Occurrence and Risk Assessment of Fluoroquinolone Residues in Chicken and Pork in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Occurrence of Fluoroquinolone Residues in Chicken and Pork
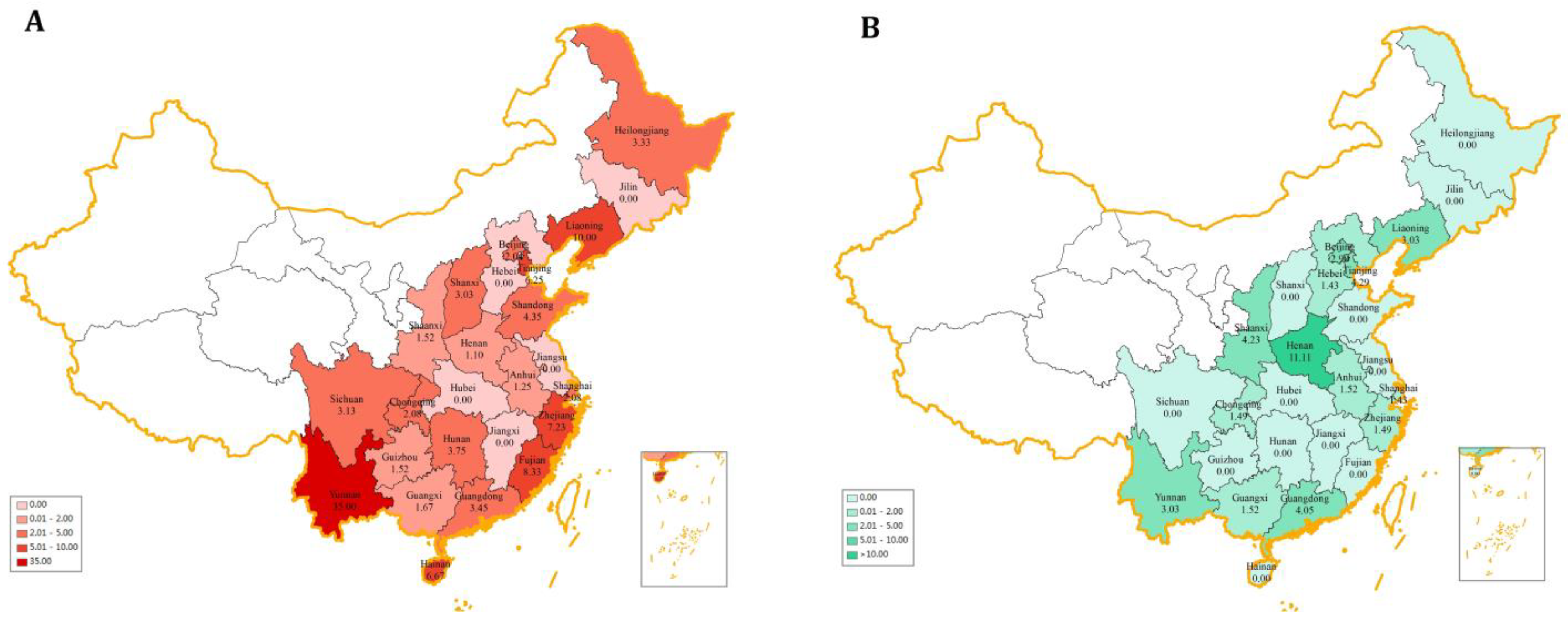
2.2. Occurrence of Fluoroquinolone Residues in Different Regions
2.3. Occurrence of Fluoroquinolone Residues in Different Sampling Site Types
2.4. Comparison with Other Studies
2.5. Risk Assessment
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sample Collection and Preparation
3.2. Chemicals and Reagents
3.3. Extraction Procedures
3.4. Instrumental Analysis
3.5. Quality Control and Quality Assurance
3.6. Statistical Analysis
3.7. Risk Assessment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Sun, L.; Cui, J.; Liu, J.; Tang, Q.; Du, F.; Liu, X.; Yao, D. Resource Utilization of Biogas Waste as Fertilizer in China Needs More Inspections Due to the Risk of Heavy Metals. Agriculture 2022, 12, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimokawa, S. Sustainable meat consumption in China. J. Integr. Agric. 2015, 14, 1023–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griboff, J.; Carrizo, J.C.; Bonansea, R.I.; Valdés, M.E.; Wunderlin, D.A.; Amé, M.V. Multiantibiotic residues in commercial fish from Argentina. The presence of mixtures of antibiotics in edible fish, a challenge to health risk assessment. Food Chem. 2020, 332, 127380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.M.; Silva, L.J.; Rodrigues, J.; Lino, C.; Pena, A. Risk assessment of fluoroquinolones from poultry muscle consumption: Comparing healthy adult and pre-school populations. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 118, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacanlı, M.; Başaran, N. Importance of antibiotic residues in animal food. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 125, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muaz, K.; Riaz, M.; Akhtar, S.; Park, S.; Ismail, A. Antibiotic residues in chicken meat: Global prevalence, threats, and decontamination strategies: A review. J. Food Prot. 2018, 81, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhogoju, S.; Nahashon, S. Recent Advances in Probiotic Application in Animal Health and Nutrition: A Review. Agriculture 2022, 12, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsène, M.; Davares, A.; Viktorovna, P.I.; Andreevna, S.L.; Sarra, S.; Khelifi, I.; Sergueïevna, D.M. The public health issue of antibiotic residues in food and feed: Causes, consequences, and potential solutions. Vet. World 2022, 15, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falagas, M.E.; Rizos, M.; Bliziotis, I.A.; Rellos, K.; Kasiakou, S.K.; Michalopoulos, A. Toxicity after prolonged (more than four weeks) administration of intravenous colistin. BMC. Infect. Dis. 2005, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shen, L.; Qin, S.; Cui, J.; Liu, Y. Quinolones antibiotics in the Baiyangdian Lake, China: Occurrence, distribution, predicted no-effect concentrations (PNECs) and ecological risks by three methods. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ying, G.; Pan, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J. Comprehensive evaluation of antibiotics emission and fate in the river basins of china: Source analysis, multimedia modeling, and linkage to bacterial resistance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 6772–6782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, M.; Ying, G.G.; Singer, A.C.; Zhu, Y.G. Review of antibiotic resistance in China and its environment. Environ. Int. 2018, 110, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortolotte, A.R.; Daniel, D.; Reyes, F.G.R. Occurrence of antimicrobial residues in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fillets produced in Brazil and available at the retail market. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 109865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Fu, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Ma, Y.; Wei, Y.; Qu, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Liao, M.; Fu, Y. Highly prevalent multidrug-resistant Salmonella from chicken and pork meat at retail markets in Guangdong, China. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouvêa, R.; Dos Santos, F.F.; De Aquino, M.H.C. Fluoroquinolones in industrial poultry production, bacterial resistance and food residues: A review. Braz. J. Poult. Sci. 2015, 17, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montfoort, J.V.; Hagenbuch, B.; Groothuis, G.; Koepsell, H.; Meier, P.; Meijer, D. Drug uptake systems in liver and kidney. Curr. Drug Metab. 2003, 4, 185–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teglia, C.M.; Guiñez, M.; Culzoni, M.J.; Cerutti, S. Determination of residual enrofloxacin in eggs due to long term administration to laying hens. Analysis of the consumer exposure assessment to egg derivatives. Food Chem. 2021, 351, 129279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadra, A.; Pinelli, E.; Lacroix, M.Z.; Bousquet-Mélou, A.; Hamdi, H.; Merlina, G.; Guiresse, M.; Hafidi, M. Assessment of the genotoxicity of quinolone and fluoroquinolones contaminated soil with the Vicia faba micronucleus test. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 76, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, M.D. Antibiotic use in animal feed and its impact on human healt. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2000, 13, 279–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griggs, D.J.; Johnson, M.M.; Frost, J.A.; Humphrey, T.; Jørgensen, F.; Piddock, L.J. Incidence and mechanism of ciprofloxacin resistance in Campylobacter spp. isolated from commercial poultry flocks in the United Kingdom before, during, and after fluoroquinolone treatment. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority. The European Union Summary Report on antimicrobial resistance in Antimicrobial resistance in zoonotic and indicator bacteria from humans, animals and food in 2011. EFSA J. 2013, 11, 3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joint Inter-agency Antimicrobial Consumption and Resistance Analysis. ECDC/EFSA/EMA second joint report on the integrated analysis of the consumption of antimicrobial agents and occurrence of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria from humans and food-producing animals. EFSA J. 2017, 15, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ren, L.; Yu, X.; Hu, J.; Chen, Y.; He, G.; Jiang, Q. Antibiotic residues in meat, milk and aquatic products in Shanghai and human exposure assessment. Food Control 2017, 80, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 31650-2019; Maximum Residue Limits for Veterinary Drugs in Foods. Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Chinese Veterinary Pharmacopoeia Committee. Veterinary Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China: Version 2020; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2021; ISBN 9787109275881. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China. 2292 Bulletin of the Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China. Available online: http://www.moa.gov.cn/nybgb/2015/jiuqi/201712/t20171219_6103873.htm (accessed on 6 May 2022).
