Antimicrobial Resistance and Molecular Characterization of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus from Two Pig Farms: Longitudinal Study of LA-MRSA
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. MRSA Prevalence and Molecular Characteristics
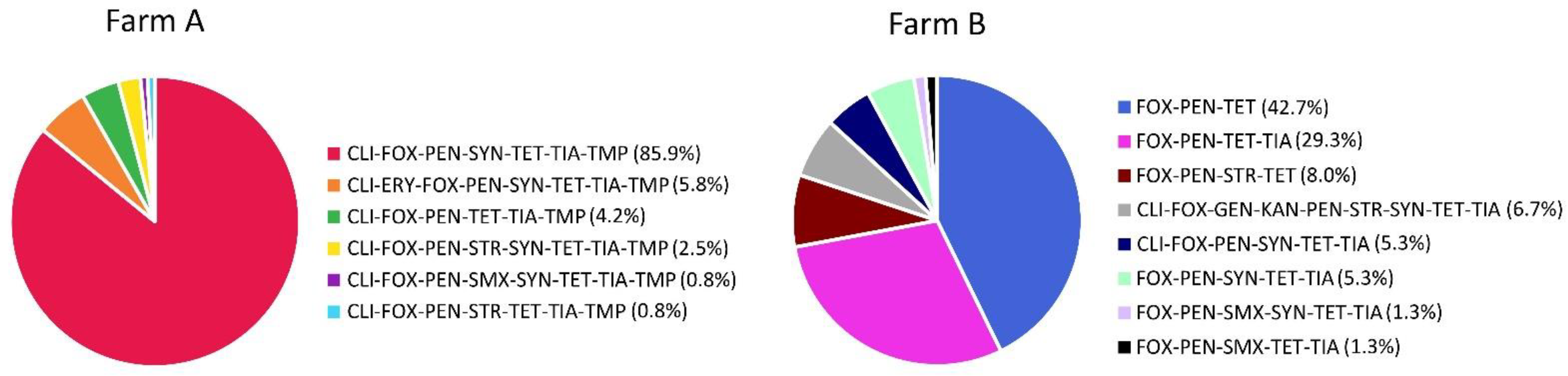
2.2. Antimicrobial Resistance of MRSA Isolates
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design and Sampling
4.2. MRSA Cultivation and Molecular Characterization
4.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebreyes, W.A.; Jackwood, D.; de Oliveira, C.J.B.; Lee, C.-W.; Hoet, A.E.; Thakur, S. Molecular epidemiology of infectious zoonotic and livestock diseases. Microbiol. Spectr. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armand-Lefevre, L.; Ruimy, R.; Andremont, A. Clonal comparison of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from healthy pig farmers, human controls, and pigs. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 711–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matuszewska, M.; Murray, G.G.R.; Harrison, E.M.; Holmes, M.A.; Weinert, L.A. The evolutionary genomics of host specificity in Staphylococcus aureus. Trends Microbiol. 2020, 28, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo-Piazuelo, D.; Lawlor, P.G. Livestock-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (LA-MRSA) prevalence in humans in close contact with animals and measures to reduce on-farm colonisation. Irish Vet. J. 2021, 74, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority). Analysis of the baseline survey on the prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in holdings with breeding pigs, in the EU, 2008—Part A: MRSA prevalence estimates. EFSA J. 2009, 7, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority); ECDC (European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control). The European union summary report on antimicrobial resistance in zoonotic and indicator bacteria from humans, animals and food in 2017/2018. EFSA J. 2020, 18, e06007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority). Analysis of the baseline survey on the prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in holdings with breeding pigs, in the EU, 2008—Part B: Factors associated with MRSA contamination of holdings. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierikx, C.M.; Hengeveld, P.D.; Veldman, K.T.; de Haan, A.; van der Voorde, S.; Dop, P.Y.; Bosch, T.; van Duijkeren, E. Ten years later: Still a high prevalence of MRSA in slaughter pigs despite a significant reduction in antimicrobial usage in pigs the Netherlands. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 2414–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goerge, T.; Lorenz, M.B.; van Alen, S.; Hübner, N.-O.; Becker, K.; Köck, R. MRSA colonization and infection among persons with occupational livestock exposure in Europe: Prevalence, preventive options and evidence. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 200, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avberšek, J.; Golob, M.; Papić, B.; Dermota, U.; Grmek Košnik, I.; Kušar, D.; Ocepek, M.; Zdovc, I. Livestock-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Establishing links between animals and humans on livestock holdings. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 789–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelbíčová, T.; Brodíková, K.; Karpíšková, R. Livestock-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Czech retailed ready-to-eat meat products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 374, 109727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mama, O.M.; Aspiroz, C.; Ruiz-Ripa, L.; Ceballos, S.; Iñiguez-Barrio, M.; Cercenado, E.; Azcona, J.M.; López-Cerero, L.; Seral, C.; López-Calleja, A.I.; et al. Prevalence and genetic characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus CC398 isolates from invasive infections in Spanish hospitals, focusing on the livestock-independent CC398-MSSA clade. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 623108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weese, J.S.; van Duijkeren, E. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus pseudintermedius in veterinary medicine. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 140, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardabassi, L.; Larsen, J.; Weese, J.S.; Butaye, P.; Battisti, A.; Kluytmans, J.; Lloyd, D.H.; Skov, R.L. Public health impact and antimicrobial selection of meticillin-resistant staphylococci in animals. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2013, 1, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdács, M. The continuing threat of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, G.Y.; Seong, H.J.; Sul, W.J.; Yang, S.-J. Genomic information on linezolid-resistant sequence-type 398 livestock-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from a pig. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2021, 18, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, E.; Conceição, T.; Poirel, L.; de Lencastre, H.; Aires-de-Sousa, M. Epidemiology and antimicrobial resistance of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates colonizing pigs with different exposure to antibiotics. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abreu, R.; Rodríguez-Álvarez, C.; Lecuona, M.; Castro, B.; González, J.; Aguirre-Jaime, A.; Arias, Á. Increased antimicrobial resistance of MRSA strains isolated from pigs in Spain between 2009 and 2018. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pirolo, M.; Gioffrè, A.; Visaggio, D.; Gherardi, M.; Pavia, G.; Samele, P.; Ciambrone, L.; Di Natale, R.; Spatari, G.; Casalinuovo, F.; et al. Prevalence, molecular epidemiology, and antimicrobial resistance of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from swine in southern Italy. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-López, P.; Filipello, V.; Di Ciccio, P.A.; Pitozzi, A.; Ghidini, S.; Scali, F.; Ianieri, A.; Zanardi, E.; Losio, M.N.; Simon, A.C.; et al. Assessment of the antibiotic resistance profile, genetic heterogeneity and biofilm production of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolated from the Italian swine production chain. Foods 2020, 9, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graveland, H.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Bergs, K.; Heesterbeek, H.; Heederik, D. Persistence of livestock associated MRSA CC398 in humans is dependent on intensity of animal contact. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Köck, R.; Schaumburg, F.; Mellmann, A.; Köksal, M.; Jurke, A.; Becker, K.; Friedrich, A.W. Livestock-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) as causes of human infection and colonization in Germany. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Effelsberg, N.; Udarcev, S.; Müller, H.; Kobusch, I.; Linnemann, S.; Boelhauve, M.; Köck, R.; Mellmann, A. Genotypic characterization of livestock-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates of clonal complex 398 in pigsty visitors: Transient carriage or persistence? J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e01276-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingham, A.C.; Urth, T.R.; Sieber, R.N.; Stegger, M.; Edslev, S.M.; Angen, Ø.; Larsen, A.R. Dynamics of the human nasal microbiota and Staphylococcus aureus CC398 carriage in pig truck drivers across one workweek. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e01225-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feld, L.; Bay, H.; Angen, Ø.; Larsen, A.R.; Madsen, A.M. Survival of LA-MRSA in dust from swine farms. Ann. Work Expo. Health 2018, 62, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bangerter, P.D.; Sidler, X.; Perreten, V.; Overesch, G. Longitudinal study on the colonisation and transmission of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in pig farms. Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 183, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weese, J.S.; Zwambag, A.; Rosendal, T.; Reid-Smith, R.; Friendship, R. Longitudinal investigation of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in piglets. Zoonoses Public Health 2011, 58, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahibzada, S.; Abraham, S.; Coombs, G.W.; Pang, S.; Hernández-Jover, M.; Jordan, D.; Heller, J. Transmission of highly virulent community-associated MRSA ST93 and livestock-associated MRSA ST398 between humans and pigs in Australia. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vanderhaeghen, W.; Hermans, K.; Haesebrouck, F.; Butaye, P. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in food production animals. Epidemiol. Infect. 2010, 138, 606–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.Y.C.; Davis, J.S.; Eichenberger, E.; Holland, T.L.; Fowler, V.G., Jr. Staphylococcus aureus infections: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and management. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 603–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grøntvedt, C.A.; Elstrøm, P.; Stegger, M.; Skov, R.L.; Andersen, P.S.; Larssen, K.W.; Urdahl, A.M.; Angen, Ø.; Larsen, J.; Åmdal, S.; et al. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus CC398 in humans and pigs in Norway: A “One Health” perspective on introduction and transmission. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, 1431–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dermota, U.; Grmek Košnik, I.; Rupnik, M.; Janežič, S.; Žohar Čretnik, T.; Petrovič, Ž.; Štrumbelj, I.; Harlander, T.; Zdolšek, B.; Kavčič, M.; et al. Dinamika slovenskih klonov MRSA z opredeljenimi vzorci občutljivosti za ne-betalaktamske antibiotike (Dynamics of Slovenian MRSA clones with defined susceptibility patterns for non-betalactam antibiotics). In 6. Likarjev simpozij: Bolnišnične okužbe, problematika odpornih bakterij; Faculty of Medicine, Ljubljana, 21 June 2016; Pirš, M., Ed.; Sekcija za klinično mikrobiologijo in bolnišnične okužbe Slovenskega Zdravniškega Društva: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2016; Available online: https://imi.si/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/Zbornik_2016.pdf (accessed on 30 September 2022). (In Slovene)
- Kinross, P.; Petersen, A.; Skov, R.; Van Hauwermeiren, E.; Pantosti, A.; Laurent, F.; Voss, A.; Kluytmans, J.; Struelens, M.J.; Heuer, O.; et al. Livestock-associated meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) among human MRSA isolates, European union/European economic area countries, 2013. Eurosurveillance 2017, 22, 16-00696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Broens, E.M.; Espinosa-Gongora, C.; Graat, E.A.; Vendrig, N.; Van Der Wolf, P.J.; Guardabassi, L.; Butaye, P.; Nielsen, J.; De Jong, M.C.; Van De Giessen, A.W. Longitudinal study on transmission of MRSA CC398 within pig herds. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, T.C.; Male, M.J.; Harper, A.L.; Kroeger, J.S.; Tinkler, G.P.; Moritz, E.D.; Capuano, A.W.; Herwaldt, L.A.; Diekema, D.J. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) strain ST398 is present in midwestern U.S. swine and swine workers. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lassok, B.; Tenhagen, B.