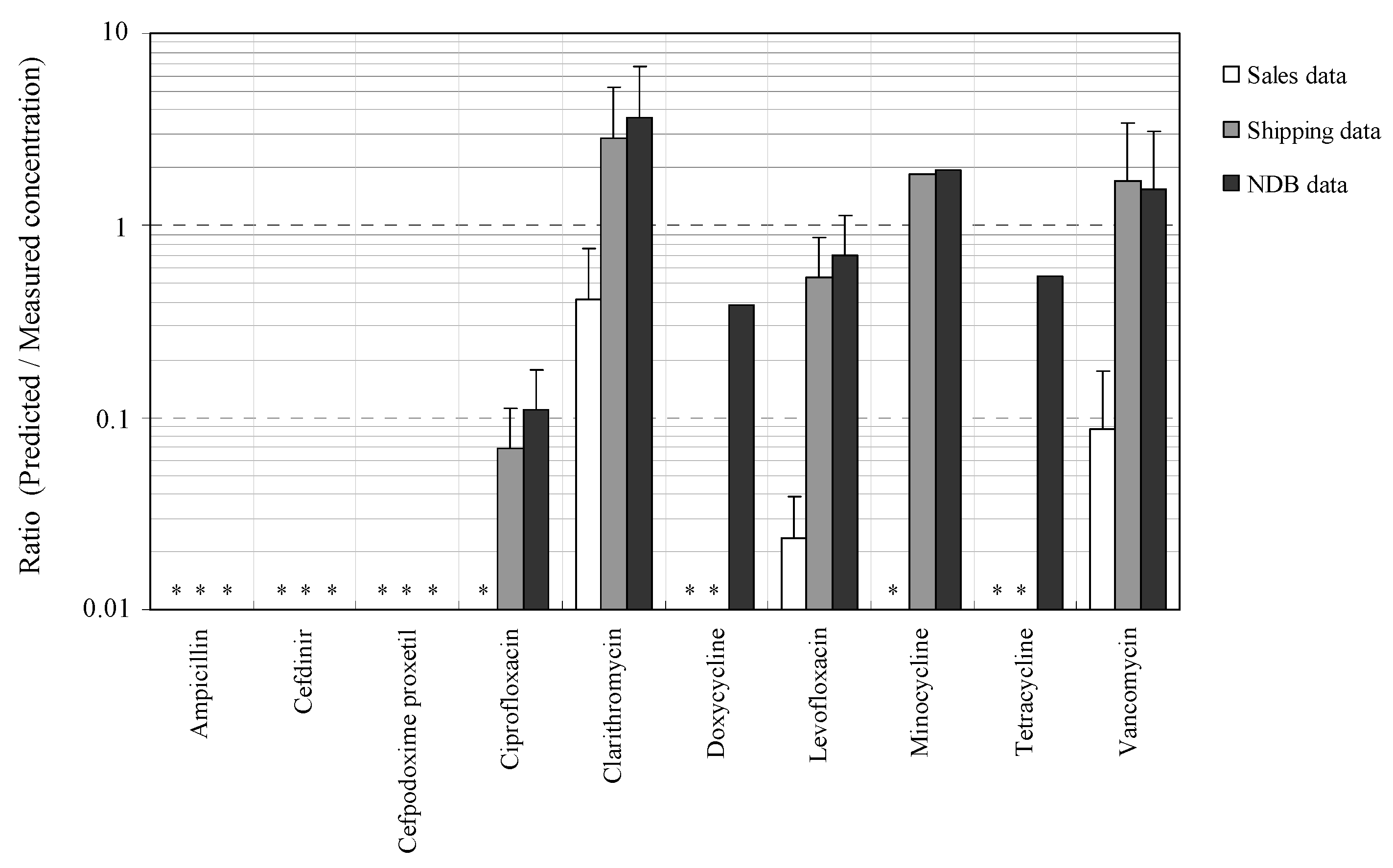
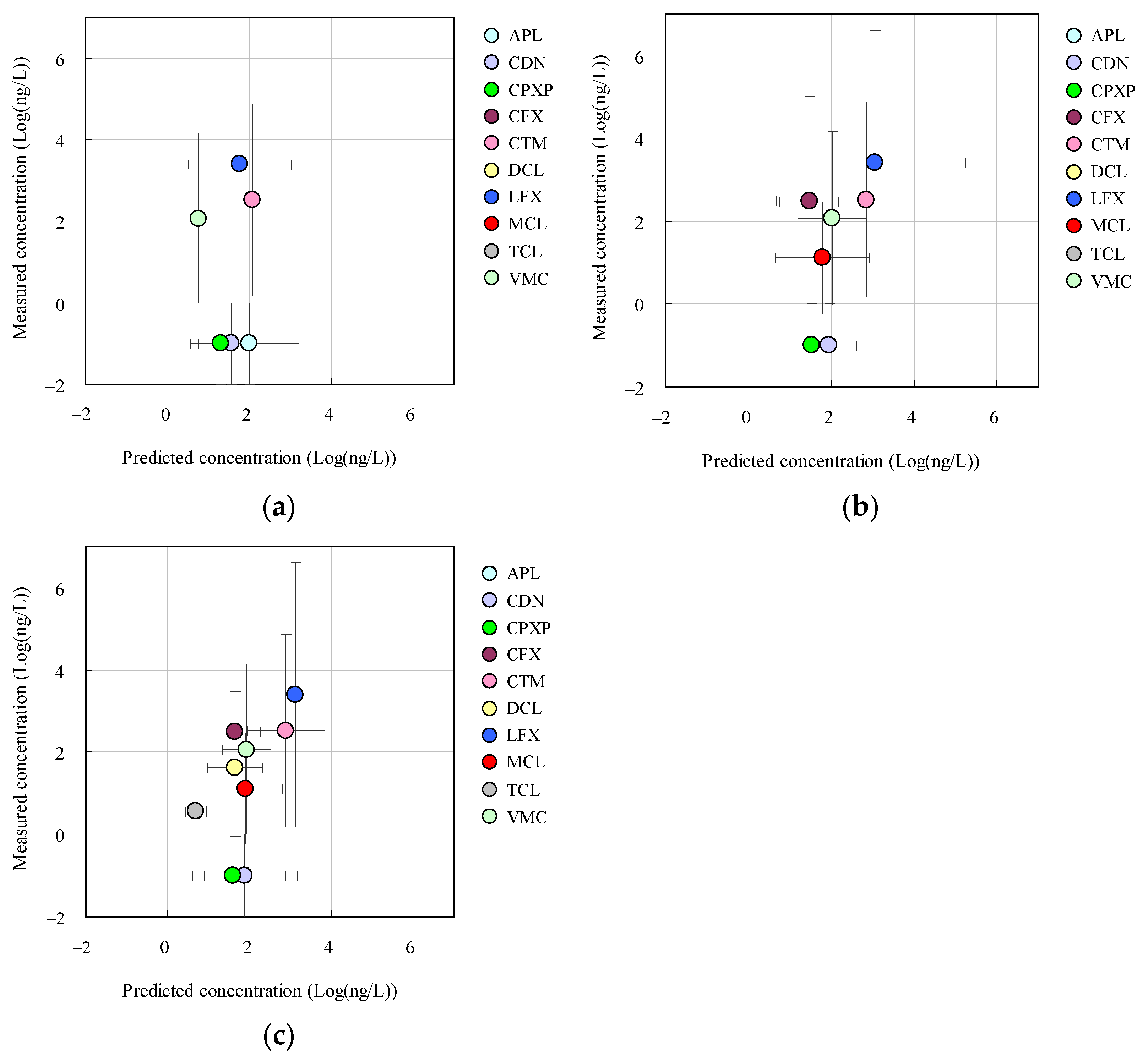
3.3. Relationships between Measured and Predicted Concentrations of Antimicrobials
3.4. Evaluation of Relationships between Concentrations of Antimicrobials Predicted by Using Sales, Shipping, and NDB Volumes
4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nathan, C.; Cars, O. Antibiotic resistance—Problems, progress, and prospects. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1761–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, T.R. A One-Health approach to antimicrobial resistance. Nature Microbiol. 2018, 3, 854–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schages, L.; Wichern, F.; Kalscheuer, R.; Bockmühl, D. Winter is coming—Impact of temperature on the variation of beta-lactamase and mcr genes in a wastewater treatment plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 136499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahill, N.; O’Connor, L.; Mahon, B.; Varley, Á.; McGrath, E.; Ryan, P.; Cormican, M.; Brehony, C.; Jolley, K.A.; Maiden, M.C.; et al. Hospital effluent: A reservoir for carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales? Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 672, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulus, G.K.; Hornstra, L.M.; Alygizakis, N.; Slobodnik, J.; Thomaidis, N.; Medema, G. The impact of on-site hospital wastewater treatment on the downstream communal wastewater system in terms of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2019, 222, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassoun-Kheir, N.; Stabholz, Y.; Kreft, J.U.; de la Cruz, R.; Romalde, J.L.; Nesme, J.; Sørensen, S.J.; Smets, B.F.; Graham, D.; Paul, M. Comparison of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and antibiotic resistance genes abundance in hospital and community wastewater: A systematic review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 743, 140804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, T.; Otomo, K.; Kunitou, M.; Shimizu, M.; Hosomaru, K.; Mikata, S.; Ishida, M.; Hisamatsu, K.; Yunoki, A.; Mino, Y.; et al. Environmental fate of pharmaceutical compounds and antimicrobial-resistant bacteria in hospital effluents, and contributions to pollutant loads in the surface waters in Japan. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainab, S.M.; Junaid, M.; Xu, N.; Malik, R.N. Antibiotics and antibiotic resistant genes (ARGs) in groundwater: A global review on dissemination, sources, interactions, environmental and human health risks. Water Res. 2020, 187, 116455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Yin, G.; Liu, M.; Chen, C.; Jiang, Y.; Hou, L.; Zheng, Y. A systematic review of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in estuarine and coastal environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 146009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazda, M.; Kumirska, J.; Stepnowski, P.; Mulkiewicz, E. Antibiotic resistance genes identified in wastewater treatment plant systems—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.Q.; Vu, H.P.; Nguyen, L.N.; Wang, Q.; Djordjevic, S.P.; Donner, E.; Yin, H.; Nghiem, L.D. Monitoring antibiotic resistance genes in wastewater treatment: Current strategies and future challenges. