Free-Floating Aggregate and Single-Cell-Initiated Biofilms of Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strain and Culture Conditions
2.2. Bacterial Aggregate Formation
2.3. Biofilm Growth Assay
2.4. Ti Disc Modification and Characterization
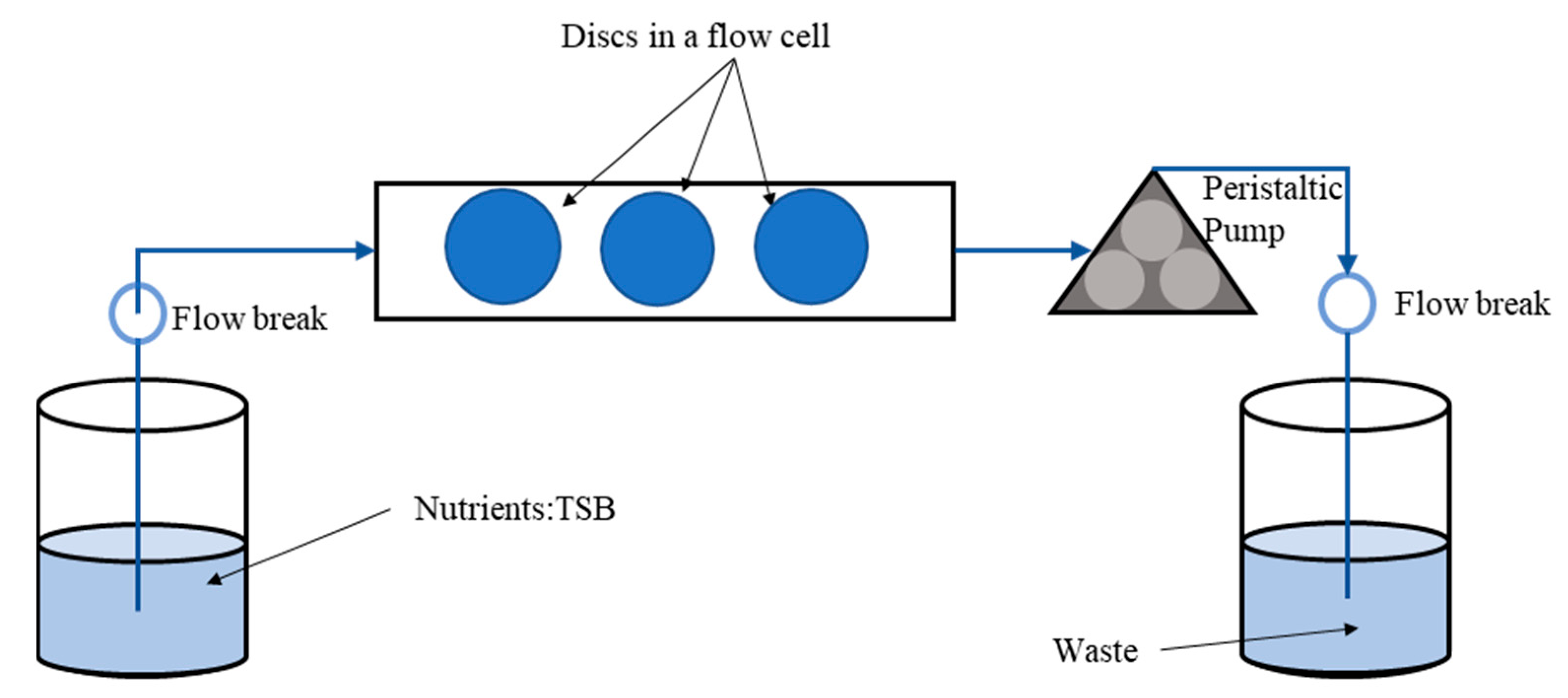
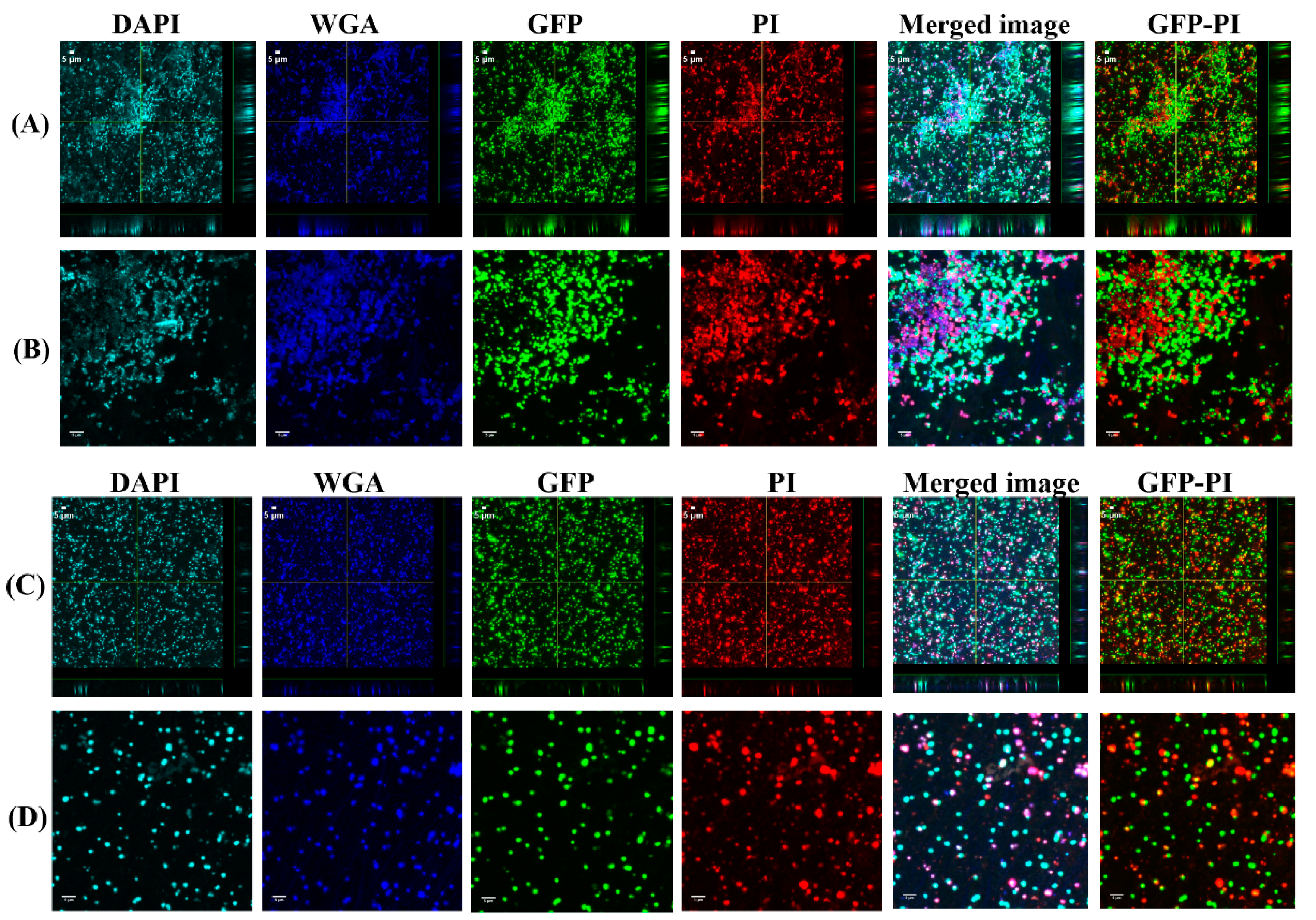
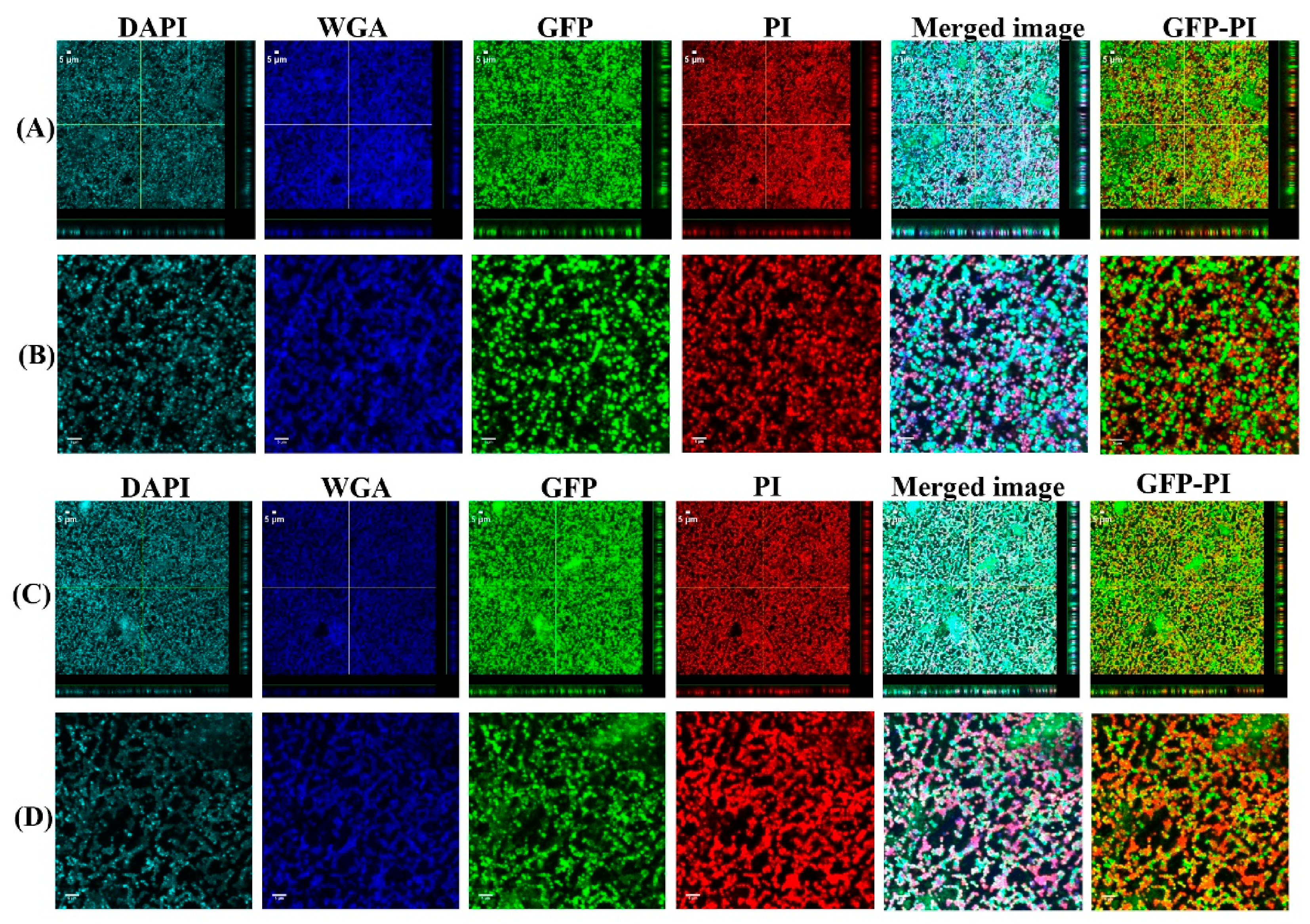
