Back to Nature: Combating Candida albicans Biofilm, Phospholipase and Hemolysin Using Plant Essential Oils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of C. albicans Isolates
2.2. MIC of Essential Oils Against C. albicans
2.3. Screening for Virulence Factors of C. albicans Isolates
2.4. Inhibition of Virulence Factors Using Sub-MIC of EOs
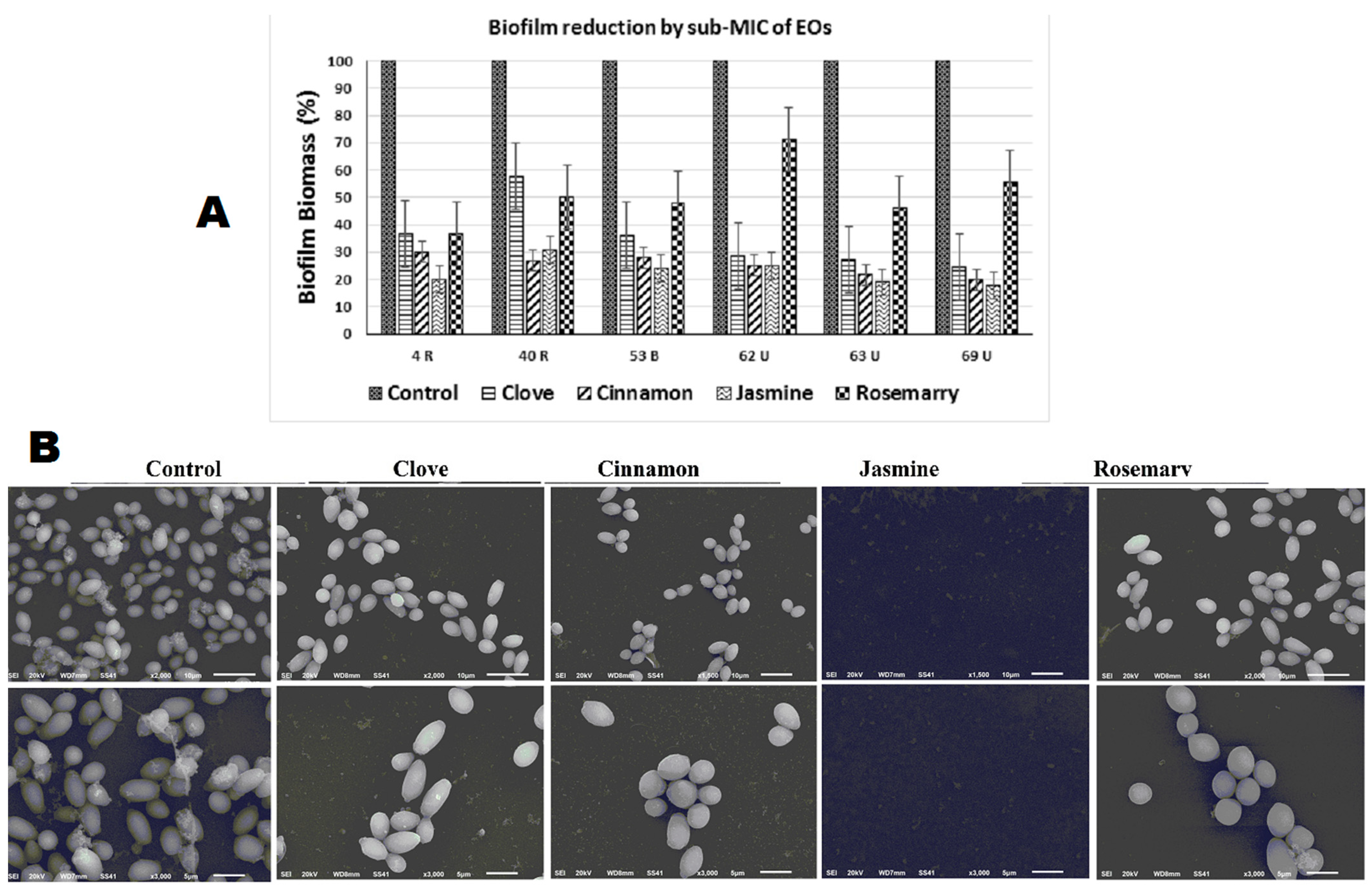
2.4.1. Biofilm Inhibition
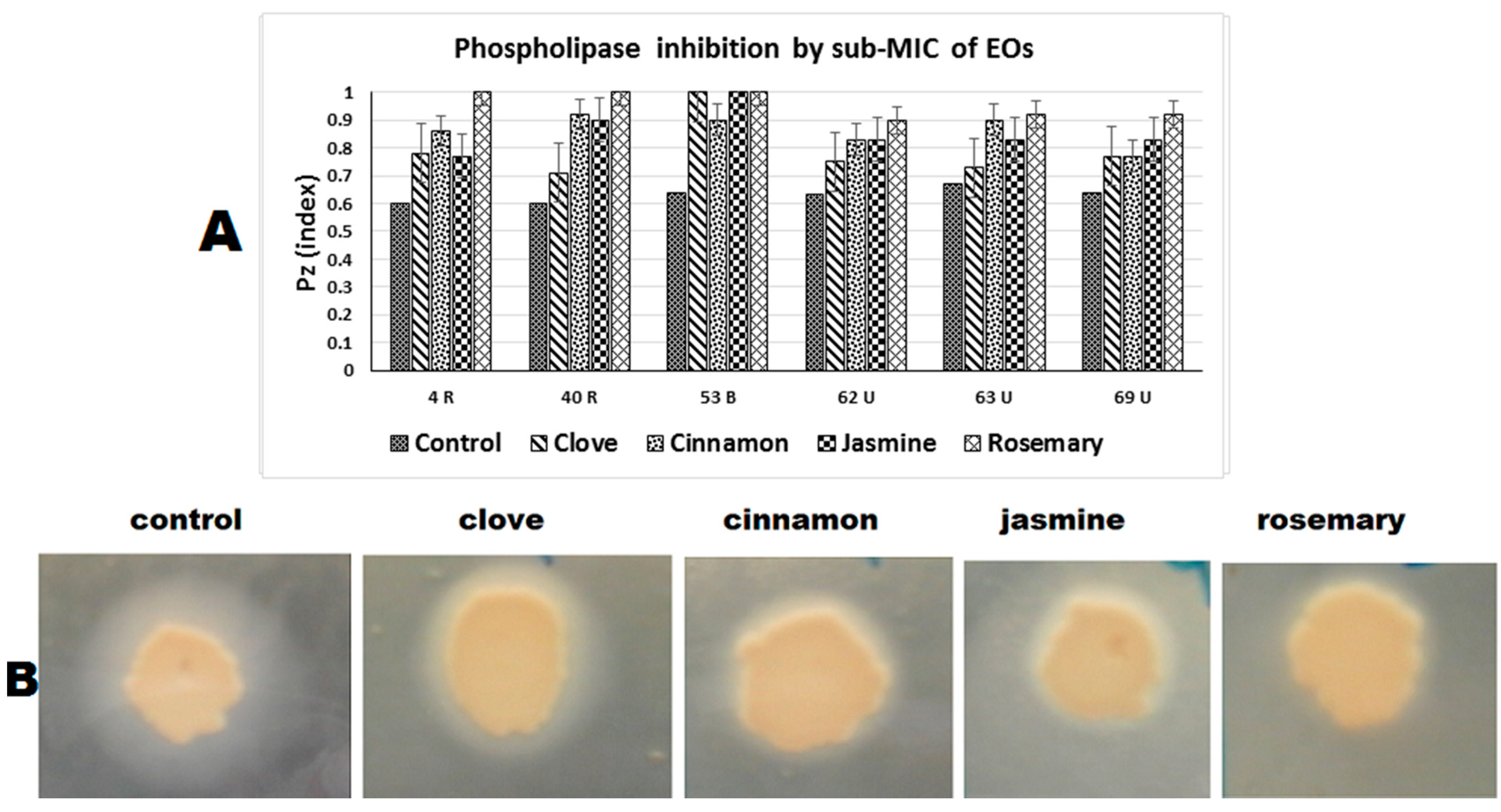
2.4.2. Phospholipase Inhibition
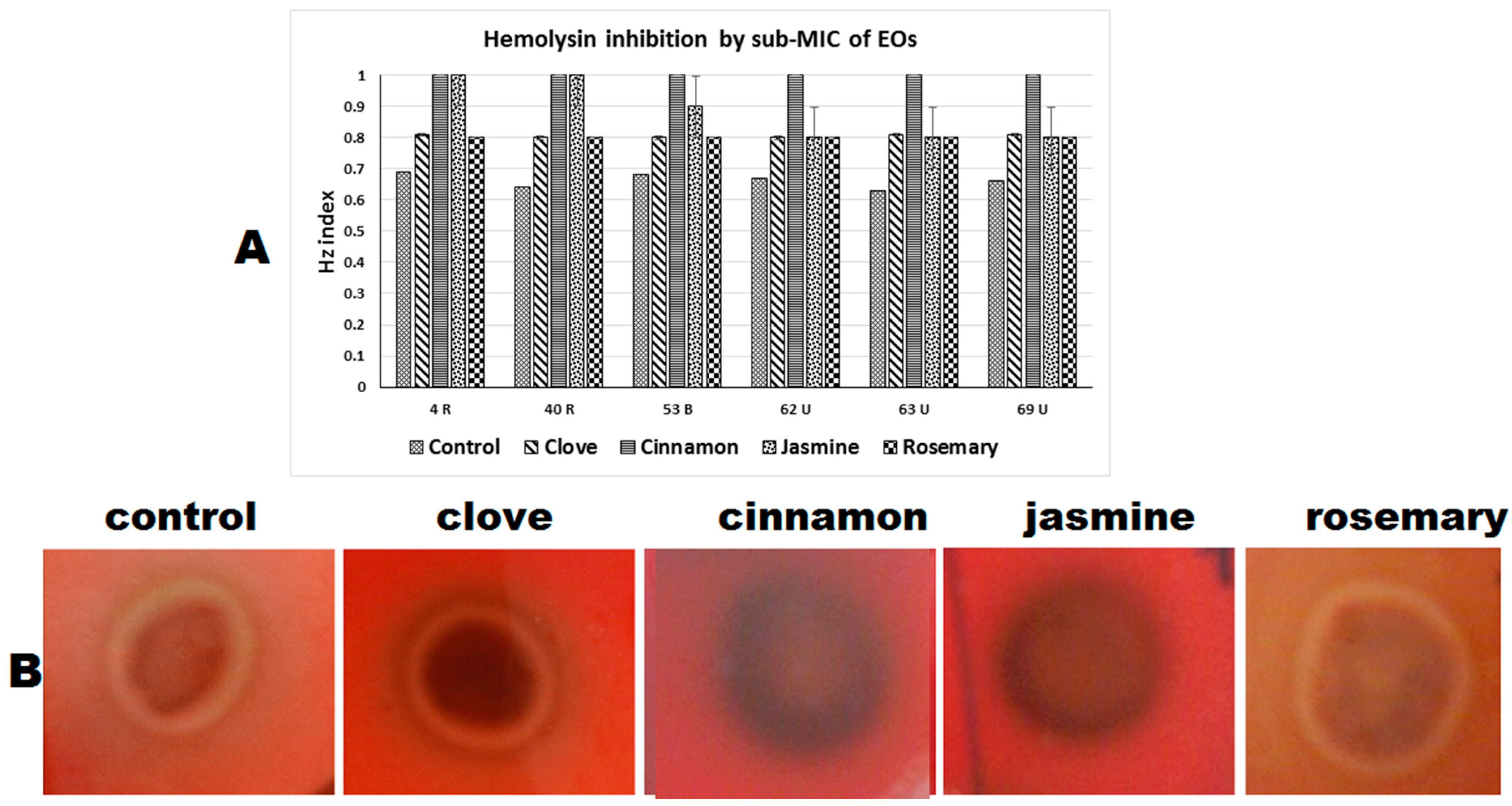
2.4.3. Hemolysin Inhibition
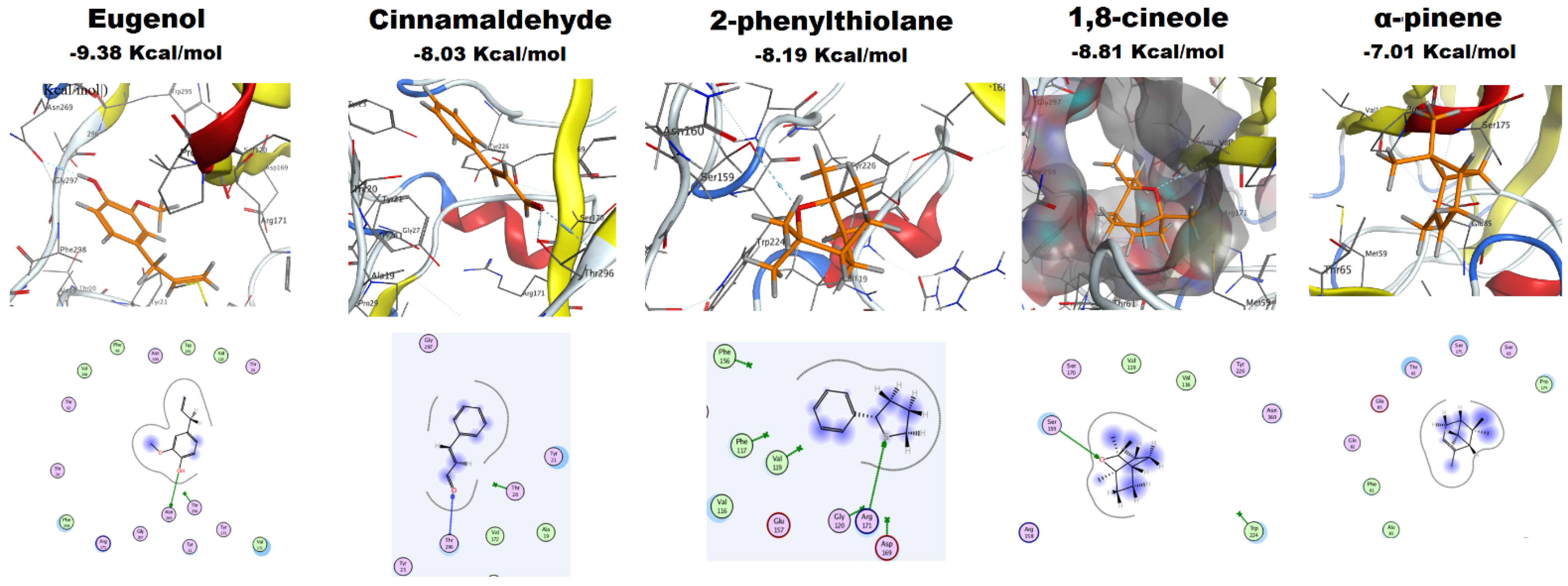
2.4.4. Molecular Docking of EOs Major Constituents with Als3 Protein
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Isolation and Identification of C. albicans Isolates
4.2. Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations (MICs) Determination for EOs
4.3. Screening and Inhibition of C. albicans Virulence Factors
4.3.1. Biofilm Formation and Inhibition
4.3.2. Phospholipase Activity and Inhibition
4.3.3. Hemolysin Activity and Inhibition
4.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
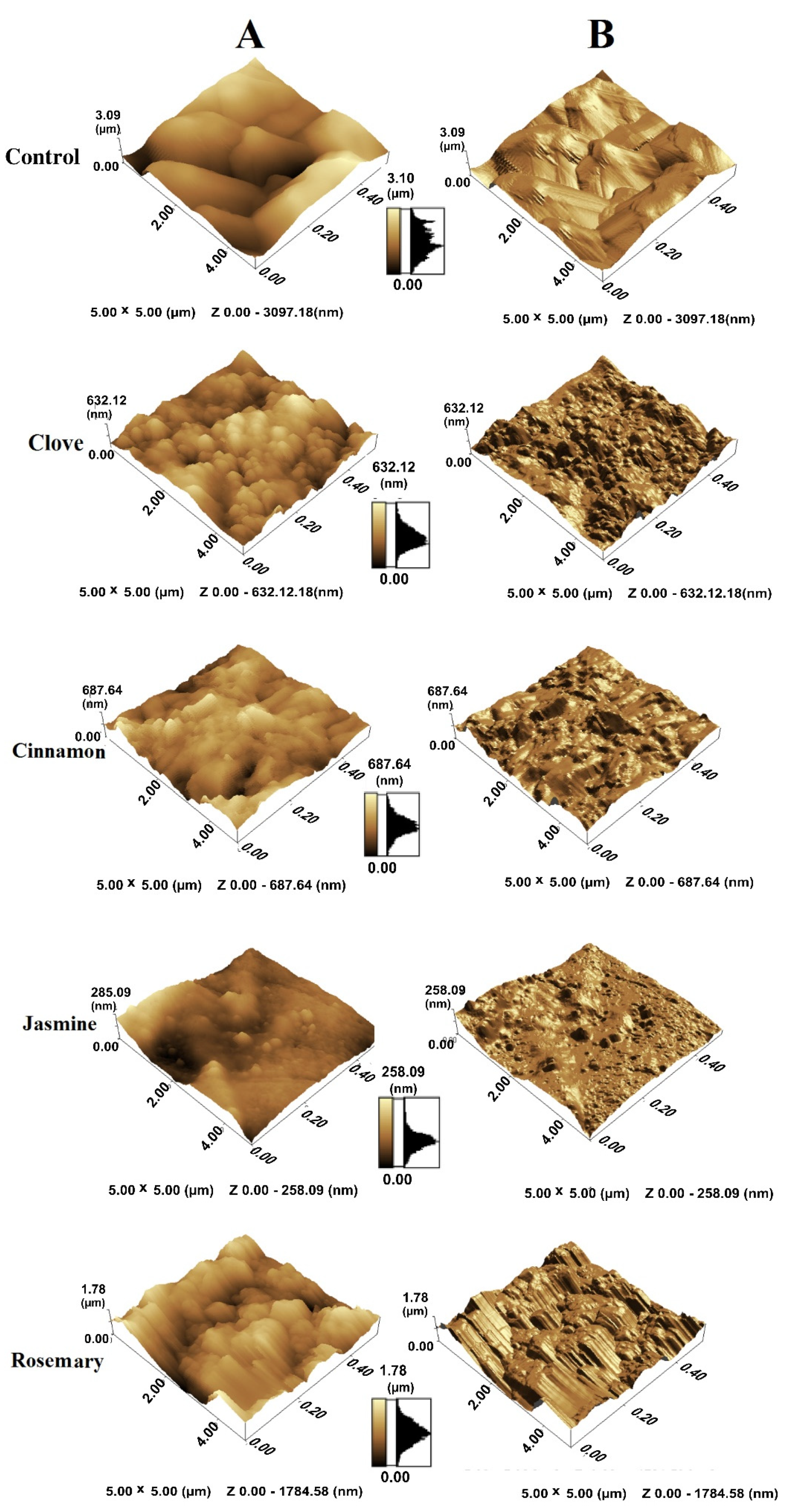
4.5. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
4.6. Molecular Docking Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bongomin, F.; Gago, S.; Oladele, R.O.; Denning, D.W. Global and multi-national prevalence of fungal diseases -estimate precision. J. Fungi 2017, 3, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papon, N.; Courdavault, V.; Clastre, M.; Bennett, R.J. Emerging and emerged pathogenic Candida species: Beyond the Candida albicans paradigm. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achkar, J.M.; Fries, B.C. Candida infections of the genitourinary tract. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 253–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaller, M.A.; Diekema, D.J. Epidemiology of invasive candidiasis: A persistent public health problem. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 133–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andes, D.R.; Safdar, N.; Baddley, J.W.; Playford, G.; Reboli, A.C.; Rex, J.H.; Sobel, J.D.; Pappas, P.G.; Kullberg, B.J. Impact of treatment strategy on outcomes in patients with candidemia and other forms of invasive candidiasis: A patient-level quantitative review of randomized trials. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, 1110–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouza, E.; Guinea, J.; Guembe, M. The role of antifungals against Candida biofilm in catheter-related candidemia. Antibiotics 2015, 4, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaller, M.A. Antifungal drug resistance: Mechanisms, epidemiology, and consequences for treatment. Am. J. Med. 2012, 125, S3–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierce, C.G.; Lopez-Ribot, J.L. Candidiasis drug discovery and development: New approaches targeting virulence for discovering and identifying new drugs. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2013, 8, 1117–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, M.; Nobile, C.J. Candida albicans biofilms: Development, regulation, and molecular mechanisms. Microbes Infect. 2016, 18, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mba, I.E.; Nweze, E.I. Mechanism of Candida pathogenesis: Revisiting the vital drivers. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 6, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramage, G.; Martínez, J.P.; López-Ribot, J.L. Candida biofilms on implanted biomaterials: A clinically significant problem. FEMS Yeast Res. 2006, 6, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, J.; Mukherjee, P.K. Candida biofilms: Development, architecture, and resistance. Microbiol. Spectr. 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, C.; Chu, F.; Leung, W.; Jin, L.; Samaranayake, L.; Siu, S. Phospholipase, proteinase and haemolytic activities of Candida albicans isolated from oral cavities of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 56, 1393–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghannoum, M.A. Potential role of phospholipases in virulence and fungal pathogenesis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 13, 122–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.; Takano, M.; Murakami, M.; Tanaka, H.; Matsuhisa, A.; Nakao, N.; Mikami, T.; Suzuki, M.; Matsumoto, T. Characterization of a haemolytic factor from Candida albicans. Microbiology 1999, 145, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouhan, S.; Sharma, K.; Guleria, S. Antimicrobial activity of some essential oils—present status and future perspectives. Medicines 2017, 4, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.; Saleem, M.; Saadullah, M.; Yaseen, H.S.; Al Zarzour, R. COVID-19 and therapy with essential oils having antiviral, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory properties. Inflammopharmacology 2020, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, V.; Lal, P.; Pruthi, V. Effect of plant oils on Candida albicans. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2010, 43, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.A.; Malik, A.; Ahmad, I. Anti-candidal activity of essential oils alone and in combination with amphotericin B or fluconazole against multi-drug resistant isolates of Candida albicans. Med. Mycol. 