A First Case of Fluorescence Polarization Biosensor-Based Assay for Rapid Monitoring of Protein API Content in Tablet Dosage Forms: Detection of Lysozyme in Tablets
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Method | Recognition Reagent | LOD | LOQ | Detection Range | Matrix | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turbidimetric | Micrococcus lysodeikticus | 1.94 µg/mL | 3.86 µg/mL | Buffer | [17] | |
| Turbidimetric | Micrococcus lysodeikticus | Nd * | Nd | 2.3–23.8 units/mL | Cell culture systems | [16] |
| Fluorescence technique | Micrococcus lysodeikticus labeled with fluorescein | Nd | Nd | 0.47–5.28 units/mL | ||
| ELISA | Purified rabbit polyclonal anti-chicken lysozyme antibody | 0.264 µg/mL | 0.38–4.8 µg/mL | Hen egg-white | [18] | |
| Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensors modified with gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) | lysozyme-imprinted (Lyz-AuNP-MIP) | 0.008 μg/mL | 0.026 μg/mL | Nd | Artificial plasma, artificial urine, and artificial tears | [19] |
| Electrochemical aptasensor | Aptamer/amino-rGO/ionic liquid/amino-mesosilica nanoparticles | 2.1 × 10−3 pM | 10−2–2 × 105 pM | Egg white, serum, tears, wine | [21] | |
| Reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography | Reversed-phase polymeric column (PLRP-S 250 4.6 mm, 300 Å pore size, 5 μm particle size) | 2.07 μg/g | 4.13 μg/g | 3.3–16.7 μg/g | Cheese | [22] |
| Fluorometric | Chitin azure | Nd | Nd | Nd | Blood sample | [9] |
| Colorimetric assay | β-D-galactosyl chitotetraose derivative [Gal(GlcN)3D] | 2–31 μg | Buffer solution | [30] | ||
| FPA | Fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled peptidoglycan | Nd | Nd | Nd | Rheumatoid synovial fluids | [31] |
| FPA | Fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled chitooligosaccharide | tears | [32] |
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Fluorescence Polarization Assay
2.3. Calibration Curve Construction
2.4. Assessment of Method Statistical Characteristics
2.5. Sample Analysis
2.6. Validation of the Method
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. FPA-Based Lysozyme Assay
3.2. Optimization of the Method for the Quantitative Determination of Lysozyme in Tablets
3.3. Results of Quantitative Determination of Lysozyme Content in Tablet Forms
