Socioeconomic Factors Contributing to Antibiotic Resistance in China: A Panel Data Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Statistical Analysis
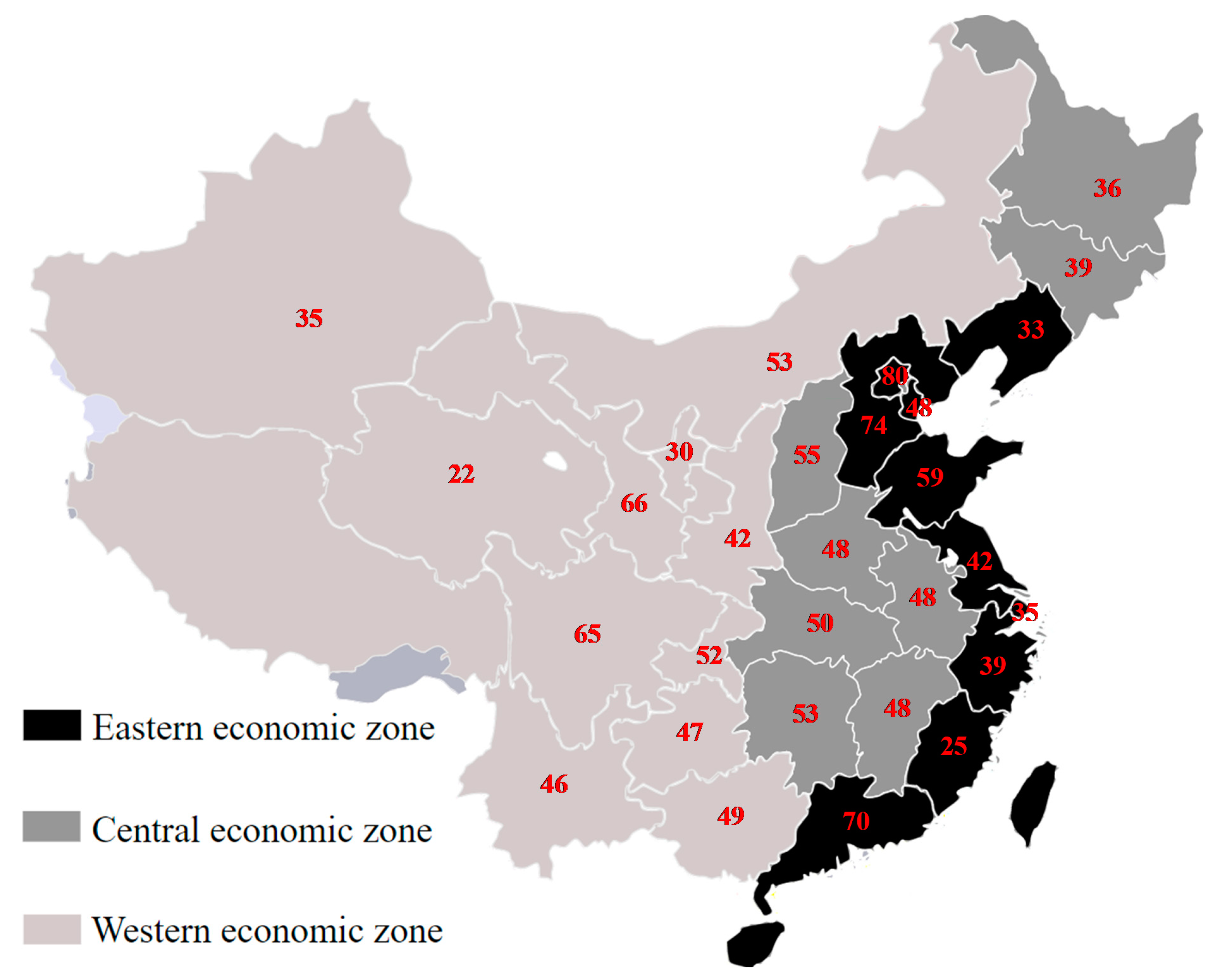
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- World Health Organization. Antibiotic Resistance. 2018. Available online: http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antibiotic-resistance (accessed on 31 August 2018).
- World Health Organization. Global Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance-Message from WHO Director-General. 2018. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/detail/18-07-2018-countries-step-up-to-tackle-antimicrobial-resistance (accessed on 14 April 2019).
- Public Health England. Health Matters: Antimicrobial Resistance. 2015. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/organisations/public-health-england (accessed on 11 December 2018).
