Abstract
Owls are nocturnal predators that inhabit urbanized and farmlands. They are in direct contact with other animals, both livestock and small wild rodents that they mostly feed on. Staphylococci can be both commensal and pathogenic bacteria that are widespread across the various ecological niches. We aimed to isolate staphylococci from owls and to characterize their antimicrobial resistance, virulence factors and genetic lineages. Swab samples were collected from the throat and cloaca of 114 owls admitted to two rehabilitation centers in Portugal. The identification of staphylococci species was performed by MALDI-TOF. Staphylococci antimicrobial resistance and virulence genes were investigated by means of the disk diffusion method and PCR. Staphylococcus aureus isolates were characterized by MLST, agr and spa-typing. Of the tested animals, 66 isolates were recovered, including 10 different species of staphylococci, of which 25 were coagulase-positive (CoPS) and 41 were coagulase-negative (CoNS). Twenty-three S. aureus were isolated, of which one mecC-MRSA was identified. The isolates were mainly resistant to penicillin, aminoglycosides, clindamycin and tetracycline. mecC-MRSA belonged to ST1245 and spa-type t843 and the remaining S. aureus were ascribed to 12 STs and 15 spa types. A high diversity of clonal lineages was identified among the S. aureus isolated from wild owls. Owls feed mainly on small rodents often exposed to waste and anthropogenic sources, which may explain the moderate prevalence of S. aureus in these animals.
1. Introduction
Staphylococcus spp. are abundant colonizers of the normal microflora of humans and animals []. Despite living in commensalism with the host, staphylococci, in particular, Staphylococcus aureus, can cause a wide spectrum of infections []. The Staphylococcus genus comprises the coagulase-negative staphylococci (CoNS) and coagulase-positive staphylococci (CoPS) []. CoNS have fewer virulence factors than S. aureus and were generally considered contaminants rather than pathogens [,]. Nevertheless, recent studies have shown that CoNS have an increasing clinical impact and can act as opportunistic pathogens, particularly in immunocompromised patients [,,,]. Staphylococci can easily acquire antimicrobial resistance genes, preventing the treatment of some infections []. Over the last few decades, methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) have been a leading cause of nosocomial infections and an emergent zoonotic pathogen []. Methicillin resistance in staphylococci is generally promoted by the mecA or mecC, including several allotypes, genes which encode for a penicillin-binding protein (PBP2a) that has a low affinity for β-lactam antimicrobials [,]. These genes are located on a mobile genetic element called the Staphylococcal chromosome cassette mec (SCCmec). SCCmec elements are highly diverse and are currently classified into 14 types as well as various subtypes []. The mecC gene was first reported over a decade ago and since then it has been detected in staphylococci isolated from several different hots and sources [,,,]. More recently, mecD and plasmid-borne mecB genes have also been identified in S. aureus and Macrococcus caseolyticus, respectively [,]. Staphylococci, both methicillin-resistant and -susceptible, have been found among a taxonomically diverse range of animals including mammals, reptiles, fish, crustaceans and birds [,,,,]. While the prevalence, antimicrobial resistance and clonal lineages of S. aureus and CoNS from livestock and companion animals was subject of intensive research, studies on strains isolated from the environment and wild animals are scarcer [,].
Routes of transmission of antimicrobial-resistant bacteria (ARB) between humans, farm animals, pets and wild animals are not fully understood. Wild birds, with their capacity for long-range movements, can carry ARB over long distances and contribute to the dissemination of those bacteria []. Environmental contamination of wild bird feces may reach surface waters, agricultural fields, livestock and companion animals, and locations with anthropogenic activity, increasing the risk of bacterial transmission [,]. Wild birds can carry a wide range of different multidrug-resistant bacteria, including staphylococci [,,]. Livestock farms and landfills are a potential source of staphylococci detected in these animals. Furthermore, predatory birds can also feed on carcasses and small animals which, in turn, may also by carriers of ARB []. Owls are nocturnal predators that regularly inhabit woodlands and farmlands but also inhabit habitats that are urbanized due to their adaptation to anthropogenic environments [,]. These owls established in the Mediterranean region due to favorable climatic conditions []. In Portugal, the most common owl species are: Barn (Tyto alba), Tawny (Strix aluco) and Little (Athene noctua) []. These particular species are also widely distributed in the central and northern Eurasia subcontinent and north Africa [,,]. Owls feed mainly on small mammals, birds, amphibians and a wide range of invertebrates, including wild mice and harmful insects [,]. Therefore, to better understand the molecular epidemiology of S. aureus and the frequency of colonization and antimicrobial resistance of CoNS in nocturnal predatory birds, we isolated staphylococci from owls admitted to two rehabilitation centers in Portugal and characterized the isolates regarding antimicrobial resistance, virulence factors and genetic lineages.
2. Results
2.1. Frequency and Distribution of Staphylococci in Night Prey
In this study, swab samples were collected from 114 owls. A total of 54 (47.4%) owls carried staphylococci, of which 9 carried more than one Staphylococcus species. Co-carriage of two different species was identified in seven owls, and four species in one animal. From the 43 tawny owls (Strix aluco), 41 barn owls (Tyto alba), 25 little owls (Athene noctua) and 5 Eurasian eagle-owls (Bubo bubo) sampled, 25 (58.1%), 13 (31.7%), 13 (52%) and 3 (60%) were positive for staphylococci, respectively (Table S1). Regarding the isolates, 66 were recovered including 10 different species of staphylococci, of which 25 were coagulase-positive (CoPS) and 41 were coagulase-negative (CoNS). From the 25 CoPS, 23 were identified as S. aureus and the remaining two were Staphylococcus pseudintermedius. CoNS included 22 Staphylococcus sciuri, 11 Staphylococcus lentus, 2 Staphylococcus vitulinus, 2 Staphylococcus haemolyticus, 2 Staphylococcus xylosus, one Staphylococcus saprophyticus and one Staphylococcus succinus. The staphylococci distribution among the four owl species in shown in Table 1. S. epidermidis and S. xylosus were isolated only from Athene noctua and Strix aluco, respectively, while S. aureus and S. sciuri were present in all four owl species.

Table 1.
The distribution of CoNS and CoPS among the four owl species.
