Clonal Diversity of Klebsiella spp. and Escherichia spp. Strains Isolated from Patients with Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
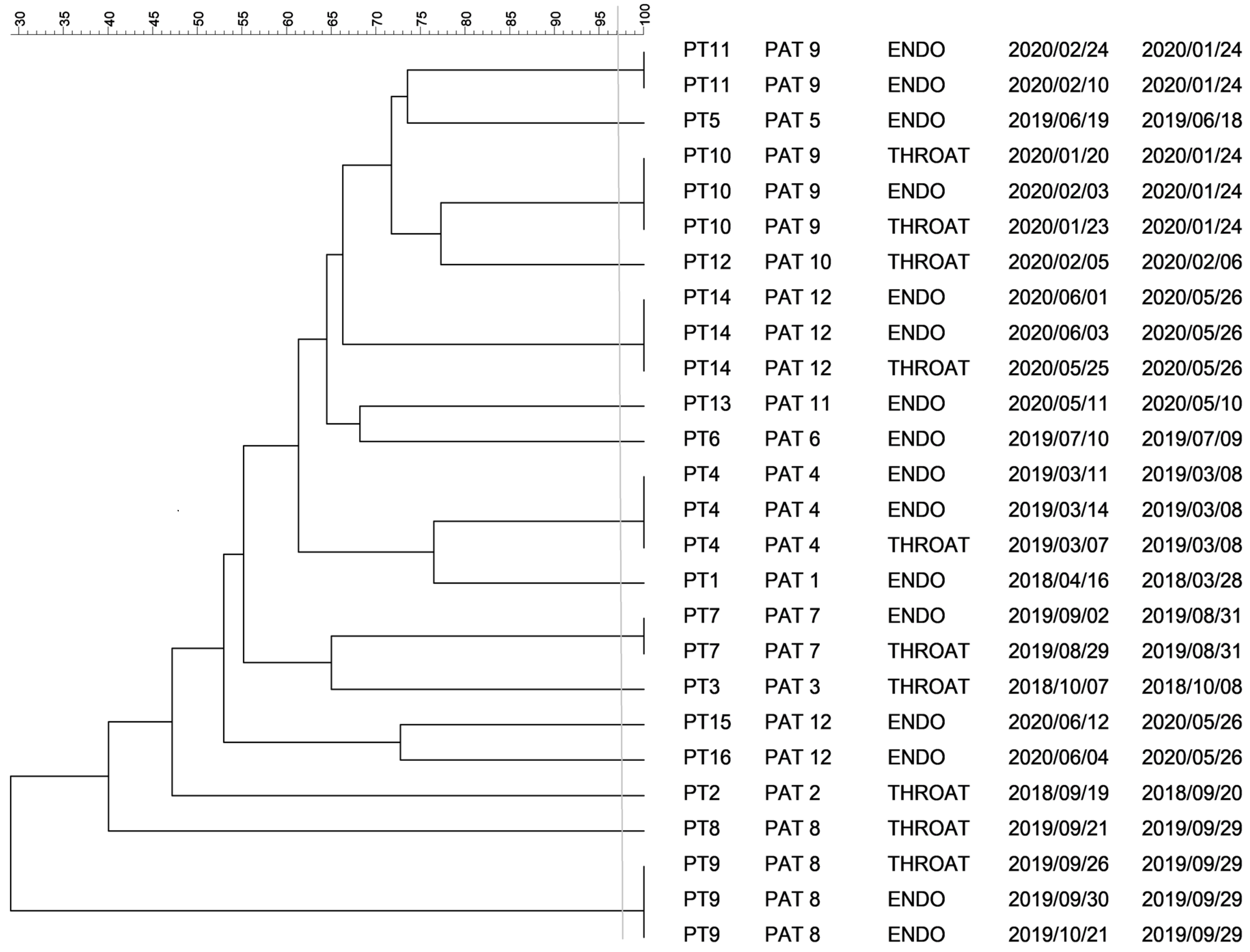
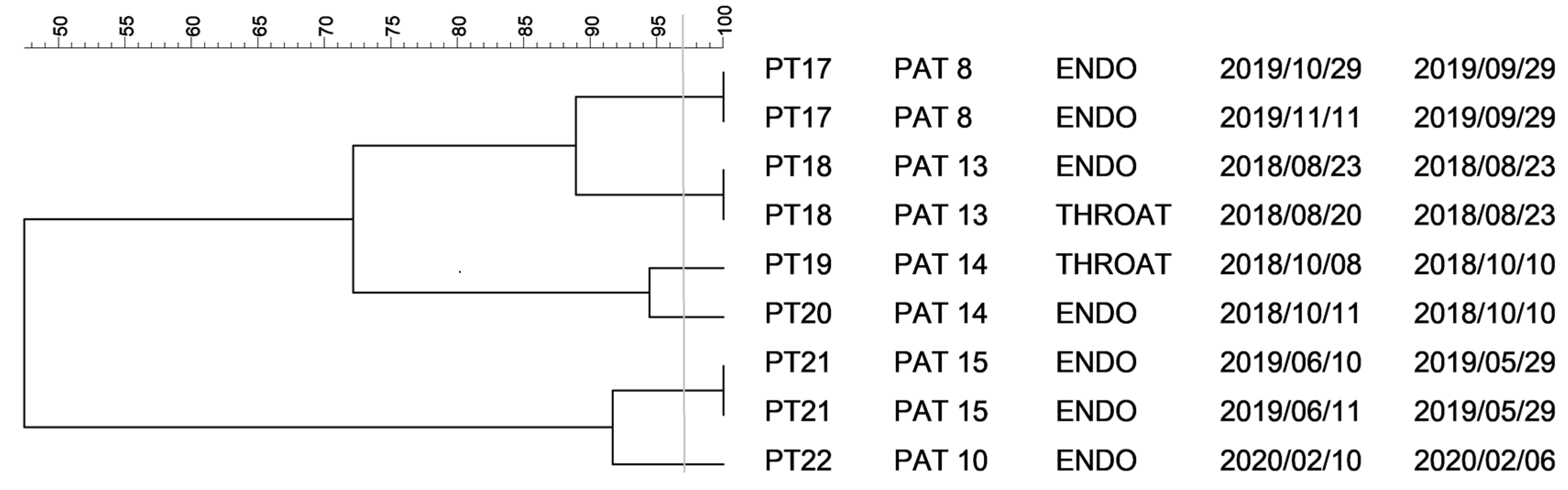
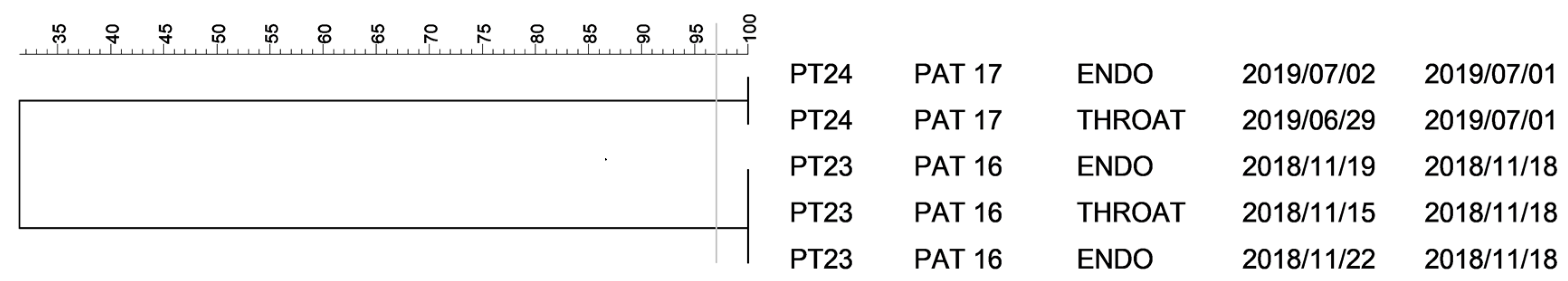
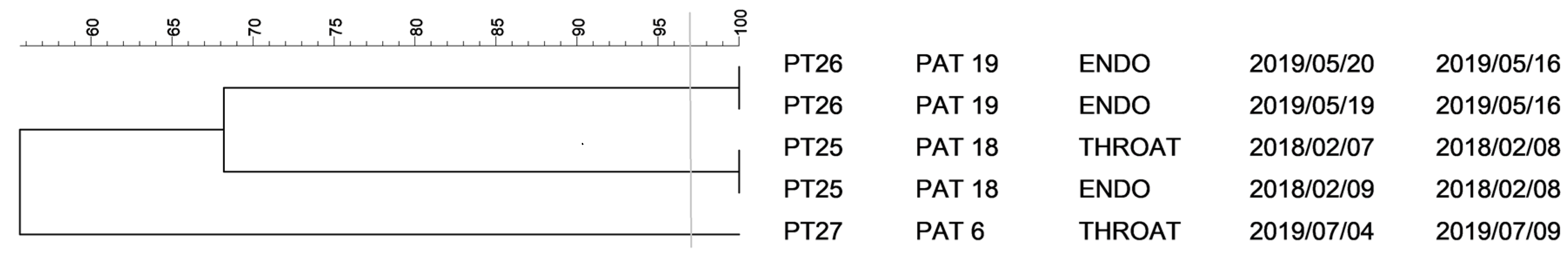
2.1. PFGE Analysis of Klebsiella spp. Isolates
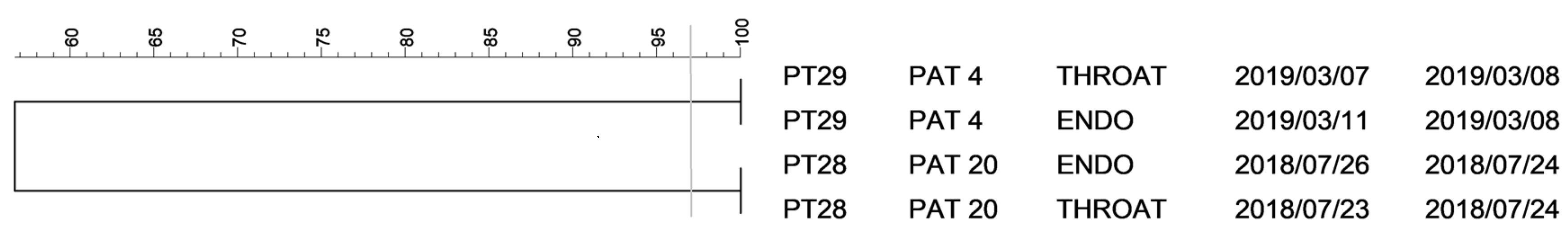
2.2. PFGE Analysis of Escherichia spp. Isolates
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients and Clinical Material
4.2. Sample Processing
4.3. Collection of Samples for Microbiological Culture and Identification of Isolated Bacteria
4.4. Genotyping of Selected Bacterial Isolates
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Thoracic Society; Infectious Diseases Society of America. Guidelines for the Management of Adults with Hospital-acquired, Ventilator-associated, and Healthcare-associated Pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 388–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chastre, J.; Fagon, J.-Y. Ventilator-associated Pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 867–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melsen, W.G.; Rovers, M.M.; Groenwold, R.H.; Bergmans, D.C.; Camus, C.; Bauer, T.T.; Hanisch, E.; Klarin, B.; Koeman, M.A.; Krueger, W.; et al. Attributable mortality of ventilator-associated pneumonia: A meta-analysis of individual patient data from randomised prevention studies. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolfaghari, P.S.; La Wyncoll, D. The tracheal tube: Gateway to ventilator-associated pneumonia. Crit. Care 2011, 15, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, J.D. Ventilator associated pneumonia. BMJ 2012, 344, e3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safdar, N.; Crnich, C.J.; Maki, D.G. The pathogenesis of ventilator-associated pneumonia: Its relevance to developing effective strategies for prevention. Respir. Care 2005, 50, 725–739. [Google Scholar]
