Virulence Factors in Staphylococcus Associated with Small Ruminant Mastitis: Biofilm Production and Antimicrobial Resistance Genes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Bacteriological Results
2.2. Staphylococci Identification
2.3. Biofilm Production
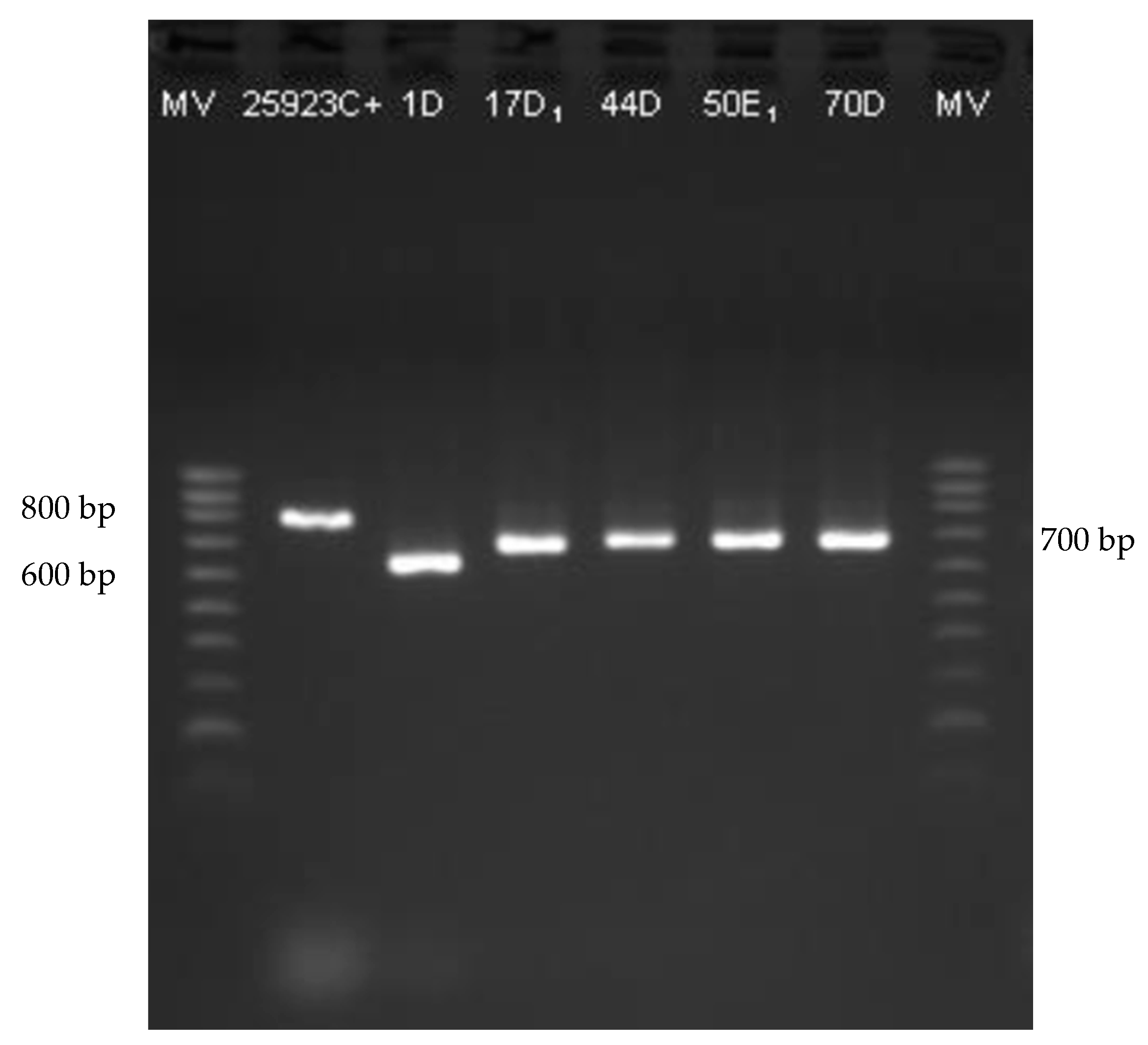
2.4. Genes Associated to Biofilm
2.5. Antimicrobial Resistance
2.6. Antimicrobial Resistance Genes
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Milk Samples Collection and Bacteriological Analyses
3.2. Phenotypic Characterisation of Staphylococcal Isolates
3.2.1. Biofilm Detection
3.2.2. Antimicrobial Sensitivity Test
3.3. Molecular Characterisation of Staphylococcal Isolates
3.3.1. Rapid DNA Extraction
3.3.2. PCR Amplification
3.4. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olechnowicz, J.; Jaśkowski, J.M. Mastitis in small ruminants. Med. Weter. 2014, 70, 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Gelasakis, A.I.; Mavrogianni, V.S.; Petridis, I.G.; Vasileiou, N.G.C.; Fthenakis, G.C. Mastitis in sheep—The last 10 years and the future of research. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 181, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Buyser, M.-L.; Dufour, B.; Maire, M.; Lafarge, V. Implication of milk and milk products in food-borne diseases in France and in different industrialised countries. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2001, 67, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argudín, M.Á.; Mendoza, M.C.; Rodicio, M.R. Food poisoning and Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins. Toxins 2010, 2, 1751–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Queiroga, M.C. Prevalence and aetiology of sheep mastitis in Alentejo region of Portugal. Small Rumin. Res. 2017, 153, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalhamed, A.M.; Zeedan, G.S.G.; Abou Zeina, H.A.A. Isolation and identification of bacteria causing mastitis in small ruminants and their susceptibility to antibiotics, honey, essential oils, and plant extracts. Vet. World 2018, 11, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayis, A.A.E.; Fadlalla, E. Antibiotic Susceptibility of Major Bacteria Cause Ovine Mastitis in River Nile State, Sudan. Imp. J. Interdiscip. Res. 2017, 3, 908–916. [Google Scholar]
- Salaberry, S.R.S.; Saidenberg, A.B.S.; Zuniga, E.; Gonsales, F.F.; Melville, P.A.; Benites, N.R. Microbiological analysis and sensitivity profile of Staphylococcus spp. in subclinical mastitis of dairy goats. Arq. Bras. Med. Veterinária Zootec. 2016, 68, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergonier, D.; Sobral, D.; Feßler, A.T.; Jacquet, E.; Gilbert, F.B.; Schwarz, S.; Treilles, M.; Bouloc, P.; Pourcel, C.; Vergnaud, G. Staphylococcus aureus from 152 cases of bovine, ovine and caprine mastitis investigated by Multiple-locus variable number of tandem repeat analysis (MLVA). Vet. Res. 2014, 45, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constable, P.D.; Hinchcliff, K.W.; Done, S.H.; Grünberg, W. Veterinary Medicine: A Textbook of the Diseases of Cattle, Horses, Sheep, Pigs, and Goats, 11th ed.; Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2017; pp. 1904–2001. ISBN 9780-7020-5246-8. [Google Scholar]
- Dore, S.; Liciardi, M.; Amatiste, S.; Bergagna, S.; Bolzoni, G.; Caligiuri, V.; Cerrone, A.; Farina, G.; Montagna, C.O.; Saletti, M.A.; et al. Survey on small ruminant bacterial mastitis in Italy, 2013–2014. Small Rumin. Res. 2016, 141, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mishra, A.K.; Sharma, N.; Singh, D.D.; Gururaj, K.; Abhishek; Kumar, V.; Sharma, D.K. Prevalence and bacterial etiology of subclinical mastitis in goats reared in organized farms. Vet. World 2018, 11, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz Romero, R.A. Identification of and antimicrobial resistance in bacteria causing caprine mastitis in three states and a city in Central Mexico under manual and mechanical milking conditions. J. Dairyvet. Anim. Res. 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitner, G.; Rovai, M.; Merin, U. Clinical and subclinical intrammamay infection caused by coagulase negative staphylococci negatively affect milk yield and its quality in dairy sheep. Small Rumin. Res. 2019, 180, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madigan, M.T.; Stahl, D.A.; Sattley, W.M.; Buckley, D.H.; Bender, K.S. Brock Biology Of Microorganisms, Global Edition; Pearson Education Limited: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, P.R.; Rosenthal, K.S.; Pfaller, M.A. Medical Microbiology, 9th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pizauro, L.J.L.; de Almeida, C.C.; Soltes, G.A.; Slavic, D.; de Ávila, F.A.; Zafalon, L.F.; MacInnes, J.I. Short communication: Detection of antibiotic resistance, mecA, and virulence genes in coagulase-negative Staphylococcus spp. from buffalo milk and the milking environment. