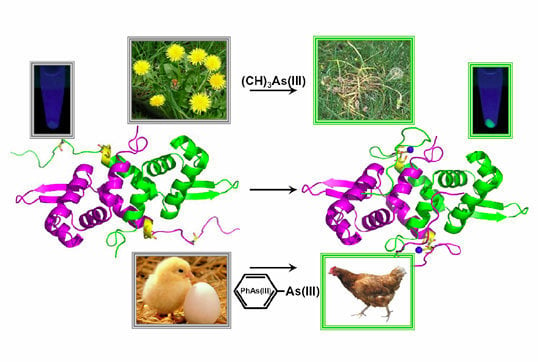
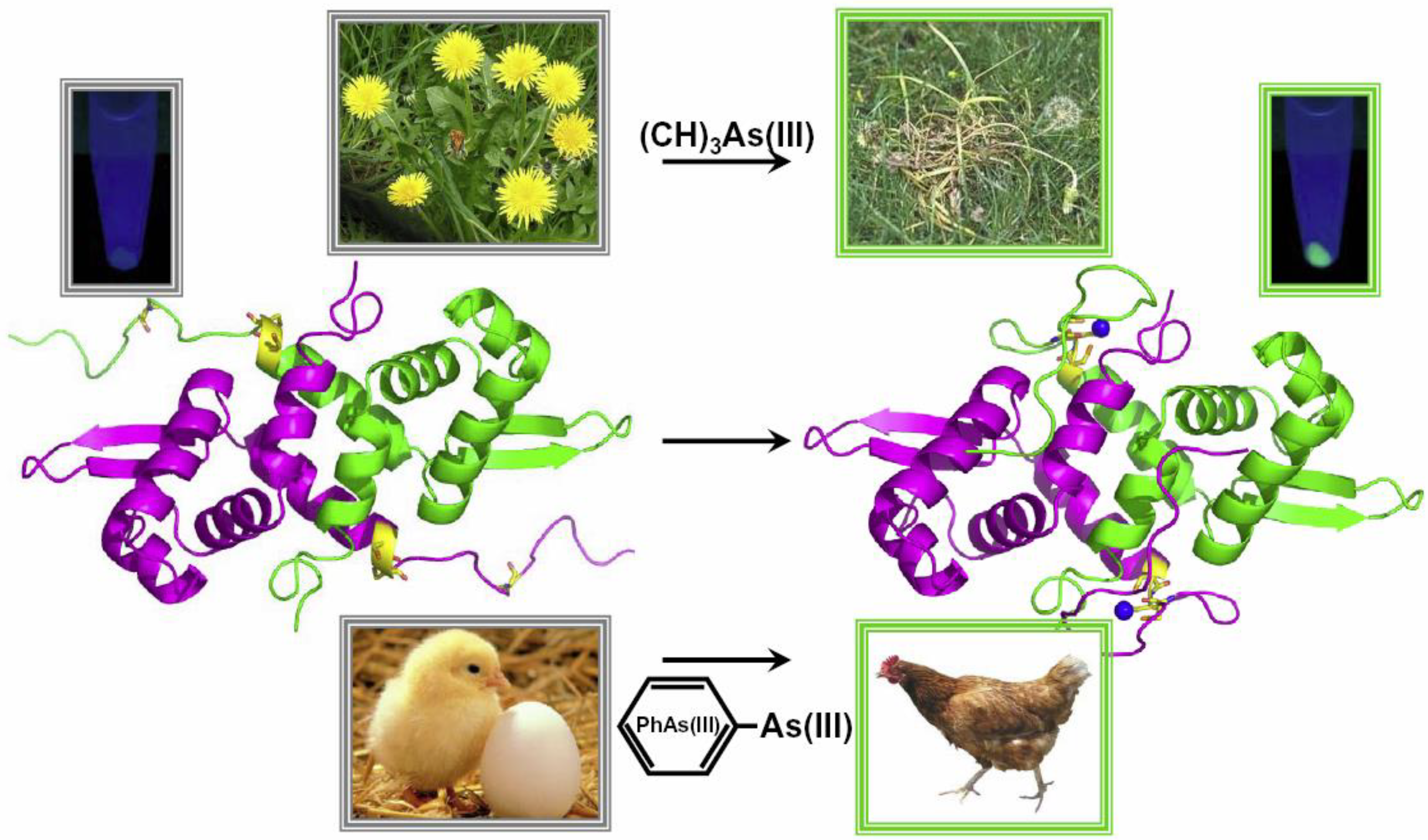
Biosensors for Inorganic and Organic Arsenicals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Development of Biosensors
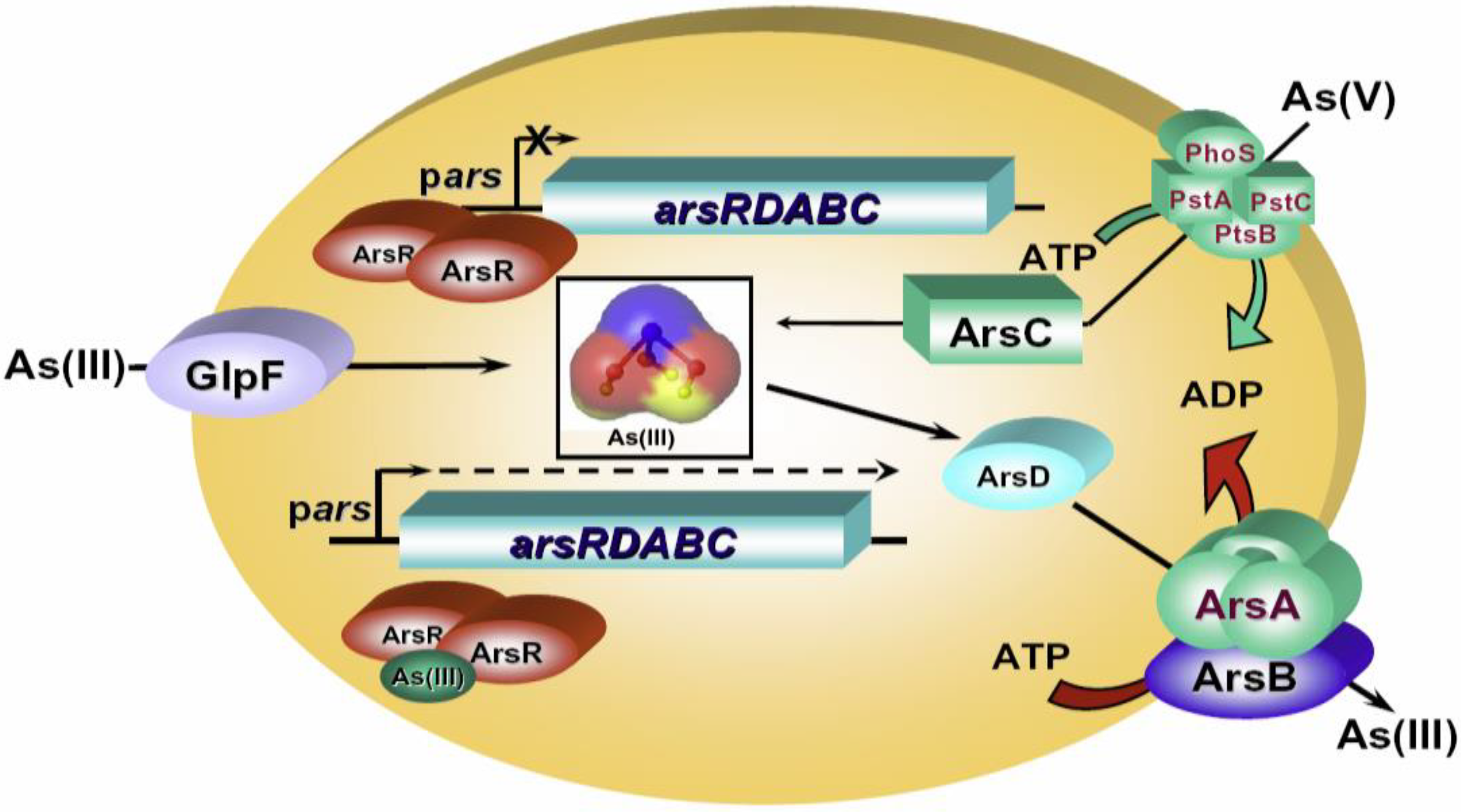
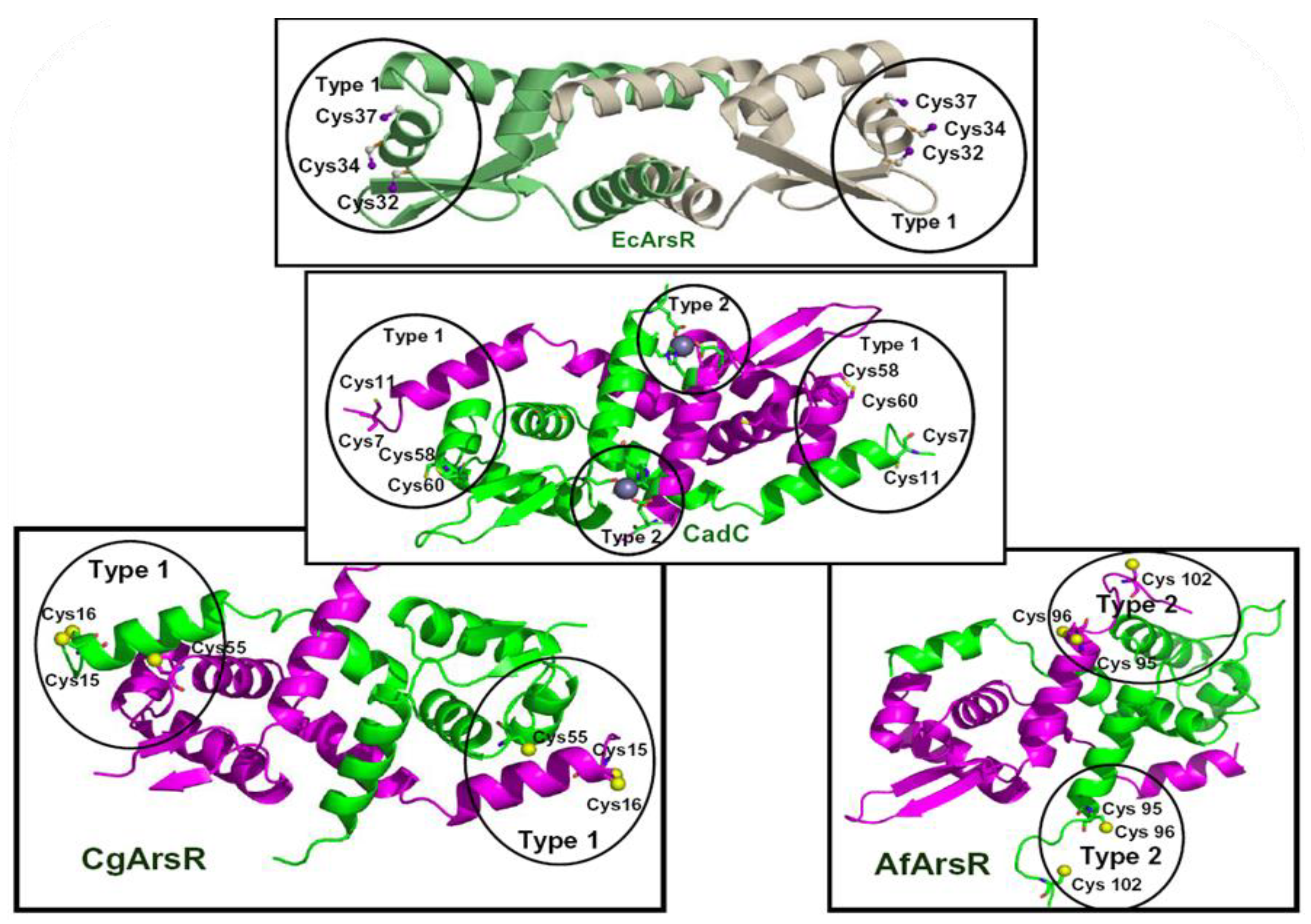
2.1. Protein or DNA Based Biosensors
2.2. Whole Cell-Based Biosensors

3. Future Challenges
3.1. Challenges of Biosensor Specificity
3.2. Challenges of Biosensor for Arsenic for In Situ Detection
3.3. Long-Term Challenges
3.4. The Challenge of Multiplexing Biosensors
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mandal, B.K.; Suzuki, K.T. Arsenic round the world: A review. Talanta 2002, 58, 201–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.G.; Yoshinaga, M.; Zhao, F.J.; Rosen, B.P. Earth abides arsenic biotransformations. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet Sci. 2014, 42, 443–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naujokas, M.F.; Anderson, B.; Ahsan, H.; Aposhian, H.V.; Graziano, J.H.; Thompson, C.; Suk, W.A. The broad scope of health effects from chronic arsenic exposure: Update on a worldwide public health problem. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, M.F.; Beck, B.D.; Chen, Y.; Lewis, A.S.; Thomas, D.J. Arsenic exposure and toxicology: A historical perspective. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 123, 305–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meliker, J.R.; Wahl, R.L.; Cameron, L.L.; Nriagu, J.O. Arsenic in drinking water and cerebrovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, and kidney disease in Michigan: A standardized mortality ratio analysis. Environ. Health 2007, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.G.; Williams, P.N.; Meharg, A.A. Exposure to inorganic arsenic from rice: A global health issue? Environ. Pollut. 2008, 154, 169–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, P.N.; Islam, M.R.; Adomako, E.E.; Raab, A.; Hossain, S.A.; Zhu, Y.G.; Feldmann, J.; Meharg, A.A. Increase in rice grain arsenic for regions of Bangladesh irrigating paddies with elevated arsenic in groundwaters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 4903–4908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jomova, K.; Jenisova, Z.; Feszterova, M.; Baros, S.; Liska, J.; Hudecova, D.; Rhodes, C.J.; Valko, M. Arsenic: Toxicity, oxidative stress and human disease. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2011, 31, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nordstrom, D.K. Public health. Worldwide occurrences of arsenic in ground water. Science 2002, 296, 2143–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengupta, M.K.; Dasgupta, P.K. An automated hydride generation interface to ICPMS for measuring total arsenic in environmental samples. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 9737–9743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- B’Hymer, C.; Caruso, J.A. Arsenic and its speciation analysis using high-performance liquid chromatography and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1045, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luong, J.H.T.; Majid, E.; Male, K.B. Analytical tools for monitoring arsenic in the environment. Open Anal. Chem. J. 2007, 1, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Sengupta, M.K.; Yuan, D.; Dasgupta, P.K. Speciation and detection of arsenic in aqueous samples: A review of recent progress in non-atomic spectrometric methods. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 831, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.L.; Ma, L.Y.; Chen, X.W. New procedures for arsenic speciation: A review. Talanta 2014, 125, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merulla, D.; Buffi, N.; Beggah, S.; Truffer, F.; Geiser, M.; Renaud, P.; van der Meer, J.R. Bioreporters and biosensors for arsenic detection. Biotechnological solutions for a world-wide pollution problem. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2012, 24, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, A. Biosensors for quickly detecting arsenic in drinking water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 378A–379A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turdean, G.L. Design and development of biosensors for the detection of heavy metal toxicity. Int. J. Electrochem. 2011, 2011, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tencaliec, A.M.; Laschi, S.; Magearu, V.; Mascini, M. A comparison study between a disposable electrochemical DNA biosensor and a Vibrio fischeri-based luminescent sensor for the detection of toxicants in water samples. Talanta 2006, 69, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J. From DNA biosensors to gene chips. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2000, 28, 3011–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palecek, E. Past, present and future of nucleic acids electrochemistry. Talanta 2002, 56, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozsoz, M.; Erdem, A.; Kerman, K.; Ozkan, D.; Tugrul, B.; Topcuoglu, N.; Ekren, H.; Taylan, M. Electrochemical genosensor based on colloidal gold nanoparticles for the detection of Factor V Leiden mutation using disposable pencil graphite electrodes. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 2181–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labuda, J.; Bubnicova, K.; Kovalova, L.; Vanickova, M.; Mattusch, J.; Wennrich, R. Voltammetric detection of damage to DNA by arsenic compounds at a DNA biosensor. Sensors 2005, 5, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, P.R.; Prabhakar, N.; Pandey, M.K.; Malhotra, B.D. Surface plasmon resonance-based DNA biosensor for arsenic trioxide detection. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2009, 89, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrita, J.F.; Abrantes, L.M.; Viana, A.S. N-hydroxysuccinimide-terminated self-assembled monolayers on gold for biomolecules immobilisation. Electrochim. Acta 2005, 50, 2117–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoytcheva, M.; Sharkova, V.; Panayotova, M. Electrochemical approach in studying the inhibition of acetylcholinesterase by arsenate (III): Analytical characterisation and application for arsenic determination. Anal. Chim. Acta 1998, 364, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosnier, S.; Mousty, C.; Cui, X.; Yang, X.; Dong, S. Specific determination of As(V) by an acid phosphatase-polyphenol oxidase biosensor. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 4985–4989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Male, K.B.; Hrapovic, S.; Santini, J.M.; Luong, J.H. Biosensor for arsenite using arsenite oxidase and multiwalled carbon nanotube modified electrodes. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 7831–7837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, P.; Banerjee, S.; Bhattacharyay, D.; Turner, A.P. Electrochemical sensing systems for arsenate estimation by oxidation of l-cysteine. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 73, 1495–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanllorente-Mendez, S.; Dominguez-Renedo, O.; Arcos-Martinez, M.J. Development of acid phosphatase based amperometric biosensors for the inhibitive determination of As(V). Talanta 2012, 93, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, H.; Kumar, R.; Babu, J.N.; Mittal, S. Advances in arsenic biosensor development—A comprehensive review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 63, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuku, X.; Iftikar, F.; Hess, E.; Iwuoha, E.; Baker, P. Cytochrome c biosensor for determination of trace levels of cyanide and arsenic compounds. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 730, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Mozaz, S.; Marco, M.P.; Lopez de Alda, M.J.; Barcelo, D. Biosensors for environmental monitoring of endocrine disruptors: A review article. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 378, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, N.; Singh, M. Biosensors for heavy metals. Biometals 2005, 18, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Checa, S.K.; Zurbriggen, M.D.; Soncini, F.C. Bacterial signaling systems as platforms for rational design of new generations of biosensors. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2012, 23, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, A.S.; Collins, J.J. Synthetic biology: Applications come of age. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Keasling, J. Biosensors and their applications in microbial metabolic engineering. Trends Microbiol. 