Electrochemical Aptasensor for the Detection of the Key Virulence Factor YadA of Yersinia enterocolitica
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Plasmids
2.2. SsDNA Library, Primers and Aptamer Sequences
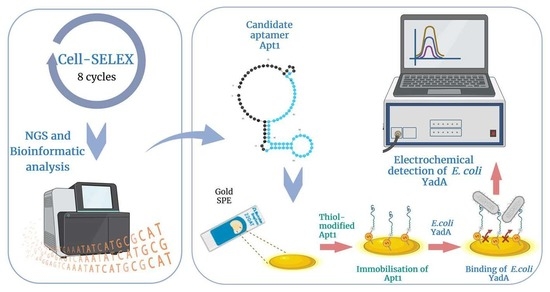
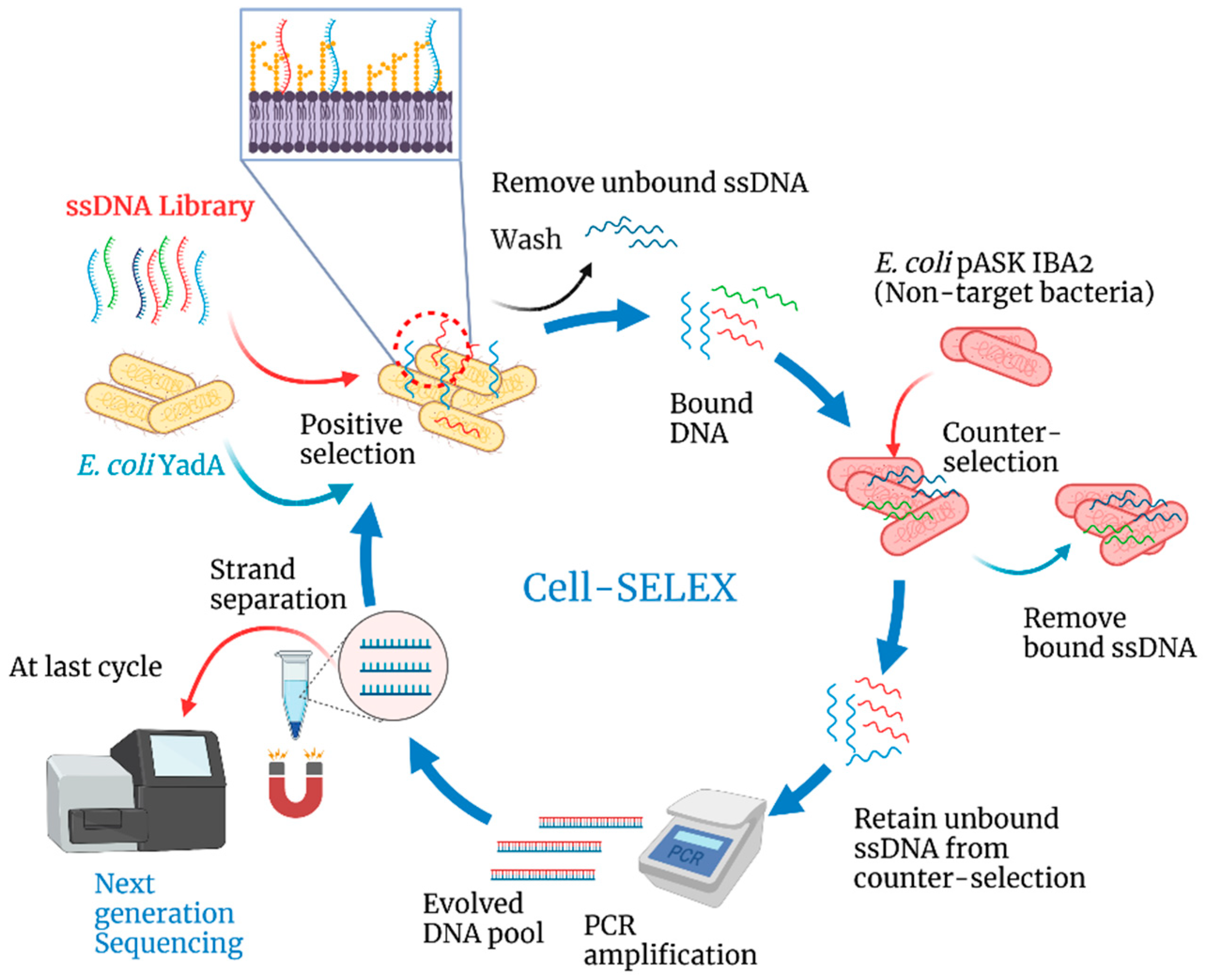
2.3. Cell-SELEX
2.4. Binding Experiments
2.5. Electrochemical Apparatus and Electrodes
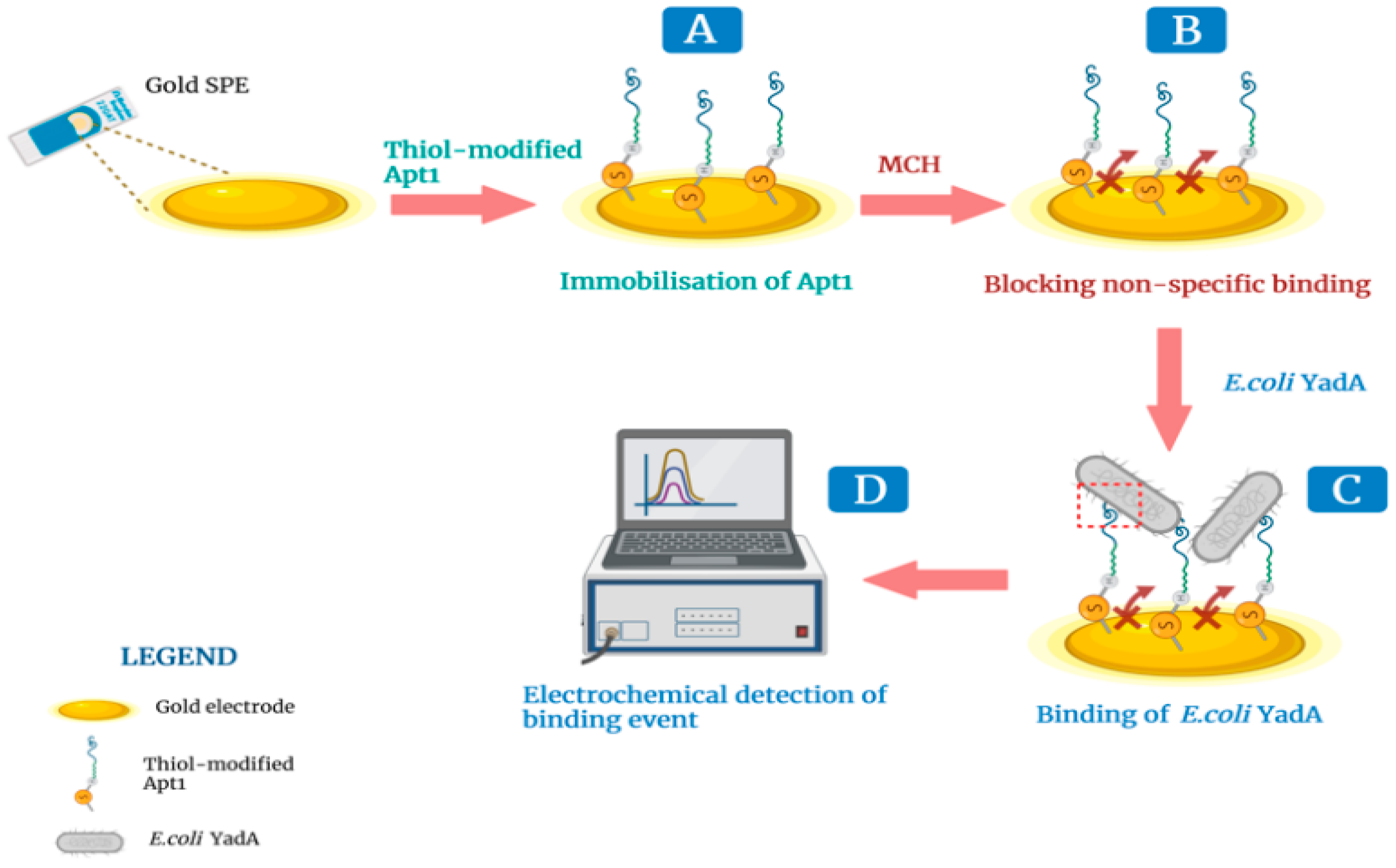
2.6. Development and Evaluation of the Aptasensor
2.6.1. Assembly of the Aptasensor on an Au SPE
2.6.2. Evaluation of the DNA Aptasensor in Standard Solutions
2.7. Electrochemical Measurements
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Selection of Aptamers against YadA through Cell-SELEX
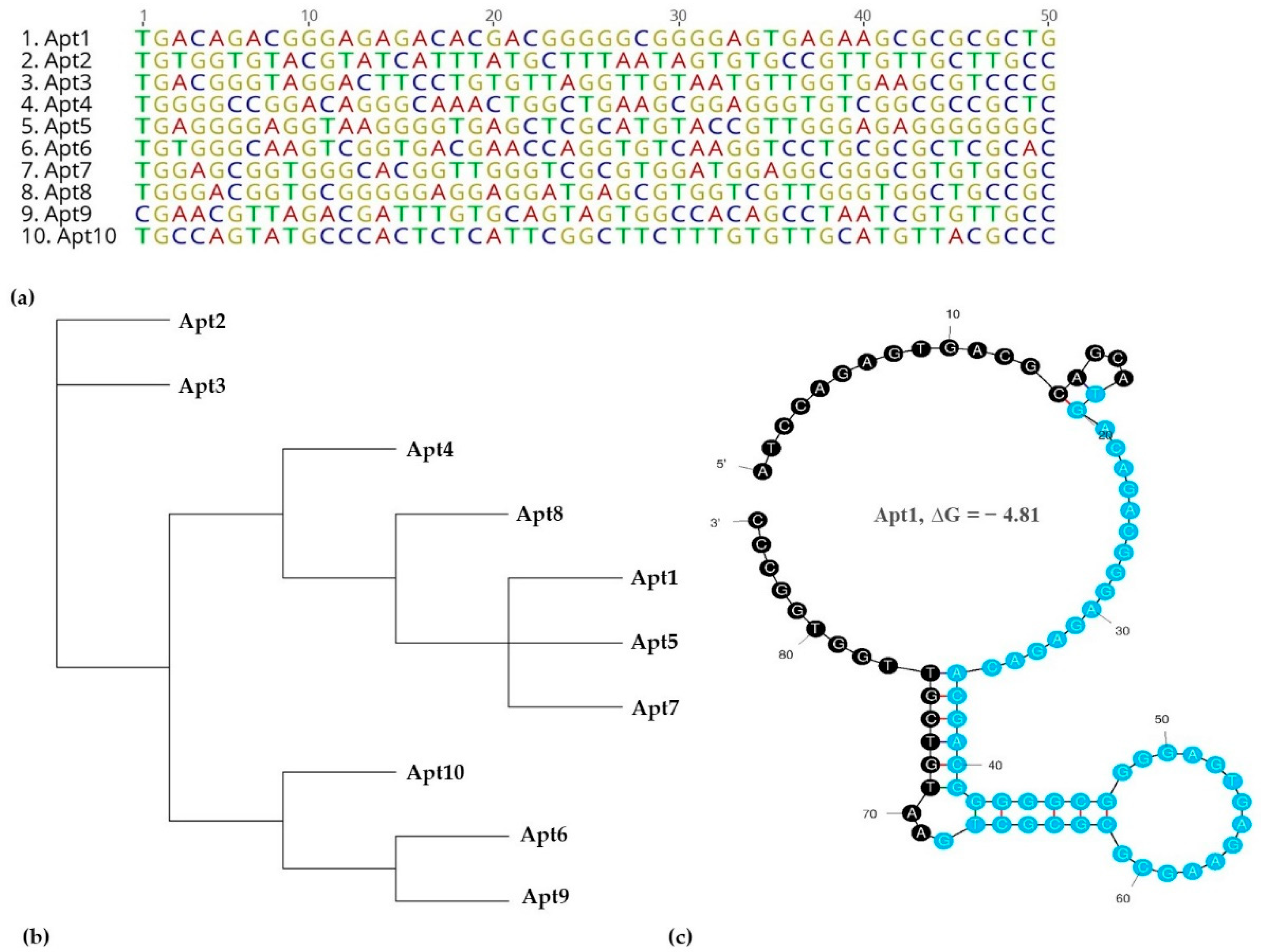
3.2. Identification of Aptamer Candidates Aided by Bioinformatics Tools
3.3. Determination of Apt1 Affinity to YadA
3.4. Electrochemical Evaluation of Aptasensor Assembly
3.5. Optimization of Experimental Conditions
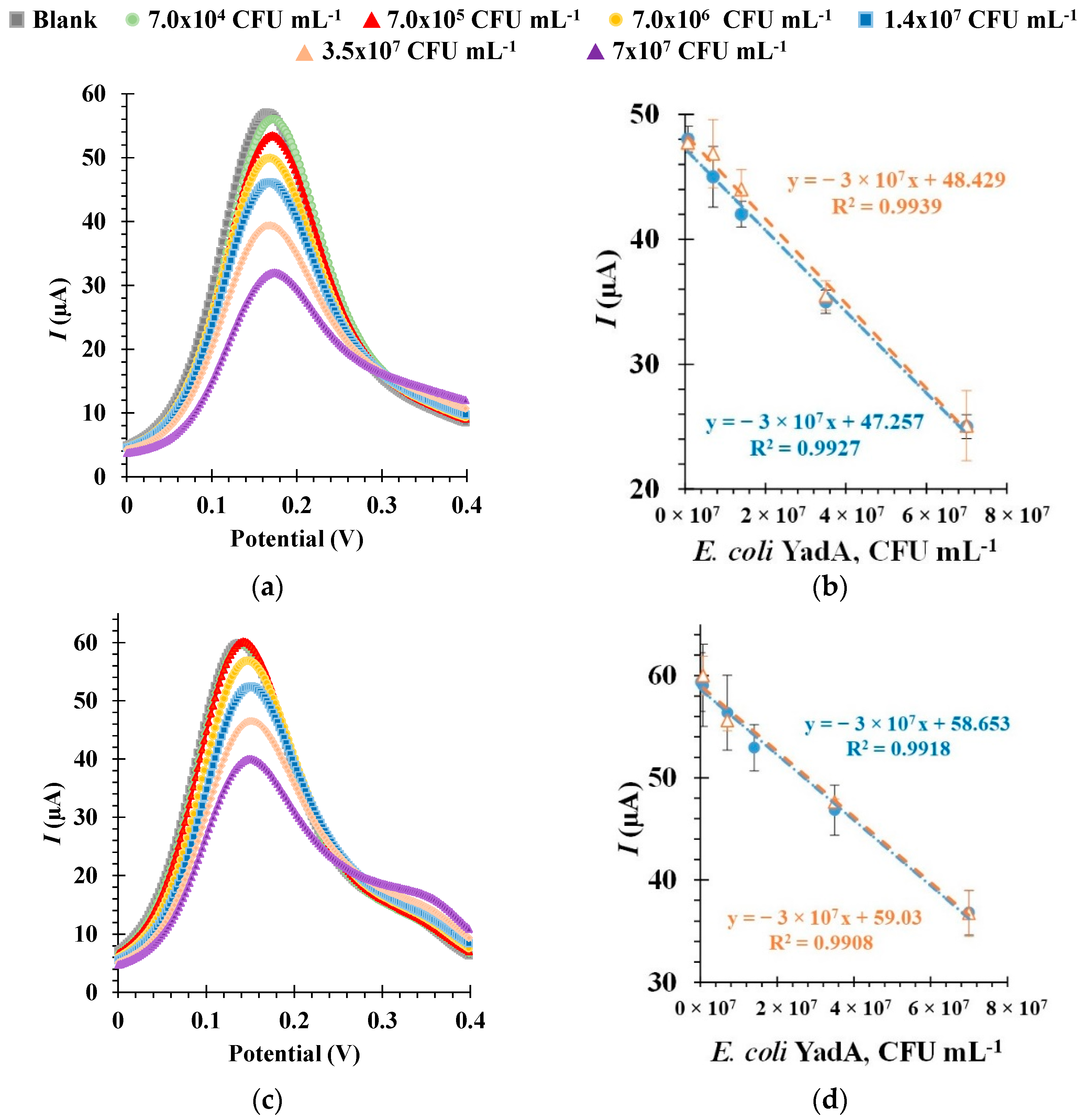
3.6. Electrochemical Detection of E. coli YadA
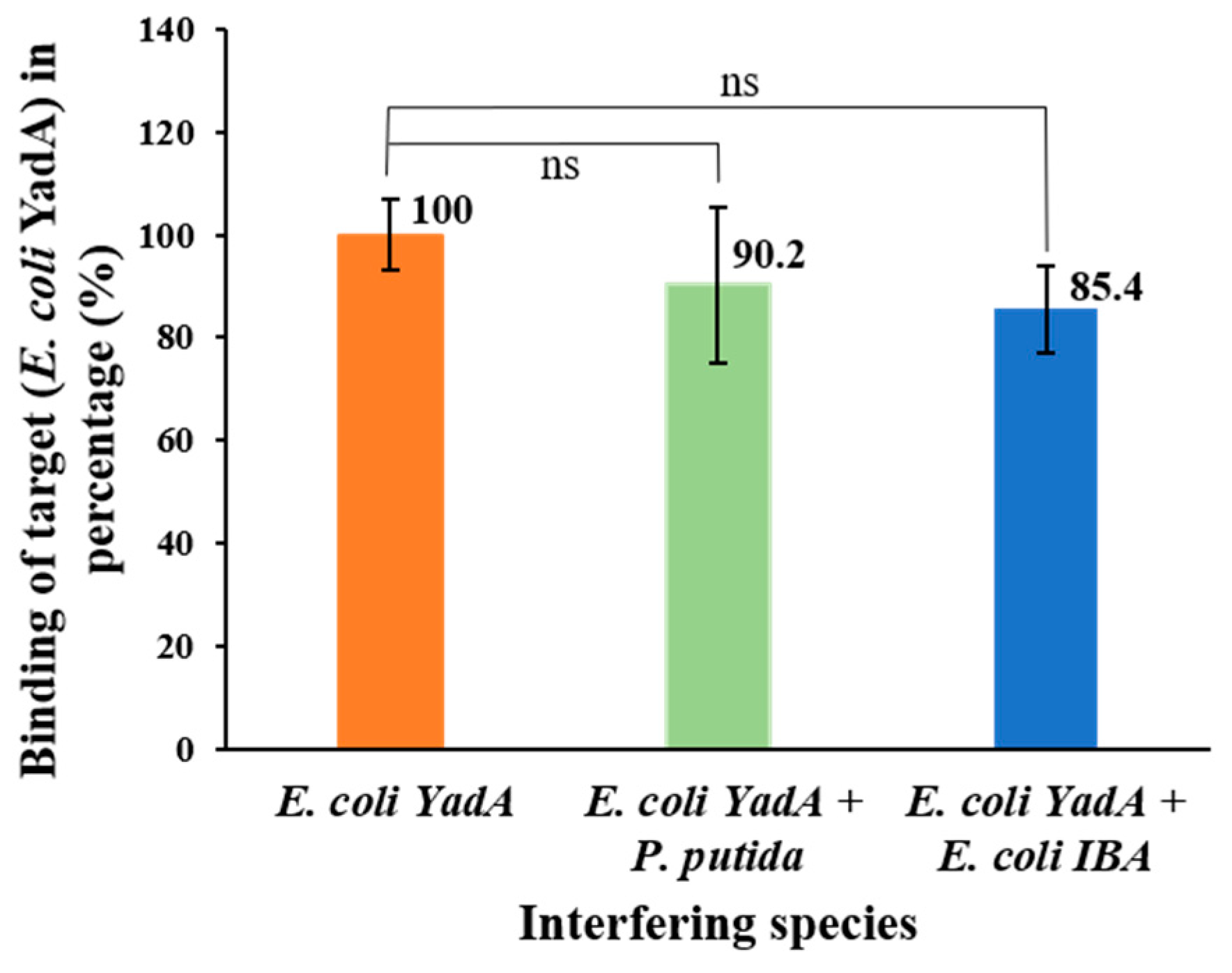
3.7. Selective Detection of E. coli YadA
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Urdea, M.; Penny, L.A.; Olmsted, S.S.; Giovanni, M.Y.; Kaspar, P.; Shepherd, A.; Wilson, P.; Dahl, C.A.; Buchsbaum, S.; Moeller, G.; et al. Requirements for high impact diagnostics in the developing world. Nature 2006, 444, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, B.; Wang, W.; Arshad, M.I.; Khurshid, M.; Muzammil, S.; Rasool, M.H.; Nisar, M.A.; Alvi, R.F.; Aslam, M.A.; Qamar, M.U.; et al. Antibiotic resistance: A rundown of a global crisis. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sande, M.G.; Rodrigues, J.L.; Ferreira, D.; Silva, C.J.; Rodrigues, L.R. Novel biorecognition elements against pathogens in the design of state-of-the-art diagnostics. Biosensors 2021, 11, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, M.; Yelamanchili, V.S. Yersinia enterocolitica. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022; p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Jagielski, M.; Rastawicki, W.; Kałuzewski, S.; Gierczyński, R. Yersiniosis—Unappreciated infectious disease. Przeglaąd Epidemiol. 2002, 56, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Bancerz-Kisiel, A.; Szweda, W. Yersiniosis—A zoonotic foodborne disease of relevance to public health. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2015, 22, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheyne, B.M.; Van Dyke, M.I.; Anderson, W.B.; Huck, P.M. The detection of Yersinia enterocolitica in surface water by quantitative PCR amplification of the ail and yadA genes. J. Water Health 2010, 8, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, M.; Shehzad, A.; Raza, H.; Niazi, S.; Khan, I.M.; Akhtar, W.; Safdar, W.; Wang, Z. A comprehensive review on the prevalence, pathogenesis and detection of: Yersinia enterocolitica. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 41010–41021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gupta, V.; Gulati, P.; Bhagat, N.; Dhar, M.S.; Virdi, J.S. Detection of Yersinia enterocolitica in food: An overview. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 34, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath, P.; Kabir, A.; Doust, S.K.; Kreais, Z.J.; Ray, A. Detection of bacterial and viral pathogens using photonic point-of-care devices. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.M.; Lv, S.; Zhang, W.; Cui, Y. Microfluidic Point-of-Care (POC) Devices in Early Diagnosis: A Review of Opportunities and Challenges. Sensors 2022, 22, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucherenko, I.S.; Soldatkin, O.O.; Dzyadevych, S.V.; Soldatkin, A.P. Electrochemical biosensors based on multienzyme systems: Main groups, advantages and limitations—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1111, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furst, A.L.; Francis, M.B. Impedance-Based Detection of Bacteria. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 700–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesewski, E.; Johnson, B.N. Electrochemical biosensors for pathogen detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 159, 112214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ropero-Vega, J.L.; Redondo-Ortega, J.F.; Galvis-Curubo, Y.J.; Rondón-Villarreal, P.; Flórez-Castillo, J.M. A bioinspired peptide in tir protein as recognition molecule on electrochemical biosensors for the detection of E. coli O157:H7 in an aqueous matrix. Molecules 2021, 26, 2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, R.; Lu, Y.; Osman, E.; Saxena, S.; Zhang, Z.; Qian, S.; Pollinzi, A.; Smieja, M.; Li, Y.; Soleymani, L.; et al. DNAzyme-Immobilizing Microgel Magnetic Beads Enable Rapid, Specific, Culture-Free, and Wash-Free Electrochemical Quantification of Bacteria in Untreated Urine. ACS Sens. 2022, 7, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salimiyan Rizi, K.; Hatamluyi, B.; Darroudi, M.; Meshkat, Z.; Aryan, E.; Soleimanpour, S.; Rezayi, M. PCR-free electrochemical genosensor for Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex detection based on two-dimensional Ti3C2 Mxene-polypyrrole signal