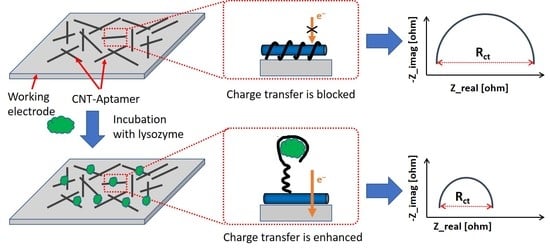
A Low-Cost Inkjet-Printed Aptamer-Based Electrochemical Biosensor for the Selective Detection of Lysozyme
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Electrochemical Assay
2.3. Ink Preparation
2.4. Inkjet-Printing
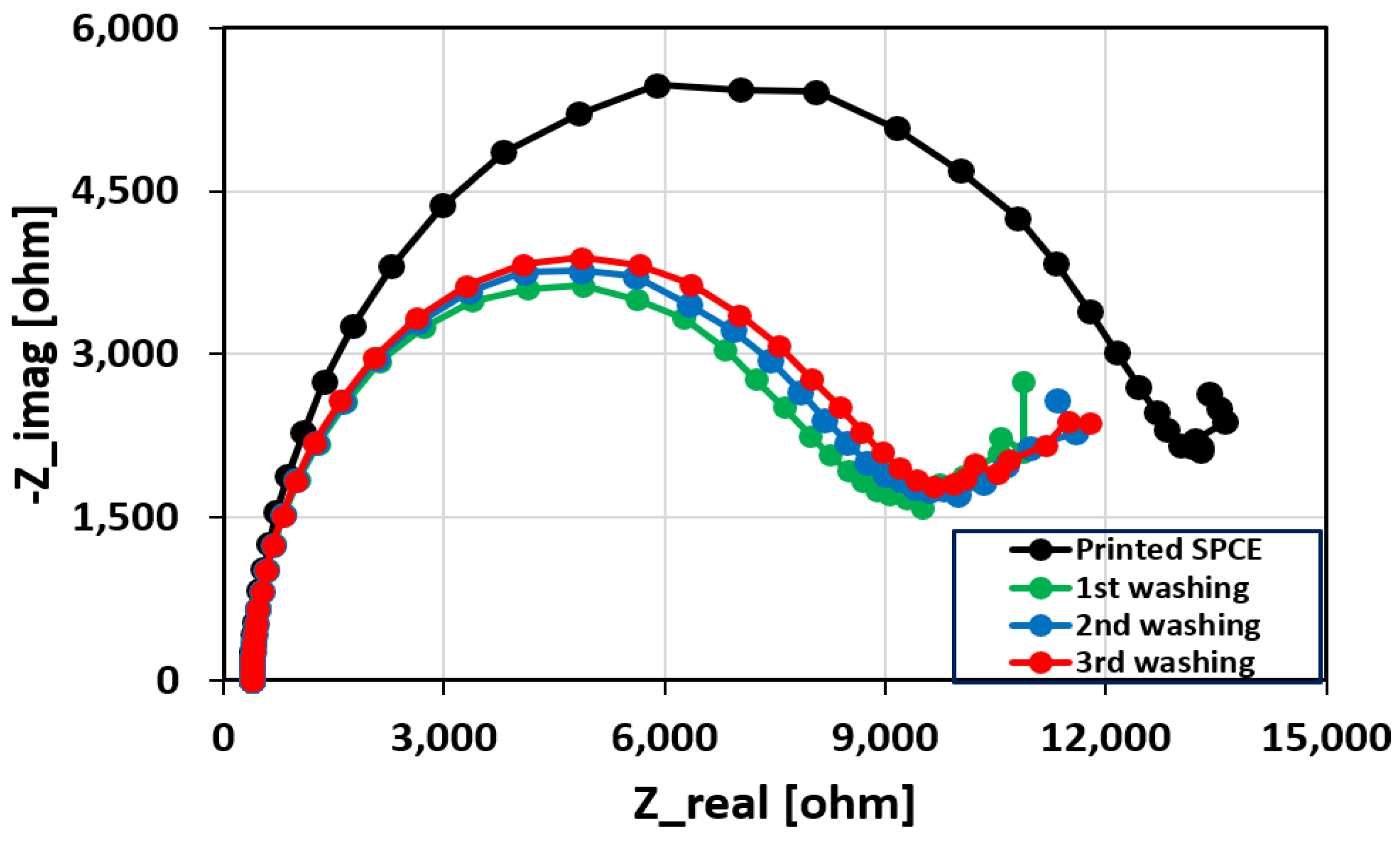
2.5. Removal of the Unbound Aptamers
2.6. EIS Measurements
2.7. Chronocoulometry Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
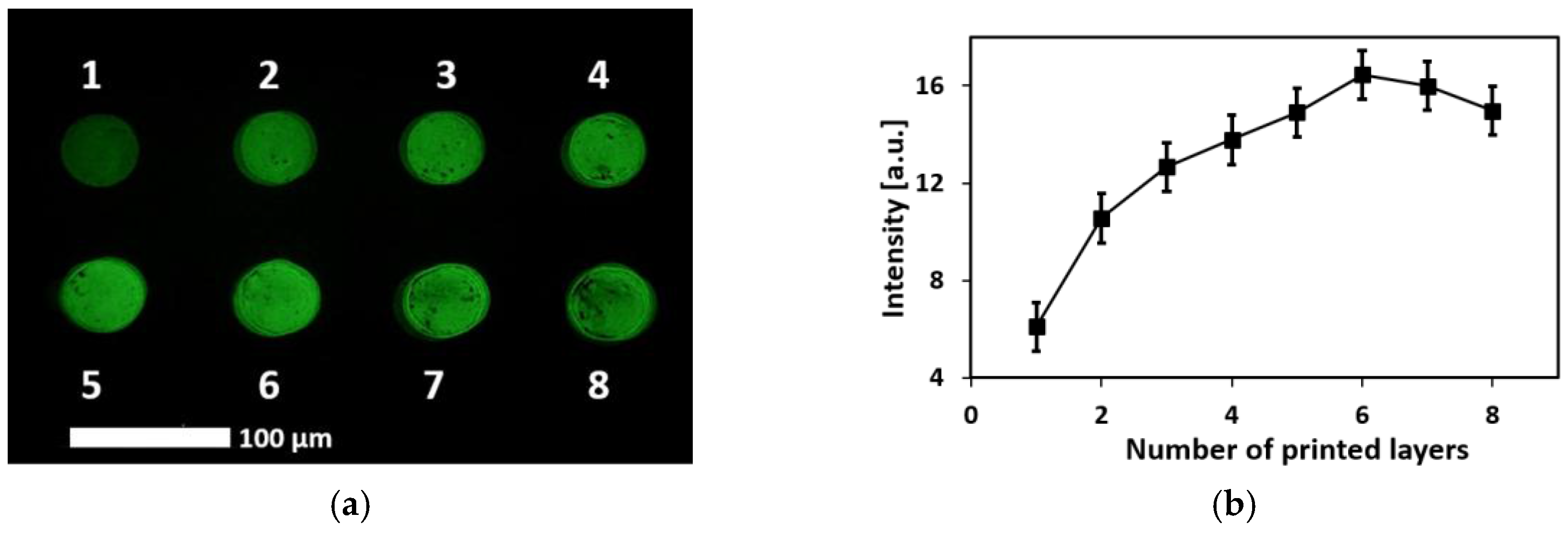
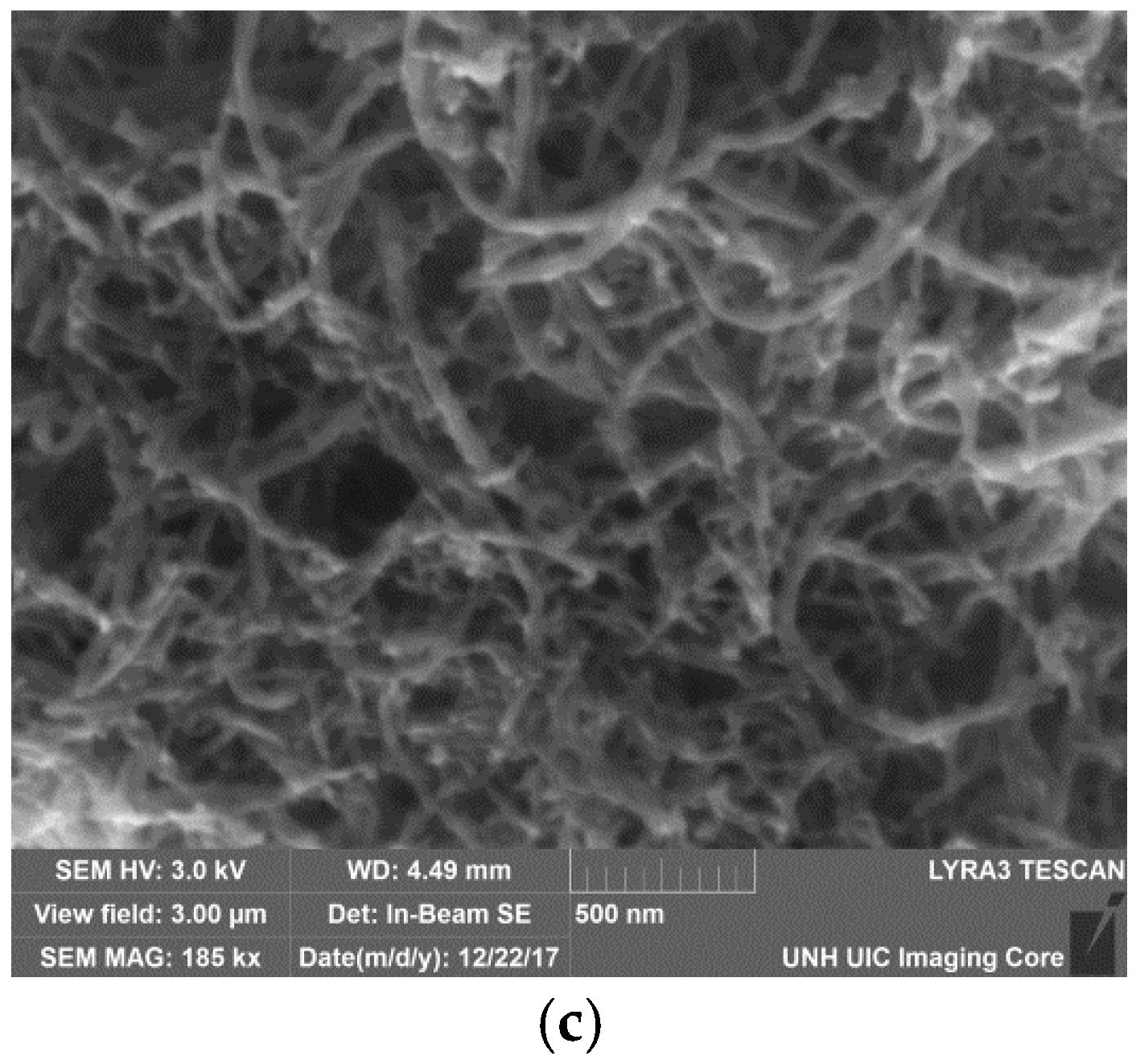
3.1. Patternability of the CNT-Aptamer Ink
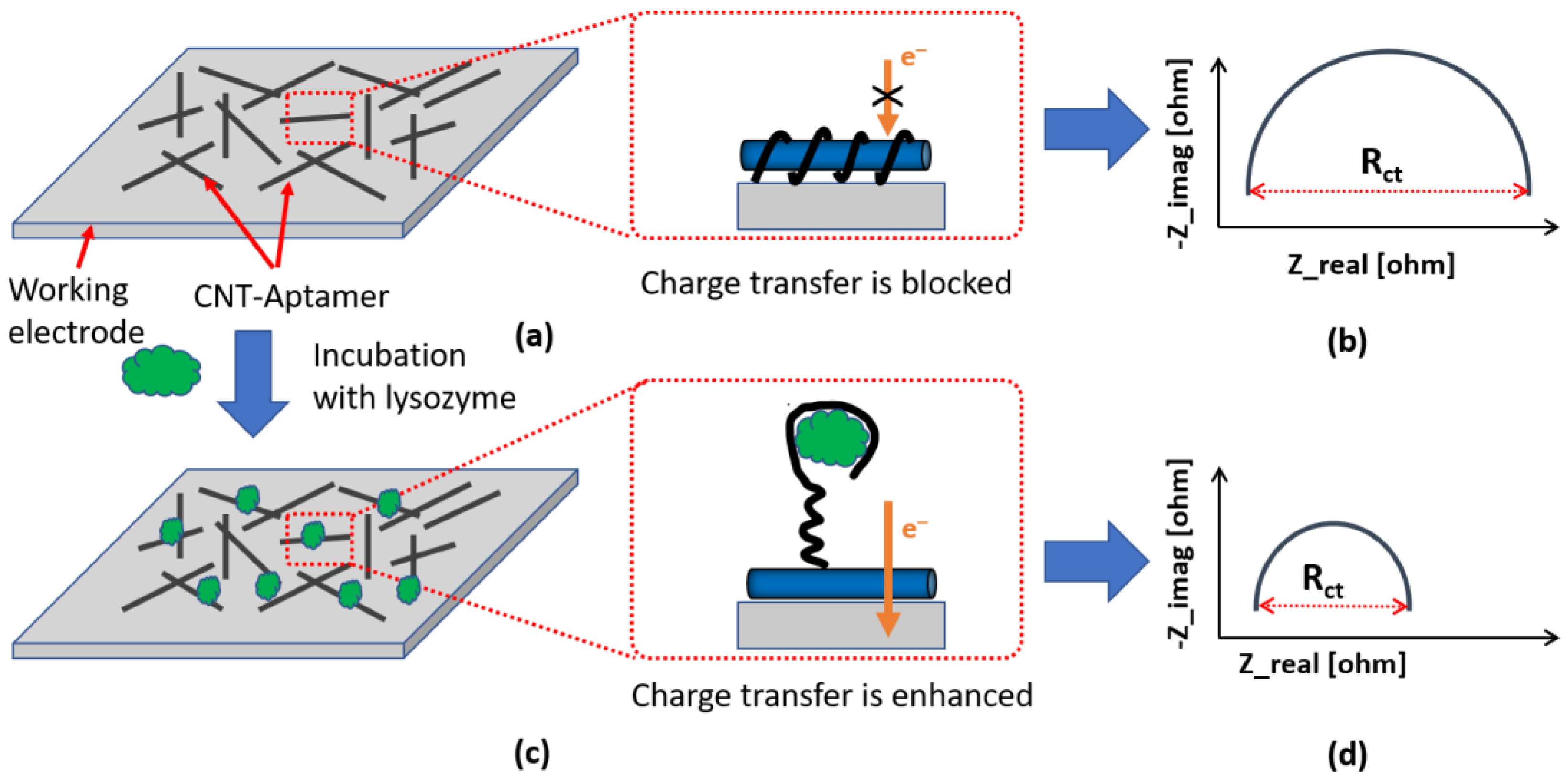
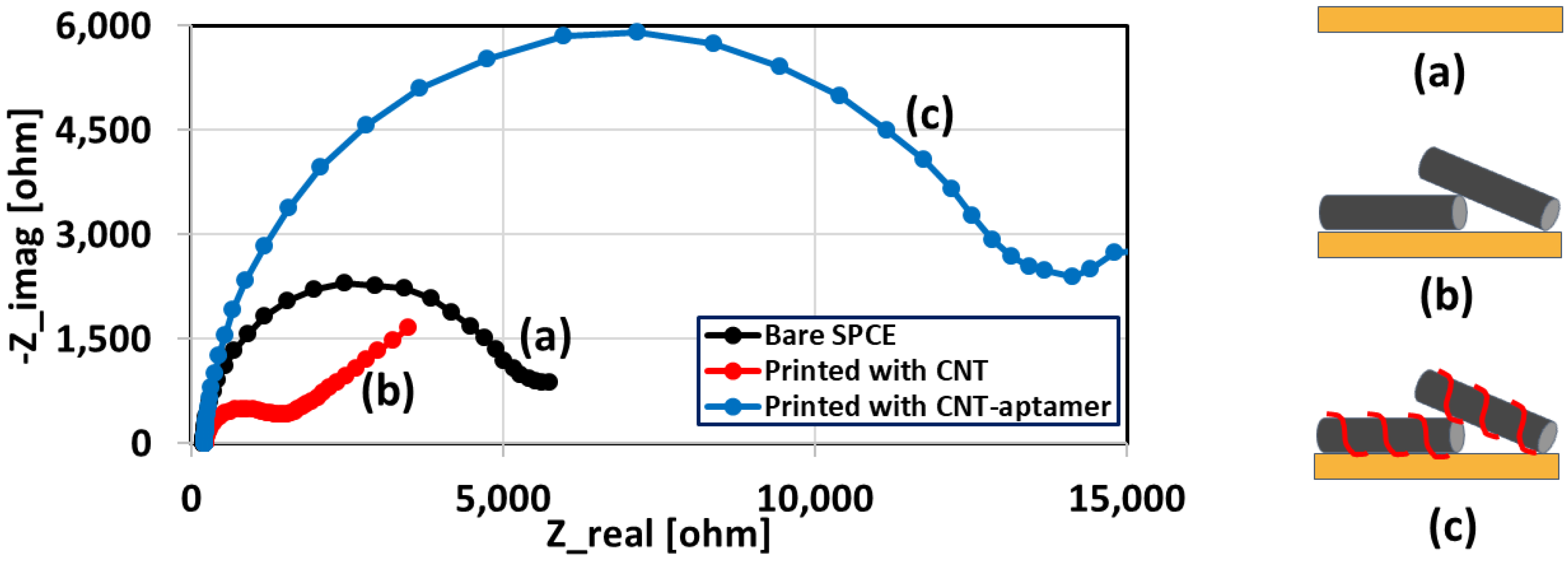
3.2. Characterization of the Sensor
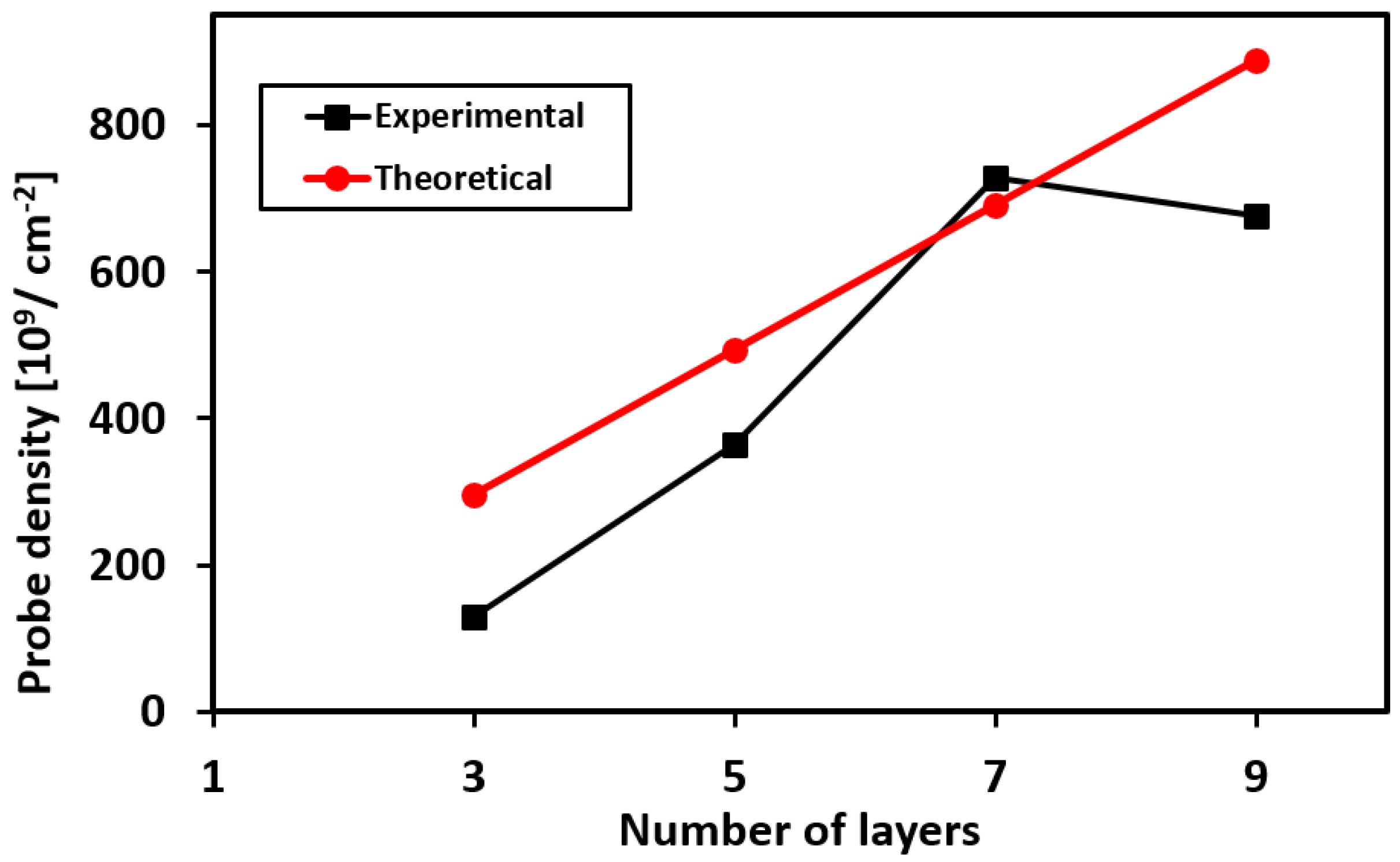
3.3. Packing Density of the Aptamer Probes
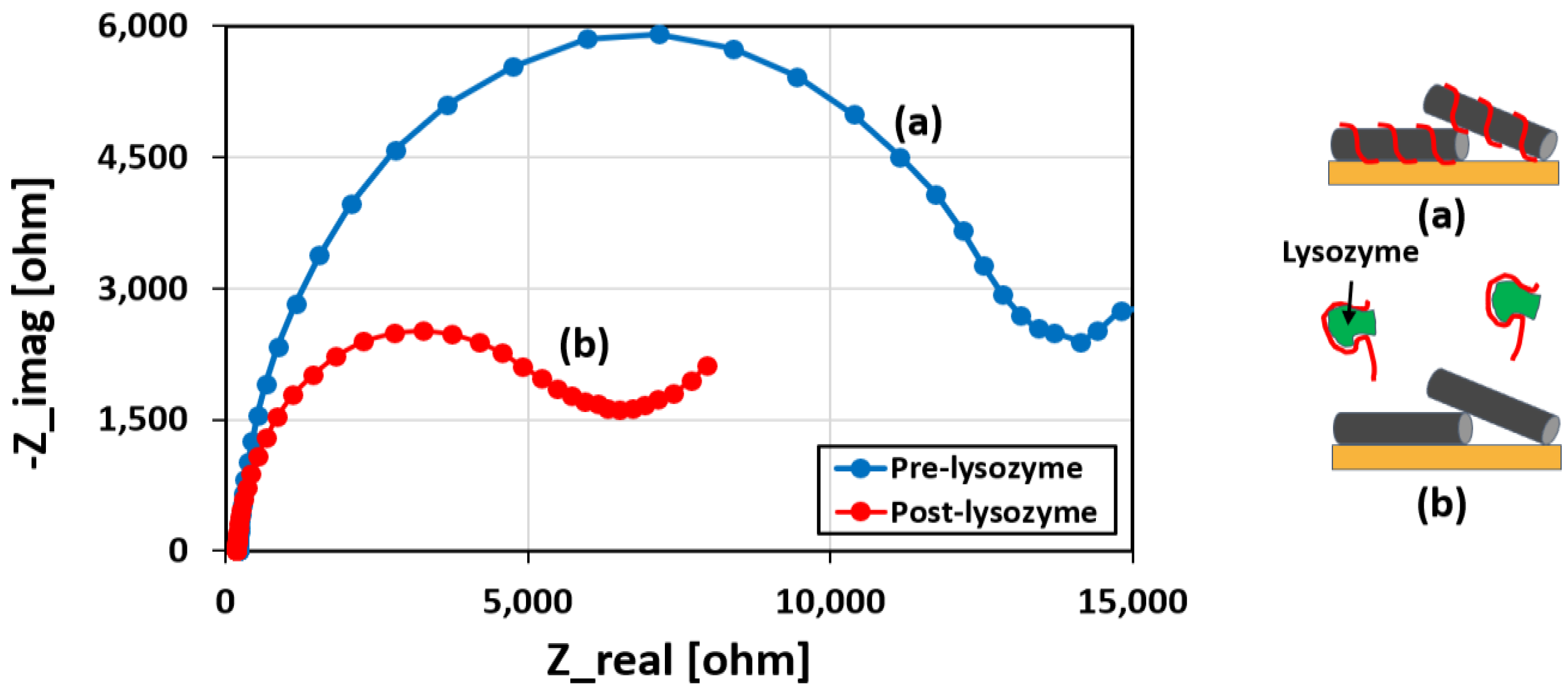
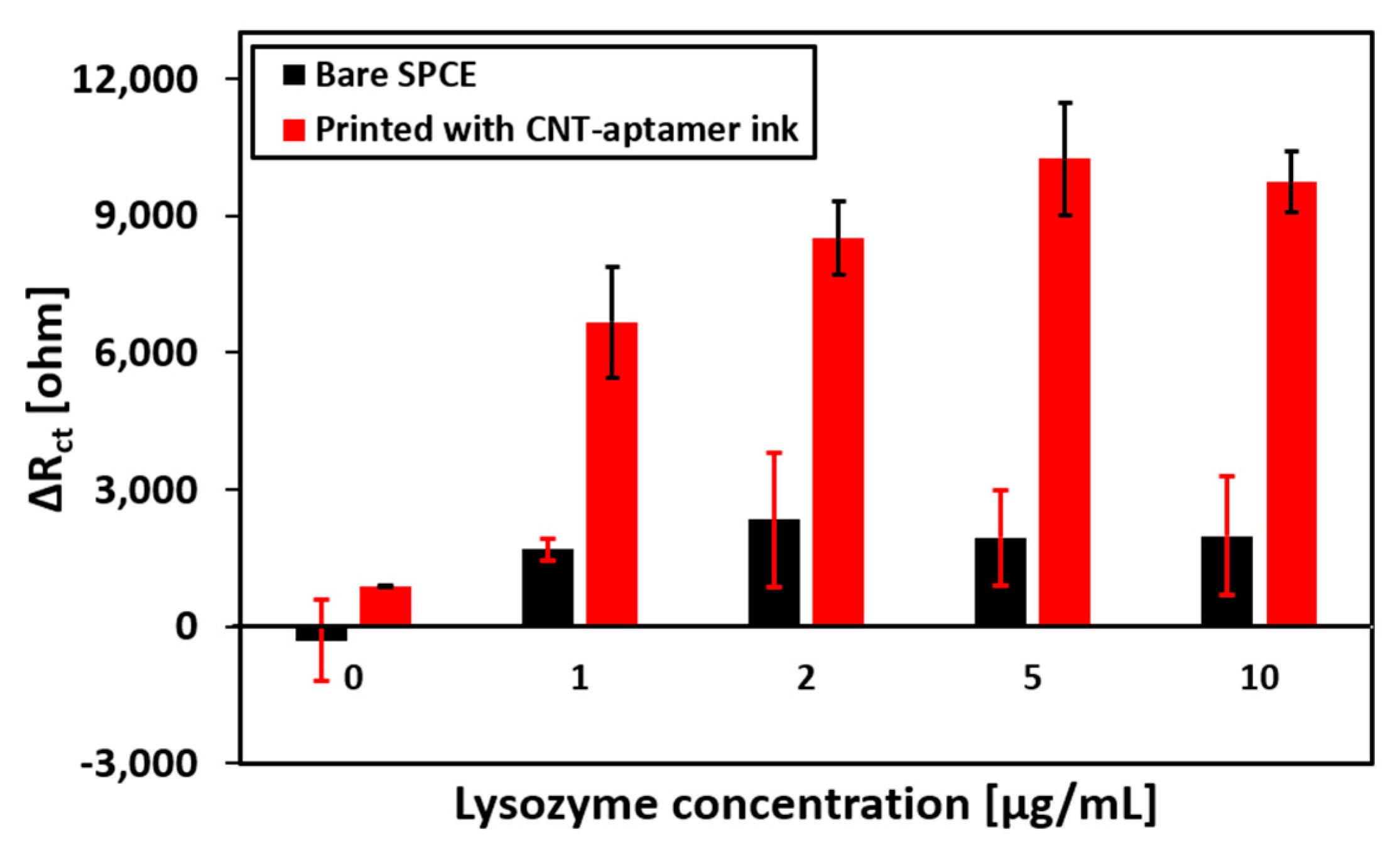
3.4. Performance of the Aptamer Sensor
3.5. Modelling of the Nyquist Curves
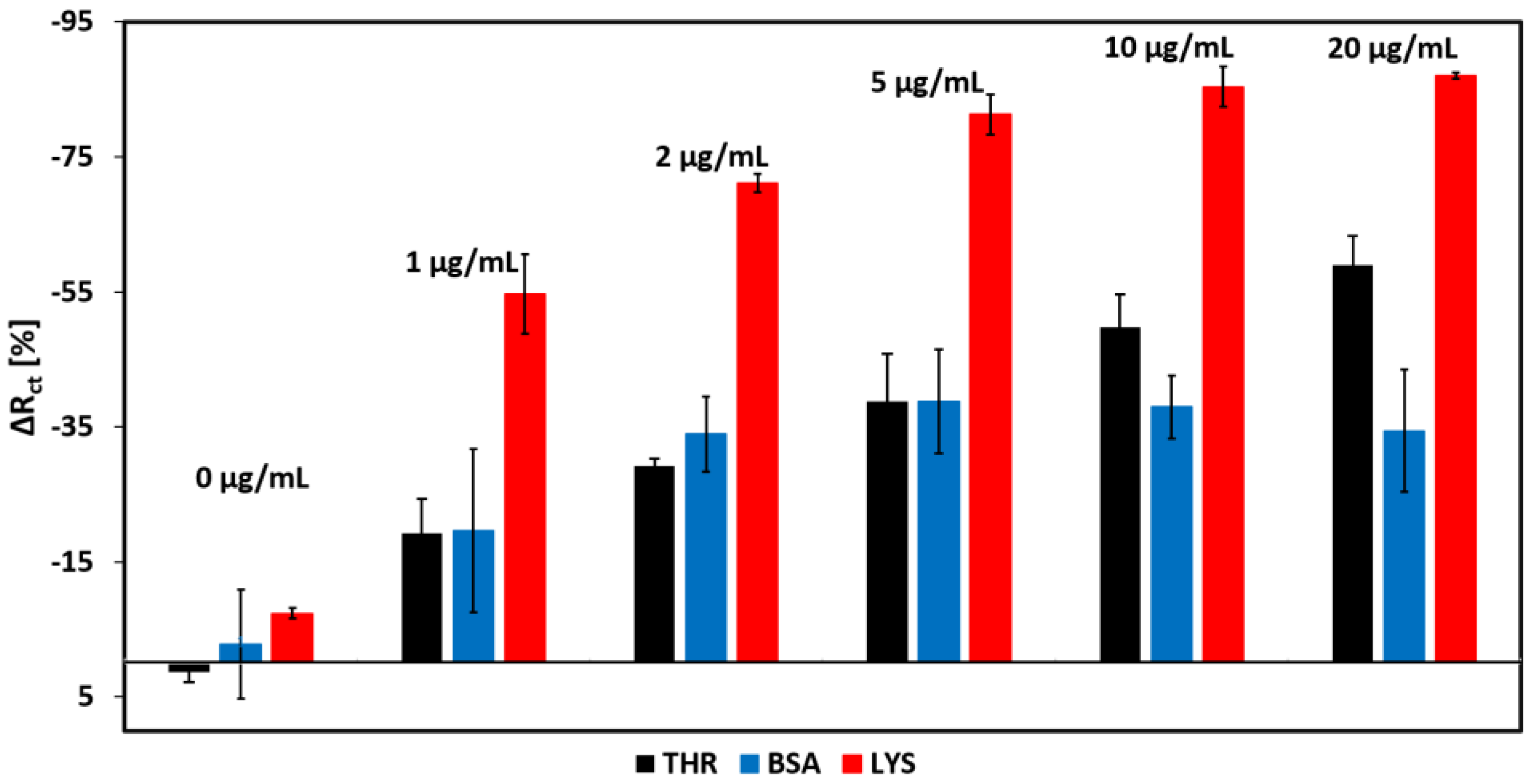
3.6. Selectivity of the Aptamer Sensor
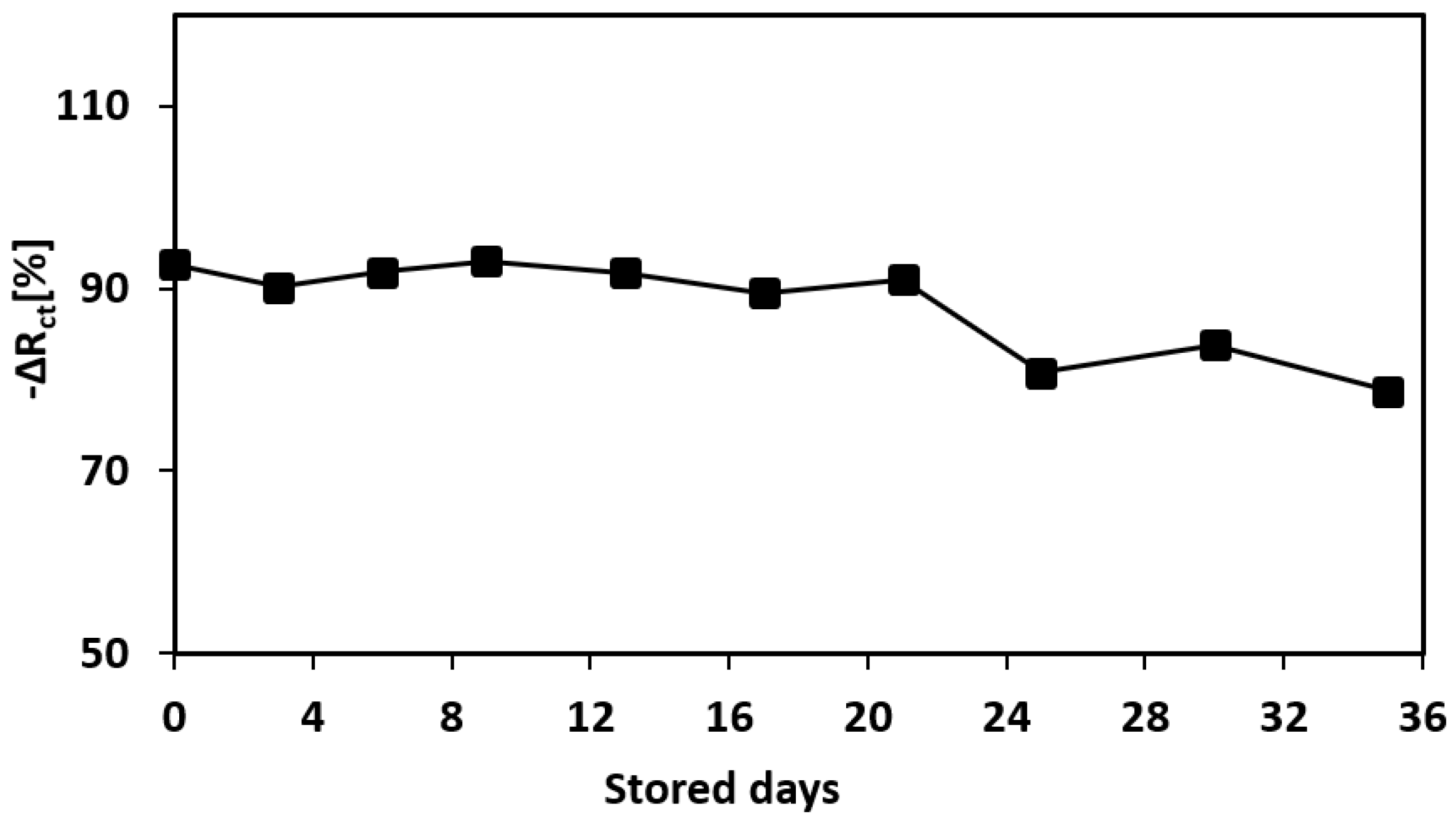
3.7. Long-Term Stability (Shelf-Life) of the Aptamer-Printed Biosensor
3.8. Comparison to Other Aptamer-Based Lysozyme Sensors
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Calculation of Printed Volume of CNT-Aptamer Ink
Appendix B
Lysozyme Binding Confirmation
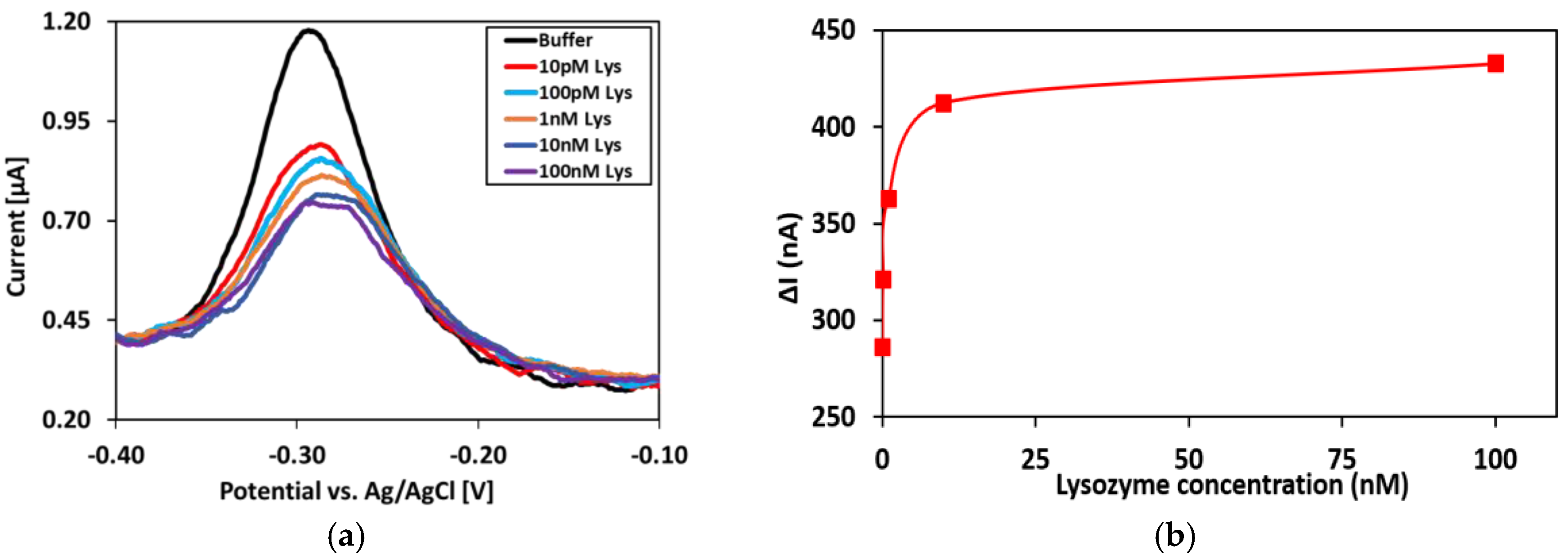
Appendix C
Chronocoulometry Experiments
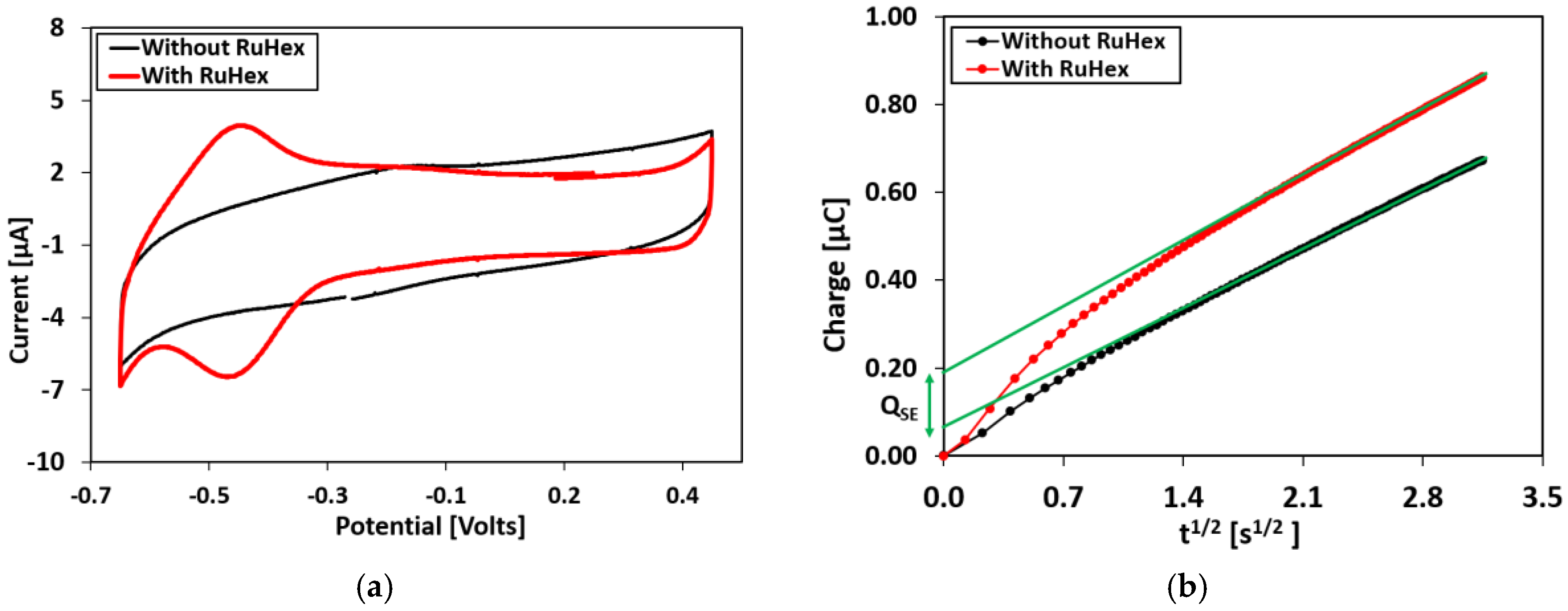
Appendix D
LOD Calculation
Appendix E
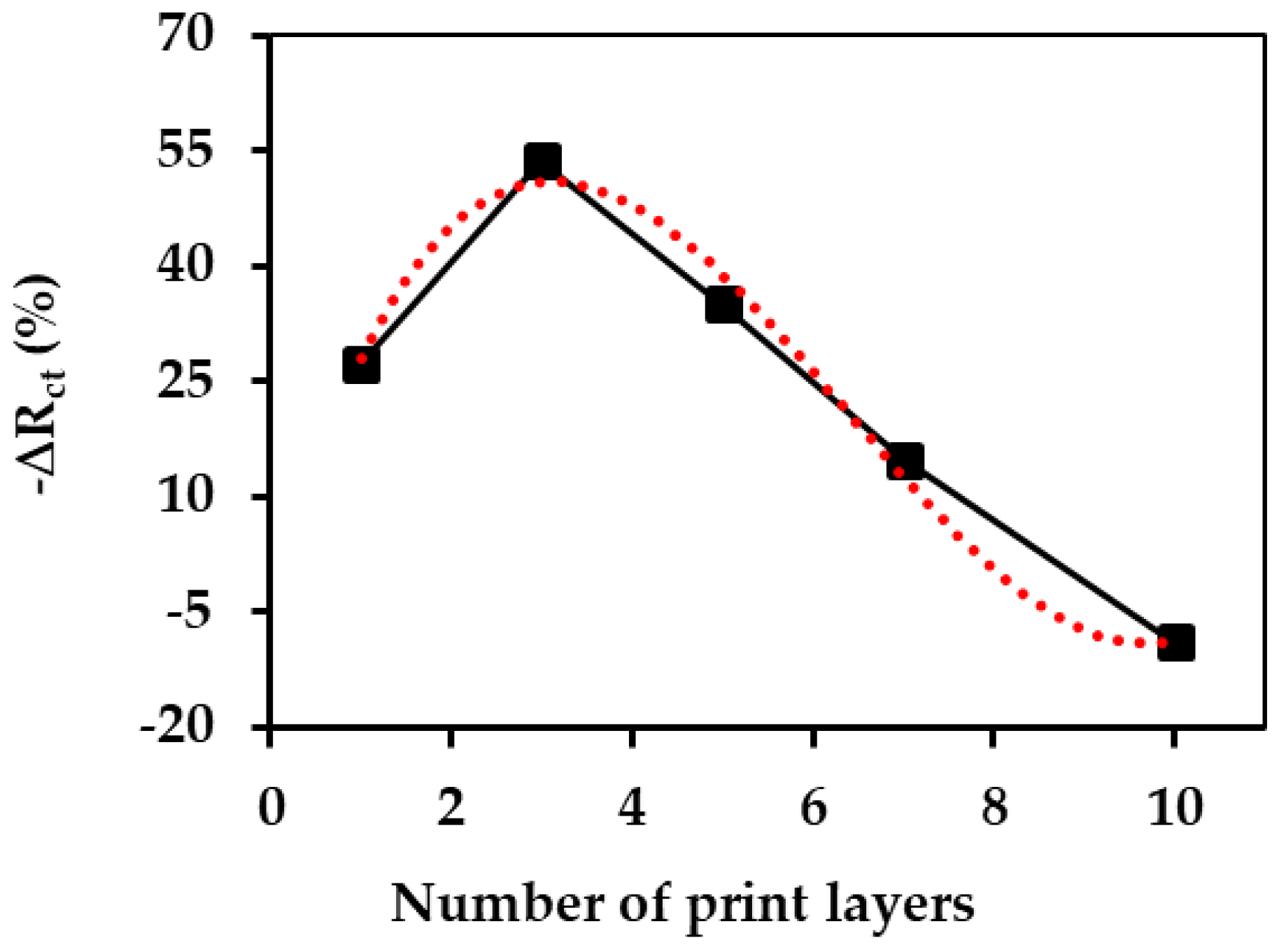
References