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. The Bacterial Challenge Time to React. 2008. Available online: https://ecdc.europa.eu/sites/portal/files/media/en/publications/Publications/0909_TER_The_Bacterial_Challenge_Time_to_React.pdf (accessed on 11 December 2018).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States. 2013. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/pdf/ar-threats-2013-508.pdf (accessed on 11 December 2018).
- O’Neill, J. Tacking Drug-Resistant Infections Globally: Final Report and Recommendations. 2016. Available online: https://amr-review.org/sites/default/files/160525_Final%20paper_with%20cover.pdf (accessed on 11 December 2018).
- Yasir, M.; Ajlan, A.M.; Shakil, S.; Jiman-Fatani, A.A.; Almasaudi, S.B.; Farman, M.; Baazeem, Z.M.; Baabdullah, R.; Alawi, M.; Al-Abdullah, N.; et al. Molecular characterization, antimicrobial resistance and clinico-bioinformatics approaches to address the problem of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli in western Saudi Arabia. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. Antimicrobial Resistance Global Report on Surveillance. 2014. Available online: https://www.who.int/drugresistance/documents/surveillancereport/en/ (accessed on 11 December 2018).
- Su, C.; Morgan, C.E.; Kambakam, S.; Rajavel, M.; Scott, H.; Huang, W.; Emerson, C.C.; Taylor, D.J.; Stewart, P.L.; Bonomo, R.A.; et al. Cryo-Electron microscopy structure of an Acinetobacter baumannii multidrug efflux pump. mBio 2019, 10, e01295-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heddini, A.; Carsm, O.; Qiangm, S.; Tomson, G. Antibiotic resistance in China—A major future challenge. Lancet 2009, 373, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Center for Disease Prevention and Control. Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance in Europe: Annual Report of the European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Network (EARS-Net) 2017. 2018. Available online: https://ecdc.europa.eu/sites/portal/files/documents/EARS-Net-report-2017-update-jan-2019.pdf (accessed on 7 August 2019).
- Chatterjee, A.; Modarai, M.; Naylor, N.R.; Boyd, S.E.; Atun, R.; Barlow, J.; Holmes, A.H.; Johnson, A.; Robotham, J.V. Quantifying drivers of antibiotic resistance in humans: A systematic review. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, e368–e378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collignon, P.; Beggs, J.J. Socioeconomic enablers for contagion: Factors impelling the antimicrobial resistance epidemic. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Collignon, P.; Athukorala, P.; Senanayake, S.; Khan, F. Antimicrobial resistance: The major contribution of poor governance and corruption to this growing problem. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, R.; Zhu, N.J.; Leather, A.J.M.; Holmes, A.; Ferlie, E.; Ahmad, R.; Birgand, G.; Castro-Sanchez, E.; Charani, E.; Dhar, P.; et al. Strengthening strategic management approaches to address antimicrobial resistance in global human health: A scoping review. BMJ Glob. Health 2019, 4, e001730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savoldi, A.; Carrara, E.; Gladstone, B.P.; Azzini, A.M.; Goepel, S.; Tacconelli, E. Gross national income and antibiotic resistance in invasive isolates: Analysis of the top-ranked antibiotic-resistant bacteria on the 2017 WHO priority list. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 3619–3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsan, M.; Schoemaker, L.; Eggleston, K.; Kammili, N.; Kolli, P.; Bhattacharya, J. Out-of-pocket health expenditures and antimicrobial resistance in low-income and middle-income countries: An economic analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collignon, P.; Beggs, J.J.; Walsh, T.R.; Gandra, S.; Laxminarayan, R. Anthropological and socioeconomic factors contributing to global antimicrobial resistance: A univariate and multivariable analysis. Lancet Planet. Health 2018, 2, e398–e405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Uria, G.; Gandra, S.; Laxminarayan, R. Poverty and prevalence of antimicrobial resistance in invasive isolates. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 52, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alividza, V.; Mariano, V.; Ahmad, R.; Charani, E.; Rawson, T.M.; Holmes, A.H.; Castro-Sanchez, E. Investigating the impact of poverty on colonization and infection with drug-resistant organisms in humans: A systematic review. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2018, 7, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Wang, W.; Regev-Yochay, G.; Lipsitch, M.; Hanage, W.P. Antibiotics in agriculture and the risk to human health: How worried should we be? Evol. Appl. 2015, 8, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ben, Y.; Fu, C.; Hu, M.; Liu, L.; Wong, M.H.; Zheng, C. Human health risk assessment of antibiotic resistance associated with antibiotic residues in the environment: A review. Environ. Res. 2019, 169, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, X.; Zhang, H.; Hu, X.; Gu, S.; Li, Y.; Gu, Y.; Huang, M.; Sun, X.; Wei, J.; Dong, H. A comparative study of catastrophic health expenditure in Zhejiang and Qinghai province, China. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2018, 18, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.; Zhu, D.; Wang, F.; Wang, M. Current status and trends of antibacterial resistance in China. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 67, S128–S134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- China Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance System. Antimicrobial resistance of bacteria: Surveillance report from China Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance System in 2014–2019. Chin. J. Infect. Control 2021, 20, 15–31. [Google Scholar]
- China Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance System. Annual Report of the China Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance, 2014–2018. 2018. Available online: http://www.carss.cn/Report/Details?aId=552 (accessed on 14 February 2019).