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 783, 146964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miłobedzka, A.; Ferreira, C.; Vaz-Moreira, I.; Calderón-Franco, D.; Gorecki, A.; Purkrtova, S.; Jan, B.; Dziewit, L.; Singleton, C.M.; Nielsen, P.H.; et al. Monitoring antibiotic resistance genes in wastewater environments: The challenges of filling a gap in the one-health cycle. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, I.T.; Santos, L. Antibiotics in the aquatic environments: A review of the european scenario. Environ. Int. 2016, 94, 736–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, M.F.; Powers, S.M.; Hampton, S.E. An evidence synthesis of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in the environment: Imbalances among compounds, sewage treatment techniques, and ecosystem types. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 12961–12973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.H.; Reinhard, M.; Gin, K.Y.H. Occurrence and fate of emerging contaminants in municipal wastewater treatment plants from different geographical regions—A review. Water Res. 2018, 133, 182–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwenzi, W.; Musiyiwa, K.; Mangori, L. Sources, behaviour and health risks of antimicrobial resistance genes in wastewaters: A hotspot reservoir. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 102220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, A.; Mazumder, P.; Tyagi, V.K.; Tushara Chaminda, G.G.; An, A.K.; Kumar, M. Occurrence and fate of emerging contaminants in water environment: A review. Groundw. Sustain. Develop. 2018, 6, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Larsson, D.G.J. Antibiotic resistance genes in the environment: Prioritizing risks. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalakova, P.; Cizmas, L.; McDonald, T.J.; Marsalek, B.; Feng, M.; Sharma, V.K. Occurrence and toxicity of antibiotics in the aquatic environment: A review. Chemosphere 2020, 251, 126351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, M.; Achmon, Y.; Cao, Y.; Liang, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, H.; Siame, B.A.; Leung, K.Y. Distribution of antibiotic resistance genes in the environment. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 285, 117402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Yang, H.; Guan, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, T. Risks of antibiotic resistance genes and antimicrobial resistance under chlorination disinfection with public health concerns. Environ. Int. 2022, 158, 106978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Z.; Chen, P.; Cui, N.; Lin, X.; Ji, F.