Soft-Template-Based Manufacturing of Gold Nanostructures for Energy and Sensing Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
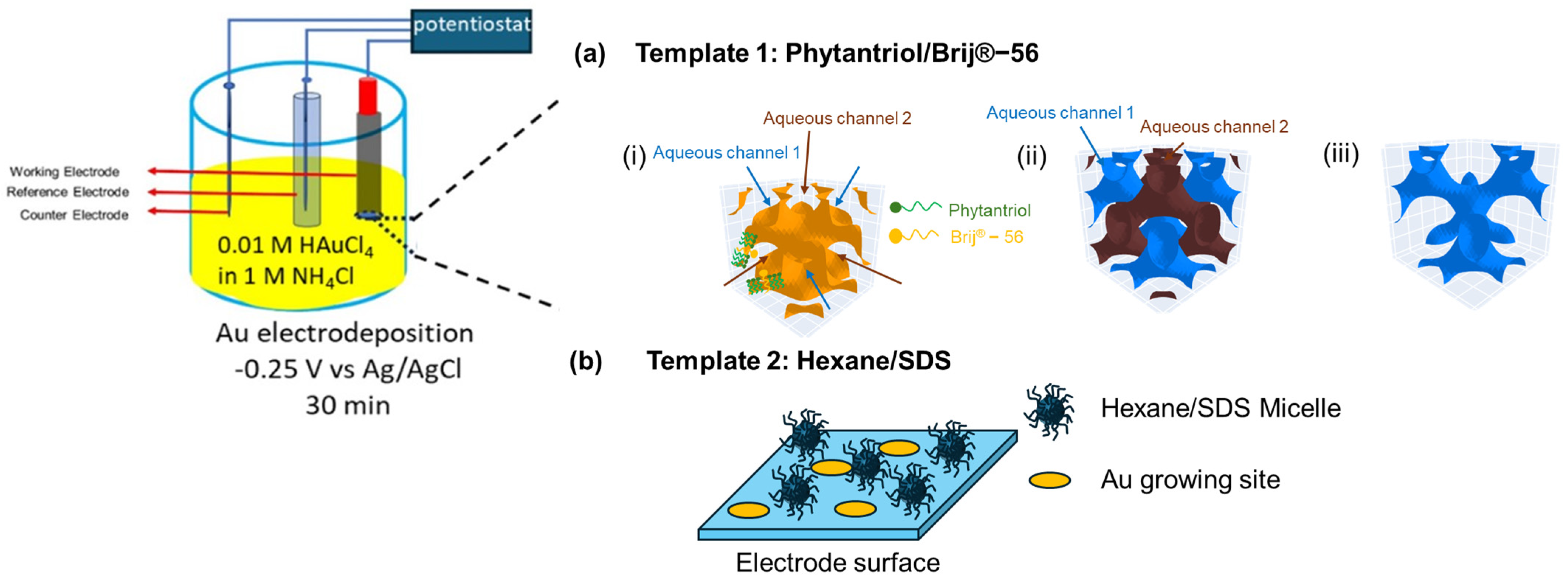
2.2. Generation of the Gold Nanostructured Electrodes
2.3. Activity towards Glucose and Fuel Cell Set-Up and Operation
3. Result and Discussion
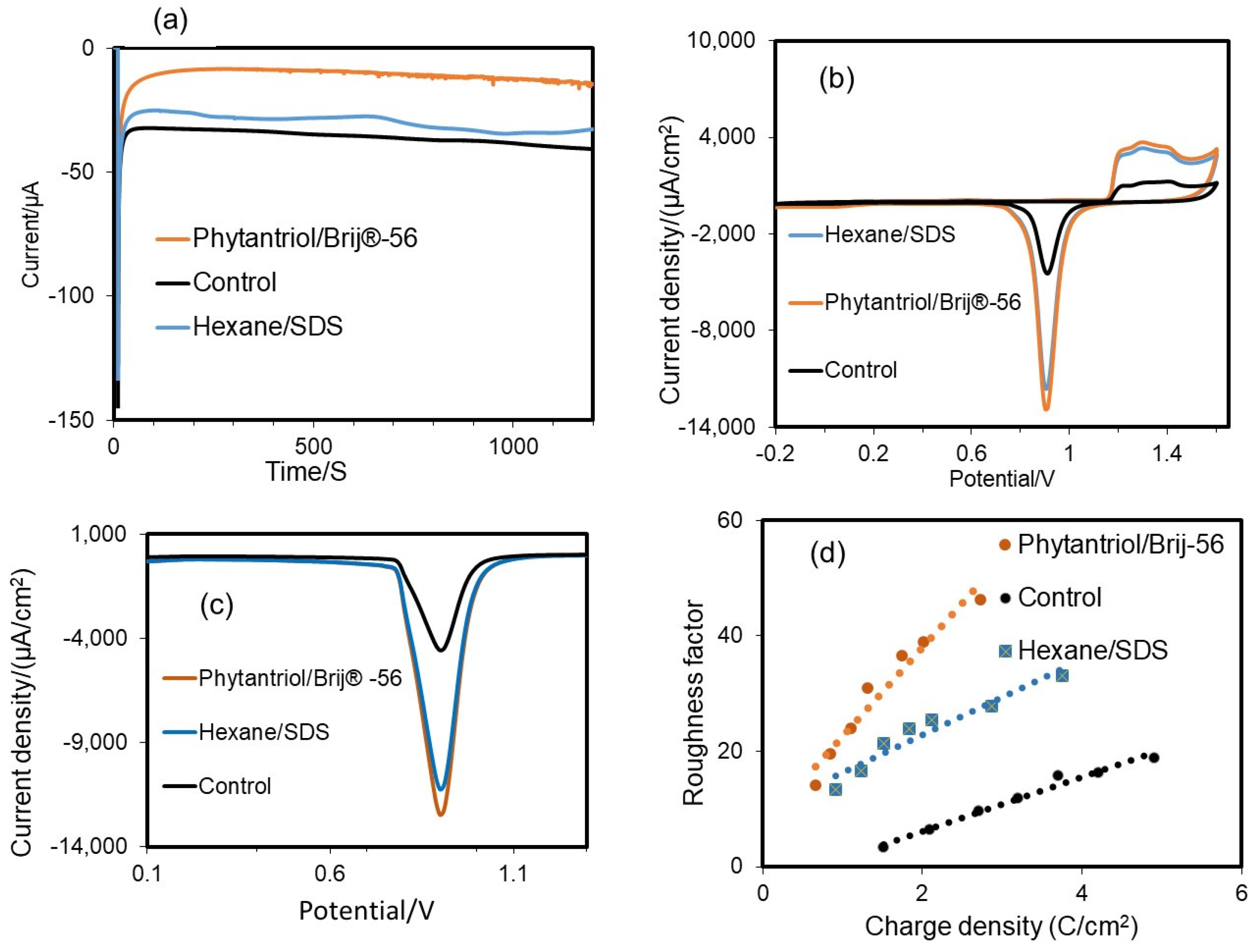
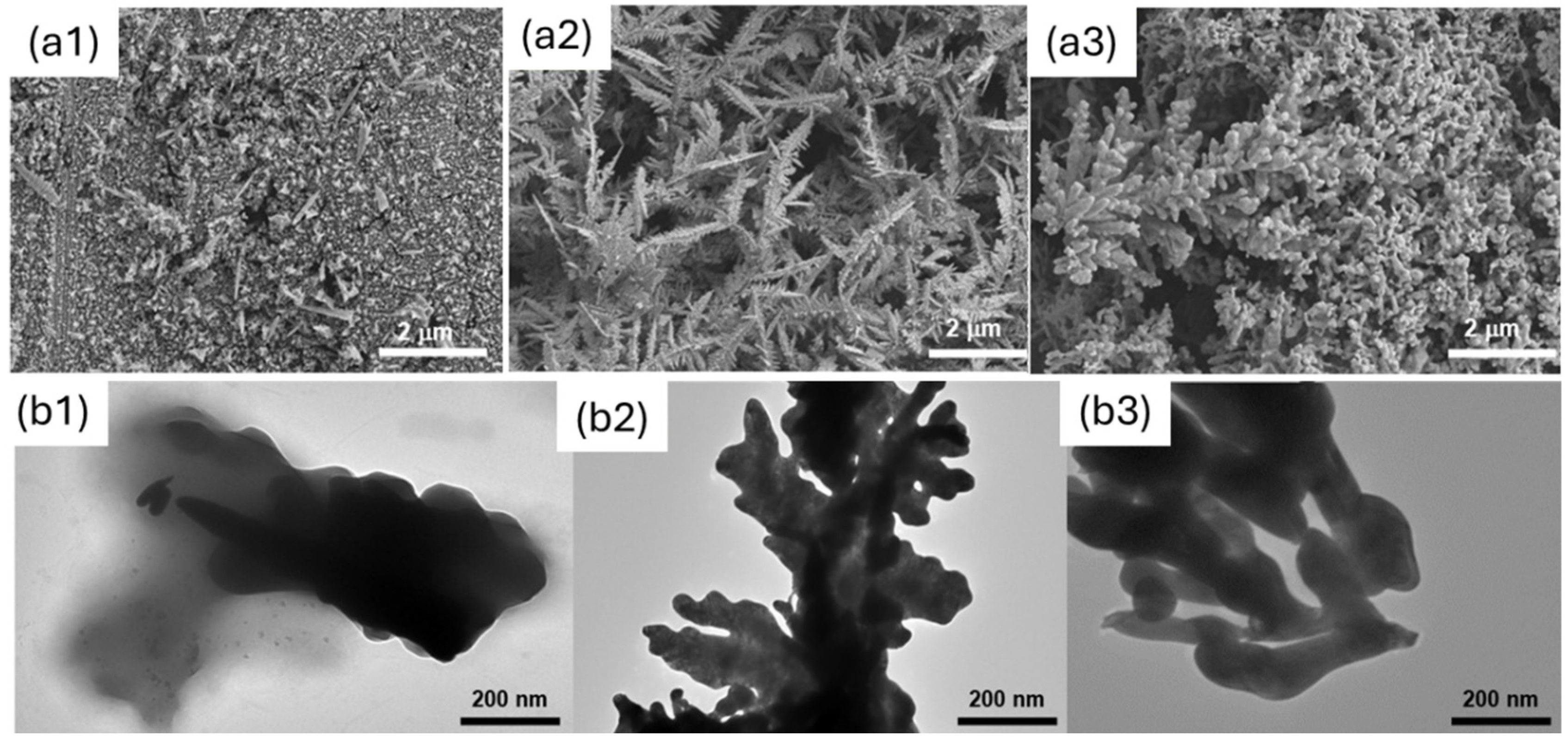
3.1. Electrode Characterisation
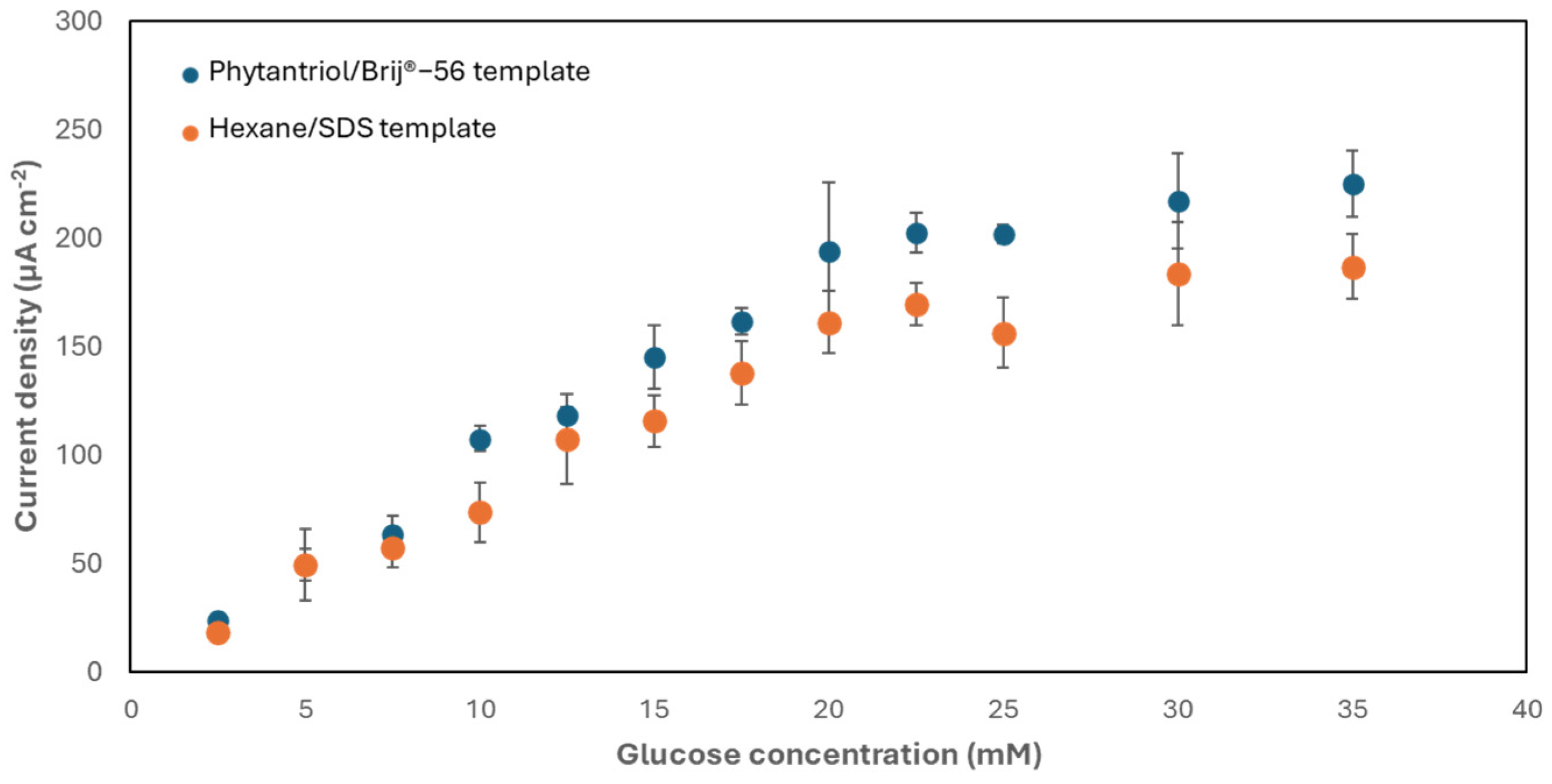
3.2. Testing the Activity of the Nanostructured Au Electrodes toward Glucose
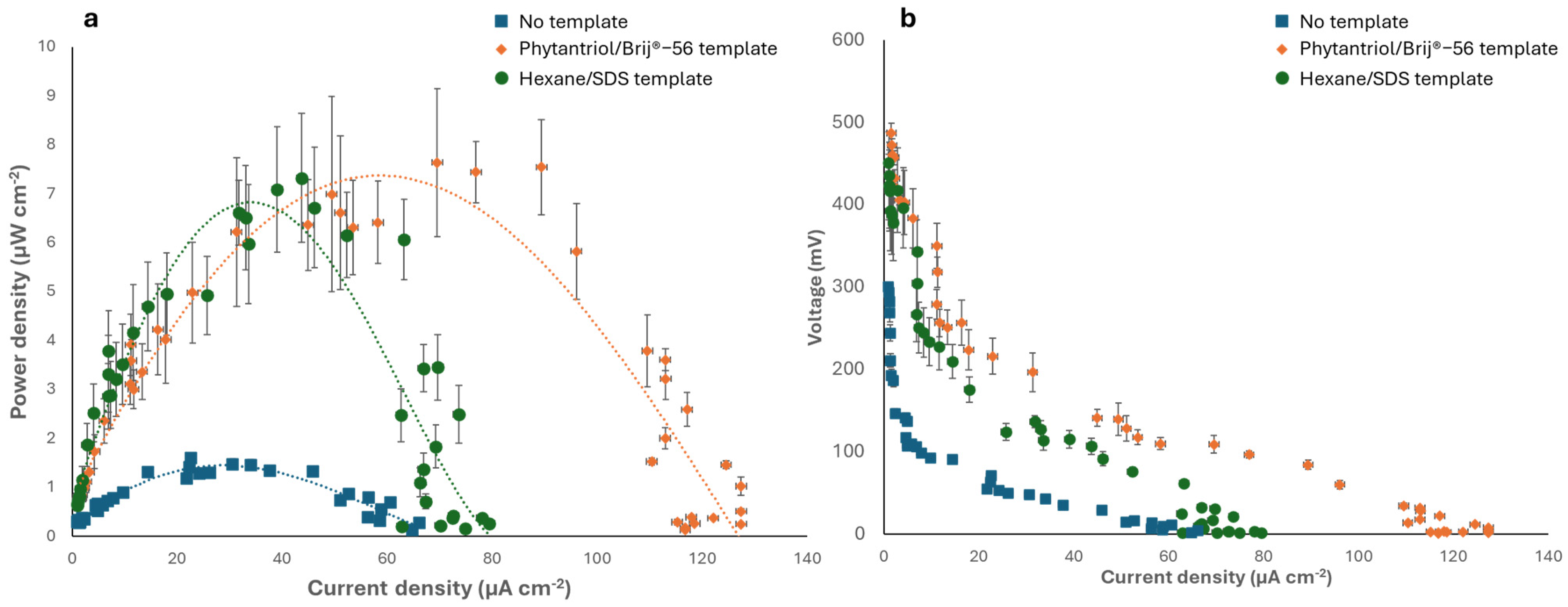
3.3. Testing the Au Nanostructured Electrodes as the Anode of an Abiotic Glucose Fuel Cell
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gonzalez-Solino, C.; Bernalte, E.; Bayona Royo, C.; Bennett, R.; Leech, D.; Di Lorenzo, M. Self-Powered Detection of Glucose by Enzymatic Glucose/Oxygen Fuel Cells on Printed Circuit Boards. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 26704–26711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antolini, E. External abiotic glucose fuel cells. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2021, 5, 5038–5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Solino, C.; Bernalte, E.; Metcalfe, B.; Moschou, D.; Di Lorenzo, M. Power generation and autonomous glucose detection with an integrated array of abiotic fuel cells on a printed circuit board. J. Power Sources 2020, 472, 228530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhiani, M.; Barzi, S.; Ahmadi, A.; Vizza, F.; Gharibi, H.; Azhari, A. Ex vivo energy harvesting by a by-pass depletion designed abiotic glucose fuel cell operated with real human blood serum. J. Power Sources 2022, 521, 230972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Akita, T.; Ishida, T.; Haruta, M.; Xu, Q. Synergistic Catalysis of Au@Ag Core—Shell Nanoparticles Stabilized. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 1304–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, E. Dendritic Au/Pt and Au/PtCu nanowires with enhanced electrocatalytic activity for methanol electrooxidation. Small 2014, 10, 3262–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henning, A.M.; Watt, J.; Miedziak, P.J.; Cheong, S.; Santonastaso, M.; Song, M.; Takeda, Y.; Kirkland, A.I.; Taylor, S.H.; Tilley, R.D. Gold–palladium core–shell nanocrystals with size and shape control optimized for catalytic performance. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 1477–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, W.; Kuang, W.; Guo, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z. Serrated Au/Pd Core/Shell Nanowires with Jagged Edges for Boosting Liquid Fuel Electrooxidation. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 2375–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Lu, D.; Su, D.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, P.; Wang, J.X.; Adzic, R.R.; et al. Surface Proton Transfer Promotes Four-Electron Oxygen Reduction on Gold Nanocrystal Surfaces in Alkaline Solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 7310–7317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohidi, M.; Mahyari, F.A.; Safavi, A. A seed-less method for synthesis of ultra-thin gold nanosheets by using a deep eutectic solvent and gum arabic and their electrocatalytic application. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 32744–32754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.-G.; Yang, S.; Qian, Q.-Y.; Xia, X.-H. Gold nanoparticles integrated in a nanotube array for electrochemical detection of glucose. Electrochem. Commun. 2009, 11, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, A.; Bilan, H.K.; Katz, E.; Smutok, O. Highly Porous Gold Electrodes—Preparation and Characterization. ChemElectroChem 2022, 9, e202200099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Slaughter, G. A tattoo-like glucose abiotic biofuel cell. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2022, 904, 115941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- du Toit, H.; Di Lorenzo, M. Electrodeposited highly porous gold microelectrodes for the direct electrocatalytic oxidation of aqueous glucose. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 192, 725–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.J.; Ryoo, R.; Liu, Z.; Terasaki, O. Template synthesis of asymmetrically mesostructured platinum networks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 1246–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, Y.; Kuroda, K. Rational design of mesoporous metals and related nanomaterials by a soft-template approach. Chem.-Asian J. 2008, 3, 664–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, C.M. Nanoporous metals: Fabrication strategies and advanced electrochemical applications in catalysis, sensing and energy systems. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7016–7031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Shantz, D.F. Ordered mesoporous silica-based inorganic nanocomposites. J. Solid State Chem. 2008, 181, 1659–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takai, A.; Doi, Y.; Yamauchi, Y.; Kuroda, K. Soft-chemical approach of noble metal nanowires templated from mesoporous silica (SBA-15) through vapor infiltration of a reducing agent. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 7586–7593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, Y.; Yamauchi, Y.; Kuroda, K. Integrated structural control of cage-type mesoporous platinum possessing both tunable large mesopores and variable surface structures by block copolymer-assisted Pt deposition in a hard-template. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 1827–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Jiang, B.; Xu, X.; Guselnikova, O.; Li, H.; Asahi, T.; Yamauchi, Y. Porous Nanoarchitectures of Nonprecious Metal Borides: From Controlled Synthesis to Heterogeneous Catalyst Applications. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 14773–14793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attard, G.S.; Corker, J.M.; Göltner, C.G.; Henke, S.; Templer, R.H. Liquid-Crystal Templates for Nanostructured Metals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1997, 36, 1315–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Iqbal, M.; Lin, J.; Luo, X.; Jiang, B.; Malgras, V.; Wu, K.C.