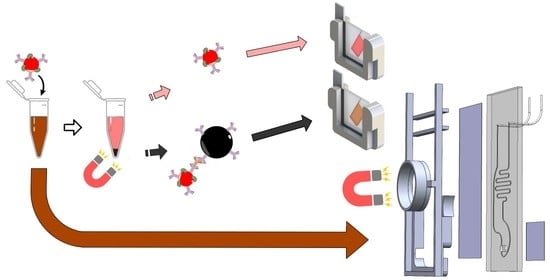
Design and Optimization of A Magneto-Plasmonic Sandwich Biosensor for Integration within Microfluidic Devices
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Buffers
2.2. Microcell for Absorption Measurements
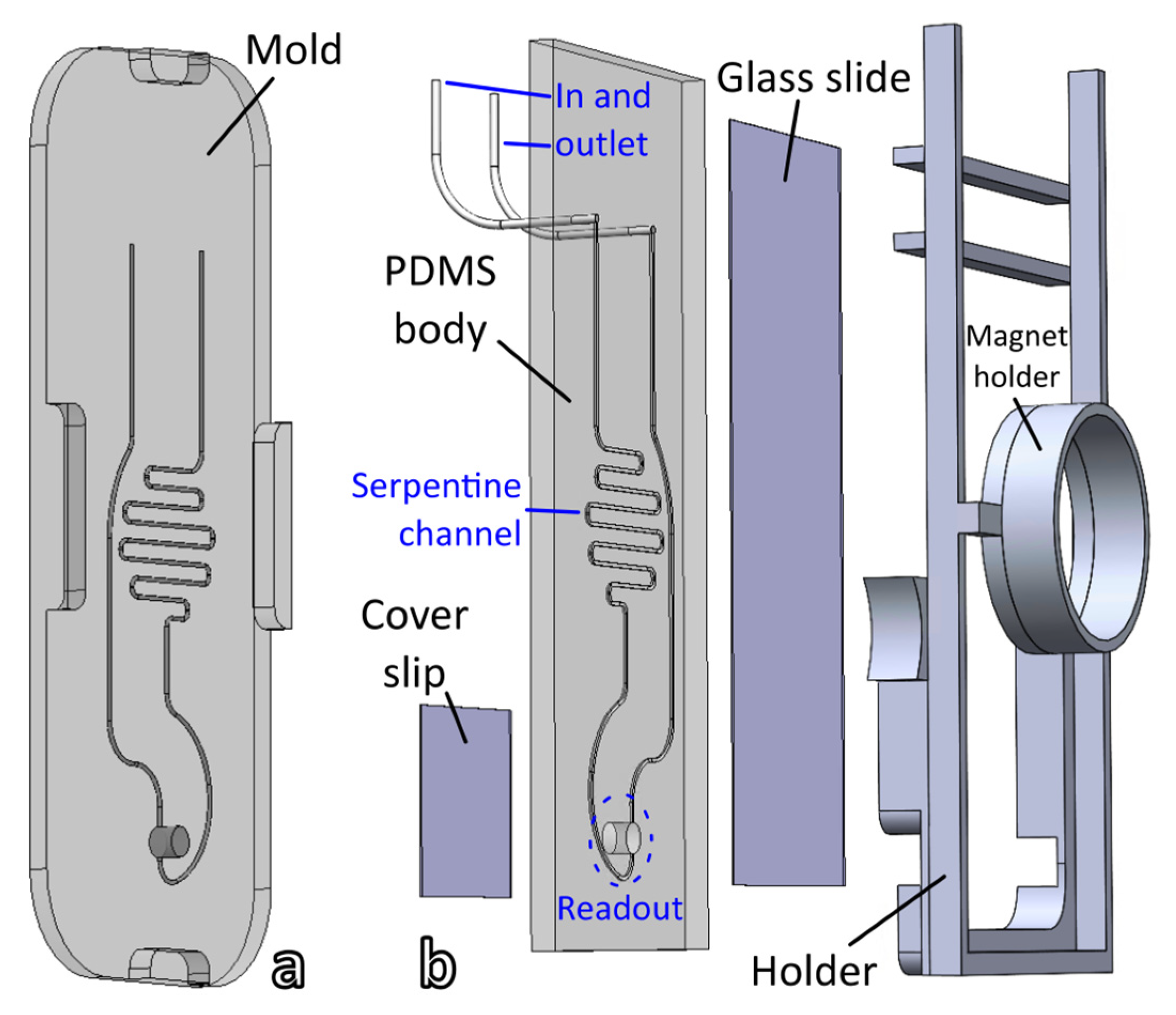
2.3. Microfluidic Cell
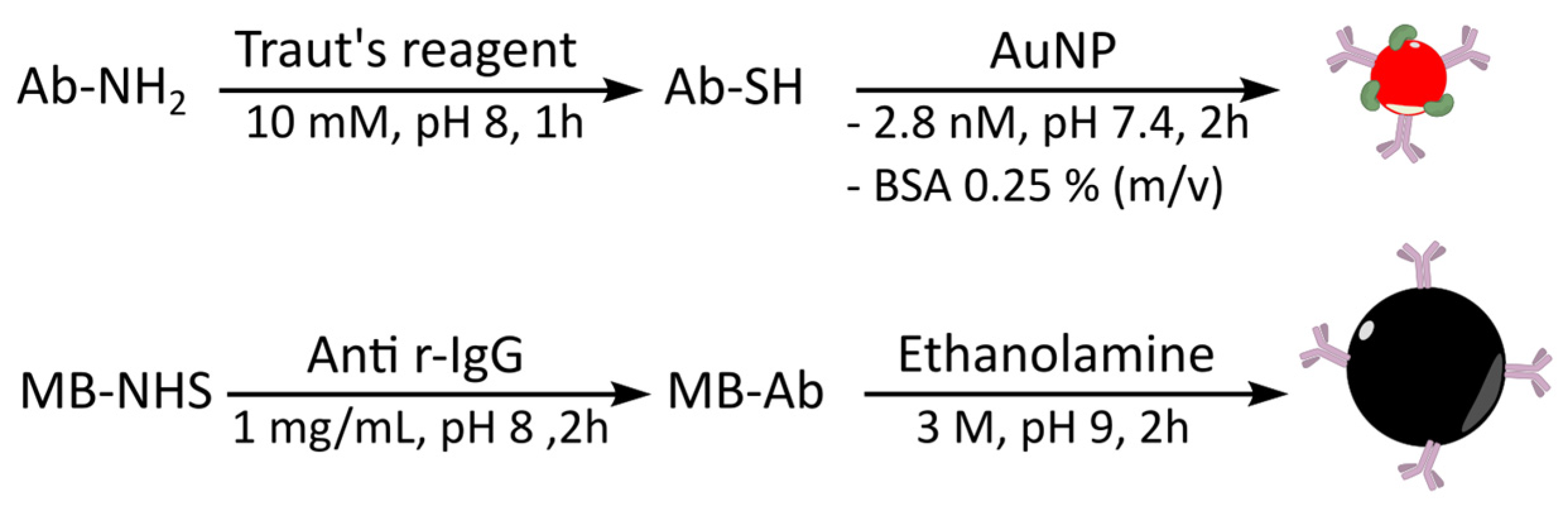
2.4. Conjugation of Goat Anti-rIgG Antibody to Magnetic Beads
2.5. ELISA Test for Validation of Antibody Attachment to Magnetic Beads
2.6. AuNP Synthesis
2.7. Conjugation of Goat Anti-rIgG to AuNP
2.8. Determination of Number of Ab Conjugated to AuNP
2.9. Magneto-Plasmonic Immunosensor
2.10. Characterization Methods and Optical Measurements
3. Results
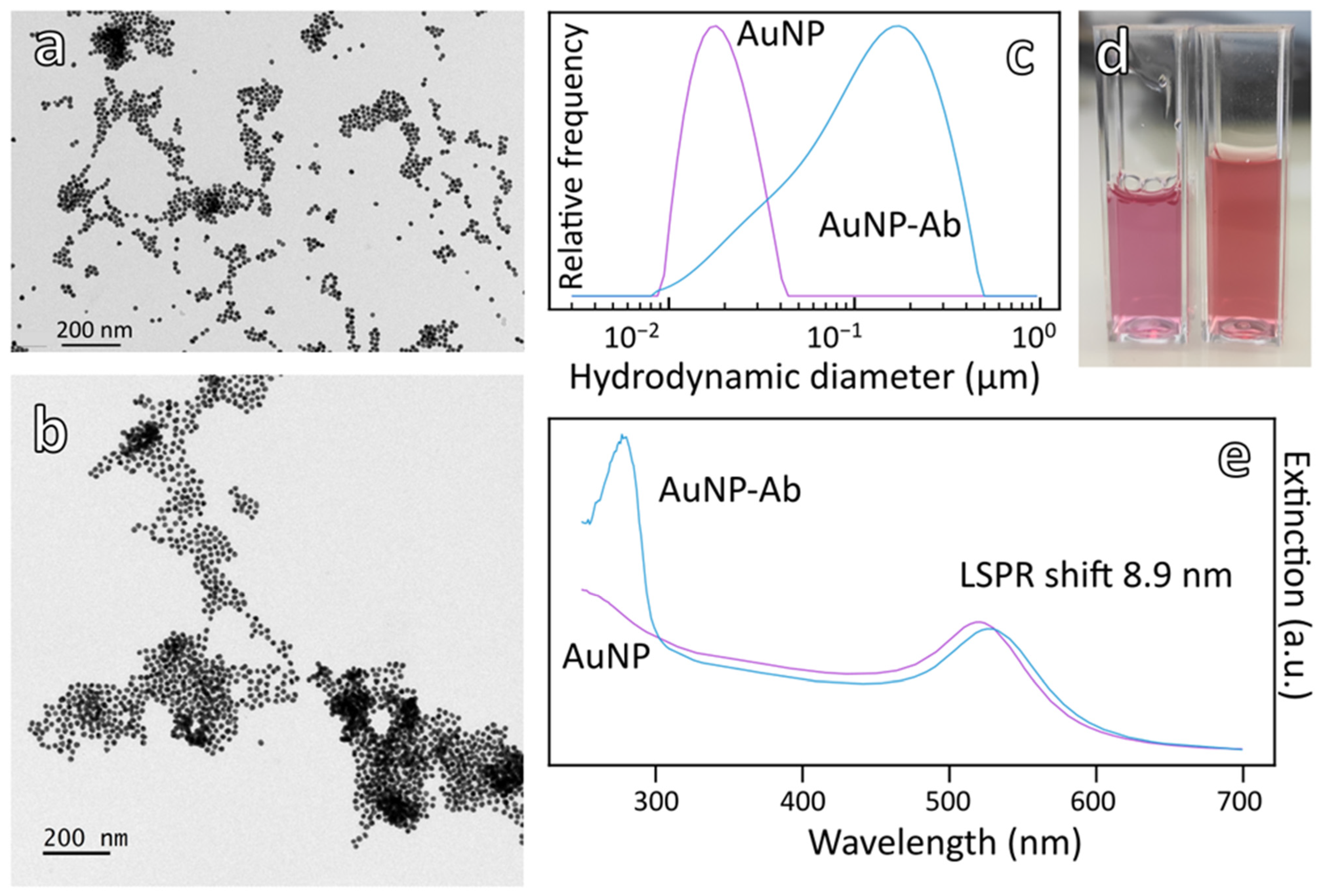
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of AuNP and Bioconjugation of Antibody
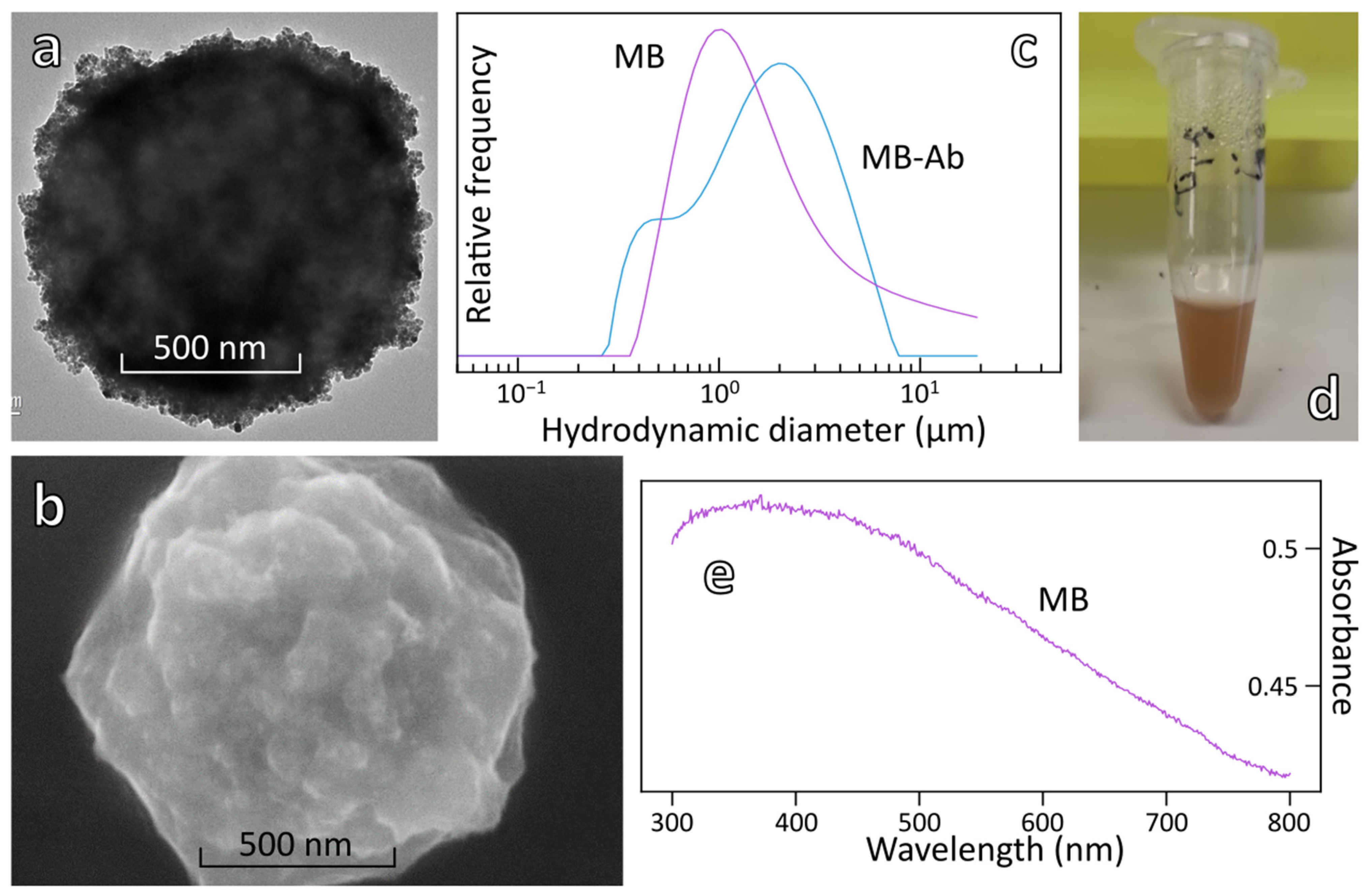
3.2. Conjugation of Antibody to Magnetic Beads
3.3. Magneto-Plasmonic Immunodetection of Rabbit IgG
3.3.1. Characterization of Magneto-Plasmonic Immunocomplex
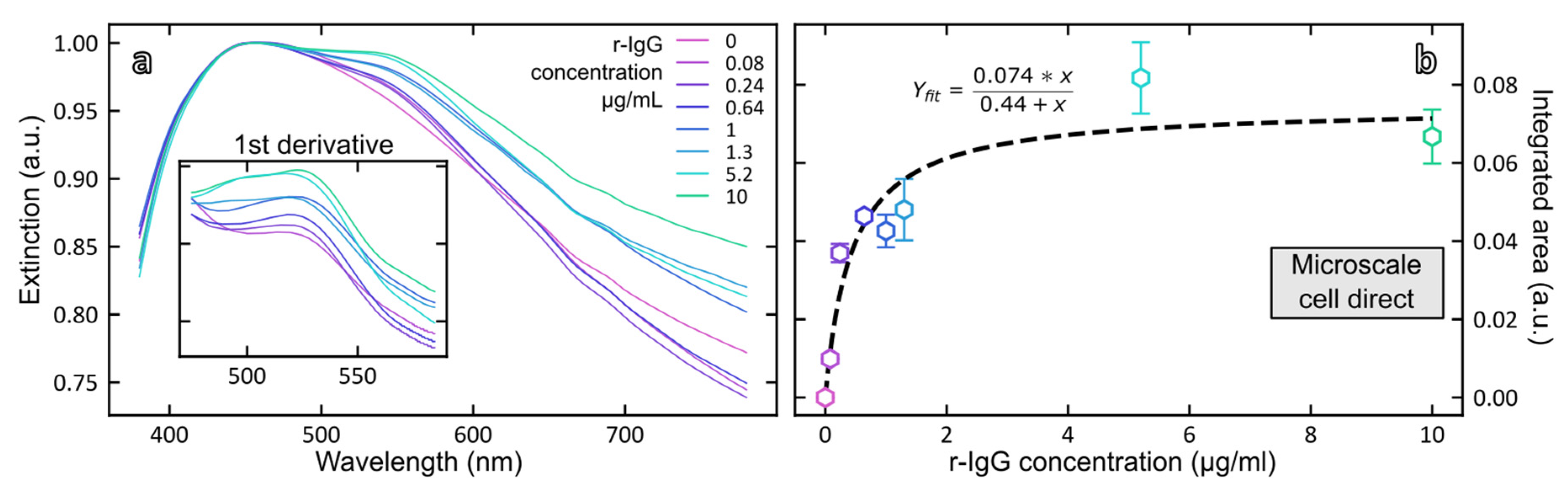
3.3.2. Direct Detection of Rabbit IgG with Magneto-Plasmonic Immunosensor
3.3.3. Indirect Detection of Rabbit IgG
3.3.4. Indirect Detection of Rabbit IgG with Microfluidic Cell
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Metkar, S.K.; Girigoswami, K. Diagnostic biosensors in medicine—A review. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 17, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbinot, S.; Srivastav, A.M.; Vidic, J.; Abdulhalim, I.; Manzano, M. Plasmonic biosensors for food control. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 111, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justino, C.I.L.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T.A.P. Recent Progress in Biosensors for Environmental Monitoring: A Review. Sensors 2017, 17, 2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Schluesener, H.J.; Xu, S. Gold nanoparticle-based biosensors. Gold Bull. 2010, 43, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler, M.; Huertas, C.S.; Lechuga, L.M. Label-free plasmonic biosensors for point-of-care diagnostics: A review. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2019, 19, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldewachi, H.; Chalati, T.; Woodroofe, M.N.; Bricklebank, N.; Sharrack, B.; Gardiner, P. Gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric biosensors. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Ji, C.; Chen, D.; Nie, L. Applications of Gold Nanoparticles in Non-Optical Biosensors. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Salmain, M.; Liedberg, B.; Boujday, S. Naked Eye Immunosensing of Food Biotoxins Using Gold Nanoparticle-Antibody Bioconjugates. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 4150–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loiseau, A.; Zhang, L.; Hu, D.; Salmain, M.; Mazouzi, Y.; Flack, R.; Liedberg, B.; Boujday, S. Core–Shell Gold/Silver Nanoparticles for Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance-Based Naked-Eye Toxin Biosensing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 46462–46471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepúlveda, B.; Angelomé, P.C.; Lechuga, L.M.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. LSPR-based nanobiosensors. Nano Today 2009, 4, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, B.; Pandey, B.; Neupane, B.; Ligler, F.S. Signal amplification strategies for microfluidic immunoassays. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 79, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekin, H.C.; Gijs, M.A.M. Ultrasensitive protein detection: A case for microfluidic magnetic bead-based assays. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 4711–4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.-M.; Luo, K.; Jung, J.-Y.; Jeong, K.-B.; Lee, E.-S.; Oh, M.-H.; Kim, Y.-R. Gold Nanoparticle-Coated Starch Magnetic Beads for the Separation, Concentration, and SERS-Based Detection of E. coli O157:H7. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 18292–18300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Lv, Z.; Mao, Y.; Yu, L.; Bi, X.; Xu, S.; Cui, J.; Wu, Y.-C. SERS-Based Pump-Free Microfluidic Chip for Highly Sensitive Immunoassay of Prostate-Specific Antigen Biomarkers. ACS Sensors 2019, 4, 938–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Ko, J.; Cha, K.; Jeon, J.H.; Rhie, G.-E.; Choi, J.; Demello, A.J.; Choo, J. Fast and sensitive detection of an anthrax biomarker using SERS-based solenoid microfluidic sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 72, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Cheng, Z.; Demello, A.J.; Choo, J. Wash-free magnetic immunoassay of the PSA cancer marker using SERS and droplet microfluidics. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 1022–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Hu, Y.; Dong, N. A novel biosensor based on competitive SERS immunoassay and magnetic separation for accurate and sensitive detection of chloramphenicol. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 80, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chon, H.; Lee, S.; Yoon, S.-Y.; Lee, E.K.; Chang, S.-I.; Choo, J. SERS-based competitive immunoassay of troponin I and CK-MB markers for early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction. Chem. Commun. 2013, 50, 1058–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temur, E.; Zengin, A.; Boyacı, I.H.; Dudak, F.C.; Torul, H.; Tamer, U. Attomole Sensitivity of Staphylococcal Enterotoxin B Detection Using an Aptamer-Modified Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Probe. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 10600–10606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chon, H.; Lim, C.; Ha, S.-M.; Ahn, Y.; Lee, E.K.; Chang, S.-I.; Seong, G.H.; Choo, J. On-Chip Immunoassay Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering of Hollow Gold Nanospheres. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 5290–5295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Casas, J.; Venkataramasubramani, M. Magnetic Nanoparticle Mediated Enhancement of Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance for Ultrasensitive Bioanalytical Assay in Human Blood Plasma. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 1431–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jans, H.; Jans, K.; Demeyer, P.-J.; Knez, K.; Stakenborg, T.; Maes, G.; Lagae, L. A simple double-bead sandwich assay for protein detection in serum using UV–vis spectroscopy. Talanta 2011, 83, 1580–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Niessner, R.; Knopp, D. Controlled growth of immunogold for amplified optical detection of aflatoxin B1. Analyst 2015, 140, 1453–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Niessner, R.; Knopp, D. Magnetic Bead-Based Colorimetric Immunoassay for Aflatoxin B1 Using Gold Nanoparticles. Sensors 2014, 14, 21535–21548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.-Z.; Chen, Y.-H.; Liang, C.-K.; Liu, C.-C.; Hou, S.-Y. A competitive immunoassay for biotin detection using magnetic beads and gold nanoparticle probes. Food Chem. 2019, 271, 440–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Huang, X.; Ren, J. Sandwich immunoassay for alpha-fetoprotein in human sera using gold nanoparticle and magnetic bead labels along with resonance Rayleigh scattering readout. Mikrochim. Acta 2013, 180, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Li, G.; Sun, S.; Tan, H.; He, Y. Digital immunoassay of a prostate-specific antigen using gold nanorods and magnetic nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 27595–27602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hu, D.; Salmain, M.; Liedberg, B.; Boujday, S. Direct