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, P.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Q.; Song, Y.; et al. Detection of enteroviruses in urban sewage by next generation sequencing and its application in environmental surveillance. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendriksen, R.S.; Munk, P.; Njage, P.; van Bunnik, B.; McNally, L.; Lukjancenko, O.; Röder, T.; Nieuwenhuijse, D.; Pedersen, S.K.; Kjeldgaard, J.; et al. Global monitoring of antimicrobial resistance based on metagenomics analyses of urban sewage. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarestrup, F.M.; Woolhouse, M.E.J. Using sewage for surveillance of antimicrobial resistance. Science 2020, 367, 630–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA (U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration). Guidance for Industry Environmental Assessment of Human Drug and Biologics Applications; FDA: Washington, DC, USA, 1998; pp. 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- EMEA (European Medicines Agency). Guideline on the Environmental Risk Assessment of Medicinal Products for Human Use; EMEA: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Tauxe-Wuersch, A.; De Alencastro, L.F.; Grandjean, D.; Tarradellas, J. Occurrence of several acidic drugs in sewage treatment plants in switzerland and risk assessment. Water Res. 2005, 39, 1761–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carballa, M.; Omil, F.; Lema, J.M. Comparison of predicted and measured concentrations of selected pharmaceuticals, fragrances and hormones in spanish sewage. Chemosphere 2008, 72, 1118–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besse, J.P.; Latour, J.F.; Garric, J. Anticancer drugs in surface waters: What can we say about the occurrence and environmental significance of cytotoxic, cytostatic and endocrine therapy drugs? Environ. Int. 2012, 39, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosterhuis, M.; Sacher, F.; ter Laak, T.L. Prediction of concentration levels of metformin and other high consumption pharmaceuticals in wastewater and regional surface water based on sales data. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 442, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, T.; Nakada, N.; Yamashita, N.; Tanaka, H. Evaluation of concentrations of pharmaceuticals detected in sewage influents in Japan by using annual shipping and sales data. Chemosphere 2015, 138, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Borthwick, A.G.; Lin, Y.; Li, Y.; Fu, J.; Wong, Y.; Liu, W. Sale-based estimation of pharmaceutical concentrations and associated environmental risk in the Japanese wastewater system. Environ. Int. 2020, 139, 105690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Tscharke, B.J.; Choi, P.M.; O’Brien, J.W.; Boogaerts, T.; Jiang, H.; Yang, M.; Hollingworth, S.A.; Thai, P.K. Using prescription and wastewater data to estimate the correction factors of atenolol, carbamazepine, and naproxen for wastewater-based epidemiology applications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 7551–7560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiho. Yakuji Handbook; Jiho: Tokyo, Japan, 2021; ISBN 978-4840753494. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Health Labour and Welfare, Japan. Annual Report on Statistics of Production by Pharmaceutical Industry in 2020. Available online: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/topics/yakuji/2020/nenpo/ (accessed on 7 March 2022). (In Japanese).
- Ministry of Health Labour and Welfare, Japan. National Database of Health Insurance Claims and Specific Health Checkups of Japan (NDB). Available online: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/seisakunitsuite/bunya/0000177182.html (accessed on 7 March 2022). (In Japanese).
- Koizumi, R.; Kusama, Y.; Muraki, Y.; Ishikane, M.; Yamasaki, D.; Tanabe, M.; Ohmagari, N. Effect of population inflow and outflow between rural and urban areas on regional antimicrobial use surveillance. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusama, Y.; Muraki, Y.; Tanaka, C.; Koizumi, R.; Ishikane, M.; Yamasaki, D.; Tanabe, M.; Ohmagari, N. Characteristics and limitations of national antimicrobial surveillance according to sales and claims data. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0251299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, T.S.; Murphy, M.; Mendola, N.; Wong, V.; Carlson, D.; Waring, L. Characterization of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in hospital effluent and waste water influent/effluent by direct-injection LC-MS-MS. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 518–519, 459–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azuma, T.; Arima, N.; Tsukada, A.; Hirami, S.; Matsuoka, R.; Moriwake, R.; Ishiuchi, H.; Inoyama, T.; Teranishi, Y.; Yamaoka, M.; et al. Detection of pharmaceuticals and phytochemicals together with their metabolites in hospital effluents in Japan, and their contribution to sewage treatment plant influents. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 548–549, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lake Biwa-Yodo River Water Quality Preservation Organization, Japan. Lake Biwa-Yodo River Water Quality Preservation Organization (BYQ) Report on Water Environment in Biwa Lake-Yodo River System 2019; BYQ: Osaka, Japan, 2021; pp. 1–90. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Health Labour and Welfare, Japan. Vital Statistics in Japan; Ministry of Health Labour and Welfare: Tokyo, Japan, 2021; pp. 1–102. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.; Nakada, N.; Yamashita, N.; Johnson, A.C.; Tanaka, H. How seasonality affects the flow of estrogens and their conjugates in one of Japan’s most populous catchments. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2906–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japan Meteorological Agency 2021. Weather Statistics. Available online: http://www.jma.go.jp/jma/index.html (accessed on 7 March 2022).
