3D-Printed PLA Hollow Microneedles Loaded with Chitosan Nanoparticles for Colorimetric Glucose Detection in Sweat Using Machine Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
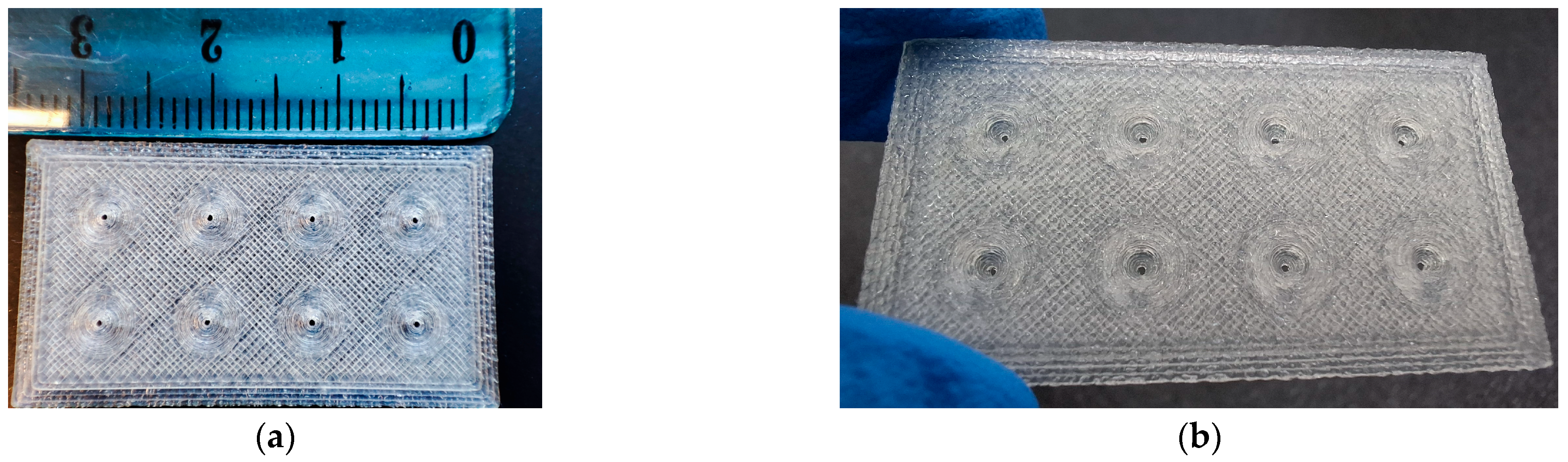
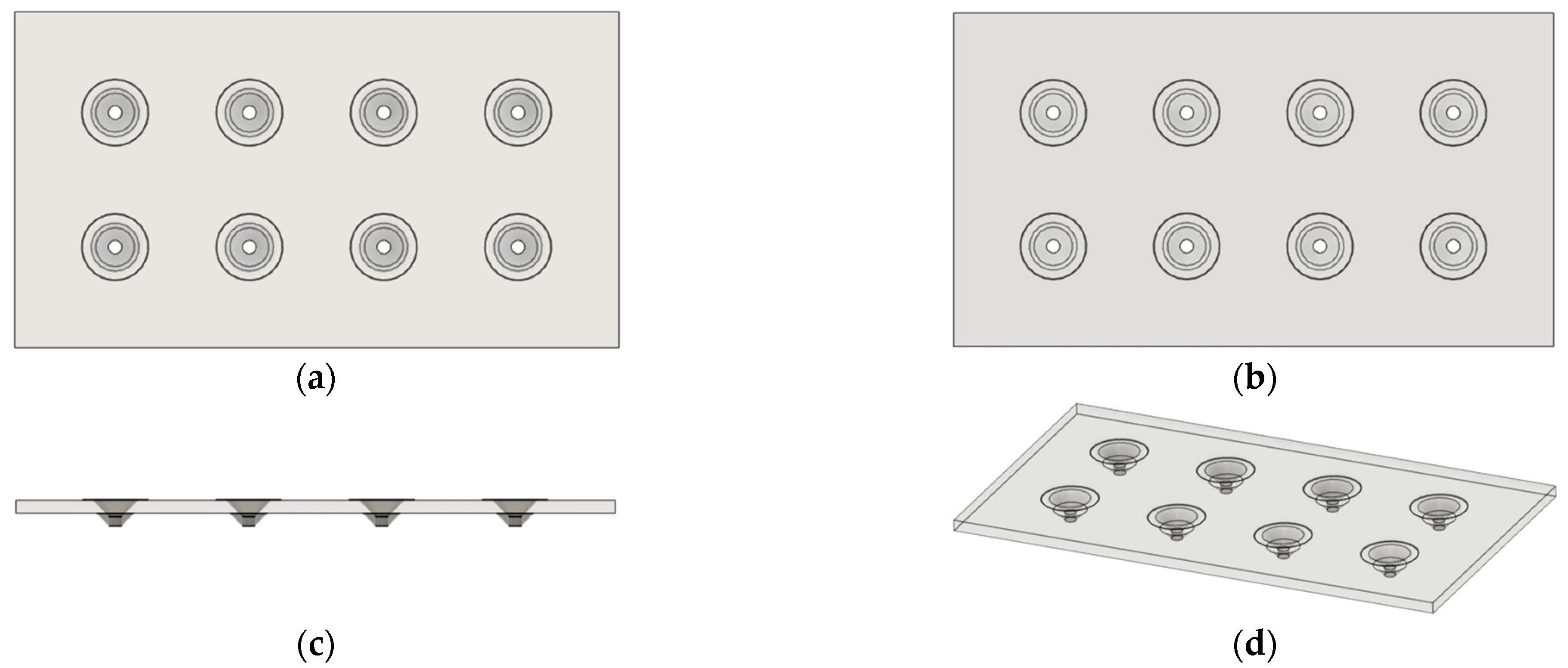
2.2. 3D Design and Printing of PLA MN Patch
2.3. Synthesis of CNPs with Encapsulation of GOx, HRP, and ABTS
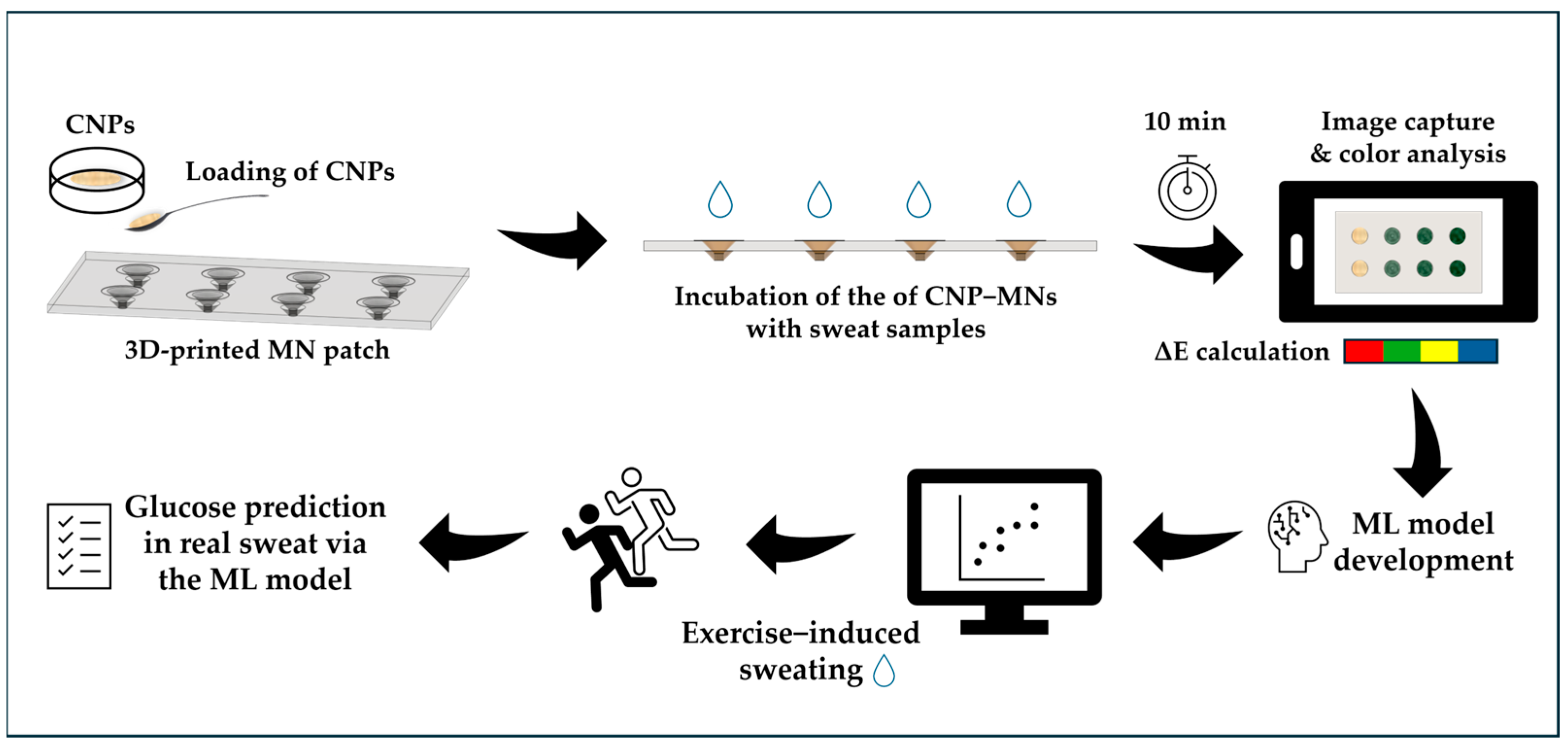
2.4. Fabrication of CNP−MN Patch Biosensor
2.5. Optimization of Glucose Detection
2.6. Glucose Determination Using CNP−MN Patch Biosensor in Artificial Sweat
2.7. Reproducibility and Storage Stability of GOx−HRP−ABTS CNPs
2.8. Analytical Performance of the Biosensor
2.9. Machine Learning for Glucose Prediction in Sweat
2.10. Spiking Study in Artificial Sweat
2.11. Glucose Determination in Real Sweat
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of Biosensor Construction
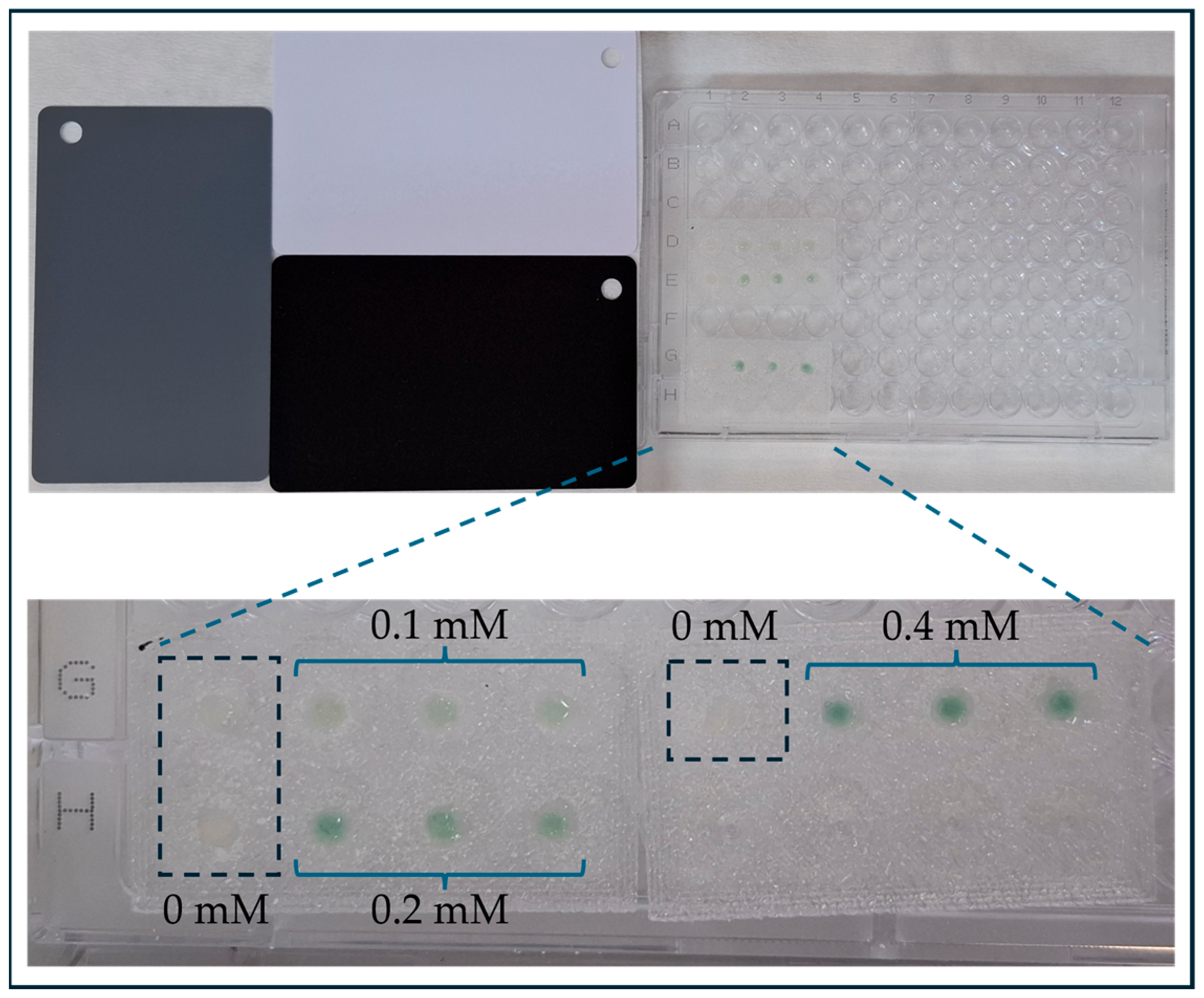
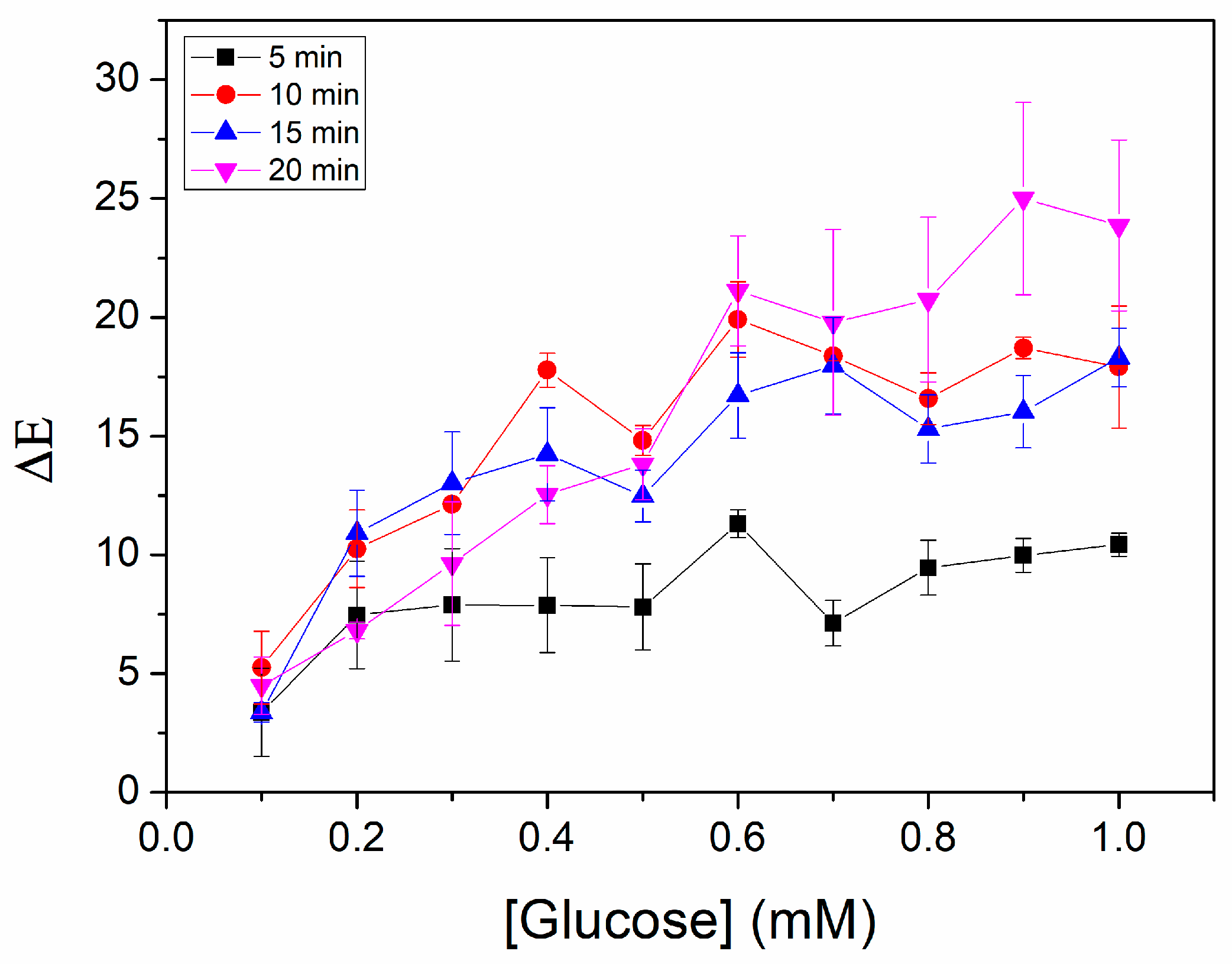
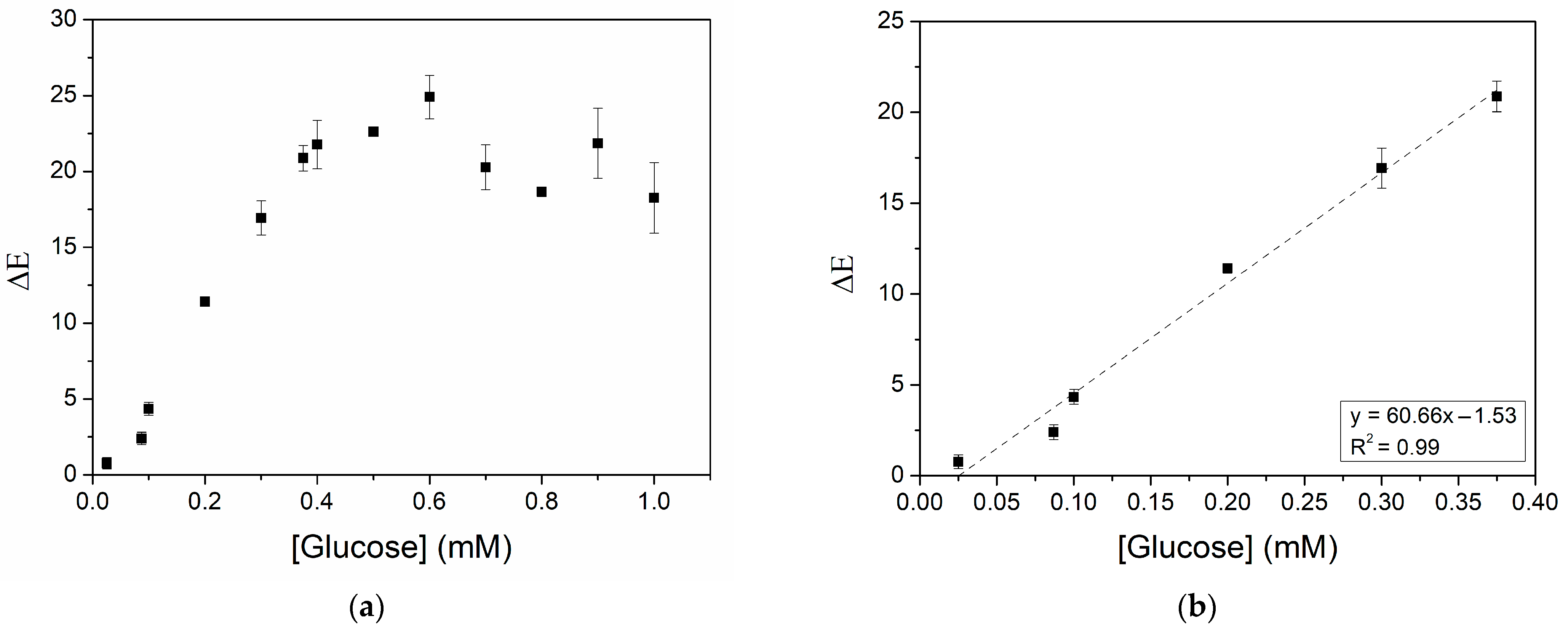
3.2. Optimization of Glucose Detection
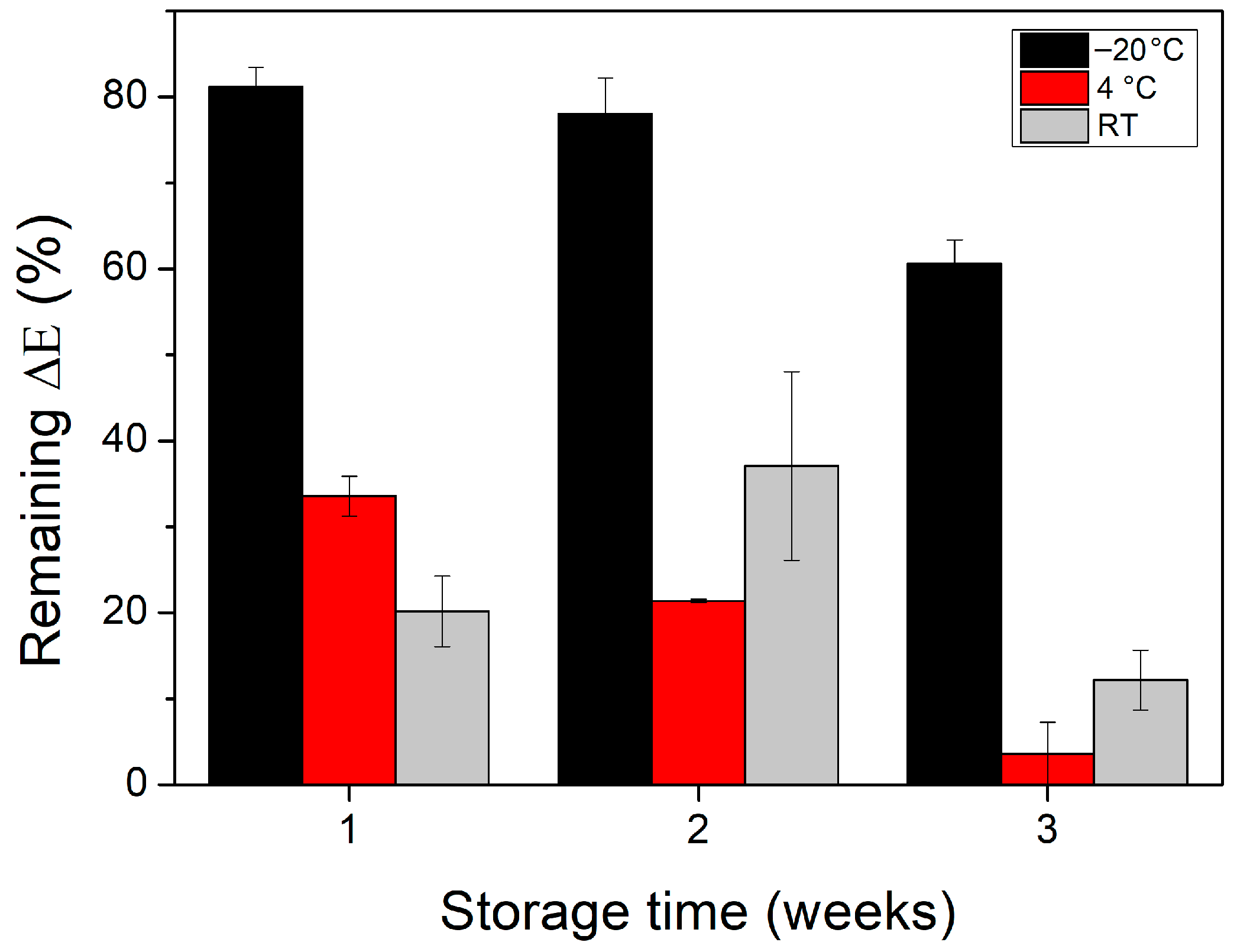
3.3. Reproducibility and Storage Stability of GOx−HRP−ABTS CNPs
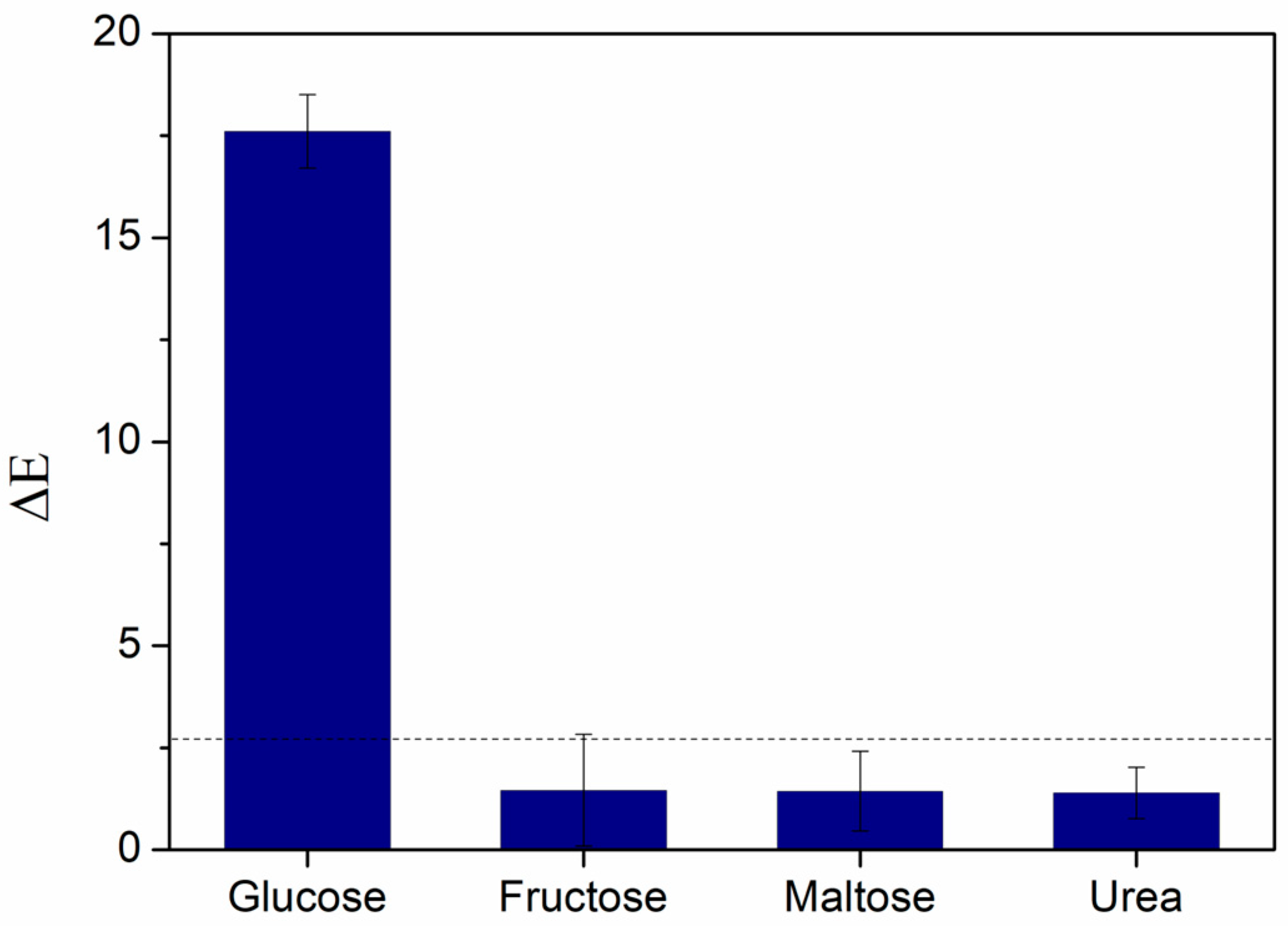
3.4. Specificity Study of the Biosensor
3.5. Analytical Performance of the Biosensor
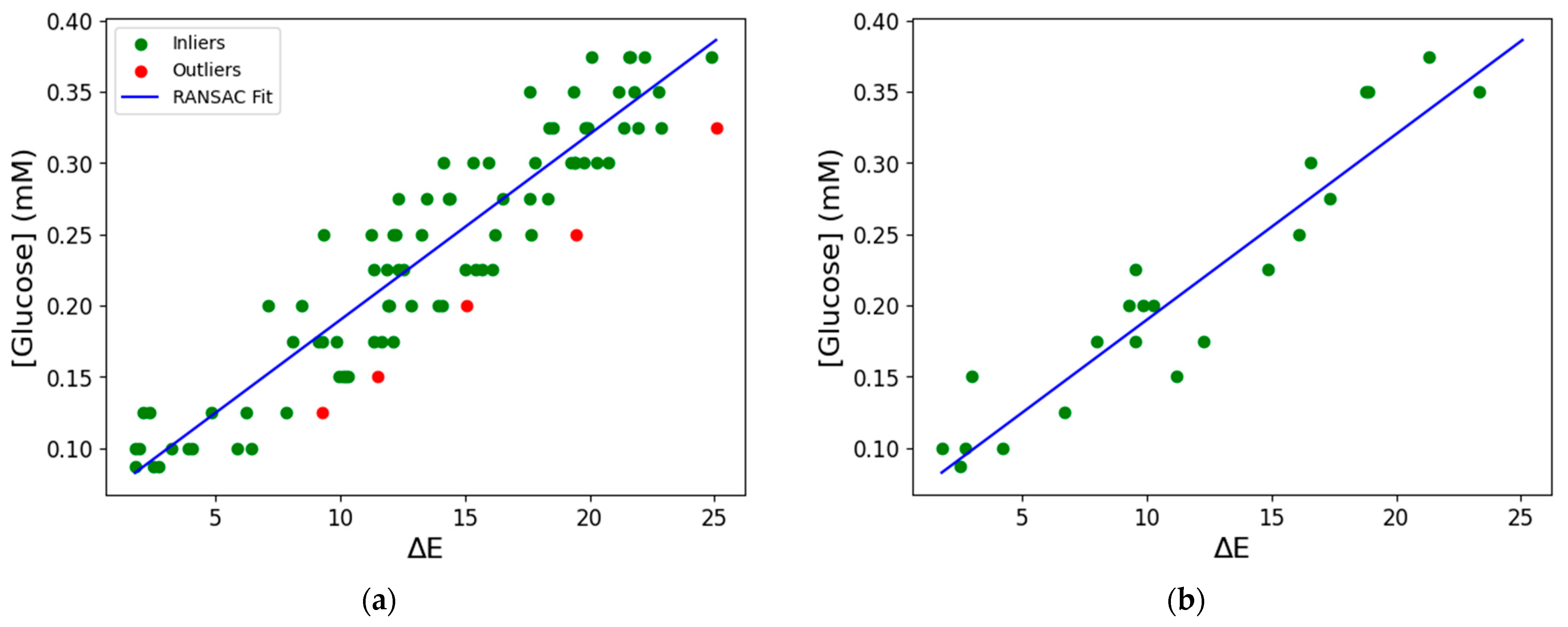
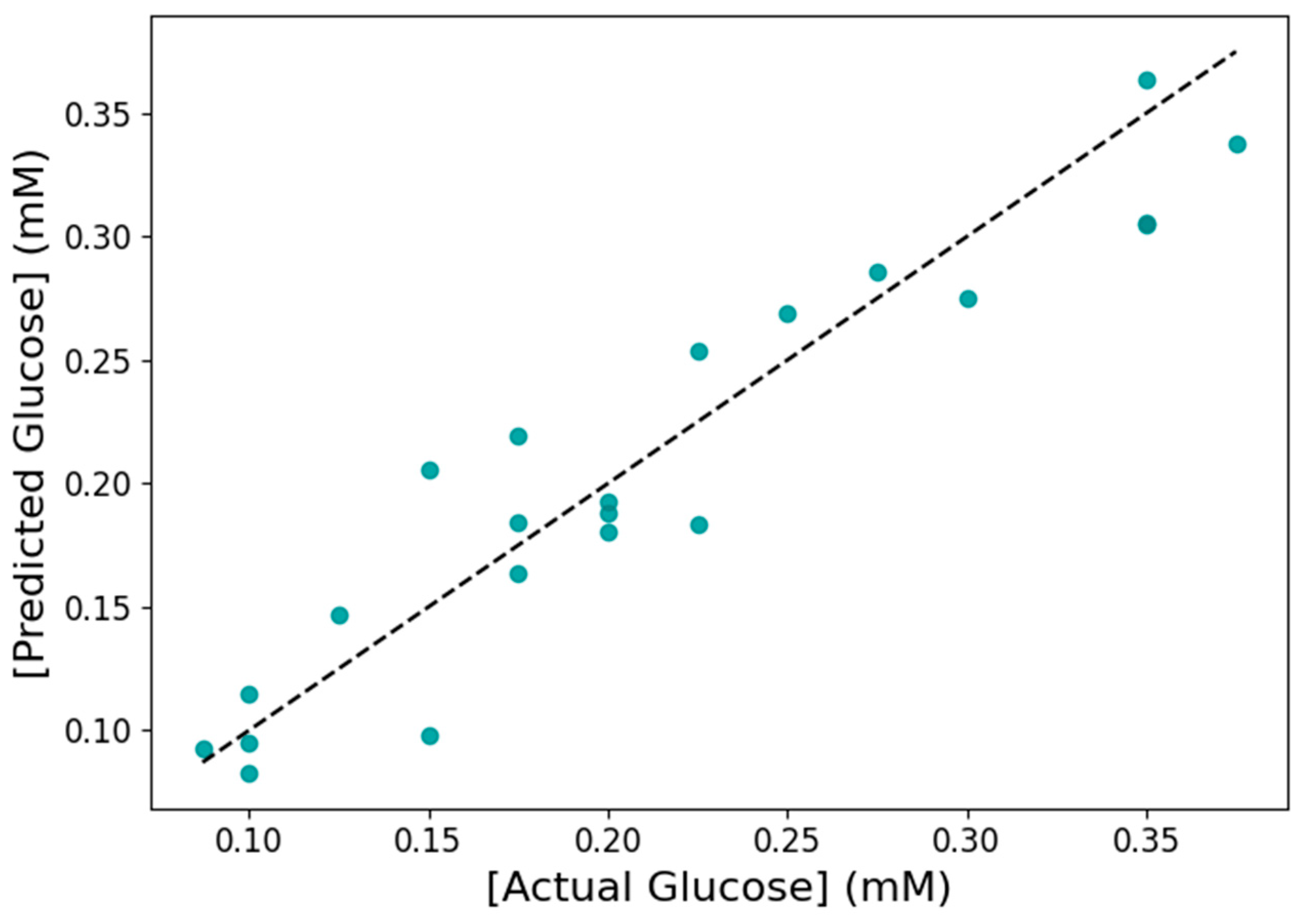
3.6. Machine Learning for Glucose Prediction in Sweat
3.7. Spiking Study Using CNP−MN Biosensor and ML
3.8. Application in Real Sweat Sample Using CNP−MNs Biosensor and ML
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MNs | Microneedles |
| CS | Chitosan |
| TPP | Sodium tripolyphosphate |
| CNPs | Chitosan nanoparticles |
| GOx | Glucose oxidase |
| HRP | Horseradish peroxidase |
| ABTS | 2,2′-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) |
| H2O2 | Hydrogen peroxide |
| EE | Encapsulation efficiency |
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
| ML | Machine learning |
| FDM | Fused deposition modeling |
| PLA | Polylactic acid |
| LR | Linear regression |
| RANSAC | Random Sample Consensus |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| LOQ | Limit of quantification |
| RSD | Relative standard deviation |
| MAE | Mean absolute error |
| RMSE | Root mean squared error |
References
