Cutting Edge Methods for Non-Invasive Disease Diagnosis Using E-Tongue and E-Nose Devices
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Current Diagnostic Methods and Motivation
1.2. “Omics” Profiling and Impact on Personalized Medicine
2. Electronic Noses and Tongue Devices Background Technology
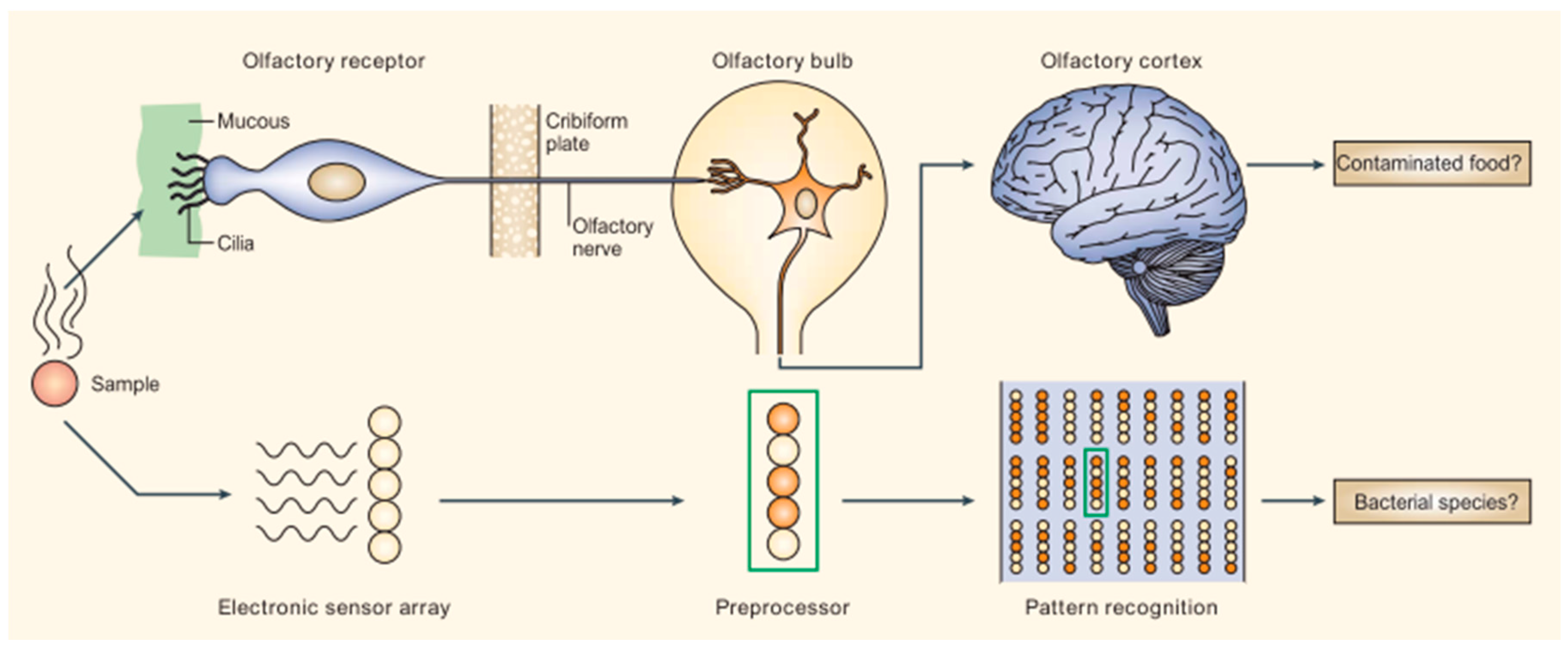
2.1. Mammalian Olfactory System as a Platform for Cross-Reactive Sensing
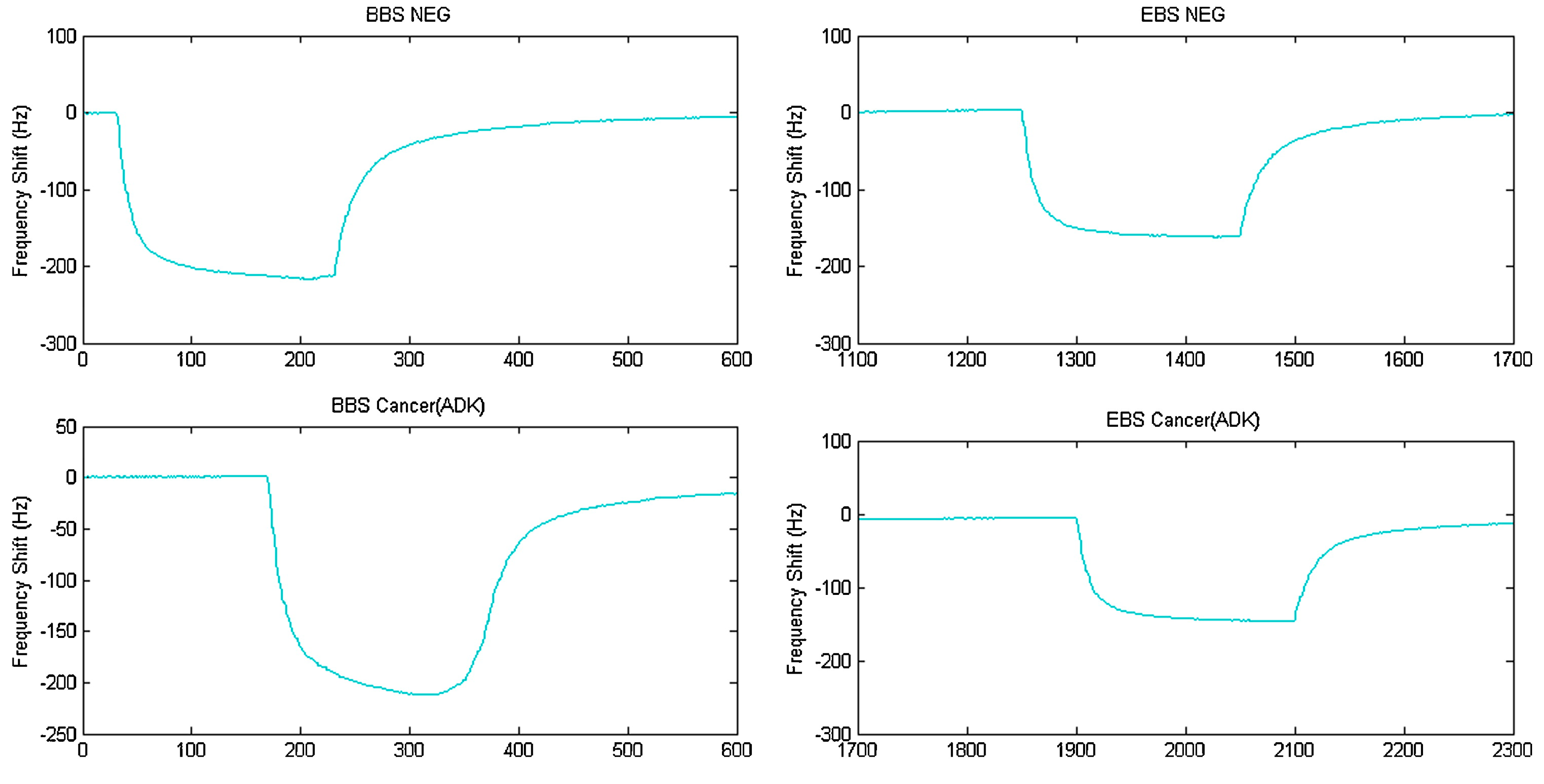
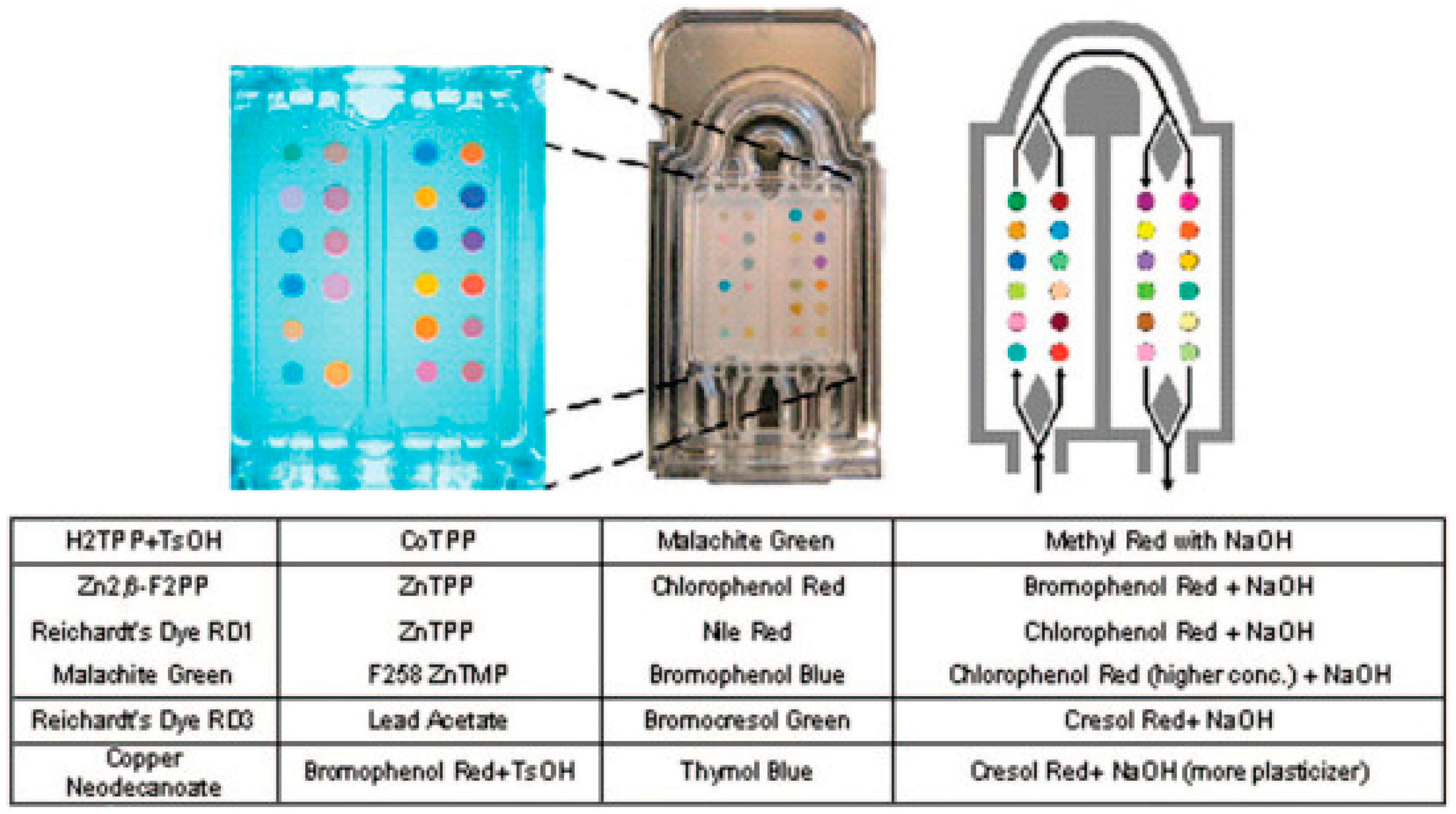
2.2. Disease Diagnoses with B-CRSAs
3. Cancer Metabolomics
3.1. Lung Cancer
3.2. Colorectal Cancer
3.3. Head and Neck Cancer
3.4. Prostate Cancer
4. Airway Diseases
4.1. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
4.2. Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
4.3. Pulmonary Sarcoidosis (PS)
5. Neurodegenerative Diseases and Mental Health
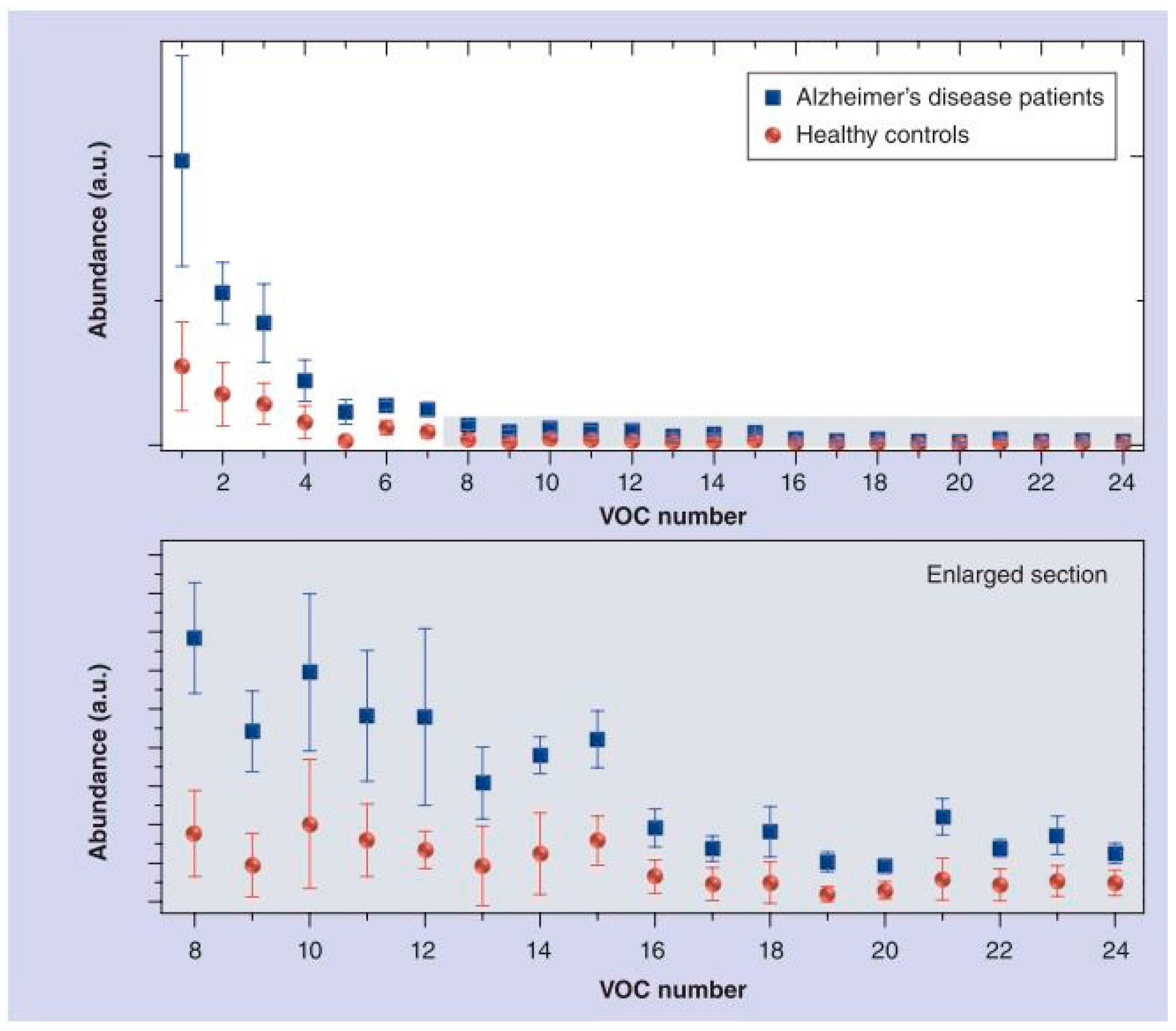
5.1. Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) and Parkinson’s Disease (PD)
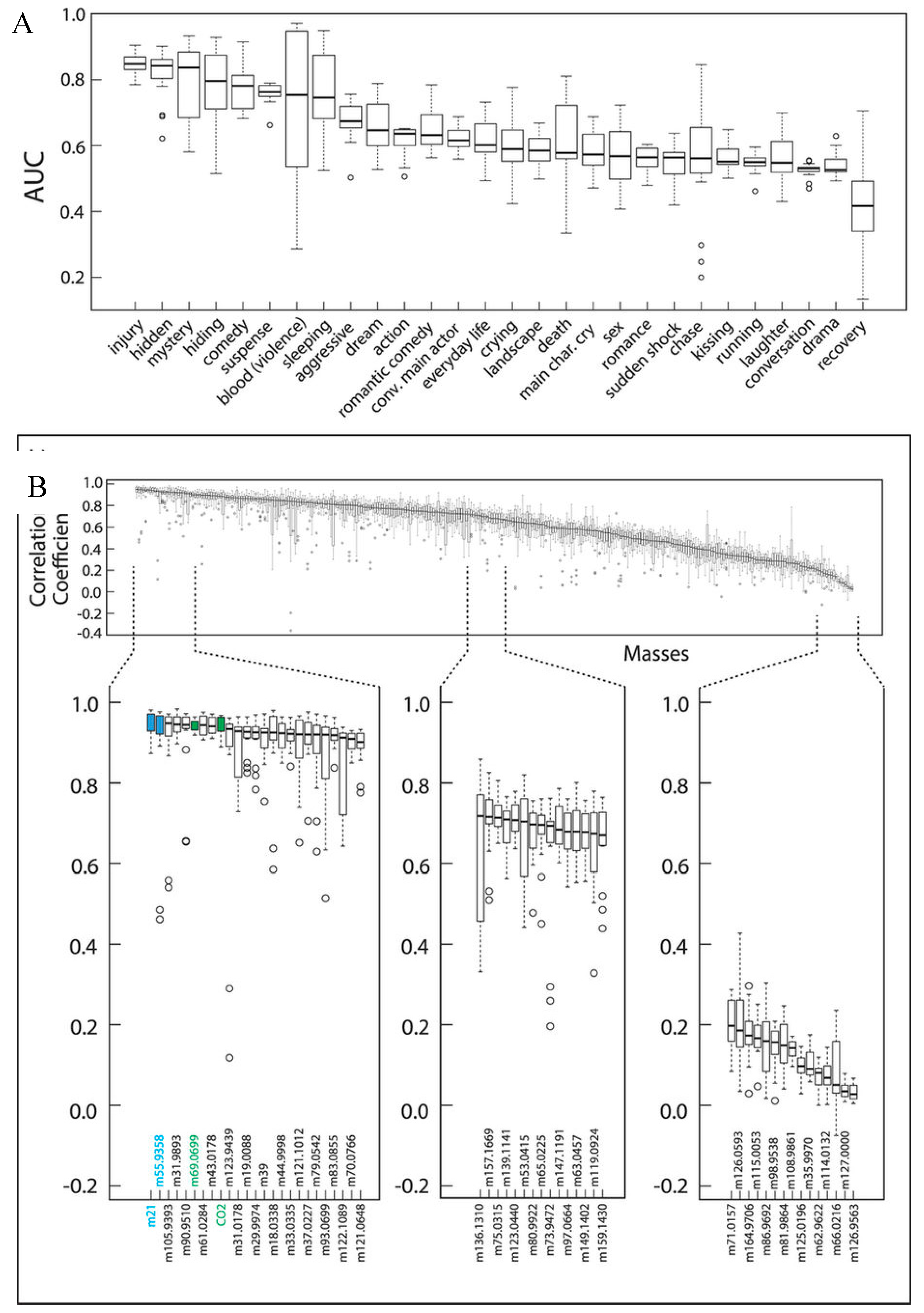
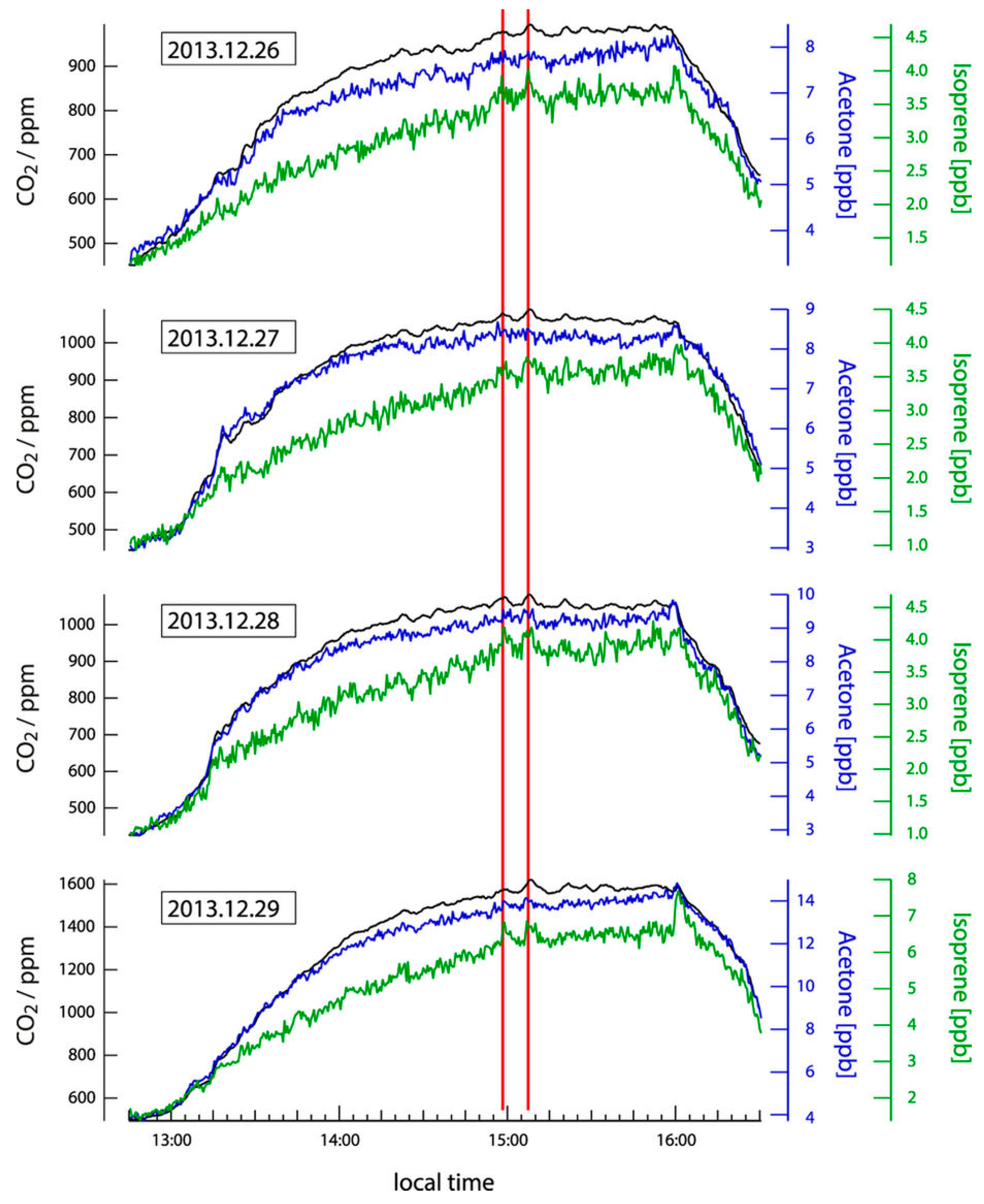
5.2. Future Direction: Chronic Stress and Anxiety
6. Metabolic Disorders
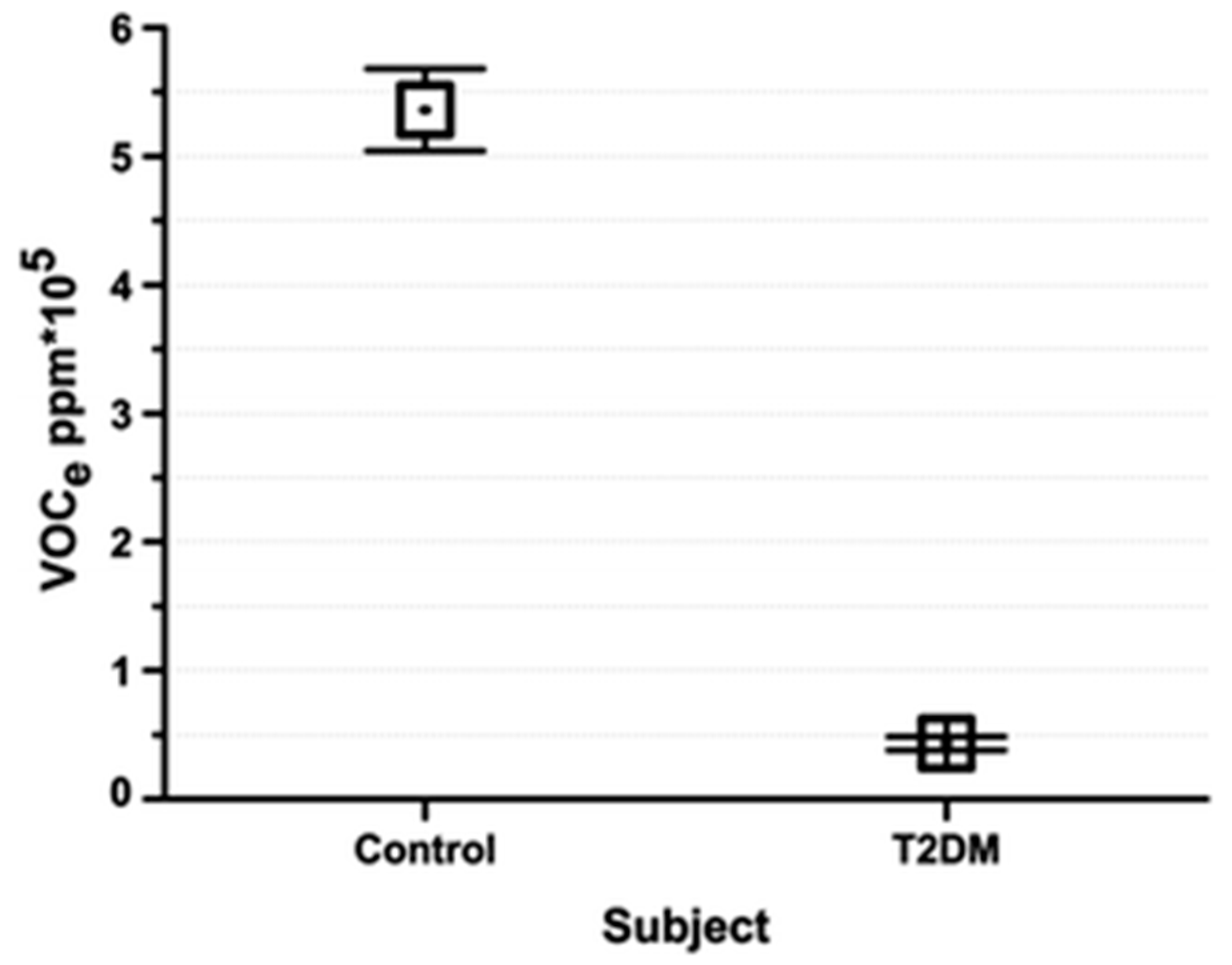
6.1. Diabetes
6.2. Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) and Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
6.3. Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
6.4. Future Direction: Plasma Lipid Measurement through Exhaled Breath
7. Future Directions and Remaining Challenges for B-CRSA Diagnostics
7.1. Remaining Technological Challenges
7.2. New Technological Improvements
7.3. Sampling
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gowda, G.A.N.; Zhang, S.; Gu, H.; Asiago, V.; Shanaiah, N.; Raftery, D. Metabolomics-based methods for early disease diagnostics. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2008, 8, 617–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walt, D.R.; Stitzel, S.E.; Aernecke, M.J. Artificial noses. Am. Sci. 2012, 100, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The American Cancer Society. Key Statistics for Lung Cancer; The American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fedewa, S.A.; Ahnen, D.J.; Meester, R.G.S.; Barzi, A.; Jemal, A. Colorectal Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts & Figures; American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Prevention & Early Detection Facts & Figures 2015–2016; American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Franklin, K.A.; Lindberg, E. Obstructive