- Kumar, V.; Nakada, N.; Yasojima, M.; Yamashita, N.; Johnson, A.C.; Tanaka, H. Rapid determination of free and conjugated estrogen in different water matrices by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 1440–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzen, J.M.; Broll, M.; Kaever, V.; Burhenne, H.; Hafer, C.; Clajus, C.; Knitsch, W.; Burkhardt, O.; Kielstein, J.T. Pharmacokinetics of ampicillin/sulbactam in critically III patients with acute kidney injury undergoing extended dialysis. Clin. J. American Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 7, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hishida, A.; Ohishi, K.; Nagashima, S.; Kanamaru, M.; Obara, M.; Kitada, A. Pharmacokinetic study of an oral cephalosporin, cefdinir, in hemodialysis patients. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1998, 42, 1718–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Todd, W.M. Cefpodoxime proxetil: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 1994, 4, 37–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Williams, K. Clinical pharmacokinetics of ciprofloxacin. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1990, 19, 503. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rodvold, K.A. Clinical pharmacokinetics of clarithromycin. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1999, 37, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saivin, S.; Houin, G. Clinical pharmacokinetics of doxycycline and minocycline. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1988, 15, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, A.; Duarte, S.; Nunes, R.; Rocha, H.; Pena, A.; Meisel, L. Human and veterinary antibiotics used in portugal—A ranking for ecosurveillance. Toxics 2014, 2, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, P.; House, F.; Inns, P.; Morrison, P.; Rogers, H.; Bradbrook, I. Effect of cimetidine on the absorption of orally administered tetracycline. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol 1980, 9, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Matzke, G.R.; Zhanel, G.G.; Guay, D.R.P. Clinical pharmacokinetics of vancomycin. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1986, 11, 257–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jesus Gaffney, V.; Almeida, C.M.M.; Rodrigues, A.; Ferreira, E.; Benoliel, M.J.; Cardoso, V.V. Occurrence of pharmaceuticals in a water supply system and related human health risk assessment. Water Res. 2015, 72, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasse, C.; Schlüsener, M.P.; Schulz, R.; Ternes, T.A. Antiviral drugs in wastewater and surface waters: A new pharmaceutical class of environmental relevance? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1728–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, T.; Ishiuchi, H.; Inoyama, T.; Teranishi, Y.; Yamaoka, M.; Sato, T.; Mino, Y. Occurrence and fate of selected anticancer, antimicrobial, and psychotropic pharmaceuticals in an urban river in a subcatchment of the Yodo River Basin, Japan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 18676–18686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabic, R.; Fick, J.; Lindberg, R.H.; Fedorova, G.; Tysklind, M. Multi-residue method for trace level determination of pharmaceuticals in environmental samples using liquid chromatography coupled to triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. Talanta 2012, 100, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrović, M.; Škrbić, B.; Živančev, J.; Ferrando-Climent, L.; Barcelo, D. Determination of 81 pharmaceutical drugs by high performance liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry with hybrid triple quadrupole-linear ion trap in different types of water in Serbia. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468–469, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlüsener, M.P.; Hardenbicker, P.; Nilson, E.; Schulz, M.; Viergutz, C.; Ternes, T.A. Occurrence of venlafaxine, other antidepressants and selected metabolites in the rhine catchment in the face of climate change. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 196, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugawara, T.; Ohkusa, Y.; Gu, Y.; Taniguchi, K.; Okabe, N. Estimation of amount of antimicrobials used by pharmacy surveillance. Jpn. J. Infect. Prevent. Control 2012, 27, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gu, Y.; Fujitomo, Y.; Ohmagari, N. Outcomes and future prospect of Japan’s National Action Plan on antimicrobial resistance (2016–2020). Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statistics Bureau Japan. Statistical Handbook of Japan 2021; Ministry of Health Labour and Welfare, Japan: Tokyo, Japan, 2021; pp. 1–197. ISBN 978-4-8223-4129-9. [Google Scholar]