- Hossain, M.J.; Al-Mamun, M.; Islam, M.R. Diabetes Mellitus, the Fastest Growing Global Public Health Concern: Early Detection Should Be Focused. Health Sci. Rep. 2024, 7, e2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antar, S.A.; Ashour, N.A.; Sharaky, M.; Khattab, M.; Ashour, N.A.; Zaid, R.T.; Roh, E.J.; Elkamhawy, A.; Al-Karmalawy, A.A. Diabetes Mellitus: Classification, Mediators, and Complications; A Gate to Identify Potential Targets for the Development of New Effective Treatments. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 168, 115734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krentz, A.J.; Hompesch, M. Glucose: Archetypal Biomarker in Diabetes Diagnosis, Clinical Management and Research. Biomark. Med. 2016, 10, 1153–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedorova, K.; Augustynek, M.; Kubicek, J.; Kudrna, P.; Bibbo, D. Review of Present Method of Glucose from Human Blood and Body Fluids Assessment. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 211, 114348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, K.; Santra, T.S.; Tseng, F.G. Advancements in Glucose Monitoring: From Traditional Methods to Wearable Sensors. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullano, S.A.; Greco, M.; Bianco, M.G.; Foti, D.; Brunetti, A.; Fiorillo, A.S. Glucose Biosensors in Clinical Practice: Principles, Limits and Perspectives of Currently Used Devices. Theranostics 2022, 12, 493–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyer, J.; Wilson, D.; Finkelshtein, I.; Wong, B.; Potts, R. Correlation Between Sweat Glucose and Blood Glucose in Subjects with Diabetes. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2012, 14, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafar, H.; Channa, A.; Jeoti, V.; Stojanović, G.M. Comprehensive Review on Wearable Sweat-Glucose Sensors for Continuous Glucose Monitoring. Sensors 2022, 22, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Hou, L.; Wang, M.; Liu, R.; Han, L.; Nikolai, M.; Zhang, S.; Cheng, C.; Hu, K. Noninvasive Glucose Monitoring Using Portable GOx-Based Biosensing System. Anal. Chim. Acta 2024, 1287, 342068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, C.; Zhang, L.; Hou, T.; Wang, Q.; Li, F.; Gai, P. Laser-Induced Nanozyme Biofuel Cell-Based Self-Powered Patch for Accelerating Diabetic Wound Healing With Real-Time Monitoring. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 2423106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apetrei, R.M.; Camurlu, P. Facile Copper-Based Nanofibrous Matrix for Glucose Sensing: Eenzymatic vs. Non-Enzymatic. Bioelectrochemistry 2021, 140, 107751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemati, S.S.; Dehghan, G.; Rashtbari, S.; Tan, T.N.; Khataee, A. Enzyme-Based and Enzyme-Free Metal-Based Glucose Biosensors: Classification and Recent Advances. Microchem. J. 2023, 193, 109038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindaraj, M.; Srivastava, A.; Muthukumaran, M.K.; Tsai, P.