2012, 50, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devkatte, A.N.; Zore, G.B.; Karuppayil, S.M. Potential of plant oils as inhibitors of Candida albicans growth. FEMS Yeast Res. 2005, 5, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Zu, Y.; Chen, L.; Shi, X.; Wang, Z.; Sun, S.; Efferth, T. Antimicrobial activity of clove and rosemary essential oils alone and in combination. Phytother. Res. 2007, 21, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santhanam, J.; Abd Ghani, F.N.; Basri, D.F. Antifungal activity of Jasminum sambac against Malassezia sp. and non-Malassezia sp. isolated from human skin samples. J. Mycol. 2014, 2014, 359630. [Google Scholar]
- Budzyńska, A.; Sadowska, B.; Więckowska-Szakiel, M.; Różalska, B. Enzymatic profile, adhesive and invasive properties of Candida albicans under the influence of selected plant essential oils. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2014, 61, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.S.; Ahmad, I.; Cameotra, S.S.; Botha, F. Sub-MICs of Carum copticum and Thymus vulgaris influence virulence factors and biofilm formation in Candida spp. BMC Complement Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, L.d.F.D.d.; Paula, J.F.d.; Almeida, R.V.D.d.; Williams, D.W.; Hebling, J.; Cavalcanti, Y.W. Efficacy of citronella and cinnamon essential oils on Candida albicans biofilms. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2016, 74, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshafie, H.S.; Camele, I. An overview of the biological effects of some mediterranean essential oils on human health. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 9268468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, K.A.; Carson, C.F.; Riley, T.V. Antimicrobial activity of essential oils and other plant extracts. J. Appl. Microbial. 1999, 86, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.d.B.d.; Guterres, S.S.; Weisheimer, V.; Schapoval, E.E. Antifungal activity of the lemongrass oil and citral against Candida spp. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 12, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leigh-de Rapper, S.; van Vuuren, S.F. Front cover: Odoriferous therapy: A review identifying essential oils against pathogens of the respiratory tract. Chem. Biodivers. 2020, 17, e2000438. [Google Scholar]