amplification. Microchem. J. 2022, 179, 107467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Qi, X.; Wu, J.; Xu, L.; Wan, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, Q. Ultrasensitive, label-free voltammetric determination of norfloxacin based on molecularly imprinted polymers and Au nanoparticle-functionalized black phosphorus nanosheet nanocomposite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 436, 129107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, M.A.; Halpern, J.M. Guide to Selecting a Biorecognition Element for Biosensors. Bioconjug. Chem. 2018, 29, 3231–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, J.L.; Ferreira, D.; Rodrigues, L.R. Synthetic biology strategies towards the development of new bioinspired technologies for medical applications. In Bioinspired Materials for Medical Applications; Rodrigues, L., Mota, M., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Kidlington, UK, 2017; pp. 451–497. ISBN 9780081007464. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Alkhamis, O.; Canoura, J.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, Y. Advances and Challenges in Small-Molecule DNA Aptamer Isolation, Characterization, and Sensor Development. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 16800–16823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sola, M.; Menon, A.P.; Moreno, B.; Meraviglia-Crivelli, D.; Soldevilla, M.M.; Cartón-García, F.; Pastor, F. Aptamers Against Live Targets: Is In Vivo SELEX Finally Coming to the Edge? Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 21, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, S.; Pinnaka, A.K.; Singhal, N.K. Naked eye colorimetric detection of Escherichia coli using aptamer conjugated graphene oxide enclosed Gold nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 329, 129100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savory, N.; Lednor, D.; Tsukakoshi, K.; Abe, K.; Yoshida, W.; Ferri, S.; Jones, B.V.; Ikebukuro, K. In silico maturation of binding-specificity of DNA aptamers against Proteus mirabilis. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2013, 110, 2573–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.H.; Wu, J.J.; Lee, G. Bin Screening of highly-specific aptamers and their applications in paper-based microfluidic chips for rapid diagnosis of multiple bacteria. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 284, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Shorie, M.; Sabherwal, P. Electrochemical aptasensor using boron-carbon nanorods decorated by nickel nanoparticles for detection of E. coli O157:H7. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoaib, M.; Shehzad, A.; Mukama, O.; Raza, H.; Niazi, S.; Khan, I.M.; Ali, B.; Akhtar, W.; Wang, Z. Selection of potential aptamers for specific growth stage detection of: Yersinia enterocolitica. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 24743–24752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, K.; Jiang, H.; Fang, Y.; Wang, L.; Jiang, D. Emerging electrochemical biosensing approaches for detection of allergen in food samples: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 121, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmi, N.; Hasanzadeh, M.; Willander, M.; Nur, O. Recent progress on the electrochemical biosensing of Escherichia coli O157:H7: Material and methods overview. Biosensors 2020, 10, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinti, S.; Volpe, G.; Piermarini, S.; Delibato, E.; Palleschi, G. Electrochemical Biosensors for Rapid Detection of Foodborne Salmonella: A Critical Overview. Sensors 2017, 17, 1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subjakova, V.; Oravczova, V.; Tatarko, M.; Hianik, T. Advances in electrochemical aptasensors and immunosensors for detection of bacterial pathogens in food. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 389, 138724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linke, D.; Riess, T.; Autenrieth, I.B.; Lupas, A.; Kempf, V.A.J. Trimeric autotransporter adhesins: Variable structure, common function. Trends Microbiol. 2006, 14, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bancerz-Kisiel, A.; Pieczywek, M.; Łada, P.; Szweda, W. The Most Important Virulence Markers of Yersinia enterocolitica and Their Role during Infection. Genes 2018, 9, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mühlenkamp, M.; Oberhettinger, P.; Leo, J.C.; Linke, D.; Schütz, M.S. Yersinia adhesin A (YadA)—Beauty & beast. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 305, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mühlenkamp, M.C.; Hallström, T.; Autenrieth, I.B.; Bohn, E.; Linke, D.; Rinker, J.; Riesbeck, K.; Singh, B.; Leo, J.C.; Hammerschmidt, S.; et al. Vitronectin binds to a specific stretch within the head region of yersinia adhesin a and thereby modulates Yersinia enterocolitica host interaction. J. Innate Immun. 2017, 9, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meuskens, I.; Leva-Bueno, J.; Millner, P.; Schütz, M.; Peyman, S.A.; Linke, D. The Trimeric Autotransporter Adhesin YadA of Yersinia enterocolitica Serotype O:9 Binds Glycan Moieties. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 738818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberhettinger, P.; Schütz, M.; Raddatz, G.; Keller, H.; Autenrieth, I.B.; Linke, D. The sequence of the pYV virulence plasmid from Yersinia enterocolitica strain WA-314 biogroup 1B serotype O:8. Plasmid 2011, 65, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosskinsky, U.; Schütz, M.; Fritz, M.; Schmid, Y.; Lamparter, M.C.; Szczesny, P.; Lupas, A.N.; Autenrieth, I.B.; Linke, D. A conserved glycine residue of trimeric autotransporter domains plays a key role in Yersinia adhesin A autotransport. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 9011–9019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, D.; Barbosa, J.; Sousa, D.A.; Silva, C.; Melo, L.D.R.; Avci-Adali, M.; Wendel, H.P.; Rodrigues, L.R. Selection of aptamers against triple negative breast cancer cells using high throughput sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Zhao, Y. Cyclic voltammetry measurements of electroactive surface area of porous nickel: Peak current and peak charge methods and diffusion layer effect. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 233, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, A.R.; Moreira, F.T.C.; Fernandes, R.; Sales, M.G.F. Novel and simple electrochemical biosensor monitoring attomolar levels of miRNA-155 in breast cancer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 80, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Wang, X.; Xu, K.; Li, Q.; Ning, L.; Yang, X. Selection of highly specific aptamers to Vibrio parahaemolyticus using cell-SELEX powered by functionalized graphene oxide and rolling circle amplification. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1052, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.R.; Song, M.Y.; Chan Kim, B. Rapid isolation of bacteria-specific aptamers with a non-SELEX-based method. Anal. Biochem. 2020, 591, 113542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamula, C.L.A.; Peng, H.; Wang, Z.; Tyrrell, G.J.; Li, X.F.; Le, X.C. An improved SELEX technique for selection of DNA aptamers binding to M-type 11 of Streptococcus pyogenes. Methods 2016, 97, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolm, C.; Cervenka, I.; Aschl, U.J.; Baumann, N.; Jakwerth, S.; Krska, R.; Mach, R.L.; Sommer, R.; DeRosa, M.C.; Kirschner, A.K.T.; et al. DNA aptamers against bacterial cells can be efficiently selected by a SELEX process using state-of-the art qPCR and ultra-deep sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoinka, J.; Berezhnoy, A.; Dao, P.; Sauna, Z.E.; Gilboa, E.; Przytycka, T.M. Large scale analysis of the mutational landscape in HT-SELEX improves aptamer discovery. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 5699–5707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.S.; Sekhon, S.S.; Shin, W.R.; Kim, H.C.; Min, J.; Ahn, J.Y.; Kim, Y.H. Detecting and discriminating Shigella sonnei using an aptamer-based fluorescent biosensor platform. Molecules 2017, 22, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, D.; Bai, Y.; Cui, Y.; Wang, D.; Shi, X. Identification and characterization of two high affinity aptamers specific for Salmonella enteritidis. Food Control 2019, 106, 106719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, J.L.; Formisano, N.; Estrela, P.; Carrara, S.; Tkac, J. Electrochemical biosensors and nanobiosensors. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Angell, D.H.; Dickinson, T. The kinetics of the ferrous/ferric and ferro/ferricyanide reactions at platinum and gold electrodes. Part I. Kinetics at bare-metal surfaces. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1972, 35, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagopoulou, M.A.; Stergiou, D.V.; Roussis, I.G.; Prodromidis, M.I. Impedimetric biosensor for the assessment of the clotting activity of rennet. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 8629–8636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.C.; Cokeliler, D.; Gunasekaran, S. Reduced Graphene Oxide/Carbon Nanotube/Gold Nanoparticles Nanocomposite Functionalized Screen-Printed Electrode for Sensitive Electrochemical Detection of Endocrine Disruptor Bisphenol A. Electroanalysis 2015, 27, 2527–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.K.H.; Ge, B.; Yu, H.Z. Aptamer-based biosensors for label-free voltammetric detection of lysozyme. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 5158–5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirceski, V.; Gulaboski, R.; Lovric, M.; Bogeski, I.; Kappl, R.; Hoth, M. Square-Wave Voltammetry: A Review on the Recent Progress. Electroanalysis 2013, 25, 2411–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Figueroa-Miranda, G.; Feng, L.; Shiu, S.C.C.; Dirkzwager, R.M.; Cheung, Y.W.; Tanner, J.A.; Schöning, M.J.; Offenhäusser, A.; Mayer, D. Aptamer-based electrochemical biosensor for highly sensitive and selective malaria detection with adjustable dynamic response range and reusability. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucero Estrada, C.S.M.; del CarmenVelázquez, L.; Favier, G.I.; Di Genaro, M.S.; Escudero, M.E. Detection of Yersinia spp. in meat products by enrichment culture, immunomagnetic separation and nested PCR. Food Microbiol. 