-W.; Kim, J.; Yamauchi, Y. Electrochemical Deposition: An Advanced Approach for Templated Synthesis of Nanoporous Metal Architectures. Accounts Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 1764–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; He, C.; Xing, W.; Li, F.; Tong, L.; Chen, Z.; Liao, X.; Steinhart, M. Nanoporous metal membranes with bicontinuous morphology from recyclable block-copolymer templates. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 2068–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takai, A.; Yamauchi, Y.; Kuroda, K. Tailored electrochemical synthesis of 2d-hexagonal, lamellar, and cage-type mesostructured pt thin films with extralarge periodicity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attard, G.S.; Bartlett, P.N.; Coleman, N.R.B.; Elliott, J.M.; Owen, J.R.; Wang, J.H. Mesoporous platinum films from lyotropic liquid crystalline phases. Science 1997, 278, 838–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, S.; Elliott, J.M.; Rittman, M.; Squires, A.M. Facile production of ordered 3D platinum nanowire networks with “single diamond” bicontinuous cubic morphology. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 1160–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, S.; Boswell, J.; Waters, S.; Williams, S.; Elliott, J.M.; Squires, A.M. Control of Pore and Wire Dimensions in Mesoporous Metal Nanowire Networks through Curvature Modulation in Lipid Templates: Implications for Use as Electrodes. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 5717–5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.; Li, C.; Wood, K.; Jiang, B.; Takei, T.; Dag, Ö.; Baba, D.; Nugraha, A.S.; Asahi, T.; Whitten, A.E.; et al. Continuous Mesoporous Pd Films by Electrochemical Deposition in Nonionic Micellar Solution. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 6405–6413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Sato, T.; Sakamoto, Y.; Tominaka, S.; Miyasaka, K.; Miyamoto, N.; Nemoto, Y.; Terasaki, O.; Yamauchi, Y. Synthesis of mesoporous Pt films with tunable pore sizes from aqueous surfactant solutions. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 1591–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Dag, Ö.; Dao, T.D.; Nagao, T.; Sakamoto, Y.; Kimura, T.; Terasaki, O.; Yamauchi, Y. Electrochemical synthesis of mesoporous gold films toward mesospace-stimulated optical properties. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, D.; Kim, J.; Henzie, J.; Li, C.; Jiang, B.; Dag, Ö.; Yamauchi, Y.; Asahi, T. Electrochemical deposition of large-sized mesoporous nickel films using polymeric micelles. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 10347–10350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Jiang, B.; Chen, H.; Imura, M.; Sang, L.; Malgras, V.; Bando, Y.; Ahamad, T.; Alshehri, S.M.; Tominaka, S.; et al. Superior electrocatalytic activity of mesoporous Au film templated from diblock copolymer micelles. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 1752–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, S.; Elliott, J.M.; Squires, A.M.; Anwar, A. Optimum conditions for electrochemical deposition of 3-D mesoporous platinum framework. J. Nanopart. Res. 2020, 22, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, S.; Boswell, J.; Worsley, C.; Elliott, J.M.; Squires, A.M. Ultrathin Uniform Platinum Nanowires via a Facile Route Using an Inverse Hexagonal Surfactant Phase Template. Langmuir 2018, 34, 6991–6996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiba, S.; Hirabayashi, S.; Niwa, O.; Kato, D.; Kunitake, M.; Matsuguchi, M. Monolithic Au Nanoscale Films with Tunable Nanoporosity Prepared via Dynamic Soft Templating for Electrocatalytic Oxidation of Methanol. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 7750–7760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, R.; Chandra, P. Electrochemical Nano-Imprinting of Trimetallic Dendritic Surface for Ultrasensitive Detection of Cephalexin in Pharmaceutical Formulations. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henning, S.; Herranz, J.; Gasteiger, H.A. Bulk-Palladium and Palladium-on-Gold Electrocatalysts for the Oxidation of Hydrogen in Alkaline Electrolyte. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, F178–F189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, L.D.; Nugent, P.F. The electrochemistry of gold: I the redox behaviour of the metal in aqueous media. Gold Bull. 1997, 30, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, P.; Hiekel, K.; Diercks, J.S.; Herranz, J.; Saveleva, V.A.; Khavlyuk, P.; Eychmüller, A.; Schmidt, T.J. Electrochemical Surface Area Quantification, CO2 Reduction Performance, and Stability Studies of Unsupported Three-Dimensional Au Aerogels versus Carbon-Supported Au Nanoparticles. ACS Mater. Au 2021, 2, 278–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Prado, E.; Dunn, J.F.; Vasconez, J.; Castillo, D.; Viscor, G. Partial pressure of oxygen in the human body: A general review. Am. J. Blood Res. 2019, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oncescu, V.; Erickson, D. High volumetric power density, non-enzymatic, glucose fuel cells. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Chung, T.D.; Kim, H.C. Nonenzymatic glucose detection using mesoporous platinum. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 3046–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.H.; Wang, K.; Xia, X.H. Highly ordered platinum-nanotubule arrays for amperometric glucose sensing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2005, 15, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Jia, W.; Zhang, L.; Beacham, C.; Zhang, H.; Lei, Y. Facile synthesis of a platinum nanoflower monolayer on a single-walled carbon nanotube membrane and its application in glucose detection. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 18121–18125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Pankratov, D.; Halder, A.; Xiao, X.; Toscano, M.D.; Zhang, J.; Ulstrup, J.; Gorton, L.; Chi, Q. Two-dimensional graphene paper supported flexible enzymatic fuel cells. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 2562–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Anode Material | Cathode Material | Linear Range (mM) | Condition | Sensitivity (μA mM−1 cm−2) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Highly porous Au | Highly porous Au | 0.01–10 | 34 mM PBS solution, pH 7.4 | 3.1 | [14] |