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 11459–11464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapotoczna, M.; McCarthy, H.; Rudkin, J.K.; O’Gara, J.P.; O’Neill, E. An Essential Role for Coagulase in Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm Development Reveals New Therapeutic Possibilities for Device-Related Infections. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, 1883–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schleifer, K.-H.; Bell, J.A. Family VIII-Staphylococcaceae fam. nov. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, 2nd ed.; Vos, P.D., Garrity, G.M., Jones, D., Krieg, N.R., Ludwig, W., Rainey, F.A., Schleifer, K.-H., Whitman, W.B., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; Volume 3, pp. 392–421. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Meng, J.; Shi, C.; Hervin, K.; Fratamico, P.M.; Shi, X. Characterization and comparative analysis of a second thermonuclease from Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 168, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berends, E.T.M.; Horswill, A.R.; Haste, N.M.; Monestier, M.; Nizet, V.; Von Köckritz-Blickwede, M. Nuclease expression by Staphylococcus aureus facilitates escape from neutrophil extracellular traps. J. Innate Immun. 2010, 2, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenny, E.F.; Herzig, A.; Krüger, R.; Muth, A.; Mondal, S.; Thompson, P.R.; Brinkmann, V.; Bernuth, H.V.; Zychlinsky, A. Diverse stimuli engage different neutrophil extracellular trap pathways. eLife 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kateete, D.P.; Kimani, C.N.; Katabazi, F.A.; Okeng, A.; Okee, M.S.; Nanteza, A.; Joloba, M.L.; Najjuka, F.C. Identification of Staphylococcus aureus: DNase and Mannitol salt agar improve the efficiency of the tube coagulase test. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2010, 9, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, G.; Vargas, K.; Sánchez-Jiménez, M.; Reyes-Velez, J.; Olivera-Angel, M. Genotypic and phenotypic characterization of biofilm production by Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from bovine intramammary infections in Colombian dairy farms. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClure, J.A.; Zaal DeLongchamp, J.; Conly, J.M.; Zhang, K. Novel Multiplex PCR Assay for Detection of Chlorhexidine-Quaternary Ammonium, Mupirocin, and Methicillin Resistance Genes, with Simultaneous Discrimination of Staphylococcus aureus from Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 1857–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudding, R. Differentiation of staphylococci on the basis of nuclease properties. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1983, 18, 1098–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, E.E.; Rice, K.C.; Boles, B.R.; Endres, J.L.; Ranjit, D.; Chandramohan, L.; Tsang, L.H.; Smeltzer, M.S.; Horswill, A.R.; Bayles, K.W. Modulation of eDNA release and degradation affects Staphylococcus aureus biofilm maturation. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiedrowski, M.R.; Kavanaugh, J.S.; Malone, C.L.; Mootz, J.M.; Voyich, J.M.; Smeltzer, M.S.; Bayles, K.W.; Horswill, A.R. Nuclease modulates biofilm formation in community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flemming, H.-C.; Wingender, J.; Szewzyk, U.; Steinberg, P.; Rice, S.A.; Kjelleberg, S. Biofilms: An emergent form of bacterial life. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turchi, B.; Bertelloni, F.; Marzoli, F.; Cerri, D.; Tola, S.; Azara, E.; Longheu, C.M.; Tassi, R.; Schiavo, M.; Cilia, G.; et al. Coagulase negative staphylococci from ovine milk: Genotypic and phenotypic characterization of susceptibility to antibiotics, disinfectants and biofilm production. Small Rumin. Res. 2020, 183, 106030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttner, H.; Dietrich, M.; Rohde, H. Structural basis of Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm formation: Mechanisms and molecular interactions. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2015, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arciola, C.R.; Campoccia, D.; Ravaioli, S.; Montanaro, L. Polysaccharide intercellular adhesin in biofilm: Structural and regulatory aspects. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2015, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilmann, C. Adhesion Mechanisms of Staphylococci. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2011, 715, 105–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, M. Staphylococcal Biofilms. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucarella, C.; Solano, C.; Valle, J.; Amorena, B.; Lasa, I.N.I.; Penadés, J.R. Bap, a Staphylococcus aureus Surface Protein Involved in Biofilm Formation. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 2888–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceniti, C.; Britti, D.; Santoro, A.M.L.; Musarella, R.; Ciambrone, L.; Casalinuovo, F.; Costanzo, N. Phenotypic antimicrobial resistance profile of isolates causing clinical mastitis in dairy animals. Ital. J. Food Saf. 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, R.D.M.; França, C.A.D.; Souza Júnior, A.F.D.; Veschi, J.L.A.; Costa, M.M.D. Etiologia e perfil de sensibilidade antimicrobiana dos isolados bacterianos da mastite em pequenos ruminantes e concordância de técnicas empregadas no diagnóstico. Pesqui. Veterinária Bras. 2010, 30, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, N.P.C.; Peixoto, R.M.; Nogueira, D.M.; Krewer, C.C.; Costa, M.M. Perfil de sensibilidade aos antimicrobianos de Staphylococcus spp. coagulase negativa de um rebanho leiteiro caprino em Santa Maria da Boa Vista-PE. Med. Veterinária 2012, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Ashmawy, M.A.; Sallam, K.I.; Abd-Elghany, S.M.; Elhadidy, M.; Tamura, T. Prevalence, Molecular Characterization, and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from Milk and Dairy Products. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2016, 13, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merz, A.; Stephan, R.; Johler, S. Staphylococcus aureus Isolates from Goat and Sheep Milk Seem to Be Closely Related and Differ from Isolates Detected from Bovine Milk. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akkou, M.; Bentayeb, L.; Ferdji, K.; Medrouh, B.; Bachtarzi, M.-A.; Ziane, H.; Kaidi, R.; Tazir, M. Phenotypic characterization of Staphylococci causing mastitis in goats and microarray-based genotyping of Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Small Rumin. Res. 2018, 169, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H. Methicillin (Oxacillin)—Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Strains Isolated from Major Food Animals and Their Potential Transmission to Humans. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 6489–6494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, Y.; Nyman, A.-K.; Söderquist, L.; Tomic, N.; Waller, K.P. Intramammary infections and somatic cell counts in meat and pelt producing ewes with clinically healthy udders. Small Rumin. Res. 2017, 156, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroga, M.C.; Laranjo, M.; Duarte, E.L. Mastitis in Sheep: A disease to be Taken Seriously. In Sheep Diseases; Papst, M., Ed.; Nova Science Publisher, Inc: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 1–91. [Google Scholar]
- Barrero-Domínguez, B.; Luque, I.; Galán-Relaño, Á.; Vega-Pla, J.L.; Huerta, B.; Román, F.; Astorga, R.J. Antimicrobial Resistance and Distribution of Staphylococcus spp. Pulsotypes Isolated from Goat and Sheep Bulk Tank Milk in Southern Spain. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2019, 16, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosselin, V.B.; Lovstad, J.; Dufour, S.; Adkins, P.R.F.; Middleton, J.R. Use of MALDI-TOF to characterize staphylococcal intramammary infections in dairy goats. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 6262–6270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergonier, D.; Berthelot, X. New advances in epizootiology and control of ewe mastitis. Livest. Prod. Sci. 2003, 79, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, K.B.; Faccioli, P.Y.; Bonesso, M.F.; Fernandes, S.; Oliveira, A.A.; Dantas, A.; Zafalon, L.F.; Cunha, M.D.L.R.S. Characteristics of resistance and virulence factors in different species of coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from milk of healthy sheep and animals with subclinical mastitis. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 2184–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.Y.; Fox, L.K.; Seo, K.S.; McGuire, M.A.; Park, Y.H.; Rurangirwa, F.R.; Sischo, W.M.; Bohach, G.A. Comparison of phenotypic and genotypic methods for the species identification of coagulase-negative staphylococcal isolates from bovine intramammary infections. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 147, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, K.; Heilmann, C.; Peters, G. Coagulase-negative staphylococci. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 870–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Queiroga, M.C.; Duarte, E.L.; Laranjo, M. Sheep mastitis Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm effects on cell adhesion and inflammatory changes. Small Rumin. Res. 2018, 168, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aher, T.; Roy, A.; Kumar, P. Molecular detection of virulence genes associated with pathogenicity of Gram positive isolates obtained from respiratory tract of apparently healthy as well as sick goats. Vet. World 2012, 5, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saei, H.D. Coa types and antimicrobial resistance profile of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from cases of bovine mastitis. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 21, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarestrup, F.M.; Dangler, C.A.; Sordillo, L.M. Prevalence of coagulase gene polymorphism in Staphylococcus aureus isolates causing bovine mastitis. Can. J. Vet. Res. 1995, 59, 124–128. [Google Scholar]
- Hookey, J.V.; Richardson, J.F.; Cookson, B.D. Molecular typing of Staphylococcus aureus based on PCR restriction fragment length polymorphism and DNA sequence analysis of the coagulase gene. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1998, 36, 1083–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltan Dallal, M.M.; Khoramizadeh, M.R.; Amiri, S.A.; Saboor Yaraghi, A.A.; Mazaheri Nezhad Fard, R. Coagulase gene polymorphism of Staphylococcus aureus isolates: A study on dairy food products and other foods in Tehran, Iran. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2016, 5, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shopsin, B.; Gomez, M.; Waddington, M.; Riehman, M.; Kreiswirth, B.N. Use of Coagulase Gene (coa) Repeat Region Nucleotide Sequences for Typing of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Strains. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 3453–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, H.K.; Sapkota, D.; Gaur, A.; Mathuria, J.P.; Singh, A.; Sen, M.R. Molecular typing of clinical Staphylococcus aureus isolates from northern India using coagulase gene PCR-RFLP. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2008, 39, 467–473. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Tan, X.; Zhang, X.; Xia, X.; Sun, H. The diversities of staphylococcal species, virulence and antibiotic resistance genes in the subclinical mastitis milk from a single Chinese cow herd. Microb. Pathog. 2015, 88, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Leeuwen, W.; Roorda, L.; Hendriks, W.; Francois, P.; Schrenzel, J. A nuc-deficient methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strain. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 54, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirotaki, S.; Sasaki, T.; Kuwahara-Arai, K.; Hiramatsu, K. Rapid and Accurate Identification of Human-Associated Staphylococci by Use of Multiplex PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 3627–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, W.P.D.; Silva, J.A.; Macedo, M.R.P.D.; Araújo, M.R.D.; Mata, M.M.; Gandra, E.A. Identification of Staphylococcus aureus, S. intermedius and S. hyicus by PCR amplification of coa and nuc genes. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2003, 34, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucarella, C.; Tormo, M.A.; Úbeda, C.; Trotonda, M.P.; Monzón, M.; Peris, C.; Amorena, B.; Lasa, I.; Penadés, J.R. Role of Biofilm-Associated Protein Bap in the Pathogenesis of Bovine Staphylococcus aureus. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 2177–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vautor, E.; Magnone, V.; Rios, G.; Le Brigand, K.; Bergonier, D.; Lina, G.; Meugnier, H.; Barbry, P.; Thiéry, R.; Pépin, M. Genetic differences among Staphylococcus aureus isolates from dairy ruminant species: A single-dye DNA microarray approach. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 133, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, K.B.; Faccioli-Martins, P.Y.; Riboli, D.F.; Pereira, V.C.; Fernandes, S.; Oliveira, A.A.; Dantas, A.; Zafalon, L.F.; da Cunha, M.E.L. Clonal profile, virulence and resistance of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from sheep milk. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2015, 46, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tormo, M.