Genomic Analysis of ESBL-Producing E. coli in Wildlife from North-Eastern Germany
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Bacterial Isolation
2.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (AST)
2.3. Whole-Genome Sequencing and Analysis
2.4. Metagenomic Sequencing and Analysis of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes
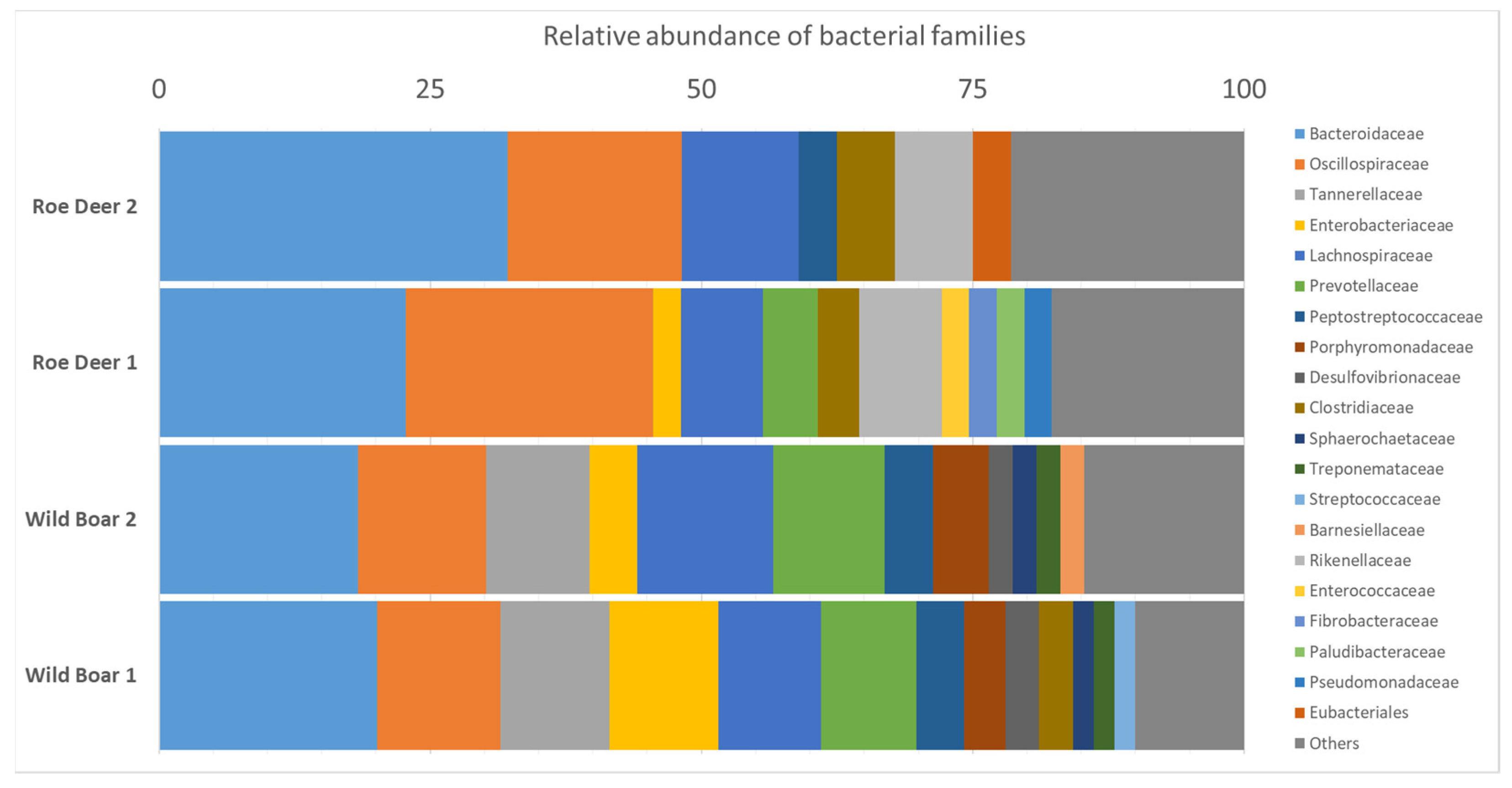
2.5. Microbiome Analysis for Bacterial Species Diversity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sampling Areas
4.2. Bacterial Isolation
4.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (AST)
4.4. Whole-genome Sequencing (WGS) and Analysis
4.5. Metagenomic Sequencing and Analysis of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes
4.6. Microbiome Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Antimicrobial Resistance Global Report on Surveillance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Verburg, I.; Garcia-Cobos, S.; Hernandez Leal, L.; Waar, K.; Friedrich, A.W.; Schmitt, H. Abundance and Antimicrobial Resistance of Three Bacterial Species Along a Complete Wastewater Pathway. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Homeier-Bachmann, T.; Heiden, S.E.; Lubcke, P.K.; Bachmann, L.; Bohnert, J.A.; Zimmermann, D.; Schaufler, K. Antibiotic-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae in Wastewater of Abattoirs. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Costa, V.M.; King, C.E.; Kalan, L.; Morar, M.; Sung, W.W.L.; Schwarz, C.; Froese, D.; Zazula, G.; Calmels, F.; Debruyne, R.; et al. Antibiotic Resistance Is Ancient. Nature 2011, 477, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, C.; Yacoob, Z.; Knobloch, M.J.; Safdar, N. Community Pharmacy Interventions to Improve Antibiotic Stewardship and Implications for Pharmacy Education: A Narrative Overview. Res. Soc. Adm. Pharm. 2019, 15, 627–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, R.T.; Fernandes, J.; Carvalho, J.; Cunha, M.V.; Caetano, T.; Mendo, S.; Serrano, E.; Fonseca, C. Wild Boar as a Reservoir of Antimicrobial Resistance. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 135001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMA-ESVAC. Sales of Veterinary Antimicrobial Agents in 31 European Countries in 2018; European Medicines Agency (EMA): Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/report/sales-veterinary-antimicrobial-agents-31-european-countries-2018-trends-2010-2018-tenth-esvac-report_en.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Binsker, U.; Käsbohrer, A.; Hammerl, J.A. Global Colistin Use: A Review of the Emergence of Resistant Enterobacterales and the Impact on Their Genetic Basis. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2021, fuab049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolhouse, M.; Ward, M.; van Bunnik, B.; Farrar, J. Antimicrobial Resistance in Humans, Livestock and the Wider Environment. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 370, 20140083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacconelli, E.; Carrara, E.; Savoldi, A.; Harbarth, S.; Mendelson, M.; Monnet, D.L.; Pulcini, C.; Kahlmeter, G.; Kluytmans, J.; Carmeli, Y.; et al. Discovery, Research, and Development of New Antibiotics: The Who Priority List of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria and Tuberculosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knothe, H.; Shah, P.; Krcmery, V.; Antal, M.; Mitsuhashi, S. Transferable Resistance to Cefotaxime, Cefoxitin, Cefamandole and Cefuroxime in Clinical Isolates of Klebsiella Pneumoniae and Serratia Marcescens. Infection 1983, 11, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, K.; Bradford, P.A. Epidemiology of Β-Lactamase-Producing Pathogens. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33, e00047-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huebner, N.O.; Dittmann, K.; Henck, V.; Wegner, C.; Kramer, A. Epidemiology of Multidrug Resistant Bacterial Organisms and Clostridium Difficile in German Hospitals in 2014: Results from a Nationwide One-Day Point Prevalence of 329 German Hospitals. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blaak, H.; van Hoek, A.H.A.M.; Hamidjaja, R.A.; van der Plaats, R.Q.J.; Kerkhof-de Heer, L.; Husman, A.M.D.; Schets, F.M. Distribution, Numbers, Diversity of Esbl-Producing E. Coli in the Poultry Farm Environment. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135402. [Google Scholar]
- Ghodousi, A.; Bonura, C.; Di Noto, A.M.; Mammina, C. Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase, Ampc-Producing, Fluoroquinolone-Resistant Escherichia Coli in Retail Broiler Chicken Meat, Italy. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2015, 12, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Savin, M.; Bierbaum, G.; Hammerl, J.A.; Heinemann, C.; Parcina, M.; Sib, E.; Voigt, A.; Kreyenschmidt, J. Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria and Antimicrobial Residues in Wastewater and Process Water from German Pig Slaughterhouses and Their Receiving Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 727, 138788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savin, M.; Bierbaum, G.; Blau, K.; Parcina, M.; Sib, E.; Smalla, K.; Schmithausen, R.; Heinemann, C.; Hammerl, J.A.; Kreyenschmidt, J. Colistin-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae Isolated from Process Waters and Wastewater from German Poultry and Pig Slaughterhouses. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 575391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Wang, Y.; Shi, X.; Wang, S.; Ren, H.; Shen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lin, J.; Wang, S. Rapid Rise of the Esbl and Mcr-1 Genes in Escherichia Coli of Chicken Origin in China, 2008–2014. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Azzopardi, E.A.; Boyce, D.E.; Thomas, D.W.; Dickson, W.A. Colistin in Burn Intensive Care: Back to the Future? Burns 2013, 39, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization—AGISAR. Critically Important Antimicrobials for Human Medicine, 5th Revision; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Holtmann, A.R.; Meemken, D.; Müller, A.; Seinige, D.; Büttner, K.; Failing, K.; Kehrenberg, C. Wild Boars Carry Extended-Spectrum Β-Lactamase- and Ampc-Producing Escherichia Coli. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaufler, K.; Semmler, T.; Wieler, L.H.; Trott, D.J.; Pitout, J.; Peirano, G.; Bonnedahl, J.; Dolejska, M.; Literak, I.; Fuchs, S.; et al. Genomic and Functional Analysis of Emerging Virulent and Multidrug-Resistant Escherichia Coli Lineage Sequence Type 648. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e00243-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schaufler, K.; Semmler, T.; Wieler, L.H.; Wöhrmann, M.; Baddam, R.; Ahmed, N.; Müller, K.; Kola, A.; Fruth, A.; Ewers, C.; et al. Clonal Spread and Interspecies Transmission of Clinically Relevant Esbl-Producing Escherichia Coli of St410--Another Successful Pandemic Clone? FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2016, 92, fiv155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dolejska, M.; Literak, I. Wildlife Is Overlooked in the Epidemiology of Medically Important Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e01167-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hendriksen, R.S.; Munk, P.; Njage, P.; van Bunnik, B.; McNally, L.; Lukjancenko, O.; Röder, T.; Nieuwenhuijse, D.; Pedersen, S.K.; Kjeldgaard, J.; et al. Global Monitoring of Antimicrobial Resistance Based on Metagenomics Analyses of Urban Sewage. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmiege, D.; Zacharias, N.; Sib, E.; Falkenberg, T.; Moebus, S.; Evers, M.; Kistemann, T. Prevalence of Multidrug-Resistant and Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia Coli in Urban Community Wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 147269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Taft, D.H.; Maldonado-Gomez, M.X.; Johnson, D.; Treiber, M.L.; Lemay, D.G.; DePeters, E.J.; Mills, D.A. The Fecal Resistome of Dairy Cattle Is Associated with Diet During Nursing. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skarżyńska, M.; Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Hendriksen, R.S.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Wasyl, D. A Metagenomic Glimpse into the Gut of Wild and Domestic Animals: Quantification of Antimicrobial Resistance and More. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Critically Important Antimicrobials for Human Medicine, 6th rev. ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- World Organisation for Animal Health. Oie List of Antimicrobial Agents of Veterinary Importance; International Committee Unanimously Adopted the List of Antimicrobial Agents of Veterinary Importance, Ed.; OIE—World Organisation for Animal Health: Paris, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Clermont, O.; Christenson, J.K.; Denamur, E.; Gordon, D.M. The Clermont Escherichia Coli Phylo-Typing Method Revisited: Improvement of Specificity and Detection of New Phylo-Groups. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2013, 5, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozwandowicz, M.; Brouwer, M.S.M.; Fischer, J.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Gonzalez-Zorn, B.; Guerra, B.; Mevius, D.J.; Hordijk, J. Plasmids Carrying Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in Enterobacteriaceae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 1121–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carattoli, A.; Zankari, E.; Garcia-Fernandez, A.; Larsen, M.V.; Lund, O.; Villa, L.