- Pena, A.; Silva, L.J.G.; Pereira, A.; Meisel, L.; Lino, C.M. Determination of fluoroquinolone residues in poultry muscle in Portugal. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 2615–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widiastuti, R.; Martindah, E.; Anastasia, Y. Detection and Dietary Exposure Assessment of Fluoroquinolones Residues in Chicken Meat from the Districts of Malang and Blitar, Indonesia. Trop. Anim. Sci. J. 2022, 45, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Cho, S.H.; Shin, D.; Kang, H.S. Prevalence of antibiotic residues and antibiotic resistance in isolates of chicken meat in Korea. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2018, 38, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jammoul, A.; El Darra, N. Evaluation of Antibiotics Residues in Chicken Meat Samples in Lebanon. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunarathna, N.B.; Perera, I.A.; Nayomi, N.T.; Munasinghe, D.M.S.; Silva, S.S.P.; Strashnov, I.; Fernando, B.R. Occurrence of enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin residues in broiler meat sold in Sri Lanka. J. Natn. Sci. Found. Sri Lanka 2021, 49, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramatla, T.; Ngoma, L.; Adetunji, M.; Mwanza, M. Evaluation of Antibiotic Residues in Raw Meat Using Different Analytical Methods. Antibiotics 2017, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Okihashi, M.; Harada, K.; Konishi, Y.; Uchida, K.; Do, M.H.N.; Bui, H.D.; Nguyen, T.D.; Nguyen, P.D.; Chau, V.V.; et al. Antibiotic residue monitoring results for pork, chicken, and beef samples in Vietnam in 2012–2013. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 5141–5145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omotoso, A.B.; Omojola, A.B. Fluoroquinolone residues in raw meat from open markets in Ibadan, Southwest, Nigeria. Int. J. Health Anim. Sci. Food Saf. 2015, 2, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehl, A.; Schmidt, L.J.; Schmidt, L.; Morlock, G.E. High-throughput planar solid-phase extraction coupled to orbitrap high-resolution mass spectrometry via the autoTLC-MS interface for screening of 66 multi-class antibiotic residues in food of animal origin. Food Chem. 2021, 351, 129211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Z.; Liu, Q.; Yang, B.; Xiong, J.; Li, K.; Ahmed, S.; Hong, L.; Chen, P.; He, Q.; Cao, J. Clinical efficacy and residue depletion of 10% enrofloxacin enteric-coated granules in pigs. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitrova, D.J.; Lashev, L.D.; Yanev, S.G.; Pandova, B. Pharmacokinetics of enrofloxacin in turkeys. Res. Vet. Sci. 2007, 82, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- San Martín, B.; Cornejo, J.; Lapierre, L.; Iragüen, D.; Pérez, F.; Hidalgo, H.; Andre, F. Withdrawal time of four pharmaceutical formulations of enrofloxacin in poultry according to different maximum residues limits. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Therap. 2010, 33, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.J. Multiresidue analysis of fluoroquinolone antibiotics in chicken tissue using automated microdialysis-liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2001, 39, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Qiu, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, L. Antibiotic residues in poultry food in Fujian Province of China. Food Addit. Contam. Part B 2020, 13, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, J.; Yan, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, M. Antibiotic residues in cattle and sheep meat and human exposure assessment in southern Xinjiang, China. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 6152–6161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Er, B.; Onurdağ, F.K.; Demirhan, B.; Özgacar, S.Ö.; Öktem, A.B.; Abbasoğlu, U. Screening of quinolone antibiotic residues in chicken meat and beef sold in the markets of Ankara, Turkey. Poult. Sci. 2013, 92, 2212–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakides, D.; Lazaris, A.C.; Arsenoglou, K.; Emmanouil, M.; Kyriakides, O.; Kavantzas, N.; Panderi, I. Dietary Exposure Assessment of Veterinary Antibiotics in Pork Meat on Children and Adolescents in Cyprus. Foods 2020, 9, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallam, K.I.; Saad, F.S.S.; Abdelkhalek, A. Health risk assessment of antimicrobial residues in sheep carcasses marketed in Kuwait. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, B.; Jia, X.; Wu, Y.; Hu, J.; Tu, X.; Zhang, J. Multi-class confirmatory method for analyzing trace levels of tetracyline and quinolone antibiotics in pig tissues by ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 21, 3487–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Evaluation of Certain Veterinary Drug Residues in Food. Available online: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/42127/1/WHO_TRS_879.pdf (accessed on 6 May 2022).