- Sobel, J.D.; Fisher, J.F.; Kauffman, C.A.; Newman, C.A. Candida urinary tract infections-epidemiology. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52 (Suppl. 6), S433–S436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danin, P.-E.; Girou, E.; Legrand, P.; Louis, B.; Fodil, R.; Christov, C.; Devaquet, J.; Isabey, D.; Brochard, L. Description and microbiology of endotracheal tube biofilm in mechanically ventilated subjects. Respir. Care 2015, 60, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadry, A.A.; El-Ganiny, A.M.; El-Baz, A.M. Relationship between Sap prevalence and biofilm formation among resistant clinical isolates of Candida albicans. Afr. Health Sci. 2018, 18, 1166–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, R.H.; Montanari, L.B.; Martins, C.H.G.; Zaia, J.E.; Almeida, A.M.F.; Matsumoto, M.T.; Mendes-Giannini, M.J.S. Anticandidal efficacy of cinnamon oil against planktonic and biofilm cultures of Candida parapsilosis and Candida orthopsilosis. Mycopathologia 2011, 172, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, V.; Lal, P.; Pruthi, V. Prevention of Candida albicans biofilm by plant oils. Mycopathologia 2008, 165, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobrado, L.; Silva-Dias, A.; Azevedo, M.; Pina-Vaz, C.; Rodrigues, A. In vivo antibiofilm effect of cerium, chitosan and hamamelitannin against usual agents of catheter-related bloodstream infections. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, T.B.; Vieira, A.A.; Paula, L.O.; Santos, E.D.; Radi, P.A.; Khouri, S.; Maciel, H.S.; Pessoa, R.S.; Vieira, L. Flexible camphor diamond-like carbon coating on polyurethane to prevent Candida albicans biofilm growth. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 68, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotedar, R.; Al-Hedaithy, S. Comparison of phospholipase and proteinase activity in Candida albicans and C. dubliniensis. Mycoses 2005, 48, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachin, C.; Ruchi, K.; Santosh, S. In vitro evaluation of proteinase, phospholipase and haemolysin activities of Candida species isolated from clinical specimens. IJMBR 2012, 1, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manns, J.M.; Mosser, D.M.; Buckley, H.R. Production of a hemolytic factor by Candida albicans. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 5154–5156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantarcioǧlu, A.S.; Yücel, A. Phospholipase and protease activities in clinical Candida isolates with reference to the sources of strains. Mycoses 2002, 45, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, M.F.; Wilkinson, I.D.; Gentry, L.O. Plate method for detection of phospholipase activity in Candida albicans. Sabouraudia 1982, 20, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borst, A.; Fluit, A.C. High levels of hydrolytic enzymes secreted by Candida albicans isolates involved in respiratory infections. J. Med. Microbiol. 