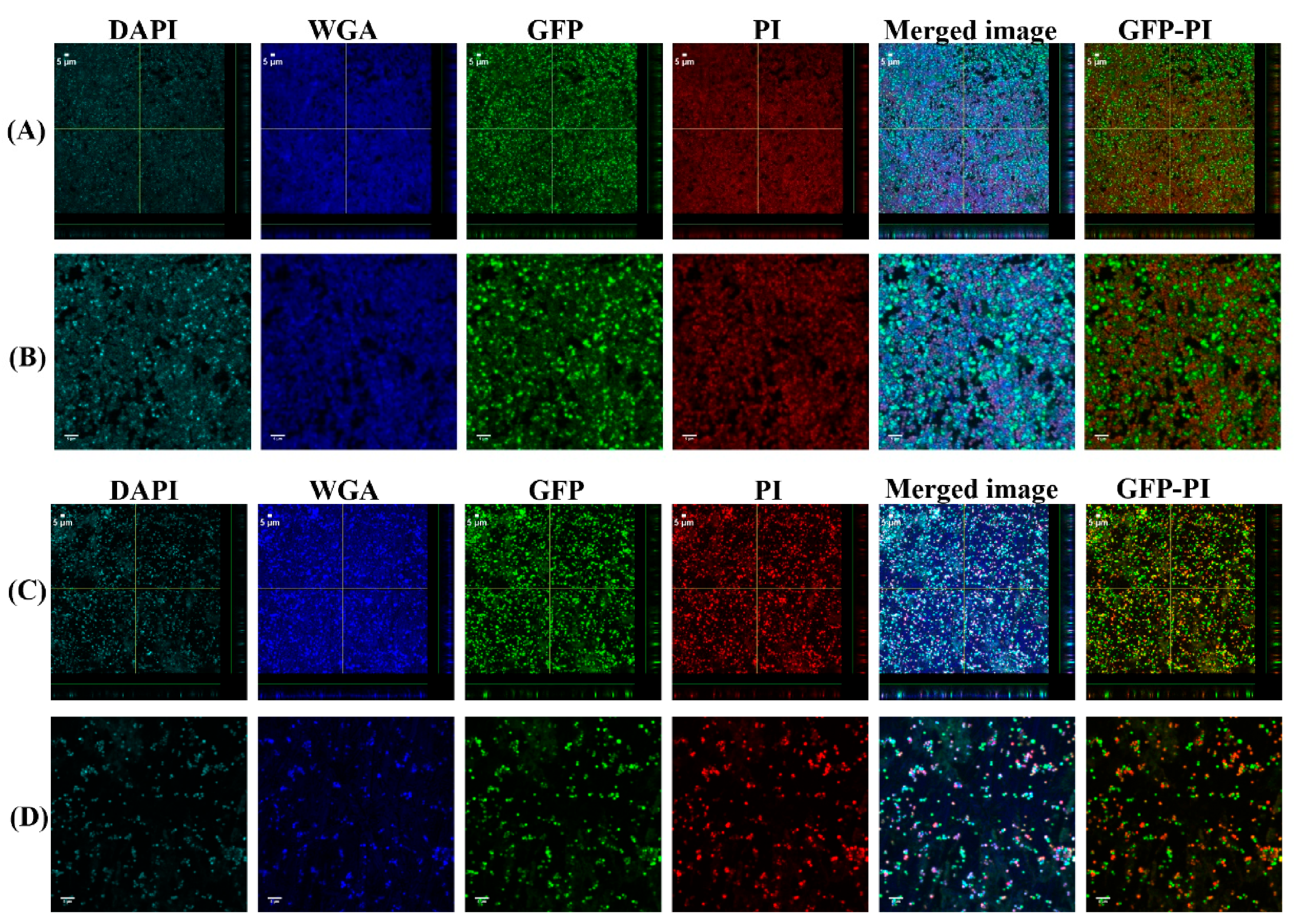
2.5. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM) Assessment of Biofilms Formed from Aggregates and Single Cells on Ti Discs
2.6. Antibiotic Treatment Exposure
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
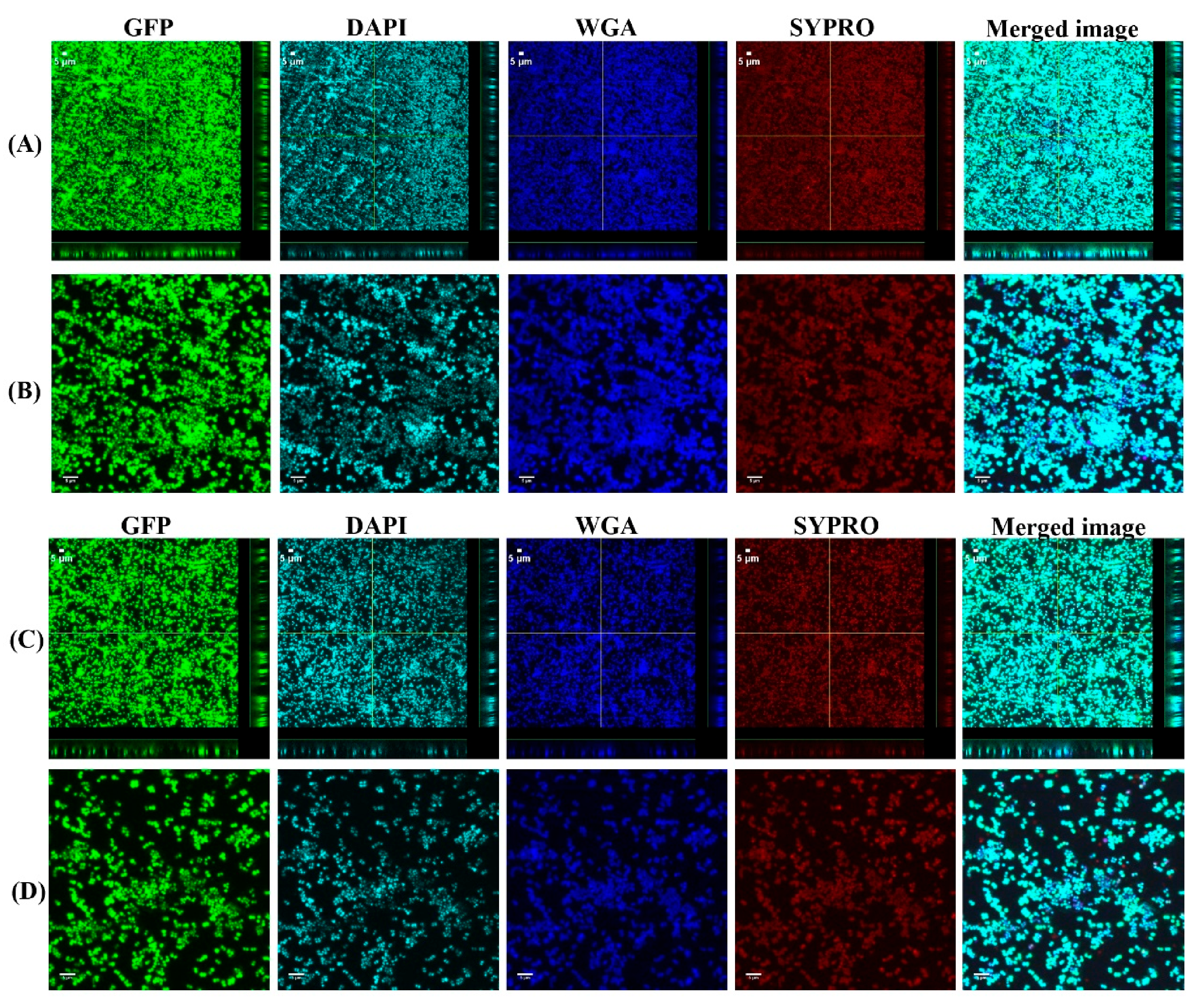
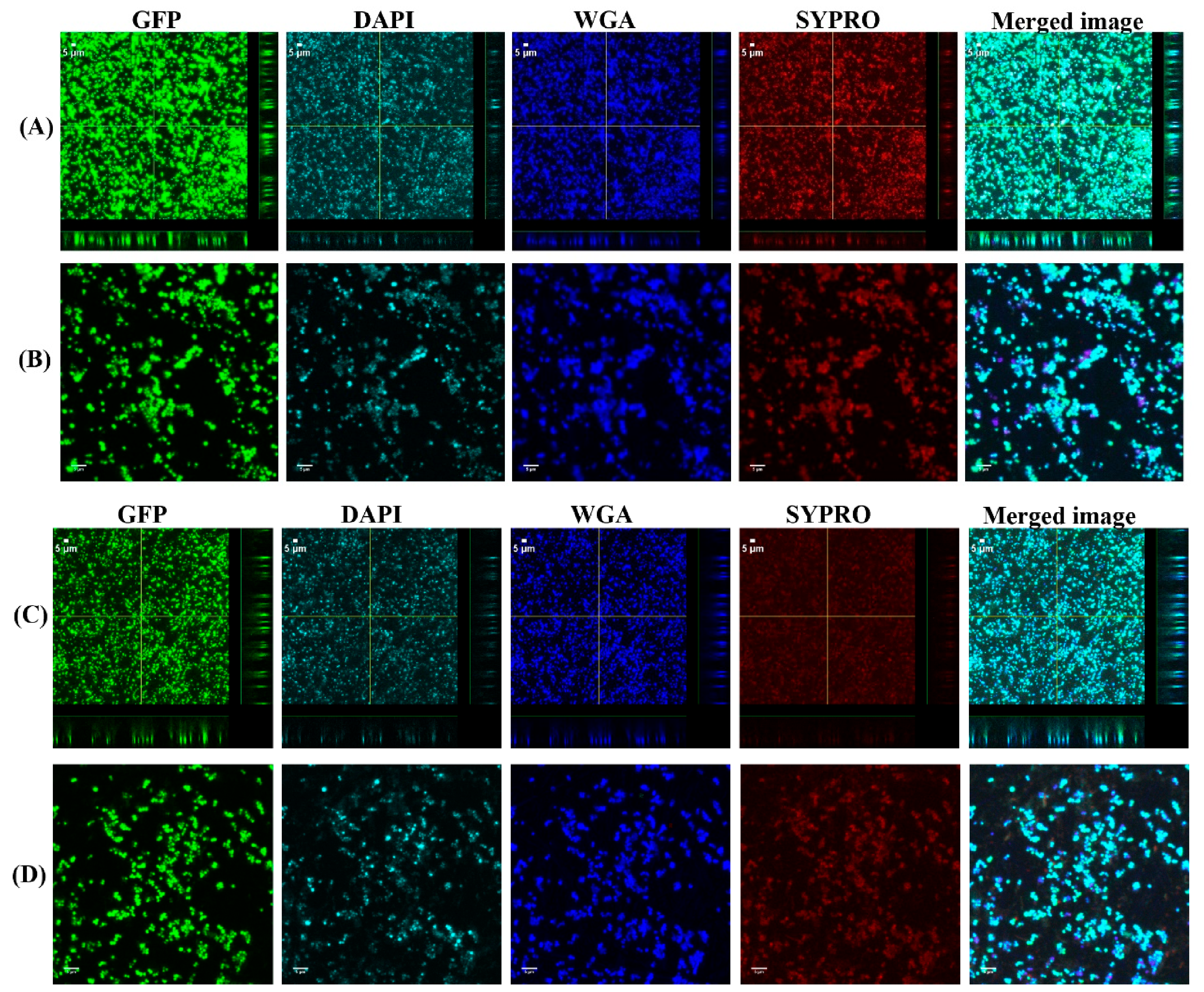