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Raja, B.K.; Rajendran, J.; Ponnusamy, V.K.; Arockia Selvi, J. Current Advancements and Prospects of Enzymatic and Non-Enzymatic Electrochemical Glucose Sensors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Zhou, K.; Wang, R.; Li, M.; Liu, W.; Li, C.; Chen, X.; Lu, Q.; Chang, Y. Wearable Biosensors for Human Sweat Glucose Detection Based on Carbon Black Nanoparticles. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2024, 416, 1407–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mwaurah, M.M.; Vinoth, R.; Nakagawa, T.; Mathiyarasu, J.; Mohan, A.M.V. A Neckband-Integrated Soft Microfluidic Biosensor for Sweat Glucose Monitoring. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 17017–17028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Liu, Y.; Su, L.; Zhao, D.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X. Microfluidic Chip-Based Wearable Colorimetric Sensor for Simple and Facile Detection of Sweat Glucose. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 14803–14807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, G.; He, J.; Chen, X.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, F.; Xia, Q.; Yu, L.; Lu, Z. A Wearable, Cotton Thread/Paper-Based Microfluidic Device Coupled with Smartphone for Sweat Glucose Sensing. Cellulose 2019, 26, 4553–4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaquer, A.; Barãn, E.; De La Rica, R. Detection of Low Glucose Levels in Sweat with Colorimetric Wearable Biosensors. Analyst 2021, 146, 3273–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Xu, F.; Zhang, L.; Ren, G.; Sheng, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, K.; Yu, L.; Wang, J.; Li, G.; et al. Simple, Skin-Attachable, and Multifunctional Colorimetric Sweat Sensor. ACS Sens. 2022, 7, 2198–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Rey, S.; Gil-Hernandez, E.; Basabe-Desmonts, L.; Benito-Lopez, F. Colorimetric Determination of Glucose in Sweat Using an Alginate-Based Biosystem. Polymers 2023, 15, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skonta, A.; Bellou, M.G.; Matikas, T.E.; Stamatis, H. Colorimetric Glucose Biosensor Based on Chitosan Films and Its Application for Glucose Detection in Beverages Using a Smartphone Application. Biosensors 2024, 14, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bocchetta, P.; Othman, A.; Gupta, M.; Andriani, G.; Martin, P.; Kumar, Y.; Joly, N.; Sacco, P.; Sufyan Javed, M. Chitosan in Electrochemical (Bio)Sensors: Nanostructuring and Methods of Synthesis. Eur. Polym. J. 2024, 213, 113092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigli, V.; Tortolini, C.; Capecchi, E.; Angeloni, A.; Lenzi, A.; Antiochia, R. Novel Amperometric Biosensor Based on Tyrosinase/Chitosan Nanoparticles for Sensitive and Interference-Free Detection of Total Catecholamine. Biosensors 2022, 12, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anusha, J.R.; Raj, C.J.; Cho, B.B.; Fleming, A.T.; Yu, K.H.; Kim, B.C. Amperometric Glucose Biosensor Based on Glucose Oxidase Immobilized over Chitosan Nanoparticles from Gladius of Uroteuthis Duvauceli. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 215, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vora, L.K.; Sabri, A.H.; McKenna, P.E.; Himawan, A.; Hutton, A.R.J.; Detamornrat, U.; Paredes, A.J.; Larrañeta, E.; Donnelly, R.F. Microneedle-Based Biosensing. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 2024, 2, 64–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezapour Sarabi, M.; Nakhjavani, S.A.; Tasoglu, S. 3D-Printed Microneedles for Point-of-Care Biosensing Applications. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrilla, M.; Vanhooydonck, A.; Johns, M.; Watts, R.; De Wael, K. 3D-Printed Microneedle-Based Potentiometric Sensor for pH Monitoring in Skin Interstitial Fluid. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 378, 133159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaghi, M.; Ninan, J.A.; Azimzadeh, M.; Askari, E.; Najafabadi, A.H.; Khademhosseini, A.; Akbari, M. Remote-Controlled Sensing and Drug Delivery via 3D-Printed Hollow Microneedles. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, 13, e2400881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cano-Vicent, A.; Tambuwala, M.M.; Hassan, S.S.; Barh, D.; Aljabali, A.A.A.; Birkett, M.; Arjunan, A.; Serrano-Aroca, Á. Fused Deposition Modelling: Current Status, Methodology, Applications and Future Prospects. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 47, 102378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzuriaga, M.A.; Berry, D.R.; Reagan, J.C.; Smaldone, R.A.; Gassensmith, J.J. Biodegradable 3D Printed Polymer Microneedles for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 1223–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, T.M.; Kallingal, A.; Suresh, A.M.; Mahapatra, D.K.; Hasanin, M.S.; Haponiuk, J.; Thomas, S. 3D Printing of Polylactic Acid: Recent Advances and Opportunities. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 125, 1015–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Park, J.; Kamaki, Y.; Kim, B. Optimization of the Fused Deposition Modeling-Based Fabrication Process for Polylactic Acid Microneedles. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2021, 7, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosraviboroujeni, A.; Mirdamadian, S.Z.; Minaiyan, M.; Taheri, A. Preparation and Characterization of 3D Printed PLA Microneedle Arrays for Prolonged Transdermal Drug Delivery of Estradiol Valerate. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2022, 12, 1195–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camović, M.; Biščević, A.; Brčić, I.; Borčak, K.; Bušatlić, S.; Ćenanović, N.; Dedović, A.; Mulalić, A.; Osmanlić, M.; Sirbubalo, M.; et al. Coated 3D Printed PLA Microneedles as Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems. In CMBEBIH 2019; Badnjevic, A., Škrbić, R., Gurbeta Pokvić, L., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 735–742. ISBN 9783030179717. [Google Scholar]
- Kouassi, M.C.; Kallel, A.; Abdallah, A.B.; Nouira, S.; Ballut, S.; Fitoussi, J.; Shirinbayan, M. Assessment of Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) Parameters for Fabrication of Solid and Hollow Microneedles Using Polylactic Acid (PLA). Polym. Adv. Technol. 2024, 35, e6548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.; Yue, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, H.S. Advancing Biosensors with Machine Learning. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 3346–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Menon, S.S.; Li, X.; Zhang, M.; Malakooti, M.H. Machine Learning Enables Reliable Colorimetric Detection of pH and Glucose in Wearable Sweat Sensors. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2024, 2401121, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankhala, D.; Sardesai, A.U.; Pali, M.; Lin, K.C.; Jagannath, B.; Muthukumar, S.; Prasad, S. A Machine Learning-Based On-Demand Sweat Glucose Reporting Platform. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maulud, D.; Abdulazeez, A.M. A Review on Linear Regression Comprehensive in Machine Learning. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. Trends 2020, 1, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaiyya, M.; Panigrahi, D.; Rewatkar, P.; Haick, H. Role of Machine Learning Assisted Biosensors in Point-of-Care- Testing For Clinical Decisions. ACS Sens. 2024, 9, 4495–4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonelli, G.; Filippi, J.; Orazio, M.D.; Curci, G.; Casti, P.; Mencattini, A.; Martinelli, E. Integrating Machine Learning and Biosensors in Microfluidic Devices: A Review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 263, 116632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raguram, R.; Frahm, J.; Pollefeys, M. A Comparative Analysis of RANSAC Techniques Leading to Adaptive Real-Time Random Sample Consensus. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2008; Forsyth, D., Torr, P., Zisserman, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 500–513. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, S.K.; Bhaiyya, M.; Dudala, S.; Hota, C.; Goel, S. A Machine Learning Approach for Electrochemiluminescence Based Point of Care Testing Device to Detect Multiple Biomarkers. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2023, 350, 114135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellou, M.G.; Skonta, A.; Chatzikonstantinou, A.V.; Polydera, A.C.; Katapodis, P.; Voutsas, E.; Stamatis, H. Enzymatic Oxidation of Hydroxytyrosol in Deep Eutectic Solvents for Chitosan Functionalization and Preparation of Bioactive Nanogels. Catalysts 2025, 15, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatachar, A.V. Comparative Assessment of Regression Models Based On Model Evaluation Metrics. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2021, 8, 853–860. [Google Scholar]
- Poddar, A.; Rangwani, N.; Palekar, S.; Kalambe, J. Glucose Monitoring System Using Machine Learning. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 73, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Jiang, W. Preparation of Chitosan-Based Nanoparticles for Enzyme immobilization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baluchi, A.; Homaei, A. Immobilization of L-Asparaginase on Chitosan Nanoparticles for the Purpose of Long-Term Application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 257, 128655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, R.; Liu, H.; Fang, T.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Han, F.; Gao, B.; Li, F.; Xu, F. A Colorimetric Dermal Tattoo Biosensor Fabricated by Microneedle Patch for Multiplexed Detection of Health-Related Biomarkers. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2103030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horta-Velázquez, A.; Ramos-Ortiz, G.; Morales-Narváez, E. The Optimal Color Space Enables Advantageous Smartphone-Based Colorimetric Sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2025, 273, 117089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitzalis, F.; Monduzzi, M.; Salis, A. A Bienzymatic Biocatalyst Constituted by Glucose Oxidase and Horseradish Peroxidase Immobilized on Ordered Mesoporous Silica. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 241, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, S.A.; Al-Malki, A.L.; Kumosani, T.A.; El-Shishtawy, R.M. Horseradish Peroxidase and Chitosan: Activation, Immobilization and Comparative Results. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 60, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Yuan, L.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Rao, D.; Bai, X.; Shi, K.; Xu, H.; Hou, S.; Yao, H. Co-Immobilized Bienzyme of Horseradish Peroxidase and Glucose Oxidase on Dopamine-Modified Cellulose-Chitosan Composite Beads as a High-Efficiency Biocatalyst for Degradation of Acridine. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 23006–23016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, M.N.; Pereira, F.M.; Rocha, M.A.; Ribeiro, J.G.; Diz, F.M.; Monteiro, W.F.; Ligabue, R.A.; Severino, P.; Fricks, A.T. Immobilization and Characterization of Horseradish Peroxidase into Chitosan and Chitosan/PEG Nanoparticles: A Comparative Study. Process. Biochem. 2020, 98, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, Y.C.; Hashim, R.; Mohd Yahya, A.R.; Bustami, Y. Colorimetric Analysis of Glucose Oxidase-Magnetic Cellulose Nanocrystals (CNCs) for Glucose Detection. Sensors 2019, 19, 2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.; Wang, S.; Miao, S.; Suo, H.; Xu, H.; Hu, Y. Co-Immobilization of Laccase and ABTS onto Amino-Functionalized Ionic Liquid-Modified Magnetic Chitosan Nanoparticles for Pollutants Removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neubauerova, K.; Carneiro, M.C.C.G.; Rodrigues, L.R.; Moreira, F.T.C.; Sales, M.G.F. Nanocellulose- Based Biosensor for Colorimetric Detection of Glucose. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2020, 29, 100368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Printing Parameter | Set Value |
|---|---|
| Layer height | 0.12 mm |
| Infill density | 100% |
| Printing temperature | 200 °C |
| Build plate temperature | 50 °C |
| Print speed | 80 mm/s |
| Immobilization Support | Detection System | Color Space/Parameter | Results | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Whatman filter paper | GOx–HRP–o-dianisidine | CIELAB/ΔΕ | Reaction time: 15 min Sample volume: 4.15 μL Linear range: 0.1−0.5 mM LOD: 0.03 mM | [16] |