| Highly porous Au | Pt catalyst | 0.3–9 | 100 mM PBS solution, pH 7.4 | 8.8 | [3] |
| Mesoporous Pt | Pt catalyst | 0−10 | 100 mM PBS solution, pH 7.4 | 9.6 | [43] |
| Ordered Pt nanotubule arrays | Pt | 2–14 | 50 mM PBS solution, pH 7.4, 0.1 M KCl | 0.1 | [44] |
| Pt nanoflower-SWCNT membrane | Pt disk electrode | 0.002–10 | 100 mM PBS solution, pH 7.4 | 7.26 | [45] |
| Au nanotube arrays | Pt platinum wire | 1–42.5 | 100 mM PBS solution, pH 7.4 | 1.13 | [11] |
| Nanocoral-like Au film | Pt flag | 2.5–20 | 100 mM PBS solution, pH 7.4 | 7.8 ± 0.8 | this study |
| Nanofeather like Au film | Pt flag | 2.5–20 | 100 mM PBS solution, pH 7.4 | 9.6 ± 1.5 | this study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kanti Maiti, T.; Liu, W.; Niyazi, A.; Squires, A.M.; Chattpoadhyay, S.; Di Lorenzo, M. Soft-Template-Based Manufacturing of Gold Nanostructures for Energy and Sensing Applications. Biosensors 2024, 14, 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14060289
Kanti Maiti T, Liu W, Niyazi A, Squires AM, Chattpoadhyay S, Di Lorenzo M. Soft-Template-Based Manufacturing of Gold Nanostructures for Energy and Sensing Applications. Biosensors. 2024; 14(6):289. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14060289
Chicago/Turabian StyleKanti Maiti, Tushar, Wanli Liu, Asghar Niyazi, Adam M. Squires, Sujay Chattpoadhyay, and Mirella Di Lorenzo. 2024. "Soft-Template-Based Manufacturing of Gold Nanostructures for Energy and Sensing Applications" Biosensors 14, no. 6: 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14060289
APA StyleKanti Maiti, T., Liu, W., Niyazi, A., Squires, A. M., Chattpoadhyay, S., & Di Lorenzo, M. (2024). Soft-Template-Based Manufacturing of Gold Nanostructures for Energy and Sensing Applications. Biosensors, 14(6), 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14060289