- Zhao, L.; He, Y. The Monitoring Report on Nutrition and Health Status of Chinese Residents (2010–2013) No. 1 Dietary and Nutrient Intake; People’s Medical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2018; p. 129. ISBN 9787117274333. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Dong, G.; Zhao, H.; Chen, M.; Quan, W.; Qu, B. Occurrence and risk assessment of fluoroquinolones and tetracyclines in cultured fish from a coastal region of northern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 8035–8043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, H.; Zhao, L.; Guo, Q.; Ju, L.; Xu, X.; Li, S.; Pu, W.; Cheng, X.; Yu, W.; Yu, D. Trends of Height, Weight and BMI in Chinese Children and Adolescents Aged 6~17. Food Nutr. China 2021, 27, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
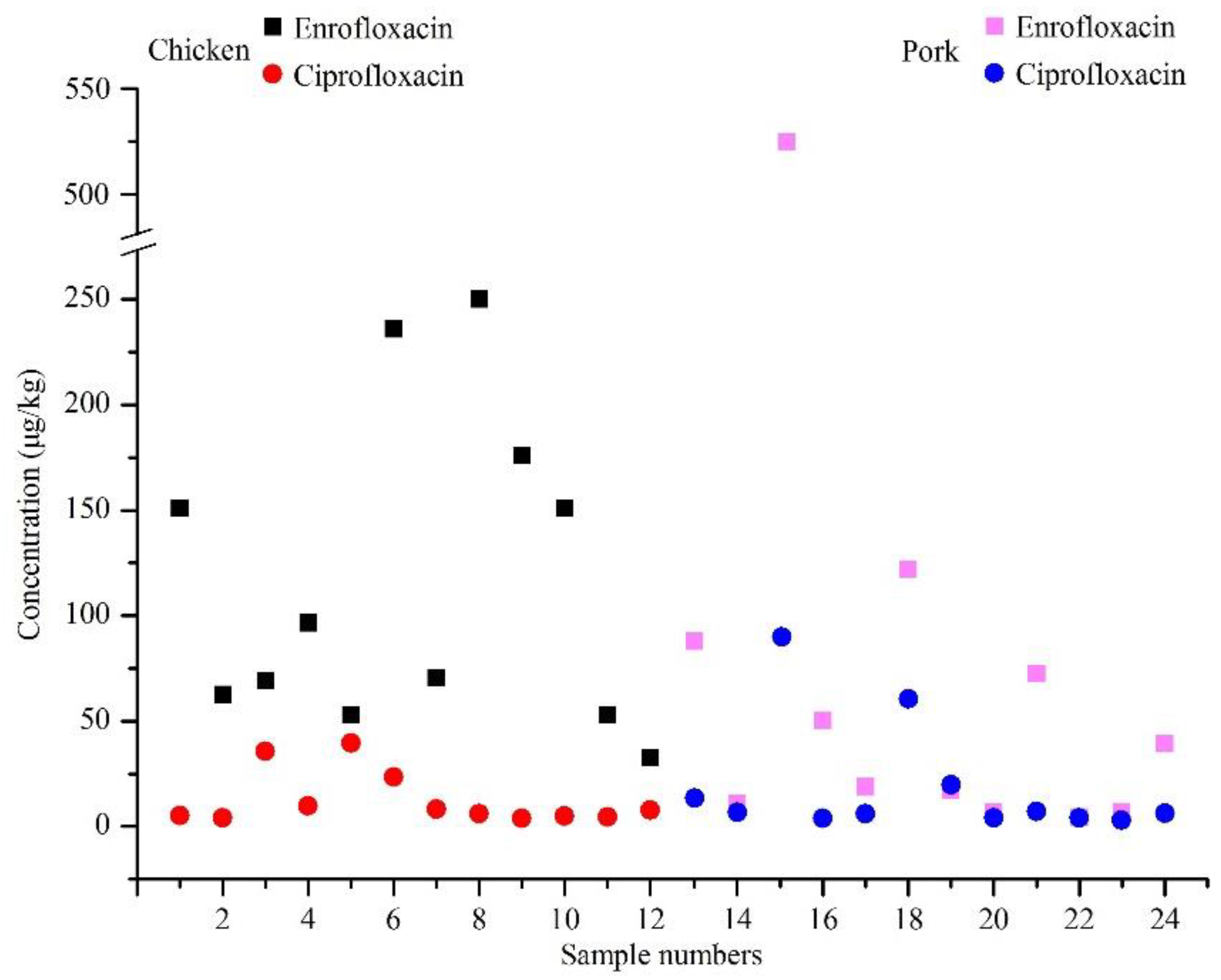
| Antibiotic | Chicken (n = 1754) | Pork (n = 1712) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DF (n, %) | Mean (μg/kg) | Min (μg/kg) | Max (μg/kg) | VF (m, %) | DF (n, %) | Mean (μg/kg) | Min (μg/kg) | Max (μg/kg) | VF (m, %) | |
| Enrofloxacin | 59, 3.36 | 2.07 | 3.05 | 1280 | - | 25, 1.46 | 0.74 | 4.81 | 529 | - |
| Ciprofloxacin | 20, 1.14 | 0.20 | 3.88 | 45.3 | - | 13, 0.76 | 0.14 | 3.88 | 89.9 | - |
| Ciprofloxacin + Enrofloxacin | 67, 3.82 | 2.26 | 3.05 | 1280 | 9, 0.51 | 26, 1.52 | 0.88 | 4.81 | 618.9 | 4, 0.23 |
| Ofloxacin | 1, 0.06 | 0.05 | 92.6 | 92.6 | 1, 0.06 | 5, 0.29 | 0.65 | 3.48 | 848 | 5, 0.29 |
| Norfloxacin | 0, 0.00 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 0, 0.00 | 0, 0.00 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 0, 0.00 |
| Pefloxacin | 0, 0.00 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 0, 0.00 | 0, 0.00 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 0, 0.00 |
| Lomefloxacin | 2, 0.11 | 0.01 | 10.5 | 10.8 | 2, 0.11 | 0, 0.00 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 0, 0.00 |