2003, 52, 971–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yenişehirli, G.; Bulut, Y.; Tuncoglu, E. Phospholipase, proteinase and hemolytic activities of Candida albicans isolates obtained from clinical specimens. Mikrobiyol. Bul. 2010, 44, 71. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jham, G.N.; Dhingra, O.D.; Jardim, C.M.; Valente, V.M. Identification of the major fungitoxic component of cinnamon bark oil. Fitopatol. Bras. 2005, 30, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, M.; Mokhtariniya, S. Essential oil composition of bark of Cinnamomum zeylanicum. J. Essent. Oil Bear. Plants 2016, 19, 786–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahina, Z.; El-Ganiny, A.M.; Minion, J.; Whiteway, M.; Sultana, T.; Dahms, T.E. Cinnamomum zeylanicum bark essential oil induces cell wall remodelling and spindle defects in Candida albicans. Fungal Biol. Biotechnol. 2018, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaieb, K.; Hajlaoui, H.; Zmantar, T.; Kahla-Nakbi, A.B.; Rouabhia, M.; Mahdouani, K.; Bakhrouf, A. The chemical composition and biological activity of clove essential oil, Eugenia caryophyllata (Syzigium aromaticum L. Myrtaceae): A short review. Phytother. Res. 2007, 21, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, S.M.L.; Sandoval, L.V.H.; Vargas, L.Y. In vitro susceptibility of Microsporum spp. and mammalian cells to Eugenia caryophyllus essential oil, eugenol and semisynthetic derivatives. Mycoses 2019, 62, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wu, N.; Fu, Y.-J.; Wang, W.; Luo, M.; Zhao, C.-J.; Zu, Y.-G.; Liu, X.-L. Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of the essential oil of Rosemary. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2011, 32, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassem, H.H.; Nour, A.H.; Yunus, R.M. Analysis of bioactive compounds for Jasmine flower via Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). Malays J. Fundam. Appl. Sci. 2018, 14, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, J.S.; Shinde, R.B.; Chauhan, N.M.; Karuppayil, S.M. Phenylpropanoids of plant origin as inhibitors of biofilm formation by Candida albicans. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 24, 1216–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pootong, A.; Norrapong, B.; Cowawintaweewat, S. Antifungal activity of cinnamaldehyde against Candida albicans. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2017, 48, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zuzarte, M.; Gonçalves, M.J.; Cavaleiro, C.; Canhoto, J.; Vale-Silva, L.; Silva, M.J.; Pinto, E.; Salgueiro, L. Chemical composition and antifungal activity of the essential oils of Lavandula viridis L’Hér. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 60, 612–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, Y.; Rastogi, S.K.; Perwez, A.; Rizvi, M.A.; Manzoor, N. β-citronellol alters cell surface properties of Candida albicans to influence pathogenicity related traits. Med. Mycol. 2020, 58, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.; Agrawal, S. Fungistatic activity of some perfumes against otomycotic pathogens. Mycoses 2002, 45, 88–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thaweboon, S.; Thaweboon, B.; Kaypetch, R. Antimicrobial activity of jasmine oil against oral microorganisms. MS&E 2018, 307, 012034. [Google Scholar]
- Kurkina, Y.N. Phytoncidal activity of essential oils of medicinal plants to some strains of mold fungi. J. Agric. Environ. 2020, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ganiny, A.M.; Shaker, G.H.; Aboelazm, A.A.; El-Dash, H.A. Prevention of bacterial biofilm formation on soft contact lenses using natural compounds. J. Ophthalmic Inflamm. Infect. 2017, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Arye, E.; Dudai, N.; Eini, A.; Torem, M.; Schiff, E.; Rakover, Y. Treatment of upper respiratory tract infections in primary care: A randomized study using aromatic herbs. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 2011, 690346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, M.A.; Yassin, A.S.; El-Gelany, F.H. Characterization, virulence factors and antifungal susceptibility of vulvovaginal candida isolated from women at Qena, Egypt. Egypt. J. Microbiol. 2019, 54, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Kim, Y.-S.; Han, I.; Kim, M.-H.; Jung, M.H.; Park, H.-K. Quantitative and qualitative analyses of the cell death process in Candida albicans treated by antifungal agents. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- El-Kirat-Chatel, S.; Beaussart, A.; Alsteens, D.; Jackson, D.N.; Lipke, P.N.; Dufrêne, Y.F. Nanoscale analysis of caspofungin-induced cell surface remodelling in Candida albicans. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 1105–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Vargas-Blanco, D.; Lynn, A.; Rosch, J.; Noreldin, R.; Salerni, A.; Lambert, C.; Rao, R.P. A pre-therapeutic coating for medical devices that prevents the attachment of Candida albicans. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2017, 16, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, M.J.; Al-Ghamdi, A.; Usmani, S.; Al-Waili, N.S.; Sharma, D.; Nuru, A.; Al-Attal, Y. Effect of jujube honey on Candida albicans growth and biofilm formation. Arch. Med. Res. 2013, 44, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, M.; Lopes, L.; Bonez, P.; Gündel, A.; Martinez, D.; Sagrillo, M.; Giongo, J.; Vaucher, R.; Raffin, R.; Boligon, A. Melaleuca alternifolia nanoparticles against Candida species biofilms. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 104, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasim, S.; Allison, D.P.; Retterer, S.T.; Hopke, A.; Wheeler, R.T.; Doktycz, M.J.; Reynolds, T.B. β-(1, 3)-glucan unmasking in some Candida albicans mutants correlates with increases in cell wall surface roughness and decreases in cell wall elasticity. Infect. Immun. 2017, 85, e00601-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyer, L.L.; Cota, E. Candida albicans agglutinin-like sequence (Als) family vignettes: A review of Als protein structure and function. Front. Microbial. 2016, 7, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marc, G.; Araniciu, C.; Oniga, S.D.; Vlase, L.; Pîrnău, A.; Duma, M.; Măruțescu, L.; Chifiriuc, M.C.; Oniga, O. New N-(oxazolylmethyl)-thiazolidinedione active against Candida albicans biofilm: Potential Als proteins inhibitors. Molecules 2018, 23, 2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadry, A.A.; El-Ganiny, A.M.; El-Baz, A.M. Comparison of methods used in identification of Candida albicans. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2018, 11, 1164–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorzoni, L.; Benaducci, T.; Almeida, A.; Silva, D.H.S.; Bolzani, V.d.S.; Mendes-Giannini, M.J.S. Comparative study of disk diffusion and microdilution methods for evaluation of antifungal activity of natural compounds against medical yeasts Candida spp and Cryptococcus spp. Rev. Ciências Farm. Básica Appl. 2007, 28, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Melo, A.S.; Bizerra, F.C.; Freymüller, E.; Arthington-Skaggs, B.A.; Colombo, A.L. Biofilm production and evaluation of antifungal susceptibility amongst clinical Candida spp. isolates, including strains of the Candida parapsilosis complex. Med. Mycol. 2011, 49, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepanović, S.; Vuković, D.; Hola, V.; Bonaventura, G.D.; Djukić, S.; Ćirković, I.; Ruzicka, F. Quantification of biofilm in microtiter plates: Overview of testing conditions and practical recommendations for assessment of biofilm production by staphylococci. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Immunol. Scand. 2007, 115, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samaranayake, L.; Raeside, J.M.; MacFarlane, T. Factors affecting the phospholipase activity of Candida species in vitro. Sabouraudia 1984, 22, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RCSB PDB-4LEE: Structure of the Als3 adhesin from Candida albicans. Available online: https://www.rcsb.org/structure/4lee (accessed on 15 January 2021).