3.4. Validation of the Method
3.5. Sample Analysis with the Abbott TDx Analyzer
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FPA | fluorescence polarization assay |
| ELISA | enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| API | active pharmaceutical ingredient |
| RSD | relative standard deviation |
| LOD | limit of detection |
References
- Ogihara, T.; Mizoi, K.; Ishii-Watabe, A. Pharmacokinetics of Biopharmaceuticals: Their Critical Role in Molecular Design. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, M.; Garcia-Sanz, J.A. Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies against Cancer: Present and Future. Cells 2023, 12, 2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, G. Proteins: Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 1st ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-0-470-66986-0. [Google Scholar]
- Thelwell, C.; Longstaff, C.; Rigsby, P. An International Collaborative Study to Establish the World Health Organization 4th International Standard for Plasmin (13/206): Communication from the SSC of the ISTH. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 14, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locke, M.; Longstaff, C.; Rigsby, P. An International Collaborative Study to Establish the WHO 3rd International Standard for Thrombin: Communication from the ISTH SSC Subcommittee on Factor XIII and Fibrinogen. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 19, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glamočlija, U.; Mehić, M.; Šukalo, A.; Tanović Avdić, A.; Džananović Jaganjac, J. Lysozyme in the Treatment of Non-Infectious Sore Throat. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2020, 20, 281–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergamo, A.; Sava, G. Lysozyme: A Natural Product with Multiple and Useful Antiviral Properties. Molecules 2024, 29, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golac-Guzina, N.; Novaković, Z.; Sarajlić, Z.; Šukalo, A.; Džananović, J.; Glamočlija, U.; Kapo, B.; Čordalija, V.; Mehić, M. Comparative Study of the Efficacy of the Lysozyme, Benzydamine and Chlorhexidine Oral Spray in the Treatment of Acute Tonsillopharyngitis—Results of a Pilot Study. Acta Medica Acad. 2019, 48, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisarzhevsky, S.A.; Globa, A.G.; Shirshov, O.N.; Marchuk, A.I.; Svetukhin, A.M.; Karelin, A.A. Method for Determining Lysozyme Activity in Blood Serum Using Chitinazur as a Substrate. Issues Med. Chem. 1977, 43, 185–190. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Wu, L.; Eckert, T.; Burg-Roderfeld, M.; Rojas-Macias, M.A.; Lütteke, T.; Krylov, V.B.; Argunov, D.A.; Datta, A.; Markart, P.; et al. Lysozyme’s Lectin-like Characteristics Facilitates Its Immune Defense Function. Q. Rev. Biophys. 2017, 50, e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, R.K.; Gazova, Z.; Bednarikova, Z.; Mroue, K.H.; Ghosh, A.; Zhang, R.; Ulicna, K.; Siebert, H.-C.; Nifantiev, N.E.; Bhunia, A. Evidence for Inhibition of Lysozyme Amyloid Fibrillization by Peptide Fragments from Human Lysozyme: A Combined Spectroscopy, Microscopy, and Docking Study. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 1998–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraboschi, P.; Ciceri, S.; Grisenti, P. Applications of Lysozyme, an Innate Immune Defense Factor, as an Alternative Antibiotic. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gojković, Z.; Rožić, J.; Gašpar, N.; Šukalo, A.; Mehić, M.; Tanović Avdić, A.; Glamočlija, U. Lysozyme-Based Spray for Treatment of Radiotherapy-Induced Oral Mucositis. Explor. Drug Sci. 2025, 3, 100886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezin, I.V.; Klesov, A.A.; Rabinovich, M.L. Kinetics of Enzymatic Reactions in Heterogeneous Systems. I. The Kinetic Regularities for the Bacterial Cell Micrococcus lysodeikticus. Bioorganicheskaya Khimiya 1976, 2, 680–688. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.-L.; Huang, G.-X. Resonance Scattering Spectra of Micrococcus lysodeikticus and Its Application to Assay of Lysozyme Activity. Clin. Chim. Acta 2007, 376, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helal, R.; Melzig, M.F. Determination of Lysozyme Activity by a Fluorescence Technique in Comparison with the Classical Turbidity Assay. Pharmazie 2008, 63, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.-H.; Brown, M.B.; Martin, G.P. Turbidimetric and HPLC Assays for the Determination of Formulated Lysozyme Activity. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2001, 53, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, M.