2.2. Characterization of CoPS Isolates
All CoPS were characterized regarding the presence of antimicrobial resistance and virulence genes. S. aureus isolates were also typed by MLST, spa- and agr-typing (Table 2). From the 23 S. aureus isolates, only one was resistant to cefoxitin and harbored the mecC gene. The MRSA isolate was also resistant to penicillin and carried the blaZ-SCCmecXI gene. The following genes encoding virulence factors hla, hlb and etd2 were also detected. The mecC-MRSA isolate was ascribed to ST1245, which belonged to the clonal complex (CC) 130, spa-type t843 and agr type III. From the 22-remaining methicillin-susceptible S. aureus (MSSA), 11 (50%) were susceptible to all antibiotics tested. Ten MSSA isolates were resistant to penicillin and six harbored the blaZ gene. The tetK gene was detected in the two isolates showing resistance to tetracycline. Two isolates had phenotypic resistance to macrolides and lincosamides and carried the ermA and mphC genes. Regarding the presence of virulence factors, all isolates carried at least one virulence gene, with the hla gene being present in all isolates and the hlb gene in 15 isolates. Six isolates were positive for the scn gene, which is a marker of the Immune Evasion Cluster (IEC) and were further screened for the presence of the chp, sak, sea and sep genes to determine the IEC group []. Four isolates harbored the scn, sak and chp genes and were ascribed to IEC type B and 2 isolates carried the scn and sak gene and were assigned to type E. MSSA isolates were ascribed to 13 STs and 15 spa types. The isolates were distributed among the four agr types. Finally, S. pseudintermedius isolates (VS2983 and VS2984) were susceptible to all antibiotics tested but one carried the mecA gene.

Table 2.
Genetic characterization and molecular typing of MRSA and MSSA isolates recovered from wild owls.
2.3. Characterization of CoNS Isolates
All CoNS were characterized regarding their phenotypic and genotypic antimicrobial resistance (Table 3). Out of the 22 S. sciuri, 8 were susceptible to all antibiotics tested. Eight isolates carried the mecA gene, which is known to be responsible for methicillin resistance. Resistance to clindamycin and tetracycline was detected in six and two isolates, respectively, conferred by the presence of the mphC and tetK genes. From the 11 S. lentus isolates, 3, 5 and 4 showed resistance to penicillin, clindamycin and tetracycline, respectively. As was also the case with the S. sciuri isolates, the genes detected were mecA, mphC and tetK. The two S. epidermidis isolates were the only ones among the CoNS that carried the blaZ gene. Both isolates had resistance to fusidic acid encoded by the fusB gene and one isolate also showed resistance to erythromycin conferred by the msr(A/B) and mphC genes. Regarding the S. haemolyticus isolates, one was susceptible to all antibiotics while the other showed resistance to erythromycin, clindamycin and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. The S. xylosus isolates carried the mphC, tetM and tetL genes. Finally, the S. saprophyticus and one of the S. vitulinus isolates carried the mecA gene and the S. succinus isolate was susceptible to all antibiotics.

Table 3.
Owl and staphylococci species identification and resistance genes identified.
3. Discussion
This report represents the largest study of staphylococci recovered from healthy wild nocturnal birds of prey. Wild birds as carriers of antimicrobial-resistant pathogens may be considered as a public health problem in the One Health context. Nevertheless, studies on the microflora of birds of prey are scarce and studies on the prevalence of staphylococci in owls are almost inexistent []. Therefore, it is not possible to make a direct comparison of the prevalence of staphylococci obtained in this study with other reports. In our study, we investigated the staphylococci colonization of 114 owls of four different species and obtained a moderate staphylococci prevalence of 47.4%. Other studies conducted with wild birds of prey, some of which included a few owls, obtained similar or higher results [,,]. In a study conducted by Dipineto et al., the pellets of 73 birds of prey, including 13 owls, were screened for the presence of staphylococci. In that study, Staphylococcus spp. was detected in 64 out of 73 samples, of which 26 (35.6%) were S. aureus, but no MRSA was isolated []. In our study, the prevalence of S. aureus was lower (20.2%). Another study conducted in Spain with 324 samples of wild birds reported a total of 27 (8%) CoPS isolates, which included only 2 staphylococci species: 15 S. aureus and 12 S. delphini []. In our study, we also obtained two species of CoPS; however, these were S. aureus and S. pseudintermedius. The rate of carriage of CoNS detected in wild owls in our study (36%) was higher than that detected in a previous study conducted in Portugal in wild hares, which suggests that raptors may be natural reservoirs of CoNS []. Two studies conducted in Portugal investigated the presence of CoNS in wild birds of prey, including Strix aluco and Athene noctua owls, and obtained a prevalence of 37.5% and 75% of CoNS [,]. The species isolated from owls were S. sciuri (n = 3), S. xylosus and S. saprophyticus. In our study, the most frequent species detected was also S. sciuri (22 out of 41 CoNS), and S. xylosus and S. saprophyticus were also isolated.
CoPS were detected in 25 (21.9%) wild owls. All four species of owls carried S. aureus, but a higher incidence of S. aureus (32%) was found in Athene noctua. One MRSA strain was isolated from Athene noctua and carried the mecC gene. Therefore, as far as we know, this is the first study reporting a mecC-postive MRSA isolated from owls. In addition to the mecC gene, this isolate also harbored blaZ-SCCmecXI, which is a blaZ allotype associated with SCCmec XI as previously reported []. In turn, the SCCmec XI is also associated with the mecC gene []. In addition to the hla and hlb virulence genes, the mecC-MRSA isolate also carried the etd2 gene, which is an exfoliative toxin that is a homologue to etd. The presence of etd2 in mecC-MRSA has been reported in human and animal strains of CC130 and may indicate an evolutionary step towards host adaptation [,,]. The MRSA isolate was ST1245, which belongs to CC130 and spa-type t843. In Portugal, the mecC gene has been reported only in two studies, one conducted in wild rodents and another in surface waters, and the clonal lineages detected in those isolates differ from the one identified in this study [,]. mecC-MRSA belonging to ST1245 has been reported in bovine samples in the UK and in a bat in Germany associated with spa-type t843, as well as in horses from France, but, in this case, was associated with a different spa-type [,,]. The mecC isolate lacked the IEC system genes, which is in accordance with most studies reporting mecC-MRSA and suggests a possible animal origin [,,,]. In fact, the presence of the IEC type E in mecC-positive isolates seems to be associated with ST1945 (CC130) since it has only been reported in those isolates [,,]. As expected, the mecC-MRSA isolate was found to belong to agr type III, which is always associated with the mecC gene and CC130 [].