- Vasilescu, A.; Wang, Q.; Li, M.; Boukherroub, R.; Szunerits, S. Aptamer-Based Electrochemical Sensing of Lysozyme. Chemosensors 2016, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrbach, F.; Karadeniz, H.; Erdem, A.; Famulok, M.; Mayer, G. Label-free impedimetric aptasensor for lysozyme detection based on carbon nanotube-modified screen-printed electrodes. Anal. Biochem. 2012, 421, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, J.S.; Rajamanickam, K. Aptamers and Their Significant Role in Cancer Therapy and Diagnosis. Biomedicines 2015, 3, 248–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, A.K.H.; Ge, B.; Yu, H.-Z. Aptamer-Based Biosensors for Label-Free Voltammetric Detection of Lysozyme. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 5158–5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.-D.; Chen, Z.-B.; Zhao, H.-T.; Guo, L.; Mu, X. An aptamer-based biosensor for the detection of lysozyme with gold nanoparticles amplification. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 149, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, C.; Vizoso, F.; Alonso, L.; Rodríguez, J.C.; González, L.O.; Fernández, M.; Lamelas, M.L.; Sánchez, L.M.; García-Muñiz, J.L.; Baltasar, A.; Medrano, J. Expression and prognostic significance of lysozyme in male breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2002, 4, R16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandin, L.; Nath, S.; Armstrong, A.; Janefjord, C.; McCann, H.; Halliday, G.M.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Brorsson, A.