- Dudeck, M.A.; Weiner, L.M.; Allen-Bridson, K.; Malpiedi, P.J.; Peterson, K.D.; Pollock, D.A.; Sievert, D.M.; Edwards, J.R. National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN) report, data summary for 2012, Device-associated module. Am. J. Infect. Control 2013, 41, 1148–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudeck, M.A.; Horan, T.C.; Peterson, K.D.; Allen-Bridson, K.; Morrell, G.; Pollock, D.A.; Edwards, J.R. National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN) Report, data summary for 2010, device-associated module. Am. J. Infect. Control 2011, 39, 798–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalil, A.C.; Metersky, M.L.; Klompas, M.; Muscedere, J.; Sweeney, D.A.; Palmer, L.B.; Napolitano, L.M.; O’Grady, N.P.; Bartlett, J.G.; Carratalà, J.; et al. Management of Adults With Hospital-acquired and Ventilator-associated Pneumonia: 2016 Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the American Thoracic Society. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, e61–e111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forel, J.-M.; Voillet, F.; Pulina, D.; Gacouin, A.; Perrin, G.; Barrau, K.; Jaber, S.; Arnal, J.-M.; Fathallah, M.; Auquier, P.; et al. Ventilator-associated pneumonia and ICU mortality in severe ARDS patients ventilated according to a lung-protective strategy. Crit. Care 2012, 16, R65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werarak, P.; Kiratisin, P.; Thamlikitkul, V. Hospital-acquired pneumonia and ventilator-associated pneumonia in adults at Siriraj Hospital: Etiology, clinical outcomes, and impact of antimicrobial resistance. J. Med. Assoc. Thai. 2010, 93, S126–S138. [Google Scholar]
- Artigas, A.T.; Dronda, S.B.; Vallés, E.C.; Marco, J.M.; Usón, M.C.V.; Figueras, P.; Suarez, F.J.; Hernández, A. Risk factors for nosocomial pneumonia in critically ill trauma patients. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 29, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herkel, T.; Uvizl, R.; Doubravska, L.; Adamus, M.; Gabrhelik, T.; Sedlakova, M.H.; Kolar, M.; Hanulik, V.; Pudova, V.; Langova, K.; et al. Epidemiology of hospital-acquired pneumonia: Results of a Central European multicenter, prospective, observational study compared with data from the European region. Biomed. Pap. 2016, 160, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthelot, P.; Grattard, F.; Mahul, P.; Pain, P.; Jospé, R.; Venet, C.; Carricajo, A.; Aubert, G.; Ros, A.; Dumont, A.; et