From the 11 MSSA showing resistance to antimicrobials, only two isolates (VS2973 and VS2978) were multidrug-resistant as they were resistant to three and four classes of antibiotics, respectively. Resistance to penicillin was shown in 12 S. sciuri isolates but only 8 carried the mecA gene and the blaZ gene was not detected, which suggests the presence of other unknown resistance mechanisms or that the breakpoints used for this antibiotic are not precise for CoNS. Two MSSA isolates showed resistance to tetracycline mediated by the tetK gene, which encodes efflux proteins []. A high diversity of clonal lineages was found among the owl isolates (Figure 1). Seven MSSA isolates belonged to ST49, which were the most frequent ST in this study. ST49 was found among MSSA from Strix aluco and Athene noctua owls. ST49 was previously reported in voles and mice in Germany, was mostly found to be associated with spa-type t208 and agr II as in our study, and was also identified as a cause of infection in red squirrels [,]. The high frequency of S. aureus ST49 in owls may be explained by the owls’ food habits. For instance, Athene noctua owls feed mainly on wild mice while Strix aluco owls have the ability to hunt for a wide range of prey including rats, mice and synanthropic birds []. Furthermore, ST49-t208 S. aureus isolates have also been detected in the natural environment in Portugal []. One of the ST49 isolates (VS2967) was positive for the scn gene and was ascribed to IEC type E. The IEC genes are usually located in Sa3int phages, also known as β-hemolysin-converting phages []. The presence of these phages is common in S. aureus isolated from humans but is much less frequent in animal isolates []. Therefore, the presence of IEC genes in our isolate may suggest a possible human origin. However, S. aureus ST49 is extremely rare in humans and has been reported once in a human isolated in 1947 []. Three isolates belonged to ST8, spa-type t121 and agr I, and were assigned to IEC type B. S. aureus ST8 is frequently associated with methicillin-resistance in humans and animals [,,,]. Nevertheless, ST8-MSSA has been isolated from wild goose feces in the USA and it seems common in the natural environment in Portugal since it has been isolated from wild rats and superficial water [,,]. Yet, the ST8-MSSA isolates recovered from the natural environment in Portugal had different spa types. The spa-type t121 identified in all ST8 isolates of our study seems to be linked with MRSA-ST8 that is frequently isolated in the African continent, where ST8-MRSA belonging to t121 is the most common clone []. Two isolates from Tyto alba belonged to ST2328, t3750 and agr III. This ST2328-MSSA-t3750/III clone seems common in wild animals from the Iberian peninsula since it was previously isolated from small mammals [] and Iberian ibex [] in Spain, and wild boars in Spain and Portugal [,]. Furthermore, ST2328 belongs to CC133, which is a lineage mostly regarded as animal specific []. Two MSSA isolates belonging to CC121 (ST2766 and ST1956) and agr IV. S. aureus ST2766 and ST1956 (associated with agr IV) have already been detected in owls’ most common prey; namely, in wood mouse and common vole in Spain [], in common vole in Germany and the Czech Republic [] and in field vole from Germany []. The only S. aureus isolated from Bubo bubo (Eurasian eagle-owl) belonged to ST718, which is an uncommon lineage and is often associated with human communities []. S. aureus ST30 was isolated from a little owl. This lineage is primarily associated with humans, but is also spread among animals, including wild boars, red deer and birds of prey [,,]. One strain isolated from Tyto alba owl was ascribed to ST692 (CC692), t1422 and agr I. S. aureus CC692 was previously isolated from wild birds of prey, such as tawny owls (Strix aluco), golden eagles and white-tailed eagles from Sweden, and red kite from Germany []. CC692 seems to be a bird-related lineage since it was previously isolated from poultry and pigeons []. One S. aureus isolate (VS2981), also isolated from a Tyto alba owl, belonged to a lineage first described in this study, ST7184, which is a single locus variant of ST692 with a one-point mutation on the glpF locus. Finally, one isolate was ST1640 agr IV, which has been identified in horses, sheep and red deer [,].
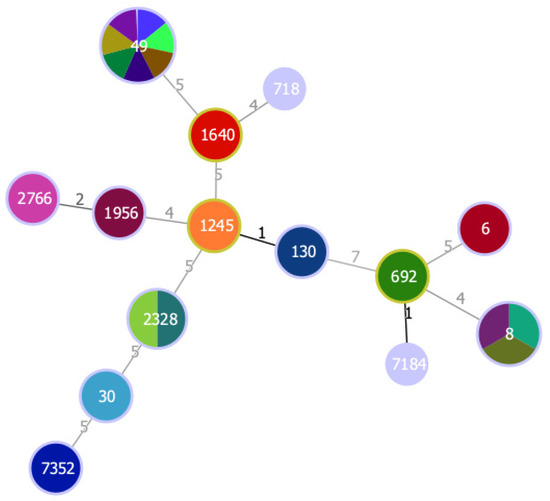
Figure 1.
Minimum spanning tree, based on MLST of 23 S. aureus isolated from wild owls. The minimum spanning tree graph (MST) was created with PHYLOViZ using the goeBURST algorithm []. The dominant STs are represented by the circles with larger diameters. Each color represents one isolate. Numbers on lines indicate locus variants between adjacent nodes.