sleep apnea is a common disorder in the population—A review on the epidemiology of sleep apnea. J. Thorac. Dis. 2015, 7, 1311–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roehrig, C. Mental Disorders Top the List of the Most Costly Conditions in the United States: $201 Billion. Health Aff. 2016, 36, 1130–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association. Estimates of Diabetes and Its Burden in the Epidemiologic Estimation Methods; National Diabetes Statistics Report; American Diabetes Association: Arlington County, VA, USA, 2014; pp. 2009–2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, G.G. The global burden of IBD: From 2015 to 2025. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosnes, J.; Gowerrousseau, C.; Seksik, P.; Cortot, A. Epidemiology and natural history of inflammatory bowel diseases. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 1785–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Sayed Zaki, M. High-throughput Screening in Medical Diagnosis and Prognosis. In OMICS: Biomedical Perspectives and Applications; Barh, D., Blum, K., Madigan, M.A., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 141–163. [Google Scholar]
- Hamburg, M.A.; Collins, F.S. The Path to Personalized Medicine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, D.F.; Markus, H.S.; Leslie, R.D.; Topol, E.J. Personalized medicine: Risk prediction, targeted therapies and mobile health technology. BMC Med. 2014, 12, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Snyder, M. Promise of personalized omics to precision medicine. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Syst. Biol. Med. 2013, 5, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katada, S.; Hirokawa, T.; Oka, Y.; Suwa, M.; Touhara, K. Structural basis for a broad but selective ligand spectrum of a mouse olfactory receptor: Mapping the odorant-binding site. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 1806–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buck, L.B. Unraveling the sense of smell (Nobel Lecture). Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 6128–6140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glenza, J. Dog Trained to Detect Thyroid Cancer “with 88% Accuracy”. US News. The Guardian. 9 March 2015. Available online: https://www.theguardian.com/us-news/2015/mar/09/dog-detects-thyroid-cancer-research (accessed on: 9 September 2017).
