A Label-Free Droplet Sorting Platform Integrating Dielectrophoretic Separation for Estimating Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Theory of DEP
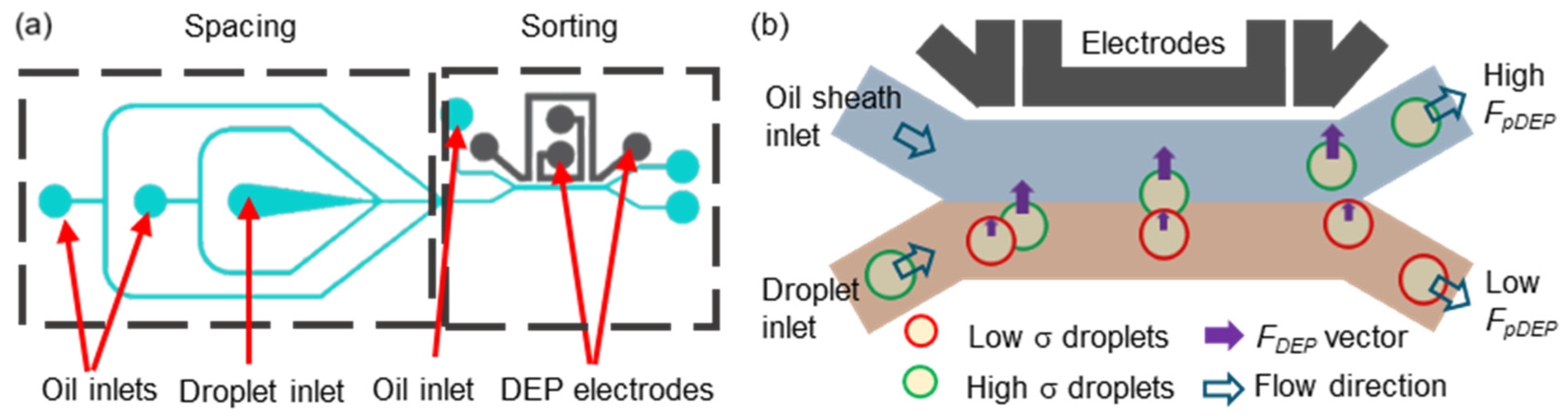
2.2. Design and Fabrication of the Droplet Sorter
2.3. Bacterial Culture
2.4. Measurement of Solution Conductivity and Bacterial Growth Rate
2.5. Droplet Generation and Sorting
3. Results and Discussion
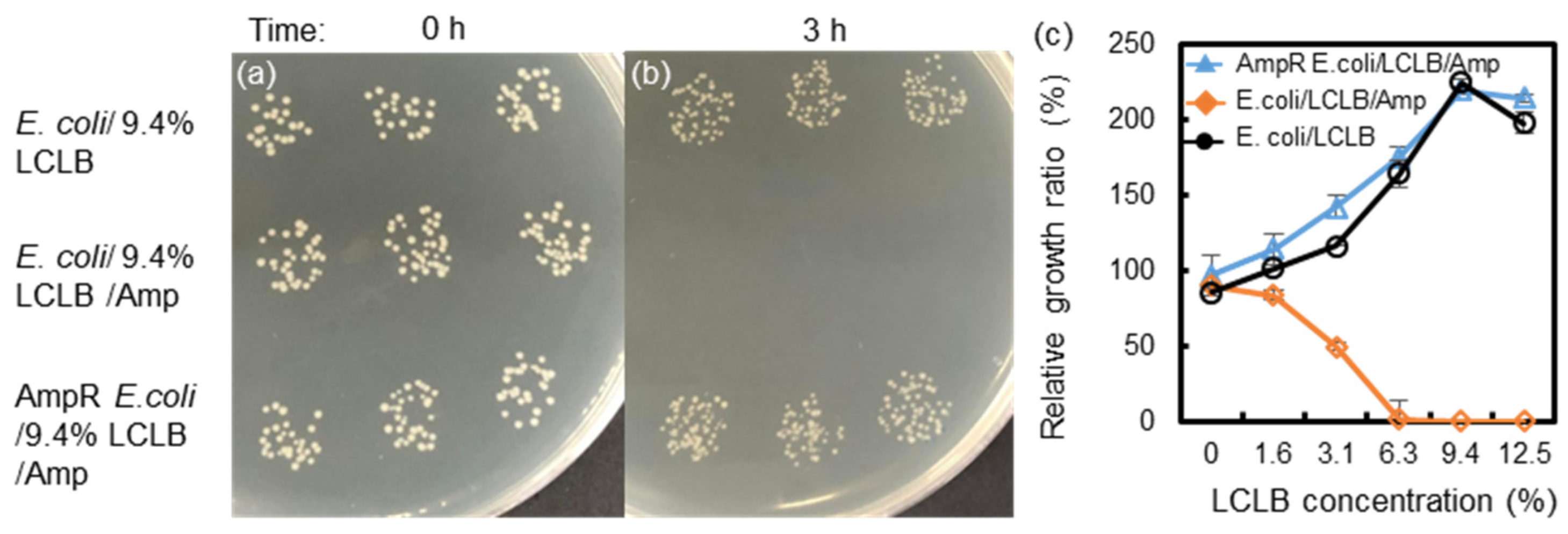
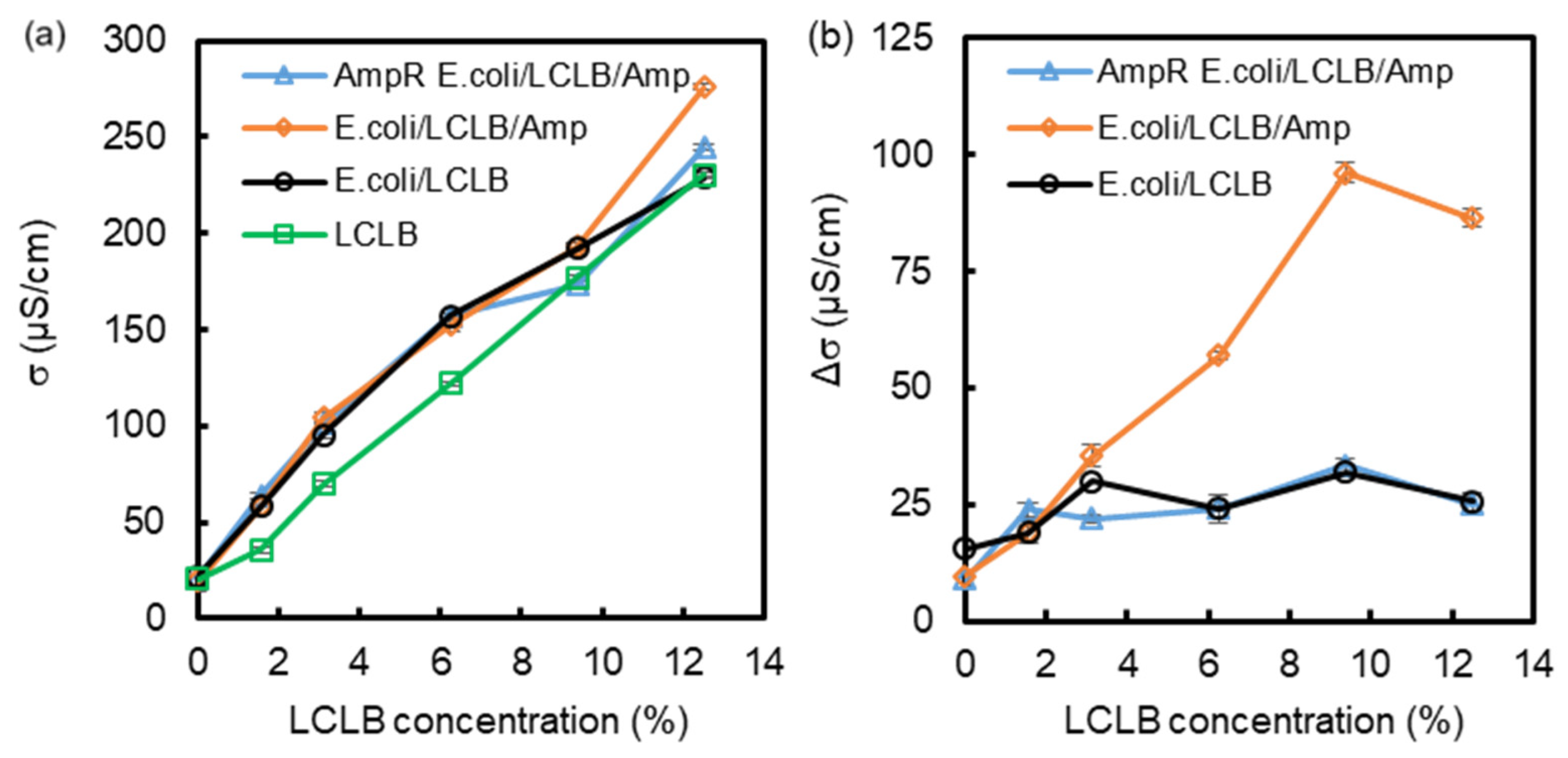
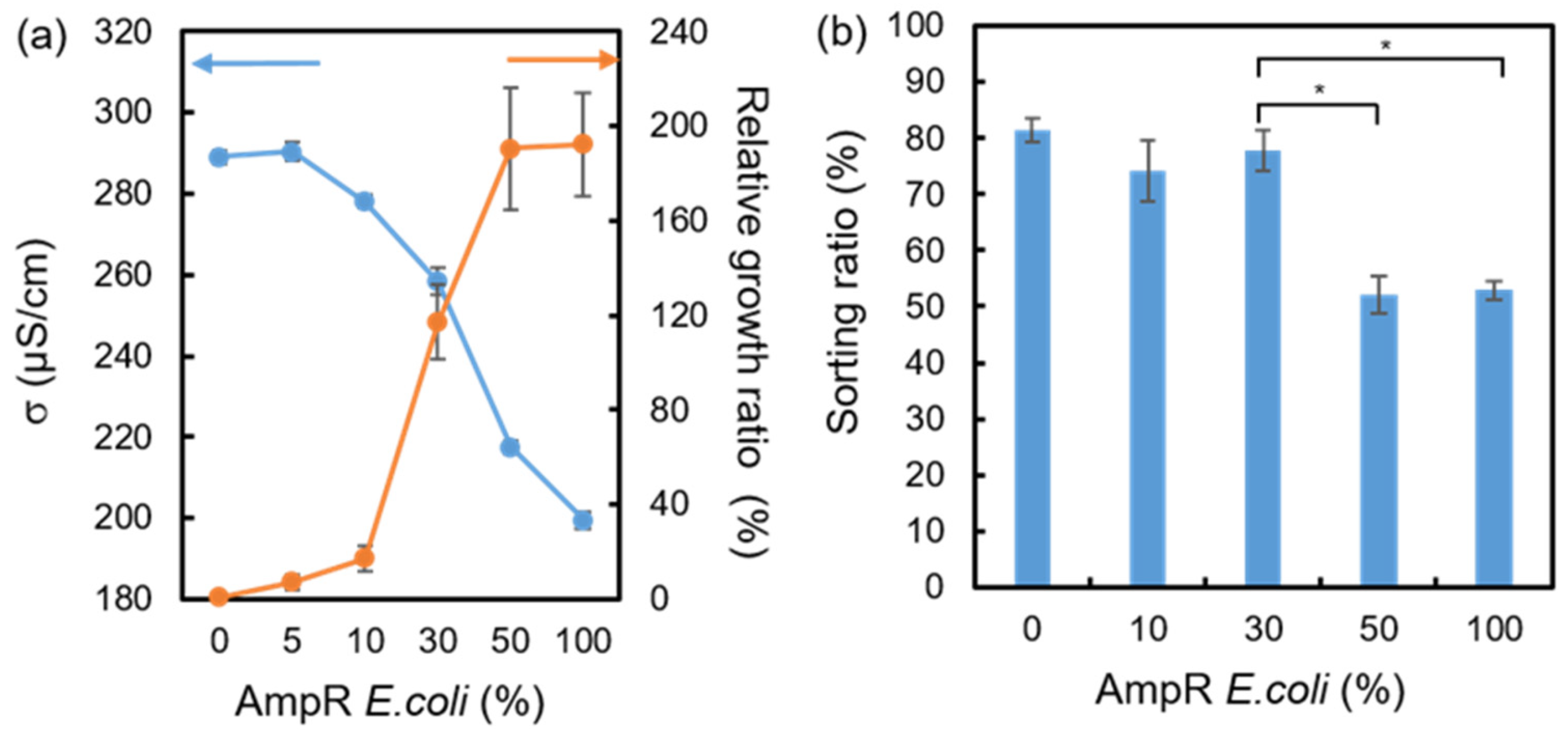
3.1. Change in E. coli Growth Ratio and LCLB Conductivity after Culture
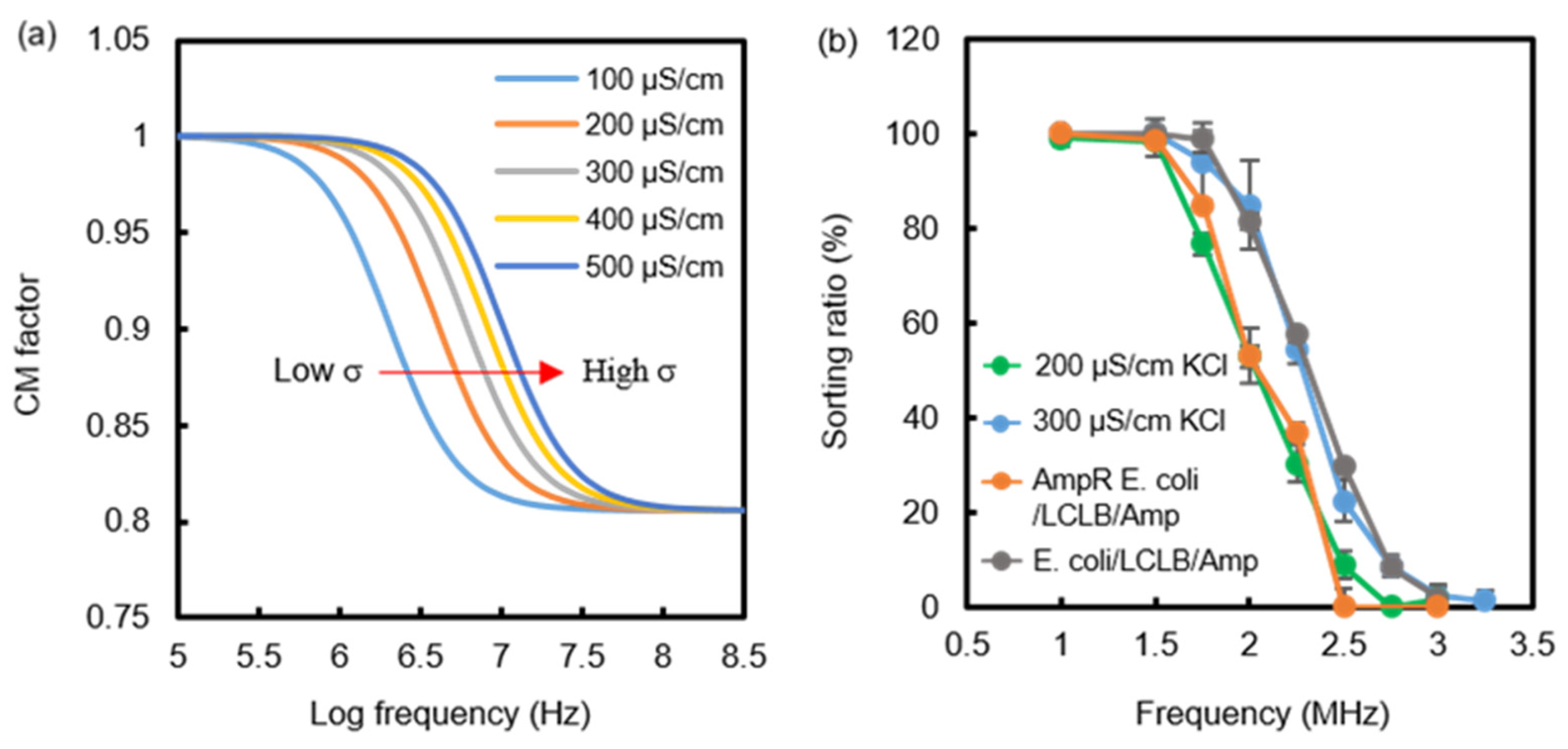
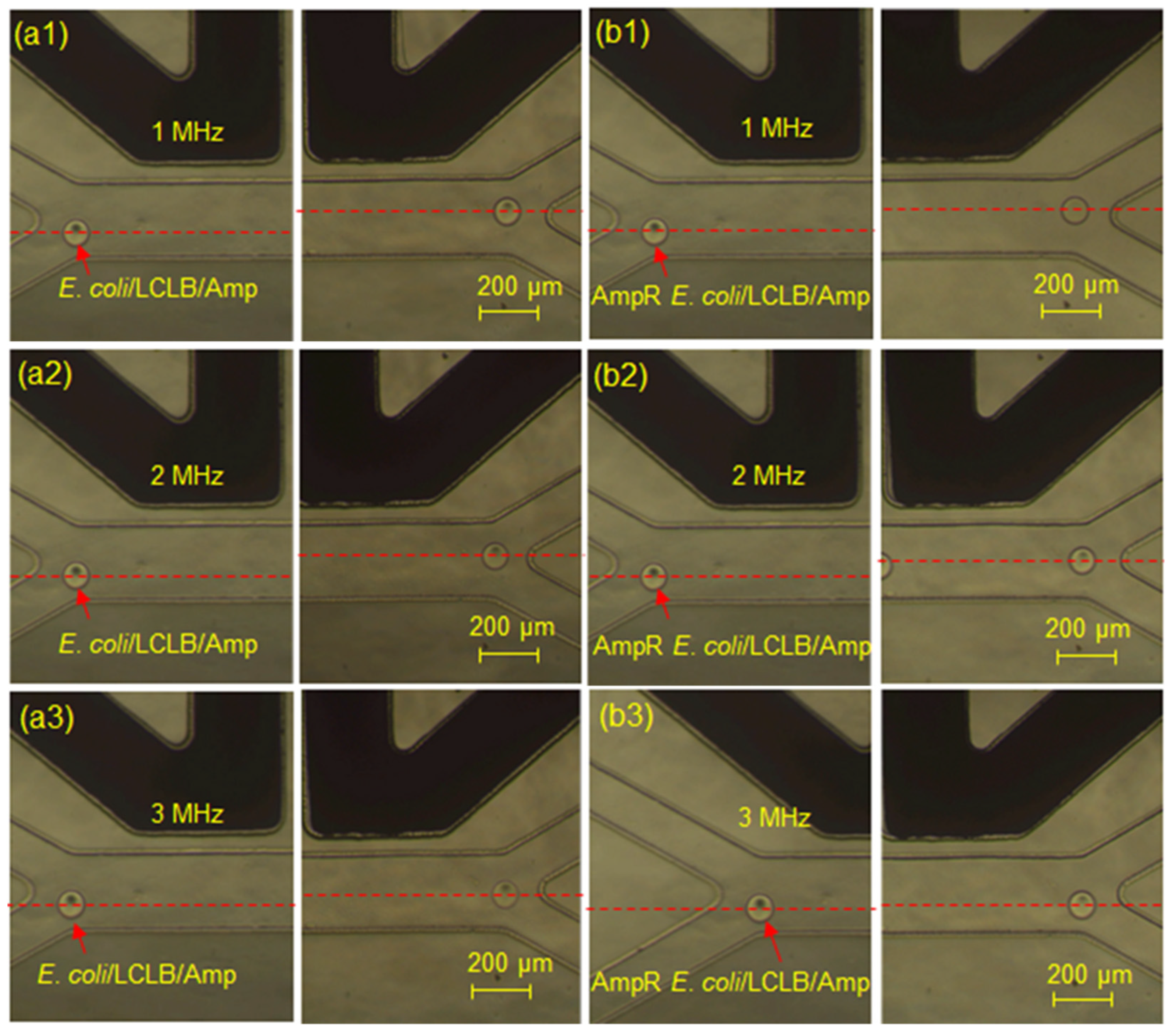
3.2. Sorting Ratios of Conductivity-Varied Droplets
3.3. Sorting Ratios of the AmpR E. coli-Mixed Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dadgostar, P. Antimicrobial resistance: Implications and costs. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 3903–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajic, I.; Kabic, J.; Kekic, D.; Jovicevic, M.; Milenkovic, M.; Mitic Culafic, D.; Trudic, A.; Ranin, L.; Opavski, N. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing: A comprehensive review of currently used methods. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, K.; Denis, O.; Roisin, S.; Mellmann, A.; Idelevich, E.A.; Knaack, D.; van Alen, S.; Kriegeskorte, A.; Köck, R.; Schaumburg, F. Detection of meca-and mecc-positive methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (mrsa) isolates by the new xpert mrsa gen 3 pcr assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashaghi, S.; Abbaspourrad, A.; Weitz, D.A.; van Oijen, A.M. Droplet microfluidics: A tool for biology, chemistry and nanotechnology. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 82, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, Y. Emerging droplet microfluidics. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 7964–8040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.T.; Rotem, A.; Heyman, J.A.; Weitz, D.A. Droplet microfluidics for high-throughput biological assays. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 2146–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payne, E.M.; Holland-Moritz, D.A.; Sun, S.; Kennedy, R.T. High-throughput screening by droplet microfluidics: Perspective into key challenges and future prospects. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 2247–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agresti, J.J.; Antipov, E.; Abate, A.R.; Ahn, K.; Rowat, A.C.; Baret, J.-C.; Marquez, M.; Klibanov, A.M.; Griffiths, A.D.; Weitz, D.A. Ultrahigh-throughput screening in drop-based microfluidics for directed evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4004–4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neun, S.; Zurek, P.J.; Kaminski, T.S.; Hollfelder, F. Ultrahigh Throughput Screening for Enzyme Function in Droplets; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 317–343. [Google Scholar]
- Beneyton, T.; Wijaya, I.P.M.; Postros, P.; Najah, M.; Leblond, P.; Couvent, A.; Mayot, E.; Griffiths, A.D.; Drevelle, A. High-throughput screening of filamentous fungi using nanoliter-range droplet-based microfluidics. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamitros, C.S.; Morvan, M.; Vigne, A.; Lim, J.; Gruner, P.J.; Beneyton, T.; Vrignon, J.; Konrad, M.; Baret, J.-C. Bacterial expression systems for enzymatic activity in droplet-based microfluidics. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 4908–4916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chokkalingam, V.; Tel, J.; Wimmers, F.; Liu, X.; Semenov, S.; Thiele, J.; Figdor, C.G.; Huck, W.T. Probing cellular heterogeneity in cytokine-secreting immune cells using droplet-based microfluidics. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 4740–4744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.G.; Kheiri, S.; Islam, S.; Kumar, H.; Yang, A.; Kim, K. An integrated microfluidic flow-focusing platform for on-chip fabrication and filtration of cell-laden microgels. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 1621–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Wu, Z.; Khan, M.; Mao, S.; Manibalan, K.; Li, N.; Lin, J.-M.; Lin, L. Multifunctional regulation of 3d cell-laden microsphere culture on an integrated microfluidic device. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 12283–12289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yu, Z.; Wu, M.; Lan, Y.; Jia, C.; Zhao, J. Single-cell sorting using integrated pneumatic valve droplet microfluidic chip. Talanta 2023, 253, 124044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postek, W.; Gargulinski, P.; Scheler, O.; Kaminski, T.S.; Garstecki, P. Microfluidic screening of antibiotic susceptibility at a single-cell level shows the inoculum effect of cefotaxime on E. coli. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 3668–3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watterson, W.J.; Tanyeri, M.; Watson, A.R.; Cham, C.M.; Shan, Y.; Chang, E.B.; Eren, A.M.; Tay, S. Droplet-based high-throughput cultivation for accurate screening of antibiotic resistant gut