-A. From pig to pork: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in the pork production chain. J. Food Prot. 2013, 76, 1095–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alt, K.; Fetsch, A.; Schroeter, A.; Guerra, B.; Hammerl, J.A.; Hertwig, S.; Senkov, N.; Geinets, A.; Mueller-Graf, C.; Braeunig, J.; et al. Factors associated with the occurrence of MRSA CC398 in herds of fattening pigs in Germany. BMC Vet. Res. 2011, 7, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sørensen, A.I.V.; Jensen, V.F.; Boklund, A.; Halasa, T.; Christensen, H.; Toft, N. Risk factors for the occurrence of livestock-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (LA-MRSA) in Danish pig herds. Prev. Vet. Med. 2018, 159, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, K.; Roesler, U.; Merle, R.; Friese, A. Persistent and transient airborne MRSA colonization of piglets in a newly established animal model. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tuominen, K.S.; Sternberg Lewerin, S.; Jacobson, M.; Rosendal, T. Modelling environmentally mediated spread of livestock-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a pig herd. Animal 2022, 16, 100450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schollenbruch, H.; Kobusch, I.; Schröter, I.; Mellmann, A.; Köck, R.; Boelhauve, M. Pilot study on alteration of LA-MRSA status of pigs during fattening period on straw bedding by two types of cleaning. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SSI (Statens Serum Institut); NFI-DTU (National Food Institute, Technical University of Denmark). DANMAP 2019: Use of Antimicrobial Agents and Occurrence of Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacteria from Food Animals, Food and Humans in Denmark; NFI-DTU: Lyngby, Denmark, 2020; Available online: https://www.danmap.org/Reports/2019 (accessed on 4 October 2022).
- Reischl, U.; Frick, J.; Hoermansdorfer, S.; Melzl, H.; Bollwein, M.; Linde, H.J.; Becker, K.; Köck, R.; Tuschak, C.; Busch, U.; et al. Single-nucleotide polymorphism in the SCCmec-orfX junction distinguishes between livestock-associated MRSA CC398 and human epidemic MRSA strains. Eurosurveillance 2009, 14, 19436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broens, E.M.; Graat, E.A.M.; van der Wolf, P.J.; van de Giessen, A.W.; van Duijkeren, E.; Wagenaar, J.A.; van Nes, A.; Mevius, D.J.; de Jong, M.C.M. MRSA CC398 in the pig production chain. Prev. Vet. Med. 2011, 98, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority); ECDC (European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control). The European union summary report on antimicrobial resistance in zoonotic and indicator bacteria from humans, animals and food in 2019–2020. EFSA J. 2022, 20, 7209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieber, R.N.; Skov, R.L.; Nielsen, J.; Schulz, J.; Price, L.B.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Larsen, A.R.; Stegger, M.; Larsen, J. Drivers and dynamics of methicillin-resistant livestock-associated Staphylococcus aureus CC398 in pigs and humans in Denmark. mBio 2018, 9, e02142-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Conceição, T.; de Lencastre, H.; Aires-de-Sousa, M. Frequent isolation of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) ST398 among healthy pigs in Portugal. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lekagul, A.; Tangcharoensathien, V.; Yeung, S. Patterns of antibiotic use in global pig production: A systematic review. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2019, 7, 100058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMA (European Medicines Agency). Sales of Veterinary Antimicrobial Agents in 31 European Countries in 2019 and 2020: Trends from 2010 to 2020, Eleventh ESVAC Report; EMA: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Available online: https://health.ec.europa.eu/publications/sales-veterinary-antimicrobial-agents-31-european-countries-2019-and-2020_en (accessed on 4 October 2022).