- Simões Da Costa, A.M.; Delgadillo, I.; Rudnitskaya, A. Detection of copper, lead, cadmium and iron in wine using electronic tongue sensor system. Talanta 2014, 129, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano, J.; Fernández, M.J.; Fontecha, J.L.; Aleixandre, M.; Santos, J.P.; Sayago, I.; Arroyo, T.; Cabellos, J.M.; Gutiérrez, F.J.; Horrillo, M.C. Wine classification with a zinc oxide SAW sensor array. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 120, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, A.M.; Dias, L.G.; Veloso, A.C.A.; Meirinho, S.G.; Morais, J.S.; MacHado, A.A.S.C. An electronic tongue for gliadins semi-quantitative detection in foodstuffs. Talanta 2011, 83, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; He, L. Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy for the Chemical Analysis of Food. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falasconi, M.; Concina, I.; Gobbi, E.; Sberveglieri, V.; Pulvirenti, A.; Sberveglieri, G. Electronic Nose for Microbiological Quality Control of Food Products. Int. J. Electrochem. 2012, 2012, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Pang, X.; Chen, D.; Cheng, H.; Hu, X.; Wu, J. Evaluation of Chinese tea by the electronic nose and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry: Correlation with sensory properties and classification according to grade level. Food Res. Int. 2013, 53, 864–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Mendez, M.L.; Preedy, V.R. (Eds.) Electronic Noses and Tongues in Food Science, 1st ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Albert, K.J.; Walt, D.R. High-speed fluorescence detection of explosives-like vapors. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 1947–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askim, J.R.; Li, Z.; LaGasse, M.K.; Rankin, J.M.; Suslick, K.S. An optoelectronic nose for identification of explosives. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brudzewski, K.; Osowski, S.; Pawlowski, W. Metal oxide sensor arrays for detection of explosives at sub-parts-per million concentration levels by the differential electronic nose. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 161, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.J.; Duragkar, N.; Rao, V.R. An ultra-sensitive piezoresistive polymer nano-composite microcantilever sensor electronic nose platform for explosive vapor detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 192, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Sun, H.; Wang, X. Saliva metabolomics opens door to biomarker discovery, disease diagnosis, and treatment. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 168, 1718–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, A.D. Advances in electronic-nose technologies for the detection of volatile biomarker metabolites in the human breath. Metabolites 2015, 5, 140–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montuschi, P.; Mores, N.; Trové, A.; Mondino, C.; Barnes, P.J. The electronic nose in respiratory medicine. Respiration 2012, 85, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roine, A.; Veskimäe, E.; Tuokko, A.; Kumpulainen, P.; Koskimäki, J.; Keinänen, T.A.; Häkkinen, M.R.; Vepsäläinen, J.; Paavonen, T.; Lekkala, J.; et al. Detection of Prostate Cancer by an Electronic Nose: A Proof of Principle Study. J. Urol. 2014, 192, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadoon, S.; Karim, S.; Akram, M.R.; Kalsoom Khan, A.; Zia, M.A.; Siddiqi, A.R.; Murtaza, G. Recent developments in sweat analysis and its applications. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigau, M.; Olivan, M.; Garcia, M.; Sequeiros, T.; Montes, M.; Colás, E.; Llauradó, M.; Planas, J.; de Torres, I.; Morote, J.; et al. The present and future of prostate cancer urine biomarkers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 12620–12649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Boer, N.K.H.; de Meij, T.G.J.; Oort, F.A.; Ben Larbi, I.; Mulder, C.J.J.; van Bodegraven, A.A.; van der Schee, M.P. The Scent of Colorectal Cancer: Detection by Volatile Organic Compound Analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 12, 1085–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tisch, U.; Nassar, M.; Axelrod, N.; Azar, F.; Marmur, A.; Aharon-peretz, J.; Haick, H. Detection of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease from exhaled breath using nanomaterial-based sensors. Nanomedicine 2013, 8, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brekelmans, M.P.; Fens, N.; Brinkman, P.; Bos, L.D.; Sterk, P.J.; Tak, P.P.; Gerlag, D.M. Smelling the Diagnosis: The Electronic Nose as Diagnostic Tool in Inflammatory Arthritis. A Case-Reference Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hicks, L.C.; Huang, J.; Kumar, S.; Powles, S.T.; Orchard, T.R.; Hanna, G.B.; Williams, H.R.T. Analysis of Exhaled Breath Volatile Organic Compounds in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Pilot Study. J. Crohns. Colitis 2015, 9, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Mias, G.I.; Li-Pook-Than, J.; Jiang, L.; Lam, H.Y.K.; Chen, R.; Miriami, E.; Karczewski, K.J.; Hariharan, M.; Dewey, F.E.; et al. Personal omics profiling reveals dynamic molecular and medical phenotypes. Cell 2012, 148, 1293–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragonieri, S.; Porcelli, F.; Longobardi, F.; Carratù, P.; Aliani, M.; Ventura, V.A.; Tutino, M.; Quaranta, V.N.; Resta, O.; de Gennaro, G. An electronic nose in the discrimination of obese patients with and without obstructive sleep apnoea. J. Breath Res. 2015, 9, 26005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agapiou, A.; Mikedi, K.; Karma, S.; Giotaki, Z.K.; Kolostoumbis, D.; Papageorgiou, C.; Zorba, E.; Spiliopoulou, C.; Amann, A.; Statheropoulos, M. Physiology and biochemistry of human subjects during entrapment. J. Breath Res. 2013, 7, 16004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Natale, C.; Macagnano, A.; Paolesse, R.; Tarizzo, E.; Mantini, A.; D’Amico, A. Human skin odor analysis by means of an electronic nose. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2000, 65, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, A.; Baier, V.; Reisch, R.; Von Roda, K.; Elsner, P.; Ahlers, H.; Stein, G. Smelling renal dysfunction via electronic nose. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2005, 33, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westenbrink, E.; Arasaradnam, R.P.; O’Connell, N.; Bailey, C.; Nwokolo, C.; Bardhan, K.D.; Covington, J.A. Development and application of a new electronic nose instrument for the detection of colorectal cancer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 67, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorn, R.M.S.; Greenman, J. Microbial volatile compounds in health and disease conditions. J. Breath Res. 2012, 6, 24001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodogiannis, V.S. Point-of-care diagnosis of bacterial pathogens in vitro, utilising an electronic nose and wavelet neural networks. Neural Comput. Appl. 2013, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arasaradnam, R.P.; Ouaret, N.; Thomas, M.G.; Quraishi, N.; Heatherington, E.; Nwokolo, C.U.; Bardhan, K.D.; Covington, J.A. A novel tool for noninvasive diagnosis and tracking of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2013, 19, 999–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Meij, T.G.; Larbi, I.B.; Van Der Schee, M.P.; Lentferink, Y.E.; Paff, T.; Terhaar Sive Droste, J.S.; Mulder, C.J.; Van Bodegraven, A.A.; De Boer, N.K. Electronic nose can discriminate colorectal carcinoma and advanced adenomas by fecal volatile biomarker analysis: Proof of principle study. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 134, 1132–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meinardi, S.; Jin, K.B.; Barletta, B.; Blake, D.R.; Vaziri, N.D. Exhaled breath and fecal volatile organic biomarkers of chronic kidney disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 2531–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Meij, T.G.J.; de Boer, N.K.H.; Benninga, M.A.; Lentferink, Y.E.; de Groot, E.F.J.; van de Velde, M.E.; van Bodegraven, A.A.; van der Scheea, M.P. Faecal Gas Analysis by Electronic Nose as a Novel, Non-invasive Method for Assessment of Active and Quiescent Paediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Proof of Principle Study. J. Crohns Colitis 2014, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oncescu, V.; O’Dell, D.; Erickson, D. Smartphone based health accessory for colorimetric detection of biomarkers in sweat and saliva. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 3232–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raiszadeh, M.M.; Ross, M.M.; Russo, P.S.; Schaepper, M.A.; Zhou, W.; Deng, J.; Ng, D.; Dickson, A.; Dickson, C.; Strom, M.; et al. Proteomic analysis of eccrine sweat: Implications for the discovery of schizophrenia biomarker proteins. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 2127–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heikenfeld, J. Bioanalytical devices: Technological leap for sweat sensing. Nature 2016, 529, 475–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, L.; Tullus, K.; Pilkington, C.; Chesters, C.; Marks, S.D.; Newland, P.; Jones, C.A.; Beresford, M.W. Urine biomarkers for monitoring juvenile lupus nephritis: A prospective longitudinal study. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2014, 29, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parikh, C.R.; Dahl, N.K.; Chapman, A.B.; Bost, J.E.; Edelstein, C.L.; Comer, D.M.; Zeltner, R.; Tian, X.; Grantham, J.J.; Somlo, S. Evaluation of urine biomarkers of kidney injury in polycystic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2012, 81, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slavish, D.C.; Graham-Engeland, J.E.; Smyth, J.M.; Engeland, C.G. Salivary markers of inflammation in response to acute stress. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 44, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonchukov, S.; Sukhinina, A.; Bakhmutov, D.; Minaeva, S. Raman spectroscopy of saliva as a perspective method for periodontitis diagnostics. Laser Phys. Lett. 2012, 9, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M.; Khalaila, R. Saliva pH as a biomarker of exam stress and a predictor of exam performance. J. Psychosom. Res. 2014, 77, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathnayake, N.; Åkerman, S.; Klinge, B.; Lundegren, N.; Jansson, H.; Tryselius, Y.; Sorsa, T.; Gustafsson, A. Salivary Biomarkers for Detection of Systemic Diseases. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshizawa, J.M.; Schafer, C.A.; Schafer, J.J.; Farrell, J.J.; Paster, B.J.; Wong, D.T.W. Salivary biomarkers: Toward future clinical and diagnostic utilities. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, V.M.; Kennedy, A.D.; Panagakos, F.; Devizio, W.; Trivedi, H.M.; Jönsson, T.; Guo, L.; Cervi, S.; Scannapieco, F.A. Global Metabolomic Analysis of Human Saliva and Plasma from Healthy and Diabetic Subjects, with and without Periodontal Disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, M.; Sabas, M.; Greenberg, J. Increased pentane and carbon disulfide in breath of patients with Schizophrenia. J. Clin. Pathol. 1993, 46, 861–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, A.P.; Magan, N. Electronic noses and disease diagnostics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alphus Dan Wilson, A.D. Recent progress in the design and clinical development of electronic-nose technologies. Nanobiosens. Dis. Diagn. 2016, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasilewski, T.; Gębicki, J.; Kamysz, W. Bioelectronic nose: Current status and perspectives. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 480–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, J.E.; Bui, E.T.H.; Simon, N.M.; Fenniri, H. Artificial Nose Technology: Status and Prospects in Diagnostics. Trends Biotechnol. 2016, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santini, G.; Mores, N.; Penas, A.; Capuano, R.; Mondino, C.; Trové, A.; Macagno, F.; Zini, G.; Cattani, P.; Martinelli, E.; et al. Electronic nose and exhaled breath NMR-based metabolomics applications in airways disease. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 1610–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amico, A.; Di Natale, C.; MacAgnano, A.; Davide, F.; Mantini, A.; Tarizzo, E.; Paolesse, R.; Boschi, T. Technologies and tools for mimicking olfaction: Status of the Rome “Tor Vergata” electronic nose. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1998, 13, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Natale, C.; Macagnano, A.; Martinelli, E.; Paolesse, R.; D’Arcangelo, G.; Roscioni, C.; Finazzi-Agrò, A.; D’Amico, A. Lung cancer identification by the analysis of breath by means of an array of non-selective gas sensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2003, 18, 1209–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santonico, M.; Lucantoni, G.; Pennazza, G.; Capuano, R.; Galluccio, G.; Roscioni, C.; La Delfa, G.; Consoli, D.; Martinelli, E.; Paolesse, R.; et al. In situ detection of lung cancer volatile fingerprints using bronchoscopic air-sampling. Lung Cancer 2012, 77, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzone, P.J.; Wang, X.-F.; Xu, Y.; Mekhail, T.; Beukemann, M.C.; Na, J.; Kemling, J.W.; Suslick, K.S.; Sasidhar, M. Exhaled breath analysis with a colorimetric sensor array for the identification and characterization of lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mañoso, E. S.; Herrera-Basurto, R.; Simonet, B. M.; Valcárcel, M. A quartz crystal microbalance modified with carbon nanotubes as a sensor for volatile organic compounds. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2013, 186, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaruwongrungsee, K.; Waiwijit, U.; Wisitsoraat, A.; Sangworasil, M.; Pintavirooj, C.; Tuantranont, A. Real-time multianalyte biosensors based on interference-free multichannel monolithic quartz crystal microbalance. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 67, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanley, A.J.; McNeil, J.B. The Meaning and Use of the Area under a Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Curve. Radiology 1982, 143, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonoda, H.; Kohnoe, S.; Yamazato, T.; Satoh, Y.; Morizono, G.; Shikata, K.; Morita, M.; Watanabe, A.; Masaru, M.; Kakeji, Y.; et al. Colorectal cancer screening with odour material by canine scent detection. Gut 2011, 60, 814–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Ke, C.; Wang, X.; Chi, C.; Guo, L.; Luo, S.; Guo, Z.; Xu, G.; Zhang, F.; Li, E. Noninvasive detection of colorectal cancer by analysis of exhaled breath. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 4757–4763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wold, S.; Esbensen, K.; Geladi, P. Principal component analysis. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 1987, 2, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izenman, A.J. Linear Discriminant Analysis. In Modern Multivariate Statistical Techniques; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 237–280. [Google Scholar]
- American Society of Clinical Oncology. Head and Neck Cancer: Statistics; American Society of Clinical Oncology: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Leunis, N.; Boumans, M.-L.; Kremer, B.; Din, S.; Stobberingh, E.; Kessels, A.G.H.; Kross, K.W. Application of an electronic nose in the diagnosis of head and neck cancer. Laryngoscope 2014, 124, 1377–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marur, S.; Forastierre, A. Head and neck cancer: Changing epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simard, E.P.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. International trends in head and neck cancer incidence rates: Differences by country, sex and anatomic site. Oral Oncol. 2014, 50, 387–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jemal, A.; Bray, F.; Ferlay, J. Global Cancer Statistics: 2011. CA Cancer J. Clin. 1999, 49, 33–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utriainen, M.; Karpanoja, E.; Paakkanen, H. Combining miniaturized ion mobility spectrometer and metal oxide gas sensor for the fast detection of toxic chemical vapors sensor for the fast detection of toxic chemical vapors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2003, 93, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosacz, N.M.; Croxton, T.L.; Ndenecho, M.N.; Kiley, J.P.; Weinmann, G.G.; Wheaton, A.G.; Ford, E.S.; Presley-Cantrell, L.R.; Croft, J.B.; Giles, W.H. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Among Adults—United States, 2011. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2012, 61, 938–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestbo, J.; Hurd, S.S.; Agustı, A.G.; Jones, P.W.; Vogelmeier, C.; Anzueto, A.; Barnes, P.J.; Fabbri, L.M.; Martinez, F.J. Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease GOLD Executive Summary. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 347–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibila, O.; Garcia-Bellmunt, L.; Giner, J.; Merino, J.L.; Suarez-Cuartin, G.; Torrego, A.; Solanes, I.; Castillo, D.; Valera, J.L.; Cosio, B.G.; et al. Identification of airway bacterial colonization by an electronic nose in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Respir. Med. 2014, 108, 1608–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragonieri, S.; Quaranta, V.N.; Carratu, P.; Ranieri, T.; Resta, O. Exhaled breath profiling in patients with COPD and OSA overlap syndrome: A pilot study. J. Breath Res. 2016, 10, 41001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bofan, M.; Mores, N.; Baron, M.; Dabrowska, M.; Valente, S.; Schmid, M.; Trové, A.; Conforto, S.; Zini, G.; Cattani, P.; et al. Within-day and between-day repeatability of measurements with an electronic nose in patients with COPD. J. Breath Res. 2013, 7, 17103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushida, C.A.; Littner, M.R.; Morgenthaler, T.; Alessi, C.A.; Bailey, D.; Coleman, J.; Friedman, L.; Hirshkowitz, M.; Kapen, S.; Kramer, M.; et al. Practice Parameters for the Indications for Polysomnography and Related Procedures: An Update for 2005. Sleep 2005, 28, 499–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greulich, T.; Hattesohl, A.; Grabisch, A.; Koepke, J.; Schmid, S.; Noeske, S.; Nell, C.; Wencker, M.; Jörres, R.A.; Vogelmeier, C.F.; et al. Detection of obstructive sleep apnoea by an electronic nose. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 42, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baughman, R.; Culver, D.; Judson, M. A concise review of pulmonary sarcoidosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 573e81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragonieri, S.; Brinkman, P.; Mouw, E.; Resta, O.; Sterk, P.J.; Jonkers, R.E. An electronic nose discriminates exhaled breath of patients with untreated pulmonary sarcoidosis from controls. Respir. Med. 2013, 107, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzheimer’s Association. 2016 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Dement 2016, 12, 459–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pringsheim, T.; Jette, N.; Frolkis, A.; Steeves, T.D.L. The prevalence of Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mov. Disord. 2014, 29, 1583–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.T.; Steven, A.C.; Murray, E.A.; Clark, C.M.; Shaw, L.M.; Mccluskey, L.; Elman, L.; Karlawish, J.; Hurtig, H.I.; Siderowf, A.; et al. Biomarker discovery for Alzheimer’s disease, frontotemporal lobar degeneration, and Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 120, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ionescu, R.; Broza, Y.; Shaltieli, H.; Sadeh, D.; Zilberman, Y.; Feng, X.; Glass-Marmor, L.; Lejbkowicz, I.; Müllen, K.; Miller, A.; et al. Detection of multiple sclerosis from exhaled breath using bilayers of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and single-wall carbon nanotubes. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2011, 2, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brereton, R. Chemometrics, Application of Mathematics Statistics to Laboratory Systems; Ellis Horwood: Chichester, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Kessler, R.; Berglund, P.; Demler, O.; Jin, R.; Merikangas, K.; Walters, E. Lifetime Prevalence and Age-of-Onset Distributions of DSM-IV Disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2005, 62, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Arlington, VA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH). Research Domain Criteria (RDoC). Available online: http://www.nimh.nih.gov/research-priorities/rdoc/nimh-research-domain-criteria-rdoc.shtml#toc_matrix (accessed on 9 June 2015).