| Fluoroquinolones | 70, 3.99 | - | - | - | 12, 0.68 | 29, 1.69 | - | - | - | 7, 0.41 |
| Sampling Site Types | Chicken | Pork | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DF a | VF b | DF c | VF d | |
| Country fairs | 4.47% (41/917) | 0.98% (9/917) | 1.88% (17/903) | 0.22% (2/903) |
| Stores | 3.46% (29/837) | 0.36% (3/837) | 1.48% (12/809) | 0.62% (5/809) |
| Sample | Antibiotic | Average Scenario Approach | Worst-Case Scenario Approach | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Children | Adolescents | Adult | Children | Adolescents | Adult | ||||||||
| EDI (ng/kg bw/day) | % ADI (×10−2) | EDI (ng/kg bw/day) | % ADI (×10−2) | EDI (ng/kg bw/day) | % ADI (×10−2) | EDI (ng/kg bw/day) | % ADI | EDI (ng/kg bw/day) | % ADI | EDI (ng/kg bw/day) | % ADI | ||
| Chicken | Ciprofloxacin | 0.965 | - | 0.664 | - | 0.538 | - | 596.8 | - | 410.8 | - | 332.8 | - |
| Enrofloxacin | 0.093 | - | 0.064 | - | 0.052 | - | 21.1 | - | 14.5 | - | 11.8 | - | |
| Ciprofloxacin + Enrofloxacin | 1.054 | 1.70 | 0.725 | 1.17 | 0.588 | 0.95 | 596.8 | 9.62 | 410.8 | 6.62 | 332.8 | 5.37 | |
| Lomefloxacin | 0.005 | - | 0.003 | - | 0.003 | - | 5.0 | - | 3.5 | - | 2.8 | - | |
| Ofloxacin | 0.023 | - | 0.016 | - | 0.013 | - | 43.2 | - | 29.7 | - | 24.1 | - | |
| Pork | Ciprofloxacin | 1.328 | - | 0.880 | - | 0.819 | - | 949.0 | - | 629.1 | - | 585.4 | - |
| Enrofloxacin | 0.251 | - | 0.166 | - | 0.155 | - | 161.3 | - | 106.9 | - | 99.5 | - | |
| Ciprofloxacin + Enrofloxacin | 1.579 | 2.55 | 1.046 | 1.69 | 0.974 | 1.57 | 1110.2 | 17.91 | 736 | 11.87 | 684.9 | 11.05 | |
| Lomefloxacin | ND | - | ND | - | ND | - | ND | - | ND | - | ND | - | |
| Ofloxacin | 1.166 | - | 0.773 | - | 0.719 | - | 1521.2 | - | 1008.5 | - | 938.4 | - | |
| Chicken + Pork | Ciprofloxacin | 2.293 | - | 1.544 | - | 1.357 | - | 1545.8 | - | 1039.9 | - | 918.2 | - |
| Enrofloxacin | 0.344 | - | 0.230 | - | 0.207 | - | 182.4 | - | 121.4 | - | 111.3 | - | |