S. sciuri was the CoNS species most commonly found among owls in this study and it was isolated from all four species of owls investigated. This is not a surprise since this species is the most primitive staphylococci species, has a broad host range and easily adapts to new hosts and environments [,]. Colonization of wild animals by S. sciuri has been reported, including wild birds [,,,]. Additionally, Sousa et al. reported the presence of S. sciuri isolates in Strix aluco and Athene noctua owls, mainly associated with resistance to clindamycin and fusidic acid, which is in accordance with our results []. It was hypothesized that the mecA gene originated from the S. sciuri group species, which includes the S. sciuri, S. lentus and S. vitulinus []. In our study, only three S. sciuri showed phenotypic resistance to cefoxitin but eight isolates were positive for the mecA gene. It was shown that although the mecA gene is present among S. sciuri strains, they may present susceptibility to β-lactams []. In fact, the two S. vitulinus isolated in this study carried the mecA gene. S. lentus was the second CoNS most common species among owls and it was mostly detected in Strix aluco. As with the other members of the S. sciuri group, only one S. lentus isolate was resistant to cefoxitin, but four isolates carried the mecA gene. S. lentus colonizes the skin and mucous membranes of several animal species. Nevertheless, it is typically associated with livestock and their food products []. Although owls regularly inhabit urbanized areas, many inhabit wood and farmlands where they may come into close contact with wild animals and livestock and be colonized by staphylococcus species such as S. lentus []. Two S. epidermidis were isolated in this study, both carrying antimicrobial resistance genes. Interestingly, S. epidermidis isolates were only recovered from Bubo bubo owls, which are considered the largest nocturnal raptor in Europe (Table S1) []. Unlike some owl species, such as Athene noctua, which only feed on small animals and insects, Bubo bubo feed on a larger variety of animals, including medium prey, for example, hedgehogs, rabbits, partridges and pigeons []. In contrast to the other CoNS species, S. epidermidis harbored the blaZ gene. Both isolates also presented the fusB gene, which confers resistance to fusidic acid and is carried on plasmids or a genomic island on the chromosome []. Two S. haemolyticus were isolated, with one of them being susceptible to all antibiotics. The other S. haemolyticus was also isolated from a Bubo bubo. This isolate had a multidrug-resistant profile and carried the mphC, msr(A/B) and tetO genes. S. haemolyticus has been isolated from wild birds in Brazil [] and in wild pheasant meat in the Slovak Republic []. One isolate of S. saprophyticus also harbored the mecA gene but was susceptible to all antibiotics tested. S. saprophyticus was isolated in one owl in Portugal but it was associated with a multidrug-resistance phenotype []. Both S. epidermidis and S. haemolyticus, followed by S. saprophyticus, are the most significant species of CoNS in human infections and the fact that they are widespread among wildlife carrying multiple resistances may lead to increased public health problems [].
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Samples and Bacterial Isolates
From 2018 to 2021, 114 samples were collected from owls admitted to the Wildlife Study and Rehabilitation Centre (CERAS) located in Castelo Branco (central Portugal) and the Wildlife Rehabilitation Centre of Parque Biológico de Gaia (North of Portugal). Swab samples were collected from the throat and cloaca of each animal and were then placed in Stuart’s transport medium and sent to the Medical Microbiology laboratory at the University of Trás-os-Montes and Alto Douro. The swabs were placed in tubes containing Brain Heart Infusion (BHI) broth with 6.5% NaCl and incubated at 37 °C for 24 h. Then, the inoculum was seeded onto Mannitol Salt agar and CHROMagarTM MRSA agar plates and incubated at 37 °C for 24 to 48 h. Up to 4 colonies per plate, showing different colony morphologies, were selected. Isolates’ species were identified by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of flight (MALDI-TOF).
4.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility
Antimicrobial susceptibility was tested using the disk-diffusion method against the following antimicrobial agents (in µg/disk): penicillin G (1U), cefoxitin (30), chloramphenicol (30), ciprofloxacin (5), clindamycin (2), erythromycin (15), fusidic acid (10), gentamicin (10), kanamycin (30), linezolid (10), mupirocin (200), tetracycline (30), tobramycin (10) and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (1.25/23.75). The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) 2019 guidelines were followed, except for testing with kanamycin, which followed the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) 2017 standards [,]. The reference strain S. aureus ATCC25923 was used as a quality control strain.
4.3. Detection of Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Genes
All isolates were screened for antimicrobial resistance and virulence determinants by PCR amplification using previously described primers []. Isolates were screened for the presence of determinants conferring resistance to: beta-lactams (blaZ, blaZ-SCCmecXI, mecA and mecC), macrolides and lincosamides (ermA, ermB, ermC, ermT, msr(A/B), lnuA, lnuB, vgaA, vgaB, vgaC), tetracycline (tetM, tetK, tetL and tetO), aminoglycosides (aac(6′)-Ie-aph(2′’)-Ia, ant(4′)-Ia and aph(3′)-IIIa), phenicols (catpC194, catpC221, catpC223, fexA, and fexB), oxazolidinones (cfr), trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (dfrA, dfrG, dfrK and dfrD) and fusidic acid (fusB, fusC and fusD). The virulence genes tested encoded for hemolysins (hla, hlb and hld), Panton-Valentine leuocidin (PVL) (lukF/lukS-PV), exfoliatins (eta, etb and etd2) and toxic shock syndrome toxin (tst) []. Additionally, the presence of the scn gene, which is a marker of the Immune Evasion Cluster (IEC), was also investigated by PCR. Isolates that were positive for scn were further screened for the presence of the chp, sak, sea and sep genes to determine the IEC group []. Positive and negative controls used in all experiments belonged to the strain collection of the University of Trás-os-Montes and Alto Douro.
4.4. Molecular Typing
All S. aureus isolates were typed by multilocus sequence typing (MLST), spa- and agr-typing. MLST was performed as described by Enright et al. []. Alleles and sequence types (STs) were assigned by submitting the DNA sequences to the MLST database (https://pubmlst.org/organisms/staphylococcus-aureus, accessed on 10 December 2021). spa-typing was performed via the amplification of the polymorphic region of the Staphylococcus protein A gene according to the previously described protocol and the obtained sequences were analyzed using the Ridom StaphType software (version 1.5, Ridom GmbH, Würzburg, Germany) []. S. aureus isolates were characterized by agr-typing using PCR for amplification of the agr genes (I-IV) using specific primers and conditions [].
