Magnetoimpedance Biosensors and Real-Time Healthcare Monitors: Progress, Opportunities, and Challenges
Abstract
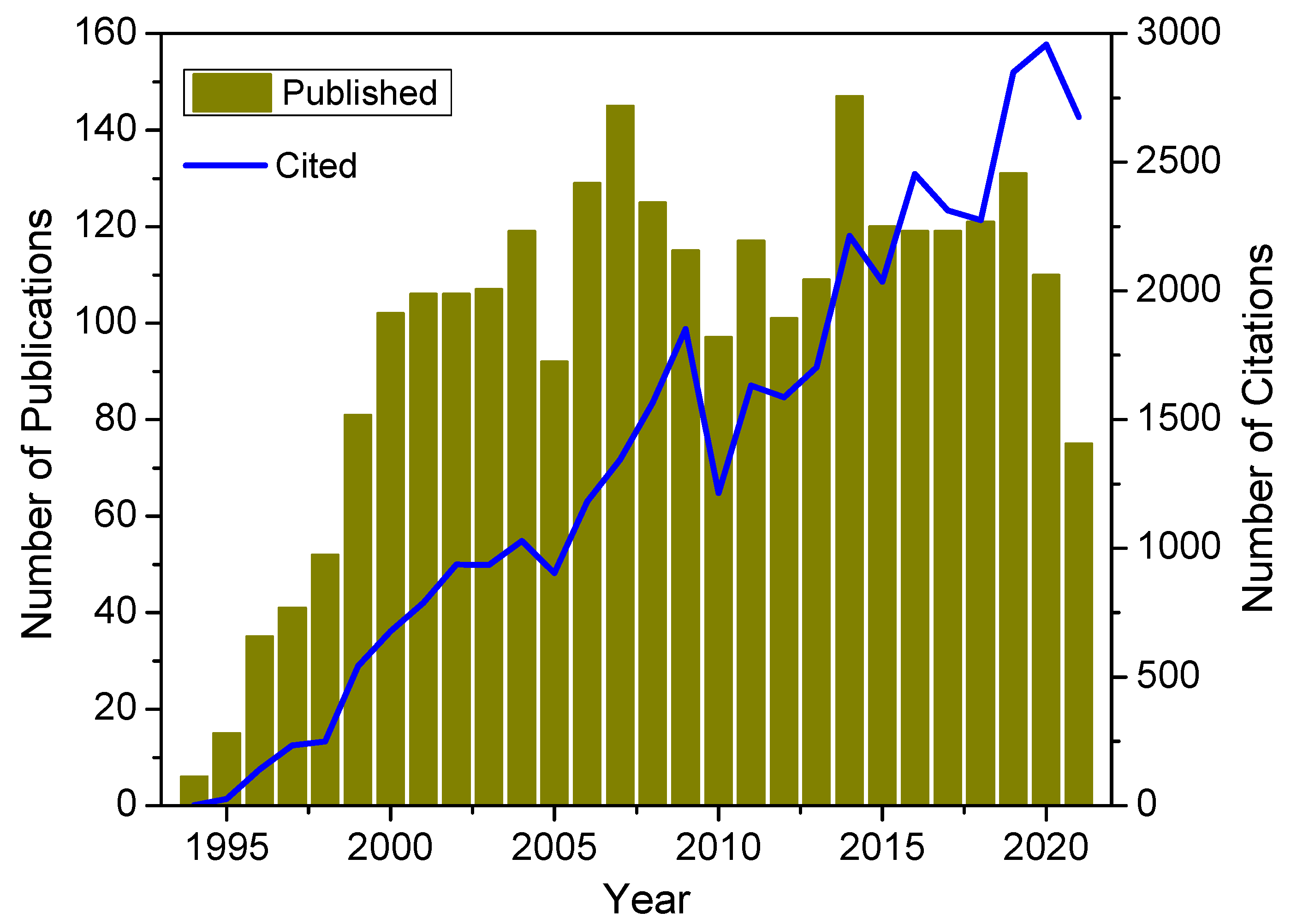
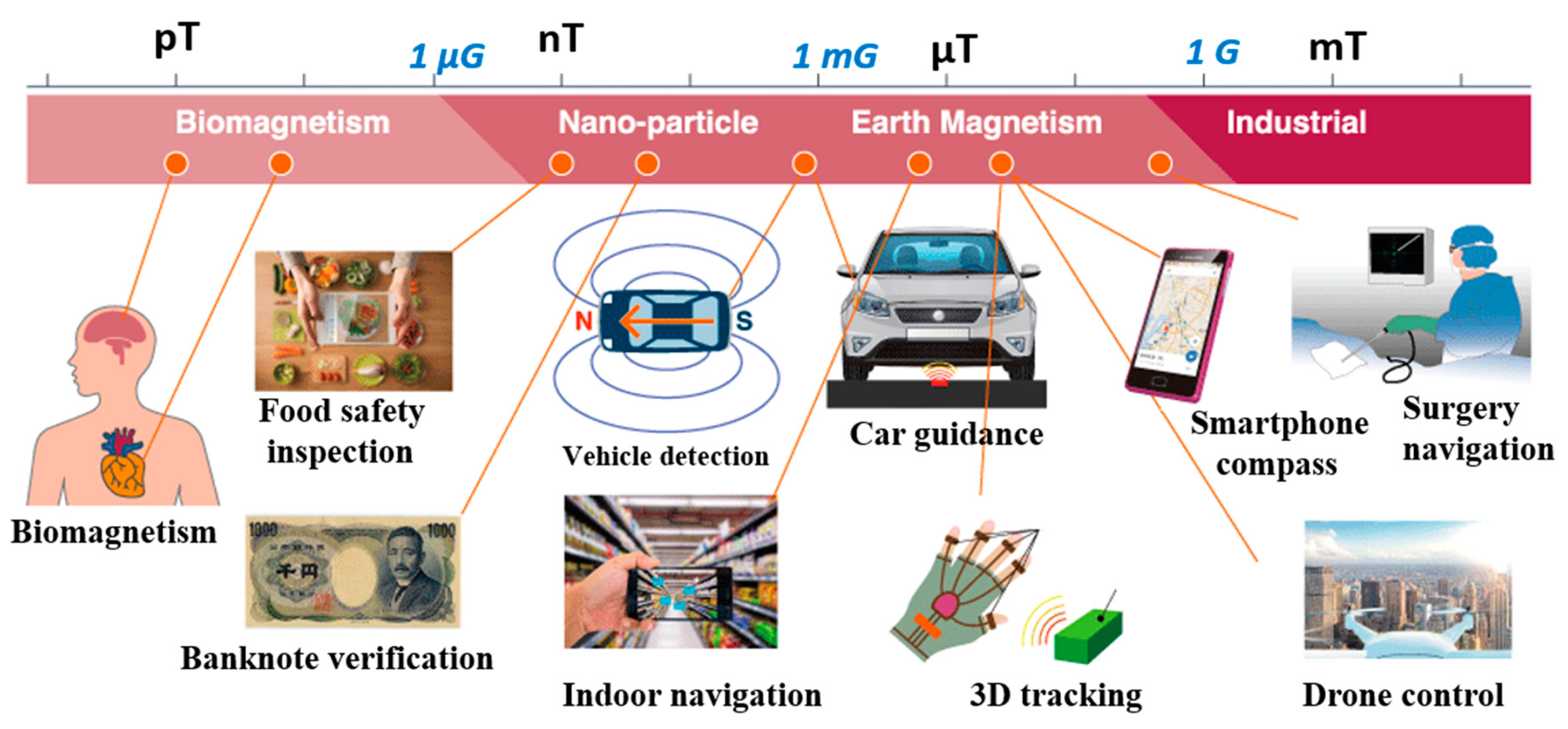
1. Introduction
2. Basic Principles
2.1. The Giant Magnetoimpedance Phenomenon
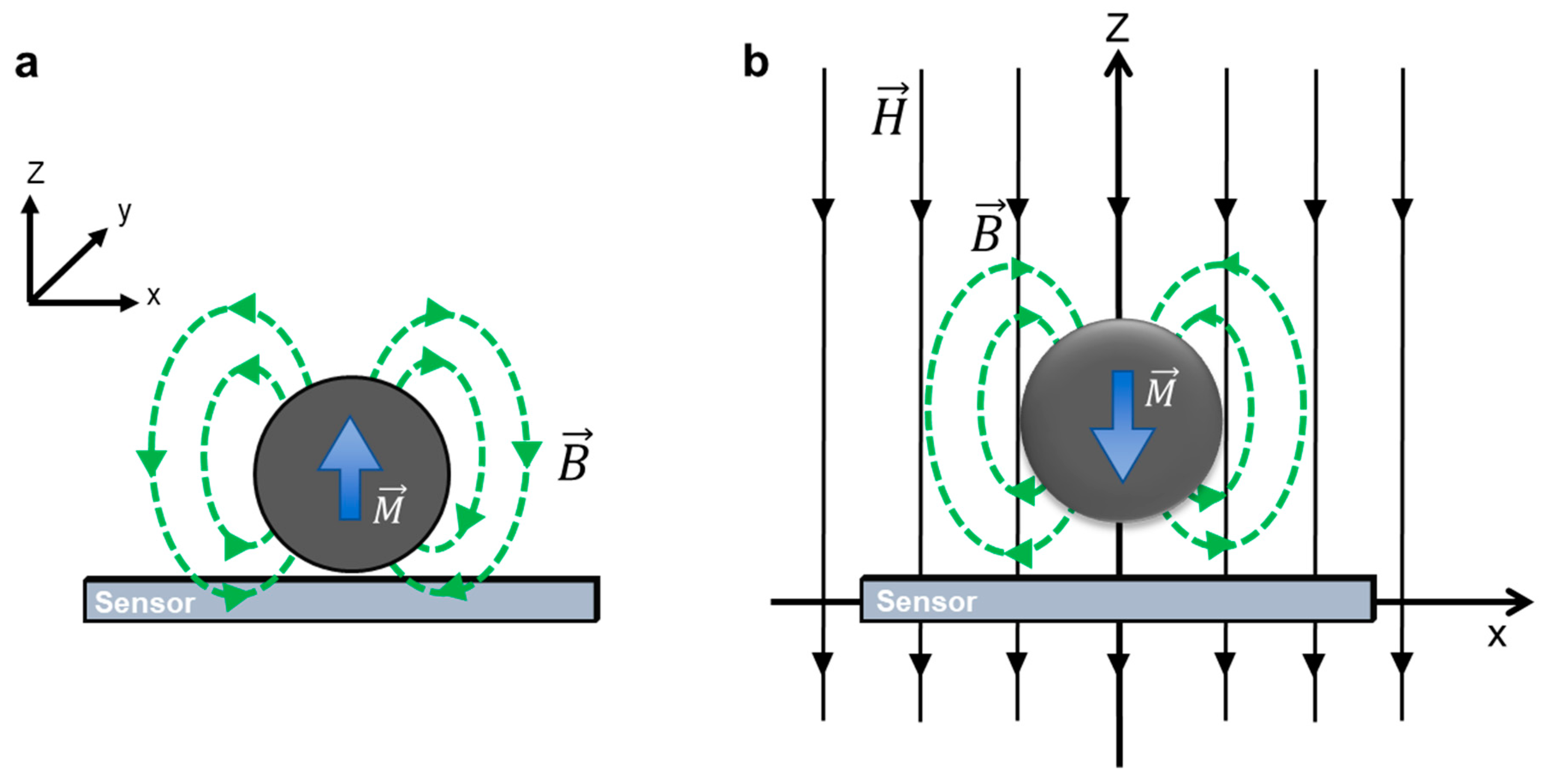
2.2. Detection Principles
3. Early Sensor Prototypes (2000–2016)
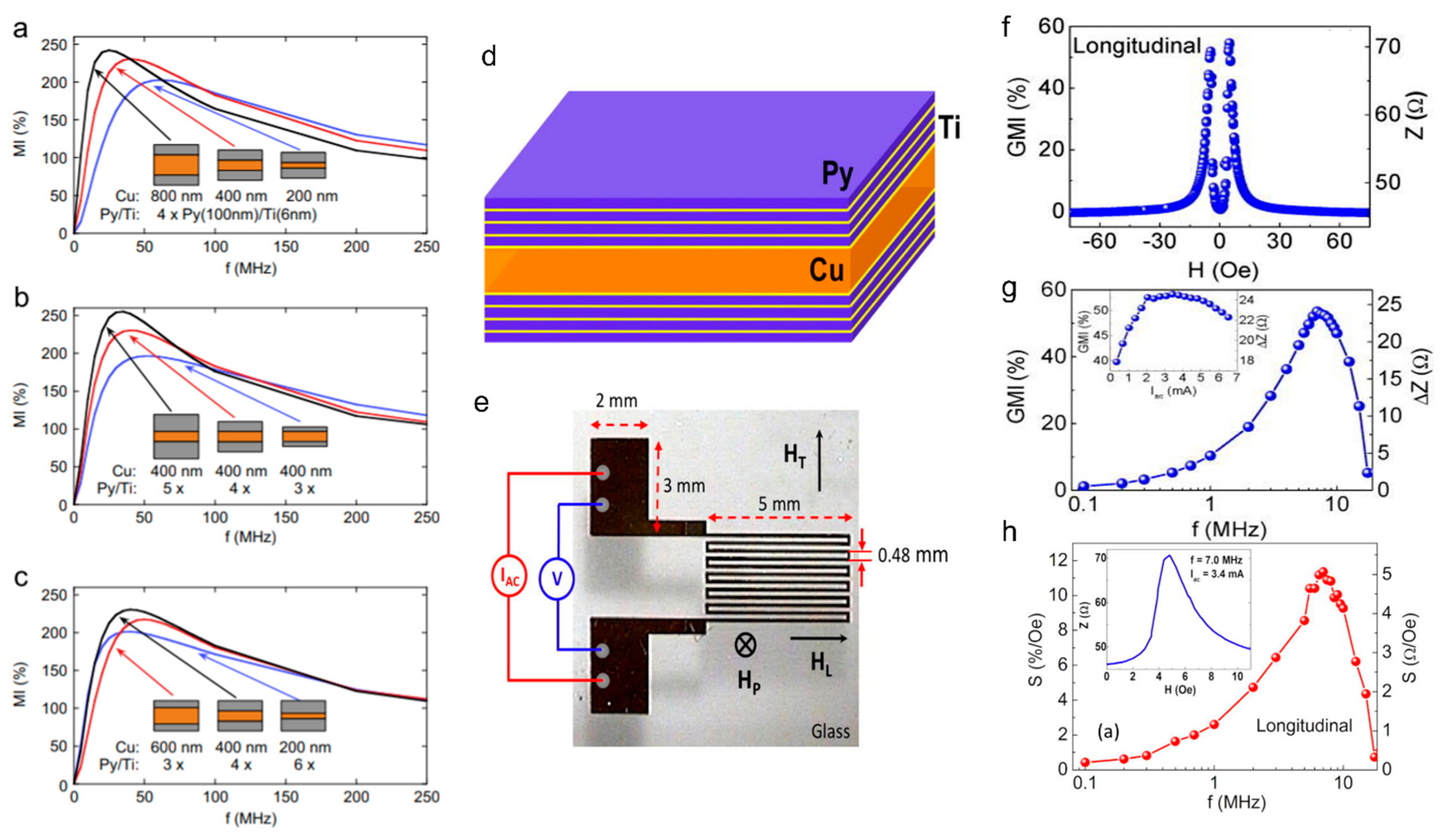
3.1. Early Planar Prototypes
3.2. Early Wire-Based Prototypes
4. Current Magnetoimpedance Biosensors and Healthcare Monitors (2016–Now)
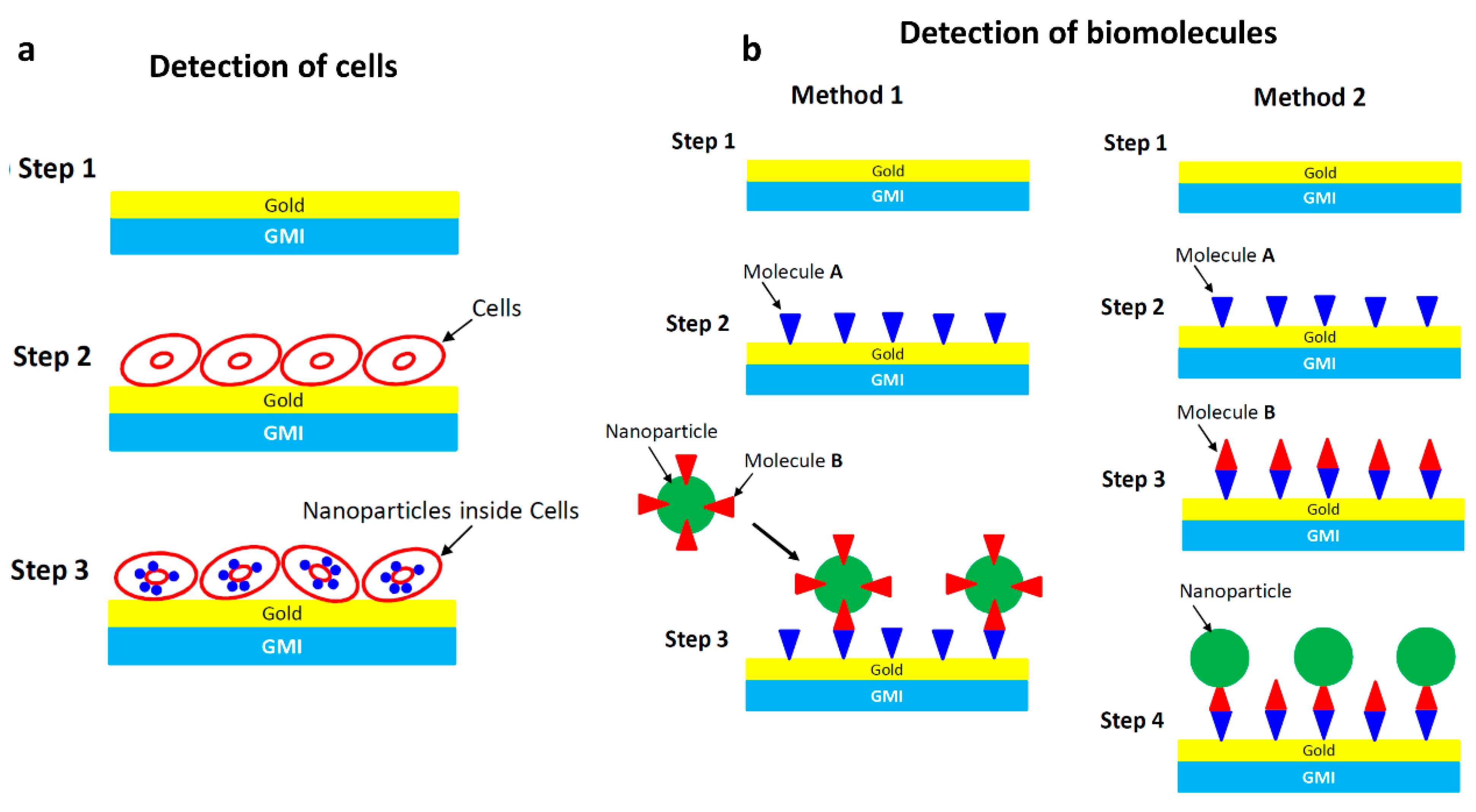
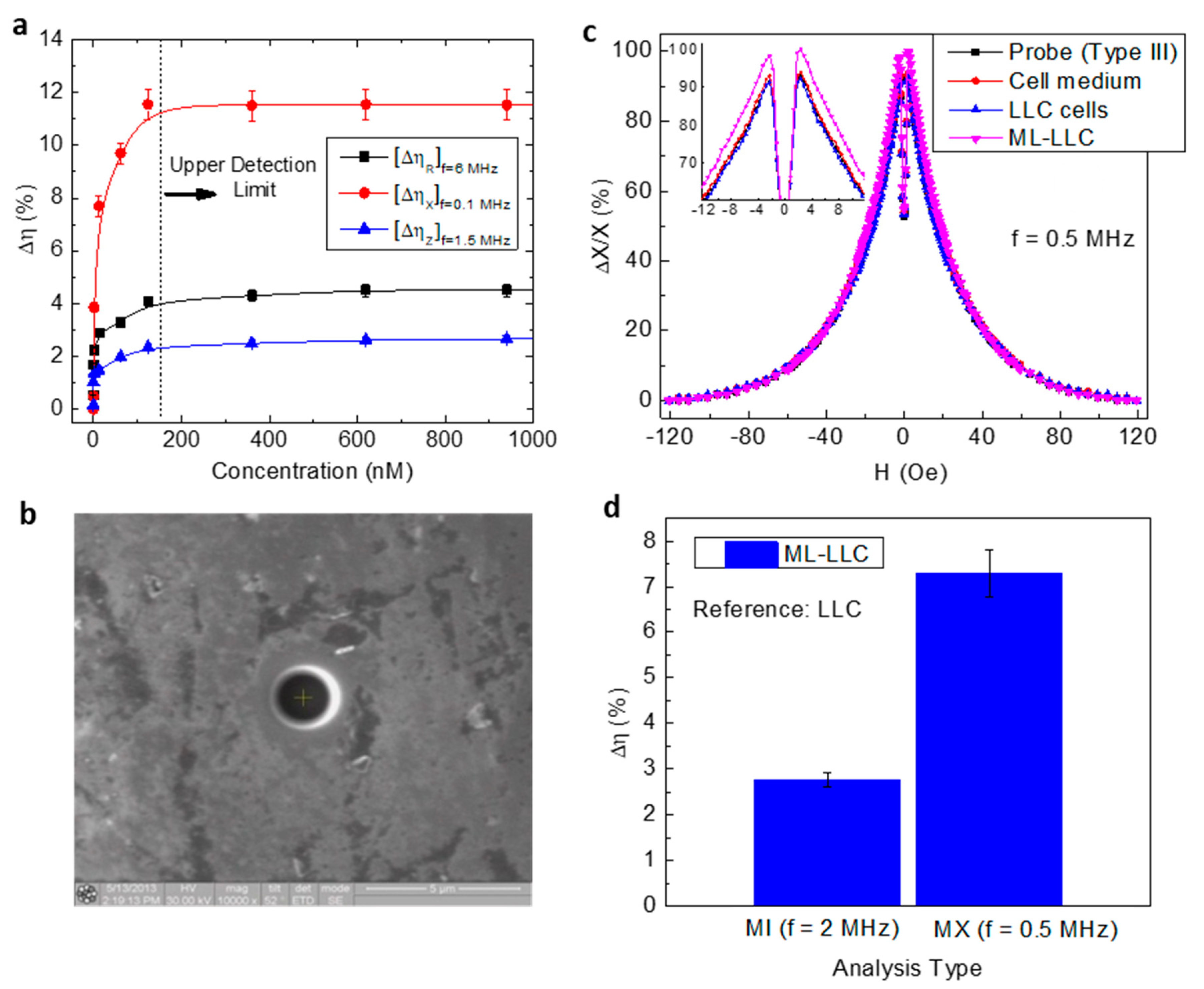
4.1. Detection of Magnetic Particles
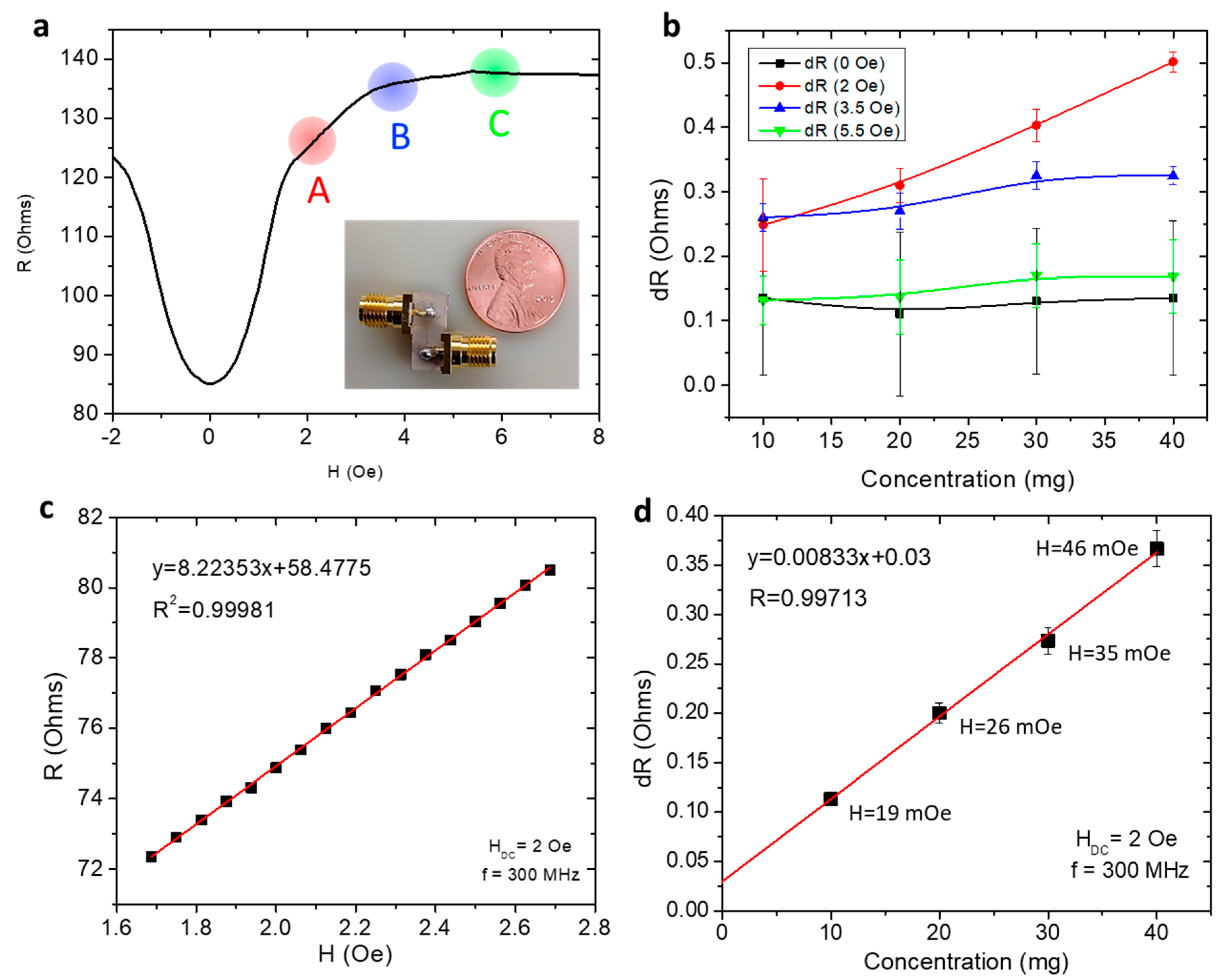
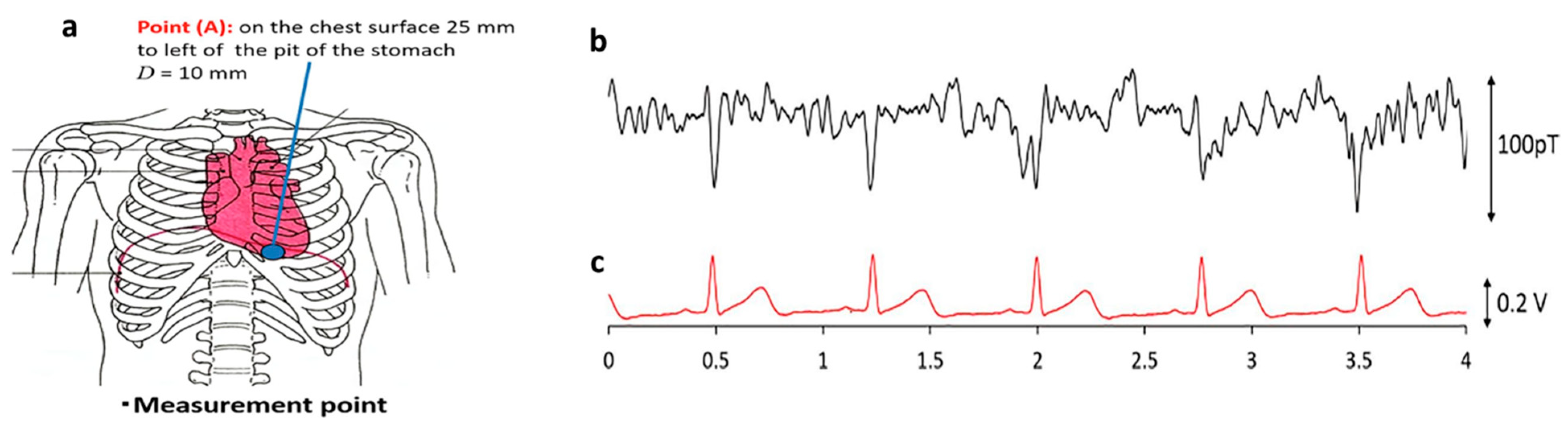
4.2. Biomagnetic Field Detection
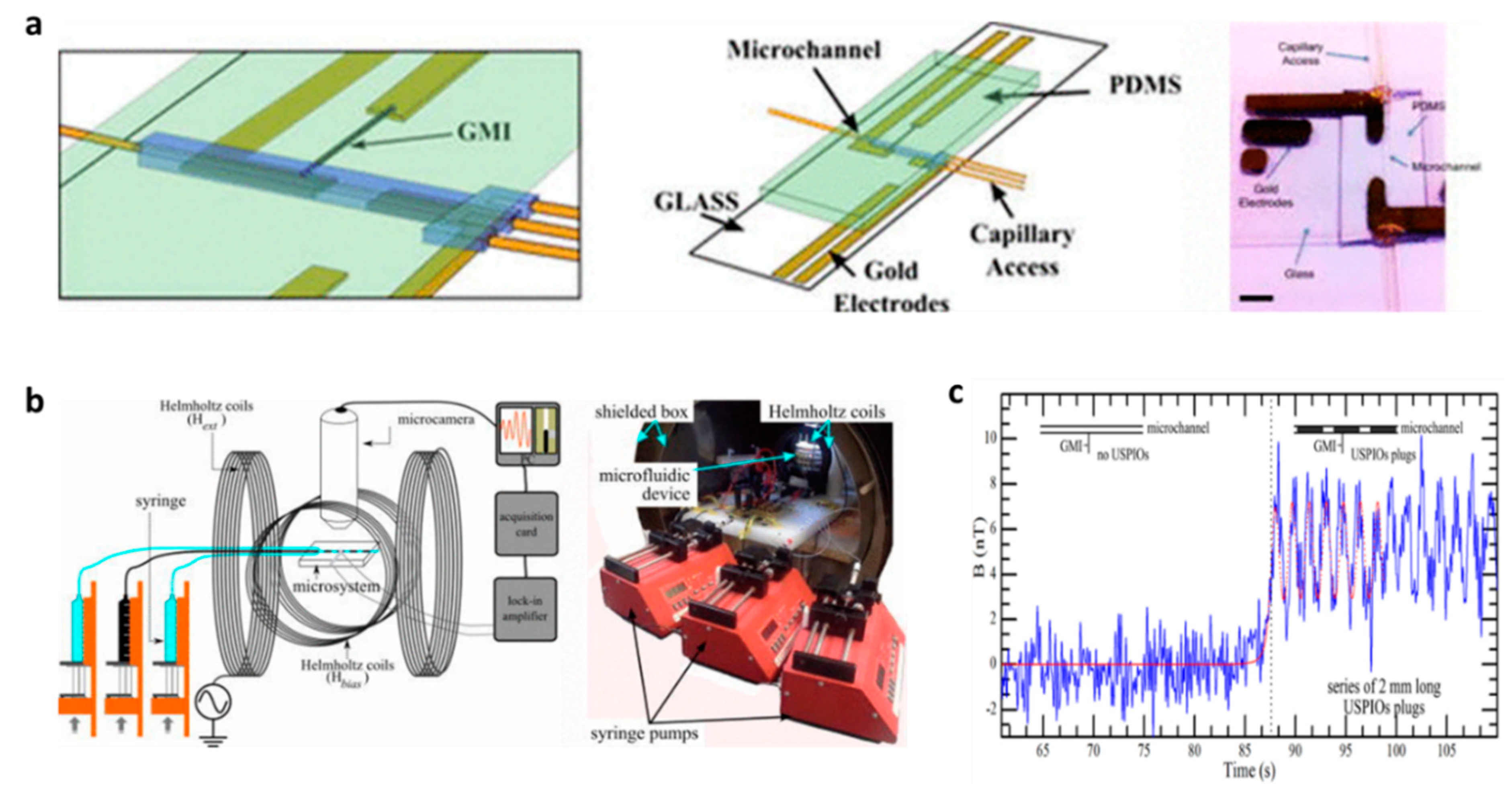
4.3. Microfluidics
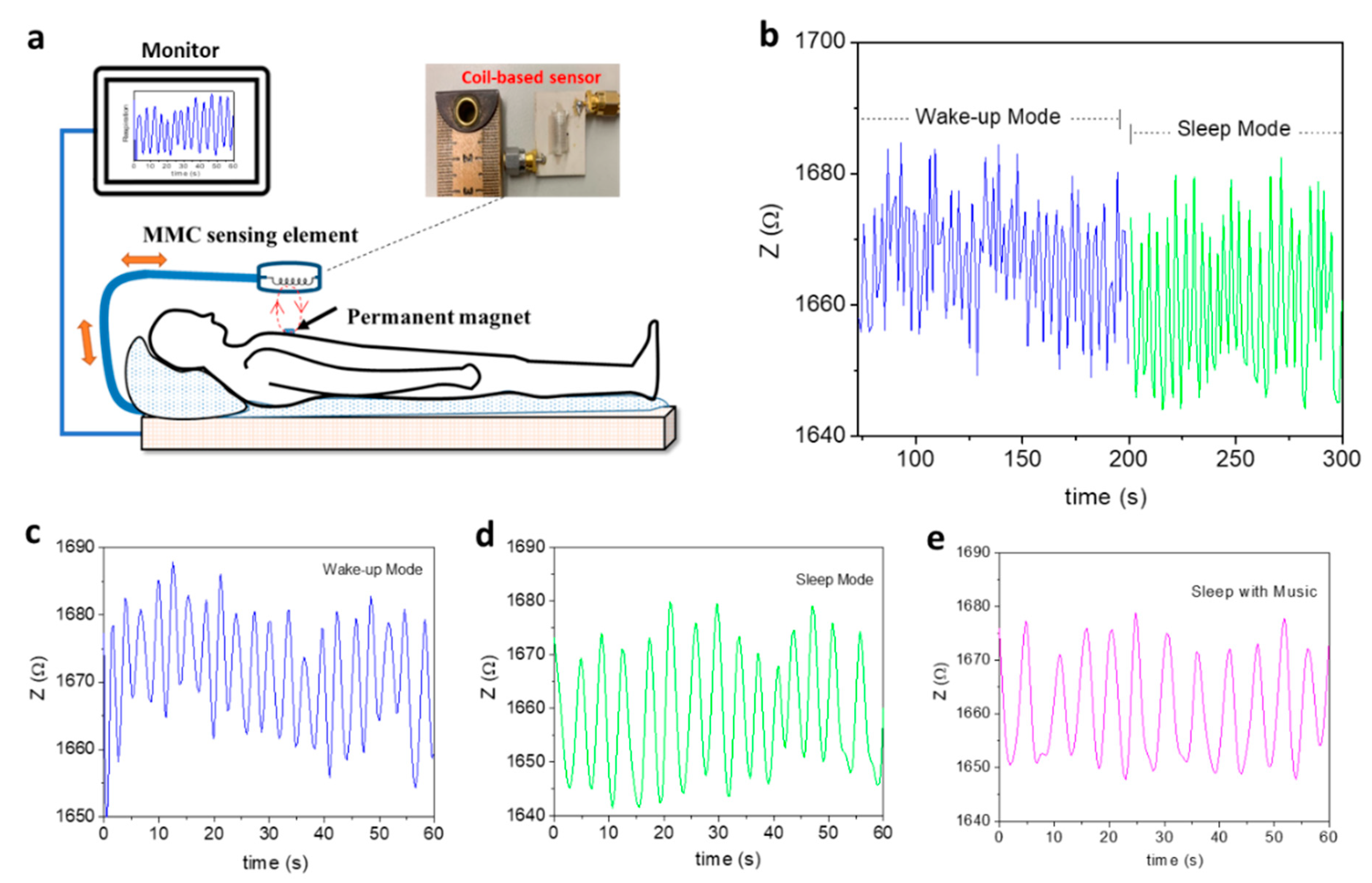
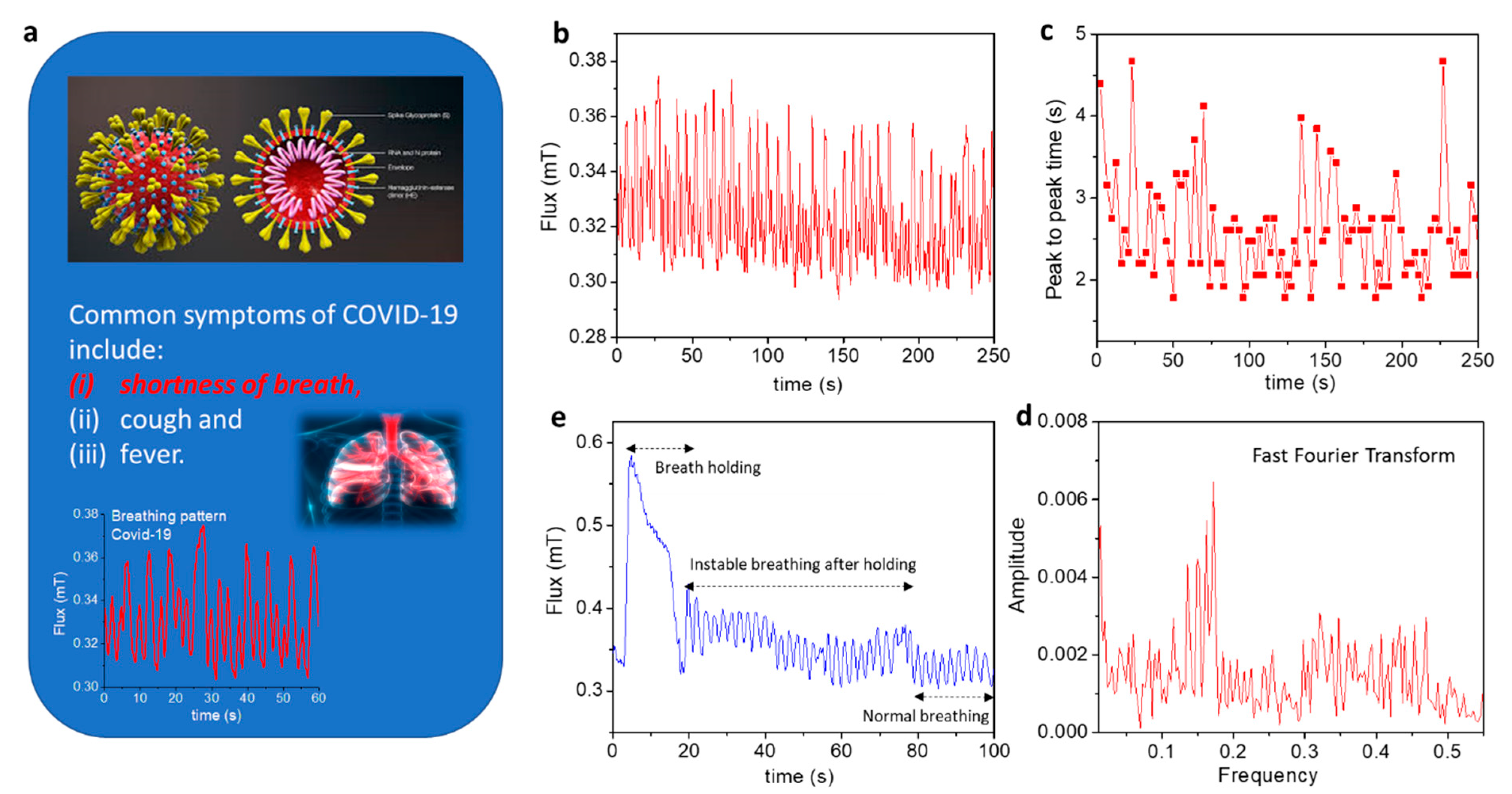
4.4. Real-Time Healthcare Monitoring of Patients with Respiratory Illness or COVID-19
5. Concluding Remarks and Future Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Su, D.; Wu, K.; Saha, R.; Peng, C.; Wang, J.-P. Advances in Magnetoresistive Biosensors. Micromachines 2020, 11, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.A.; Sun, J.; Li, B.; Przybysz, A.; Kosel, J. Magnetic Sensors-A Review and Recent Technologies. Eng. Res. Express 2021, 3, 022005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cheng, H.; Alhalili, Z.; Xu, G.; Gao, G. The Progress of Magnetic Sensor Applied in Biomedicine: A Review of Non-Invasive Techniques and Sensors. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2021, 68, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Makarov, D.; Schmidt, O.G. Magnetic Sensing Platform Technologies for Biomedical Applications. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 1884–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denmark, D.J.; Bustos-Perez, X.; Swain, A.; Phan, M.-H.; Mohapatra, S.; Mohapatra, S.S. Readiness of Magnetic Nanobiosensors for Point-of-Care Commercialization. J. Electron. Mater. 2019, 48, 4749–4761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabaei, V.; Chandrawati, R.; Heidari, H. Magnetic Biosensors: Modelling and Simulation. Biosens. Bioelectron 2018, 103, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripka, P. Magnetic Sensors: Principles and Applications. In Encyclopedia of Materials: Science and Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.X.; Li, G.X. Advances in Giant Magnetoresistance Biosensors with Magnetic Nanoparticle Tags: Review and Outlook. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2008, 44, 1687–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, E.P.; Turney, G.L.; Rowe, H. Electrical Properties of Wires of High Permeability. Nature 1935, 135, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhotkin, V.E.; Shurukhin, B.P.; Lopatin, V.A.; Marchukov, P.Y.; Levin, Y.K. Magnetic Field Sensors Based on Amorphous Ribbons. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 1991, 27, 759–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beach, R.S.; Berkowitz, A.E. Giant Magnetic Field Dependent Impedance of Amorphous FeCoSiB Wire. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1994, 64, 3652–3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panina, L.V.; Mohri, K. Magneto-impedance Effect in Amorphous Wires. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1994, 65, 1189–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knobel, M.; Vázquez, M.; Kraus, L. Giant Magnetoimpedance. In Handbook of Magnetic Materials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 497–563. ISBN 9780444514592. [Google Scholar]