3.1. Biofilms Formed from SF Induced Aggregate and Single Cells on Ti discs
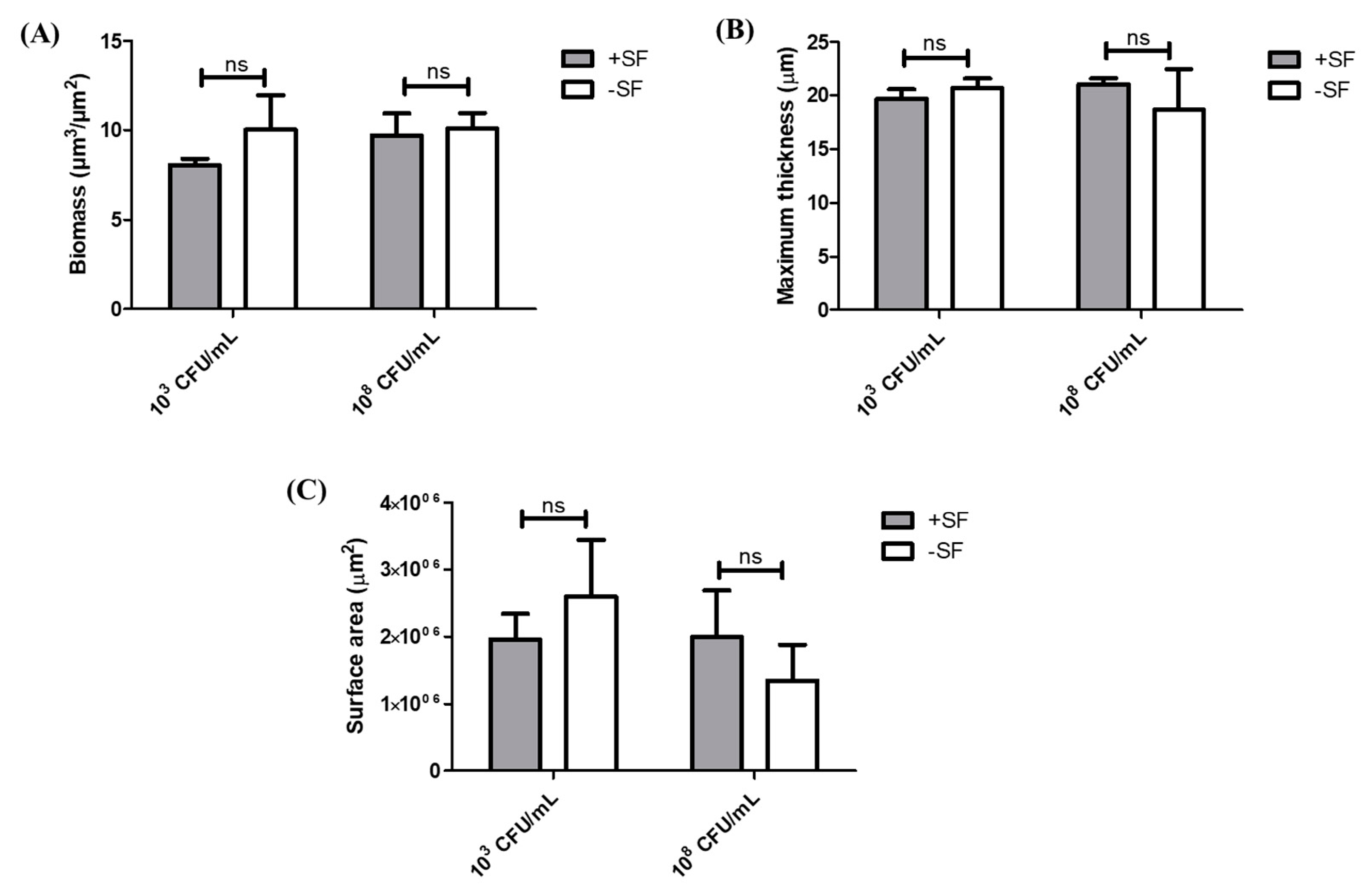
3.2. COMSTAT Analysis of Biofilm Formed from SF Induced Aggregates and Single Cells
3.3. Vancomycin Treatment of Biofilms Formed from SF Induced Aggregate and Single Cells on Ti
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zimmerli, W. Clinical presentation and treatment of orthopaedic implant-associated infection. J. Intern. Med. 2014, 276, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, E.M.; Parvizi, J.; Gehrke, T.; Aiyer, A.; Battenberg, A.; Brown, S.A.; Callaghan, J.J.; Citak, M.; Egol, K.; Garrigues, G.E. 2018 international consensus meeting on musculoskeletal infection: Research priorities from the general assembly questions. J. Orthop. Res. 2019, 37, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremers, H.M.; Larson, D.R.; Crowson, C.S.; Kremers, W.K.; Washington, R.E.; Steiner, C.A.; Jiranek, W.A.; Berry, D.J. Prevalence of total hip and knee replacement in the United States. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Vol. 2015, 97, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anonymous. National Hospital Discharge Survey: 2010 Table, Procedures by Selected Patient Characteristics. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, GA, USA. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhds/4procedures/2010pro4_numberprocedureage.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2019).