-C.; Kagedal, K. The role of lysozyme in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2015, 11, 477–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torsteinsdóttir, I.; Hâkansson, L.; Hällgren, R.; Gudbjörnsson, B.; Arvidson, N.G.; Venge, P. Serum lysozyme: A potential marker of monocyte/macrophage activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 1999, 38, 1249–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prato, M.; Polimeni, M.; Tullio, V. Human Lysozyme in Malaria Patients: Possible Role as Biomarker for Disease Severity. In Human and Mosquito Lysozymes; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 83–90. ISBN 978-3-319-09431-1. [Google Scholar]
- Elevated beta 2-microglobulin and lysozyme levels in patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Available online: http://europepmc.org/abstract/med/6375920 (accessed on 4 September 2017).
- Near, K.A.; Lefford, M.J. Use of serum antibody and lysozyme levels for diagnosis of leprosy and tuberculosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1992, 30, 1105–1110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pascual, R.S.; Gee, J.B.; Finch, S.C. Usefulness of serum lysozyme measurement in diagnosis and evaluation of sarcoidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1973, 289, 1074–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falchuk, K.R.; Perrotto, J.L.; Isselbacher, K.J. Serum lysozyme in Crohn’s disease. A useful index of disease activity. Gastroenterology 1975, 69, 893–896. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lian, Y.; He, F.; Mi, X.; Tong, F.; Shi, X. Lysozyme aptamer biosensor based on electron transfer from SWCNTs to SPQC-IDE. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 199, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Man, Y.; Jin, X.; Pan, L.; Liu, X. Aptamer-based biosensor for label-free detection of ethanolamine by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 936, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Li, L.; Zhao, H.; Guo, L.; Mu, X. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy detection of lysozyme based on electrodeposited gold nanoparticles. Talanta 2011, 83, 1501–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kara, P.; de la Escosura-Muñiz, A.; Maltez-da Costa, M.; Guix, M.; Ozsoz, M.; Merkoçi, A. Aptamers based electrochemical biosensor for protein detection using carbon nanotubes platforms. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 1715–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.-D.; Zhao, H.-T.; Chen, Z.-B.; Mu, X.-J.; Guo, L. Aptamer biosensor for label-free impedance spectroscopy detection of thrombin based on gold nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 157, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, M.C.; Kawde, A.-N.; Wang, J. Aptamer biosensor for label-free impedance spectroscopy detection of proteins based on recognition-induced switching of the surface charge. Chem. Commun. 2005, 4267–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, M.; Yang, T.; Zhao, C.; Jiao, K. Electrochemical logic aptasensor based on graphene. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 169, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Jagota, A.; Semke, E.D.; Diner, B.A.; Mclean, R.S.; Lustig, S.R.; Richardson, R.E.; Tassi, N.G. DNA-assisted dispersion and separation of carbon nanotubes. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, E.; da Costa, T.H.; Choi, J.-W. A chemiresistive glucose sensor fabricated by inkjet printing. Microsyst. Technol. 2017, 23, 3505–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddaus, A.; Curley, P.; Griswold, M.A.; Costa, B.D.; Hou, S.; Jeong, K.J.; Song, E.; Deravi, L.F. Design and fabrication of bio-hybrid materials using inkjet printing. Biointerphases 2016, 11, 041002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, T.H.; Song, E.; Tortorich, R.P.; Choi, J.-W. A Paper-Based Electrochemical Sensor Using Inkjet-Printed Carbon Nanotube Electrodes. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2015, 4, S3044–S3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J.C.; Ellington, A.D. Automated selection of anti-protein aptamers. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2001, 9, 2525–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimatix Materials Printer DMP-2850 | Deposition Products | Industrial Inkjet Printheads|Fujifilm USA. Available online: http://www.fujifilmusa.com/products/industrial_inkjet_printheads/deposition-products/dmp-2800/ (accessed on 13 August 2017).