- National Bureau of Statistics. China Statistical Yearbook (2015–2019). 2018. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/ndsj/2018/indexch.htm (accessed on 7 May 2020).
- National Health Commission. China Health Statistical Yearbook (2015–2019). 2018. Available online: http://www.nhc.gov.cn/wjw/tjnj/list.shtml (accessed on 7 May 2020).
- Zhen, X.; Stålsby Lundborg, C.; Sun, X.; Hu, X.; Dong, H. The Clinical and Economic Impact of Antibiotic Resistance in China: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, Y.; Li, L. China’s national plan to combat antimicrobial resistance. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 1216–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A. Antibiotic Resistance: China Battles Population, Size. 2020. Available online: https://www.downtoearth.org.in/news/health/antibiotic-resistance-china-battles-population-size-68958 (accessed on 20 May 2021).
- Klein, E.Y.; Van Boeckel, T.P.; Martinez, E.M.; Pant, S.; Gandra, S.; Levin, S.A.; Goossens, H.; Laxminarayan, R. Global increase and geographic convergence in antibiotic consumption between 2000 and 2015. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E3463–E3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clemens, J.; Gottlieb, J.D. Do physicians’ financial incentives affect medical treatment and patient health? Am. Econ. Rev. 2014, 104, 1320–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, H.J.; Bogg, L.; Rehnberg, C.; Diwan, V. Association between health insurance and antibiotics prescribing in four counties in rural China. Health Policy 1999, 48, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, H.; Ferech, M.; Vander, S.R.; Elseviers, M. Outpatient antibiotic use in Europe and association with resistance: A cross-national database study. Lancet 2005, 365, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masiero, G.; Filippini, M.; Ferech, M.; Goossens, H. Socioeconomic determinants of outpatient antibiotic use in Europe. Int. J. Public Health 2010, 55, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rusic, D.; Bozic, J.; Bukic, J.; Vilovic, M.; Tomicic, M.; Seselja, P.A.; Leskur, D.; Modun, D.; Cohadzic, T.; Tomic, S. Antimicrobial resistance: Physicians’ and pharmacists’ perspective. Microb. Drug Resist. 2020, 27, 670–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, P.J. Corruption in global health: The open secret. Lancet 2019, 394, 2119–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vian, T. Anti-corruption, transparency and accountability in health: Concepts, frameworks, and approaches. Glob. Health Action 2020, 13, 1694744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Variables | 30 Provinces | Eastern Economic Zone | Central Economic Zone | Western Economic Zone | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| Aggregate resistance, % | 41.0 | 6.7 | 43.0 | 6.4 | 43.0 | 7.9 | 37.6 | 4.6 |
| MRSA, % | 32.9 | 8.4 | 35.6 | 8.5 | 32.9 | 9.2 | 30.2 | 6.9 |
| 3GCREC, % | 56.4 | 5.4 | 56.5 | 5.2 | 58.7 | 6.0 | 54.6 | 4.5 |
| 3GCRKP, % | 33.8 | 9.5 | 37.0 | 7.8 | 37.3 | 10.2 | 28.0 | 7.7 |
| Education, % of finishing secondary education | 69.0 | 8.6 | 75.0 | 7.6 | 70.6 | 3.9 | 61.8 | 6.7 |
| GDP per capita, log | 14,813.5 | 1.5 | 21,306.2 | 1.5 | 12,304.8 | 1.2 | 11,787.3 | 1.4 |