microbes. eLife 2020, 9, e56998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churski, K.; Kaminski, T.S.; Jakiela, S.; Kamysz, W.; Baranska-Rybak, W.; Weibel, D.B.; Garstecki, P. Rapid screening of antibiotic toxicity in an automated microdroplet system. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 1629–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaramakrishnan, M.; Kothandan, R.; Govindarajan, D.K.; Meganathan, Y.; Kandaswamy, K. Active microfluidic systems for cell sorting and separation. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 13, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirifar, L.; Besanjideh, M.; Nasiri, R.; Shamloo, A.; Nasrollahi, F.; de Barros, N.R.; Davoodi, E.; Erdem, A.; Mahmoodi, M.; Hosseini, V. Droplet-based microfluidics in biomedical applications. Biofabrication 2022, 14, 022001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, H.-D.; Zheng, H.; Guo, W.; Gañán-Calvo, A.M.; Ai, Y.; Tsao, C.-W.; Zhou, J.; Li, W.; Huang, Y.; Nguyen, N.-T. Active droplet sorting in microfluidics: A review. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 751–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Han, S.-I.; Zhang, H.; Han, A. Tutorial on lateral dielectrophoretic manipulations in microfluidic systems. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2022, 17, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, H.; Green, N.G. Ac Electrokinetics: Colloids and Nanoparticles; Research Studies Press: Baldock, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Caen, O.; Schütz, S.; Jammalamadaka, M.S.; Vrignon, J.; Nizard, P.; Schneider, T.M.; Baret, J.-C.; Taly, V. High-throughput multiplexed fluorescence-activated droplet sorting. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2018, 4, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Y.; Hu, R.; Chen, D.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Yu, H.; Fu, Y.; Li, C.; Dong, Z.; Weng, Y.-X. Fluorescence-activated droplet sorting of pet degrading microorganisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Zeng, W.; Xu, S.; Zhou, J. Fluorescence-activated droplet sorting for enhanced pyruvic acid accumulation by candida glabrata. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 318, 124258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncombe, T.A.; Ponti, A.; Seebeck, F.P.; Dittrich, P.S. Uv–vis spectra-activated droplet sorting for label-free chemical identification and collection of droplets. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 13008–13013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gielen, F.; Hours, R.; Emond, S.; Fischlechner, M.; Schell, U.; Hollfelder, F. Ultrahigh-throughput–directed enzyme evolution by absorbance-activated droplet sorting (aads). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E7383–E7389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Ren, L.; Su, Y.; Ji, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Hu, Q. Raman-activated droplet sorting (rads) for label-free high-throughput screening of microalgal single-cells. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 12569–12577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Painter, R.; Enesa, K.; Holmes, D.; Whyte, G.; Garlisi, C.; Monsma, F.; Rehak, M.; Craig, F.; Smith, C.A. High-throughput screening of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in picodroplets. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 1636–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girault, M.; Kim, H.; Arakawa, H.; Matsuura, K.; Odaka, M.; Hattori, A.; Terazono, H.; Yasuda, K. An on-chip imaging droplet-sorting system: A real-time shape recognition method to screen target cells in droplets with single cell resolution. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, R.H.; Tang, S.-Y.; Siltanen, C.A.; Shahi, P.; Zhang, J.Q.; Poust, S.; Gartner, Z.J.; Abate, A.R. Printed droplet microfluidics for on demand dispensing of picoliter droplets and cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 8728–8733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deivasigamani, R.; Maidin, N.N.M.; Wee, M.M.R.; Mohamed, M.A.; Buyong, M.R. Dielectrophoresis prototypic polystyrene particle synchronization toward alive keratinocyte cells for rapid chronic wound healing. Sensors 2021, 21, 3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Agarwal, P.; Zhao, S.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, X.; He, X. Continuous on-chip cell separation based on conductivity-induced dielectrophoresis with 3d self-assembled ionic liquid electrodes. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 8264–8271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pethig, R. Dielectrophoresis: Status of the theory, technology, and applications. Biomicrofluidics 2010, 4, 022811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schütz, S.S.; Beneyton, T.; Baret, J.-C.; Schneider, T.M. Rational design of a high-throughput droplet sorter. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 2220–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, H.W.; Roulland-Dussoix, D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 1969, 41, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donowitz, G.R.; Mandell, G.L. Beta-lactam antibiotics. N. Engl. J. Med. 1988, 318, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mortari, A.; Adami, A.; Lorenzelli, L. An unconventional approach to impedance microbiology: Detection of culture media conductivity variations due to bacteriophage generated lyses of host bacteria. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 67, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheler, O.; Makuch, K.; Debski, P.R.; Horka, M.; Ruszczak, A.; Pacocha, N.; Sozański, K.; Smolander, O.-P.; Postek, W.; Garstecki, P. Droplet-based digital antibiotic susceptibility screen reveals single-cell clonal heteroresistance in an isogenic bacterial population. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scanlon, T.C.; Dostal, S.M.; Griswold, K.E. A high-throughput screen for antibiotic drug discovery. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2014, 111, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahler, L.; Wink, K.; Beulig, R.J.; Scherlach, K.; Tovar, M.; Zang, E.; Martin, K.; Hertweck, C.; Belder, D.; Roth, M. Detection of antibiotics synthetized in microfluidic picolitre-droplets by various actinobacteria. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eun, Y.-J.; Utada, A.S.; Copeland, M.F.; Takeuchi, S.; Weibel, D.B. Encapsulating bacteria in agarose microparticles using microfluidics for high-throughput cell analysis and isolation. ACS Chem. Biol. 2011, 6, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Bacteria in Droplets | Antibiotics | Detection/Label or Label-Free | Culture Time (h) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli HS151 | fusidic acid | light scattering/label-free | 6–8 | [30] |