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Hasman, H. In Silico Detection and Typing of Plasmids Using Plasmidfinder and Plasmid Multilocus Sequence Typing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marcelino, V.R.; Clausen, P.T.L.C.; Buchmann, J.P.; Wille, M.; Iredell, J.R.; Meyer, W.; Lund, O.; Sorrell, T.C.; Holmes, E.C. Ccmetagen: Comprehensive and Accurate Identification of Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes in Metagenomic Data. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza-Rodríguez, C.; Alt, K.; Grobbel, M.; Hammerl, J.A.; Irrgang, A.; Szabo, I.; Stingl, K.; Schuh, E.; Wiehle, L.; Pfefferkorn, B.; et al. Wildlife as Sentinels of Antimicrobial Resistance in Germany? Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 627821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasyl, D.; Zając, M.; Lalak, A.; Skarżyńska, M.; Samcik, I.; Kwit, R.; Jabłoński, A.; Bocian, Ł.; Woźniakowski, G.; Hoszowski, A.; et al. Antimicrobial Resistance in Escherichia Coli Isolated from Wild Animals in Poland. Microb. Drug Resist. 2018, 24, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Formenti, N.; Calò, S.; Parisio, G.; Guarneri, F.; Birbes, L.; Pitozzi, A.; Scali, F.; Tonni, M.; Guadagno, F.; Giovannini, S.; et al. Esbl/Ampc-Producing Escherichia Coli in Wild Boar: Epidemiology and Risk Factors. Animals 2021, 11, 1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, M.; Gonçalves, A.; Silva, N.; Serra, R.; Alcaide, E.; Zorrilla, I.; Torres, C.; Caniça, M.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P. Acquired Antibiotic Resistance among Wild Animals: The Case of Iberian Lynx (Lynx Pardinus). Vet. Q. 2014, 34, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thanner, S.; Drissner, D.; Walsh, F. Antimicrobial Resistance in Agriculture. mBio 2016, 7, e02227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larsen, J.; Raisen, C.L.; Ba, X.; Sadgrove, N.J.; Padilla-González, G.F.; Simmonds, M.S.J.; Loncaric, I.; Kerschner, H.; Apfalter, P.; Hartl, R.; et al. Emergence of Methicillin Resistance Predates the Clinical Use of Antibiotics. Nature 2022, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutscher Wetterdienst. CDC—Climate Data Center, Germany. 2021. Available online: https://cdc.dwd.de/portal/Offenbach (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- ElBaradei, A.; Maharem, D.A.; Kader, O.; Ghareeb, M.K.; Naga, I.S. Fecal Carriage of Esbl-Producing Escherichia Coli in Egyptian Patients Admitted to the Medical Research Institute Hospital, Alexandria University. AIMS Microbiol. 2020, 6, 422–433. [Google Scholar]
- Usein, C.R.; Papagheorghe, R.; Oprea, M.; Condei, M.; Strãuţ, M. Molecular Characterization of Bacteremic Escherichia Coli Isolates in Romania. Folia Microbiol. 2016, 61, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, S.; Silva, V.; Dapkevicius, M.L.E.; Caniça, M.; Tejedor-Junco, M.T.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P. Escherichia Coli as Commensal and Pathogenic Bacteria among Food-Producing Animals: Health Implications of Extended Spectrum Β-Lactamase (Esbl) Production. Animals 2020, 10, 2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraniak, A.; Izdebski, R.; Fiett, J.; Herda, M.; Derde, L.P.; Bonten, M.J.; Adler, A.; Carmeli, Y.; Goossens, H.; Hryniewicz, W.; et al. Kpc-Like Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae Colonizing Patients in Europe and Israel. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 60, 1912–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hazen, T.H.; Zhao, L.; Boutin, M.A.; Stancil, A.; Robinson, G.; Harris, A.D.; Rasko, D.A.; Johnson, J.K. Comparative Genomics of an Inca/C Multidrug Resistance Plasmid from Escherichia Coli and Klebsiella Isolates from Intensive Care Unit Patients and the Utility of Whole-Genome Sequencing in Health Care Settings. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 4814–4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Decraene, V.; Phan, H.T.T.; George, R.; Wyllie, D.H.; Akinremi, O.; Aiken, Z.; Cleary, P.; Dodgson, A.; Pankhurst, L.; Crook, D.W.; et al. A Large, Refractory Nosocomial Outbreak of Klebsiella Pneumoniae Carbapenemase-Producing Escherichia Coli Demonstrates Carbapenemase Gene Outbreaks Involving Sink Sites Require Novel Approaches to Infection Control. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e01689-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tarabai, H.; Wyrsch, E.R.; Bitar, I.; Dolejska, M.; Djordjevic, S.P. Epidemic Hi2 Plasmids Mobilising the Carbapenemase Gene Bla(Imp-4) in Australian Clinical Samples Identified in Multiple Sublineages of Escherichia Coli St216 Colonising Silver Gulls. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnoletti, F.; Brunetta, R.; Bano, L.; Drigo, I.; Mazzolini, E. Longitudinal Study on Antimicrobial Consumption and Resistance in Rabbit Farming. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2018, 51, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferjani, S.; Saidani, M.; Hamzaoui, Z.; Alonso, C.A.; Torres, C.; Maamar, E.; Slim, A.F.; Boutiba, B.I. Community Fecal Carriage of Broad-Spectrum Cephalosporin-Resistant Escherichia Coli in Tunisian Children. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 87, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izdebski, R.; Baraniak, A.; Fiett, J.; Adler, A.; Kazma, M.; Salomon, J.; Lawrence, C.; Rossini, A.; Salvia, A.; Samso, J.V.; et al. Clonal Structure, Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamases, Acquired Ampc-Type Cephalosporinases of Escherichia Coli Populations Colonizing Patients in Rehabilitation Centers in Four Countries. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2013, 57, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manges, A.R.; Geum, H.M.; Guo, A.; Edens, T.J.; Fibke, C.D.; Pitout, J.D.D. Global Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia Coli (Expec) Lineages. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00135-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osei Sekyere, J.; Reta, M.A. Genomic and Resistance Epidemiology of Gram-Negative Bacteria in Africa: A Systematic Review and Phylogenomic Analyses from a One Health Perspective. Msystems 2020, 5, e00897-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landesforst, M.V. “Landesforst MV—A Brief Profi Le”. Available online: https://www.wald-mv.de/Unser-Wald/Wald%E2%80%93in%E2%80%93Zahlen/?id=18071&processor=veroeff (accessed on 5 January 2022).
