Biplane Enhancement Coil for Magnetic Induction Tomography of Cerebral Hemorrhage
Abstract
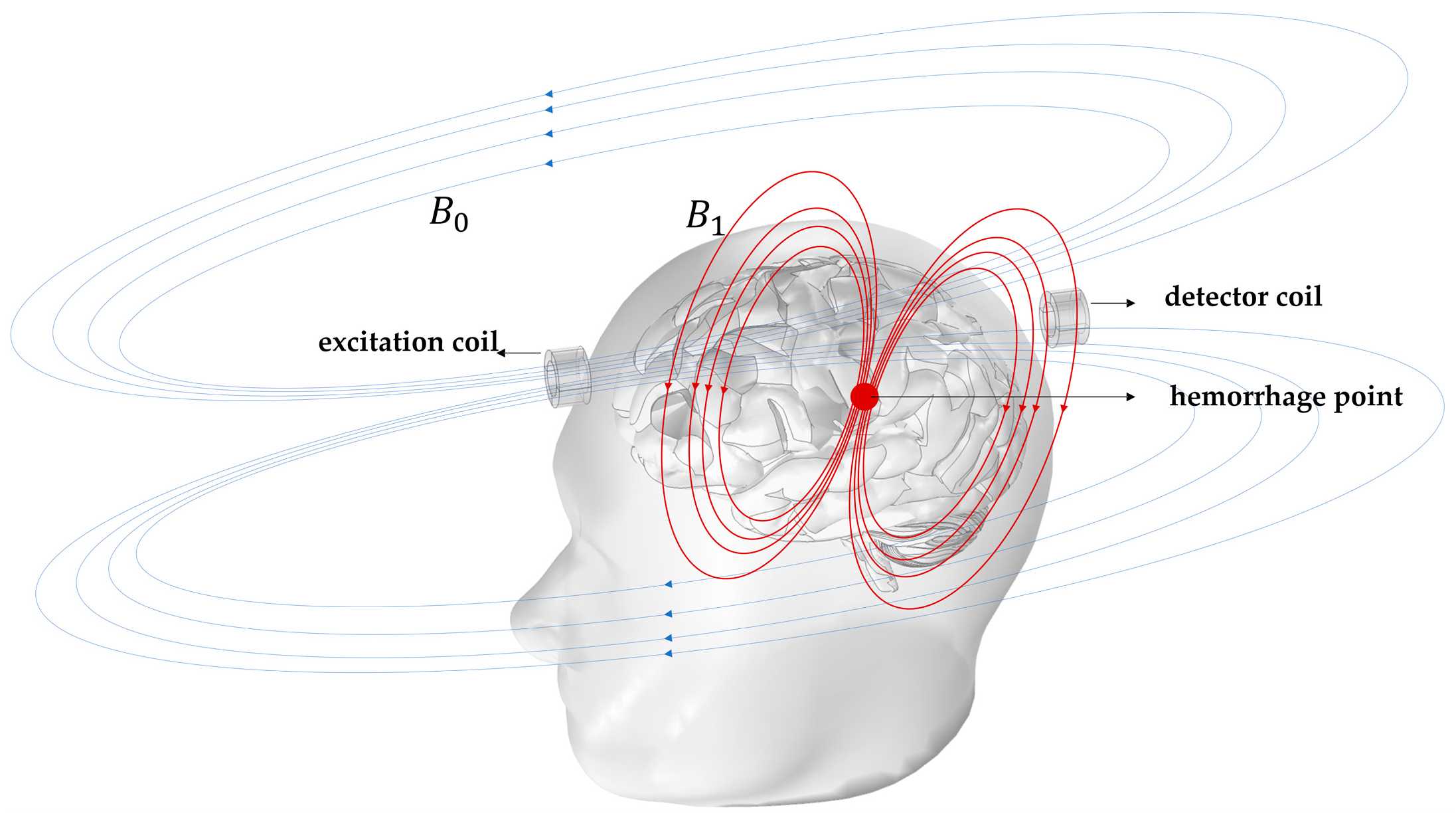
1. Introduction
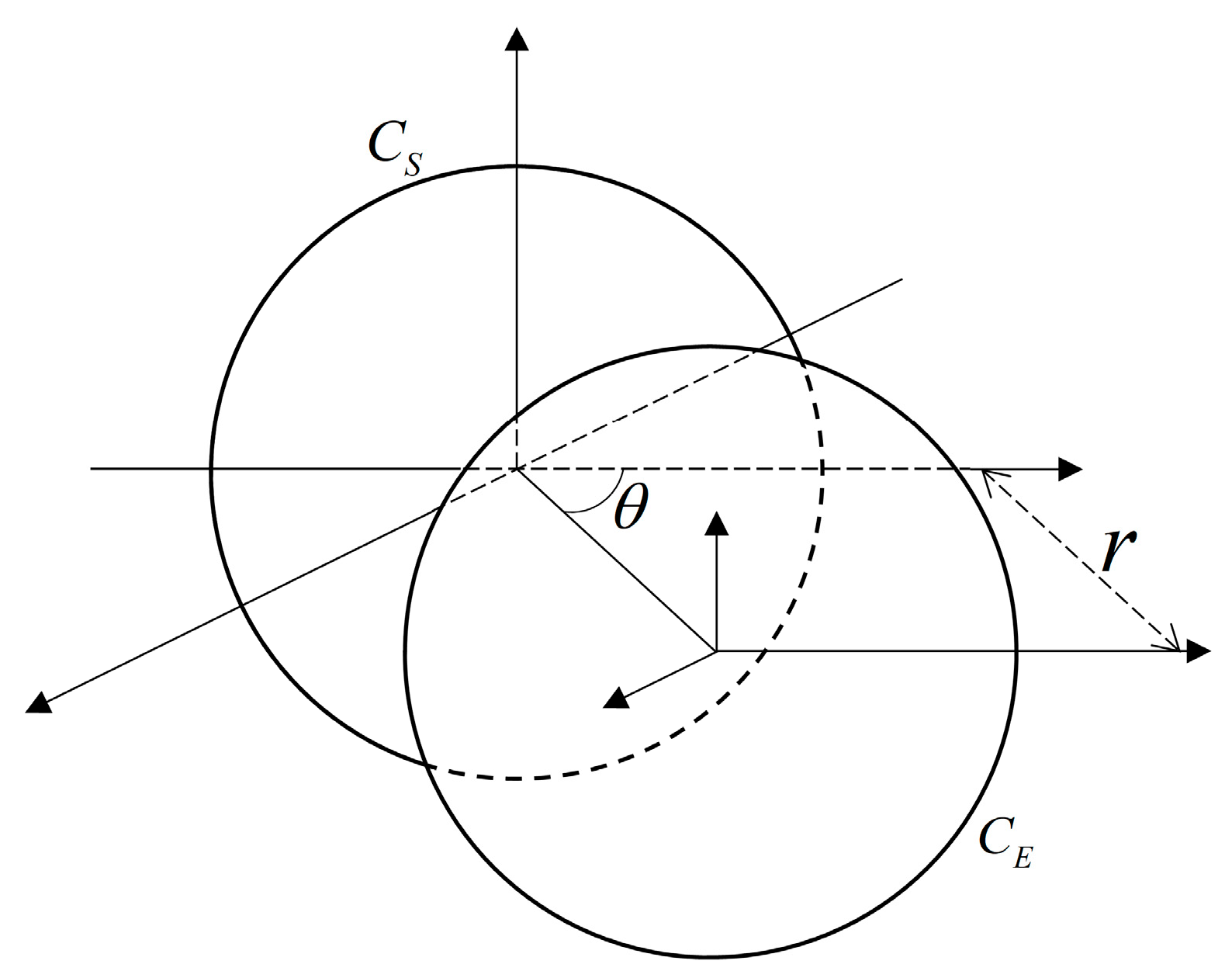
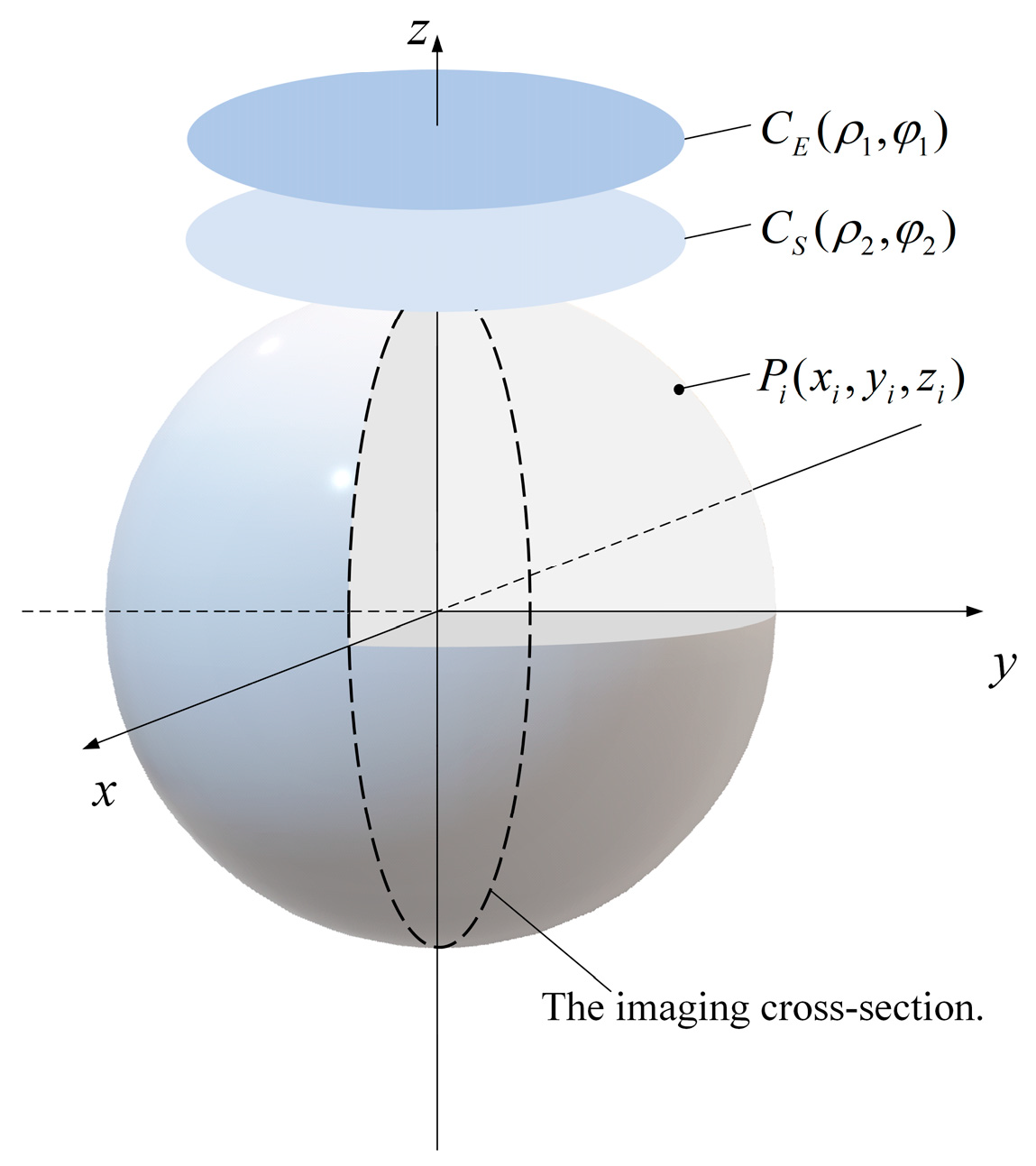
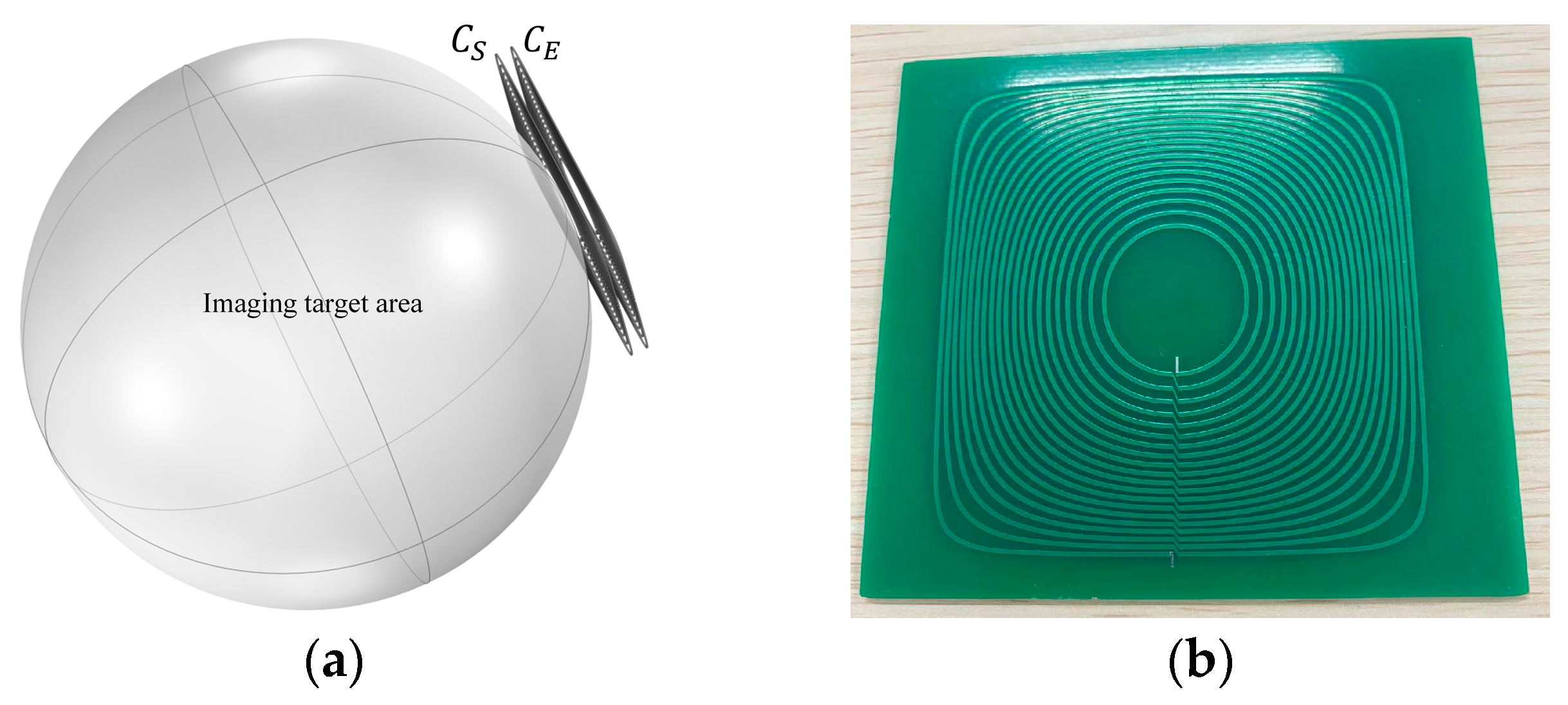
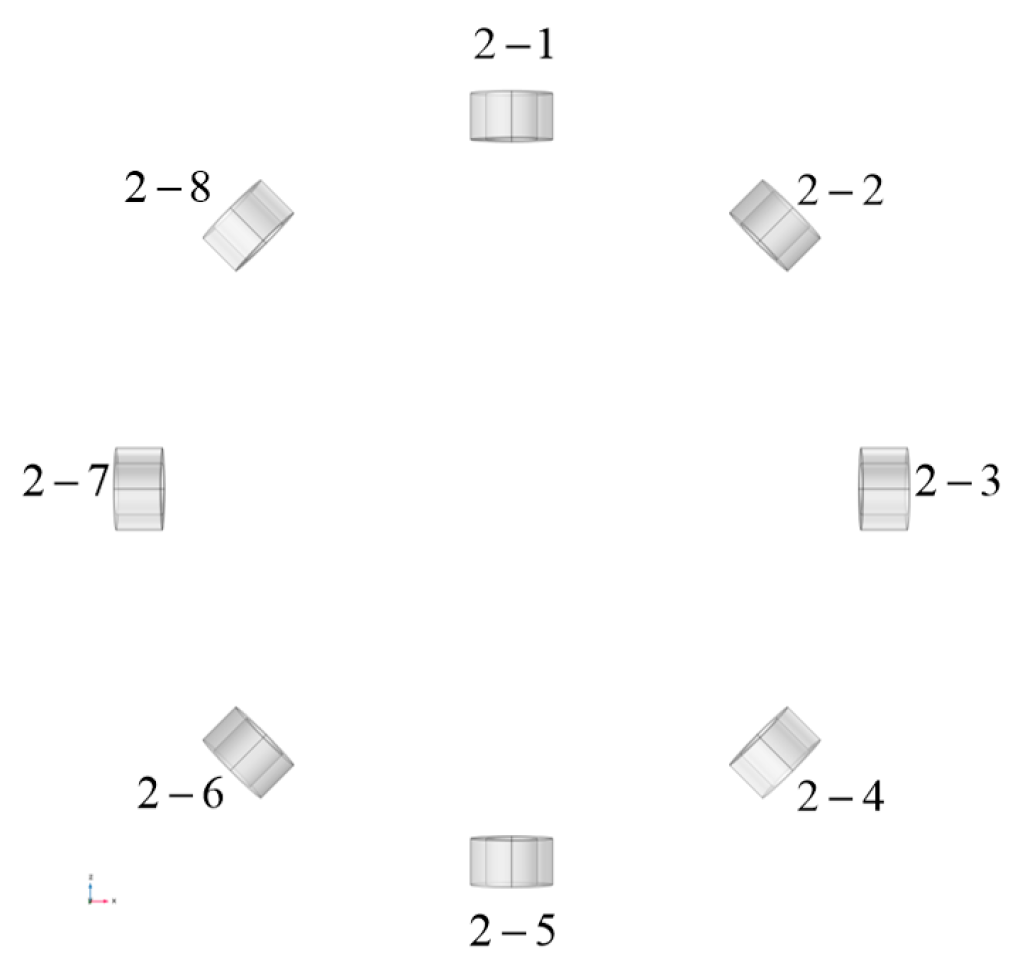
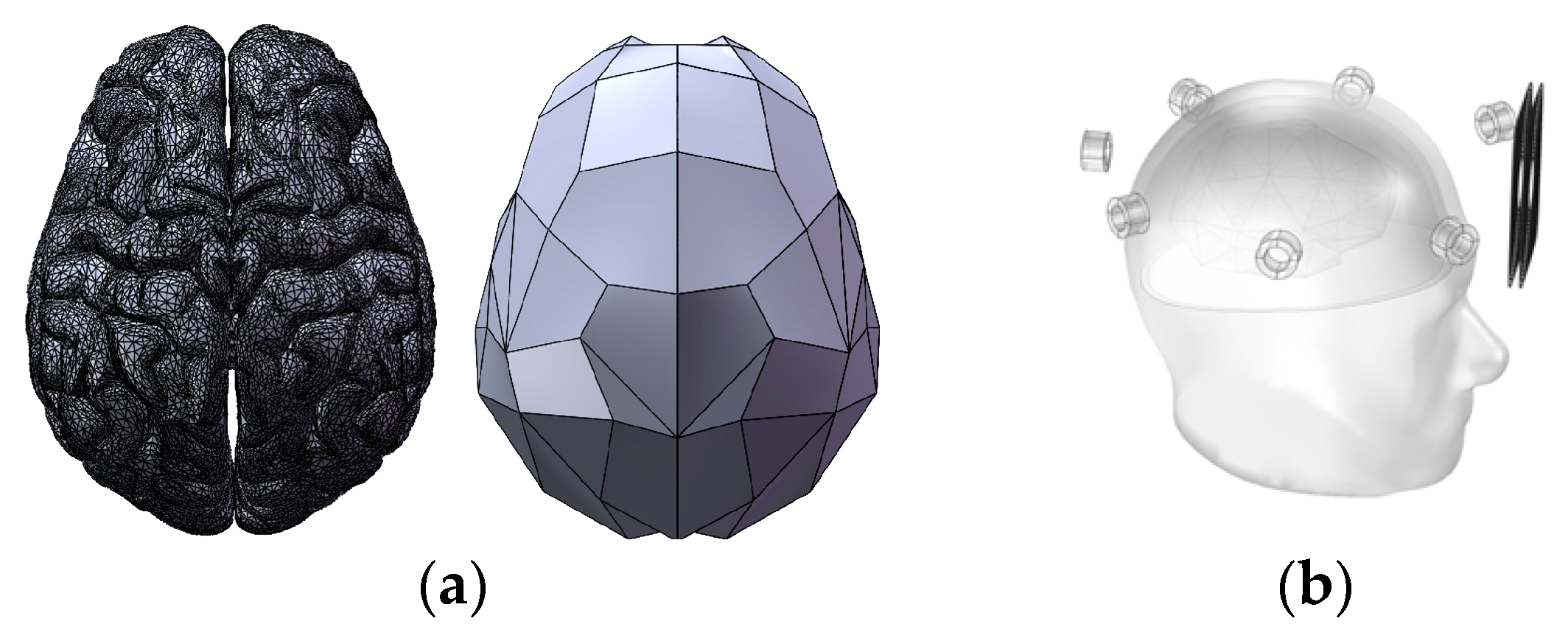
2. Design Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
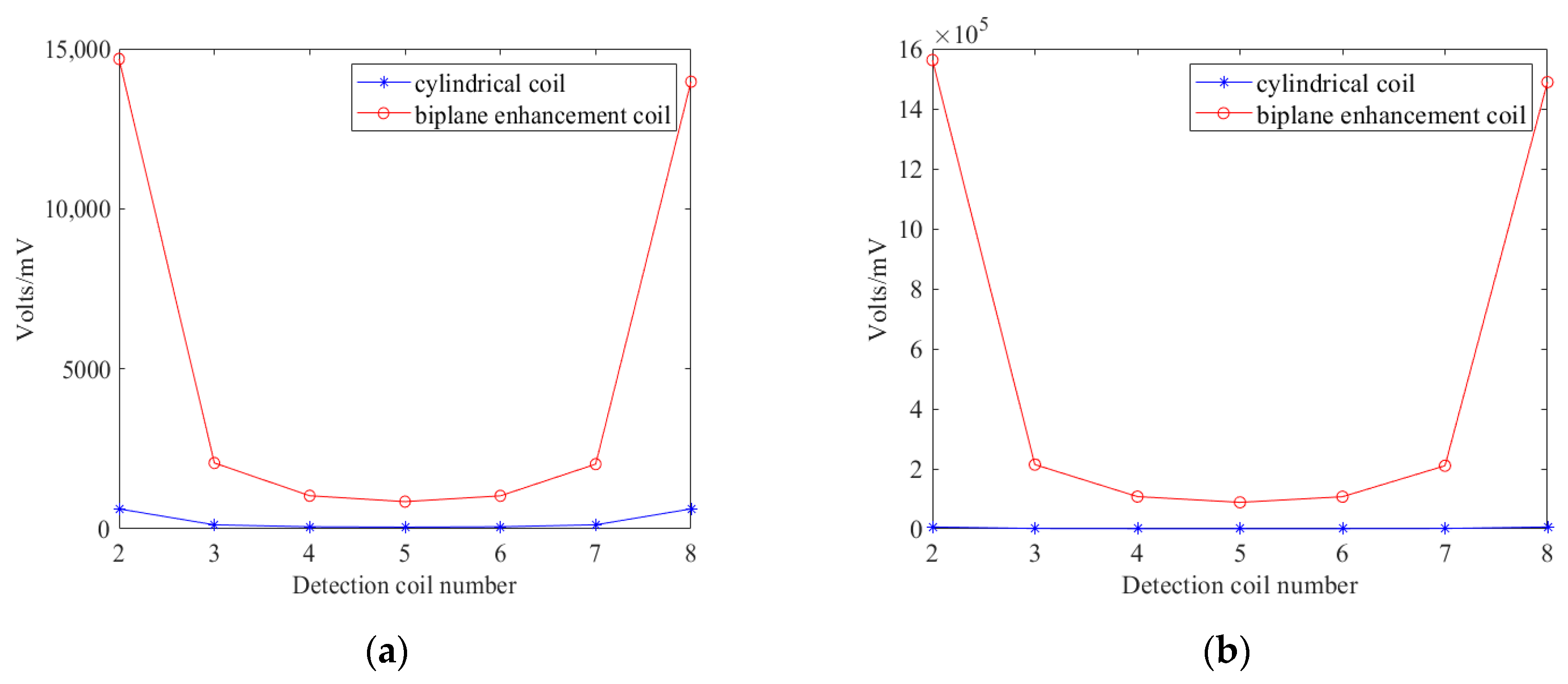
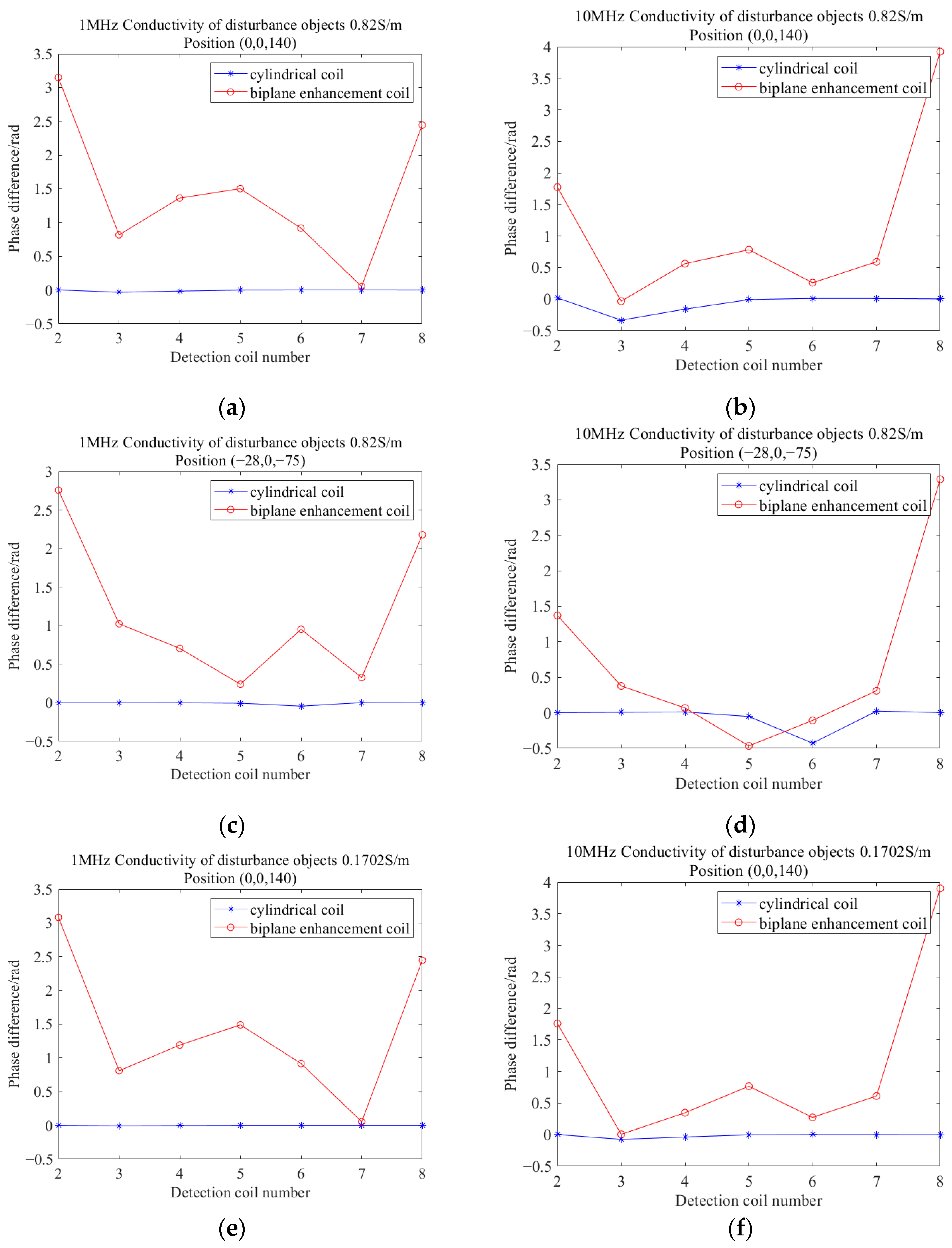
3.1. Simulation Analysis
3.2. Analysis of Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruan, X.; Shi, T.; Chen, H.; Yao, H. Feature extraction and research based on MRI image of cerebral hemorrhage. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Computer Network, Electronic and Automation (ICCNEA), Xi’an, China, 25–27 September 2020; pp. 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, W.R.; Liu, X.C.; Liu, R.G. Research progresses of principle and application of biomedical magnetic induction tomography. Chin. Med. Equip. J. 2022, 43, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, J.F.; Arshad, S.H.; Telfer, B.A.; Snider, E.J.; Convertino, V.A. Noninvasive Monitoring of Simulated Hemorrhage and Whole Blood Resuscitation. Biosensors 2022, 12, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Yu, H.J.; Tan, C.D.; Duan, X.J.; Liu, F.L. Analytical reconstruction algorithm of source translation based CT. Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 2022, 43, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.F.; Lu, L.; Wu, L.; Xu, W.; Wang, Y. The research of MRI reconstruction method by using weighted Schatten P-norm minimization. Acta Electron. Sin. 2019, 47, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.Y.; Soleimanil, M. Electromagnetic tomography for medical and industrial applications: Challenges and opportunities [point of view]. Proc. IEEE 2013, 101, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, H. Magnetic induction tomography. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2001, 12, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Ye, B.; Luo, S.; Bao, J. Carbon fiber reinforced polymer defect detection using magnetic induction tomography method. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Far East NDT New Technology & Application Forum (FENDT), Kunming, China, 14–17 December 2021; pp. 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y. Design of a magnetic induction tomography system by gradiometer coils for conductive fluid imaging. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 56733–56744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldkamp, J.R.; Quirk, S. Single-coil magnetic induction tomography using the LDC-1101 chip. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 21, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Huang, J.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, H. Technologies for magnetic induction tomography sensors and image reconstruction in medical assisted diagnosis: A review. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2020, 91, 091501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tan, C.; Dong, F. Multifrequency weighted difference