Á.; Knecht, E.; Götz, F.; Lasa, I.; Penadés, J.R. Bap-dependent biofilm formation by pathogenic species of Staphylococcus: Evidence of horizontal gene transfer? Microbiology 2005, 151, 2465–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szweda, P.; Schielmann, M.; Milewski, S.; Frankowska, A.; Jakubczak, A. Biofilm production and presence of ica and bap genes in Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from cows with mastitis in the eastern Poland. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2012, 61, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, V.F.; Motta, C.C.D.; Soares, B.D.S.; Melo, D.A.D.; Coelho, S.D.M.D.O.; Coelho, I.D.S.; Barbosa, H.S.; Souza, M.M.S.D. Biofilm production and beta-lactamic resistance in Brazilian Staphylococcus aureus isolates from bovine mastitis. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2017, 48, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoramian, B.; Jabalameli, F.; Niasari-Naslaji, A.; Taherikalani, M.; Emaneini, M. Comparison of virulence factors and biofilm formation among Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from human and bovine infections. Microb. Pathog. 2015, 88, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, M.; Galluzzo, P.; Buffa, P.G.; Carlino, E.; Spezia, O.; Alduina, R. Comparison of Antibiotic Resistance Profile and Biofilm Production of Staphylococcus aureus Isolates Derived from Human Specimens and Animal-Derived Samples. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuniga, E.; Melville, P.A.; Saidenberg, A.B.S.; Laes, M.A.; Gonsales, F.F.; Salaberry, S.R.S.; Gregori, F.; Brandão, P.E.; dos Santos, F.G.B.; Lincopan, N.E.; et al. Occurrence of genes coding for MSCRAMM and biofilm-associated protein Bap in Staphylococcus spp. isolated from bovine subclinical mastitis and relationship with somatic cell counts. Microb. Pathog. 2015, 89, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notcovich, S.; DeNicolo, G.; Flint, S.; Williamson, N.; Gedye, K.; Grinberg, A.; Lopez-Villalobos, N. Biofilm-Forming Potential of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Bovine Mastitis in New Zealand. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- França, C.A.; Peixoto, R.M.; Cavalcante, M.B.; Melo, N.F.; Oliveira, C.J.B.; Veschi, J.A.; Mota, R.A.; Costa, M.M. Antimicrobial resistance of Staphylococcus spp. from small ruminant mastitis in Brazil. Pesqui. Veterinária Bras. 2012, 32, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taponen, S.; Pyorala, S. Coagulase-negative staphylococci as cause of bovine mastitis—Not so different from Staphylococcus aureus? Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 134, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasileiou, N.G.C.; Sarrou, S.; Papagiannitsis, C.; Chatzopoulos, D.C.; Malli, E.; Mavrogianni, V.S.; Petinaki, E.; Fthenakis, G.C. Antimicrobial Agent Susceptibility and Typing of Staphylococcal Isolates from Subclinical Mastitis in Ewes. Microb. Drug Resist. 2019, 25, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Queiroga, M.C.; Andrade, N.; Laranjo, M. Antimicrobial Action of Propolis Extracts Against Staphylococci. In Understanding Microbial Pathogens: Current Knowledge and Educational Ideas on Antimicrobial Research; Torres-Hergueta, E., Méndez-Vilas, A., Eds.; Formatex Research Center: Badajoz, Spain, 2018; pp. 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- CLSI. M100S-Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing-Approved Standard, 26th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Reading, C.; Cole, M. Clavulanic acid: A beta-lactamase-inhiting beta-lactam from Streptomyces clavuligerus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1977, 11, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbier, F.; Ruppé, E.; Hernandez, D.; Lebeaux, D.; Francois, P.; Felix, B.; Desprez, A.; Maiga, A.; Woerther, P.L.; Gaillard, K.; et al. Methicillin-Resistant Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci in the Community: High Homology of SCCmec IVa between Staphylococcus epidermidis and Major Clones of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, K.; Namikawa, H.; Fujimoto, H.; Nakaie, K.; Takizawa, E.; Okada, Y.; Fujita, A.; Kawaguchi, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Abe, J.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Methicillin-resistant Coagulase-negative Staphylococcal Bacteremia in a Tertiary Hospital. Intern. Med. 2017, 56, 781–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Razik, K.A.A.; Arafa, A.A.; Hedia, R.H.; Ibrahim, E.S. Tetracycline resistance phenotypes and genotypes of coagulase-negative staphylococcal isolates from bubaline mastitis in Egypt. Vet. World 2017, 10, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Feghaly, R.E.; Stamm, J.E.; Fritz, S.A.; Burnham, C.