- Crombé, F.; Willems, G.; Dispas, M.; Hallin, M.; Denis, O.; Suetens, C.; Gordts, B.; Struelens, M.; Butaye, P. Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus among pigs in Belgium. Microb. Drug Resist. 2012, 18, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sahibzada, S.; Pang, S.; Hernández-Jover, M.; Jordan, D.; Abraham, S.; O’Dea, M.; Heller, J. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of MRSA across different pig age groups in an intensive pig production system in Australia. Zoonoses Public Health 2020, 67, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Wilson, B.; Gould, I.M. Current and future treatment options for community-associated MRSA infection. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2018, 19, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority). Technical specifications on the harmonised monitoring and reporting of antimicrobial resistance in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in food-producing animals and food. EFSA J. 2012, 10, 2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, A.B. Detection of methicillin resistance in coagulase-negative staphylococci and in staphylococci directly from simulated blood cultures using the EVIGENE MRSA detection kit. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 51, 419–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stegger, M.; Andersen, P.S.; Kearns, A.; Pichon, B.; Holmes, M.A.; Edwards, G.; Laurent, F.; Teale, C.; Skov, R.; Larsen, A.R. Rapid detection, differentiation and typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus harbouring either mecA or the new mecA homologue mecALGA251. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Farm | Samples: Positive/Collected | Spa Type | Spa Repeat Succession * | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pigs | Environment | Total | |||
| A | 87/125 (69.6%) | 33/36 (91.7%) | 120/161 (74.5%) | t571 (30/61, 49.2%) t034 (26/61, 42.6%) t1250 (4/61, 6.6%) t898 (1/61, 1.6%) | 08-16-02-25-02-25-34-25 08-16-02-25-02-25-34-24-25 08-16-02-25-02-25 08-16-02-25-02-25-34-34-24-25 |
| B | 40/81 (49.4%) | 35/38 (92.1%) | 75/119 (63.0%) | t1451 (51/75, 68.0%) t011 (24/75, 32.0%) | 08-16-02-25-34-25 08-16-02-25-34-24-25 |
| Farm A | 1–6 d a.p. | 0–2 d p.p. | 7–12 d p.p. | 14–19 d p.p. | 21–26 d p.p. | 35–40 d p.p. | 2 mth p.p. | 3 mth p.p. | 3.5 mth p.p. | 4.5 mth p.p. | 6 mth p.p. | 9 mth p.p. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | |
| Sow 1 | □ | ■ | ■ | ** | ||||||||
| Piglets 1 | ■ | □ | □ | □ | ||||||||
| Sow 2 | ■ | ■ | ■ | □ | □ * | □ * | ||||||
| Piglets 2 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||||
| Sow 3 | □ | ■ | ■ | ■ | □ * | □ | ||||||
| Piglets 3 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||||
| Sow 4 | □ | ■ | ■ | # | □ * | ** | ||||||
| Piglets 4 | ■ | □ | ■ | ■ | ||||||||
| Sow 5 | □ | ■ | ■ | ■ | □ | □ | ||||||
| Piglets 5 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||||
| Sow 6 | □ | ■ | ■ | ■ | □ | ** | ||||||
| Piglets 6 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||||
| Sow 7 | □ | ■ | ■ | ■ | □ | ** | ||||||
| Piglets 7 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||||
| Sow 8 | □ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ** | ||||||
| Piglets 8 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||||
| Sow 9 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | □ * | □ * | ||||||
| Piglets 9 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||||
| Sow 10 | ■ | ■ | ■ | # | □ | □ * | ||||||
| Piglets 10 | ■ | □ | ■ | ■ | ||||||||
| Growers 1/fattening pigs 1 | ■ | ■ | ■ | □ | ■ | □ | □ | |||||
| Growers 2/fattening pigs 2 | ■ | ■ | ■ | □ | ■ | □ | □ | |||||
| Growers 3/fattening pigs 3 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | □ | ■ | |||||
| Growers 4/fattening pigs 4 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | □ | ■ | ■ | |||||