5. Conclusions
In this study, a moderate prevalence of staphylococci was isolated from owls admitted to a recovery center in Portugal. Nocturnal birds of prey may represent a reservoir of both CoNS and S. aureus presenting antimicrobial resistance determinants. A high diversity of S. aureus clonal lineages was identified, including one CC130 mecC-MRSA. Owls feed mostly on small mammals and insects, thus posing as vectors for transmission of pathogens. This may be the source of the staphylococci found among owls and the cause of the high diversity of staphylococci species and clonal lineages. Owls are in direct contact with many species of wild rodents, thus posing as vectors for the transmission of pathogens. Furthermore, antimicrobial resistance in wildlife may be a considerable hazard to human and animal health due to transmission through waterways and other environmental sources.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/antibiotics11020240/s1, Table S1: Owl species, date of sample collection and distribution of the 66 staphylococci among owl samples.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.S. (Vanessa Silva) and P.P.; methodology, V.S. (Vanessa Silva); software, V.S. (Vanessa Silva); validation, M.C. and P.P.; investigation, V.S. (Vanessa Silva) and V.M.; resources, A.F.L. and V.S. (Vanessa Soeiro); data curation, V.S. (Vanessa Silva); writing—original draft preparation, V.S. (Vanessa Silva); writing—review and editing, V.S. (Vanessa Silva) and P.P.; visualization, J.E.P. and L.M.; supervision, G.I., J.L.C. and P.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the R&D Project CAREBIO2: Comparative assessment of antimicrobial resistance in environmental biofilms through proteomics—towards innovative theranostic biomarkers, with reference NORTE-01-0145-FEDER-030101 and PTDC/SAU-INF/30101/2017, financed by the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) through the Northern Regional Operational Program (NORTE 2020) and the Foundation for Science and Technology (FCT). This work was supported by the Associate Laboratory for Green Chemistry-LAQV, which is financed by national funds from FCT/MCTES (UIDB/50006/2020 and UIDP/50006/2020) and by the UIDB/CVT/00772/2020 project funded by the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology (FCT). Vanessa Silva is grateful to FCT (Fundacão para a Ciência e a Tecnologia) for financial support through the PhD grant SFRH/BD/137947/2018.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the Helsinki Declaration (ICH-GCP principles), was in compliance with Schedule Y/ICMR Guidelines and the Oviedo Convention, and was approved by the Ethics Committee of the University of Trás-os-Montes e Alto Douro (EC-UTAD, 8 November 2019).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- França, A.; Gaio, V.; Lopes, N.; Melo, L.D.R. Virulence Factors in Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci. Pathogens 2021, 10, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, D.; Goncheva, M.I.; Flannagan, R.S.; Deecker, S.R.; Guariglia-Oropeza, V.; Ensminger, A.W.; Heinrichs, D.E. Coagulase-negative staphylococci release a purine analog that inhibits Staphylococcus aureus virulence. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natsis, N.E.; Cohen, P.R. Coagulase-negative staphylococcus skin and soft tissue infections. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2018, 19, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, K.; Both, A.; Weißelberg, S.; Heilmann, C.; Rohde, H. Emergence of coagulase-negative staphylococci. Expert Rev. Anti. Infect. Ther. 2020, 18, 349–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dao, T.H.; Alsallaq, R.; Parsons, J.B.; Ferrolino, J.; Hayden, R.T.; Rubnitz, J.E.; Rafiqullah, I.M.; Robinson, D.A.; Margolis, E.B.; Rosch, J.W. Vancomycin heteroresistance and clinical outcomes in bloodstream infections caused by coagulase-negative staphylococci. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e00944-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medis, L.S.D.; Dissanayake, D.; Kottahachchi, J.; Weerasekera, M.M.; Namali, D. Detection of biofilm forming ability of coagulase negative Staphylococcus isolated from patients with central venous catheter infections and catheter colonization at a tertiary care hospital in Colombo. In Proceedings of the Research Conference in Health Sciences 2021, Nugegoda, Sri Lanka, 31 March 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Algammal, A.M.; Hetta, H.F.; Elkelish, A.; Alkhalifah, D.H.H.; Hozzein, W.N.; Batiha, G.E.-S.; El Nahhas, N.; Mabrok, M.A. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA): One Health Perspective Approach to the Bacterium Epidemiology, Virulence Factors, Antibiotic-Resistance, and Zoonotic Impact. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 3255–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carretto, E.; Visiello, R.; Nardini, P. Chapter 17—Methicillin Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. In Pet-to-Man Travelling Staphylococci; Savini, V., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 225–235. ISBN 978-0-12-813547-1. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, K.; van Alen, S.; Idelevich, E.A.; Schleimer, N.; Seggewiß, J.; Mellmann, A.; Kaspar, U.; Peters, G. Plasmid-Encoded Transferable mecB-Mediated Methicillin Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urushibara, N.; Aung, M.S.; Kawaguchiya, M.; Kobayashi, N. Novel staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec) type XIV (5A) and a truncated SCCmec element in SCC composite islands carrying speG in ST5 MRSA in Japan. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.; Capelo, J.L.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P. Molecular Epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus Lineages in Wild Animals in Europe: A Review. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Porrero, M.C.; Valverde, A.; Fernández-Llario, P.; Díez-Guerrier, A.; Mateos, A.; Lavín, S.; Cantón, R.; Fernández-Garayzabal, J.-F.; Domínguez, L. Staphylococcus aureus carrying mecC gene in animals and urban wastewater, Spain. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 899–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, V.; Ferreira, E.; Manageiro, V.; Reis, L.; Tejedor-Junco, M.T.; Sampaio, A.; Capelo, J.L.; Caniça, M.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P. Distribution and Clonal Diversity of Staphylococcus aureus and Other Staphylococci in Surface Waters: Detection of ST425-t742 and ST130-t843 mecC-Positive MRSA Strains. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhaouadi, S.; Soufi, L.; Campanile, F.; Dhaouadi, F.; Sociale, M.; Lazzaro, L.; Cherif, A.; Stefani, S.; Elandoulsi, R.B. Prevalence of meticillin-resistant and -susceptible coagulase-negative staphylococci with the first detection of the mecC gene among cows, humans and manure in Tunisia. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 55, 105826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwendener, S.; Cotting, K.; Perreten, V. Novel methicillin resistance gene mecD in clinical Macrococcus caseolyticus strains from bovine and canine sources. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Úngari, L.P.; Santos, A.L.Q.; Paiva, G.C.M.; Mota, K.C.P.; de Almeida Borges, L.F.; Cury, M.C. Concomitant infection of Haemogregarina sp. and Staphylococcus aureus in free-living yellow-spotted river turtle (Podocnemis unifilis): Case report. Arch. Vet. Sci. 2018, 23, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fri, J.; Njom, H.A.; Ateba, C.N.; Ndip, R.N. Antibiotic resistance and virulence gene characteristics of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolated from healthy Edible Marine Fish. Int. J. Microbiol. 2020, 2020, 9803903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukułowicz, A.; Steinka, I.; Siwek, A. Presence of Antibiotic-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Fish and Seafood Originating from Points of Sale in the Tri-City Area (Poland). J. Food Prot. 2021, 84, 1911–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, M.; Silva, N.; Igrejas, G.; Silva, F.; Sargo, R.; Alegria, N.; Benito, D.; Gómez, P.; Lozano, C.; Gómez-Sanz, E.; et al. Antimicrobial resistance determinants in Staphylococcus spp. recovered from birds of prey in Portugal. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 171, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.; Gabriel, S.I.; Borrego, S.B.; Tejedor-Junco, M.T.; Manageiro, V.; Ferreira, E.; Reis, L.; Caniça, M.; Capelo, J.L.; Igrejas, G.; et al. Antimicrobial Resistance and Genetic Lineages of Staphylococcus aureus from Wild Rodents: First Report of mecC-Positive Methicillin-Resistant S. aureus (MRSA) in Portugal. Animals 2021, 11, 1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seinige, D.; Von Altrock, A.; Kehrenberg, C. Genetic diversity and antibiotic susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from wild boars. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 54, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza-Rodríguez, C.; Alt, K.; Grobbel, M.; Hammerl, J.A.; Irrgang, A.; Szabo, I.; Stingl, K.; Schuh, E.; Wiehle, L.; Pfefferkorn, B.; et al. Wildlife as Sentinels of Antimicrobial Resistance in Germany? Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 7, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mencía-Gutiérrez, A.; Martín-Maldonado, B.; Pastor-Tiburón, N.; Moraleda, V.; González, F.; García-Peña, F.J.; Pérez-Cobo, I.; Revuelta, L.; Marín, M. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter from wild birds of prey in Spain. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 79, 101712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Ma, Z.-B.; Zeng, Z.-L.; Yang, X.-W.; Huang, Y.; Liu, J.-H. The role of wildlife (wild birds) in the global transmission of antimicrobial resistance genes. Zool. Res. 2017, 38, 55–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruiz-Ripa, L.; Gómez, P.; Alonso, C.A.; Camacho, M.C.; Ramiro, Y.; de la Puente, J.; Fernández-Fernández, R.; Quevedo, M.Á.; Blanco, J.M.; Báguena, G.; et al. Frequency and Characterization of Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Genes of Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci from Wild Birds in Spain. Detection of tst-Carrying S. sciuri Isolates. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Mesquita Souza Saraiva, M.; de Leon, C.M.C.G.; da Silva, N.M.V.; Raso, T.F.; Serafini, P.P.; Givisiez, P.E.N.; Gebreyes, W.A.; de Oliveira, C.J.B. Staphylococcus sciuri as a Reservoir of mecA to Staphylococcus aureus in Non-Migratory Seabirds from a Remote Oceanic Island. Microb. Drug Resist. 2020, 27, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambino, D.; Vicari, D.; Vitale, M.; Schirò, G.; Mira, F.; Giglia, M.L.; Riccardi, A.; Gentile, A.; Giardina, S.; Carrozzo, A.; et al. Study on Bacteria Isolates and Antimicrobial Resistance in Wildlife in Sicily, Southern Italy. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peri, A. Censusing a tawny owl (Strix aluco) population living at high density merging two consolidated techniques. Écoscience 2018, 25, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröhlich, A.; Ciach, M. Noise pollution and decreased size of wooded areas reduces the probability of occurrence of Tawny Owl Strix aluco. Ibis (Lond. 1859) 2018, 160, 634–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, R.; Roque, I.; Tomé, R. Relatório do Programa NOCTUA Portugal (2009/10–2019/20); Sociedade Portuguesa para o Estudo das Aves: Lisbon, Portugal, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.-H.; Liu, H.-Y.; Min, X.; Lu, C.-H. Mitogenome of the little owl Athene noctua and phylogenetic analysis of Strigidae. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 151, 924–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, W.; Lee, J.-H.; Sung, H.-C. A case study of male tawny owl (Strix aluco) vocalizations in South Korea: Call feature, individuality, and the potential use for census. Anim. Cells Syst. (Seoul) 2019, 23, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Machado, A.P.; Clément, L.; Uva, V.; Goudet, J.; Roulin, A. The Rocky Mountains as a dispersal barrier between barn owl (Tyto alba) populations in North America. J. Biogeogr. 2018, 45, 1288–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moysi, M.; Christou, M.; Goutner, V.; Kassinis, N.; Iezekiel, S. Spatial and temporal patterns in the diet of barn owl (Tyto alba) in Cyprus. J. Biol. Res. 2018, 25, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Wamel, W.J.B.; Rooijakkers, S.H.M.; Ruyken, M.; van Kessel, K.P.M.; van Strijp, J.A.G. The innate immune modulators staphylococcal complement inhibitor and chemotaxis inhibitory protein of Staphylococcus aureus are located on beta-hemolysin-converting bacteriophages. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 1310–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vidal, A.; Baldomà, L.; Molina-López, R.A.; Martin, M.; Darwich, L. Microbiological diagnosis and antimicrobial sensitivity profiles in diseased free-living raptors. Avian Pathol. 2017, 46, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sousa, M.; Silva, N.; Igrejas, G.; Sargo, R.; Benito, D.; Gómez, P.; Lozano, C.; Manageiro, V.; Torres, C.; Caniça, M.; et al. Genetic Diversity and Antibiotic Resistance Among Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Recovered from Birds of Prey in Portugal. Microb. Drug Resist. 2016, 22, 727–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dipineto, L.; Bossa, L.M.D.L.; Pace, A.; Russo, T.P.; Gargiulo, A.; Ciccarelli, F.; Raia, P.; Caputo, V.; Fioretti, A. Microbiological survey of birds of prey pellets. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 41, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Ripa, L.; Gómez, P.; Alonso, C.A.; Camacho, M.C.; de la Puente, J.; Fernández-Fernández, R.; Ramiro, Y.; Quevedo, M.A.; Blanco, J.M.; Zarazaga, M.; et al. Detection of MRSA of Lineages CC130-mecC and CC398-mecA and Staphylococcus delphini-lnu(A) in Magpies and Cinereous Vultures in Spain. Microb. Ecol. 2019, 78, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.; Pereira, J.E.; Maltez, L.; Ferreira, E.; Manageiro, V.; Caniça, M.; Capelo, J.L.