- Williams, J.; Stönner, C.; Wicker, J.; Krauter, N.; Derstroff, B.; Bourtsoukidis, E.; Klüpfel, T.; Kramer, S. Cinema audiences reproducibly vary the chemical composition of air during films, by broadcasting scene specific emissions on breath. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ionicon Proton Transfer Reaction—Mass Spectrometry. Available online: http://www.ionicon.com/information/technology/ptr-ms (accessed on 9 September 2017).
- Smith, D.; Spaněl, P.; Fryer, A.A.; Hanna, F.; Ferns, G.A.A. Can volatile compounds in exhaled breath be used to monitor control in diabetes mellitus? J. Breath Res. 2011, 5, 22001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzatenta, A.; Di Giulio, C.; Pokorski, M. Pathologies currently identified by exhaled biomarkers. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2013, 187, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirasu, M.; Touhara, K. The scent of disease: Volatile organic compounds of the human body related to disease and disorder. J. Biochem. 2011, 150, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minh, T.D.C.; Oliver, S.R.; Ngo, J.; Flores, R.; Midyett, J.; Meinardi, S.; Carlson, M.K.; Rowland, F.S.; Blake, D.R.; Galassetti, P.R. Noninvasive measurement of plasma glucose from exhaled breath in healthy and type 1 diabetic subjects. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 300, E1166–E1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzatenta, A.; Pokorski, M.; Di Giulio, C. Real Time Breath Analysis in Type 2 Diabetes Patients during Cognitive Effort. In Neurobiology of Respiration; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 247–253. [Google Scholar]
- Landon, M.B.; Gabbe, S.G. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Obstet. Gynecol. 2011, 118, 1379–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, D.; Zhang, D.; Li, N.; Zhang, L.; Yang, J. Diabetes identification and classification by means of a breath analysis system. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2010, 6165 LNCS, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, P. Volatile metabolic monitoring of glycemic status in diabetes using electronic olfaction. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2004, 6, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minh Tdo, C.; Oliver, S.R.; Flores, R.L.; Ngo, J.; Meinardi, S.; Carlson, M.K.; Midyett, J.; Rowland, F.S.; Blake, D.R.; Galassetti, P.R. Noninvasive measurement of plasma triglycerides and free fatty acids from exhaled breath. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2012, 6, 86–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Healthline. The Difference between Crohn’s, UC, and IBD; Healthline: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Canavan, C.; West, J.; Card, T. The epidemiology of irritable bowel syndrome. Clin. Epidemiol. 2014, 6, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conte, M.; Schippa, S.; Zamboni, I.; Penta, M.; Chiarini, F.; Seganti, L.; Osborn, J.; Falconieri, P.; Borrelli, O.; Cucchiara, S.; et al. Gut-associated bacterial microbiotia in paediatric patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 2006, 55, 1760–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, M.; Wang, P. Virtual Electronic Nose with Diagnosis Model for the Detection of Hydrogen and Methane in Breath from Gastrointestinal Bacteria. In 2017 ISOCS/IEEE International Symposium on Olfaction and Electronic Nose; IEEE: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2017; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Španěl, P.; Smith, D. Progress in SIFT-MS: Breath Analysis and Other Applications. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2010, 30, 236–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parodi, A.; Lauritano, E.C.; Nardone, G.; Fontana, L.; Savarino, V.; Gasbarrini, A. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. Dig. Liver Dis. Suppl. 2009, 3, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, A.C.; Spiegel, B.M.; Talley, N.J.; Moayyedi, P. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 7, 1279–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, V.; Garcia-Garcia, G.; Iseki, K.; Li, Z.; Naicker, S.; Plattner, B.; Saran, R.; Wang, A.Y.M.; Yang, C.W. Chronic kidney disease: Global dimension and perspectives. Lancet 2013, 382, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gansevoort, R.T.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Hemmelgarn, B.R.; Jafar, T.H.