| OOP health expenditure, % of total health expenditures | 29.3 | 4.9 | 27.3 | 5.8 | 32.9 | 3.4 | 28.8 | 3.3 |
| Hospital bed density, number of beds per 1000 population | 5.4 | 0.8 | 5.1 | 0.8 | 5.5 | 0.7 | 5.8 | 0.7 |
| Physician density, number of physicians per 1000 population | 6.3 | 1.2 | 6.8 | 1.5 | 5.7 | 0.7 | 6.3 | 0.9 |
| Public toilet density, number of public toilets per 10,000 population | 2.9 | 1.1 | 2.7 | 0.8 | 2.9 | 0.8 | 3.3 | 1.4 |
| Variables | 30 Provinces | Eastern Economic Zone | Central Economic Zone | Western Economic Zone | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | SE | p-Value | 95% CI | B | SE | p-Value | 95% CI | B | SE | p-Value | 95% CI | B | SE | p-Value | 95% CI | |||||
| Education, % of finishing secondary education | 0.08 | 0.13 | 0.547 | −0.17 | 0.33 | −0.13 | 0.24 | 0.581 | −0.62 | 0.35 | −0.37 | 0.36 | 0.303 | −1.07 | 0.33 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.361 | −0.16 | 0.43 |
| GDP per capita, log | 11.64 | 5.76 | 0.046 | 0.22 | 23.07 | 26.64 | 8.54 | 0.004 | 9.28 | 44.00 | 28.24 | 24.31 | 0.245 | −19.40 | 75.89 | 3.40 | 10.11 | 0.739 | −17.15 | 23.95 |
| OOP health expenditure, % of total health expenditures | −0.09 | 0.12 | 0.458 | −0.33 | 0.15 | −0.01 | 0.28 | 0.967 | −0.57 | 0.55 | −0.70 | 0.45 | 0.116 | −1.58 | 0.17 | −0.05 | 0.17 | 0.746 | −0.39 | 0.28 |
| Hospital bed density, number of beds per 1000 population | −0.87 | 0.90 | 0.339 | −2.66 | 0.92 | −0.08 | 1.93 | 0.966 | −4.00 | 3.84 | −2.74 | 2.79 | 0.326 | −8.21 | 2.73 | 1.21 | 1.24 | 0.335 | −1.30 | 3.72 |
| Physician density, number of physicians per 1000 population | 0.18 | 0.87 | 0.836 | −1.54 | 1.90 | −0.66 | 1.80 | 0.717 | −4.32 | 3.00 | −0.05 | 3.41 | 0.989 | −6.74 | 6.64 | −1.85 | 1.11 | 0.106 | −4.11 | 0.41 |
| Public toilet density, number of public toilets per 10,000 population | 0.04 | 0.26 | 0.889 | −0.48 | 0.55 | −0.51 | 0.41 | 0.221 | −1.33 | 0.32 | 1.05 | 1.24 | 0.397 | −1.38 | 3.49 | −0.04 | 0.38 | 0.923 | −0.81 | 0.74 |
| Year | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015 | −2.66 | 1.11 | 0.018 | −4.86 | -0.46 | −5.52 | 1.61 | 0.002 | −8.78 | −2.25 | −6.79 | 5.20 | 0.192 | −16.99 | 3.40 | −0.87 | 1.73 | 0.617 | −4.39 | 2.64 |
| 2016 | −3.52 | 0.81 | <0.000 | −5.12 | -1.92 | −3.68 | 1.23 | 0.005 | −6.18 | −1.18 | −6.37 | 3.31 | 0.055 | −12.86 | 0.13 | −2.85 | 0.99 | 0.007 | −4.86 | −0.83 |
| 2017 | −6.73 | 1.42 | <0.000 | −9.55 | -3.91 | −8.36 | 2.32 | 0.001 | −13.07 | −3.64 | −11.87 | 6.24 | 0.057 | −24.10 | 0.36 | −4.36 | 1.79 | 0.020 | −8.00 | −0.73 |
| 2018 | −6.77 | 1.45 | <0.000 | −9.65 | -3.89 | −6.59 | 2.49 | 0.012 | −11.64 | −1.53 | −9.86 | 5.18 | 0.057 | −20.00 | 0.29 | −5.22 | 1.87 | 0.009 | −9.03 | −1.42 |
| (Constant) | 0.08 | 0.13 | 0.547 | −0.17 | 0.33 | −0.13 | 0.24 | 0.581 | −0.62 | 0.35 | -0.37 | 0.36 | 0.303 | −1.07 | 0.33 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.361 | −0.16 | 0.43 |
| p-value | <0.000 | <0.000 | <0.000 | <0.000 | ||||||||||||||||
| R2 | 0.768 | 0.817 | 0.823 | 0.828 | ||||||||||||||||
| Model (Hausman test) | Fixed effects (0.8969) | Fixed effects (0.0927) | Random effects (0.0441) | Fixed effects (0.8549) | ||||||||||||||||
| Variables | MRSA | 3GCREC | 3GCRKP | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | SE | p-Value | 95% CI | B | SE | p-Value | 95% CI | B | SE | p-Value | 95% CI | ||||
