Effective Enrichment of Plasmonic Hotspots for SERS by Spinning Droplets on a Slippery Concave Dome Array
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methodology
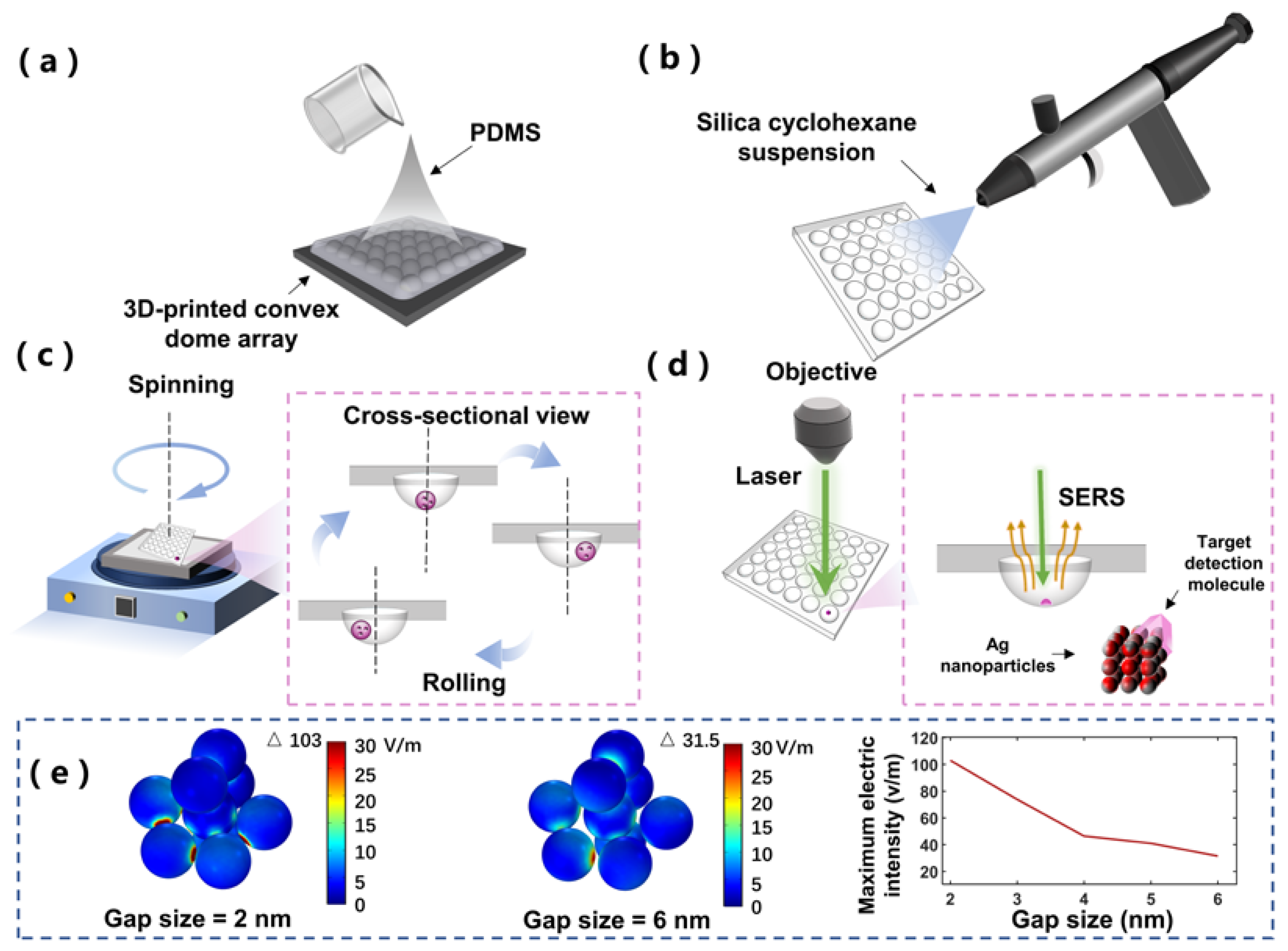
2.1. Preparation of SCDA
2.2. Working Mechanism
2.3. Materials
2.4. Characterization and Experimental Setup
2.5. Numerical Simulation for SERS
3. Results and Discussion
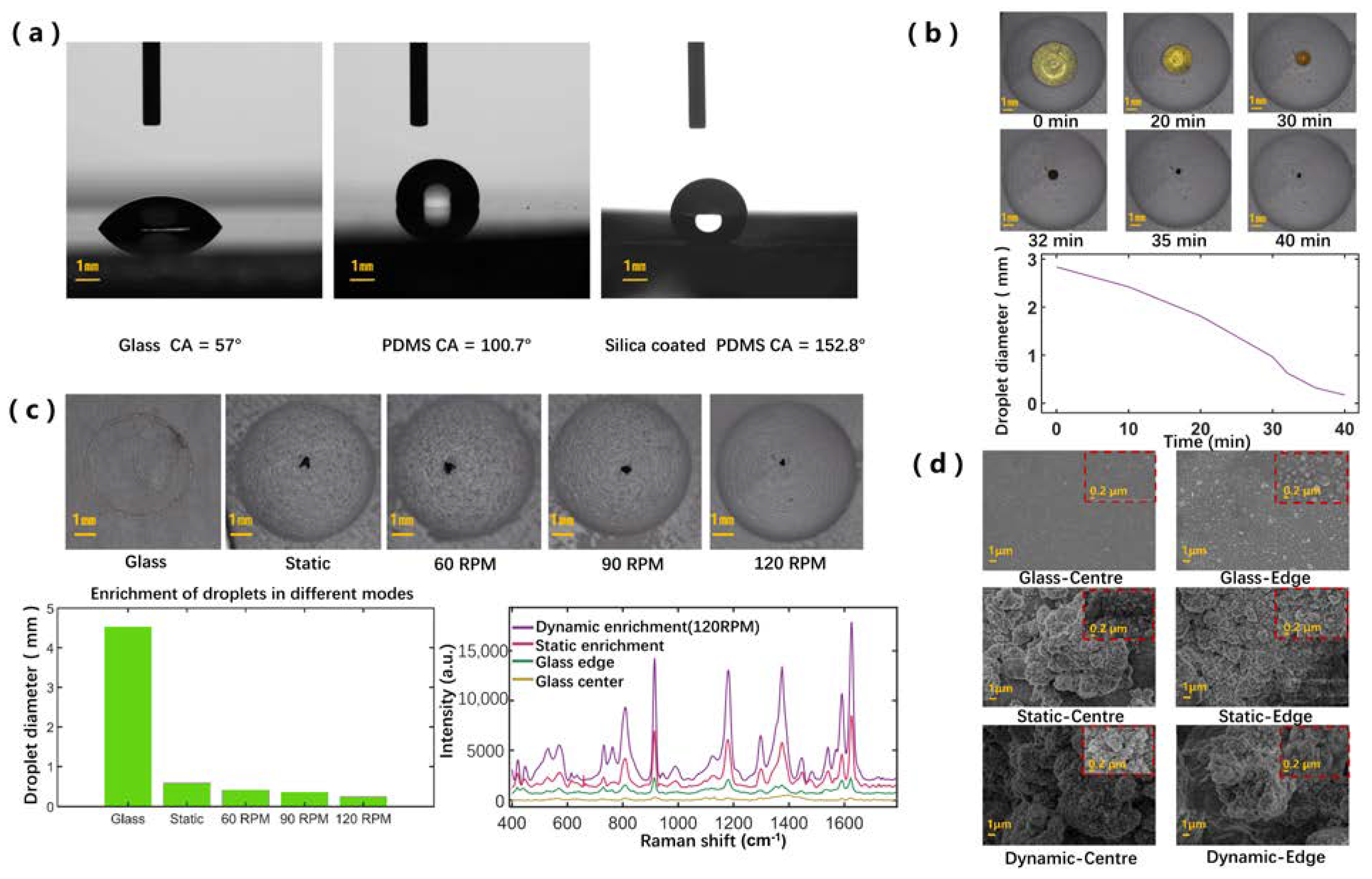
3.1. Investigation of SCDA
3.2. Comparison of the Deposition Patterns and SERS Performance Based on Different Enrichment Modes
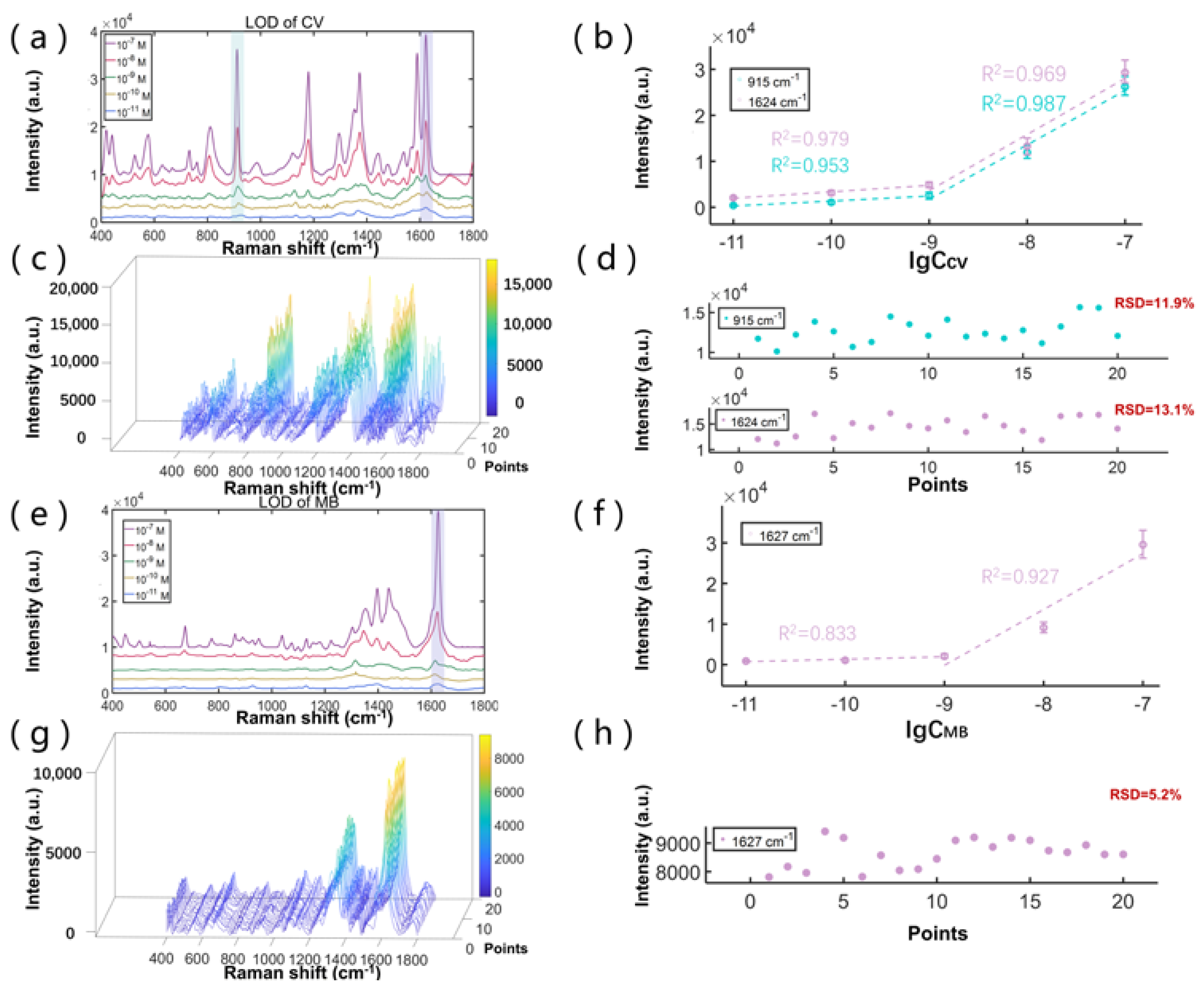
3.3. SERS Performance Study of the SCDA
3.4. SERS Detection of Melamine
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deegan, R.D.; Bakajin, O.; Dupont, T.F.; Huber, G.; Nagel, S.R.; Witten, T.A. Capillary flow as the cause of ring stains from dried liquid drops. Nature 1997, 389, 827–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunker, P.J.; Still, T.; Lohr, M.A.; Yodh, A.G. Suppression of the coffee-ring effect by shape-dependent capillary interactions. Nature 2011, 476, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deegan, R.D.; Bakajin, O.; Dupont, T.F.; Huber, G.; Nagel, S.R.; Witten, T.A. Contact line deposits in an evaporating drop. Phys. Rev. E 2000, 62, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deegan, R.D. Pattern formation in drying drops. Phys. Rev. E 2000, 61, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bigioni, T.P.; Lin, X.-M.; Nguyen, T.; Corwin, E.I.; Witten, T.A.; Jaeger, H.M. Kinetically driven self assembly of highly ordered nanoparticle monolayers. Nat. Mater. 2006, 5, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Dong, J.; Li, Y.; Sun, X.; Yuan, C.; Qian, W. The strategy of two-scale interface enrichment for constructing ultrasensitive SERS substrates based on the coffee ring effect of AgNP@β-CD. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 29586–29591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertaeg, M.J.; Rees-Zimmerman, C.; Tabor, R.F.; Routh, A.F.; Garnier, G. Predicting coffee ring formation upon drying in droplets of particle suspensions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 591, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Hirdes, D.; Folch, A. Gray-scale photolithography using microfluidic photomasks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 1499–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Groves, T.R.; Pickard, D.; Rafferty, B.; Crosland, N.; Adam, D.; Schubert, G. Maskless electron beam lithography: Prospects, progress, and challenges. Microelectron. Eng. 2002, 61, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchels, F.P.W.; Feijen, J.; Grijpma, D.W. A review on stereolithography and its applications in biomedical engineering. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 6121–6130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, H.; Huang, Y.; Lou, X.; Xia, F. Bioinspired superwetting surfaces for biosensing. VIEW 2021, 2, 20200053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Zhu, Q.; Feng, L.; Li, X.; Zhu, H.; Miao, H.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. Light-Trapping SERS Substrate with Regular Bioinspired Arrays for Detecting Trace Dyes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 11535–11542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Yang, Q.; Hou, J.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Song, Y. Bioinspired Micropatterned Superhydrophilic Au-Areoles for Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) Trace Detection. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1800448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozhina, E.P.; Bedin, S.; Nechaeva, N.; Podoynitsyn, S.; Tarakanov, V.; Andreev, S.; Grigoriev, Y.; Naumov, A. Ag-Nanowire Bundles with Gap Hot Spots Synthesized in Track-Etched Membranes as Effective SERS-Substrates. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Dai, X.; Stogin, B.B.; Wong, T.S. Ultrasensitive surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection in common fluids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, G.; Dai, Z.; Ji, B.; Li, S.; Chen, X.; Gao, Y.; Wen, W.; Zhou, B. Dynamic enrichment of plasmonic hot-spots and analytes on superhydrophobic and magnetically functionalized platform for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 319, 128297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Dai, Z.; Li, S.; Huang, Y.; Xu, Y.; She, J.; Zhou, B. Magnetically Responsive Film Decorated with Microcilia for Robust and Controllable Manipulation of Droplets. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 1754–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Chen, X.; Zheng, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhang, H.-R.; Zhang, S. Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Trace-Detection Platform Based on Continuous-Rolling-Assisted Evaporation on Superhydrophobic Surfaces. Acs Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 4767–4776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yang, Z.; Meng, L.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, L.; Liu, J.; Tian, Z. Three-Dimensional and Time-Ordered Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Hotspot Matrix. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 5332–5341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Li, P.; Zhou, G.; Chen, S.; Han, W.; Qin, F.; Nie, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qin, M.; Huang, G.; et al. General Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Method for Actively Capturing Target Molecules in Small Gaps. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 7769–7776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormashenko, E.; Bormashenko, Y.; Oleg, G. On the Nature of the Friction between Nonstick Droplets and Solid Substrates. Langmuir 2010, 26, 12479–12482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, J.; Ma, L.; Sun, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, T.; Peng, S. Preparation of the plasmonic Ag/AgBr/ZnO film substrate for reusable SERS detection: Implication to the Z-scheme photocatalytic mechanism. Spectrochim. Acta Part A-Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 224, 117381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Ru, E.C.; Blackie, E.; Meyer, M.; Etchegoin, P.G. Surface enhanced Raman scattering enhancement factors: A comprehensive study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 13794–13803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.-N.; Man, S.-Q. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering of methylene blue adsorbed on cap-shaped Silver nanoparticles. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2007, 447, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.A.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.-L.; Sun, M.-L.; Zhang, W. Superhydrophobic SERS chip based on a Ag coated natural taro-leaf. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 11487–11493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauer, L.J.; Chernyshova, A.L.; Hiatt, A.; Deering, A.; Davis, R. Melamine Detection in Infant Formula Powder Using Near- and Mid-Infrared Spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 3974–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.; Barcelo, S.J.; Williams, R.S.; Li, Z. Melamine sensing in milk products by using surface enhanced Raman scattering. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 9303–9309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Method | Analyte | Time | LOD | Droplet Manipulation | Number of Droplets Prepared Simultaneously | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Light-trapping SERS substrate | R6G | Not available | 10−13 M | Not applicable | 1 | [12] |