-A.D. Presence of the blaZ beta-lactamase gene in isolates of Staphylococcus aureus that appear penicillin susceptible by conventional phenotypic methods. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 74, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, G.K.; Harrison, E.M.; Holmes, M.A. The emergence of mecC methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Trends Microbiol. 2014, 22, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Shi, L.; Alam, M.J.; Li, L.; Yamasaki, S. Integron-bearing methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative staphylococci in South China, 2001–2004. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 278, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, K.; van Alen, S.; Idelevich, E.A.; Schleimer, N.; Seggewiß, J.; Mellmann, A.; Kaspar, U.; Peters, G. Plasmid-Encoded Transferable mecB-Mediated Methicillin Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpaka, P.E.; Roberts, R.; Monecke, S. Molecular characterization of antimicrobial resistance genes against Staphylococcus aureus isolates from Trinidad and Tobago. J. Infect. Public Health 2017, 10, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, E.Ş.; Aslantaş, Ö. Antimicrobial resistance and underlying mechanisms in Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2017, 10, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markey, B.; Leonard, F.; Archambault, M.; Cullinane, A.; Maguire, D. Clinical Veterinary Microbiology, 2nd ed.; Mosby Ltd.: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Laranjo, M.; Machado, J.; Young, J.P.W.; Oliveira, S. High diversity of chickpea Mesorhizobium species isolated in a Portuguese agricultural region. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2004, 48, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merino, N.; Toledo-Arana, A.; Vergara-Irigaray, M.; Valle, J.; Solano, C.; Calvo, E.; Lopez, J.A.; Foster, T.J.; Penadés, J.R.; Lasa, I. Protein A-mediated multicellular behavior in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 832–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CLSI. M02-A11-Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk Susceptibility Tests-Approved Standard-Eleventh Edition; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI): Wayne, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- EUCAST. European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing-Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters; Version 10.0; UCAST: Växjö, Sweden, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Rivas, R.; Vizcaino, N.; Buey, R.M.; Mateos, P.F.; Martinez-Molina, E.; Velazquez, E. An effective, rapid and simple method for total RNA extraction from bacteria and yeast. J. Microbiol. Methods 2001, 47, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brakstad, O.D.D.G.; Aasbakk, K.; Maeland, J.A. Detection of Staphylococcus aureus by Polymerase Chain Reaction Amplification of the nuc Gene. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1992, 30, 1654–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasudevan, P.; Nair, M.K.; Annamalai, T.; Venkitanarayanan, K.S. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of bovine mastitis isolates of Staphylococcus aureus for biofilm formation. Vet. Microbiol. 2003, 92, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawant, A.; Gillespie, B.; Oliver, S. Antimicrobial susceptibility of coagulase-negative Staphylococcus species isolated from bovine milk. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 134, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strommenger, B.; Kettlitz, C.; Werner, G. Multiplex PCR assay for simultaneous detection of nine clinically relevant antibiotic resistance genes in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 4089–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegger, M.; Andersen, P.S.; Kearns, A.; Pichon, B.; Holmes, M.A.; Edwards, G.; Laurent, F.; Teale, C.; Skov, R.; Larsen, A.R. Rapid detection, differentiation and typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus harbouring either mecA or the new mecA homologue mecALGA251. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.M.; Martins, K.B.; Silva, V.R.D.; Mondelli, A.L.; Cunha, M.D.L.R.D.S.D. Correlation of phenotypic tests with the presence of the blaZ gene for detection of beta-lactamase. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2017, 48, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstkotte, M.A.; Knobloch, J.K.M.; Rohde, H.; Mack, D. Rapid Detection of Methicillin Resistance in Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci by a Penicillin-Binding Protein 2a-Specific Latex Agglutination Test. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 3700–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Coelho, S.D.M.D.O.; Moraes, R.A.M.; Soares, L.D.C.; Pereira, I.A.; Gomes, L.P.; Souza, M.M.S.D. Mapeamento do perfil de resistência e detecção do gene mecA em Staphylococcus aureus e Staphylococcus intermedius oxacilina-resistentes isolados de espécies humanas e animais. Ciência Rural 2007, 37, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Isolate | Origin | Animal | Bacterial Species | coa | nuc | bap | icaA | icaD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1D | PT | goat | S. aureus | + | + | − | + | + |
| 13D1 | PT | goat | S. warneri | − | + | − | − | − |
| 17D1 | PT | goat | S. aureus | + | + | − | − | + |
| 44D | PT | goat | S. aureus | + | + | − | + | + |
| 47D2 | PT | goat | S. chromogenes | − | + | + | − | − |
| 50E1 | PT | goat | S. aureus | + | + | − | + | + |
| 54E1 | PT | goat | S. warneri | − | + | + | − | − |
| 54E2 | PT | goat | S. warneri | − | + | − | + | − |
| 55D1 | PT | goat | S. capitis | − | + | − | − | − |
| 60D2 | PT | goat | S. chromogenes | − | + | + | − | − |
| 65D | PT | goat | S. caprae | − | + | − | − | − |
| 70D | PT | sheep | S. aureus | + | + | − | − | + |
| 71E | PT | sheep | S. aureus | + | + | − | − | − |
| 72D | PT | sheep | S. aureus | + | + | − | − | + |
| 72E | PT | sheep | S. aureus | + | + | − | − | + |
| 83D | PT | sheep | S. aureus | + | + | − | − | − |
| B51E | BR | goat | S. chromogenes | − | + | − | − | − |
| B64 | BR | goat | S. chromogenes | − | + | − | − | − |
| B76E | BR | goat | S. chromogenes | − | + | + | − | − |
| B101 | BR | goat | S. warneri | − | + | − | + | − |
| B159D | BR | goat | S. chromogenes | − | + | + | − | − |
| B159E | BR | goat | S. chromogenes | − | + | + | − | − |
| B190D | BR | goat | S. auricularis | − | + | − | − | − |
| B209D2 | BR | goat | S. simulans | − | + | + | − | − |
| B209E | BR | goat | S. simulans | − | + | − | − | − |
| B219D3 | BR | sheep | S. auricularis | − | + | − | − | − |
| B219D5 | BR | sheep | S. aureus | + | + | − | − | − |
| B223D | BR | sheep | S. aureus | + | + | − | − | − |
| B250D | BR | sheep | S. auricularis | − | + | + | − | − |
| CQ152E1 | PT | sheep | S. aureus | + | + | − | + | + |
| CQ185D1 | PT | sheep | S. aureus | + | + | − | + | + |
| CQ196E | PT | sheep | S. aureus | + | + | − | − | + |
| CQ201E | PT | sheep | S. aureus | + | + | − | − | + |
| CQ268D1 | PT | sheep | S. aureus | + | + | − | − | + |
| CQ270E1 | PT | sheep | S. aureus | + | + | − | − | − |
| CQ285D | PT | sheep | S. aureus | + | + | − | − | + |
| CQ286D | PT | sheep | S. aureus | + | + | − | − | + |
| CQ290D1 | PT | sheep | S. aureus | + | + | − | − | + |
| CQ290D2 | PT | sheep | S. aureus | + | + | − | − | + |
| CQ296D | PT | sheep | S. aureus | + | + | − | − | + |
| CQ335E | PT | sheep | S. aureus | + | + | − | − | − |
| CQ336E2 | PT | sheep | S. aureus | + | + | − | − | + |
| CQ349D | PT | sheep | S. aureus | + | + | − | − | − |
| CQ354D | PT | sheep | S. aureus | + | + | − | − | + |
| Isolate | Origin | Animal | Bacterial Species | P | AMP | OB | AMC | OXA | TET | blaZ | mecA | mecC | tetK | tetM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1D | PT | goat | S. aureus | R | R | R | S | S | S | + | - | - | - | |
| 13D1 | PT | goat | S. warneri | S | S | S | S | S | S | - | - | - | - | |
| 17D1 | PT | goat | S. aureus | R | R | R | S | S | R | + | - | - | + | |
| 44D | PT | goat | S. aureus | R | R | S | S | S | S | + | - | - | - | |
| 47D2 | PT | goat | S. chromogenes | R | R | R | R | R | S | + | - | - | - | - |
| 50E1 | PT | goat | S. aureus | S | S | S | S | S | S | - | - | - | - | |
| 54E1 | PT | goat | S. warneri | S | S | R | S | S | S | + | - | - | - | |
| 54E2 | PT | goat | S. warneri | S | S | R | S | R | S | - | - | - | - | - |
| 55D1 | PT | goat | S. capitis | S | S | S | S | S | S | - | - | - | - | |
| 60D2 | PT | goat | S. chromogenes | R | R | S | S | S | S | + | - | - | - | |
| 65D | PT | goat | S. caprae | R | R | S | S | S | S | + | - | - | - | |
| 70D | PT | sheep | S. aureus | S | S | S | S | S | S | - | - | - | - | |
| 71E | PT | sheep | S. aureus | S | S | R | S | S | S | - | - | - | - | |
| 72D | PT | sheep | S. aureus | S | S | S | S | S | S | - | - | - | - | |
| 72E | PT | sheep | S. aureus | S | S | S | S | S | S | - | - | - | - | |
| 83D | PT | sheep | S. aureus | S | S | S | S | S | S | - | - | - | - | |
| B51E | BR | goat | S. chromogenes | S | S | S | S | S | S | + | - | - | - | |
| B64 | BR | goat | S. chromogenes | S | S | S | S | S | S | + | - | - | - | |