- Kurtz, S.; Ong, K.; Lau, E.; Mowat, F.; Halpern, M. Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2007, 89, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zmistowski, B.; Karam, J.A.; Durinka, J.B.; Casper, D.S.; Parvizi, J. Periprosthetic joint infection increases the risk of one-year mortality. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2013, 95, 2177–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, Y.; Chang, C.-H.; Lin, Y.-C.; Lee, S.-H.; Hsieh, P.-H.; Chang, Y. Different microbiological profiles between hip and knee prosthetic joint infections. J. Orthop. Surg. 2019, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alhede, M.; Kragh, K.N.; Qvortrup, K.; Allesen-Holm, M.; van Gennip, M.; Christensen, L.D.; Jensen, P.Ø.; Nielsen, A.K.; Parsek, M.; Wozniak, D. Phenotypes of non-attached Pseudomonas aeruginosa aggregates resemble surface attached biofilm. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragh, K.N.; Hutchison, J.B.; Melaugh, G.; Rodesney, C.; Roberts, A.E.; Irie, Y.; Jensen, P.Ø.; Diggle, S.P.; Allen, R.J.; Gordon, V. Role of multicellular aggregates in biofilm formation. MBio 2016, 7, e00237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindsay, D.; Von Holy, A. Bacterial biofilms within the clinical setting: What healthcare professionals should know. J. Hosp. Infect. 2006, 64, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoodley, P.; Conti, S.F.; DeMeo, P.J.; Nistico, L.; Melton-Kreft, R.; Johnson, S.; Darabi, A.; Ehrlich, G.D.; Costerton, J.W.; Kathju, S. Characterization of a mixed MRSA/MRSE biofilm in an explanted total ankle arthroplasty. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 62, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gilbertie, J.M.; Schnabel, L.V.; Hickok, N.J.; Jacob, M.E.; Conlon, B.P.; Shapiro, I.M.; Parvizi, J.; Schaer, T.P. Equine or porcine synovial fluid as a novel ex vivo model for the study of bacterial free-floating biofilms that form in human joint infections. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bay, L.; Kragh, K.N.; Eickhardt, S.R.; Poulsen, S.S.; Gjerdrum, L.M.R.; Ghathian, K.; Calum, H.; Ågren, M.S.; Bjarnsholt, T. Bacterial aggregates establish at the edges of acute epidermal wounds. Adv. Wound Care 2018, 7, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirketerp-Møller, K.; Jensen, P.Ø.; Fazli, M.; Madsen, K.G.; Pedersen, J.; Moser, C.; Tolker-Nielsen, T.; Høiby, N.; Givskov, M.; Bjarnsholt, T. Distribution, organization, and ecology of bacteria in chronic wounds. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 2717–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fazli, M.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Kirketerp-Møller, K.; Jørgensen, B.; Andersen, A.S.; Krogfelt, K.A.; Givskov, M.; Tolker-Nielsen, T. Nonrandom distribution of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus in chronic wounds. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 4084–4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crosby, H.A.; Kwiecinski, J.; Horswill, A.R. Staphylococcus aureus aggregation and coagulation mechanisms, and their function in host–pathogen interactions. In Advances in Applied Microbiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 41, pp. 1–41. [Google Scholar]
- Dastgheyb, S.S.; Hammoud, S.; Ketonis, C.; Liu, A.Y.; Fitzgerald, K.; Parvizi, J.; Purtill, J.; Ciccotti, M.; Shapiro, I.M.; Otto, M. Staphylococcal persistence due to biofilm formation in synovial fluid containing prophylactic cefazolin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 2122–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dastgheyb, S.S.; Villaruz, A.E.; Le, K.Y.; Tan, V.Y.; Duong, A.C.; Chatterjee, S.S.; Cheung, G.Y.; Joo, H.-S.; Hickok, N.J.; Otto, M. Role of phenol-soluble modulins in formation of Staphylococcus aureus biofilms in synovial fluid. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 2966–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perez, K.; Patel, R. Biofilm-like aggregation of Staphylococcus epidermidis in synovial fluid. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gruber, B.F.; Miller, B.S.; Onnen, J.; Welling, R.; Wojtys, E.M. Antibacterial properties of synovial fluid in the knee. J. Knee Surg. 2008, 21, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastgheyb, S.; Parvizi, J.; Shapiro, I.M.; Hickok, N.J.; Otto, M. Effect of biofilms on recalcitrance of staphylococcal joint infection to antibiotic treatment. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 211, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, G.L.; Miller, H.G.; Borenstein, D.G. Synovial fluid inhibits killing of Staphylococcus aureus by neutrophils. Infect. Immun. 1983, 40, 1004–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Özcan, M.; Hämmerle, C. Titanium as a reconstruction and implant material in dentistry: Advantages and pitfalls. Materials 2012, 5, 1528–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fürst, M.M.; Salvi, G.E.; Lang, N.P.; Persson, G.R. Bacterial colonization immediately after installation on oral titanium implants. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2007, 18, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Noort, R. Titanium: The implant material of today. J. Mater. Sci. 1987, 22, 3801–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, L.G.; Richards, R.G. Staphylococci and implant surfaces: A review. Injury 2006, 37, S3–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meto, A.; Conserva, E.; Liccardi, F.; Colombari, B.; Consolo, U.; Blasi, E. Differential efficacy of two dental implant decontamination techniques in reducing microbial biofilm and re-growth onto titanium disks in vitro. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, T.T.; Gupta, N.K.; Pestrak, M.J.; Dusane, D.H.; Harro, J.M.; Horswill, A.R.; Stoodley, P. Staphylococcus aureus Aggregates on Orthopedic Materials under Varying Levels of Shear Stress. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e01234-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestrak, M.J.; Gupta, T.T.; Dusane, D.H.; Guzior, D.V.; Staats, A.; Harro, J.; Horswill, A.R.; Stoodley, P. Investigation of synovial fluid induced Staphylococcus aureus aggregate development and its impact on surface attachment and biofilm formation. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231791. [Google Scholar]
- Chiu, I.M.; Heesters, B.A.; Ghasemlou, N.; Von Hehn, C.A.; Zhao, F.; Tran, J.; Wainger, B.; Strominger, A.; Muralidharan, S.; Horswill, A.R. Bacteria activate sensory neurons that modulate pain and inflammation. Nature 2013, 501, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heydorn, A.; Nielsen, A.T.; Hentzer, M.; Sternberg, C.; Givskov, M.; Ersbøll, B.K.; Molin, S. Quantification of biofilm structures by the novel computer program COMSTAT. Microbiology 2000, 146, 2395–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vorregaard, M. Comstat2-a Modern 3D Image Analysis Environment for Biofilms. Master’s Thesis, Technical University of Denmark, Lyngby, Denmark, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ibberson, C.B.; Parlet, C.P.; Kwiecinski, J.; Crosby, H.A.; Meyerholz, D.K.; Horswill, A.R. Hyaluronan modulation impacts Staphylococcus aureus biofilm infection. Infect. Immun. 2016, 84, 1917–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurtz, S.M.; Lau, E.; Watson, H.; Schmier, J.K.; Parvizi, J. Economic burden of periprosthetic joint infection in the United States. J. Arthroplast. 2012, 27, 61–65.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swearingen, M.C.; DiBartola, A.C.; Dusane, D.; Granger, J.; Stoodley, P. 16S rRNA analysis provides evidence of biofilms on all components of three infected periprosthetic knees including permanent braided suture. Pathog. Dis. 2016, 74, ftw083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bidossi, A.; Bottagisio, M.; Savadori, P.; De Vecchi, E. Identification and Characterization of Planktonic Biofilm-Like Aggregates in Infected Synovial Fluids From Joint Infections. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervino, G.; Meto, A.; Fiorillo, L.; Odorici, A.; Meto, A.; D’Amico, C.; Oteri, G.; Cicciù, M. Surface Treatment of the Dental Implant with Hyaluronic Acid: An Overview of Recent Data. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melaugh, G.; Hutchison, J.; Kragh, K.N.; Irie, Y.; Roberts, A.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Diggle, S.P.; Gordon, V.D.; Allen, R.J. Shaping the growth behaviour of biofilms initiated from bacterial aggregates. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haaber, J.; Cohn, M.T.; Frees, D.; Andersen, T.J.; Ingmer, H. Planktonic aggregates of Staphylococcus aureus protect against common antibiotics. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inman, R.; Chiu, B. Comparative microbicidal activity of synovial fluid on arthritogenic organisms. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1996, 104, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gupta, T.T.; Gupta, N.K.; Burback, P.; Stoodley, P. Free-Floating Aggregate and Single-Cell-Initiated Biofilms of Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 889. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10080889
Gupta TT, Gupta NK, Burback P, Stoodley P. Free-Floating Aggregate and Single-Cell-Initiated Biofilms of Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(8):889. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10080889
Chicago/Turabian StyleGupta, Tripti Thapa, Niraj K. Gupta, Peter Burback, and Paul Stoodley. 2021. "Free-Floating Aggregate and Single-Cell-Initiated Biofilms of Staphylococcus aureus" Antibiotics 10, no. 8: 889. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10080889
APA StyleGupta, T. T., Gupta, N. K., Burback, P., & Stoodley, P. (2021). Free-Floating Aggregate and Single-Cell-Initiated Biofilms of Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics, 10(8), 889. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10080889





