Ultra-Sensitive Detection of Chloramphenicol by CdS@NiMoS Nanorods-Based Photoelectrochemical Aptasensor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Apparatus
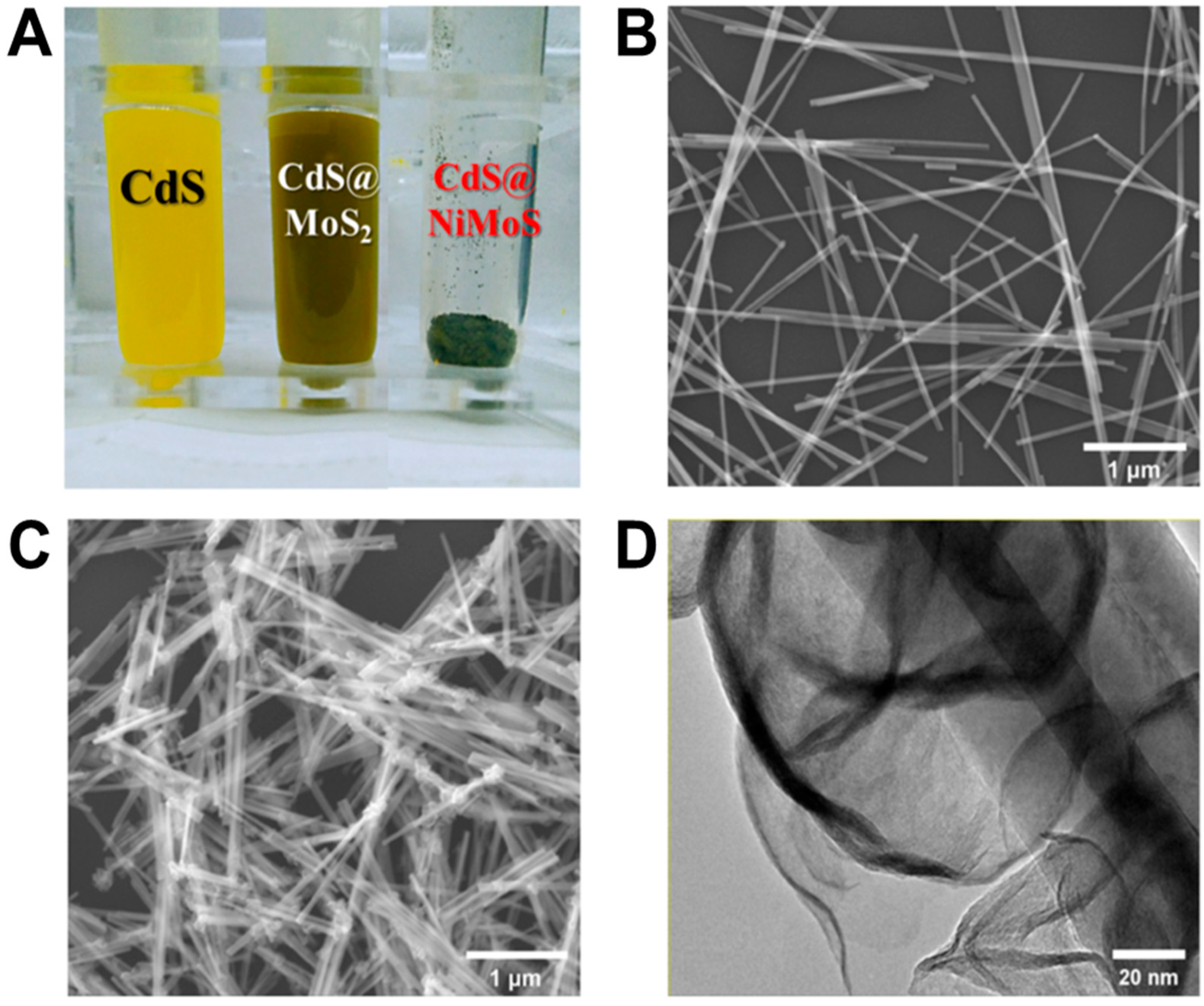
2.2. CdS@NiMoS Nanorods Synthesis
2.3. Fabrication of PEC-Aptasensor
2.4. Preparation of Nanofilm
2.5. PEC Detection
3. Results
3.1. Sensing Mechanism
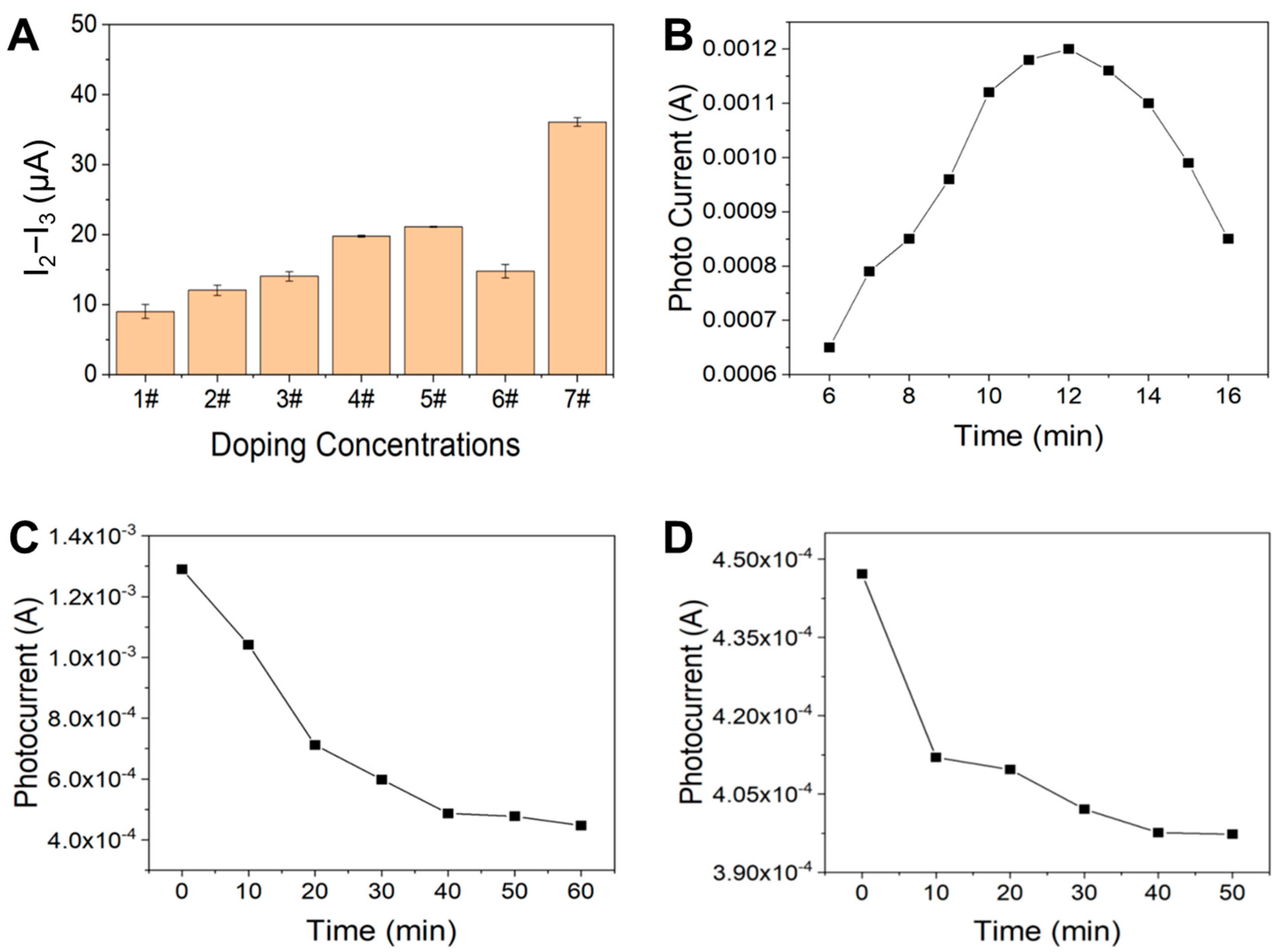
3.2. Optimization of Experimental Conditions
3.3. Characterization of CdS@NiMoS Nanorods on ITO Glass
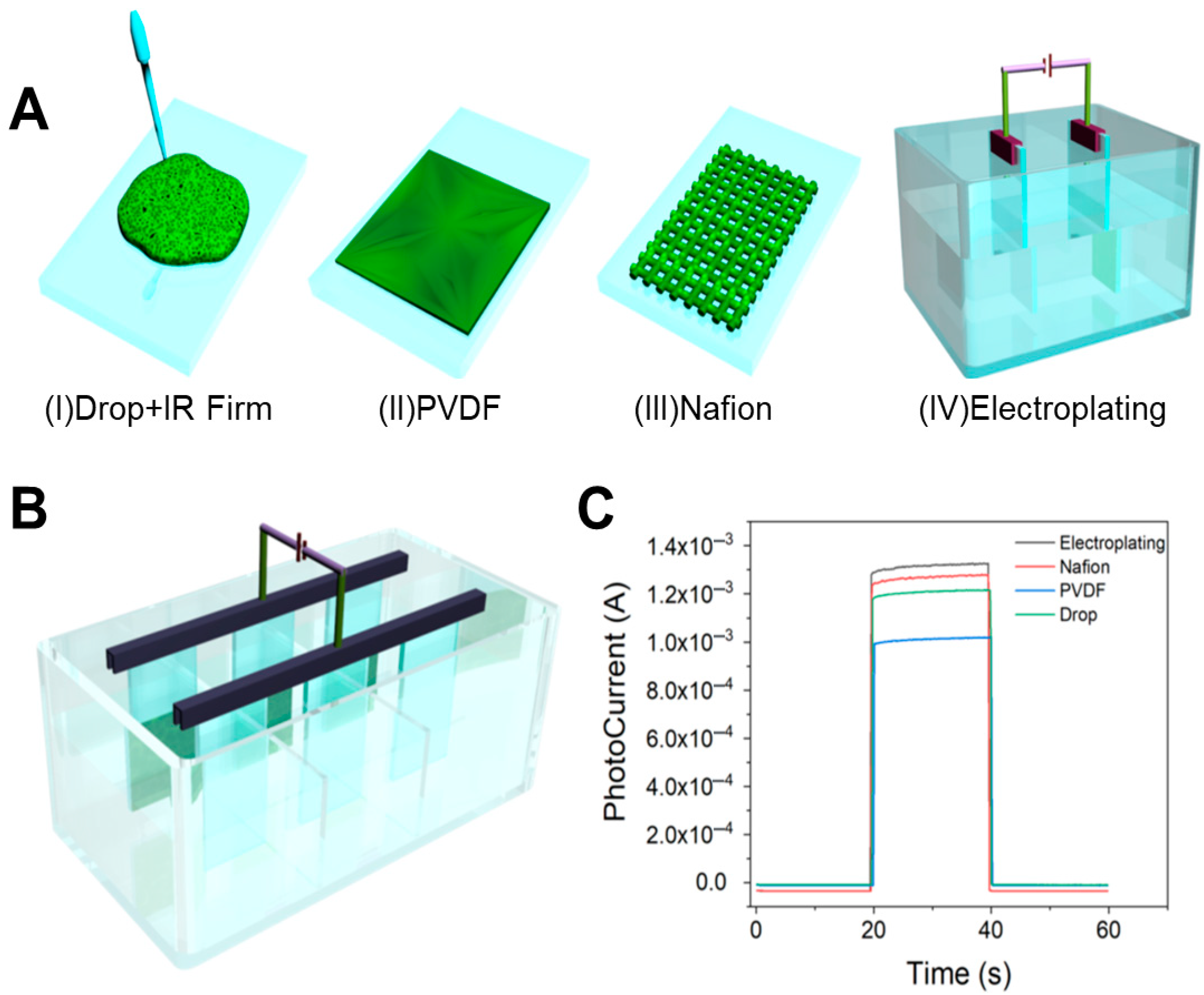
3.4. Exploring Film Formation
3.5. Detection Feasibility Assay
3.6. Detection Performances
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hanekamp, J.C.; Bast, A. Antibiotics Exposure and Health Risks: Chloramphenicol. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 39, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, S.; Kehrenberg, C.; Doublet, B.; Cloeckaert, A. Molecular Basis of Bacterial Resistance to Chloramphenicol and Florfenicol. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 28, 519–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feder, H.M.; Osier, C.; Maderazo, E.G. Chloramphenicol: A Review of Its Use in Clinical Practice. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1981, 3, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, P.; Bansode, F.W.; Singh, R.K. Chloramphenicol Toxicity: A Review. J. Med. Med. Sci. 2011, 2, 1313–1316. [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi, H.; Sakai, T.; Teshima, R.; Nemoto, S.; Akiyama, H. Total Determination of Chloramphenicol Residues in Foods by Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Food Chem. 2017, 230, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain (CONTAM). Scientific Opinion on Chloramphenicol in Food and Feed. EFSA J. 2014, 12, 3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.; Wushouer, H.; Huang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, L.; Yang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Zheng, B.; Guan, X.; Shi, L. The Changes of Different Restriction Level Adjustments on Antibiotic Use in China. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2024, 63, 107073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danner, M.