- Japan Sewage Works Association. Statistics of Sewerage; Japan Sewage Works Association: Tokyo, Japan, 2021. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.R.; Angeles, L.F.; Butryn, D.M.; Metch, J.W.; Garner, E.; Vikesland, P.J.; Aga, D.S. Towards a harmonized method for the global reconnaissance of multi-class antimicrobials and other pharmaceuticals in wastewater and receiving surface waters. Environ. Int. 2019, 124, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, C.F.; Lange, L.C.; Amaral, M.C.S. Occurrence, fate and removal of pharmaceutically active compounds (PhACs) in water and wastewater treatment plants—A review. J. Water Proc. Eng. 2019, 32, 100927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeleye, A.S.; Xue, J.; Zhao, Y.; Taylor, A.A.; Zenobio, J.E.; Sun, Y.; Han, Z.; Salawu, O.A.; Zhu, Y. Abundance, fate, and effects of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in aquatic environments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Li, X.; Huang, H.; Wang, T.; Wang, Z.; Fu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Du, P.; Li, X. Simultaneous determination of seven antibiotics and five of their metabolites in municipal wastewater and evaluation of their stability under laboratory conditions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Jimenez, L.E.; Aranda-Aguirre, E.; Castelan-Ortega, O.A.; Shettino-Bermudez, B.S.; Ortiz-Salinas, R.; Miranda, M.; Li, X.; Angeles-Hernandez, J.C.; Vargas-Bello-Pérez, E.; Gonzalez-Ronquillo, M. Worldwide traceability of antibiotic residues from livestock in wastewater and soil: A systematic review. Animals 2022, 12, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, P.; Shukla, P.; Giri, B.S.; Chowdhary, P.; Chandra, R.; Gupta, P.; Pandey, A. Prevalence and hazardous impact of pharmaceutical and personal care products and antibiotics in environment: A review on emerging contaminants. Environ. Res. 2021, 194, 110664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lin, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Meng, F. Antibiotics in mariculture systems: A review of occurrence, environmental behavior, and ecological effects. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 293, 118541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, L.M.; Silva, B.N.M.d.; Barbosa, G.; Barreiro, E.J. β-lactam antibiotics: An overview from a medicinal chemistry perspective. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 208, 112829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bound, J.P.; Voulvoulis, N. Household disposal of pharmaceuticals as a pathway for aquatic contamination in the United Kingdom. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 1705–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiozaki, Y. The action for the antimicobial resistance issue in Japan. J. Jpn. Assoc. Infect. Dis. 2018, 91, 915–923. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, Y. Dissemination of antimicrobial-resistant bacteria based on the one health concept. Jpn. J. Chemother. 2018, 66, 715–728. [Google Scholar]
- Tasho, R.P.; Cho, J.Y. Veterinary antibiotics in animal waste, its distribution in soil and uptake by plants: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 563–564, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verlicchi, P.; Al Aukidy, M.; Jelic, A.; Petrović, M.; Barceló, D. Comparison of measured and predicted concentrations of selected pharmaceuticals in wastewater and surface water: A case study of a catchment area in the Po Valley (Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470–471, 844–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comber, S.; Gardner, M.; Sörme, P.; Ellor, B. The removal of pharmaceuticals during wastewater treatment: Can it be predicted accurately? Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 676, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroda, K.; Li, C.; Dhangar, K.; Kumar, M. Predicted occurrence, ecotoxicological risk and environmentally acquired resistance of antiviral drugs associated with COVID-19 in environmental waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 776, 145740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán, F.J.; Rey, A. Free radical and direct ozone reaction competition to remove priority and pharmaceutical water contaminants with single and hydrogen peroxide ozonation systems. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2018, 40, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharel, S.; Stapf, M.; Miehe, U.; Ekblad, M.; Cimbritz, M.; Falås, P.; Nilsson, J.; Sehlén, R.; Bester, K. Ozone dose dependent formation and removal of ozonation products of pharmaceuticals in pilot and full-scale municipal wastewater treatment plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 731, 139064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangla, D.; Annu; Sharma, A.; Ikram, S. Critical review on adsorptive removal of antibiotics: Present situation, challenges and future perspective. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 425, 127946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natarajan, R.; Saikia, K.; Ponnusamy, S.K.; Rathankumar, A.K.; Rajendran, D.S.; Venkataraman, S.; Tannani, D.B.; Arvind, V.; Somanna, T.; Banerjee, K.; et al. Understanding the factors affecting adsorption of pharmaceuticals on different adsorbents—A critical literature update. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 131958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiviskä, T.; Risteelä, S. Analysis of pharmaceuticals, hormones and bacterial communities in a municipal wastewater treatment plant—Comparison of parallel full-scale membrane bioreactor and activated sludge systems. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292, 118433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengar, A.; Vijayanandan, A. Effects of pharmaceuticals on membrane bioreactor: Review on membrane fouling mechanisms and fouling control strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 808, 152132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Ren, L.; Qi, K.; Li, Q.; Lai, M.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Z. Enhanced removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products from real municipal wastewater using an electrochemical membrane bioreactor. Bioresource Technol. 2020, 311, 123579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, B.; Yang, J.; Zhi, D. Current progress in electrochemical anodic-oxidation of pharmaceuticals: Mechanisms, influencing factors, and new technique. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 418, 126313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Sun, P.; Zhang, L.; Huang, C.H. UV/peracetic acid for degradation of pharmaceuticals and reactive species evaluation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 14217–14224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Liu, Y.; Feng, L.; Zhang, L. Oxidation of pyrazolone pharmaceuticals by peracetic acid: Kinetics, mechanism and genetic toxicity variations. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Cui, H.; Jia, X.; Huang, X. Occurrence and ecotoxicity of sulfonamides in the aquatic environment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 820, 153178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guironnet, A.; Sanchez-Cid, C.; Vogel, T.M.; Wiest, L.; Vulliet, E. Aminoglycosides analysis optimization using ion pairing liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry and application on wastewater samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1651, 462133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.; Ryu, H.D.; Chung, E.G.; Kim, Y.; Lee, J.K. A review of analytical procedures for the simultaneous determination of medically important veterinary antibiotics in environmental water: Sample preparation, liquid chromatography, and mass spectrometry. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 217, 629–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehring, T.; Deineko, E.; Hobus, I.; Kolisch, G.; Lübken, M.; Wichern, M. Effect of sewage sampling frequency on determination of design parameters for municipal wastewater treatment plants. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 84, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristóvão, M.B.; Bento-Silva, A.; Bronze, M.R.; Crespo, J.G.; Pereira, V.J. Detection of anticancer drugs in wastewater effluents: Grab versus passive sampling. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 786, 147477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Antimicrobials | Ionization Mode | Precursor Ion (m/z) | Product Ion (m/z) | Cone Voltage (V) | Collision Energy (eV) | Recovery (% (SD)) | LOD (ng/L) | LOQ (ng/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ampicillin (APL) | ESI+ | 350.2 | 105.9, 192.0 | 29 | 24 | 75 (33) | 1.6 | 5.4 |