2011, 19, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- San Francisco, M.J.; Hope, C.L.; Owolabi, J.B.; Tisa, L.S.; Rosen, B.P. Identification of the metalloregulatory element of the plasmid-encoded arsenical resistance operon. Nucleic. Acids Res. 1990, 18, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Rosen, B.P. Metalloregulated expression of the ars operon. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.F.; Walmsley, A.R.; Rosen, B.P. An arsenic metallochaperone for an arsenic detoxification pump. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 15617–15622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, O.I.; Rensing, C.; Kuroda, M.; Mitra, B.; Rosen, B.P. Antimonite is accumulated by the glycerol facilitator GlpF in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1997, 179, 3365–3367. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, R.; Bhattacharjee, H.; Rosen, B.P. Aquaglyceroporins: Generalized metalloid channels. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1840, 1583–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Wu, J.; Rosen, B.P. Identification of a putative metal binding site in a new family of metalloregulatory proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 19826–19829. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yoon, K.P.; Silver, S. A second gene in the Staphylococcus aureus cadA cadmium resistance determinant of plasmid pI258. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 7636–7642. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Wong, M.D.; Rosen, B.P. Role of cysteinyl residues in sensing Pb(II), Cd(II), and Zn(II) by the plasmid pI258 CadC repressor. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 14955–14960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Kandegedara, A.; Martin, P.; Rosen, B.P. Crystal structure of the Staphylococcus aureus pI258 CadC Cd(II)/Pb(II)/Zn(II)-responsive repressor. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 4214–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butcher, B.G.; Rawlings, D.E. The divergent chromosomal ars operon of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans is regulated by an atypical ArsR protein. Microbiology 2002, 148, 3983–3992. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ordóñez, E.; Letek, M.; Valbuena, N.; Gil, J.A.; Mateos, L.M. Analysis of genes involved in arsenic resistance in Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 6206–6215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ordóñez, E.; Thiyagarajan, S.; Cook, J.D.; Stemmler, T.L.; Gil, J.A.; Mateos, L.M.; Rosen, B.P. Evolution of metal (loid) binding sites in transcriptional regulators. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 25706–25714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tauriainen, S.; Karp, M.; Chang, W.; Virta, M. Recombinant luminescent bacteria for measuring bioavailable arsenite and antimonite. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 4456–4461. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Scott, D.L.; Ramanathan, S.; Shi, W.; Rosen, B.P.; Daunert, S. Genetically engineered bacteria: Electrochemical sensing systems for antimonite and arsenite. Anal. Chem. 1997, 69, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanathan, S.; Shi, W.; Rosen, B.P.; Daunert, S. Sensing antimonite and arsenite at the subattomole level with genetically engineered bioluminescent bacteria. Anal. Chem. 1997, 69, 3380–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetty, R.S.; Deo, S.K.; Shah, P.; Sun, Y.; Rosen, B.P.; Daunert, S. Luminescence-based whole-cell-sensing systems for cadmium and lead using genetically engineered bacteria. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2003, 376, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Petänen, T.; Romantschuk, M. Use of bioluminescent bacterial sensors as an alternative method for measuring heavy metals in soil extracts. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 456, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, J.; Balluch, D.; Gsell, M.; Harms, H.; Feliciano, J.; Daunert, S.; Malik, K.A.; van der Meer, J.R. Development of a set of simple bacterial biosensors for quantitative and rapid measurements of arsenite and arsenate in potable water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 4743–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegfried, K.; Endes, C.; Bhuiyan, A.F.; Kuppardt, A.; Mattusch, J.; van der Meer, J.R.; Chatzinotas, A.; Harms, H. Field testing of arsenic in groundwater samples of Bangladesh using a test kit based on lyophilized bioreporter bacteria. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3281–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Asad, S.; Ali, A. Bioluminescent bioreporter for assessment of arsenic contamination in water samples of India. J. Biosci. 2013, 38, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberto, F.F.; Barnes, J.M.; Bruhn, D.F. Evaluation of a GFP reporter gene construct for environmental arsenic detection. Talanta 2002, 58, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tani, C.; Inoue, K.; Tani, Y.; Harun-ur-Rashid, M.; Azuma, N.; Ueda, S.; Yoshida, K.; Maeda, I. Sensitive fluorescent microplate bioassay using recombinant Escherichia coli with multiple promoter-reporter units in tandem for detection of arsenic. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2009, 108, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theytaz, J.; Braschler, T.; van Lintel, H.; Renaud, P.; Diesel, E.; Merulla, D.; van der Meer, J. Biochip with E. coli bacteria for detection of arsenic in drinking water. Procedia Chem. 2009, 1, 1003–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiki, M.S.; Kawakami, Y.; Ueda, S.; Maeda, I. Solid phase biosensors for arsenic or cadmium composed of a trans factor and cis element complex. Sensors 2012, 11, 10063–10073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truffer, F.; Buffi, N.; Merulla, D.; Beggah, S.; van Lintel, H.; Renaud, P.; van der Meer, J.R.; Geiser, M. Compact portable biosensor for arsenic detection in aqueous samples with Escherichia coli bioreporter cells. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2014, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, S.I.; Gravelat, F.N.; al Abdallah, Q.; Lee, M.J.; Gibbs, B.F.; Sheppard, D.C. Role of Aspergillus niger acrA in arsenic resistance and its use as the basis for an arsenic biosensor. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 3855–3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobrowicz, P.; Wysocki, R.; Owsianik, G.; Goffeau, A.; Ulaszewski, S. Isolation of three contiguous genes, ACR1, ACR2 and ACR3, involved in resistance to arsenic compounds in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 1997, 13, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.C.; Fu, H.L.; Lin, Y.F.; Rosen, B.P. Pathways of arsenic uptake and efflux. Curr. Top. Membr. 2012, 69, 325–358. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yoshinaga, M.; Cai, Y.; Rosen, B.P. Demethylation of methylarsonic acid by a microbial community. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1205–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbarino, J.R.; Bednar, A.J.; Rutherford, D.W.; Beyer, R.S.; Wershaw, R.L. Environmental fate of roxarsone in poultry litter. I. Degradation of roxarsone during composting. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 1509–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolz, J.F.; Perera, E.; Kilonzo, B.; Kail, B.; Crable, B.; Fisher, E.; Ranganathan, M.; Wormer, L.; Basu, P. Biotransformation of 3-nitro-4-hydroxybenzene arsonic acid (roxarsone) and release of inorganic arsenic by Clostridium species. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 818–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makris, K.C.; Quazi, S.; Punamiya, P.; Sarkar, D.; Datta, R. Fate of arsenic in swine waste from concentrated animal feeding operations. J. Environ. Qual. 2008, 37, 1626–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Endt, D.W.; Kearney, P.C.; Kafman, D.D. Degradation of monosodium methanearsonic acid by soil microorganisms. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1968, 16, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Schrlau, J.E.; Snyder, R.; Snyder, G.H.; Chen, M.; Cisar, J.L.; Cai, Y. Arsenic transport and transformation associated with MSMA application on a golf course green. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 3556–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Sun, S.; Li, C.Z.; Zhu, Y.G.; Rosen, B.P. Biosensor for organoarsenical herbicides and growth promoters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 1141–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.M.; Mukherjee, D.; Sengupta, M.K.; Chowdhury, U.K.; Lodh, D.C.; Roy, S.; Selim, M.; Quamruzzaman, Q.; Milton, A.H.; Shahidullah, S.M.; et al. Effectiveness and reliability of arsenic field testing kits: Are the million dollar screening projects effective or not? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 5385–5394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinniburgh, D.G.; Kosmus, W. Arsenic contamination in groundwater: Some analytical considerations. Talanta 2002, 58, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, B.E. Field kits fail to provide accurate measure of arsenic in groundwater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 35A–38A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlin, A.; Shi, W.; Dey, S.; Rosen, B.P. The ars operon of Escherichia coli confers arsenical and antimonial resistance. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 981–986. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, Y.G.; Rosen, B.P. A novel biosensor selective for organoarsenicals. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 7145–7147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edmonds, J.S.; Francesconi, K.A. Transformations of arsenic in the marine environment. Experientia 1987, 43, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trang, P.T.; Berg, M.; Viet, P.H.; van Mui, N.; van der Meer, J.R. Bacterial bioassay for rapid and accurate analysis of arsenic in highly variable groundwater samples. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 7625–7630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tauriainen, S.M.; Virta, M.; Karp, M. Detecting bioavailable toxic metal and metalloids from natural water samples using luminescent sensor bacteria. Water Res. 2000, 34, 2661–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, M.; Tran, H.C.; Nguyen, T.C.; Pham, H.V.; Schertenleib, R.; Giger, W. Arsenic contamination of groundwater and drinking water in Vietnam: A human health threat. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 2621–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tareq, S.M.; Safiullah, S.; Anawar, H.M.; Rahman, M.M.; Ishizuka, T. Arsenic pollution in groundwater: A self-organizing complex geochemical process in the deltaic sedimentary environment, Bangladesh. Sci. Total. Environ. 2003, 313, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bednar, A.J.; Garbarino, J.R.; Ranville, J.F.; Wildeman, T.R. Preserving the distribution of inorganic arsenic species in groundwater and acid mine drainage samples. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 2213–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, P.A.; Schwegel, C.A.; Parks, A.; Gamble, B.M.; Wymer, L.; Creed, J.T. Preservation of As(III) and As(V) in drinking water supply samples from across the United States using EDTA and acetic acid as a means of minimizing iron-arsenic coprecipitation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 2919–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjerketorp, J.; Hakansson, S.; Belkin, S.; Jansson, J.K. Advances in preservation methods: Keeping biosensor microorganisms alive and active. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2006, 17, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.W.; Park, K.W.; Lee, D.B.; Lee, W.; Lee, W.H. Cell immobilization using self-assembled synthetic oligopeptide and its application to biological toxicity detection using surface plasmon resonance. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 20, 2300–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, S.; Aranda-Olmedo, I.; Ramos, J.L. Controlling bacterial physiology for optimal expression of gene reporter constructs. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2006, 17, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotman, B.; Cote, M.A. Application of a real-time biosensor to detect bacteria in platelet concentrates. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 300, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Mora, K.; Joshi, N.; Balint, B.L.; Ward, F.B.; Elfick, A.; French, C.E. A pH-based biosensor for detection of arsenic in drinking water. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 400, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes-Salazar, F.; Beggah, S.; van der Meer, J.R.; Girault, H.H. Electrochemical As(III) whole-cell based biochip sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 47, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, N.; Kaya, T.; Nagamine, K.; Yasukawa, T.; Shiku, H.; Matsue, T. Electrochemical mutagen screening using microbial chip. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 21, 1202–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng Vollmer, A.; van Dyk, T.K. Stress responsive bacteria: Biosensors as environmental monitors. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 2004, 49, 131–174. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Popovtzer, R.; Neufeld, T.; Biran, D.; Ron, E.Z.; Rishpon, J.; Shacham-Diamand, Y. Novel integrated electrochemical nano-biochip for toxicity detection in water. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 1023–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Rosen, B.P. Biosensors for Inorganic and Organic Arsenicals. Biosensors 2014, 4, 494-512. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios4040494
Chen J, Rosen BP. Biosensors for Inorganic and Organic Arsenicals. Biosensors. 2014; 4(4):494-512. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios4040494
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jian, and Barry P. Rosen. 2014. "Biosensors for Inorganic and Organic Arsenicals" Biosensors 4, no. 4: 494-512. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios4040494
APA StyleChen, J., & Rosen, B. P. (2014). Biosensors for Inorganic and Organic Arsenicals. Biosensors, 4(4), 494-512. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios4040494