-C.; Robertson, A.; Behrends, V.; Reiss, J. Antibiotic Pollution in Surface Fresh Waters: Occurrence and Effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 664, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.C. Occurrence, Sources, and Fate of Pharmaceuticals in Aquatic Environment and Soil. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 187, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Mhungu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Luo, X.; Pan, X.; Huang, J.; Zhong, X.; et al. Probabilistic Risk Assessment of Dietary Exposure to Chloramphenicol in Guangzhou, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alosaimi, E.H. Recent Developments in Colorimetric and Fluorimetric Chemosensors for the Detection of Mn2+ Ions: A Review (2010–2024). Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2025, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, B.; Yu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Guo, M.; Zhu, D.; Dai, J.; Zheng, M. Point-of-Care Testing for Streptomycin Based on Aptamer Recognizing and Digital Image Colorimetry by Smartphone. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.-M.; Jeong, E.; Jeon, W.; Cho, M.; Ban, C. Aptasensor for Ampicillin Using Gold Nanoparticle Based Dual Fluorescence-Colorimetric Methods. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 2153–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Cheng, M.; Liu, G.; Lu, H.; Gao, Y.; Yan, X.; Liu, F.; Sun, P.; Lu, G. A Fluorescent Biosensor Based on Molybdenum Disulfide Nanosheets and Protein Aptamer for Sensitive Detection of Carcinoembryonic Antigen. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 273, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.-J. State-of-the-Art Strategies of Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensors in Clinical Analysis: A Comprehensive Review. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 520, 216149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafi, S.A.; Emon, W.; Rafsan, A.A.; Mahmud, R.R.; Nayan, M.F.; Eid, M.M.A.; Rashed, A.N.Z. Optical Based Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensor for the Detection of the Various Kind of Cancerous Cell. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2025, 83, 689–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Gupta, R.; Bansal, D.; Bhateria, R.; Sharma, M. A Review on Recent Trends and Future Developments in Electrochemical Sensing. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 7336–7356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaani, M.; Azimzadeh, M.; Büyüktaş, D.; Carullo, D.; Farris, S. Electrochemical Sensors in the Food Sector: A Review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 24170–24190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, X.; Yue, L.; Tian, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Song, E. Sensitive and On-Site Detection of Staphylococcus Aureus Based on CRISPR/Cas 13a-Assisted Chemiluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 9270–9277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giagu, G.; Fracassa, A.; Fiorani, A.; Villani, E.; Paolucci, F.; Valenti, G.; Zanut, A. From Theory to Practice: Understanding the Challenges in the Implementation of Electrogenerated Chemiluminescence for Analytical Applications. Mikrochim. Acta 2024, 191, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Hou, X.; Gao, X.; Peng, Y.; Li, Q.; Niu, Q.; Liu, Q. Recent Trends in Self-Powered Photoelectrochemical Sensors: From the Perspective of Signal Output. ACS Sens. 2024, 9, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Jing, X.; Yu, L.; Bai, B.; Bo, T.; Zhang, J.; Qian, H.; Gu, Y. Self-Powered Molecularly Imprinted Photoelectrochemical Sensor Based on Ppy/QD/HOF Heterojunction for the Detection of Bisphenol A. Food Chem. 2024, 443, 138499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Cui, J.; Yang, J.; Khan, M.U.; Yang, L.; Li, S.; Li, M.; Liu, S.; Kong, L.; Chen, Z. A Novel Aptamer-Based Photoelectrochemical Sensor for Zearalenone Detection: Integration of g-C3N4/BiOBr with in Situ Growth Ag2S Quantum Dots. Bioelectrochemistry 2025, 162, 108853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ju, P.; Liu, W.; Chi, J.; Jiang, T.; Chi, Z.; Wang, S.; Qiu, R.; Sun, C. A Novel Photoelectrochemical Self-Screening Aptamer Biosensor Based on CAU-17-Derived Bi2WO6/Bi2S3 for Rapid Detection of Quorum Sensing Signal Molecules. Anal. Chim. Acta 2024, 1304, 342558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gu, W.; Zhu, C.; Hu, L. Recent Advances in Photoelectrochemical Sensing for Food Safety. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 8855–8867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Kumar, P.; Ghotra, H.S. A Review on Advances in Photoelectrochemical (PEC-Type) Photodetectors: A Trending Thrust Research Area. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 49, 1095–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domsicova, M.; Korcekova, J.; Poturnayova, A.; Breier, A. New Insights into Aptamers: An Alternative to Antibodies in the Detection of Molecular Biomarkers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Xu, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, J.; Chen, L.; Gu, Y.; Yang, G.; Qu, L.-L. Signal-off Based Dual-Mode Sensing Platform for Ultrasensitive Detection of Antibiotics in Food Samples. Talanta 2025, 284, 127248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, L.; Gong, F.; Ma, Z.; Li, K.; Ma, L.; Chen, W. Self-Powered Photoelectrochemical Aptasensor with a TiO2/CdTe/PEDOT-Sensitized Photoanode and a RGO-Enhanced Sensing Cathode for Thrombin Detection. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2025, 8, 8855–8864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zou, K.; Chen, Q.; Wei, J.; Jiao, T.; Chen, M.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Chen, X. A Dual-Signal-Amplified Photoelectrochemical Aptasensor for Dual Detection of β-Lactoglobulin and Ara H1 Allergens. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 513, 162540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yan, K.; Okoth, O.K.; Zhang, J. A Label-Free Photoelectrochemical Aptasensor Based on Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots for Chloramphenicol Determination. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 1016–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Wang, Q.; Geng, L.; Shu, X.; Wang, Y. A “Signal-on” Photoelectrochemical Aptasensor Based on Graphene Quantum Dots-Sensitized TiO2 Nanotube Arrays for Sensitive Detection of Chloramphenicol. Talanta 2019, 197, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Wei, H.; Tian, J.; Lu, J. An Aptasensor for Chloramphenicol Determination Based on Dual Signal Output of Photoelectrochemistry and Colorimetry. Talanta 2024, 277, 126430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Wei, Z.; Liu, J.; Guo, W.; Zhu, Y.; Chi, J.; Jiang, Z.; Shangguan, W. One-Pot Synthesized Visible-Light-Responsive MoS2@CdS Nanosheets-on- Nanospheres for Hydrogen Evolution from the Antibiotic Wastewater: Waste to Energy Insight. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 21577–21587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, X.; Yan, H.; Wu, G.; Ma, G.; Wen, F.; Wang, L.; Li, C. Enhancement of Photocatalytic H2 Evolution on CdS by Loading MoS2 as Cocatalyst under Visible Light Irradiation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 7176–7177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.A.; Khan, I.; Yuan, A. MoS2 as a Co-Catalyst for Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production: A Mini Review. Molecules 2022, 27, 3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Ahn, Y.-H. Synthesis and Application of CdS Nanorods for LED-Based Photocatalytic Degradation of Tetracycline Antibiotic. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Ling, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Huang, S. New Insights into the Efficient Charge Transfer by Construction of Adjustable Dominant Facet of BiOI/CdS Heterojunction for Antibiotics Degradation and Chromium Cr(VI) Reduction under Visible-Light Irradiation. Chemosphere 2022, 302, 134862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaizoğullar, A.İ. Ternary CdS/MoS2/ZnO Photocatalyst: Synthesis, Characterization and Degradation of Ofloxacin Under Visible Light Irradiation. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 2020, 30, 4129–4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Lai, Y.; Zhang, N.; Bai, J.; Xian, Y.; Jin, L. Photoelectrochemical Immunosensor Array Based on Thioglycolic Acid Capped CdS Quantum Dots for Multiplexed Detection of Veterinary Drug Residues. Chin. J. Chem. 2012, 30, 1168–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Gao, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, H. Selection and Identification of Chloramphenicol-Specific DNA Aptamers by Mag-SELEX. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2016, 180, 1644–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Yu, L.; Gao, X.; Huang, Y.; Sun, X.; Pak, Y.L.; Guo, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.; et al. A Portable Photoelectrochemical Aptasensor Based on Voltage-Resolved Dual-Signal Output for the Determination of Chloramphenicol. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 490, 137748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, J.; Yu, S.; Yang, X.; Luo, X.; He, Y. Ultrasensitive Detection Strategy for CAP by Molecularity Imprinted SERS Sensor Based on Multiple Synergistic Enhancement of SiO2@AuAg with MOFs@Au Signal Carrier. Food Chem. 2024, 445, 138717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.; Luo, M.; Zhu, G.; Mokeira, K.D.; Yang, Y.; Lv, Y.; Tan, Q.; Lei, X.; Zeng, H.; Cheng, H.; et al. A Facile Electrochemical Aptasensor for Chloramphenicol Detection Based on Synergistically Photosensitization Enhanced by SYBR Green I and MoS2. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2024, 672, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Han, Q.; Wang, X.; Song, C.; Wang, S.; Zhao, S. Occurrence, Distribution and Risk Assessment of Antibiotics at Various Aquaculture Stages in Typical Aquaculture Areas Surrounding the Yellow Sea. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 126, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, A.; Ni, X.; Cao, Y.; Cao, G. Colorimetric Chemosensor for Chloramphenicol Based on Colloidal Magnetically Assembled Molecularly Imprinted Photonic Crystals. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2017, 64, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, H.; Sun, Y.; Qi, T.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Liang, L. Ultra-Sensitive Detection of Chloramphenicol by CdS@NiMoS Nanorods-Based Photoelectrochemical Aptasensor. Biosensors 2025, 15, 454. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15070454
Sun H, Sun Y, Qi T, Wang Z, Zhao J, Liang L. Ultra-Sensitive Detection of Chloramphenicol by CdS@NiMoS Nanorods-Based Photoelectrochemical Aptasensor. Biosensors. 2025; 15(7):454. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15070454
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Hebin, Yimeng Sun, Tong Qi, Zhenyu Wang, Jianlong Zhao, and Lijuan Liang. 2025. "Ultra-Sensitive Detection of Chloramphenicol by CdS@NiMoS Nanorods-Based Photoelectrochemical Aptasensor" Biosensors 15, no. 7: 454. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15070454
APA StyleSun, H., Sun, Y., Qi, T., Wang, Z., Zhao, J., & Liang, L. (2025). Ultra-Sensitive Detection of Chloramphenicol by CdS@NiMoS Nanorods-Based Photoelectrochemical Aptasensor. Biosensors, 15(7), 454. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15070454