-L.; Gautron, J.; Nys, Y. Development of an ELISA for Quantifying Lysozyme in Hen Egg White. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 2379–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriş, Ş.; Çimen, D.; Denizli, A. Lysozyme-Imprinted Surface Plasmon Resonance Chips Decorated with Gold Nanoparticles for Lysozyme Detection. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 28055–28064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishi, M.; Mousavinia, S.M.; Soleimany, R.; Heidari, M.M.; Mohammadi, M.; Rastmanesh, S.; Mobed, A. Innovative Nanosensing Methods for Lysozyme Identification. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2025, 192, 110745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamei, H.R.; Rezaei, B.; Ensafi, A.A. An Ultrasensitive Electrochemical Anti-Lysozyme Aptasensor with Biorecognition Surface Based on Aptamer/Amino-rGO/Ionic Liquid/Amino-Mesosilica Nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 181, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerkaert, B.; Mestdagh, F.; De Meulenaer, B. Detection of Hen’s Egg White Lysozyme in Food: Comparison between a Sensitive HPLC and a Commercial ELISA Method. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raines, R.T. Fluorescence Polarization Assay to Quantify Protein-Protein Interactions: An Update. In Protein-Protein Interactions; Meyerkord, C.L., Fu, H., Eds.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 1278, pp. 323–327. ISBN 978-1-4939-2424-0. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, Q. Antibody- and Aptamer-Based Competitive Fluorescence Polarization/Anisotropy Assays for Ochratoxin A with Tetramethylrhodamine-Labeled Ochratoxin A. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 1612–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schade, S.Z.; Jolley, M.E.; Sarauer, B.J.; Simonson, L.G. BODIPY–α-Casein, a pH-Independent Protein Substrate for Protease Assays Using Fluorescence Polarization. Anal. Biochem. 1996, 243, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolley, M.E. Fluorescence Polarization Assays for the Detection of Proteases and Their Inhibitors. SLAS Discov. 