2012, 30, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magliulo, M.; Simoni, P.; Guardigli, M.; Michelini, E.; Luciani, M.; Lelli, R.; Roda, A. A rapid multiplexed chemiluminescent immunoassay for the detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7, Yersinia enterocolitica, Salmonella typhimurium, and Listeria monocytogenes pathogen bacteria. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 4933–4939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhan, A.; Lee, J.; Park, M.K.; Oh, J.H. Rapid detection of Yersinia enterocolitica using a single–walled carbon nanotube-based biosensor for Kimchi product. LWT 2019, 108, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, B.K.; Lee, W.; Chun, B.S.; Bae, Y.M.; Lee, W.H.; Choi, J.W. Surface plasmon resonance immunosensor for the detection of Yersinia enterocolitica. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2005, 257–258, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savas, S.; Altintas, Z. Graphene quantum dots as nanozymes for electrochemical sensing of Yersinia enterocolitica in milk and human serum. Materials 2019, 12, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rusak, L.A.; de Castro Lisboa Pereira, R.; Freitag, I.G.; Hofer, C.B.; Hofer, E.; Asensi, M.D.; Vallim, D.C. Rapid detection of Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O:3 using a duplex PCR assay. J. Microbiol. Methods 2018, 154, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielkoszynski, T.; Moghaddam, A.; Bäckman, A.; Broden, J.; Piotrowski, R.; Mond-Paszek, R.; Kozarenko, A.; Ny, T.; Wilczynska, M. Novel diagnostic ELISA test for discrimination between infections with Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 37, 2301–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dalby, T.; Rasmussen, E.; Schiellerup, P.; Krogfelt, K.A. Development of an LPS-based ELISA for diagnosis of Yersinia enterocolitica O:3 infections in Danish patients: A follow-up study. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| Cycles | E. coli YadA (µL) | Incubation (minutes) | Washes (After Selection) | PCR (Cycles) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 500 | 60 | 2 | 35 |
| 2 | 500 | 60 | 2 | 30 |
| 3 | 500 | 60 | 3 | 30 |
| 4 | 400 | 50 | 3 | 30 |
| 5 | 400 (counter selection) | 50 | 3 | 20 |
| 6 | 400 | 40 | 4 | 25 |
| 7 | 350 (counter selection) | 35 | 4 | 15 |
| 8 | 350 | 35 | 4 | 20 |
| Aptamer | Sequences (5′–3′) | Copies |
|---|---|---|
| Apt1 | TGACAGACGGGAGAGACACGACGGGGGCGGGGAGTGAGAAGCGCGCGCTG | 6647 |
| Apt2 | TGTGGTGTACGTATCATTTATGCTTTAATAGTGTGCCGTTGTTGCTTGCC | 4531 |
| Apt3 | TGACGGGTAGGACTTCCTGTGTTAGGTTGTAATGTTGGTGAAGCGTCCCG | 1755 |