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Mann, J.F.; Matsushita, K.; Wen, C.P. Chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular risk: Epidemiology, mechanisms, and prevention. Lancet 2013, 382, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaziri, N.D. CKD impairs barrier function and alters microbial flora of the intestine: A major link to inflammation and uremic toxicity. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2012, 21, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narasimhan, L.R.; Goodman, W.; Patel, C.K. Correlation of breath ammonia with blood urea nitrogen and creatinine during hemodialysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 4617–4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marom, O.; Nakhoul, F.; Tisch, U.; Shiban, A.; Abassi, Z.; Haick, H. Gold nanoparticle sensors for detecting chronic kidney disease and disease progression. Nanomedicine 2012, 7, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, G.; Tisch, U.; Adams, O.; Hakim, M.; Shehada, N.; Broza, Y.Y.; Billan, S.; Abdah-Bortnyak, R.; Kuten, A.; Haick, H. Diagnosing lung cancer in exhaled breath using gold nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, G.; Hakim, M.; Broza, Y.Y.; Billan, S.; Abdah-Bortnyak, R.; Kuten, A.; Tisch, U.; Haick, H. Detection of lung, breast, colorectal, and prostate cancers from exhaled breath using a single array of nanosensors. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 103, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 30, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, J.E.; Fenniri, H. Biomimetic cross-reactive sensor arrays: prospects in biodiagnostics. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 80468–80484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickinson, T.A.; White, J.; Kauer, J.S.; Walt, D. R. A chemical-detecting system based on a cross-reactive optical sensor array. Nature 1996, 382, 697–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Ma, Q.; Lin, Z.; Chen, S.; Li, Y.; Lu, L.; Qu, H.; Su, X. Multiplex electrochemiluminescence DNA sensor for determination of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus based on multicolor quantum dots and Au nanoparticles. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 916, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Hu, C.; Hu, S. Ultrasensitive Photoelectrochemical Biosensing of Multiple Biomarkers on a Single Electrode by a Light Addressing Strategy. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 9368–9375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, J.E.; Zhu, J.; Bravo-Vasquez, J.P.; Fenniri, H. Cross-reactive, self-encoded polymer film arrays for sensor applications. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 82616–82624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askim, J.R.; Suslick, K.S. Hand-Held Reader for Colorimetric Sensor Arrays. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 7810–7816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
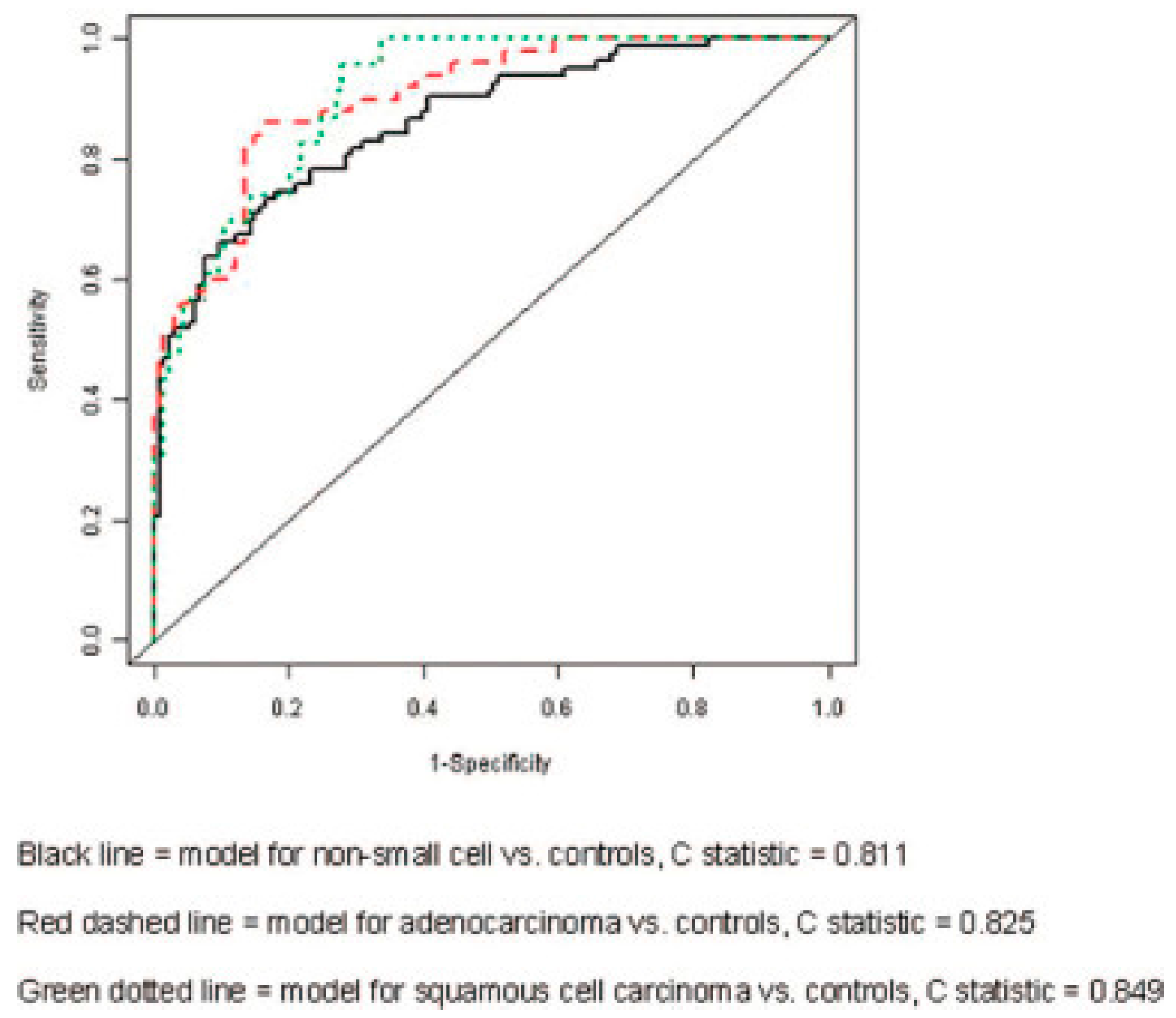
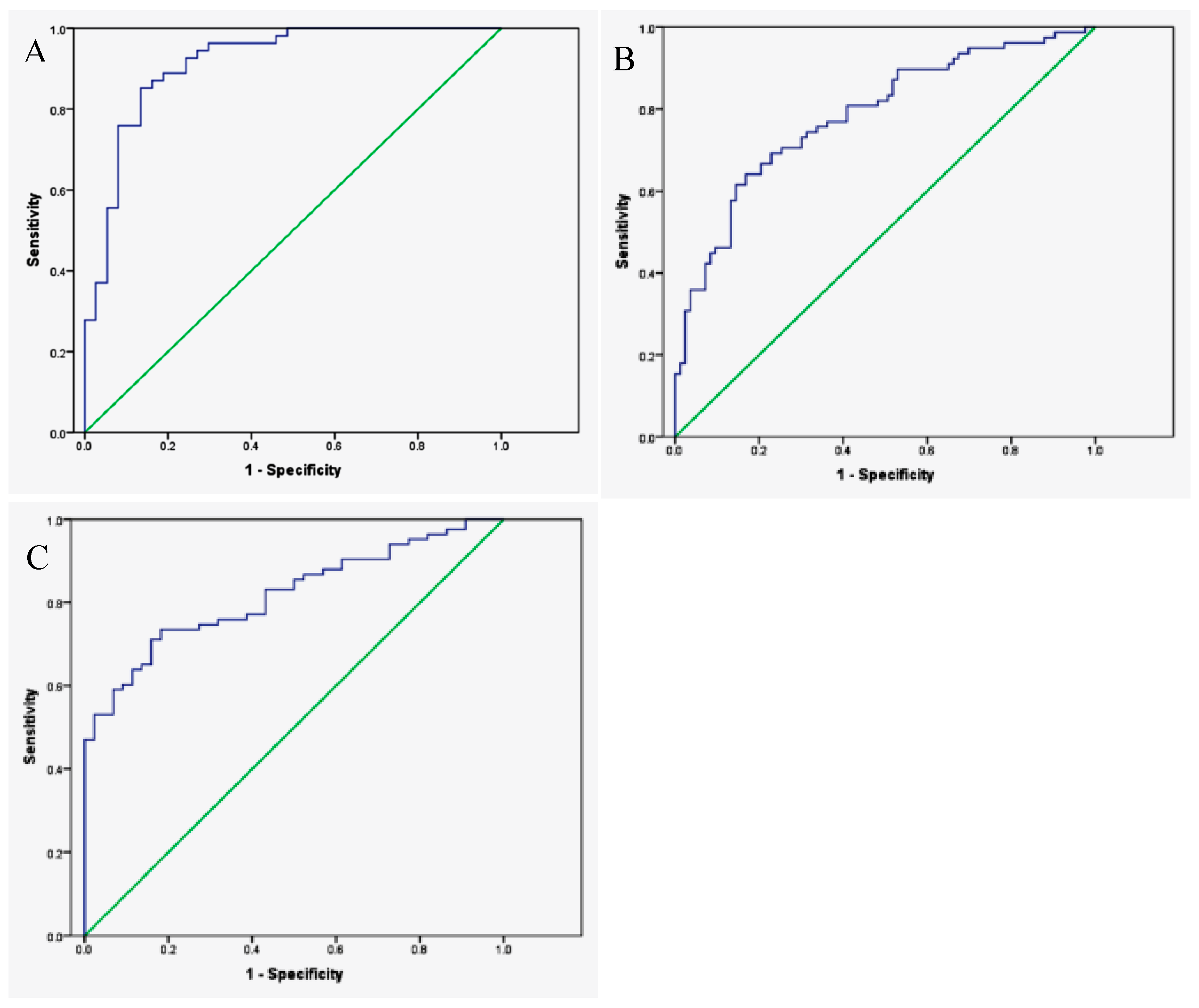
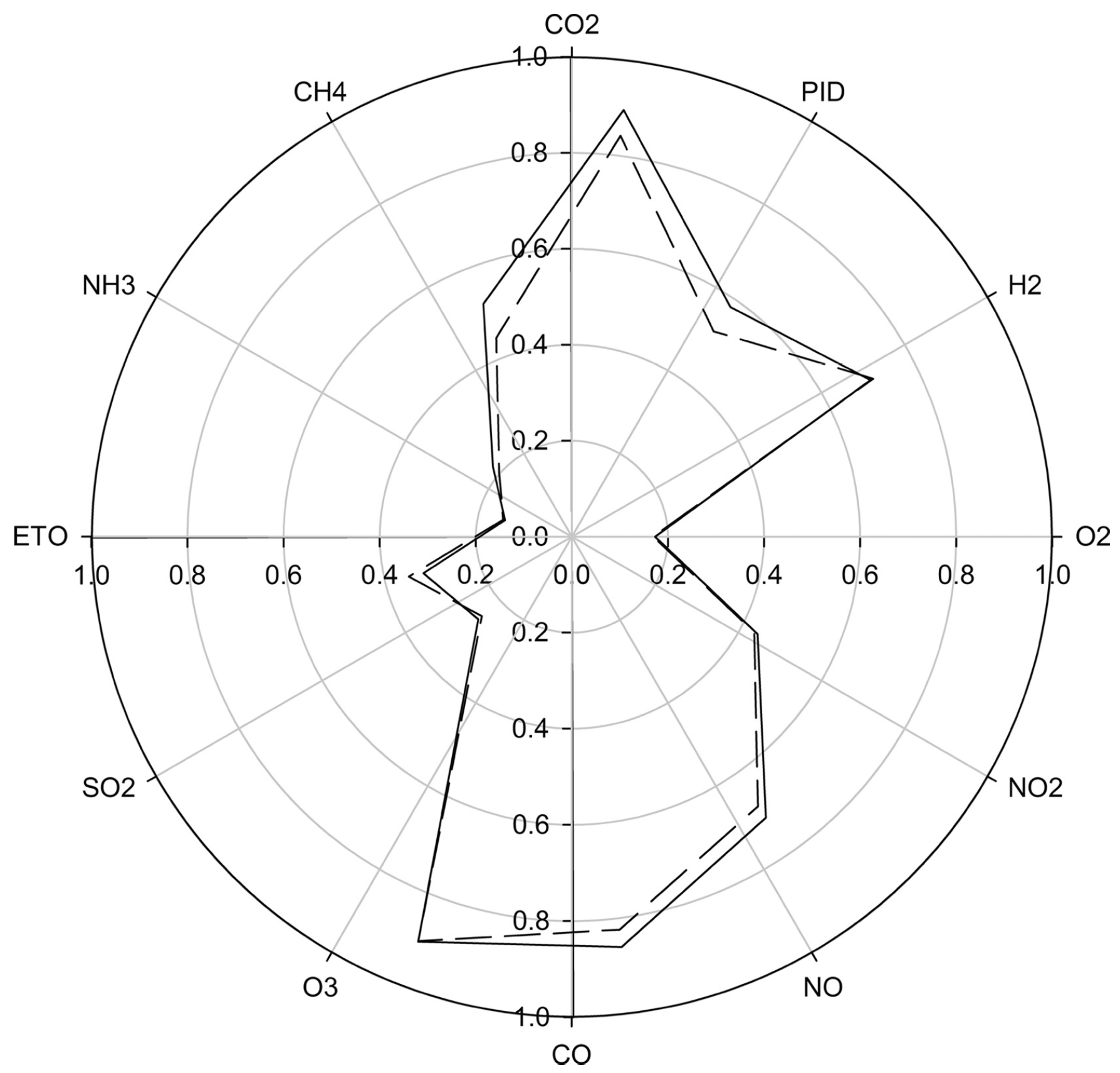

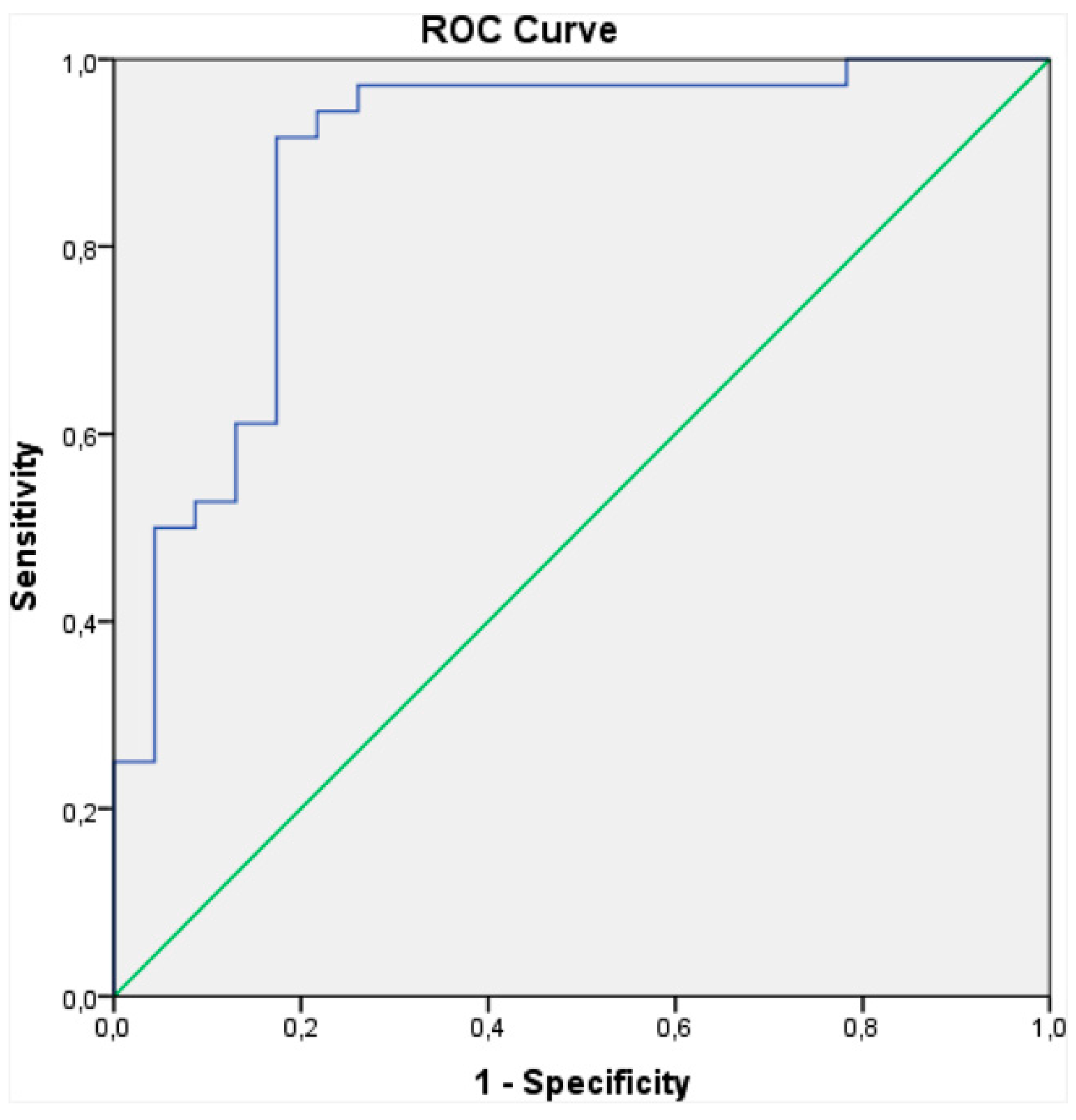
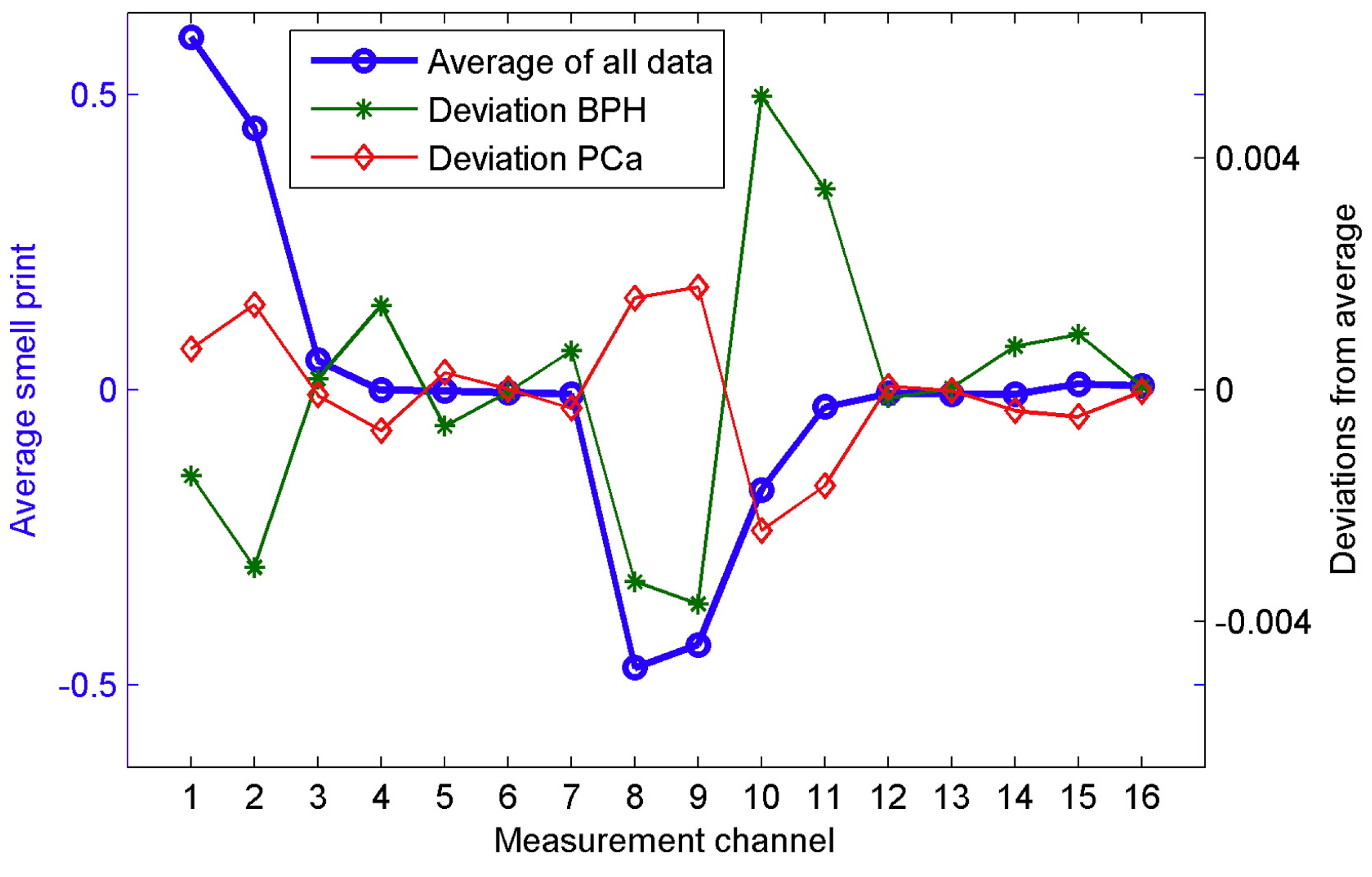
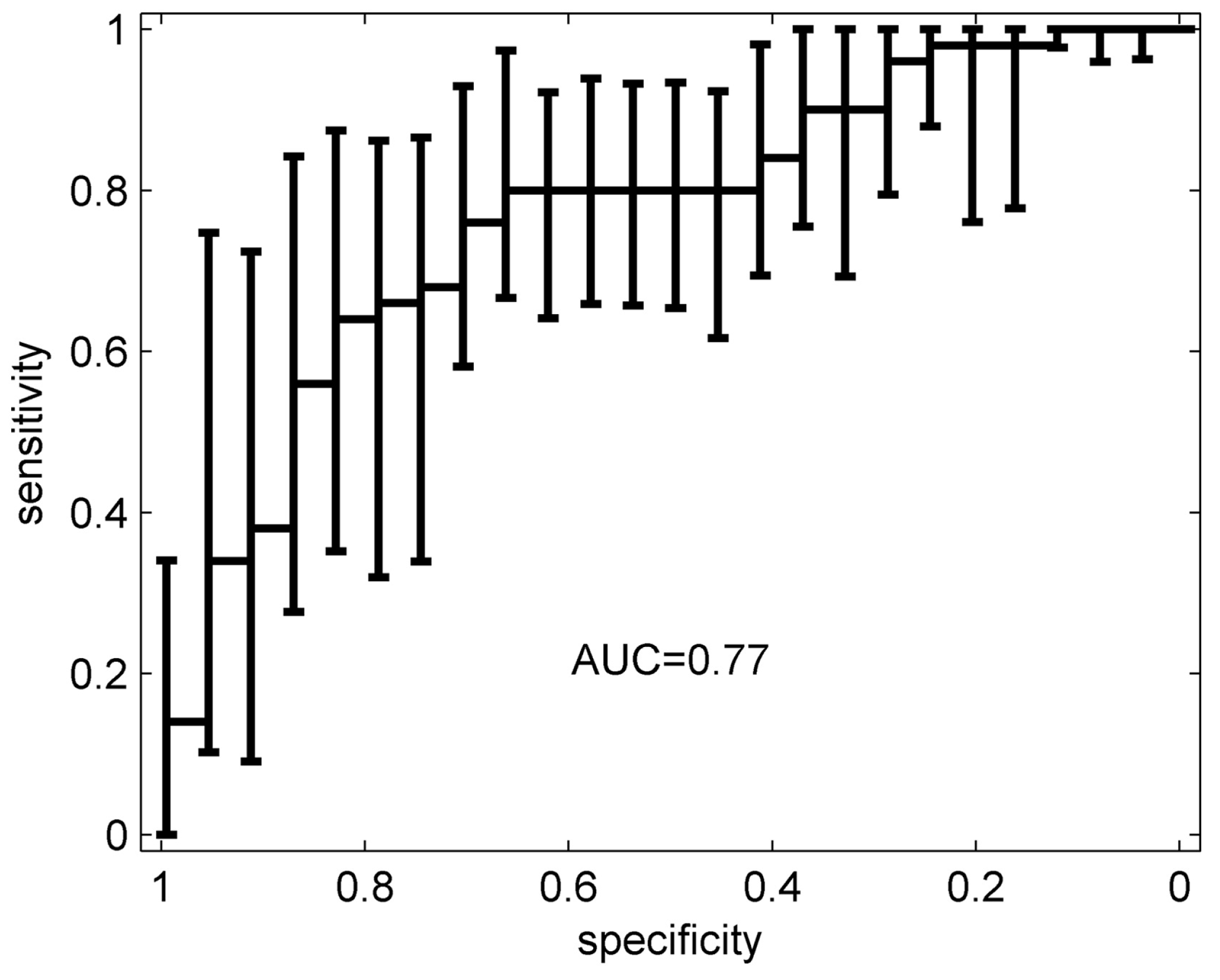
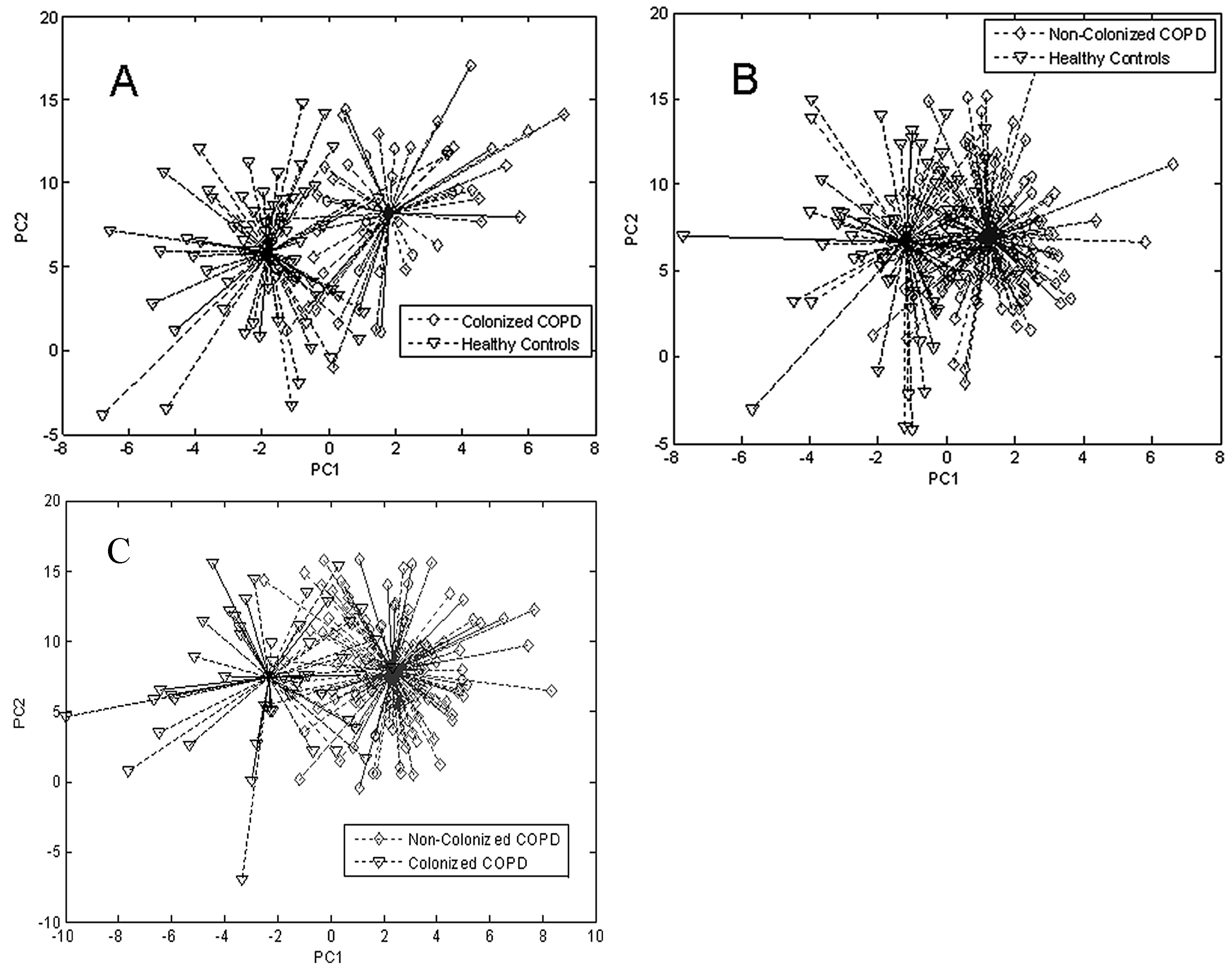
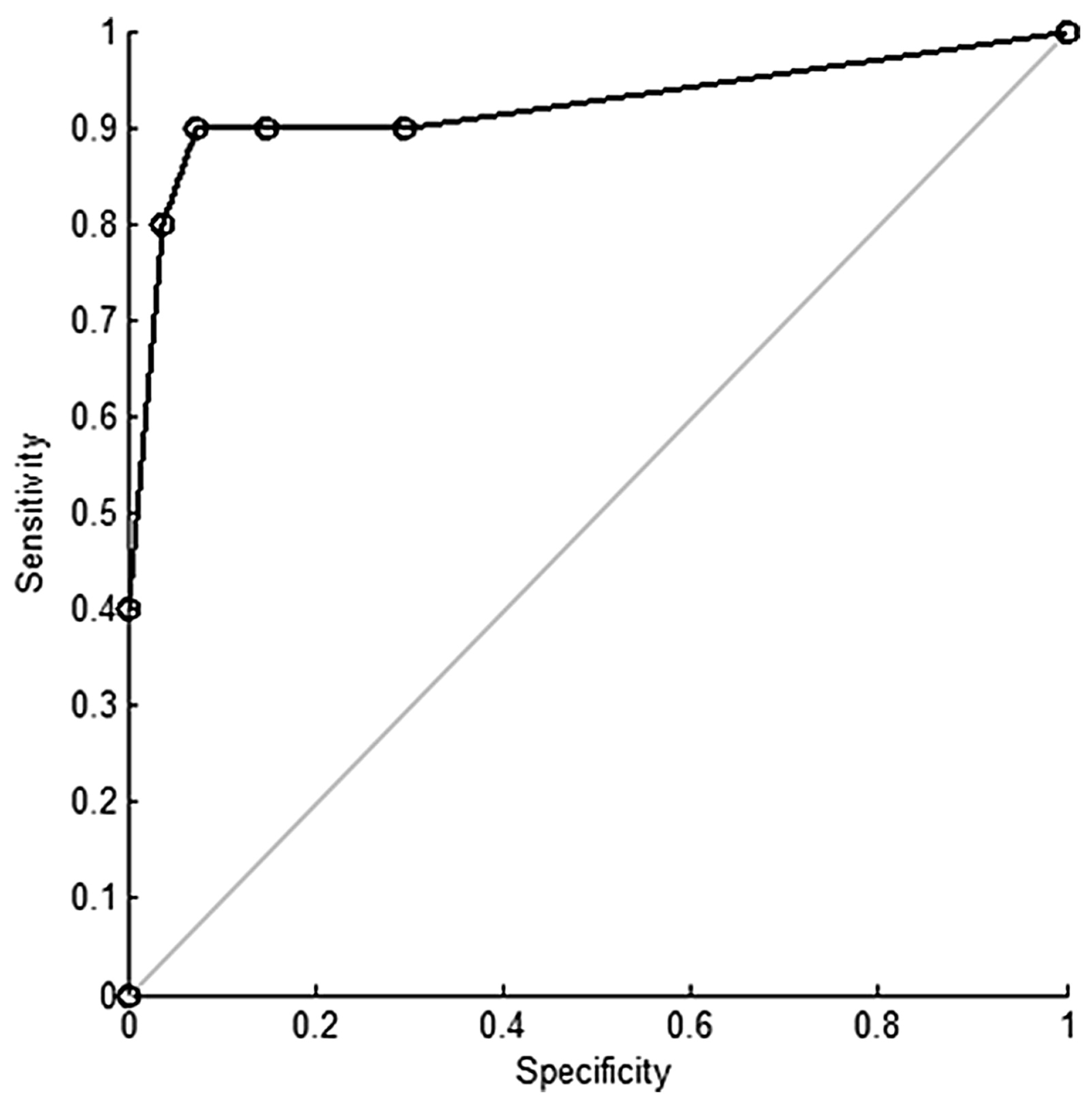
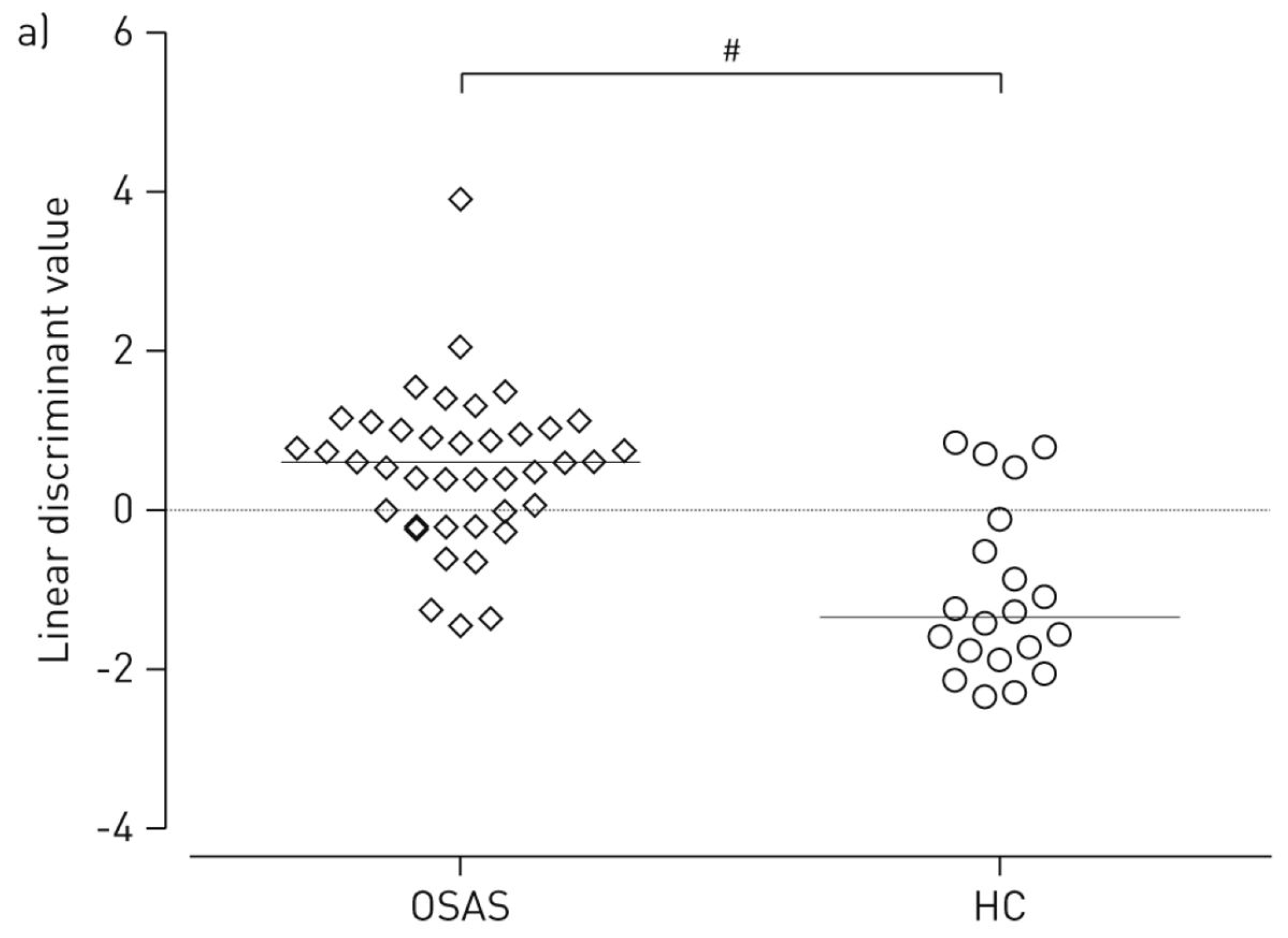
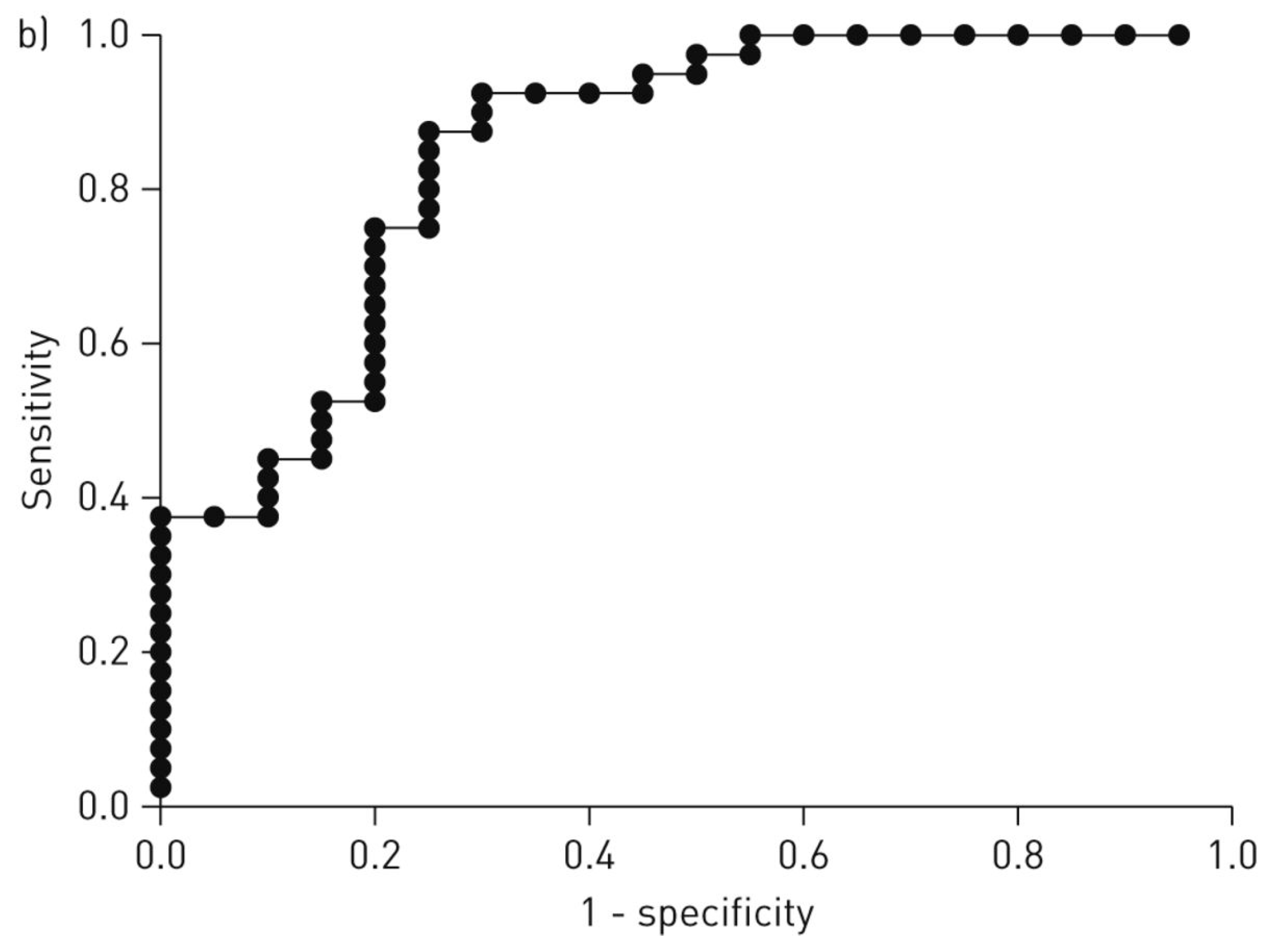
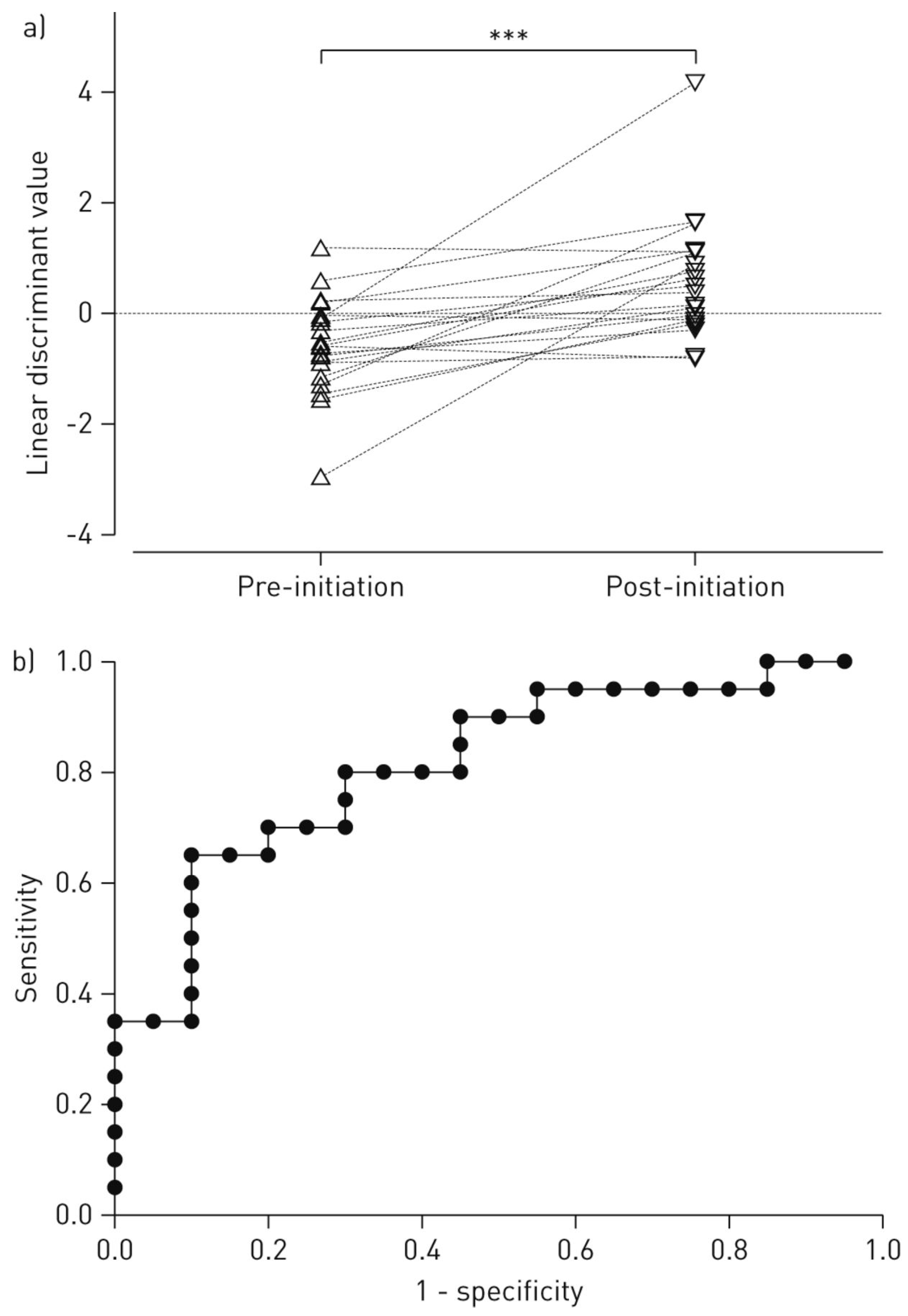
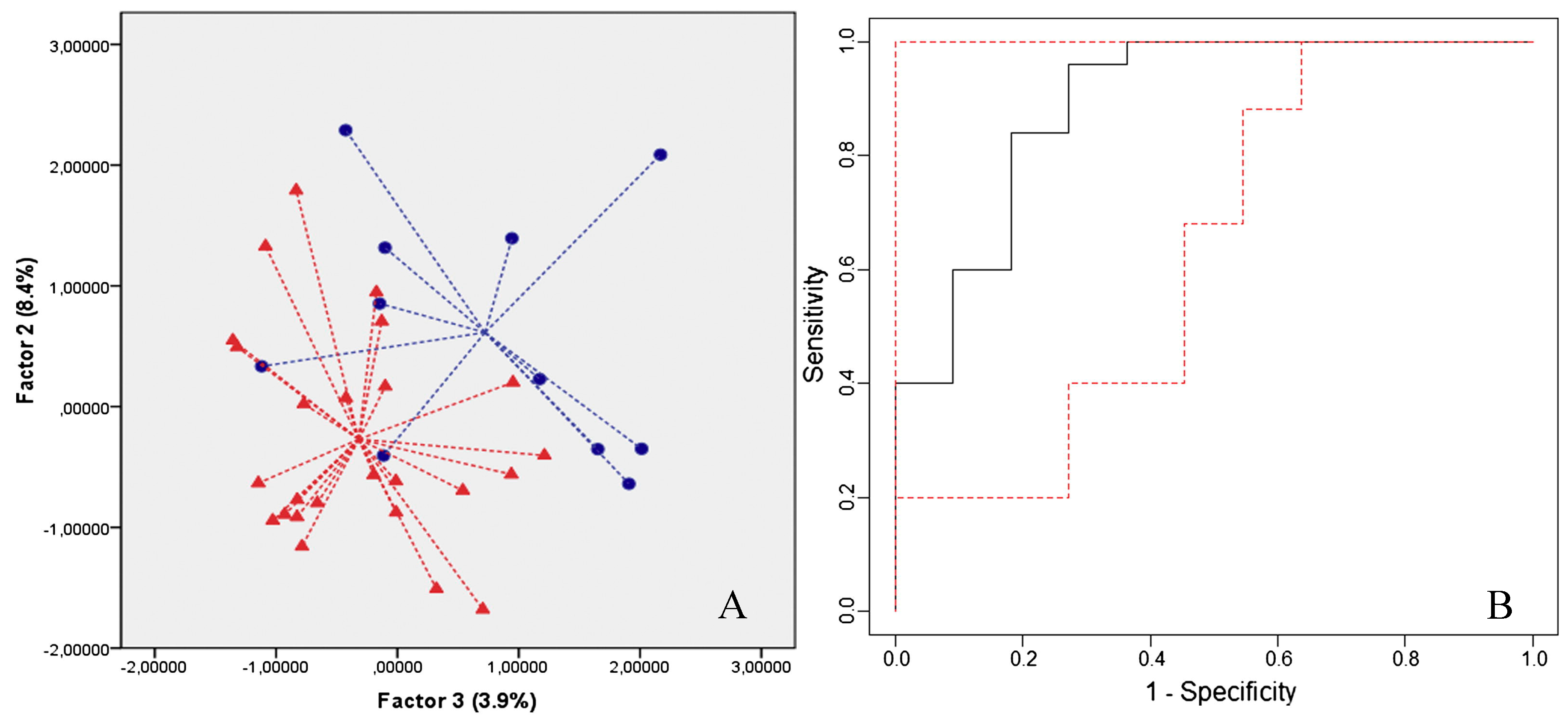
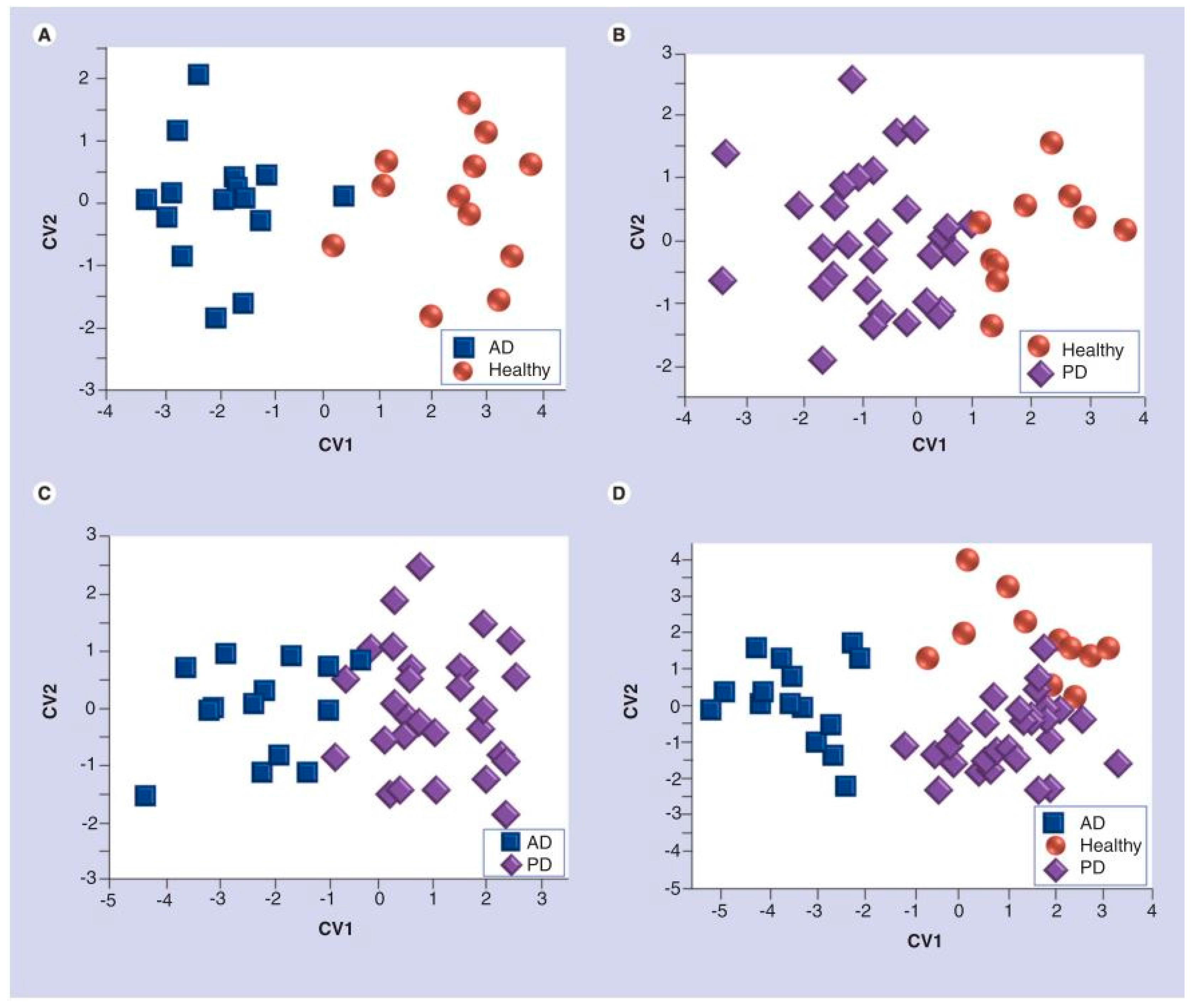
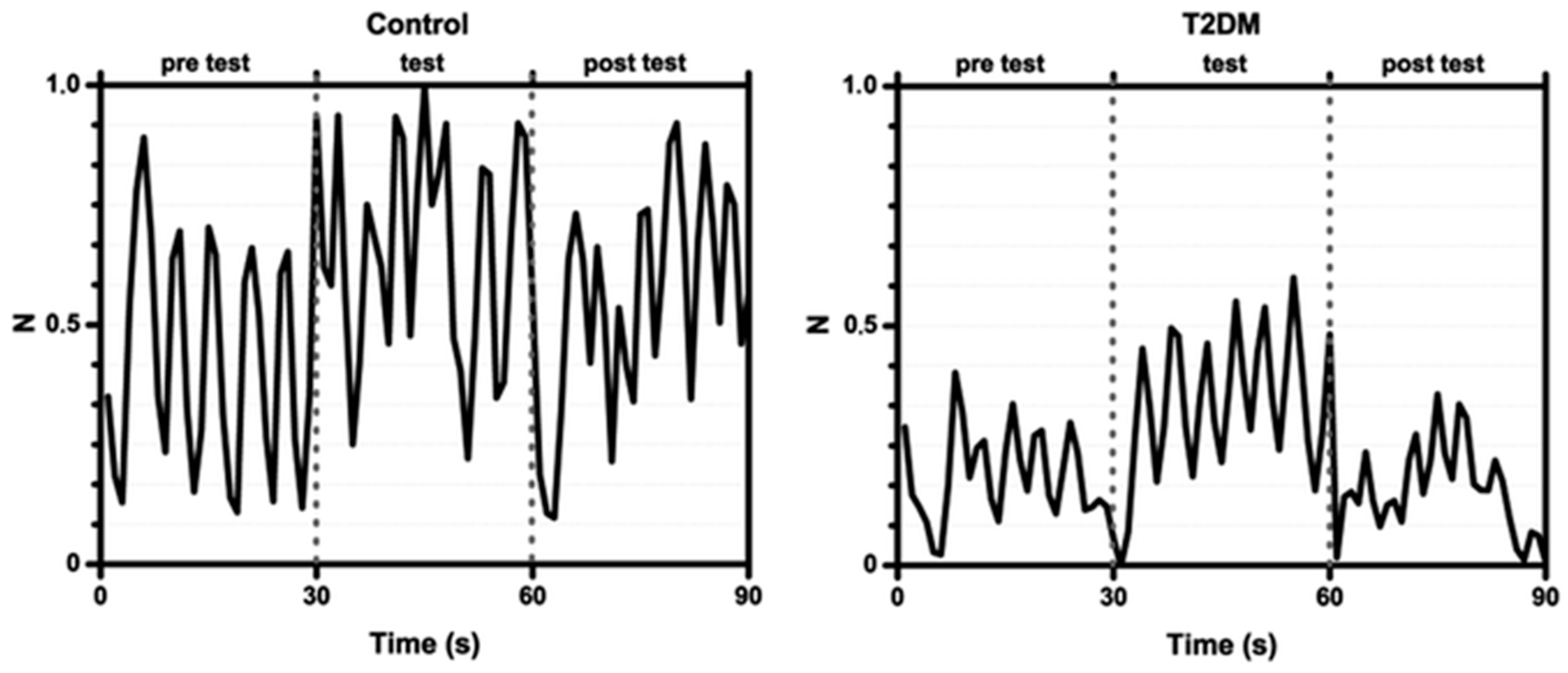
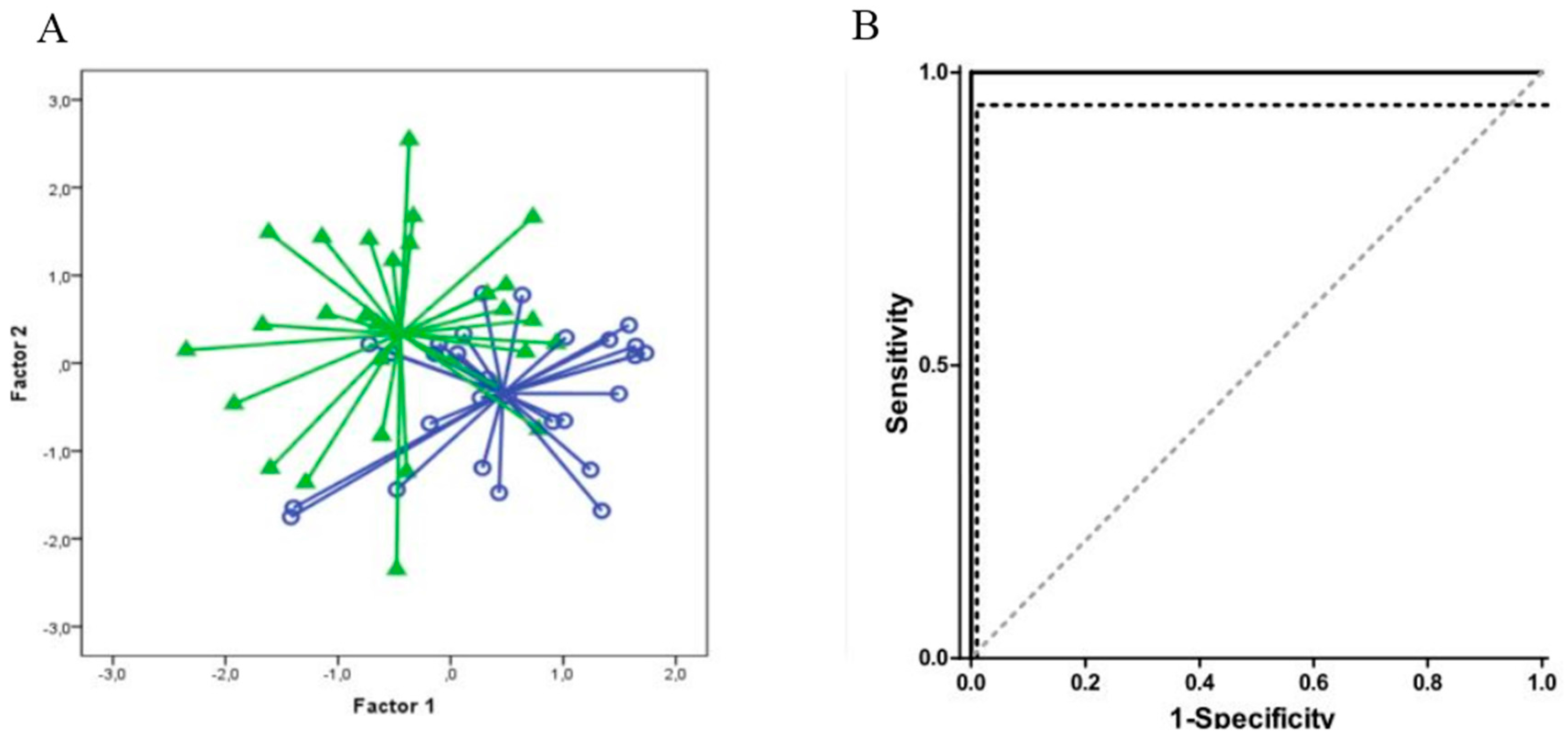
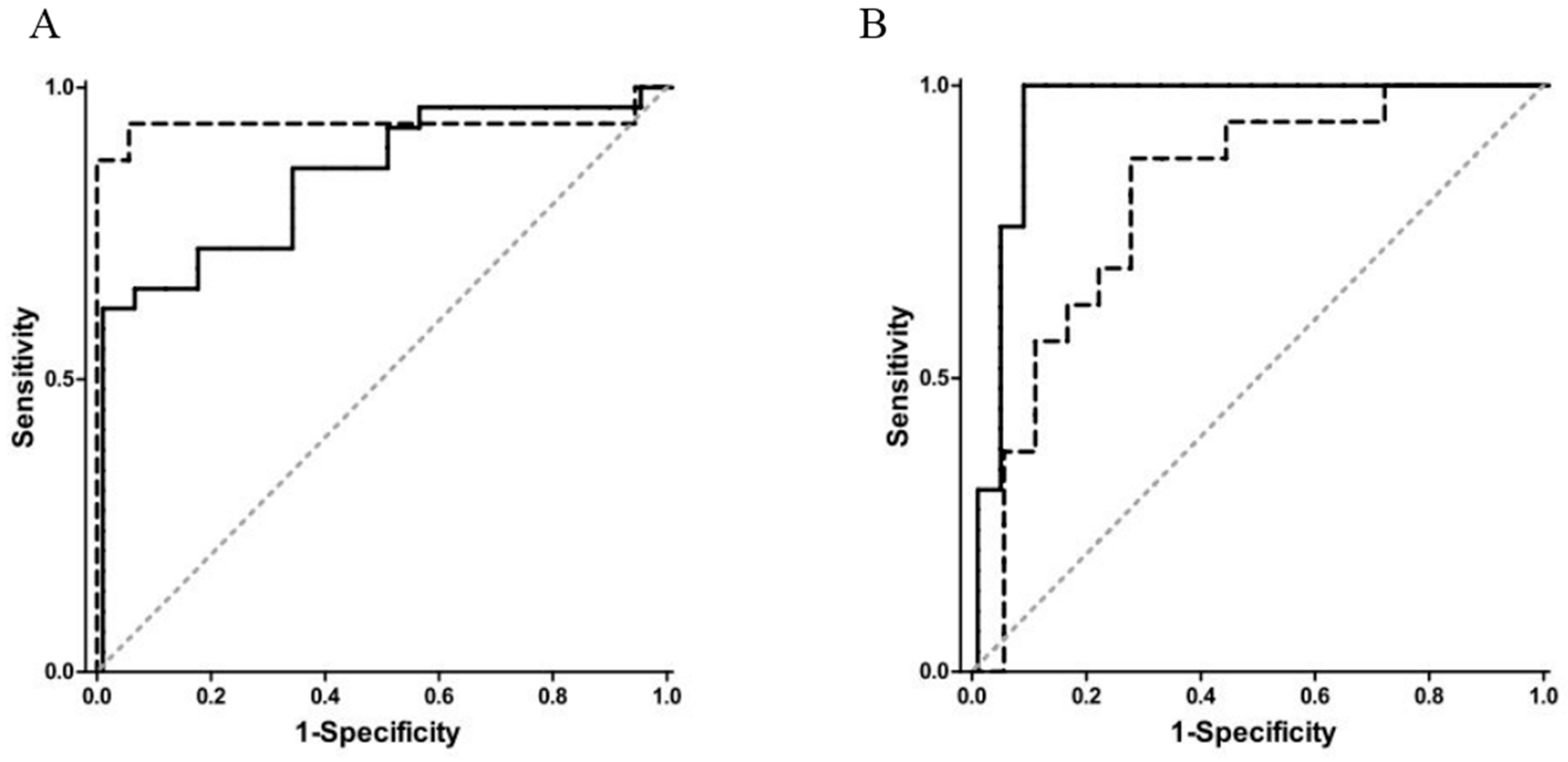

| Groups Compared (n) | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-small cell (83) Controls (137) | 0.701 | 0.811 | 0.761 | 0.710 |
| Adenocarcinoma (50) Controls (137) | 0.784 | 0.747 | 0.825 | 0.695 |
| Squamous cell (23) Controls (137) | 0.708 | 0.841 | 0.849 | 0.768 |
| Adenocarcinoma (50) Squamous cell (22) | 0.889 | 0.742 | 0.864 | 0.517 |
| Small cell (9) Controls (137) | 0.800 | 0.824 | 0.890 | 0.763 |
| Small cell (9) Non-small cell (83) | 0.752 | 0.752 | 0.781 | 0.584 |
| Stages I and II (41) Stages III and IV (42) | 0.792 | 0.793 | 0.784 | 0.460 |
| Survival Survival <12 mo (24) >12 mo (68) | 0.768 | 0.761 | 0.770 | 0.576 |
| Colonized vs. Non-Colonized COPD Patients | Colonized COPD Patients vs. Healthy Controls | Non-colonized COPD Patients vs. Healthy Controls | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cross-validation accuracy | 89% | 88% | 83% |
