Exploiting the Nucleic Acid Nature of Aptamers for Signal Amplification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Aptamer Preparation
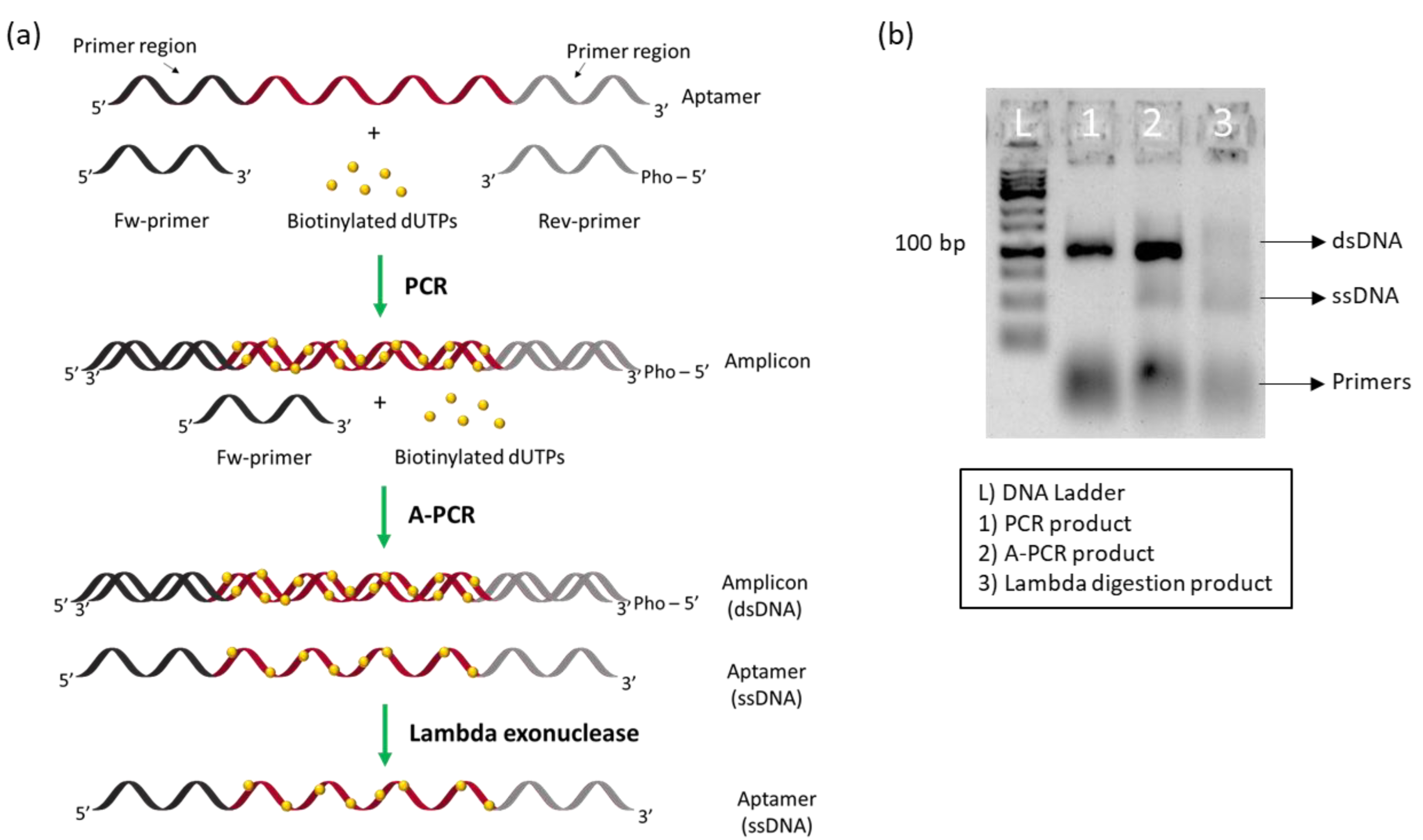
2.2.1. Incorporation of Biotinylated dNTPs
2.2.2. Asymmetric Polymerase Chain Reaction (A-PCR)
2.2.3. Enzyme Digestion
2.3. Affinity Studies: Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR)
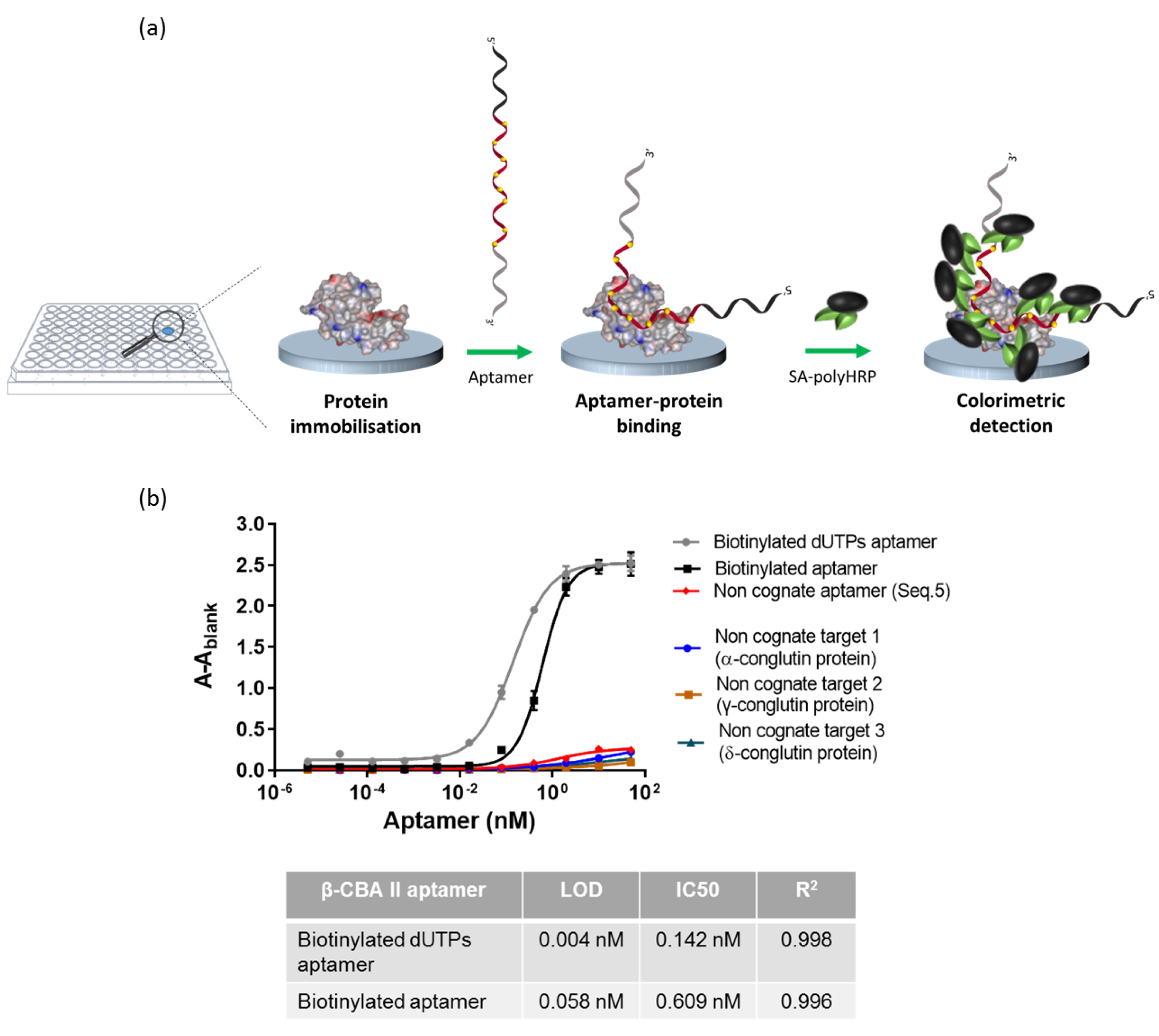
2.4. Enzyme Linked Aptamer Assay (ELAA)
2.4.1. Evaluation of Biotinylated Aptamer
2.4.2. Competition Assay
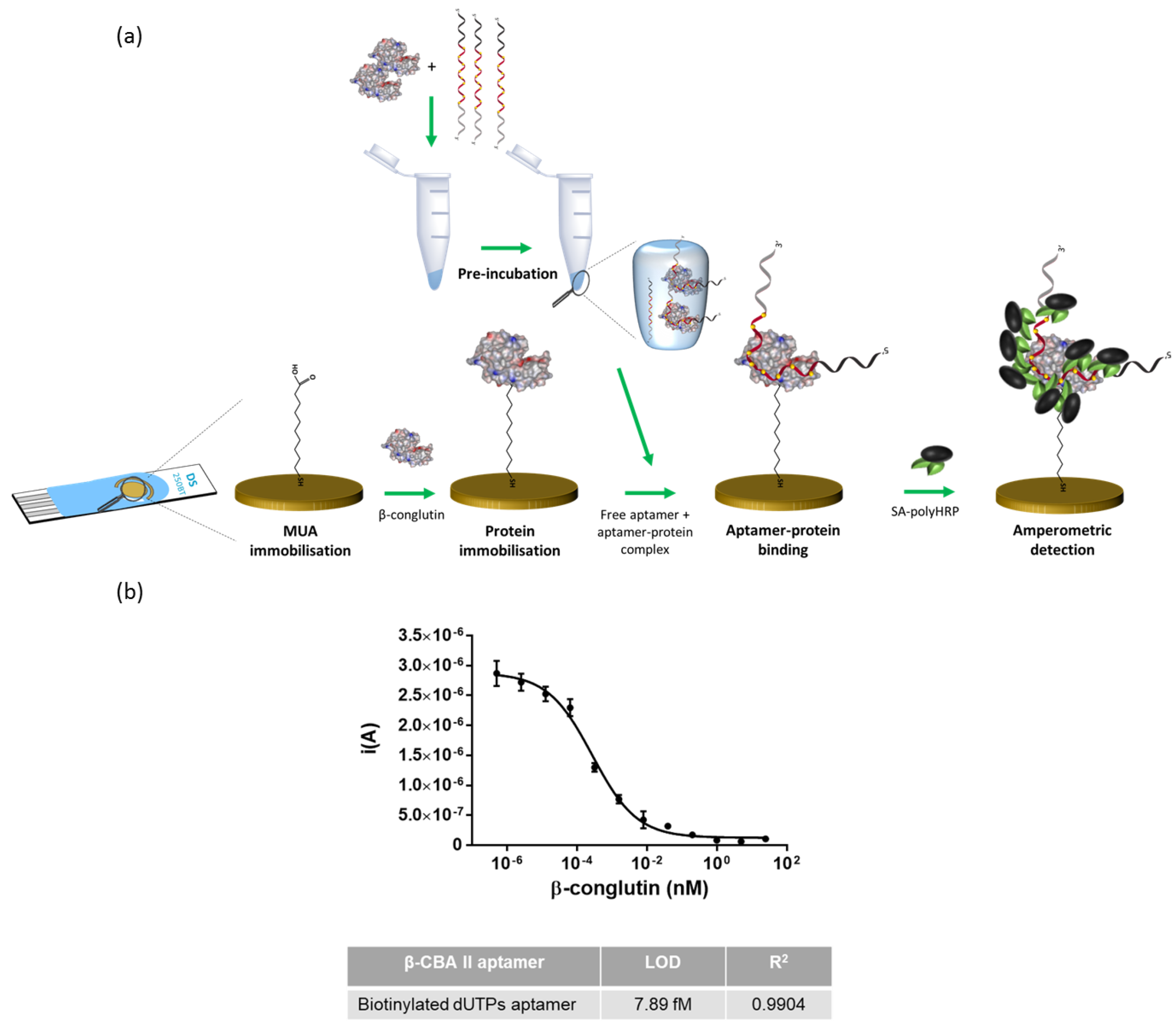
2.5. Electrochemical Detection
2.5.1. Instrumentation
2.5.2. Functionalization of the Screen-Printed Electrodes
2.5.3. Evaluation of the Functionalized Screen-Printed Electrodes (SPEs)
2.5.4. Competition on Screen-Printed Electrodes
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Aptamer Preparation: Incorporation of Biotinylated dNTPs
3.2. Evaluation of the Binding Affinity of the Biotinylated Aptamer
3.3. Evaluation of the Sensitivity of Biotinylated Aptamer Using an Enzyme-Linked Aptamer Assay (ELAA)
3.4. Competition Assay on Microtiter Plate: Enzyme-Linked Aptamer Assay (ELAA)
3.5. Electrochemical Detection
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hasegawa, H.; Savory, N.; Abe, K.; Ikebukuro, K. Methods for Improving Aptamer Binding Affinity. Molecules 2016, 21, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalra, P.; Dhiman, A.; Cho, W.C.; Bruno, J.G.; Sharma, T.K. Simple Methods and Rational Design for Enhancing Aptamer Sensitivity and Specificity. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2018, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gold, L.; Ayers, D.; Bertino, J.; Bock, C.; Bock, A.; Brody, E.N.; Carter, J.; Dalby, A.B.; Eaton, B.E.; Fitzwater, T.; et al. Aptamer-Based Multiplexed Proteomic Technology for Biomarker Discovery. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimoto, M.; Yamashige, R.; Matsunaga, K.-I.; Yokoyama, S.; Hirao, I. Generation of high-affinity DNA aptamers using an expanded genetic alphabet. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohloff, J.C.; Gelinas, A.D.; Jarvis, T.C.; Ochsner, U.A.; Schneider, D.J.; Gold, L.; Janjic, N. Nucleic Acid Ligands with Protein-like Side Chains: Modified Aptamers and Their Use as Diagnostic and Therapeutic Agents. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2014, 3, e201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chen, C.; Larcher, L.M.; Barrero, R.A.; Veedu, R.N. Three decades of nucleic acid aptamer technologies: Lessons learned, progress and opportunities on aptamer development. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 37, 28–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, D.R.; Gelinas, A.D.; Zhang, C.; Rohloff, J.C.; Carter, J.D.; O’Connell, D.; Waugh, S.M.; Wolk, S.K.; Mayfield, W.S.; Burgin, A.B.; et al. Unique motifs and hydrophobic interactions shape the binding of modified DNA ligands to protein targets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 19971–19976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapa, S.A.; Chudinov, A.V.; Timofeev, E.N. The Toolbox for Modified Aptamers. Mol. Biotechnol. 2015, 58, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Hirota, M.; Waugh, S.M.; Murakami, I.; Suzuki, T.; Muraguchi, M.; Shibamori, M.; Ishikawa, Y.; Jarvis, T.C.; Carter, J.D.; et al. Chemically Modified DNA Aptamers Bind Interleukin-6 with High Affinity and Inhibit Signaling by Blocking Its Interaction with Interleukin-6 Receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 8706–8719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwahara, M.; Obika, S. In vitro selection of BNA (LNA) aptamers. Artif. DNA PNA XNA 2013, 4, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsen, K.K.; Wengel, J. Locked Nucleic Acid and Aptamers. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2012, 22, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broker, T.R.; Angerer, L.M.; Yen, P.H.; Hershey, N.D.; Davidson, N. Electron microscopic visualization of tRNA genes with ferritin-avidin: Biotin labels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978, 5, 363–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sodja, A.; Davidson, N. Gene mapping and gene enrichment by the avidin-biotin interaction: Use of cytochrome-c as a polyamine bridge. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978, 5, 385–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Langer, P.R.; A Waldrop, A.; Ward, D.C. Enzymatic synthesis of biotin-labeled polynucleotides: Novel nucleic acid affinity probes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 6633–6637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brigati, D.J.; Myerson, D.; Leary, J.J.; Spalholz, B.; Travis, S.Z.; Fong, C.K.; Hsiung, G.; Ward, D.C. Detection of viral genomes in cultured cells and paraffin-embedded tissue sections using biotin-labeled hybridization probes. Virology 1983, 126, 32–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leary, J.J.; Brigati, D.J.; Ward, D.C. Rapid and sensitive colorimetric method for visualizing biotin-labeled DNA probes hybridized to DNA or RNA immobilized on nitrocellulose: Bio-blots. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1983, 80, 4045–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebeyehu, G.; Rao, P.Y.; Soochan, P.; Simms, D.; Klevan, L. Novel biotinylated nucleotide—Analogs for labeling and colorimetric detection of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987, 15, 4513–4534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, A.C.; Mclnnes, J.L.; Skingle, D.C.; Symons, R.H. Non-radioactive hybridization probes prepared by the chemical labelling of DNA and RNA with a novel reagent, photobiotin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985, 13, 745–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viscidi, R.P.; Connelly, C.J.; Yolken, R.H. Novel chemical method for the preparation of nucleic acids for nonisotopic hybridization. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1986, 23, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flickinger, J.; Gebeyehu, G.; Buchman, G.; Rashtchian, A. Differential incorporation of biotinylated nucleotides by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992, 20, 2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasara, T.; Angerer, B.; Damond, M.; Winter, H.; Dörhöfer, S.; Hübscher, U.; Amacker, M. Incorporation of reporter molecule-labeled nucleotides by DNA polymerases. II. High-density labeling of natural DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 2636–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, N.; Yee, J. PCR