A Smartphone Integrated Platform for Ratiometric Fluorescent Sensitive and Selective Determination of Dipicolinic Acid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of CDs
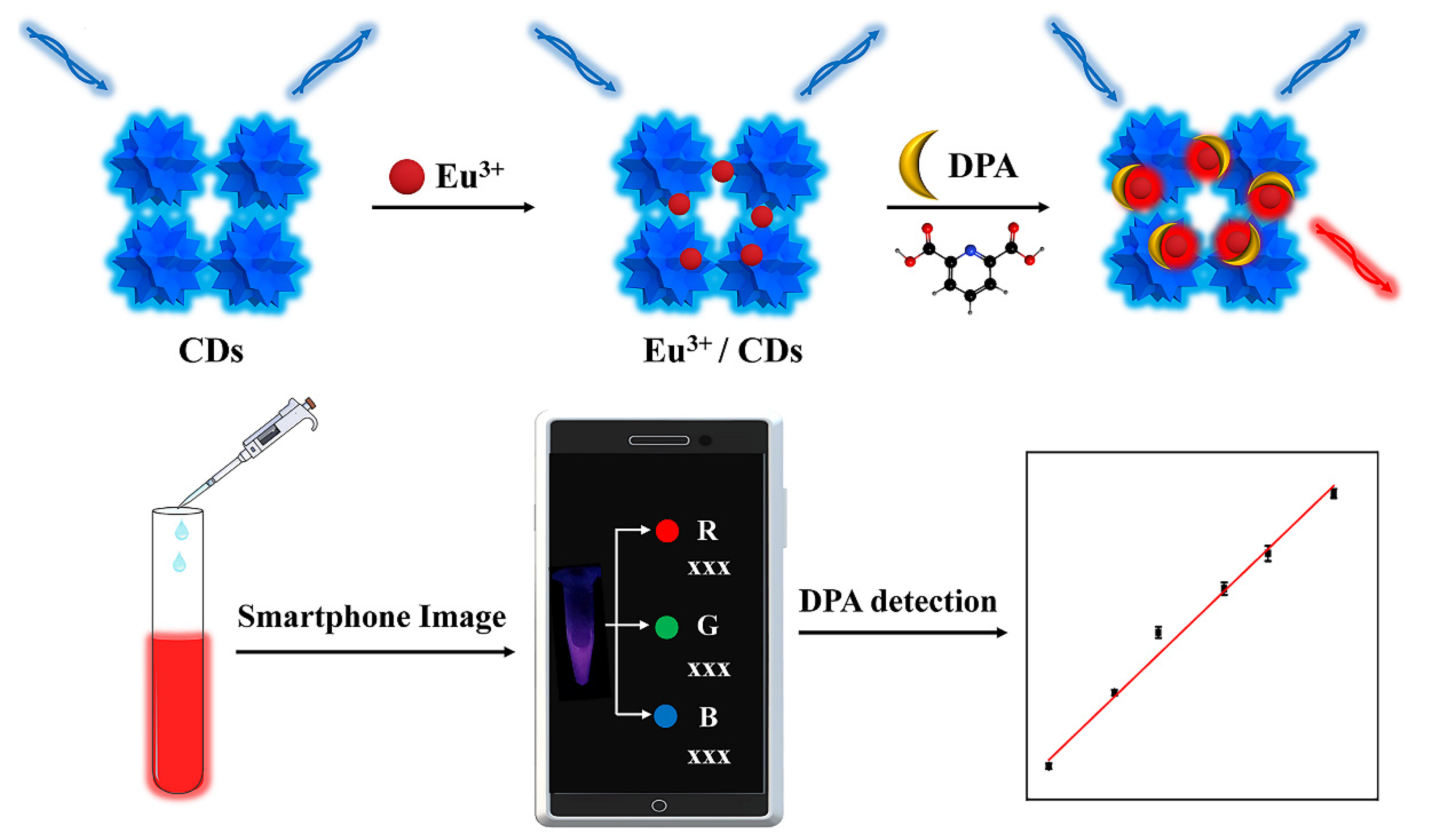
2.3. Determination of DPA with Eu3+/CDs Sensing System
2.4. DPA Sensing in Real Samples
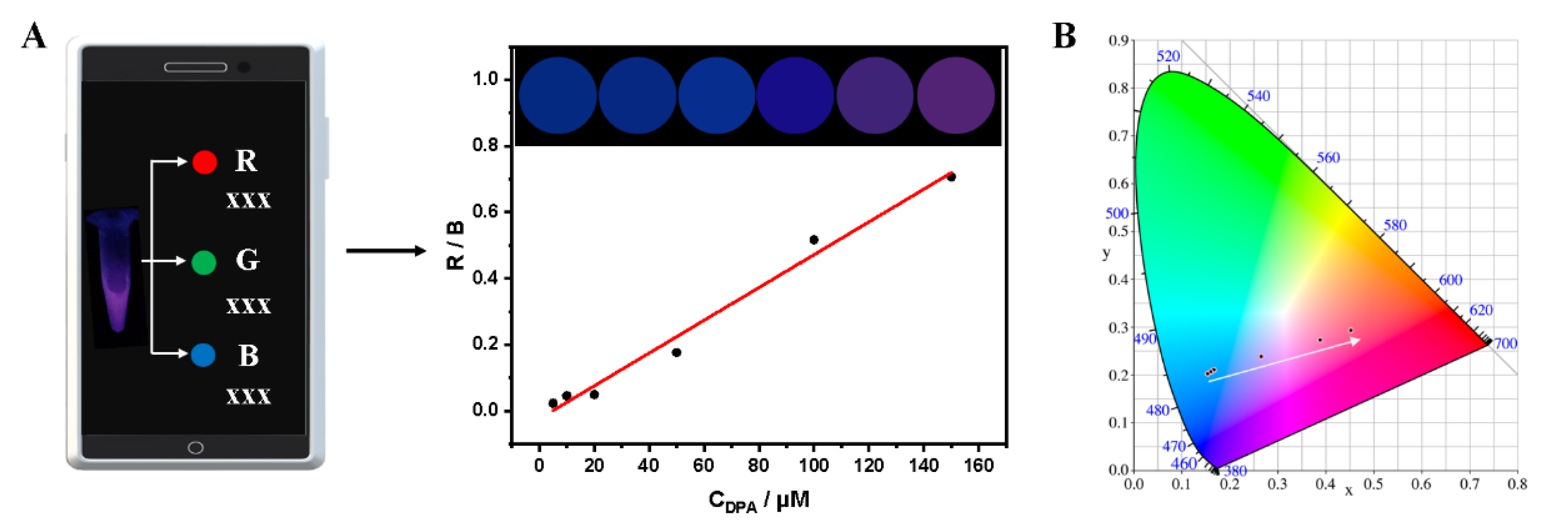
2.5. The Smartphone-Integrated Assay for DPA Detection
3. Results
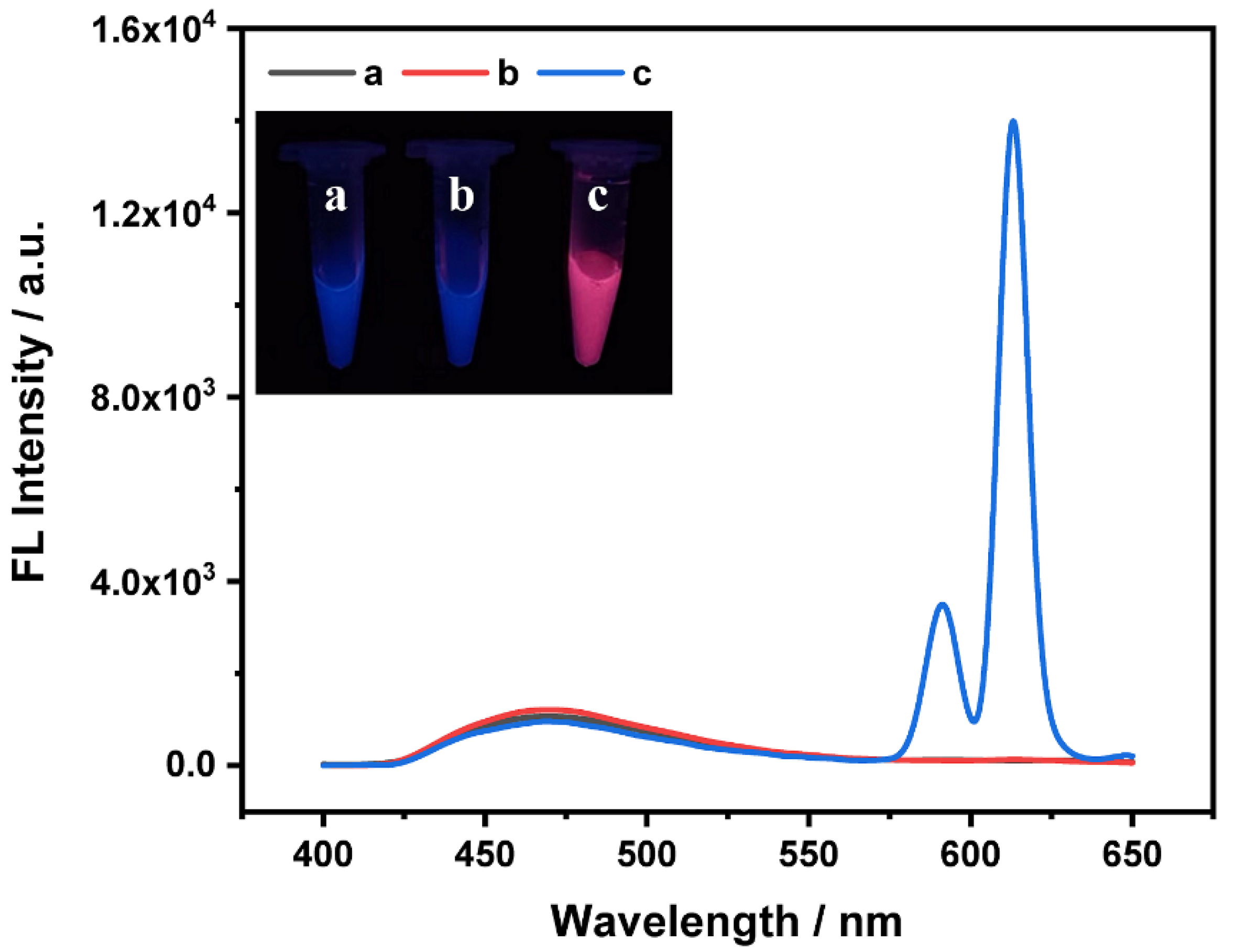
3.1. The Principle of Ratiometric Fluorescence Strategy for DPA Determination
3.2. Optimization of Detection Experimental Conditions
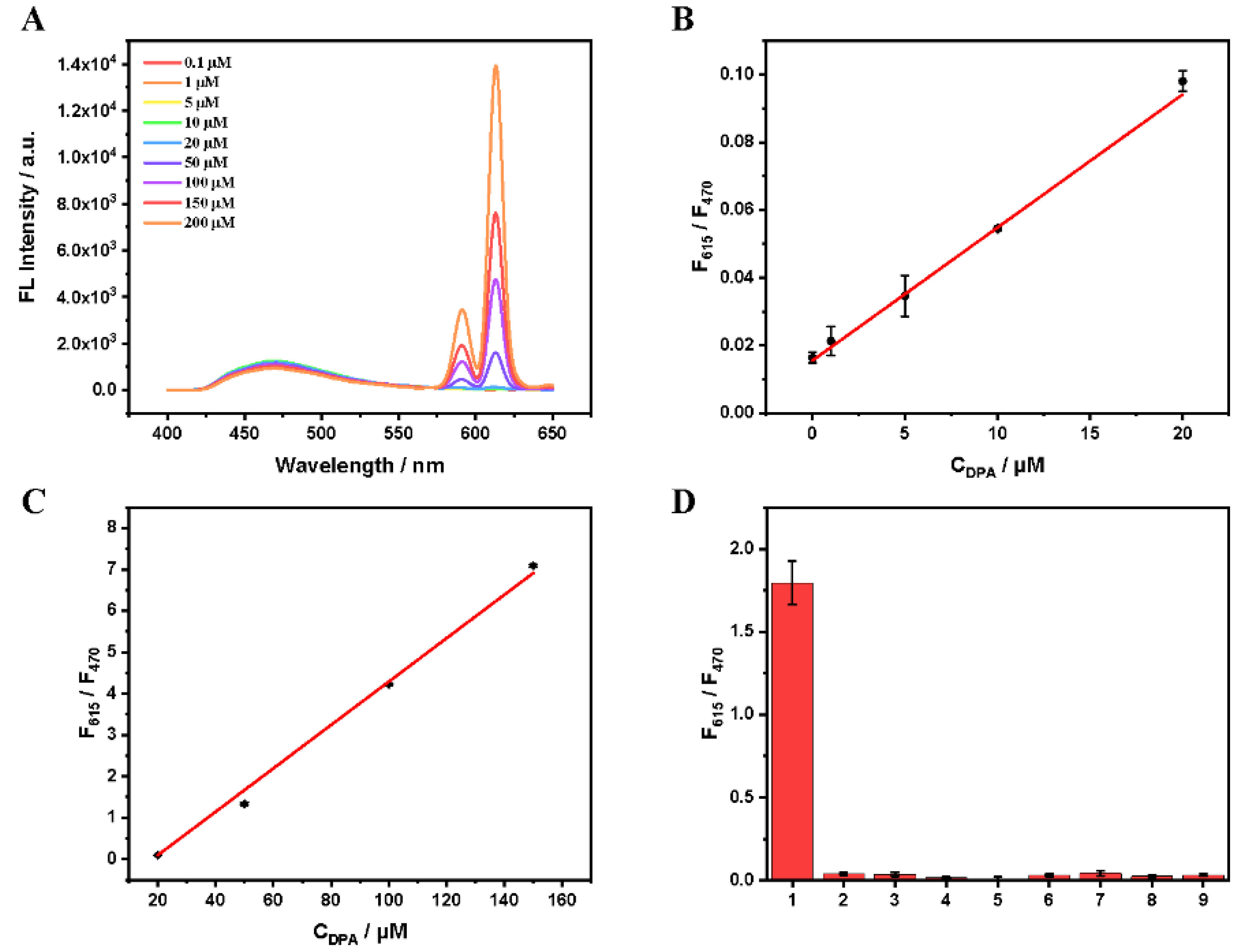
3.3. The DPA Detection with Eu3+/CDs Probe
3.4. Sensitive Detection of DPA in Real Samples
3.5. Smartphone-Integrated DPA Detection in Real Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- King, D.; Luna, V.; Cannons, A.; Cattani, J.; Amuso, P. Performance Assessment of Three Commercial Assays for Direct Detection of Bacillus anthracis Spores. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 3454–3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hurtle, W.; Bode, E.; Kulesh, D.A.; Kaplan, R.S.; Garrison, J.; Bridge, D.; House, M.; Frye, M.S.; Loveless, B.; Norwood, D. Detection of the Bacillus anthracis gyrA Gene by Using a Minor Groove Binder Probe. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Enserink, M. This Time it was Real: Knowledge of Anthrax Put to the Test. Science 2001, 294, 490–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Zhao, J.; Whitney, A.V.; Elam, J.W.; Duyne, R.P.V. Ultrastable Substrates for Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy: Al2O3 Overlayers Fabricated by Atomic Layer Deposition Yield Improved Anthrax Biomarker Detection. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 10304–10309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.L.; Chen, B.B.; He, J.H.; Li, C.M.; Li, Y.F.; Huang, C.Z. Anthrax biomarker: An ultrasensitive fluorescent ratiometry of dipicolinic acid by using terbium (III)-modified carbon dots. Talanta 2019, 191, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.W.; Huan, S.Y.; Yu, R.Q. Nanoparticle-based substrates for surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection of bacterial spores. Analyst 2012, 137, 3601–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, G.F.; Karp, S.; Sacks, L.E. Ultraviolet-Absorption Spectra of Dry Bacterial Spores. J. Bacteriol. 1965, 89, 984–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cable, M.L.; Kirby, J.P.; Sorasaenee, K.; Gray, H.B.; Ponce, A. Bacterial Spore Detection by [Tb3+(macrocycle)(dipicolinate)] Luminescence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 1474–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rode, L.J.; Foster, J.W. Germination of Bacterial Spores by Long-Chain Alkyl Amines. Nature 1960, 188, 1132–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratiu, I.A.; Bocos-Bintintan, V.; Patrut, A.; Moll, V.H.; Turner, M.; Thomasd, C.L.P. Discrimination of bacteria by rapid sensing their metabolic volatiles using an aspiration-type ion mobility spectrometer (a-IMS) and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry GC-MS. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 982, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Truong, T.V.; Bills, T.M.; Holt, B.C.; VanDerwerken, D.N.; Williams, J.R.; Acharya, A.; Robison, R.A.; Tolley, H.D.; Milton, L.; et al. GC/MS Method for Positive Detection of Bacillus anthracis Endospores. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 1637–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.L.; Liu, B.; Xu, L.; Jiao, H. Ratiometric fluorescence detection of anthrax biomarker 2,6-dipicolinic acid using hetero MOF sensors through ligand regulation. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 4392–4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.N.; Tong, C.L. Europium (III)-Modified Silver Nanoparticles as Ratiometric Colorimetric and Fluorescent Dual-Mode Probes for Selective Detection of Dipicolinic Acid in Bacterial Spores and Lake Waters. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 5469–5477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donmez, M.; Yilmaz, M.D.; Kilbas, B. Fluorescent detection of dipicolinic acid as a biomarker of bacterial spores using lanthanide-chelated gold nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 324, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Shen, X.K.; Jia, L.; Zhang, M.M.; Zhou, T.; Wei, Y.K. Facile ratiometric fluorapatite nanoprobes for rapid and sensitive bacterial spore biomarker detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 991–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, L.F.; Huang, K.Y.; Zhu, C.T.; Zhang, Q.; Peng, H.P.; Xia, X.H.; Chen, W.; Deng, H.H. Rare-Earth Eu3+/Gold Nanocluster Ensemble-Based Fluorescent Photoinduced Electron Transfer Sensor for Biomarker Dipicolinic Acid Detection. Langmuir 2021, 37, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donmez, M.; Oktem, H.A.; Yilmaz, M.D. Ratiometric fluorescence detection of an anthrax biomarker with Eu3+-chelated chitosan biopolymers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 180, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.R.; Wang, M.M.; Wang, X.S.; Yin, X.B. Boric-Acid-Functional Lanthanide Metal-Organic Frameworks for Selective Ratiometric Fluorescence Detection of Fluoride Ions. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 1930–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, M.C.; Deng, X.Z.; Chi, S.T.; Huang, L.Z.; Zhou, Y.B.; Shen, Y.N.; Chen, X. Ratiometric fluorometric determination of the anthrax biomarker 2, 6-dipicolinic acid by using europium (III)-doped carbon dots in a test stripe. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, M.D.; Oktem, H.A. Eriochrome Black T-Eu3+ Complex as a Ratiometric Colorimetric and Fluorescent Probe for the Detection of Dipicolinic Acid, a Biomarker of Bacterial Spores. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 4221–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Young, M.A.; Lyandres, O.; Duyne, R.P.V. Rapid Detection of an Anthrax Biomarker by Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 4484–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, K.; Zhang, B.H.; Lu, L.H. Europium-based fluorescence nanoparticle sensor for rapid and ultrasensitive detection of an anthrax biomarker. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.H.; Kim, J.S.; Sessler, J.L. Small molecule-based ratiometric fluorescence probes for cations, anions, and biomolecules. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4185–4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.Y.; Du, Q.Q.; Zhang, X.D.; Huang, Y.M. Ratiometric detection of tetracycline based on gold nanocluster enhanced Eu3+ fluorescence. Talanta 2020, 206, 120202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Li, H.X.; Zheng, W.S.; Su, X.G. Visual and Fluorescent Detection of Tyrosinase Activity by Using a Dual-Emission Ratiometric Fluorescence Probe. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 904–8909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.L.; Li, N.; Li, D.; Zhang, M.M.; Lin, Y.W.; Liu, Z.; Lin, X.; Shui, L. Cesium-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots as Ratiometric Fluorescence Sensors for Blood Glucose Detection. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 8437–8446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.J.; Yang, S.T.; Chen, L.F.; Zeng, Y.B.; Li, L.; Lin, Z.Y.; Guo, L.H.; Xu, W. Ultrahigh Efficient FRET Ratiometric Fluorescence Biosensor for Visual Detection of Alkaline Phosphatase Activity and Its Inhibitor. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 12922–12929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, T.; Wei, X.; Nie, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yan, Y.; Zhou, J. An eco-friendly molecularly imprinted fluorescence composite material based on carbon dots for fluorescent detection of 4-nitrophenol. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 2197–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.L.; Mei, Q.S.; Tao, Z.H.; Wu, H.T.; Zhao, M.Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.Q. A smartphone-integrated ratiometric fluorescence sensing platform for visual and quantitative point-of-care testing of tetracycline. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 148, 111791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Q.; Luo, J.J.; Deng, L.; Ma, F.H.; Yang, M.H. In situ incorporation of fluorophores in zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8) for ratio-dependent detecting a biomarker of anthrax spores. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 7114–7122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.H.; Wang, S.; Lu, S.S.; Sun, J.; Yang, X.R. A luminescent europium-dipicolinic acid nanohybrid for the rapid and selective sensing of pyrophosphate and alkaline phosphatase activity. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 7163–7170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.L.; Ji, X.Y.; Tao, Z.H.; Zhou, X.; Hao, Z.; Wang, X.K.; Gao, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.Q. Dual stimuli-responsive lanthanide-based phosphors for an advanced full-color anti-counterfeiting system. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 15573–15578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.W.; Li, X.; Xu, S.L.; Guo, S.J.; Xue, Q.W.; Wang, H.S. Efficient ratiometric fluorescence probe based on dual-emission luminescent lanthanide coordination polymer for amyloid β-peptide detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 352, 131052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, C.F.; Hao, Y.; Tian, X.M.; He, Y.L.; Li, J.; Shahid, M.; Iyer, P.K.; Gao, R.X. Aggregation and Binding-Directed FRET Modulation of Conjugated Polymer Materials for Selective and Point-of-Care Monitoring of Serum Albumins. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 10685–10694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Malika, A.H.; Iyer, P.K. FRET-assisted selective detection of flavins via cationic conjugated polyelectrolyte under physiological conditions. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 4439–4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.K.; Hussain, S.; Iyer, P.K. Aggregation-Induced FRET via Polymer-Surfactant Complexation: A New Strategy for the Detection of Spermine. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 7358–7364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Zehra, N.; Choudhury, A.; Iyer, P.K. Wearable Sensing Devices for Point of Care Diagnostics. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 47–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | Spiked (μM) | Found | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Milk | 0 | - | - | - |
| 10 | 9.9 | 99 | 1.65 | |
| 20 | 19.8 | 99 | 4.05 | |
| 50 | 48.5 | 97 | 2.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Wu, J.; Hu, H.; Liu, F.; Wang, J. A Smartphone Integrated Platform for Ratiometric Fluorescent Sensitive and Selective Determination of Dipicolinic Acid. Biosensors 2022, 12, 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12080668
Li X, Wu J, Hu H, Liu F, Wang J. A Smartphone Integrated Platform for Ratiometric Fluorescent Sensitive and Selective Determination of Dipicolinic Acid. Biosensors. 2022; 12(8):668. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12080668
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiang, Junsong Wu, Huaguang Hu, Fangfang Liu, and Jialian Wang. 2022. "A Smartphone Integrated Platform for Ratiometric Fluorescent Sensitive and Selective Determination of Dipicolinic Acid" Biosensors 12, no. 8: 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12080668
APA StyleLi, X., Wu, J., Hu, H., Liu, F., & Wang, J. (2022). A Smartphone Integrated Platform for Ratiometric Fluorescent Sensitive and Selective Determination of Dipicolinic Acid. Biosensors, 12(8), 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12080668