| Environment 1 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | □ | ■ | □ | ■ |
| Environment 2 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | □ | ■ | ■ | ■ |
| Environment 3 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ |
| Farm B | 1 mth a.p. | 4 d a.p. | 2 d p.p. | 10 d p.p. | 16 d p.p. | 24 d p.p. | 38 d p.p. | 2 mth p.p. | 3 mth p.p. | 4 mth p.p. | 5 mth p.p. | 6 mth p.p. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | |
| Sow 1 | □ | □ | □ | ■ | □ | ■ | ■ | |||||
| Piglets 1 | □ | □ | ■ | □ | ||||||||
| Sow 2 | ■ | ■ | ■ | □ | □ | □ | ■ | |||||
| Piglets 2 | ■ | ■ | □ | □ | ||||||||
| Sow 3 | ■ | □ | □ | ■ | □ | □ | □ | |||||
| Piglets 3 | □ | □ | ■ | □ | ||||||||
| Sow 4 | ■ | □ | □ | □ | ■ | □ | □ | |||||
| Piglets 4 | ■ | □ | □ | □ | ||||||||
| Sow 5 | ■ | ■ | □ | ■ | ■ | ■ | □ | |||||
| Piglets 5 | □ | □ | ■ | □ | ||||||||
| Sow 6 | ■ | □ | ** | |||||||||
| Sow 7 | ■ | ■ | □ | ■ | □ | ■ | □ | |||||
| Piglets 7 | □ | ■ | ■ | □ | ||||||||
| Growers 1/fattening pigs 1 | ■ | ■ | ■ | □ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| Growers 2/fattening pigs 2 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | □ | ■ | ||||||
| Growers 3/fattening pigs 3 | ■ | |||||||||||
| Environment 1 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | □ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ |
| Environment 2 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | □ |
| Environment 3 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | □ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ |
| Environment 4 § | ■ | ■ |
| PCR Assay | Gene | Primer | Primer Sequence (5′➝3′) | Amplicon Size (bp) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 16S rDNA | 16S-1 | GTGCCAGCAGCCGCGGTAA | 886 | [55] |
| 16S-2 | AGACCCGGGAACGTATTCAC | ||||
| mecA | mecA-1 | GGGATCATAGCGTCATTATTC | 527 | ||
| mecA-2 | AACGATTGTGACACGATAGCC | ||||
| nuc | nuc-1 | TCAGCAAATGCATCACAAACAG | 255 | ||
| nuc-2 | CGTAAATGCACTTGCTTCAGG | ||||
| 2 | spa | spa-1113f | TAAAGACGATCCTTCGGTGAGC | 180–600 | [56] |
| spa-1514r | CAGCAGTAGTGCCGTTTGCTT | ||||
| lukF-PV | pvl-FP | GCTGGACAAAACTTCTTGGAATAT | 83 | ||
| pvl-RP | GATAGGACACCAATAAATTCTGGATTG | ||||
| mecC | mecALGA251MultiFP | GAAAAAAAGGCTTAGAACGCCTC | 138 | ||
| mecALGA251MultiRP | GAAGATCTTTTCCGTTTTCAGC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Golob, M.; Pate, M.; Kušar, D.; Zajc, U.; Papić, B.; Ocepek, M.; Zdovc, I.; Avberšek, J. Antimicrobial Resistance and Molecular Characterization of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus from Two Pig Farms: Longitudinal Study of LA-MRSA. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1532. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111532
Golob M, Pate M, Kušar D, Zajc U, Papić B, Ocepek M, Zdovc I, Avberšek J. Antimicrobial Resistance and Molecular Characterization of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus from Two Pig Farms: Longitudinal Study of LA-MRSA. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(11):1532. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111532
Chicago/Turabian StyleGolob, Majda, Mateja Pate, Darja Kušar, Urška Zajc, Bojan Papić, Matjaž Ocepek, Irena Zdovc, and Jana Avberšek. 2022. "Antimicrobial Resistance and Molecular Characterization of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus from Two Pig Farms: Longitudinal Study of LA-MRSA" Antibiotics 11, no. 11: 1532. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111532
APA StyleGolob, M., Pate, M., Kušar, D., Zajc, U., Papić, B., Ocepek, M., Zdovc, I., & Avberšek, J. (2022). Antimicrobial Resistance and Molecular Characterization of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus from Two Pig Farms: Longitudinal Study of LA-MRSA. Antibiotics, 11(11), 1532. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111532