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P. Diversity of methicillin-resistant staphylococci among wild Lepus granatensis: First detection of mecA-MRSA in hares. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2019, 96, fiz204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFadyen, A.C.; Harrison, E.M.; Ellington, M.J.; Parkhill, J.; Holmes, M.A.; Paterson, G.K. A highly conserved mecC-encoding SCCmec type XI in a bovine isolate of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus xylosus. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 3516–3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Gongora, C.; Harrison, E.M.; Moodley, A.; Guardabassi, L.; Holmes, M.A. MRSA carrying mecC in captive mara. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 70, 1622–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monecke, S.; Gavier-Widen, D.; Mattsson, R.; Rangstrup-Christensen, L.; Lazaris, A.; Coleman, D.C.; Shore, A.C.; Ehricht, R. Detection of mecC-Positive Staphylococcus aureus (CC130-MRSA-XI) in Diseased European Hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) in Sweden. PLoS One 2013, 8, e66166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shore, A.C.; Deasy, E.C.; Slickers, P.; Brennan, G.; O’Connell, B.; Monecke, S.; Ehricht, R.; Coleman, D.C. Detection of staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec type XI carrying highly divergent mecA, mecI, mecR1, blaZ, and ccr genes in human clinical isolates of clonal complex 130 methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 3765–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haenni, M.; Châtre, P.; Dupieux, C.; Métayer, V.; Maillard, K.; Bes, M.; Madec, J.-Y.; Laurent, F. mecC-positive MRSA in horses. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 70, 3401–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- García-Álvarez, L.; Holden, M.T.G.; Lindsay, H.; Webb, C.R.; Brown, D.F.J.; Curran, M.D.; Walpole, E.; Brooks, K.; Pickard, D.J.; Teale, C.; et al. Meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus with a novel mecA homologue in human and bovine populations in the UK and Denmark: A descriptive study. Lancet. Infect. Dis. 2011, 11, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feßler, A.T.; Thomas, P.; Mühldorfer, K.; Grobbel, M.; Brombach, J.; Eichhorn, I.; Monecke, S.; Ehricht, R.; Schwarz, S. Phenotypic and genotypic characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from zoo and wild animals. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 218, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacinti, G.; Carfora, V.; Caprioli, A.; Sagrafoli, D.; Marri, N.; Giangolini, G.; Amoruso, R.; Iurescia, M.; Stravino, F.; Dottarelli, S.; et al. Prevalence and characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus carrying mecA or mecC and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus in dairy sheep farms in central Italy. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 7857–7863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gómez, P.; Lozano, C.; Camacho, M.C.; Lima-Barbero, J.-F.; Hernández, J.-M.; Zarazaga, M.; Höfle, Ú.; Torres, C. Detection of MRSA ST3061-t843-mecC and ST398-t011-mecA in white stork nestlings exposed to human residues. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 71, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gómez, P.; González-Barrio, D.; Benito, D.; García, J.T.; Viñuela, J.; Zarazaga, M.; Ruiz-Fons, F.; Torres, C. Detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) carrying the mecC gene in wild small mammals in Spain. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 2061–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gómez, P.; Lozano, C.; González-Barrio, D.; Zarazaga, M.; Ruiz-Fons, F.; Torres, C. High prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) carrying the mecC gene in a semi-extensive red deer (Cervus elaphus hispanicus) farm in Southern Spain. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 177, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, C.; Stamm, I.; Ziebuhr, W.; Marincola, G.; Bischoff, M.; Strommenger, B.; Jaschkowitz, G.; Marciniak, T.; Cuny, C.; Witte, W.; et al. Silence as a way of niche adaptation: mecC-MRSA with variations in the accessory gene regulator (agr) functionality express kaleidoscopic phenotypes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehra, A.; Singh, R.; Kaur, S.; Gill, J.P.S. Molecular characterization of antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from livestock (bovine and swine). Vet. world 2017, 10, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrochen, D.M.; Schulz, D.; Fischer, S.; Jeske, K.; El Gohary, H.; Reil, D.; Imholt, C.; Trübe, P.; Suchomel, J.; Tricaud, E.; et al. Wild rodents and shrews are natural hosts of Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 308, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, V.; Davison, N.; Hudson, L.; Enright, M.; Whatmore, A.M. Staphylococcus aureus ST49 infection in red squirrels. Vet. Rec. 2010, 167, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gryz, J.; Krauze-Gryz, D. Changes in the tawny owl Strix aluco diet along an urbanisation gradient. Biologia (Bratisl) 2019, 74, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rohmer, C.; Wolz, C. The Role of hlb-Converting Bacteriophages in Staphylococcus aureus Host Adaption. Microb. Physiol. 2021, 31, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, P.; Abdelbary, M.M.H.; Kraushaar, B.; Fetsch, A.; Geisel, J.; Herrmann, M.; Witte, W.; Cuny, C.; Bischoff, M. Impact of bacteriophage Saint3 carriage on the immune evasion capacity and hemolytic potential of Staphylococcus aureus CC398. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 200, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, R.; Hossain, M.J.; Liles, M.R.; Panizzi, P. Complete genome sequence of Staphylococcus aureus Tager 104, a sequence type 49 ancestor. Genome Announc. 2013, 1, e00706-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nowakiewicz, A.; Ziółkowska, G.; Zięba, P.; Gnat, S.; Wojtanowicz-Markiewicz, K.; Trościańczyk, A. Coagulase-positive Staphylococcus isolated from wildlife: Identification, molecular characterization and evaluation of resistance profiles with focus on a methicillin-resistant strain. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 44, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strauß, L.; Stegger, M.; Akpaka, P.E.; Alabi, A.; Breurec, S.; Coombs, G.; Egyir, B.; Larsen, A.R.; Laurent, F.; Monecke, S.; et al. Origin, evolution, and global transmission of community-acquired Staphylococcus aureus ST8. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E10596–E10604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bernier-Lachance, J.; Arsenault, J.; Usongo, V.; Parent, É.; Labrie, J.; Jacques, M.; Malouin, F.; Archambault, M. Prevalence and characteristics of Livestock-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (LA-MRSA) isolated from chicken meat in the province of Quebec, Canada. PLoS One 2020, 15, e0227183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.; Monteiro, A.; Porto, M.; Sampaio, A.; Maltez, L.; Pereira, J.E.; Aonofriesei, F.; Capelo, J.L.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P. Molecular Diversity of Methicillin-Resistant and -Susceptible Staphylococcus aureus Detected in Animals: A Focus on Aquatic Animals. Diversity 2021, 13, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapaliya, D.; Dalman, M.; Kadariya, J.; Little, K.; Mansell, V.; Taha, M.Y.; Grenier, D.; Smith, T.C. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus in Goose Feces from State Parks in Northeast Ohio. Ecohealth 2017, 14, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porrero, M.C.; Mentaberre, G.; Sánchez, S.; Fernández-Llario, P.; Casas-Díaz, E.; Mateos, A.; Vidal, D.; Lavín, S.; Fernández-Garayzábal, J.-F.; Domínguez, L. Carriage of Staphylococcus aureus by Free-Living Wild Animals in Spain. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 4865–4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sousa, M.; Silva, N.; Manageiro, V.; Ramos, S.; Coelho, A.; Gonçalves, D.; Caniça, M.; Torres, C.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P. First report on MRSA CC398 recovered from wild boars in the north of Portugal. Are we facing a problem? Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 596–597, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, H.; Dorothee, G.; Veronika, B.; Annette, B.; Julia, K.; André, G.; Stefan, W.; Birte, H.; Bauerfeind, S.S.; Paula, D.; et al. Molecular Epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus in the General Population in Northeast Germany: Results of the Study of Health in Pomerania (SHIP-TREND-0). J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 2774–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monecke, S.; Gavier-Widén, D.; Hotzel, H.; Peters, M.; Guenther, S.; Lazaris, A.; Loncaric, I.; Müller, E.; Reissig, A.; Ruppelt-Lorz, A.; et al. Diversity of Staphylococcus aureus Isolates in European Wildlife. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0168433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mama, O.M.; Gómez, P.; Ruiz-Ripa, L.; Gómez-Sanz, E.; Zarazaga, M.; Torres, C. Antimicrobial Resistance, Virulence, and Genetic Lineages of Staphylococci from Horses Destined for Human Consumption: High Detection of S. aureus Isolates of Lineage ST1640 and Those Carrying the lukPQ Gene. Animals 2019, 9, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fountain, K.; Blackett, T.; Butler, H.; Carchedi, C.; Schilling, A.-K.; Meredith, A.; Gibbon, M.J.; Lloyd, D.H.; Loeffler, A.; Feil, E.J. Fatal exudative dermatitis in island populations of red squirrels (Sciurus vulgaris): Spillover of a virulent Staphylococcus aureus clone (ST49) from reservoir hosts. Microb. Genom. 2021, 7, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, A.P.; Vaz, C.; Monteiro, P.T.; Melo-Cristino, J.; Ramirez, M.; Carriço, J.A. PHYLOViZ: Phylogenetic inference and data visualization for sequence based typing methods. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loncaric, I.; Kübber-Heiss, A.; Posautz, A.; Ruppitsch, W.; Lepuschitz, S.; Schauer, B.; Feßler, A.T.; Krametter-Frötscher, R.; Harrison, E.M.; Holmes, M.A.; et al. Characterization of mecC gene-carrying coagulase-negative Staphylococcus spp. isolated from various animals. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 230, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsubakishita, S.; Kuwahara-Arai, K.; Sasaki, T.; Hiramatsu, K. Origin and molecular evolution of the determinant of methicillin resistance in staphylococci. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 4352–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Becker, K.; Heilmann, C.; Peters, G. Coagulase-negative staphylococci. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 870–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sybille, S.; Vincent, P. New MLSB Resistance Gene erm(43) in Staphylococcus lentus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 4746–4752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edslev, S.M.; Clausen, M.-L.; Agner, T.; Stegger, M.; Andersen, P.S. Genomic analysis reveals different mechanisms of fusidic acid resistance in Staphylococcus aureus from Danish atopic dermatitis patients. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 856–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matias, C.A.R.; Pereira, I.A.; Rodrigues, D.P.; Siciliano, S. Staphylococcus spp. isolated from wild birds apprehended in the local illegal trade in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, and relevance in public health. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regecová, I.; Pipová, M.; Jevinová, P.; Kmet’, V.; Výrostková, J.; Sopková, D. Antimicrobial Resistance of Coagulase-negative Species of Staphylococci Isolated from the Meat of Wild Pheasants (Phasianus Colchicus). Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 13, 3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUCAST European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST). Breakpoint tables for interpretation of MICs and Zone diameters Version 8.0; EUCAST European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST): Växjö, Sweden, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- CLSI Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, V.; Vieira-Pinto, M.; Saraiva, C.; Manageiro, V.; Reis, L.; Ferreira, E.; Caniça, M.; Capelo, J.L.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P. Prevalence and Characteristics of Multidrug-Resistant Livestock-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (LA-MRSA) CC398 Isolated from Quails (Coturnix Coturnix Japonica) Slaughtered for Human Consumption. Animals 2021, 11, 2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enright, M.C.; Day, N.P.; Davies, C.E.; Peacock, S.J.; Spratt, B.G. Multilocus sequence typing for characterization of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible clones of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harmsen, D.; Claus, H.H.H.H.; Witte, W.; Rothgänger, J.; Claus, H.H.H.H.; Turnwald, D.; Vogel, U. Typing of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a University Hospital Setting by Using Novel Software for spa Repeat Determination and Database Management. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 5442–5448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shopsin, B.; Gomez, M.; Montgomery, S.O.; Smith, D.H.; Waddington, M.; Dodge, D.E.; Bost, D.A.; Riehman, M.; Naidich, S.; Kreiswirth, B.N. Evaluation of protein A gene polymorphic region DNA sequencing for typing of Staphylococcus aureus strains. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 3556–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).