1996, 1, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, N.G.; Jameson, D.M. Steady-State Fluorescence Polarization/Anisotropy for the Study of Protein Interactions. In Fluorescence Spectroscopy and Microscopy; Methods in Molecular Biology; Engelborghs, Y., Visser, A.J.W.G., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2014; Volume 1076, pp. 29–42. ISBN 978-1-62703-648-1. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda, H. A New Lysozyme Assay Based on Fluorescence Polarization or Fluorescence Intensity Utilizing a Fluorescent Peptidoglycan Substrate 1. J. Biochem. 1980, 88, 1185–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, S.; De Ruyck, K.; Beloglazova, N.V.; Eremin, S.A.; De Saeger, S.; Zhang, S.; Shen, J.; Wang, Z. Fluorescence Polarization Assays for Chemical Contaminants in Food and Environmental Analyses. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 114, 293–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, M.; Matsui, M.; Kono, H.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Kato, Y.; Usui, T. A Novel Analytical Procedure for Assaying Lysozyme Activity Using an End-Blocked Chitotetraose Derivative as Substrate. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 538, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, T.; Ueda, K.; Maeda, H.; Kambara, T. Determination of Lysozyme Activity by Fluorescence Polarization in Rheumatoid Synovial Fluids and Release of Lysozyme from Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes by Chemotactic Factors. J. Immunol. Methods 1987, 103, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhametova, L.I.; Zherdev, D.O.; Kuznetsov, A.N.; Yudina, O.N.; Tsvetkov, Y.E.; Eremin, S.A.; Krylov, V.B.; Nifantiev, N.E. Fluorescence-Polarization-Based Assaying of Lysozyme with Chitooligosaccharide Tracers. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhametova, L.I.; Zherdev, D.O.; Eremin, S.A.; Levashov, P.A.; Siebert, H.-C.; Tsvetkov, Y.E.; Yudina, O.N.; Krylov, V.B.; Nifantiev, N.E. Application of the Chitooligosaccharides and Fluorescence Polarization Technique for the Assay of Active Lysozyme in Hen Egg White. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.S.; Eremin, S.A. Fluorescence Polarization Immunoassays and Related Methods for Simple, High-Throughput Screening of Small Molecules. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 391, 1499–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eremin, S.A.; Mukhametova, L.I.; Krylov, V.B.; Nifantiev, N.E. Fluorescence Polarization Assay for Infection Diagnostics: A Review. Molecules 2024, 29, 4712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkov, T.M.; Tsvetkov, Y.E.; Yashunsky, D.V.; Kuznetsov, A.N.; Sclyarov, O.D.; Babicheva, O.V.; Zherdev, D.O.; Mukhametova, L.I.; Eremin, S.A.; Krylov, V.B.; et al. Synthesis of Oligo-α-(1→2)-4,6-Dideoxy-4-Formamido-d-Mannopyranosides Related to the A Epitope of the Brucella O-Polysaccharide and Their Use for Assaying of Serum Immunoglobulins. Front. Chem. 2025, 13, 1662885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyamu, I.D.; Huang, R. Development of Fluorescence Polarization-Based Competition Assay for Nicotinamide N-Methyltransferase. Anal. Biochem. 2020, 604, 113833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Jadhav, P.; Wen, Y.; Tan, H.; Wang, J. Development of a Fluorescence Polarization Assay for the SARS-CoV-2 Papain-like Protease. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2025, 8, 774–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.R.; AlOthman, Z.A.; Rahman, N. Analytical Techniques in Pharmaceutical Analysis: A Review. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S1409–S1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabel, J.; Gnegel, G.; Kessler, W.; Sacré, P.-Y.; Heide, L. Verification of the Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient in Tablets Using a Low-Cost near-Infrared Spectrometer. Talanta Open 2023, 8, 100270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Bansal, V.; Madhavan, A.; Kumar, M.; Sindhu, R.; Awasthi, M.K.; Binod, P.; Saran, S. Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) Chemicals: A Critical Review of Current Biotechnological Approaches. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 4309–4327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
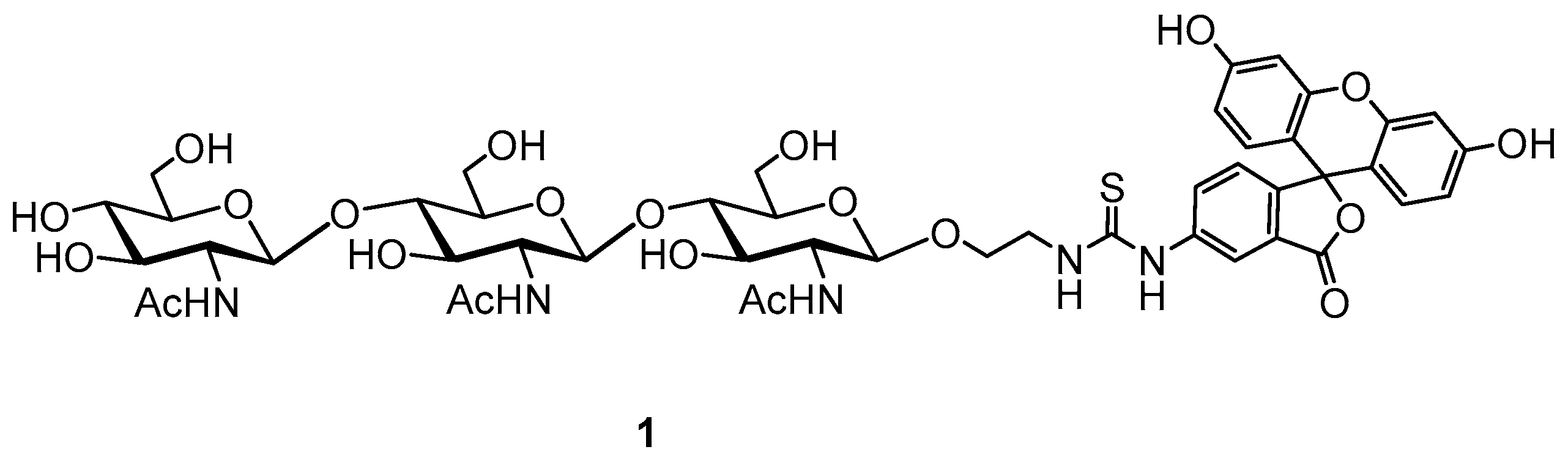
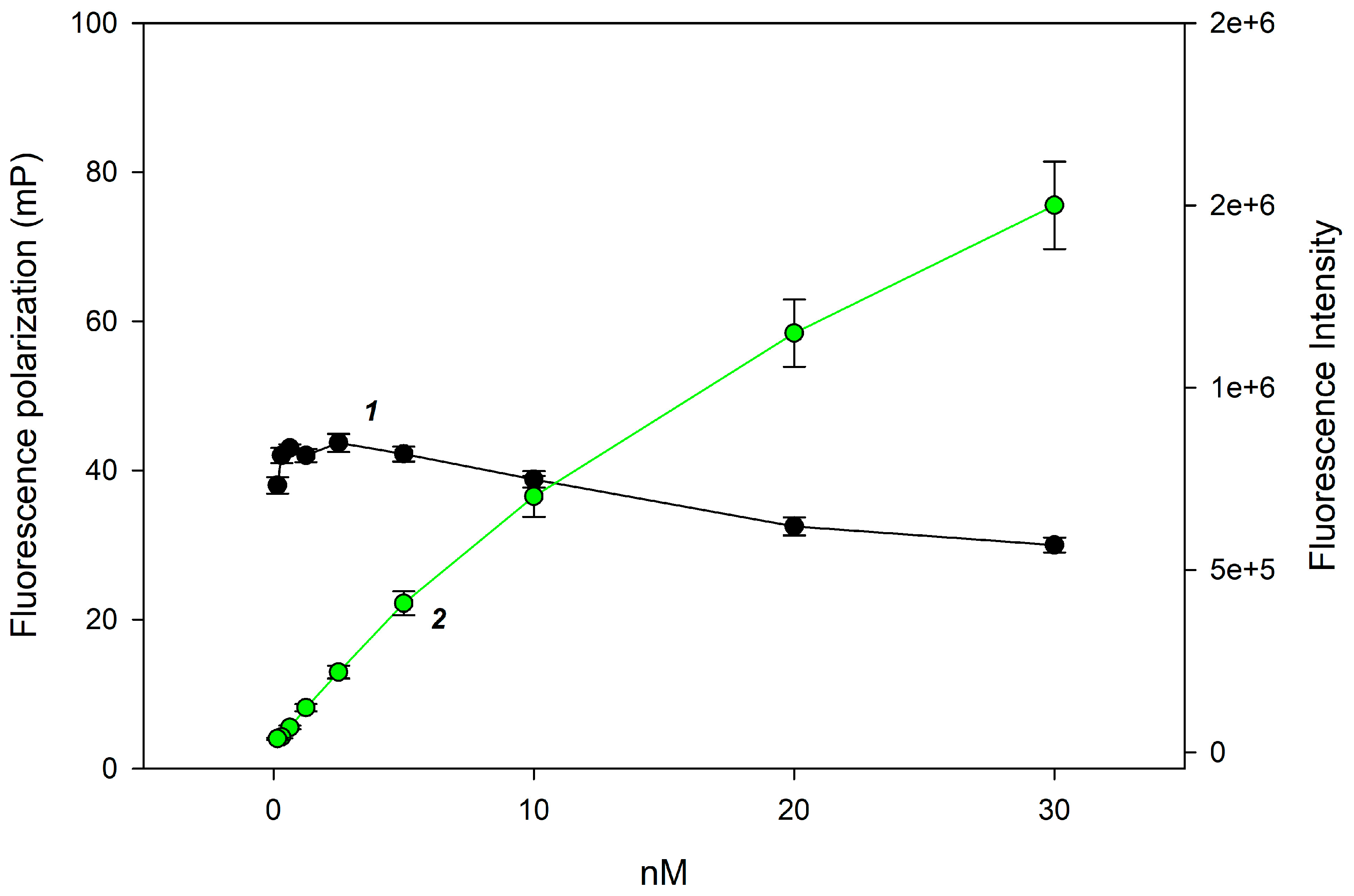
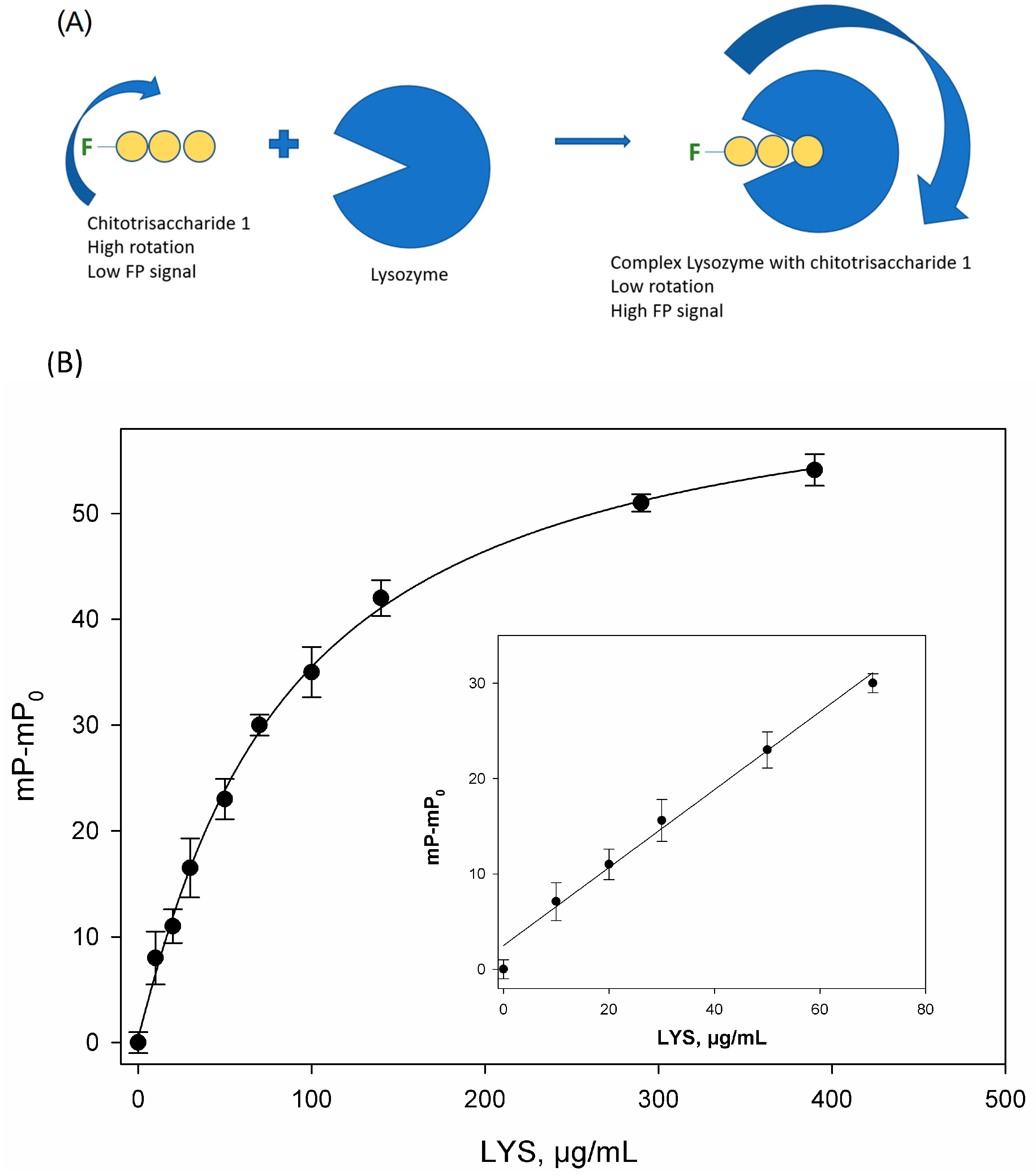
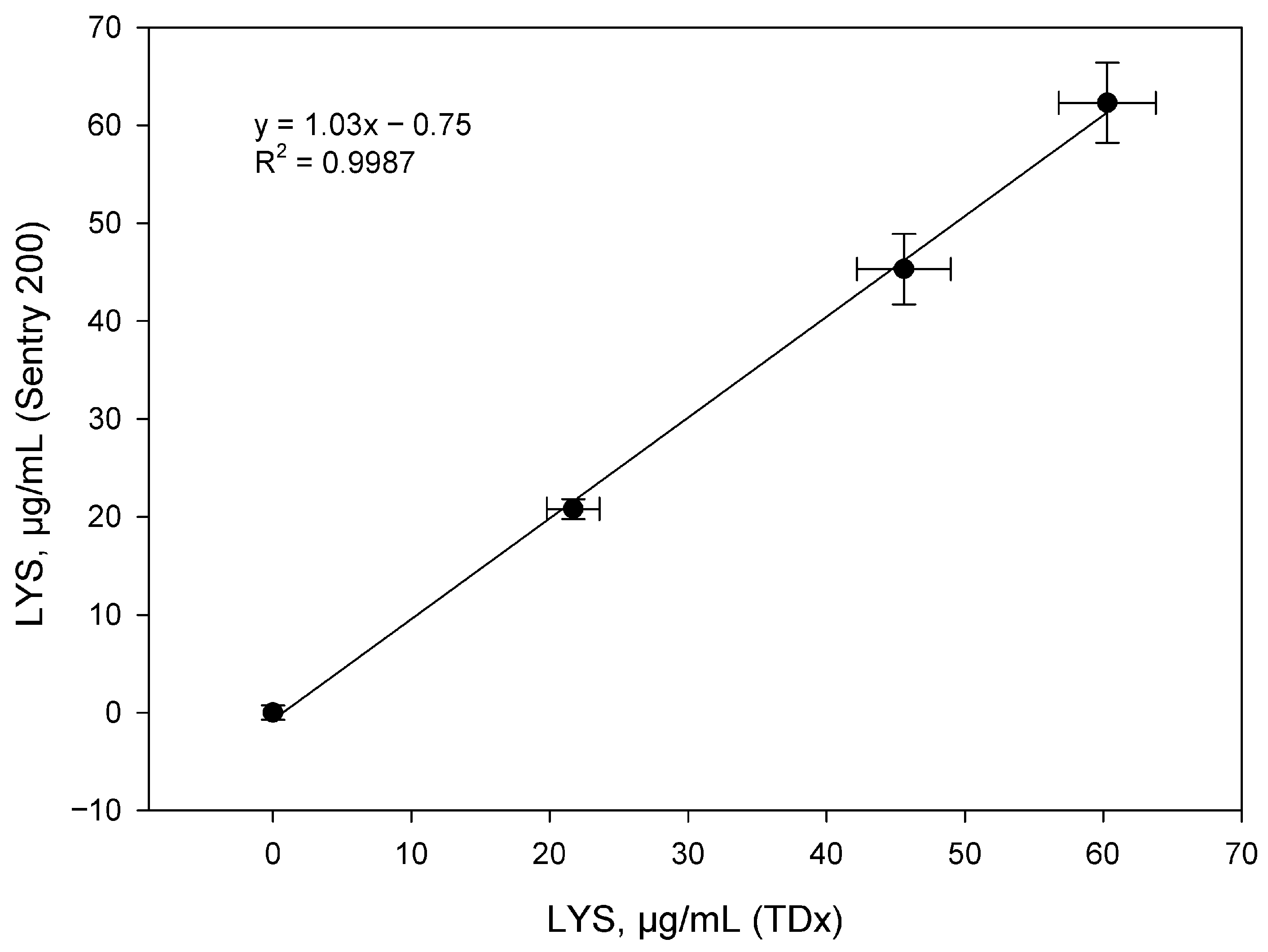
| Sample | Average Tablet Weight, mg | Lysozyme Content (mg) Per 1 Tablet | Average Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200.0 mg * | 400.0 mg * | 600.0 mg * | |||
| 1 | 201.8 | 22.3 ± 1.9 | 22.8 ± 5.4 | 20.1 ± 3.5 | 21.7 ± 3.6 |