- White, R.J.; Phares, N.; Lubin, A.A.; Xiao, Y.; Plaxco, K.W. Optimization of Electrochemical Aptamer-Based Sensors via Optimization of Probe Packing Density and Surface Chemistry. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2008, 24, 10513–10518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.T.; Ho, C.-M.; Lillehoj, P.B. Coffee Ring Aptasensor for Rapid Protein Detection. Langmuir 2013, 29, 8440–8446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steel, A.B.; Herne, T.M.; Tarlov, M.J. Electrochemical Quantitation of DNA Immobilized on Gold. Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 4670–4677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balamurugan, S.; Obubuafo, A.; McCarley, R.L.; Soper, S.A.; Spivak, D.A. Effect of Linker Structure on Surface Density of Aptamer Monolayers and their Corresponding Protein Binding Efficiency. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 9630–9634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Zuo, Y.; Cui, C.; Yang, W.; Ma, H.; Wang, X. Rapid Quantitative Detection of Brucella melitensis by a Label-Free Impedance Immunosensor Based on a Gold Nanoparticle-Modified Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode. Sensors 2013, 13, 8551–8563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoar Abouzari, M.R.; Berkemeier, F.; Schmitz, G.; Wilmer, D. On the physical interpretation of constant phase elements. Solid State Ion. 2009, 180, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EC-Lab Software User’s Manual. Available online: http://mmrc.caltech.edu/BioLogic%20Echem/ECLab%20Manuals/EC-Lab%20software%20user’s%20manual.pdf (accessed on 13 August 2017).