| Cefdinir (CDN) | ESI+ | 369.2 | 170.0, 227.0 | 30 | 20 | 72 (15) | 0.2 | 0.8 |
| Cefpodoxime proxetil (CPXP) | ESI+ | 557.5 | 409.8, 525.2 | 30 | 18 | 89 (5) | 1.2 | 3.9 |
| Ciprofloxacin (CFX) | ESI+ | 332.2 | 288.2, 314.2 | 40 | 25 | 57 (3) | 0.7 | 2.2 |
| Clarithromycin (CTM) | ESI+ | 748.2 | 316.6, 558.3 | 38 | 18 | 74 (11) | 0.5 | 1.6 |
| Doxycycline (DCL) | ESI+ | 445.2 | 428.3 | 32 | 18 | 80 (9) | 0.3 | 1.0 |
| Levofloxacin (LFX) | ESI+ | 362.2 | 261.2, 318.2 | 40 | 21 | 52 (6) | 0.3 | 1.0 |
| Minocycline (MCL) | ESI+ | 458.3 | 441.0 | 36 | 21 | 106 (18) | 0.3 | 1.0 |
| Tetracycline (TCL) | ESI+ | 445.2 | 409.9, 427.1 | 28 | 20 | 70 (20) | 0.4 | 1.3 |
| Vancomycin (VMC) | ESI+ | 724.2 | 82.9, 100.2 | 17 | 18 | 110 (8) | 0.6 | 1.9 |
| Antimicrobials | Antimicrobial Usage (Mean (SD)) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sales * [34] (kg/year) | Shipping * [35] (kg/year) | NDB ** [36] (kg/year) | |
| Ampicillin (APL) | 3313 (562) | N.A. | 182 (22) |
| Cefdinir (CDN) | 2810 (181) | 6707 (953) | 410 (101) |
| Cefpodoxime proxetil (CPXP) | 975 (276) | 1588 (588) | 130 (12) |
| Ciprofloxacin (CFX) | N.A. | 1405 (241) | 148 (13) |
| Clarithromycin (CTM) | 11,592 (3970) | 71,850 (15,086) | 5499 (63) |
| Doxycycline (DCL) | N.A. | N.A. | 93 (9) |
| Levofloxacin (LFX) | 1683 (536) | 32,548 (4441) | 2665 (11) |
| Minocycline (MCL) | N.A. | 4157 (905) | 377 (36) |
| Tetracycline (TCL) | N.A. | N.A. | 14 (6) |
| Vancomycin (VMC) | 158 (25) | 2905 (186) | 169 (7) |
| Antimicrobials | Predicted Concentrations in the Targeted STP Influent (ng/L) (Mean (SD)) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sales | Shipping | NDB | |
| Ampicillin (APL) | 99 (17) | N.A. | 78 (10) |
| Cefdinir (CDN) | 37 (2.4) | 87 (12) | 77 (19) |
| Cefpodoxime proxetil (CPXP) | 20 (5.8) | 33 (12) | 39 (3.4) |
| Ciprofloxacin (CFX) | N.A. | 29 (5.1) | 44 (4.2) |
| Clarithromycin (CTM) | 117 (40) | 724 (152) | 790 (0.1) |
| Doxycycline (DCL) | N.A. | N.A. | 48 (4.8) |
| Levofloxacin (LFX) | 59 (19) | 1134 (155) | 1335 (4.9) |
| Minocycline (MCL) | N.A. | 63 (14) | 82 (7.9) |
| Tetracycline (TCL) | N.A. | N.A. | 4.9 (1.8) |
| Vancomycin (VMC) | 5.6 (0.9) | 104 (6.6) | 87 (4.0) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Azuma, T.; Nakano, T.; Koizumi, R.; Matsunaga, N.; Ohmagari, N.; Hayashi, T. Evaluation of the Correspondence between the Concentration of Antimicrobials Entering Sewage Treatment Plant Influent and the Predicted Concentration of Antimicrobials Using Annual Sales, Shipping, and Prescriptions Data. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11040472
Azuma T, Nakano T, Koizumi R, Matsunaga N, Ohmagari N, Hayashi T. Evaluation of the Correspondence between the Concentration of Antimicrobials Entering Sewage Treatment Plant Influent and the Predicted Concentration of Antimicrobials Using Annual Sales, Shipping, and Prescriptions Data. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(4):472. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11040472
Chicago/Turabian StyleAzuma, Takashi, Takashi Nakano, Ryuji Koizumi, Nobuaki Matsunaga, Norio Ohmagari, and Tetsuya Hayashi. 2022. "Evaluation of the Correspondence between the Concentration of Antimicrobials Entering Sewage Treatment Plant Influent and the Predicted Concentration of Antimicrobials Using Annual Sales, Shipping, and Prescriptions Data" Antibiotics 11, no. 4: 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11040472
APA StyleAzuma, T., Nakano, T., Koizumi, R., Matsunaga, N., Ohmagari, N., & Hayashi, T. (2022). Evaluation of the Correspondence between the Concentration of Antimicrobials Entering Sewage Treatment Plant Influent and the Predicted Concentration of Antimicrobials Using Annual Sales, Shipping, and Prescriptions Data. Antibiotics, 11(4), 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11040472