| 2 | 200.9 | 20.6 ± 4.9 | 22.6 ± 3.6 | 20.9 ± 2.2 | 21.3 ± 3.6 |
| 3 | 197.1 | 22.4 ± 5.4 | 21.3 ± 4.5 | 21.1 ± 2.3 | 21.6 ± 4.4 |
| 4 | 200.4 | 22.8 ± 9.6 | 21.7 ± 5.8 | 25.2 ± 7.1 | 23.2 ± 5.2 |
| 5 | 200.8 | 22.9 ± 5.3 | 22.5 ± 0.2 | 22.5 ± 0.1 | 22.6 ± 1.8 |
| Added, mg | Found, mg (n = 3) | Recovery, % |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 22.8 ± 1.8 | 0 |
| 10 | 32.8 ± 2.8 | 100.2 |
| 20 | 44.0 ± 3.2 | 106.0 |
| Lysozyme Content in % of Nominal | Found, mg (n = 3) | Found, % |
|---|---|---|
| 80% | 17.7 ± 3.6 | 98.3 |
| 100% | 19.6 ± 4.1 | 98.0 |
| 120% | 22.7 ± 2.7 | 100.1 |
| Sample Weight, mg | RSD, % |
|---|---|
| 200.0 | 10.8 |
| 400.0 | 8.9 |
| 600.0 | 13.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Filimonova, S.M.; Balyklova, K.S.; Zherdev, D.O.; Eremin, S.A.; Mukhametova, L.I.; Krylov, V.B.; Nifantiev, N.E. A First Case of Fluorescence Polarization Biosensor-Based Assay for Rapid Monitoring of Protein API Content in Tablet Dosage Forms: Detection of Lysozyme in Tablets. Biosensors 2025, 15, 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15110724
Filimonova SM, Balyklova KS, Zherdev DO, Eremin SA, Mukhametova LI, Krylov VB, Nifantiev NE. A First Case of Fluorescence Polarization Biosensor-Based Assay for Rapid Monitoring of Protein API Content in Tablet Dosage Forms: Detection of Lysozyme in Tablets. Biosensors. 2025; 15(11):724. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15110724
Chicago/Turabian StyleFilimonova, Svetlana M., Ksenia S. Balyklova, Dmitry O. Zherdev, Sergei A. Eremin, Liliya I. Mukhametova, Vadim B. Krylov, and Nikolay E. Nifantiev. 2025. "A First Case of Fluorescence Polarization Biosensor-Based Assay for Rapid Monitoring of Protein API Content in Tablet Dosage Forms: Detection of Lysozyme in Tablets" Biosensors 15, no. 11: 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15110724
APA StyleFilimonova, S. M., Balyklova, K. S., Zherdev, D. O., Eremin, S. A., Mukhametova, L. I., Krylov, V. B., & Nifantiev, N. E. (2025). A First Case of Fluorescence Polarization Biosensor-Based Assay for Rapid Monitoring of Protein API Content in Tablet Dosage Forms: Detection of Lysozyme in Tablets. Biosensors, 15(11), 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15110724