| E. coli DH5α | cefotaxime | yellow fluorescent protein/label | overnight | [40] |
| Staphylococcus aureus | cefazolin | SyTox Orange viability dye/label | 15–17 | [41] |
| E. coli ECJW992 | streptothricin F | fluorescent protein/label | 24 | [42] |
| E. coli MG1655 | rifampicin | enhanced green fluorescent protein /label | 12–18 | [43] |
| E. coli HB101 | ampicillin | droplet conductivity/label-free | 3 | this work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, J.-D.; Yang, C.-Y.; Han, A.; Wu, C.-C. A Label-Free Droplet Sorting Platform Integrating Dielectrophoretic Separation for Estimating Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance. Biosensors 2024, 14, 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14050218
Yan J-D, Yang C-Y, Han A, Wu C-C. A Label-Free Droplet Sorting Platform Integrating Dielectrophoretic Separation for Estimating Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance. Biosensors. 2024; 14(5):218. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14050218
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Jia-De, Chiou-Ying Yang, Arum Han, and Ching-Chou Wu. 2024. "A Label-Free Droplet Sorting Platform Integrating Dielectrophoretic Separation for Estimating Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance" Biosensors 14, no. 5: 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14050218
APA StyleYan, J.-D., Yang, C.-Y., Han, A., & Wu, C.-C. (2024). A Label-Free Droplet Sorting Platform Integrating Dielectrophoretic Separation for Estimating Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance. Biosensors, 14(5), 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14050218