- Phan, M.-H.; Peng, H.-X. Giant Magnetoimpedance Materials: Fundamentals and Applications. Pro. Mater. Sci. 2008, 53, 323–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohri, K.; Bushida, K.; Noda, M.; Yoshida, H.; Panina, L.V.; Uchiyama, T. Magneto-Impedance Element. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1995, 31, 2455–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurlyandskaya, G.V. Giant Magnetoimpedance for Biosensing: Advantages and Shortcomings. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009, 321, 659–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Lei, C.; Luo, J.; Xie, S.; Pu, H. Magnetic Impedance Biosensor: A Review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 90, 418–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayad, A.; Skafidas, E.; Kwan, P. Magneto-Impedance Biosensor Sensitivity: Effect and Enhancement. Sensors 2020, 20, 5213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, T.; Nakayama, S. Magnetic Sensors Using Amorphous Metal Materials: Detection of Premature Ventricular Magnetic Waves. Physiol. Rep. 2013, 1, e00030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, T.; Nakayama, S.; Mohri, K.; Bushida, K. Biomagnetic Field Detection Using Very High Sensitivity Magnetoimpedance Sensors for Medical Applications. Phys. Status Solidi A 2009, 206, 639–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, T.; Mohri, K.; Honkura, Y.; Panina, L.V. Recent Advances of Pico-Tesla Resolution Magneto-Impedance Sensor Based on Amorphous Wire CMOS IC MI Sensor. Element. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 3833–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohri, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Uchiyama, T. Application Topics of Amorphous Wire CMOS IC Magneto-Impedance Micromagnetic Sensors for I-o-T Smart Society. J. Sens. 2019, 2019, 8285240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aichi Steel Corporation. Available online: https://www.aichi-mi.com/e-applications/ (accessed on 7 May 2022).
- Chiriac, H.; Tibu, M.; Moga, A.E.; Herea, D.D. Magnetic GMI Sensor for Detection of Biomolecules. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 293, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiriac, H.; Herea, D.D.; Corodeanu, S. Microwire Array for Giant Magneto-Impedance Detection of Magnetic Particles for Biosensor Prototype. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 311, 425–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiriac, H.; Herea, D.D. Magneto-Impedance Sensor for Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Appl. Electromagn. 2007, 25, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huong Giang, D.T.; Dang, D.X.; Toan, N.X.; Tuan, N.V.; Phung, A.T.; Duc, N.H. Distance Magnetic Nanoparticle Detection Using a Magnetoelectric Sensor for Clinical Interventions. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2017, 88, 015004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melnikov, G.Y.; Lepalovskij, V.N.; Svalov, A.V.; Safronov, A.P.; Kurlyandskaya, G.V. Magnetoimpedance Thin Film Sensor for Detecting of Stray Fields of Magnetic Particles in Blood Vessel. Sensors 2021, 21, 3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fodil, K.; Denoual, M.; Dolabdjian, C.; Harnois, M.; Senez, V. Dynamic Sensing of Magnetic Nanoparticles in Microchannel Using GMI Technology. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 49, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Materón, E.M.; Miyazaki, C.M.; Carr, O.; Joshi, N.; Picciani, P.H.S.; Dalmaschio, C.J.; Dacis, F.; Shimizu, F.M. Magnetic Nanoparticles in Biomedical Applications: A Review. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2021, 6, 100163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S.D.; Gwenin, V.V.; Gwenin, C.D. Magnetic Functionalized Nanoparticles for Biomedical, Drug Delivery and Imaging Applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murzin, D.; Mapps, D.J.; Levada, K.; Belyaev, V.; Omelyanchik, A.; Panina, L.; Rodionova, V. Ultrasensitive Magnetic Field Sensors for Biomedical Applications. Sensors 2020, 20, 1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupin, D.D.; Kuzina, E.A.; Abelit, A.A.; Emelyanov, A.K.; Nikolaev, D.M.; Ryazantsev, M.N.; Koniakhin, S.V.; Dubina, M.V. Bioimpedance Spectroscopy: Basics and Applications. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 1962–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.X.; Qin, F.; Phan, M.-H. Ferromagnetic Microwire Composites: From Sensors to Microwave Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; ISBN 9783319292762. [Google Scholar]
- Landau, L.D.; Lifshitz, E.M.; King, A.L. Electrodynamics of Continuous Media. Am. J. Phys. 1961, 29, 647–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, L.G.C..; Ciureanu, P.; Yelon, A. Permeability Deduced from Impedance Measurements at Microwave Frequencies. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2002, 249, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ménard, D.; Frankland, D.; Ciureanu, P.; Yelon, A.; Rouabhi, M.; Cochrane, R.W.; Chiriac, H.; Óvári, T.A. Modeling of Domain Structure and Anisotropy in Glass-Covered Amorphous Wires. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 83, 6566–6568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, L. GMI Modeling and Material Optimization. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2003, 106, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Rubio, A.; García-Miquel, H.; García-Chocano, V.M. In-Plane Omnidirectional Magnetic Field Sensor Based on Giant Magneto Impedance (GMI). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 444, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, R.L.; Chien, C.L. Role of Magnetic Anisotropy in the Magnetoimpedance Effect in Amorphous Alloys. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1995, 67, 857–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannous, C.; Gieraltowski, J. Giant Magneto-Impedance and Its Applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 15, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dressel, M.; Grüner, G. Electrodynamics of Solids: Optical Properties of Electrons in Matter; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002; ISBN 9780521592536. [Google Scholar]
- Rife, J.C.; Miller, M.M.; Sheehan, P.E.; Tamanaha, C.R.; Tondra, M.; Whitman, L.J. Design and Performance of GMR Sensors for the Detection of Magnetic Microbeads in Biosensors. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2003, 107, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, S.; Uchiyama, T. Real-Time Measurement of Biomagnetic Vector Fields in Functional Syncytium Using Amorphous Metal. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurlyandskaya, G.V.; Sánchez, M.L.; Hernando, B.; Prida, V.M.; Gorria, P.; Tejedor, M. Giant-Magnetoimpedance-Based Sensitive Element as a Model for Biosensors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 82, 3053–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurlyandskaya, G.V.; Levit, V. Magnetic Dynabeads® Detection by Sensitive Element Based on Giant Magnetoimpedance. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 20, 1611–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurlyandskaya, G.V.; Fal Miyar, V. Surface Modified Amorphous Ribbon Based Magnetoimpedance Biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 2341–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Chen, L.; Lei, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, D.; Zhou, Z.M.; Bao, C.C.; Hu, H.Y.; Chen, X.; Cui, F.; et al. Giant Magnetoimpedance-Based Microchannel System for Quick and Parallel Genotyping of Human Papilloma Virus Type 16/18. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 043702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Arribas, A.; Martínez, F.; Fernández, E.; Ozaeta, I.; Kurlyandskaya, G.V.; Svalov, A.V.; Berganzo, J.; Barandiaran, J.M. GMI Detection of Magnetic-Particle Concentration in Continuous Flow. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2011, 172, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devkota, J.; Wang, C.; Ruiz, A.; Mohapatra, S.; Mukherjee, P.; Srikanth, H.; Phan, M.-H. Detection of Low-Concentration Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles Using an Integrated Radio Frequency Magnetic Biosensor. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 104701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devkota, J.; Mai, T.T.T.; Stojak, K.; Ha, P.T.; Pham, H.N.; Nguyen, X.P.; Mukherjee, P.; Srikanth, H.; Phan, M.-H. Synthesis, Inductive Heating, and Magnetoimpedance-Based Detection of Multifunctional Fe3O4 Nanoconjugates. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 190, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devkota, J.; Wingo, J.; Mai, T.T.T.; Nguyen, X.P.; Huong, N.T.; Mukherjee, P.; Srikanth, H.; Phan, M.-H. A Highly Sensitive Magnetic Biosensor for Detection and Quantification of Anticancer Drugs Tagged to Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 178503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devkota, J.; Ruiz, A.; Mukherjee, P.; Srikanth, H.; Phan, M.-H. Magneto-Impedance Biosensor with Enhanced Sensitivity for Highly Sensitive Detection of Nanomag-D Beads. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 49, 4060–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devkota, J. Enhanced Magnetoimpedance and Microwave Absorption Responses of Soft Ferromagnetic Materials for Biodetection and Energy Sensing. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of South Florida, Tampa, FL, USA, 7 April 2015. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usf.edu/etd/5862/ (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- Sato, T.; Fujine, T.; Miyazaki, J. Variation of Magnetic Properties along ribbon length in an amorphous Fe80.5Si6.5B12C1 Alloy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater 1988, 71, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, A.; Baghbaderani, H.A.; Strom, V.; Stamenov, P.; McCloskey, P.; Mathuna, C.O.; Kulkarni, S. Facbrication and Soft Magnetic Properties of Rapidly Quenched Co-Fe-B-Si-Nb Ultra-Thin Amorphous Ribbons. J. Magn. Magn. Mater 2019, 483, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S.; Li, D.; Wang, N.; Roy, S.; Mathuna, C.O.; Young, G.; McCloskey, P. Low Loss Magnetic Thin Films for Off-Line Power Conversion. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 50, 2004404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethke, C.; Yakabchuk, H.; Tarasenko, V.; Hammer, H.; Kisker, E.; Koppers, E.; Christoph, S.; Zirwes, R.; Müller, J. Detektion Superparamagnetischer Marker Mittels GMI-Sensorik. TM Tech. Mess. 2003, 70, 574–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulin, J.; Woytasik, M.; Shahosseini, I.; Alves, F. Micropatterning of Sandwiched FeCuNbSiB/Cu/FeCuNbSiB for the Realization of Magneto-Impedance Microsensors. Microsyst. Technol. 2011, 17, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volchkov, S.O.; Svalov, A.V.; Kurlyandskaya, G.V. Giant Magnetic Impedance of Film Nanostructures Adapted for Biodetection. Russ. Phys. J. 2009, 52, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Lei, C.; Lei, J.; Yang, Z. Development of an Ingenious Method for Determination of Dynabeads Protein A Based on a Giant Magnetoimpedance Sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 186, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Lei, C.; Lei, J.; Yang, Z. Ultrasensitive Detection of Dynabeads Protein A Using the Giant Magnetoimpedance Effect. Microchim. Acta 2013, 180, 1211–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzschild, B.M. Weak Magnetic Fields in Human Body. Phys. Today 1979, 32, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panina, L.V.; Mohri, K.; Uchiyama, T.; Noda, M.; Bushida, K. Giant Magneto-Impedance in Co-Rich Amorphous Wires and Films. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1995, 31, 1249–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, T.; Mohri, K.; Shinkai, M.; Ohshima, A.; Honda, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Wakabayashi, T.; Yoshida, J. Position Sensing of Magnetite Gel Using MI Sensor for Brain Tumor Detection. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1997, 33, 4266–4268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodil, K.; Denoual, M.; Dolabdjian, C.; Treizebre, A.; Senez, V. Model Calculation of the Magnetic Induction Generated by Magnetic Nanoparticles Flowing into a Microfluidic System: Performance Analysis of the Detection. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 50, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodil, K.; Denoual, M.; Dolabdjian, C.; Treizebre, A.; Senez, V. In-Flow Detection of Ultra-Small Magnetic Particles by an Integrated Giant Magnetic Impedance Sensor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 108, 173701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Arribas, A.; Fernández, E.; Svalov, A.; Kurlyandskaya, G.v.; Barandiaran, J.M. Thin-Film Magneto-Impedance Structures with Very Large Sensitivity. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 400, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurlyandskaya, G.V.; Shcherbinin, S.V.; Buznikov, N.A.; Chlenova, A.A.; Svalov, A.V. Magnetic Materials for Thin Film Based Magnetoimpedance Biosensing. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 2019, 120, 1243–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurlyandskaya, G.V.; Fernández, E.; Safronov, A.P.; Svalov, A.V.; Beketov, I.; Beitia, A.B.; García-Arribas, A.; Blyakhman, F.A. Giant Magnetoimpedance Biosensor for Ferrogel Detection: Model System to Evaluate Properties of Natural Tissue. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 193702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilela, G.L.S.; Monsalve, J.G.; Rodrigues, A.R.; Azevedo, A.; Machado, F.L.A. Giant Magnetoimpedance Effect in a Thin-Film Multilayer Meander-like Sensor. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 121, 124501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodewijk, K.J.; Fernandez, E.; Garcia-Arribas, A.; Kurlyandskaya, G.V.; Lepalovskij, V.N.; Safronov, A.P.; Kooi, B.J. Magnetoimpedance of Thin Film Meander with Composite Coating Layer Containing Ni Nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 17A323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Lei, C.; Lei, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, Y. Preparation of Meander Thin-Film Microsensor and Investigation the Influence of Structural Parameters on the Giant Magnetoimpedance Effect. Appl. Phys. A 2012, 109, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Yang, Z.; Lei, C.; Lei, J.; Zhou, Y. An Integrated Giant Magnetoimpedance Biosensor for Detection of Biomarker. Biosens. Bioelectron 2014, 58, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, L.; Lei, C. Transverse, Longitudinal and Perpendicular Giant Magnetoimpedance Effects in a Compact Multiturn Meander NiFe/Cu/NiFe Trilayer Film Sensor. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2011, 22, 035202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buznikov, N.A.; Safronov, A.P.; Orue, I.; Golubeva, E.V.; Lepalovskij, V.N.; Svalov, A.V.; Chlenova, A.A.; Kurlyandskaya, G.V. Modelling of Magnetoimpedance Response of Thin Film Sensitive Element in the Presence of Ferrogel: Next Step toward Development of Biosensor for in-Tissue Embedded Magnetic Nanoparticles Detection. Biosens. Bioelectron 2018, 117, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chen, Y.; Wang, B.; He, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, M.; Rao, J.; Wu, Z.; Xie, S.; Luo, J. A Giant Magnetoimpedance-Based Separable-Type Method for Supersensitive Detection of 10 Magnetic Beads at High Frequency. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2019, 300, 111656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Arribas, A. The Performance of the Magneto-Impedance Effect for the Detection of Superparamagnetic Particles. Sensors 2020, 20, 1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, J.; Khurshid, H.; Devkota, J.; Nemati, Z.; Khadka, N.K.; Srikanth, H.; Pan, J.; Phan, M.-H. Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles Encapsulated in Lipid Vesicles for Advanced Magnetic Hyperthermia and Biodetection. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 119, 083904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa Silva, E.; Hall Barbosa, C.R.; Gusmao, L.A.P.; Leipner, Y.; Fortaleza, L.G.S.; Costa Monteiro, E. Point Matching: A New Electronic Method for Homogenizing the Phase Characteristics of Giant Magnetoimpedance Sensors. Rev. Sci. Instrum 2014, 85, 084708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Pan, Z.; Zhuo, H.; Zhang, W. Magnetic Sensor Based on Giant Magneto-Impedance Effect Using the Self-Regulating Technology on the Bias Magnetic Field. Sens. Actuator A Phys. 2016, 249, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.; Tu, X.; Wang, J.; Yang, B.; Dong, K.; Mo, W.; Hui, Y.; Peng, J.; Jiang, J.; Xu, L.; et al. Noise Modeling and Simulation of Giant Magnetic Impedance (GMI) Magnetic Sensor. Sensors 2020, 20, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, T.; Takiya, T. Development of Precise Off-Diagonal Magnetoimpedance Gradiometer for Magnetocardiography. AIP Adv. 2017, 7, 056644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takiya, T.; Uchiyama, T. Development of an Active Shielding-Type MI Gradiometer: Its Application for Magnetocardiography. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53, 4002804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Uchiyama, T. Development of Peak-to-Peak Voltage Detector-Type MI Gradiometer for Magnetocardiography. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2018, 54, 5000605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, T.; Ma, J. Development of Pico Tesla Resolution Amorphous Wire Magneto-Impedance Sensor for Bio-Magnetic Field Measurements. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 514, 167148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Cai, C.; Yamamoto, M.; Uchiyama, T. Real-Time Brain Activity Measurement and Signal Processing System Using Highly Sensitive MI Sensor. AIP Adv. 2017, 7, 056635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Uchiyama, T. Alpha Rhythm and Visual Event-Related Fields Measurements at Room Temperature Using Magneto-Impedance Sensor System. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2019, 55, 4002706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Pan, H.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Z. Detection of AFP with an Ultra-Sensitive Giant Magnetoimpedance Biosensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 293, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Zhi, S.; Guo, L.; Zhou, Y.; Lei, C. An Integrated Magnetic Microfluidic Chip for Rapid Immunodetection of the Prostate Specific Antigen Using Immunomagnetic Beads. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khalidi, F.Q.; Saatchi, R.; Burke, D.; Elphick, H.; Tan, S. Respiration Rate Monitoring Methods: A Review. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2011, 46, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padasdao, B.; Shahhaidar, E.; Stickley, C.; Boric-Lubecke, O. Electromagnetic Biosensing of Respiratory Rate. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 4204–4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekr, A.R.; Janidarmian, M.; Radecka, K.; Zilic, Z. A Medical Cloud-Based Platform for Respiration Rate Measurement and Hierarchical Classification of Breath Disorders. Sensors 2014, 14, 11204–11224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiabgoh, O.; Eggers, T.; Phan, M.H. A New Contactless Magneto-LC Resonance Technology for Real-Time Respiratory Motion Monitoring. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2017, 265, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, K.Y.; Jimenez, V.O.; Muchharla, B.; Eggers, T.; Le, A.T.; Lam, V.D.; Phan, M.H. A Novel Magnetic Respiratory Sensor for Human Healthcare. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiabgoh, O. Novel Magneto-LC Resonance Sensors for Industrial and Bioengineering Applications. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of South Florida, Tampa, FL, USA, 26 March 2018. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usf.edu/etd/7650/ (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- Canga, B.; Azoulay, R.; Raskin, J.; Loewy, J. AIR: Advances in Respiration—Music Therapy in the Treatment of Chronic Pulmonary Disease. Respir. Med. 2015, 109, 1532–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, Y.; Aiba, E. Relationship between Musical Characteristics and Temporal Breathing Pattern in Piano Performance. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, T.; Vara, M.; Cristino, C.; Zanella, T.; Nogueira-Neto, G.; Nohama, P. Breathing Monitoring and Pattern Recognition with Wearable Sensors. In Wearable Devices—The Big Wave of Innovation; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spackman, E.; Senne, D.A.; Myers, T.J.; Bulaga, L.L.; Garber, L.P.; Perdue, M.L.; Lohman, K.; Daum, L.T.; Suarez, D.L. Development of a Real-Time Reverse Transcriptase PCR Assay for Type A Influenza Virus and the Avian H5 and H7 Hemagglutinin Subtypes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 3256–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marras, S.A.E. Interactive Fluorophore and Quencher Pairs for Labeling Fluorescent Nucleic Acid Hybridization Probes. Mol. Biotechnol. 