magnetic induction tomography for intracranial hemorrhage detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 71, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Li, Y.; Fu, F.; You, F.; Shi, X.; Dong, X. Time-difference imaging of magnetic induction tomography in a three-layer brain physical phantom. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2014, 25, 065402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-zeibak, S.; Saunders, N.H. A feasibility study of in vivo electromagnetic imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 1993, 38, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korjenevsky, A.; Cherepenin, V.; Sapetsky, S. Magnetic induction tomography: Experimental realization. Physiol. Meas. 2000, 21, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lei, H.; Liu, P.; Zhou, D. Sensitivity study for improved magnetic induction tomography (MIT) coil system. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Symposium on Antennas & Propagation, Nanjing, China, 23–25 October 2013; Volume 2, pp. 1317–1320. [Google Scholar]
- Merwa, R.; Hollaus, K.; Brunner, P.; Scharfetter, H. Solution of the inverse problem of magnetic induction tomography (MIT). Physiol. Meas. 2005, 26, S241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.Y.; Soleimani, M. Theoretical and experimental evaluation of rotational magnetic induction tomography. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2012, 61, 3324–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wang, R.; Du, Q. Research on the Sector Rotation Scanning Method of Magnetic Induction Tomography. In Proceedings of the 2017 First International Conference on Electronics Instrumentation & Information Systems (EIIS), Harbin, China, 3–5 June 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, L.; Wang, C.; Du, Q.; Qi, H. Design of magnetic induction detection system for deep intracranial excitation. Chin. Med. Equip. J. 2020, 41, 46–51. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, H. Research on Magnetic Induction Signal Enhancement and Tomography Method of Deep Cerebral Hemorrhage; Shenyang University of Technology: Shenyang, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Haikka, S.; Hyttinen, J.; Dekdouk, B. Sensitivity analysis of circular and helmet coil arrays in magnetic induction tomography for stroke detection. In Proceedings of the 2022 44th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Glasgow, UK, 11–15 July 2022; pp. 584–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, L.K.; Crozier, S. A novel target-field method for finite-length magnetic resonance shim coils: I. Zonal shims. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2001, 34, 3447–3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasi, D. Stream function optimization for gradient coil design. Magn. Reson. Med. Off. J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 2001, 45, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, L.; Cao, F.Q.; Du, Q. Back-projection matrix calculation and data processing methods used in magnetic induction tomography. Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 2014, 35, 2256–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



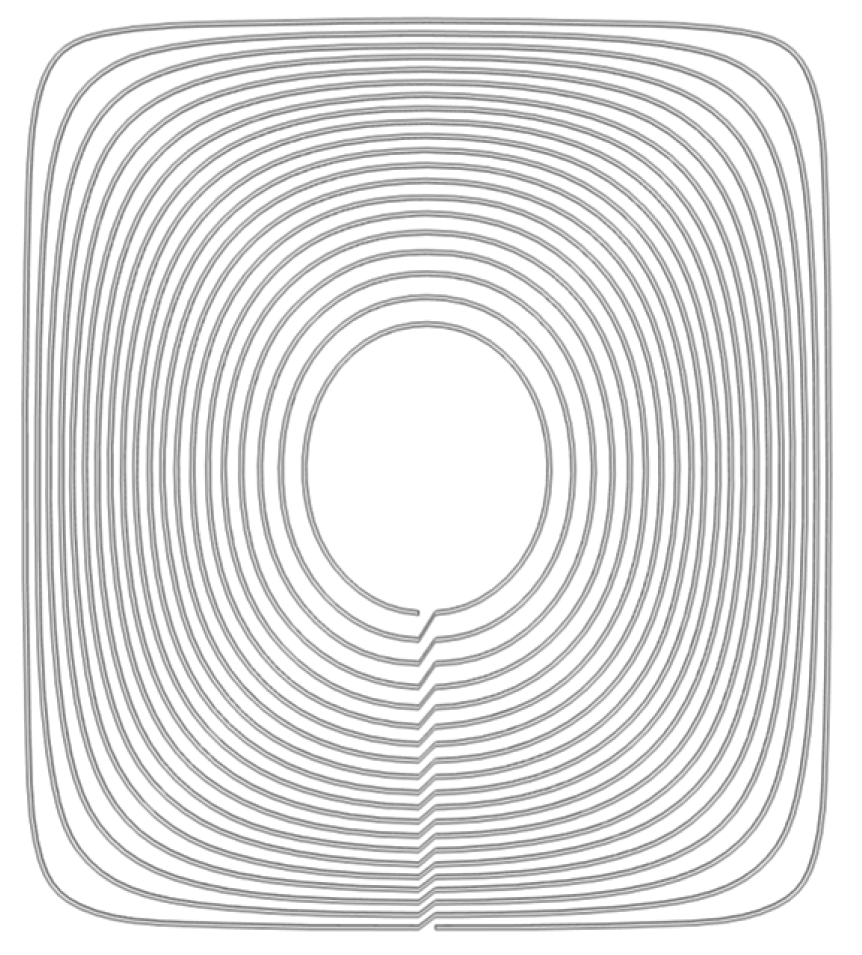
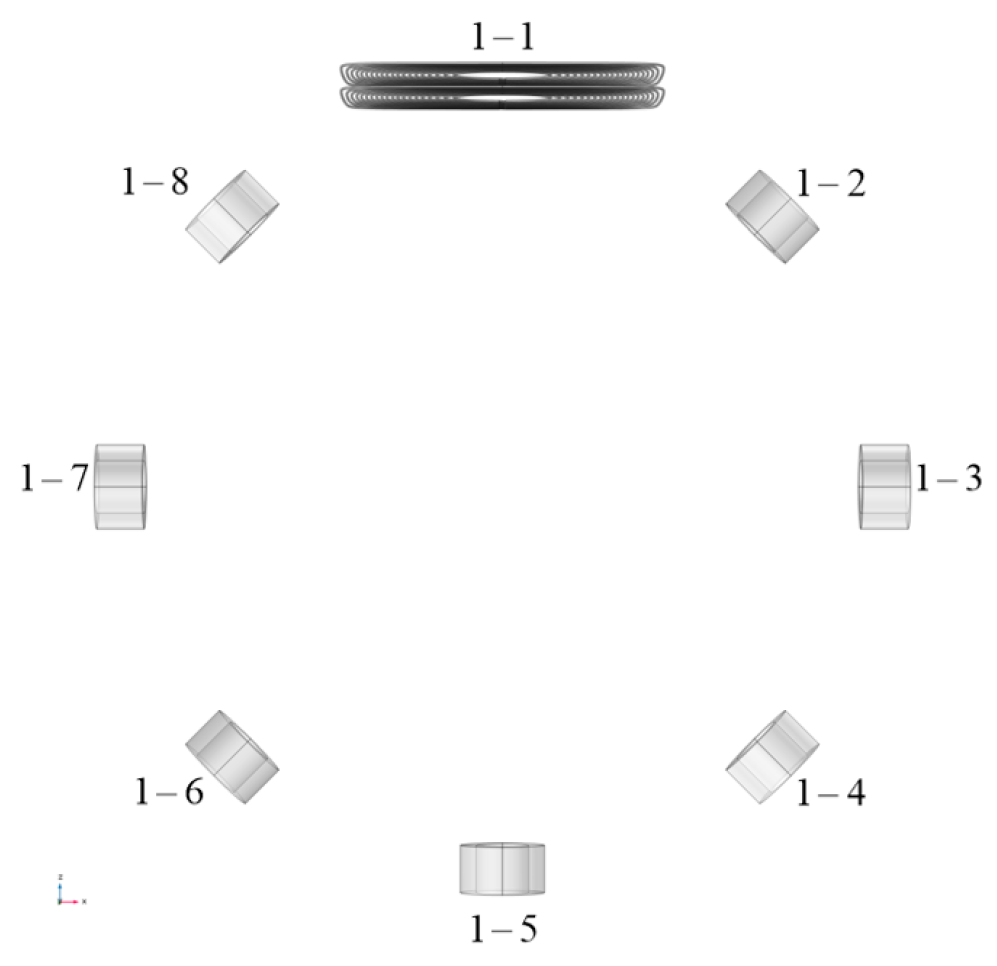
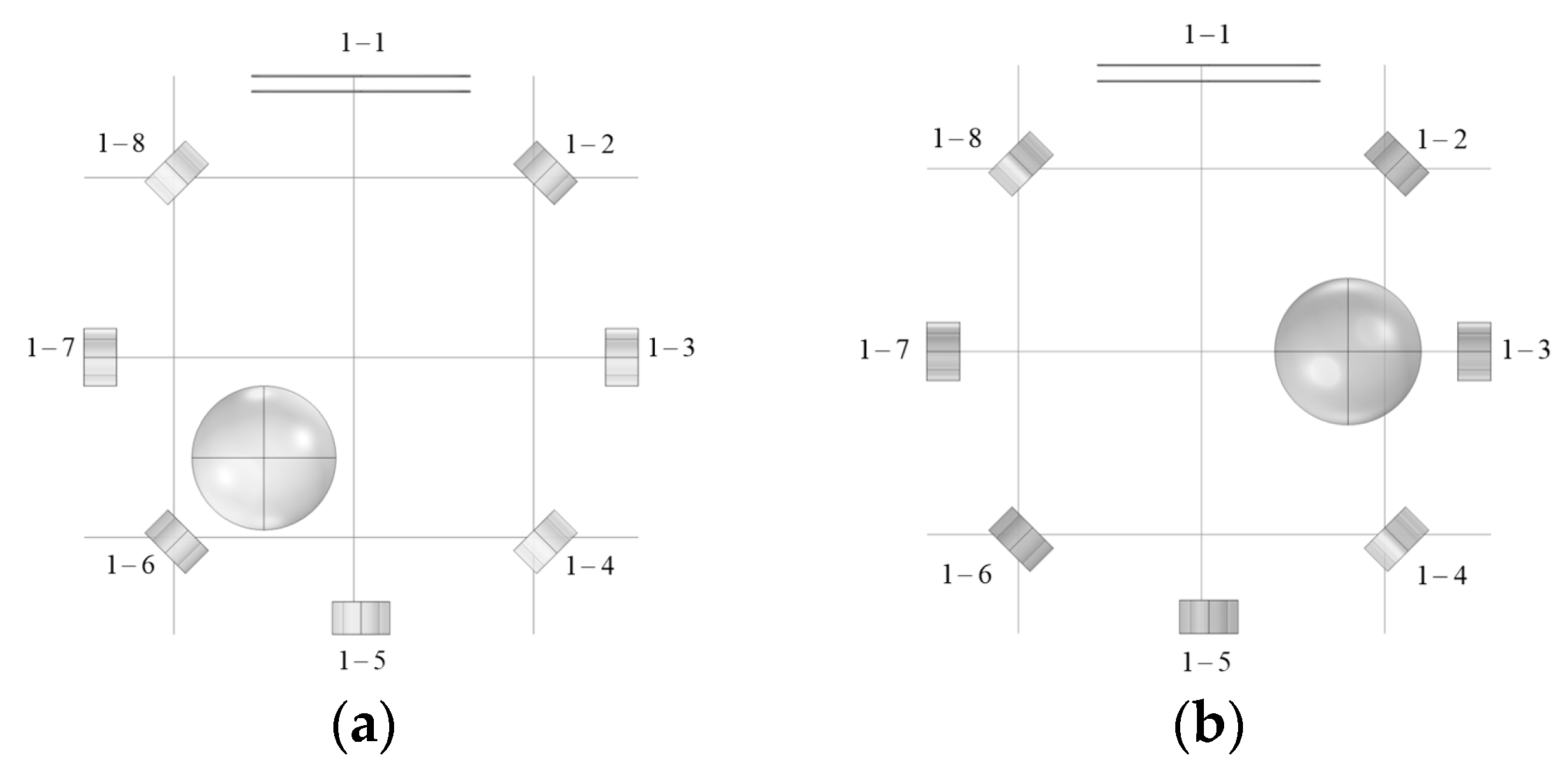
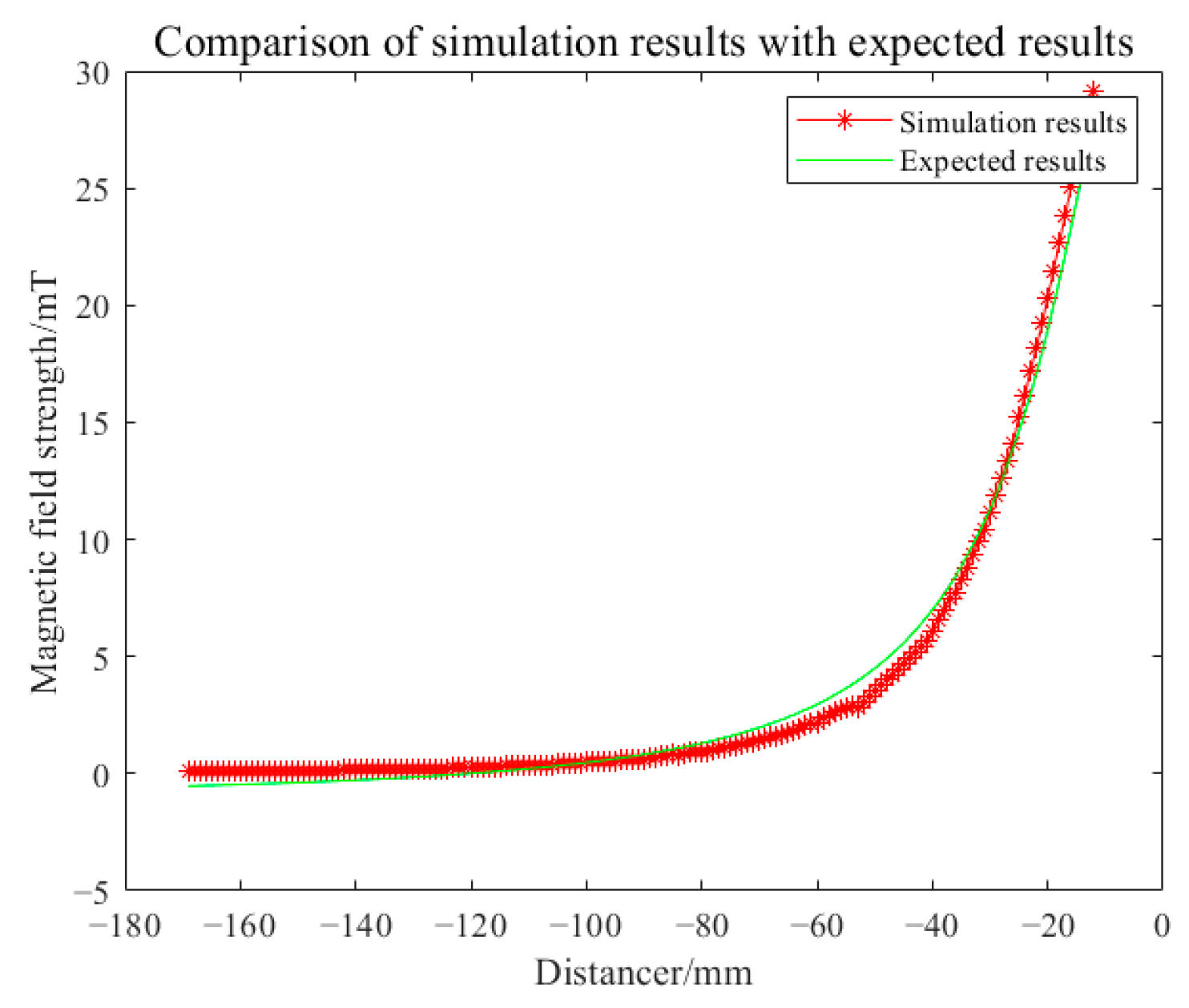

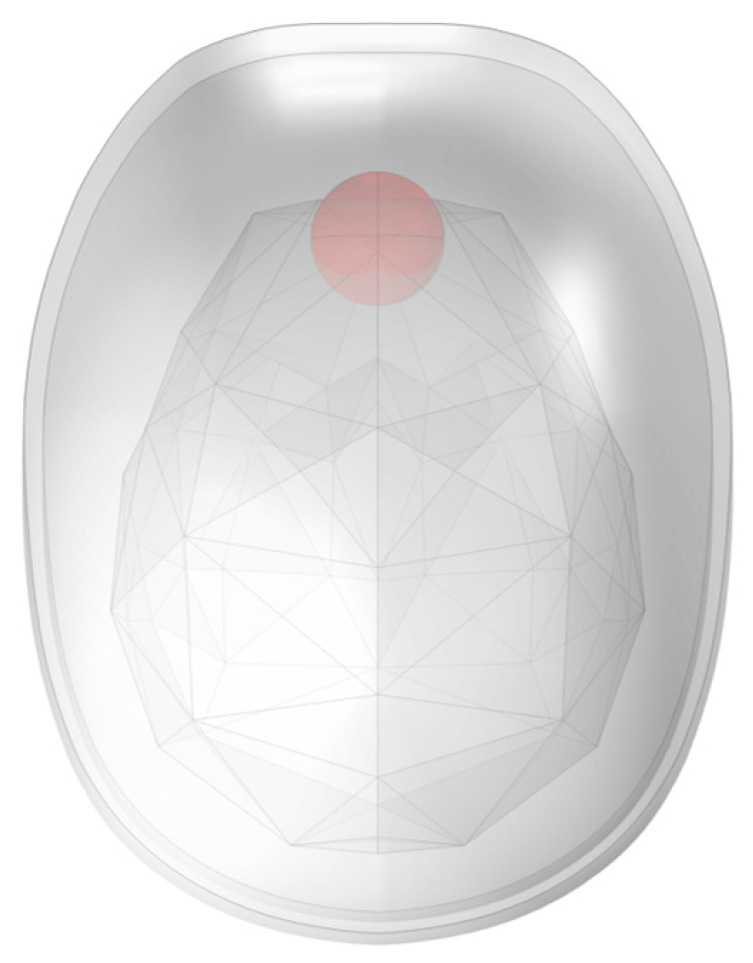
| Radius of Imaging Target Area (mm) | Excitation Current (A) | Excitation Frequency | Conductivity of Disturbance Objects (S/m) | Position of Disturbance Object (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 85 | 1 | 1 | 0.1762 | (0, 0, 140) (−28, 0, −75) |
| 0.82 | (0, 0, 140) (−28, 0, −75) | |||
| 10 | 0.1762 | (0, 0, 140) (−28, 0, −75) | ||
| 0.82 | (0, 0, 140) (−28, 0, −75) |
| Coil Type | |
|---|---|
| biplane enhancement coil | 0.738365 |
| cylindrical coil | 0.461274 |
| Area | Scalp | Skull | Cerebrospinal Fluid | Brain Tissue | Hemorrhage Area |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conductivity (S/m) | 0.044 | 0.024 | 2 | 0.0275 | 0.822 |
| Relative permittivity | 50.8 | 145 | 109 | 480 | 3030 |
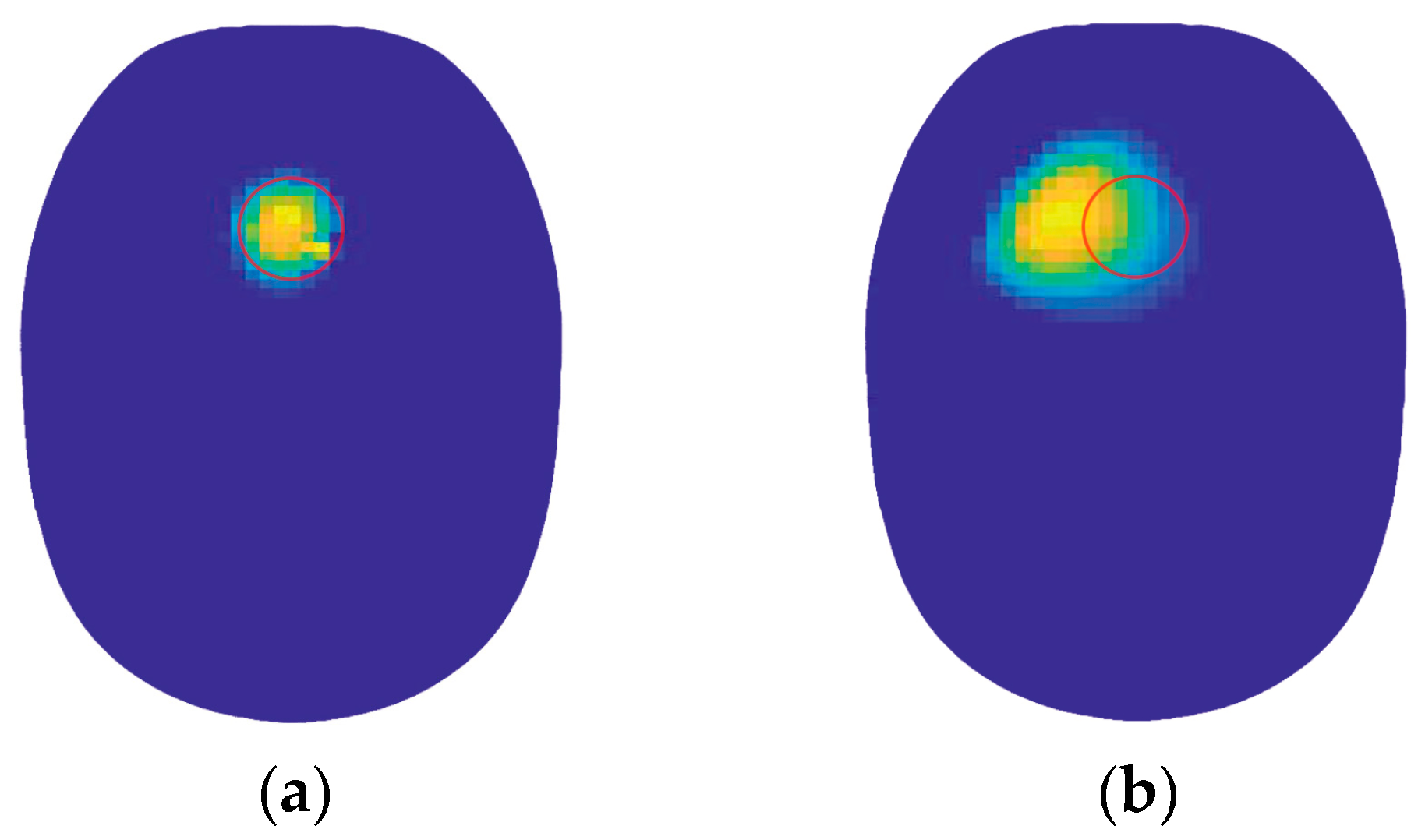
| Reconstructed Image | |
|---|---|
| Reconstructed image(a) | 0.9771 |
| Reconstructed image(b) | 0.8262 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, Z.; Ye, B.; Cao, H.; Zou, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Xing, H. Biplane Enhancement Coil for Magnetic Induction Tomography of Cerebral Hemorrhage. Biosensors 2024, 14, 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14050217
Cao Z, Ye B, Cao H, Zou Y, Zhu Z, Xing H. Biplane Enhancement Coil for Magnetic Induction Tomography of Cerebral Hemorrhage. Biosensors. 2024; 14(5):217. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14050217
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Zhongkai, Bo Ye, Honggui Cao, Yangkun Zou, Zhizhen Zhu, and Hongbin Xing. 2024. "Biplane Enhancement Coil for Magnetic Induction Tomography of Cerebral Hemorrhage" Biosensors 14, no. 5: 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14050217
APA StyleCao, Z., Ye, B., Cao, H., Zou, Y., Zhu, Z., & Xing, H. (2024). Biplane Enhancement Coil for Magnetic Induction Tomography of Cerebral Hemorrhage. Biosensors, 14(5), 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14050217