- Katz, E.; Willner, I. Probing Biomolecular Interactions at Conductive and Semiconductive Surfaces by Impedance Spectroscopy: Routes to Impedimetric Immunosensors, DNA-Sensors, and Enzyme Biosensors. Electroanalysis 2003, 15, 913–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, R.; Cho, E.J.; Gehrke, B.; Bayer, T.; Park, Y.S.; Neikirk, D.P.; McDevitt, J.T.; Ellington, A.D. Aptamer-Based Sensor Arrays for the Detection and Quantitation of Proteins. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 4066–4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Zhai, S.; Ye, Z.; He, L.; Peng, D.; Feng, X.; Yang, Y.; Fang, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z. An electrochemical aptasensor based on a TiO2/three-dimensional reduced graphene oxide/PPy nanocomposite for the sensitive detection of lysozyme. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 6473–6479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, D.; Li, C.; Shangguan, L.; Qi, H.; Xue, D.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, C. Click chemistry-assisted self-assembly of DNA aptamer on gold nanoparticles-modified screen-printed carbon electrodes for label-free electrochemical aptasensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 192, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Lai, R.Y.; Plaxco, K.W. Preparation of electrode-immobilized, redox-modified oligonucleotides for electrochemical DNA and aptamer-based sensing. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 2875–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Lubin, A.A.; Heeger, A.J.; Plaxco, K.W. Label-free electronic detection of thrombin in blood serum by using an aptamer-based sensor. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed Engl. 2005, 44, 5456–5459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macazo, F.C.; Karpel, R.L.; White, R.J. Monitoring Cooperative Binding Using Electrochemical DNA-Based Sensors. Langmuir 2015, 31, 868–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lao, R.; Song, S.; Wu, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; He, L.; Fan, C. Electrochemical Interrogation of DNA Monolayers on Gold Surfaces. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 6475–6480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrivastava, A.; Gupta, V. Methods for the determination of limit of detection and limit of quantitation of the analytical methods. Chron. Young Sci. 2011, 2, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