| Education, % of finishing secondary education | −0.03 | 0.22 | 0.887 | −0.46 | 0.40 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.788 | −0.22 | 0.29 | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.276 | −0.18 | 0.63 |
| GDP per capita, log | 44.49 | 9.95 | <0.000 | 24.77 | 64.20 | −11.43 | 5.86 | 0.054 | −23.05 | 0.19 | 1.84 | 9.41 | 0.845 | −16.81 | 20.49 |
| OOP health expenditure, % of total health expenditures | 0.38 | 0.21 | 0.070 | −0.03 | 0.80 | −0.04 | 0.12 | 0.750 | −0.28 | 0.20 | −0.61 | 0.20 | 0.002 | −1.01 | −0.22 |
| Hospital bed density, number of beds per 1000 population | 0.52 | 1.56 | 0.740 | −2.57 | 3.61 | −1.22 | 0.92 | 0.187 | −3.04 | 0.60 | −1.91 | 1.48 | 0.198 | −4.84 | 1.01 |
| Physician density, number of physicians per 1000 population | −3.04 | 1.50 | 0.045 | −6.01 | −0.07 | 2.10 | 0.88 | 0.019 | 0.35 | 3.85 | 1.48 | 1.42 | 0.298 | −1.33 | 4.29 |
| Public toilet density, number of public toilets per 10,000 population | 0.60 | 0.45 | 0.183 | −0.29 | 1.48 | −0.24 | 0.26 | 0.361 | −0.76 | 0.28 | −0.25 | 0.42 | 0.557 | −1.09 | 0.59 |
| Year | |||||||||||||||
| 2015 | −6.75 | 1.91 | 0.001 | −10.54 | −2.96 | 0.90 | 1.13 | 0.428 | −1.34 | 3.13 | −2.11 | 1.81 | 0.245 | −5.70 | 1.47 |
| 2016 | −1.96 | 1.39 | 0.161 | −4.72 | 0.80 | −3.29 | 0.82 | <0.000 | −4.91 | −1.66 | −5.31 | 1.32 | <0.000 | −7.92 | −2.70 |
| 2017 | −8.79 | 2.45 | 0.001 | −13.65 | −3.92 | −4.41 | 1.45 | 0.003 | −7.28 | −1.54 | −6.99 | 2.32 | 0.003 | −11.59 | −2.39 |
| 2018 | −5.45 | 2.51 | 0.032 | −10.41 | −0.48 | −7.01 | 1.48 | <0.000 | −9.94 | −4.09 | −7.84 | 2.37 | 0.001 | −12.54 | −3.14 |
| (Constant) | −0.03 | 0.22 | 0.887 | −0.46 | 0.40 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.788 | −0.22 | 0.29 | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.276 | −0.18 | 0.63 |
| p-value | <0.000 | <0.000 | <0.000 | ||||||||||||
| R2 | 0.580 | 0.791 | 0.527 | ||||||||||||
| Model (Hausman test) | Fixed-effects (0.2943) | Fixed-effects (0.5773) | Fixed-effects (0.4293) | ||||||||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhen, X.; Chen, J.; Sun, X.; Sun, Q.; Guo, S.; Stålsby Lundborg, C. Socioeconomic Factors Contributing to Antibiotic Resistance in China: A Panel Data Analysis. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 994. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10080994
Zhen X, Chen J, Sun X, Sun Q, Guo S, Stålsby Lundborg C. Socioeconomic Factors Contributing to Antibiotic Resistance in China: A Panel Data Analysis. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(8):994. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10080994
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhen, Xuemei, Jingchunyu Chen, Xueshan Sun, Qiang Sun, Shasha Guo, and Cecilia Stålsby Lundborg. 2021. "Socioeconomic Factors Contributing to Antibiotic Resistance in China: A Panel Data Analysis" Antibiotics 10, no. 8: 994. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10080994
APA StyleZhen, X., Chen, J., Sun, X., Sun, Q., Guo, S., & Stålsby Lundborg, C. (2021). Socioeconomic Factors Contributing to Antibiotic Resistance in China: A Panel Data Analysis. Antibiotics, 10(8), 994. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10080994