- Chemical Computing Group Inc. Molecular Operating Environment (MOE), 2019.01; Chemical Computing Group Inc.: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- MarvinSketch, ChemAxon. 2018. Available online: https://chemaxon.com/products/marvin (accessed on 15 January 2021).
| Strains | ATCC 10231 | Clinical Isolates (n = 52) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Essential Oil | MIC (µg/mL) | MIC Range (µg/mL) | MIC50 (µg/mL) |
| Clove oil | 125 | 64–2000 | 500 |
| Cinnamon oil | 250 | 64–500 | 250 |
| Jasmine oil | 500 | 16–2000 | 500 |
| Rosemary oil | 500 | 16–2000 | 500 |
| Number (%) of C. albicans Producing | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Biofilm | Phospholipase | Hemolysin | |
| According to degree of production | |||
| Strong (S) | 11 (21.2%) | 14 (26.9%) | 6 (11.5%) |
| Moderate (M) | 1(1.9%) | 14 (26.9%) | 26 (50%) |
| Weak (W) | 9 (17.3%) | 17 (32.7%) | 9 (17.3%) |
| According to source of strain | |||
| Respiratory (30) | 7 (23.3%) | 26 (86.7%) | 25 (83%) |
| Urine (16) | 13 (81%) | 13 (81%) | 11 (69%) |
| Blood (6) | 1 (16.7%) | 6 (100%) | 5 (83%) |
| Total positive | 21 (40.4%) | 45 (86.5%) | 41 (78.8%) |
| Isolate No. (Source) | Control | Clove | Cinnamon | Jasmine | Rosemary |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biofilm (absorbance (ODt) at 590 nm) | |||||
| 4 (R) | 0.3 a | 0.11 b | 0.09 c | 0.06 c | 0.11 b |
| 40(R) | 0.29 a | 0.15 b | 0.07 c | 0.08 c | 0.13 b |
| 53 (B) | 0.29 a | 0.09 b | 0.07 b,c | 0.06 c | 0.12 d |
| 62 (U) | 0.3 a | 0.07 b | 0.07 b | 0.07 b | 0.2 c |
| 63 (U) | 0.37 a | 0.1 b | 0.08 b,c | 0.07 c | 0.17 d |
| 69 (U) | 0.45 a | 0.11 b | 0.09 b | 0.08 b | 0.25 c |
| Phospholipase (Pz index) | |||||
| 3 (R) | 0.6 a | 0.78 b | 0.86 c | 0.77 b | 1 d |
| 4 (R) | 0.6 a | 0.71 b | 0.92 c | 0.9 c | 1 d |
| 20 (B) | 0.64 a | 1 b | 0.9 c | 1 b | 1 b |
| 32 (B) | 0.63 a | 0.75 b | 0.83 c | 0.83 c | 0.9 d |
| 56 (U) | 0.67 a | 0.73 b | 0.9 c | 0.83 d | 0.92 c |
| 67 (U) | 0.64 a | 0.77 b | 0.77 b | 0.83 c | 0.92 d |
| Hemolysin (Hz index) | |||||
| 4 (R) | 0.69 a | 0.81 b | 1 c | 1 c | 0.8 b |
| 14 (R) | 0.64 a | 0.8 b | 1 c | 1 c | 0.8 b |
| 46 (R) | 0.68 a | 0.8 b | 1 c | 0.9 d | 0.8 b |
| 47 (R) | 0.67 a | 0.8 b | 1 c | 0.8 b | 0.8 b |
| 65 (U) | 0.63 a | 0.81 b | 1 c | 0.8 b | 0.8 b |
| 69 (U) | 0.66 a | 0.81 b | 1 c | 0.8 b | 0.8 b |
| EO | Major Constituents | Binding Free Energy (Kcal/mol) | H-Bond |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clove | Eugenol | −9.38 | Asn 269 |
| Cinnamon | Cinnamaldehyde | −8.03 | Thr 296 |
| Jasmine | 2-phenylthiolane | −8.19 | Arg 171 |
| Rosemary | 1,8-cineole | −8.81 | Val 172 |
| α-pinene | −7.01 | None |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El-Baz, A.M.; Mosbah, R.A.; Goda, R.M.; Mansour, B.; Sultana, T.; Dahms, T.E.S.; El-Ganiny, A.M. Back to Nature: Combating Candida albicans Biofilm, Phospholipase and Hemolysin Using Plant Essential Oils. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10010081
El-Baz AM, Mosbah RA, Goda RM, Mansour B, Sultana T, Dahms TES, El-Ganiny AM. Back to Nature: Combating Candida albicans Biofilm, Phospholipase and Hemolysin Using Plant Essential Oils. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(1):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10010081
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl-Baz, Ahmed M., Rasha A. Mosbah, Reham M. Goda, Basem Mansour, Taranum Sultana, Tanya E. S. Dahms, and Amira M. El-Ganiny. 2021. "Back to Nature: Combating Candida albicans Biofilm, Phospholipase and Hemolysin Using Plant Essential Oils" Antibiotics 10, no. 1: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10010081
APA StyleEl-Baz, A. M., Mosbah, R. A., Goda, R. M., Mansour, B., Sultana, T., Dahms, T. E. S., & El-Ganiny, A. M. (2021). Back to Nature: Combating Candida albicans Biofilm, Phospholipase and Hemolysin Using Plant Essential Oils. Antibiotics, 10(1), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10010081