2008, 38, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Peng, Z.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, X.; Yan, R.; Luo, J. Detection and Analysis of Nucleic Acid in Various Biological Samples of COVID-19 Patients. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 37, 101673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, K.Y.; Chapel, W.; Jimenez, V.O.; Muchharla, B. Data, Real-Time Monitoring of Coronavirus Progress Using Magnetic Sensing and Machine Learning. US20200029862A1, 2021. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US20210369137A1/en (accessed on 1 March 2022).

| Structure (Thickness) | Dimensions | Max MI Ratio (%) | Max Sensitivity | MP Detection Applications | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Straight line | |||||
| [Py(100 nm)/Ti(6 nm)]4/Cu(400 nm)/[Ti(6 nm)/Py(100 nm)]4 | 10 mm × 0.5 mm 1.5 mm × 90 microns | 350 220 | 300%/Oe 75%/Oe | N/A | [68] |
| [Fe21Ni79(100 nm)/Cu(3 nm)]5/Cu(500 nm)/[Cu(3 nm)/Fe21Ni79(100 nm)]5 | 10 mm × 0.5 mm | 160 | 41%/Oe | Stray field of MP in blood vessels | [28] |
| [Fe19Ni81(50 nm)/Ti(6 nm)]6/Cu(500 nm)/[Ti(6 nm)/Fe19Ni81(50 nm)]6 | 1 mm × 10 mm | ~135 | 0.4 Ω/Oe | N/A | [69] |
| [FeNi(170 nm)/Ti(6 nm)]3/Cu(500 nm)/[Ti(6 nm)/FeNi(170 nm]3/Ti(6 nm ) | 10 mm × 0.5 mm | 50%/Oe | Ferrogel detection | [70] | |
| Meander | |||||
| [Py(100 nm)/Ti(6 nm)]4/Cu(400 nm)/[Py(100 nm/Ti(6 nm)]4 | 5 mm × 4 mm, 12 strips 0.16 mm wide each | 53.5 | 5.1 Ω/Oe | N/A | [71] |
| [FeNi(100 nm)/Cu(3 nm)]4/FeNi(100 nm)/Cu(500 nm)[FeNi(100 nm)/Cu(3 nm)]4/FeNi(100 nm) | 200 microns wide, 14 strips 300 microns wide, 10 strips | 60 165 | - | Detection of polymer/MNP composites | [72] |
| Fe17Ni83(2 microns)/Cu(140 microns)/Fe17Ni83(2 microns) | 5 mm long, 3 turns 6 turns | 55.2 161.6 | - | N/A | [73] |
| NiFe/Cu/NiFe | 5 mm long 1.26 mm wide, 3 turns | 97.54 | 0.1 μg mL−1 DPA concentration, 1 ng/mL AFP concentration | Dynabeads protein A, Alpha-fetoprotein detection | [61,74] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jimenez, V.O.; Hwang, K.Y.; Nguyen, D.; Rahman, Y.; Albrecht, C.; Senator, B.; Thiabgoh, O.; Devkota, J.; Bui, V.D.A.; Lam, D.S.; et al. Magnetoimpedance Biosensors and Real-Time Healthcare Monitors: Progress, Opportunities, and Challenges. Biosensors 2022, 12, 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12070517
Jimenez VO, Hwang KY, Nguyen D, Rahman Y, Albrecht C, Senator B, Thiabgoh O, Devkota J, Bui VDA, Lam DS, et al. Magnetoimpedance Biosensors and Real-Time Healthcare Monitors: Progress, Opportunities, and Challenges. Biosensors. 2022; 12(7):517. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12070517
Chicago/Turabian StyleJimenez, Valery Ortiz, Kee Young Hwang, Dang Nguyen, Yasif Rahman, Claire Albrecht, Baylee Senator, Ongard Thiabgoh, Jagannath Devkota, Vinh Duc An Bui, Dao Son Lam, and et al. 2022. "Magnetoimpedance Biosensors and Real-Time Healthcare Monitors: Progress, Opportunities, and Challenges" Biosensors 12, no. 7: 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12070517
APA StyleJimenez, V. O., Hwang, K. Y., Nguyen, D., Rahman, Y., Albrecht, C., Senator, B., Thiabgoh, O., Devkota, J., Bui, V. D. A., Lam, D. S., Eggers, T., & Phan, M.-H. (2022). Magnetoimpedance Biosensors and Real-Time Healthcare Monitors: Progress, Opportunities, and Challenges. Biosensors, 12(7), 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12070517