| Sensitivity | 0.82 | 0.80 | 0.81 |
| Specificity | 0.96 | 0.93 | 0.86 |
| AUROC | 0.922 | 0.986 | 0.937 |
| Positive predictive value | 0.87 | 0.89 | 0.92 |
| Negative predictive value | 0.92 | 0.87 | 0.72 |
| AUROC: area under the receiver operating characteristic. | |||
| Base Material | Sensor No. | Organic Functionality | DFA Model 1 1 | DFA Model 2 2 | DFA Model 3 3 | DFA Model 4 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RN-CNTs | 1 | α-CD | X | |||
| 1 | β-CD | X | ||||
| 2 | Carboxy-methylated β-CD | X | ||||
| 3 | Hydroxypropyl-β-CD | X | X | X | ||
| 4 | Heptakis(2,3,6-tri-O-methyl)-β-CD | X | X | |||
| GNPs | 5 | 2-mercapto-benzoxazole | X | |||
| 6 | 3-mercapto-propionate | X | X | X |
| T1 | T2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SD | M | SD | t(67) | |
| Threat appraisal | 5.93 | 1.56 | 4.70 | 1.61 | 5.55 ** |
| Challenge appraisal | 7.10 | 1.12 | 6.95 | 0.89 | 0.98 |
| Experienced stress | 6.01 | 1.89 | 5.72 | 1.27 | 2.05 * |
| Worry | 2.28 | 0.70 | 2.18 | 0.75 | 1.17 |
| Emotionality | 2.59 | 0.68 | 2.45 | 0.74 | 1.70 |
| Text anxiety (total score) | 2.53 | 0.59 | 2.32 | 0.63 | 2.50 * |
| pH | 6.95 | 0.60 | 7.41 | 0.74 | −4.33 ** |
| Test performance | 69.33 | 14.11 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fitzgerald, J.; Fenniri, H. Cutting Edge Methods for Non-Invasive Disease Diagnosis Using E-Tongue and E-Nose Devices. Biosensors 2017, 7, 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7040059
Fitzgerald J, Fenniri H. Cutting Edge Methods for Non-Invasive Disease Diagnosis Using E-Tongue and E-Nose Devices. Biosensors. 2017; 7(4):59. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7040059
Chicago/Turabian StyleFitzgerald, Jessica, and Hicham Fenniri. 2017. "Cutting Edge Methods for Non-Invasive Disease Diagnosis Using E-Tongue and E-Nose Devices" Biosensors 7, no. 4: 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7040059
APA StyleFitzgerald, J., & Fenniri, H. (2017). Cutting Edge Methods for Non-Invasive Disease Diagnosis Using E-Tongue and E-Nose Devices. Biosensors, 7(4), 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7040059