al. Prospective study of nosocomial colonization and infection due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa in mechanically ventilated patients. Intensiv. Care Med. 2001, 27, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uvizl, R.; Kolar, M.; Herkel, T.; Vobrova, M.; Langova, K. Possibilities for modifying risk factors for the development of hospital-acquired pneumonia in intensive care patients: Results of a retrospective, observational study. Biomed. Pap. 2017, 161, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doubravská, L.; Uvízl, R.; Herkel’, T.; Kolář, M.; Gabrhelík, T.; Röderová, M.; Htoutou Sedláková, M.; Langová, K.; Kolek, V.; Jakubec, P.; et al. Detection of the etiological agents of hospital-acquired pneumonia—Validity and comparison of different types of biological sample collection: A prospective, observational study in intensive care patients. Epidemiol. Mikrobiol. Imunol. 2017, 66, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fernando, S.M.; Tran, A.; Cheng, W.; Klompas, M.; Kyeremanteng, K.; Mehta, S.; English, S.; Muscedere, J.; Cook, D.J.; Torres, A.; et al. Diagnosis of ventilator-associated pneumonia in critically ill adult patients—A systematic review and meta-analysis. Intensiv. Care Med. 2020, 46, 1170–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanulík, V.; Uvízl, R.; Husičková, V.; Htoutou Sedláková, M.; Kolář, M. Pneumonia-causing bacterial pathogens in intensive care patients. Klin. Mikrobiol. Infekc. Lek. 2011, 17, 135–140. [Google Scholar]
- Pudová, V.; Working Group; Sedláková, M.H.; Kolář, M. Clonality of Bacterial Pathogens Causing Hospital-Acquired Pneumonia. Curr. Microbiol. 2016, 73, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, E.R.; Aly, S.A.; Halby, H.M.; Ahmed, S.H.; Zakaria, A.M.; El-Asheer, O.M. Epidemiological typing of multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae, which causes paediatric ventilator-associated pneumonia in Egypt. J. Med. Microbiol. 2017, 66, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Zhou, M.; Liu, W.-E.; Zou, M. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae induced ventilator-associated pneumonia in mechanically ventilated patients in China. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 35, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabrizi, A.M.A.; Badmasti, F.; Shahcheraghi, F.; Azizi, O. Outbreak of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae harbouring blaVIM-2 among mechanically-ventilated drug-poisoning patients with high mortality rate in Iran. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2018, 15, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croxatto, A.; Prod’hom, G.; Greub, G. Applications of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry in clinical diagnostic microbiology. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 36, 80–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husickova, V.; Cekanova, L.; Chroma, M.; Htoutou-Sedlakova, M.; Hricova, K.; Kolář, M. Carriage of ESBL- and AmpC-positive Enterobacteriaceae in the gastrointestinal tract of community subjects and hospitalized patients in the Czech Republic. Biomed. Pap. 2012, 156, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Papajk, J.; Mezerová, K.; Uvízl, R.; Štosová, T.; Kolář, M. Clonal Diversity of Klebsiella spp. and Escherichia spp. Strains Isolated from Patients with Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 674. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10060674
Papajk J, Mezerová K, Uvízl R, Štosová T, Kolář M. Clonal Diversity of Klebsiella spp. and Escherichia spp. Strains Isolated from Patients with Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(6):674. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10060674
Chicago/Turabian StylePapajk, Jan, Kristýna Mezerová, Radovan Uvízl, Taťána Štosová, and Milan Kolář. 2021. "Clonal Diversity of Klebsiella spp. and Escherichia spp. Strains Isolated from Patients with Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia" Antibiotics 10, no. 6: 674. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10060674
APA StylePapajk, J., Mezerová, K., Uvízl, R., Štosová, T., & Kolář, M. (2021). Clonal Diversity of Klebsiella spp. and Escherichia spp. Strains Isolated from Patients with Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia. Antibiotics, 10(6), 674. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10060674