| B76E | BR | goat | S. chromogenes | S | S | S | S | S | S | + | - | - | - | |
| B101 | BR | goat | S. warneri | S | S | S | S | S | R | + | - | - | - | |
| B159D | BR | goat | S. chromogenes | S | S | S | S | S | S | + | - | - | - | |
| B159E | BR | goat | S. chromogenes | S | S | S | S | S | S | + | - | - | - | |
| B190D | BR | goat | S. auricularis | R | S | S | S | S | S | - | - | - | - | |
| B209D2 | BR | goat | S. simulans | S | S | S | S | S | S | - | - | - | - | |
| B209E | BR | goat | S. simulans | S | S | S | S | S | S | + | - | - | - | |
| B219D3 | BR | sheep | S. auricularis | S | S | S | S | S | S | - | - | - | - | |
| B219D5 | BR | sheep | S. aureus | S | S | S | S | S | S | - | - | - | - | |
| B223D | BR | sheep | S. aureus | S | S | S | S | R | S | - | - | - | - | - |
| B250D | BR | sheep | S. auricularis | S | S | S | S | S | S | + | - | - | - | |
| CQ152E1 | PT | sheep | S. aureus | S | S | S | S | S | S | - | - | - | - | |
| CQ185D1 | PT | sheep | S. aureus | S | S | S | S | S | S | - | - | - | - | |
| CQ196E | PT | sheep | S. aureus | S | S | S | S | S | S | - | - | - | - | |
| CQ201E | PT | sheep | S. aureus | S | S | S | S | S | S | - | - | - | - | |
| CQ268D1 | PT | sheep | S. aureus | S | S | R | S | S | S | - | - | - | - | |
| CQ270E1 | PT | sheep | S. aureus | S | S | R | S | S | S | - | - | - | - | |
| CQ285D | PT | sheep | S. aureus | S | S | S | S | S | S | - | - | - | - | |
| CQ286D | PT | sheep | S. aureus | S | S | S | S | S | S | - | - | - | - | |
| CQ290D1 | PT | sheep | S. aureus | S | S | R | S | S | S | - | - | - | - | |
| CQ290D2 | PT | sheep | S. aureus | S | S | S | S | S | S | - | - | - | - | |
| CQ296D | PT | sheep | S. aureus | S | S | S | S | S | R | - | - | + | - | |
| CQ335E | PT | sheep | S. aureus | S | S | S | S | S | S | - | - | - | - | |
| CQ336E2 | PT | sheep | S. aureus | S | S | S | S | S | S | - | - | - | - | |
| CQ349D | PT | sheep | S. aureus | S | S | S | S | S | S | - | - | - | - | |
| CQ354D | PT | sheep | S. aureus | S | S | S | S | S | S | - | - | - | - |
| Gene | Primer | Sequence | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| coa | coa-F | 5′ ATA GAG ATG CTG GTA CAG G 3′ | [55] |
| coa-R | 5′ GCT TCC GAT TGT TCG ATG C 3′ | ||
| coa | coa2-F | 5′ TA CTC AAC CGA CGA CAC CG 3′ | [54] |
| coa2-R | 5′ GAT TTT GGA TGA AGC GGA TT 3′ | ||
| nuc | nuc-F | 5′ GCG ATT GAT GGT GAT ACG GTT 3′ | [95] |
| nuc-R | 5′ AGC CAA GCC TTG ACG AAC TAA AGC 3′ | ||
| bap | bap-F | 5′ CCC TAT ATC GAA GGT GTA GAA TTG CAC 3′ | [35] |
| bap-R | 5′ GCT GTT GAA GTT AAT ACT GTA CCT GC 3′ | ||
| icaA | icaA-F | 5′ CCT AAC TAA CGA AAG GTA G 3′ | [96] |
| icaA-R | 5′ AAG ATA TAG CGA TAA GTG C 3′ | ||
| icaD | icaD-F | 5′ AAA CGT AAG AGA GGT GG 3′ | [96] |
| icaD-R | 5′ GGC AAT ATG ATC AAG ATA C 3′ | ||
| blaZ | blaZ-F | 5′ AAG AGA TTT GCC TAT GCT TC 3′ | [97] |
| blaZ-R | 5′ GCT TGA CCA CTT TTA TCA GC 3′ | ||
| mecA | mecA-F | 5′ AAA ATC GAT GGT AAA GGT TGG C 3′ | [98] |
| mecA-R | 5′ AGT TCT GCA GTA CCG GAT TTG C 3′ | ||
| mecC | mecC-F | 5′ GAA AAA AAG GCT TAG AAC GCC TC 3′ | [99] |
| mecC-R | 5′ GAA GAT CTT TTC CGT TTT CAG C 3′ | ||
| tetK | tetK-F | 5′ GTA GCG ACA ATA GGT AAT AGT 3′ | [59] |
| tetK-R | 5′ TAG TGA CAA TAA ACC TCC TA 3′ | ||
| tetM | tetM-F | 5′ AGT GGA GCG ATT ACA GAA 3′ | [59] |
| tetM-R | 5′ CAT ATG TCC TGG CGT GTC TA 3′ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Andrade, N.C.; Laranjo, M.; Costa, M.M.; Queiroga, M.C. Virulence Factors in Staphylococcus Associated with Small Ruminant Mastitis: Biofilm Production and Antimicrobial Resistance Genes. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 633. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10060633
Andrade NC, Laranjo M, Costa MM, Queiroga MC. Virulence Factors in Staphylococcus Associated with Small Ruminant Mastitis: Biofilm Production and Antimicrobial Resistance Genes. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(6):633. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10060633
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndrade, Nara Cavalcanti, Marta Laranjo, Mateus Matiuzzi Costa, and Maria Cristina Queiroga. 2021. "Virulence Factors in Staphylococcus Associated with Small Ruminant Mastitis: Biofilm Production and Antimicrobial Resistance Genes" Antibiotics 10, no. 6: 633. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10060633
APA StyleAndrade, N. C., Laranjo, M., Costa, M. M., & Queiroga, M. C. (2021). Virulence Factors in Staphylococcus Associated with Small Ruminant Mastitis: Biofilm Production and Antimicrobial Resistance Genes. Antibiotics, 10(6), 633. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10060633