- FAO. The Fao Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance 2021–2025; FAO: Rome, Italty, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Damm, G.R. A Matter of Taste—Wild Game Meat, the Consumption Thereof, Is Important in Germany—and Should Be Worldwide. Conserv. Frontlines 2021, 3, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Baym, M.; Kryazhimskiy, S.; Lieberman, T.D.; Chung, H.; Desai, M.M.; Kishony, R. Inexpensive Multiplexed Library Preparation for Megabase-Sized Genomes. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. Spades: A New Genome Assembly Algorithm and Its Applications to Single-Cell Sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and Accurate Short Read Alignment with Burrows-Wheeler Transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R.; Proc, G.P.D. The Sequence Alignment/Map Format and Samtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walker, B.J.; Abeel, T.; Shea, T.; Priest, M.; Abouelliel, A.; Sakthikumar, S.; Cuomo, C.A.; Zeng, Q.D.; Wortman, J.; Young, S.K.; et al. Pilon: An Integrated Tool for Comprehensive Microbial Variant Detection and Genome Assembly Improvement. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, D.H.; Imelfort, M.; Skennerton, C.T.; Hugenholtz, P.; Tyson, G.W. Checkm: Assessing the Quality of Microbial Genomes Recovered from Isolates, Single Cells, and Metagenomes. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jolley, K.A.; Bray, J.E.; Maiden, M.C. Open-Access Bacterial Population Genomics: Bigsdb Software, the Pubmlst.Org Website and Their Applications [Version 1; Peer Review: 2 Approved]. Wellcome Open Res. 2018, 3, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Zheng, D.D.; Jin, Q.; Chen, L.H.; Yang, J. Vfdb 2019: A Comparative Pathogenomic Platform with an Interactive Web Interface. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2019, 47, D687–D692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zankari, E.; Hasman, H.; Cosentino, S.; Vestergaard, M.; Rasmussen, S.; Lund, O.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Larsen, M.V. Identification of Acquired Antimicrobial Resistance Genes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2640–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, C.; Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Rensing, C.; Kristiansson, E.; Larsson, D.G.J. Bacmet: Antibacterial Biocide and Metal Resistance Genes Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D737–D743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gupta, S.K.; Padmanabhan, B.R.; Diene, S.M.; Lopez-Rojas, R.; Kempf, M.; Landraud, L.; Rolain, J.M. Arg-Annot, a New Bioinformatic Tool to Discover Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Bacterial Genomes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Knudsen, B.E.; Bergmark, L.; Munk, P.; Lukjancenko, O.; Prieme, A.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Pamp, S.J. Impact of Sample Type and DNA Isolation Procedure on Genomic Inference of Microbiome Composition. Msystems 2016, 1, e00095-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lakin, S.M.; Dean, C.; Noyes, N.R.; Dettenwanger, A.; Ross, A.S.; Doster, E.; Rovira, P.; Abdo, Z.; Jones, K.L.; Ruiz, J.; et al. Megares: An Antimicrobial Resistance Database for High Throughput Sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D574–D580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doster, E.; Lakin, S.M.; Dean, C.J.; Wolfe, C.; Young, J.G.; Boucher, C.; Belk, K.E.; Noyes, N.R.; Morley, P.S. Megares 2.0: A Database for Classification of Antimicrobial Drug, Biocide and Metal Resistance Determinants in Metagenomic Sequence Data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 48, D561–D569. [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Hartmann, M.; Eriksson, K.M.; Pal, C.; Thorell, K.; Larsson, D.G.J.; Nilsson, R.H. Metaxa2: Improved Identification and Taxonomic Classification of Small and Large Subunit Rrna in Metagenomic Data. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2015, 15, 1403–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Yang, Y.; Ma, L.; Ju, F.; Guo, F.; Tiedje, J.M.; Zhang, T. Metagenomic and Network Analysis Reveal Wide Distribution and Co-Occurrence of Environmental Antibiotic Resistance Genes. ISME J. 2015, 9, 2490–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clausen, P.T.L.C.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Lund, O. Rapid and Precise Alignment of Raw Reads against Redundant Databases with Kma. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Designation | Species of Origin | Amikacin | Amoxicillin/Clavulanic Acid | Ampicillin | Cefotaxim | Ceftazidim | Cefepim | Colistin | Imipenem | Meropenem | Gentamicin | Tobramycin | Ciprofloxacin | Tetracycline | Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazol | ESBL | MDR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 257 | WR | S | R | R | R | R | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | + | - |
| 258 | WR | S | R | R | R | R | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S | + | + |
| 259 | WR | S | R | R | R | R | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S | + | + |
| 260 | WB | S | R | R | R | R | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | + | - |
| 261 | WB | S | R | R | R | R | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S | + | + |
| 262 | WB | S | R | R | R | R | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | + | - |
| 263 | WB | S | R | R | R | R | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | + | - |
| 264 | WB | S | R | R | R | R | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | + | - |
| 265 | WB | S | R | R | R | R | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | + | - |
| 266 | WB | S | R | R | R | R | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | + | - |
| 267 | WB | S | R | R | R | R | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | + | - |
| 268 | WB | S | R | R | R | R | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | + | - |
| 269 | WB | S | R | R | R | R | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | + | - |
| 270 | WB | S | R | R | R | R | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | + | - |
| 271 | WB | S | R | R | R | R | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | + | - |
| 272 | WB | S | R | R | R | R | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | + | - |
| 1031 | WB | S | R | R | R | R | R | S | S | S | R | R | S | R | S | + | + |
| 1114 | WB | S | R | R | R | R | R | S | S | S | R | R | S | R | S | + | + |
| 1115 | WB | S | R | R | R | R | R | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | R | + | + |
| Class | Wild Boar 1 | Wild Boar 2 | Roe Deer 1 | Roe Deer 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aminocoumarins | 2.0 | 1.1 | 3.0 | 1.5 |
| Aminoglycosides | 10.6 | 8.3 | 15.2 | 18.3 |
| Bacitracin | 0.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Beta-lactams | 5.8 | 6.9 | 8.5 | 6.6 |
| Cationic antimicrobial peptides | 1.4 | 1.3 | 0.6 | 1.2 |
| Elfamycins | 1.6 | 0.8 | 1.9 | 2.7 |
| Fluoroquinolones | 1.4 | 1.3 | 2.6 | 4.8 |
| Fusidic acid | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.6 | 0.9 |
| Glycopeptides | 0.7 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.2 |
| MLS | 31.1 | 39.6 | 27.6 | 28.8 |
| Multi-drug resistance | 11.7 | 8.7 | 9.8 | 9.0 |
| Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific Drug | 0.1 | 0.3 | 2.0 | 1.8 |
| Phenicol | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.9 |
| Rifampin | 2.0 | 1.5 | 4.5 | 2.4 |
| Sulfonamides | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1.7 | 0.0 |
| Tetracyclines | 29.2 | 28.1 | 19.3 | 18.0 |
| Trimethoprim | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
| Fosfomycin | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.9 | 1.5 |
| Wild Boar 1 | Wild Boar 2 | Roe Deer 1 | Roe Deer 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.049 | 0.042 | 0.033 | 0.028 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Homeier-Bachmann, T.; Schütz, A.K.; Dreyer, S.; Glanz, J.; Schaufler, K.; Conraths, F.J. Genomic Analysis of ESBL-Producing E. coli in Wildlife from North-Eastern Germany. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11020123
Homeier-Bachmann T, Schütz AK, Dreyer S, Glanz J, Schaufler K, Conraths FJ. Genomic Analysis of ESBL-Producing E. coli in Wildlife from North-Eastern Germany. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(2):123. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11020123
Chicago/Turabian StyleHomeier-Bachmann, Timo, Anne K. Schütz, Sylvia Dreyer, Julien Glanz, Katharina Schaufler, and Franz J. Conraths. 2022. "Genomic Analysis of ESBL-Producing E. coli in Wildlife from North-Eastern Germany" Antibiotics 11, no. 2: 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11020123
APA StyleHomeier-Bachmann, T., Schütz, A. K., Dreyer, S., Glanz, J., Schaufler, K., & Conraths, F. J. (2022). Genomic Analysis of ESBL-Producing E. coli in Wildlife from North-Eastern Germany. Antibiotics, 11(2), 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11020123