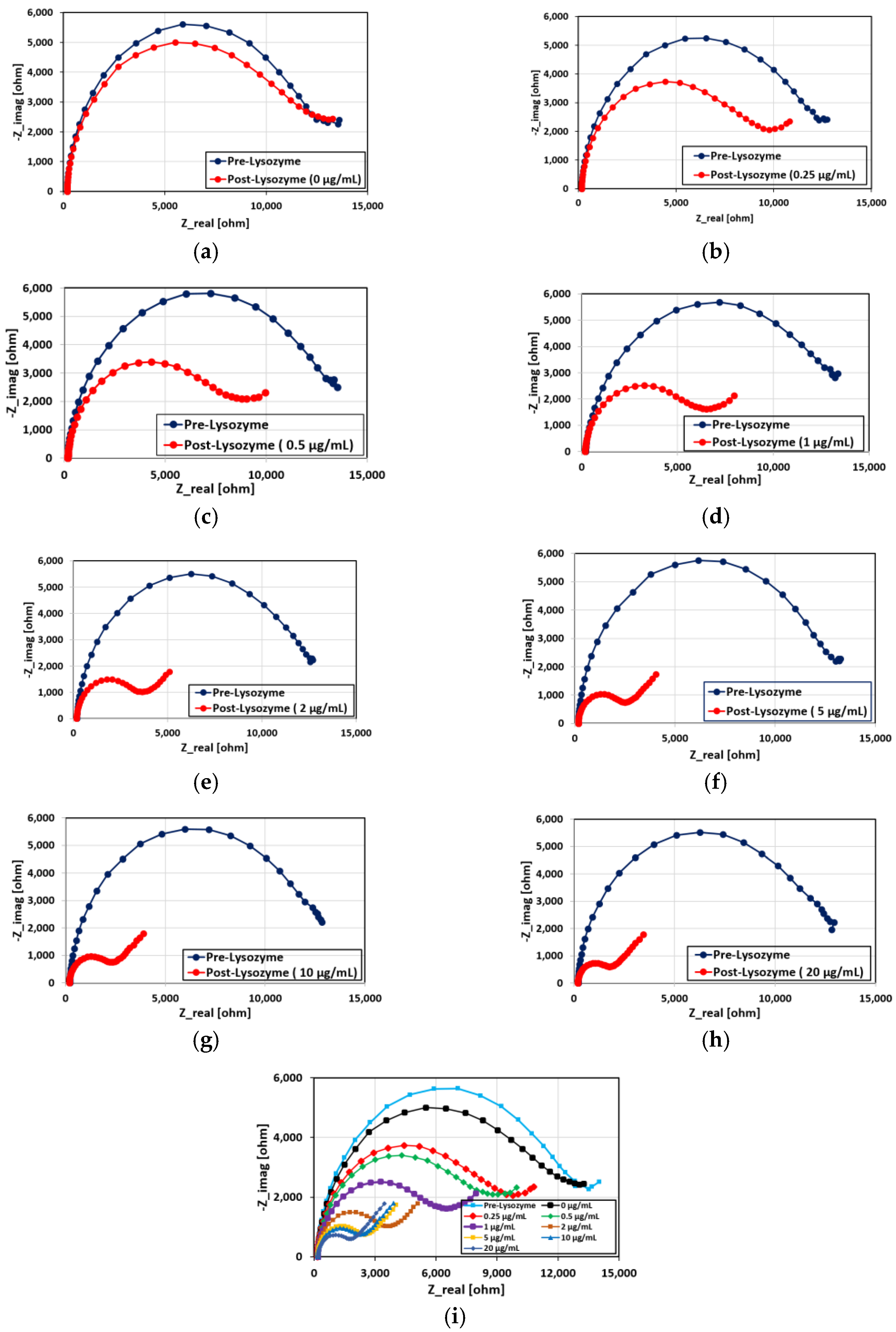
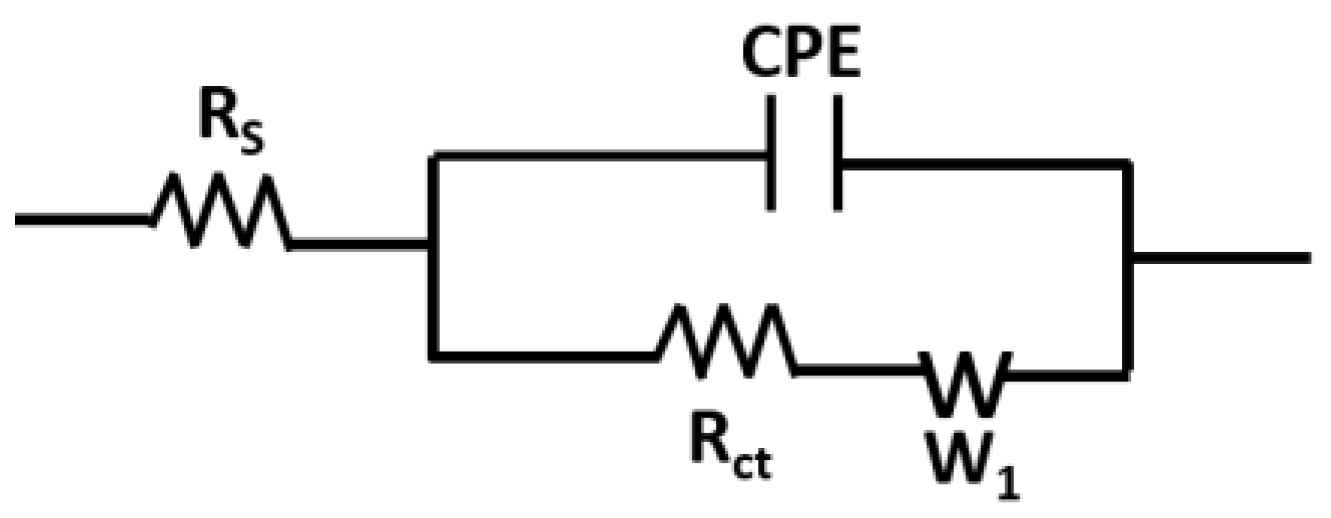
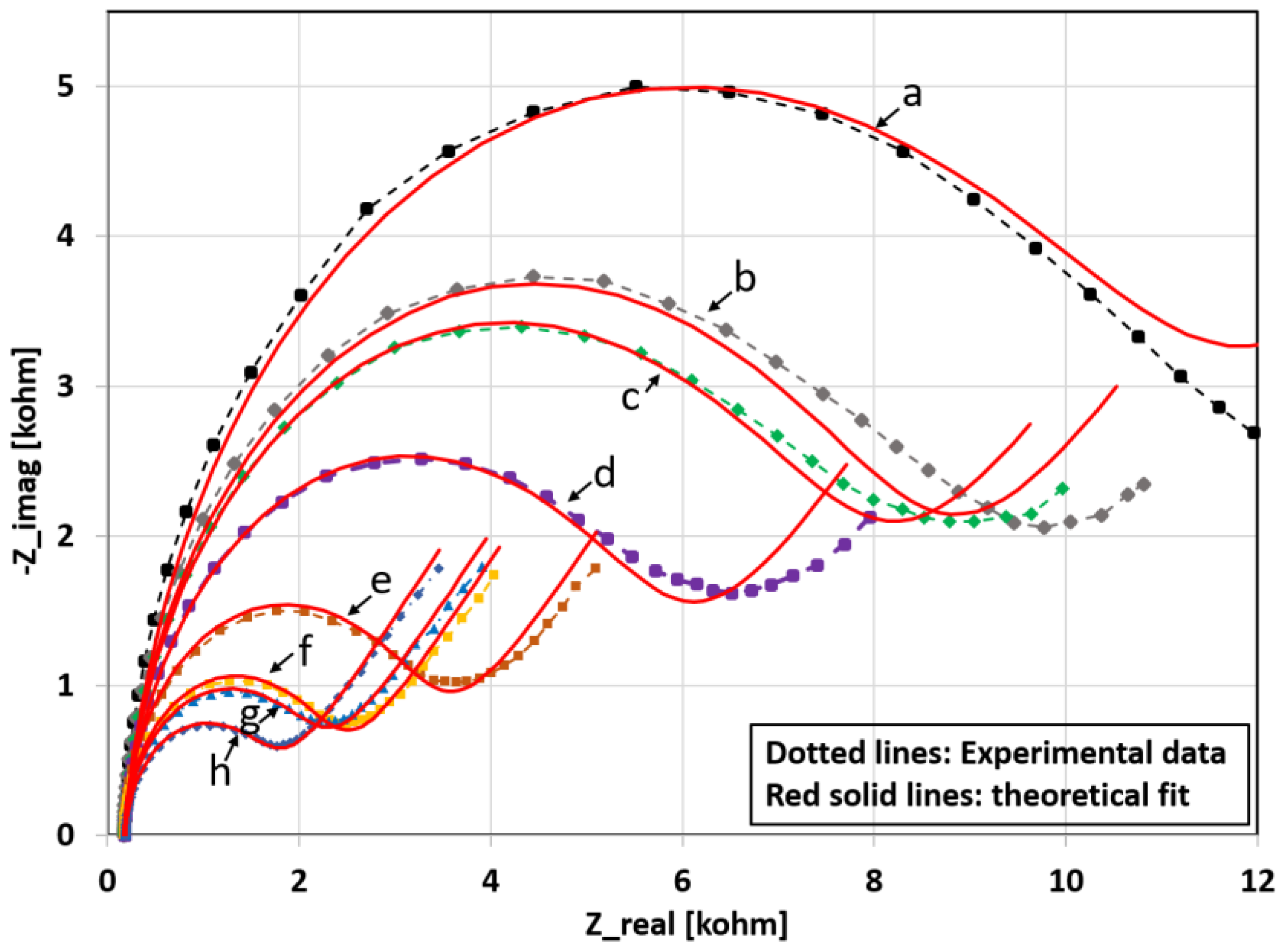
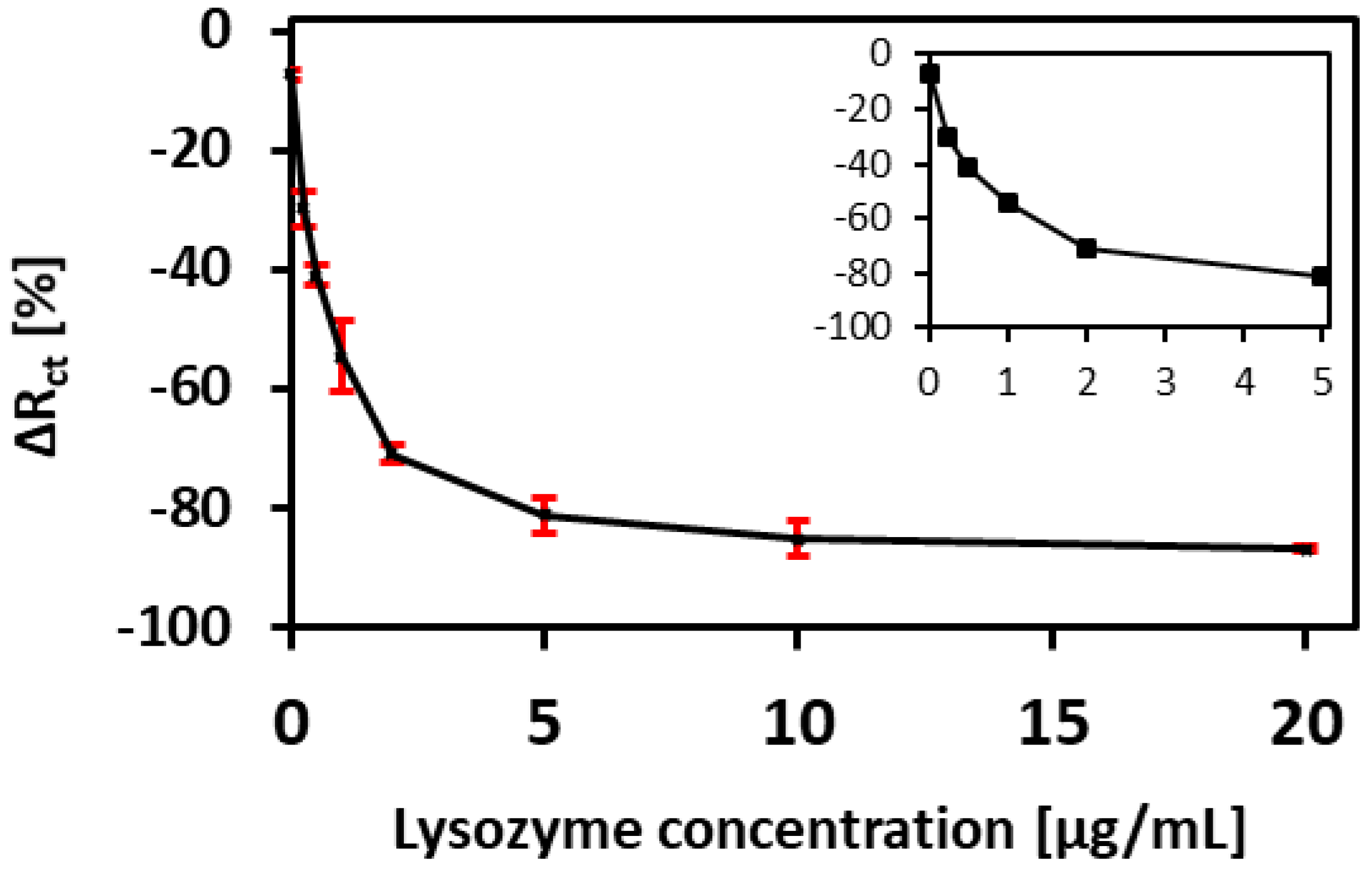
| Lys Concentration (µg/mL) | Rct (Ohm∙s) | CPE (µF∙sn−1) | α1 | Rs (Ohm∙s) | δ1 (Ohm∙s1/2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10511 | 4.734 | 0.962 | 186 | 2086 |
| 0.25 | 7850 | 4.567 | 0.963 | 172 | 2154 |
| 0.50 | 7251 | 6.158 | 0.944 | 178 | 1928 |
| 1 | 5359 | 5.313 | 0.943 | 185 | 1833 |
| 2 | 3028 | 4.917 | 0.968 | 175 | 1554 |
| 5 | 2064 | 4.449 | 0.970 | 178 | 1501 |
| 10 | 1869 | 5.518 | 0.969 | 189 | 1542 |
| 20 | 1435 | 5.526 | 0.961 | 192 | 1491 |
| LOD | Linear Range | Immobilization Technique | Detection Mechanism | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12.09 µg/mL | 0–200 µg/mL | Covalent | EIS | [2] |
| 1.4 fg/mL | 1.4 fg/mL–14 ng/mL | Thiol-Gold | SWV | [5] |
| 7 ng/mL | 14 ng/mL–1.12 µg/mL | Thiol-Gold | SPQC | [14] |
| 0.14 fg/mL | 1.4 fg/mL–6.96 pg/mL | Thiol-Gold | EIS | [16] |
| 200 ng/mL | 0–10 µg/mL | Biotin-Avidin | EIS | [19] |
| 76.6 fg/mL | 98.2 pg/mL–49.1 ng/mL | π–π stacking | DPV | [36] |
| 0.4 pg/mL | 1–50 pg/mL | Covalent | SWV | [37] |
| 90 ng/mL | 0–1.0 µg/mL | π–π stacking | EIS | This work |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, N.I.; Maddaus, A.G.; Song, E. A Low-Cost Inkjet-Printed Aptamer-Based Electrochemical Biosensor for the Selective Detection of Lysozyme. Biosensors 2018, 8, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios8010007
Khan NI, Maddaus AG, Song E. A Low-Cost Inkjet-Printed Aptamer-Based Electrochemical Biosensor for the Selective Detection of Lysozyme. Biosensors. 2018; 8(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios8010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Niazul Islam, Alec G. Maddaus, and Edward Song. 2018. "A Low-Cost Inkjet-Printed Aptamer-Based Electrochemical Biosensor for the Selective Detection of Lysozyme" Biosensors 8, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios8010007
APA StyleKhan, N. I., Maddaus, A. G., & Song, E. (2018). A Low-Cost Inkjet-Printed Aptamer-Based Electrochemical Biosensor for the Selective Detection of Lysozyme. Biosensors, 8(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios8010007