| Apt4 | TGGGGCCGGACAGGGCAAACTGGCTGAAGCGGAGGGTGTCGGCGCCGCTC | 1443 |
| Apt5 | TGAGGGGAGGTAAGGGGTGAGCTCGCATGTACCGTTGGGAGAGGGGGGGC | 1281 |
| Apt6 | TGTGGGCAAGTCGGTGACGAACCAGGTGTCAAGGTCCTGCGCGCTCGCAC | 1214 |
| Apt7 | TGGAGCGGTGGGCACGGTTGGGTCGCGTGGATGGAGGCGGGCGTGTGCGC | 1168 |
| Apt8 | TGGGACGGTGCGGGGGAGGAGGATGAGCGTGGTCGTTGGGTGGCTGCCGC | 1080 |
| Apt9 | CGAACGTTAGACGATTTGTGCAGTAGTGGCCACAGCCTAATCGTGTTGCC | 1023 |
| Apt10 | TGCCAGTATGCCCACTCTCATTCGGCTTCTTTGTGTTGCATGTTACGCCC | 1012 |
| Biorecognition Element | Detection Method | LOD | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yersinia-specific antibody; yadA gene | immunomagnetic separation and nested PCR | 104 to 107 CFU mL−1 | [56] |
| Y. enterocolitica-specific antibody | surface plasmon resonance-based immunosensor | 102 to 107 CFU mL−1 | [59] |
| Y. enterocolitica-specific antibody | sandwich chemiluminescent enzyme immunoassay | 104−105 CFU mL−1 | [57] |
| Y. enterocolitica-specific antibody | single-walled carbon nanotube-based biosensor | 104 CFU mL−1 | [58] |
| Y. enterocolitica-specific monoclonal antibody | graphene quantum dots-based immunosensor | 30 CFU mL−1 | [60] |
| YadA aptamer | Cell-SELEX and electrochemical biosensor | 104 CFU mL−1 | Present study |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sande, M.G.; Ferreira, D.; Rodrigues, J.L.; Melo, L.D.R.; Linke, D.; Silva, C.J.; Moreira, F.T.C.; Sales, M.G.F.; Rodrigues, L.R. Electrochemical Aptasensor for the Detection of the Key Virulence Factor YadA of Yersinia enterocolitica. Biosensors 2022, 12, 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12080614
Sande MG, Ferreira D, Rodrigues JL, Melo LDR, Linke D, Silva CJ, Moreira FTC, Sales MGF, Rodrigues LR. Electrochemical Aptasensor for the Detection of the Key Virulence Factor YadA of Yersinia enterocolitica. Biosensors. 2022; 12(8):614. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12080614
Chicago/Turabian StyleSande, Maria G., Débora Ferreira, Joana L. Rodrigues, Luís D. R. Melo, Dirk Linke, Carla J. Silva, Felismina T. C. Moreira, Maria Goreti F. Sales, and Ligia R. Rodrigues. 2022. "Electrochemical Aptasensor for the Detection of the Key Virulence Factor YadA of Yersinia enterocolitica" Biosensors 12, no. 8: 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12080614
APA StyleSande, M. G., Ferreira, D., Rodrigues, J. L., Melo, L. D. R., Linke, D., Silva, C. J., Moreira, F. T. C., Sales, M. G. F., & Rodrigues, L. R. (2022). Electrochemical Aptasensor for the Detection of the Key Virulence Factor YadA of Yersinia enterocolitica. Biosensors, 12(8), 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12080614