| Filter paper/CS | GOx−HRP−TMB 1 | RGB/R 2 | Reaction time: 10 min Sample volume: 23.8 ± 1.1 μL Linear range: 50–250 μM LOD: ~35 μΜ Sensitivity: −0.19 μM−1 | [17] |
| Filter paper | GOx−HRP−TMB | Pixel intensity | Reaction time: 3 min Sample volume: 3 μL Linear range: 0.01–0.15 mM LOD: 0.01 mM | [18] |
| Whatman filter paper/CS | GOx−KI | RGB/G | Sample volume: 2.5 μL Linear range: 0–2 mM LOD: 0.046 mΜ | [19] |
| Alginate beads | GOx−HRP−TMB | B/W 3, R, G, B | Reaction time: 13 min Sample volume: 150 μL Linear range: 10–1000 µM LOD: 3.8 µM LOQ: 12.7 µM | [20] |
| Cotton fabric | GOx−HRP−TMB GOx−HRP−KI | RGB/R, G, B and CIELAB/L, a, b | Reaction time: 3 min Sample volume: 10 μL Linear range: 0.03–1 mM LOD: 0.03 mM | [37] |
| CNPs | GOx−HRP−ABTS | CIELAB/ΔΕ | Reaction time: 10 min Sample volume: 4.94 ± 0.25 μL Linear range: 0.025–0.375 mM LOD: 0.023 mM LOQ: 0.078 mM | This work |
| Evaluation Method | R2 | MAE (mM) | RMSE (mM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Test set | 0.89 | 0.0245 | 0.0292 |
| 5-fold cross-validation | 0.85 ± 0.02 | 0.0267 ± 0.0015 | 0.0324 ± 0.0022 |
| Spiked Glucose (mM) | Predicted Glucose (mM) | Recovery Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.100 | 0.110 | 112 ± 3 |
| 0.200 | 0.180 | 89 ± 2 |
| 0.375 | 0.320 | 86 ± 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skonta, A.; Bellou, M.G.; Stamatis, H. 3D-Printed PLA Hollow Microneedles Loaded with Chitosan Nanoparticles for Colorimetric Glucose Detection in Sweat Using Machine Learning. Biosensors 2025, 15, 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15070461
Skonta A, Bellou MG, Stamatis H. 3D-Printed PLA Hollow Microneedles Loaded with Chitosan Nanoparticles for Colorimetric Glucose Detection in Sweat Using Machine Learning. Biosensors. 2025; 15(7):461. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15070461
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkonta, Anastasia, Myrto G. Bellou, and Haralambos Stamatis. 2025. "3D-Printed PLA Hollow Microneedles Loaded with Chitosan Nanoparticles for Colorimetric Glucose Detection in Sweat Using Machine Learning" Biosensors 15, no. 7: 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15070461
APA StyleSkonta, A., Bellou, M. G., & Stamatis, H. (2025). 3D-Printed PLA Hollow Microneedles Loaded with Chitosan Nanoparticles for Colorimetric Glucose Detection in Sweat Using Machine Learning. Biosensors, 15(7), 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15070461




_Stamatis.png)