| Ciprofloxacin + Enrofloxacin | 2.633 | 4.25 | 1.771 | 2.86 | 1.562 | 2.52 | 1707.0 | 27.53 | 1146.8 | 18.50 | 1017.7 | 16.41 | |
| Lomefloxacin | 0.005 | - | 0.003 | - | 0.003 | - | 5.0 | - | 3.5 | - | 2.8 | - | |
| Ofloxacin | 1.189 | - | 0.789 | - | 0.732 | - | 1564.4 | - | 1038.2 | - | 962.5 | - | |
| Antibiotic | Formula | Parention (m/z) | Daughter Ion (m/z) | Cone Voltage (V) | Collision Energy (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ciprofloxacin | C17H18N3FO3 | 332.2 | 314.3 */288.3 | 36/36 | 19/17 |
| Enrofloxacin | C19H22FN3O3 | 360.3 | 316.4 */342.3 | 38/38 | 19/23 |
| Lomefloxacin | C17H19F2N3O3 | 352.3 | 265.2 */308.3 | 36/36 | 23/17 |
| Norfloxacin | C16H18FN3O3 | 320.3 | 302.3 */276.3 | 50/50 | 19/17 |
| Ofloxacin | C18H20FN3O4 | 362.2 | 318.3 */261.2 | 38/38 | 18/27 |
| Pefloxacin | C17H20FN3O3 | 334.3 | 290.3 */233.2 | 38/38 | 17/25 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fei, Z.; Song, S.; Yang, X.; Jiang, D.; Gao, J.; Yang, D. Occurrence and Risk Assessment of Fluoroquinolone Residues in Chicken and Pork in China. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1292. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101292
Fei Z, Song S, Yang X, Jiang D, Gao J, Yang D. Occurrence and Risk Assessment of Fluoroquinolone Residues in Chicken and Pork in China. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(10):1292. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101292
Chicago/Turabian StyleFei, Zhixin, Shufeng Song, Xin Yang, Dingguo Jiang, Jie Gao, and Dajin Yang. 2022. "Occurrence and Risk Assessment of Fluoroquinolone Residues in Chicken and Pork in China" Antibiotics 11, no. 10: 1292. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101292
APA StyleFei, Z., Song, S., Yang, X., Jiang, D., Gao, J., & Yang, D. (2022). Occurrence and Risk Assessment of Fluoroquinolone Residues in Chicken and Pork in China. Antibiotics, 11(10), 1292. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101292