incorporation of modified dNTPs: The substrate properties of biotinylated dNTPs. BioTechniques 2010, 48, 333–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, B.F.; Chao, J.; Zhu, Z.; DeBiasio, R.L.; Fisher, G. Signal Amplification in the Detection of Single-copy DNA and RNA by Enzyme-catalyzed Deposition (CARD) of the Novel Fluorescent Reporter Substrate Cy3. 29-Tyramide. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1997, 45, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vora, G.J.; Meador, C.E.; Anderson, G.P.; Taitt, C.R. Comparison of detection and signal amplification methods for DNA microarrays. Mol. Cell. Probes 2008, 22, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorwerk, S.; Ganter, K.; Cheng, Y.; Hoheisel, J.; Stähler, P.F.; Beier, M. Microfluidic-based enzymatic on-chip labeling of miRNAs. New Biotechnol. 2008, 25, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, M.; Boisguérin, V. Microfluidic Primer Extension Assay. In Next-Generation MicroRNA Expression Profiling Technology: Methods and Protocols; Fan, J.-B., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 143–152. ISBN 978-1-61779-427-8. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, N.R.Y.; Lim, G.S.; Sundah, N.R.; Lim, D.; Loh, T.P.; Shao, H. Visual and modular detection of pathogen nucleic acids with enzyme–DNA molecular complexes. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plucnara, M.; Eksin, E.; Erdem, A.; Fojta, M. Electrochemical Detection of SNP in Human Mitochondrial DNA Using Cyclic Primer Extension with Biotinylated Nucletides and Enzymatic Labeling at Disposable Pencil Graphite Electrodes. Electroanalysis 2018, 30, 2321–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortli, S.; Jauset-Rubio, M.; Tomaso, H.; Abbas, M.N.; Bashammakh, A.S.; El-Shahawi, M.S.; Alyoubi, A.O.; Ben-Ali, M.; O’Sullivan, C.K. Yersinia pestis detection using biotinylated dNTPs for signal enhancement in lateral flow assays. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1112, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Mei, C.; Liu, A.; Jin, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, J. Cascade signal amplification for electrochemical immunosensing by integrating biobarcode probes, surface-initiated enzymatic polymerization and silver nanoparticle deposition. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 66, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Warmt, C.; Henkel, J.; Schrick, L.; Nitsche, A.; Bier, F.F. Lateral flow–based nucleic acid detection of SARS-CoV-2 using enzymatic incorporation of biotin-labeled dUTP for POCT use. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 3177–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odeh, F.; Nsairat, H.; Alshaer, W.; Ismail, M.A.; Esawi, E.; Qaqish, B.; Al Bawab, A.; Ismail, S.I. Aptamers Chemistry: Chemical Modifications and Conjugation Strategies. Molecules 2019, 25, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo-Gómez, R.; González-Robles, D.; Miranda-Castro, R.; De-Los-Santos-Álvarez, N.; Lobo-Castañón, M.J. On the Electrochemical Detection of Alpha-Fetoprotein Using Aptamers: DNA Isothermal Amplification Strategies to Improve the Performance of Weak Aptamers. Biosensors 2020, 10, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio, M.J.; Svobodová, M.; Mairal, T.; O’Sullivan, C.K. Surface plasmon resonance imaging (SPRi) for analysis of DNA aptamer:β-conglutin interactions. Methods 2016, 97, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio, M.J.; Svobodova, M.; Mairal, T.; Schubert, T.; Künne, S.; Mayer, G.; O’Sullivan, C.K. β-Conglutin dual aptamers binding distinct aptatopes. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 408, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauset-Rubio, M.; Svobodová, M.; Mairal, T.; McNeil, C.; Keegan, N.; El-Shahawi, M.S.; Bashammakh, A.S.; Alyoubi, A.O.; O’Sullivan, C.K. Aptamer Lateral Flow Assays for Ultrasensitive Detection of β-Conglutin Combining Recombinase Polymerase Amplification and Tailed Primers. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 10701–10709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauset-Rubio, M.; del Río, J.S.; Mairal, T.; Svobodová, M.; El-Shahawi, M.S.; Bashammakh, A.S.; Alyoubi, A.O.; O’Sullivan, C.K. Ultrasensitive and rapid detection of β-conglutin combining aptamers and isothermal recombinase polymerase amplification. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 409, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civit, L.; Fragoso, A.; O’Sullivan, C.K. Evaluation of techniques for generation of single-stranded DNA for quantitative detection. Anal. Biochem. 2012, 431, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svobodova, M.; Pinto, A.; Nadal, P.; Sullivan, C.K.O. Comparison of different methods for generation of single-stranded DNA for SELEX processes. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 404, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, K.L.; Devanarayan, V.; Kriauciunas, A.; Manetta, J.; Montrose, C.; Sittampalam, S. Immunoassay Methods. 1 May 2012 [Updated 8 July 2019]. In Assay Guidance Manual [Internet]; Markossian, S., Grossman, A., Brimacombe, K., Markossian, S., Grossman, A., Brimacombe, K., Arkin, M., Auld, D., Austin, C., Baell, J., et al., Eds.; Eli Lilly & Company and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2004. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK92434/ (accessed on 26 September 2022).
- Jalalian, S.H.; Karimabadi, N.; Ramezani, M.; Abnous, K.; Taghdisi, S.M. Electrochemical and optical aptamer-based sensors for detection of tetracyclines. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 73, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jauset-Rubio, M.; Ortiz, M.; O’Sullivan, C.K. Exploiting the Nucleic Acid Nature of Aptamers for Signal Amplification. Biosensors 2022, 12, 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12110972
Jauset-Rubio M, Ortiz M, O’Sullivan CK. Exploiting the Nucleic Acid Nature of Aptamers for Signal Amplification. Biosensors. 2022; 12(11):972. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12110972
Chicago/Turabian StyleJauset-Rubio, Miriam, Mayreli Ortiz, and Ciara K. O’Sullivan. 2022. "Exploiting the Nucleic Acid Nature of Aptamers for Signal Amplification" Biosensors 12, no. 11: 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12110972
APA StyleJauset-Rubio, M., Ortiz, M., & O’Sullivan, C. K. (2022). Exploiting the Nucleic Acid Nature of Aptamers for Signal Amplification. Biosensors, 12(11), 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12110972