| Taro-leaf@Ag | R6G | 120 min (4 μL) | 10−8 M | Not applicable | 3 | [25] |
| Slippery liquid-infused porous surface | R6G | 5 min (50 μL) | 10−18 M | Not applicable | 1 | [15] |
| Continuous-rolling-assisted evaporation on a superhydrophobic surface | CV | 9 min (50 μL) | 10−15 M | Feasible | 1 | [18] |
| Superhydrophobic magnetically functionalized PDMS | R6G | 180 min (20 μL) | 10−17 M | Feasible | 9 | [16,17] |
| Superhydrophobic concave dome array | CV | 40 min (13 μL) | 10−11 M | Feasible | 36 (can be scalable) | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Cai, J.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, H.; Yan, S. Effective Enrichment of Plasmonic Hotspots for SERS by Spinning Droplets on a Slippery Concave Dome Array. Biosensors 2022, 12, 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12050270
Wu J, Cai J, Fan Y, Zhang Y, Fang H, Yan S. Effective Enrichment of Plasmonic Hotspots for SERS by Spinning Droplets on a Slippery Concave Dome Array. Biosensors. 2022; 12(5):270. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12050270
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jialin, Jianpeng Cai, Yuan Fan, Ying Zhang, Hui Fang, and Sheng Yan. 2022. "Effective Enrichment of Plasmonic Hotspots for SERS by Spinning Droplets on a Slippery Concave Dome Array" Biosensors 12, no. 5: 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12050270
APA StyleWu, J., Cai, J., Fan, Y., Zhang, Y., Fang, H., & Yan, S. (2022). Effective Enrichment of Plasmonic Hotspots for SERS by Spinning Droplets on a Slippery Concave Dome Array. Biosensors, 12(5), 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12050270