quantification of surface coverage of antibody in IgG-Gold nanoparticles conjugates. Talanta 2019, 204, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Haddada, M.; Hu, D.; Salmain, M.; Zhang, L.; Peng, C.; Wang, Y.; Liedberg, B.; Boujday, S. Gold nanoparticle-based localized surface plasmon immunosensor for staphylococcal enterotoxin A (SEA) detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 6227–6234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turkevich, J.; Stevenson, P.C.; Hillier, J. A study of the nucleation and growth processes in the synthesis of colloidal gold. Discuss. Faraday Soc. 1951, 11, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Atwater, M.; Wang, J.; Huo, Q. Extinction coefficient of gold nanoparticles with different sizes and different capping ligands. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2007, 58, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| HD (nm) | PD (%) | Zeta Pot. (mV) | TEM Size (nm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AuNP | 18.6 | 16.5 | −59.2 ± 0.9 | 15.3 ± 1.5 |
| AuNP-Ab | 105.3 | 28.2 | −19.1 ± 0.6 | 16.2 ± 1.2 |
| HD (µm) | Zeta Pot. (mV) | TEM Size (µm) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MB | 1.11 | −23.3 ± 0.5 | 1.1 ± 0.1 |
| MB-Ab | 1.24 | −17.3 ± 1.1 |
| Microscale Cell | Microfluidic Cell | |
|---|---|---|
| Indirect detection | χ2 = 0.00065 | χ2 = 0.00028 |
| R2 = 0.979 | R2 = 0.976 | |
| IC50 = 0.42 ± 0.06 µg/mL | IC50 = 4.9 ± 2.2 ng/mL | |
| LoD = 230 ng/mL a | LoD = 1.2 ng/mL b | |
| Direct detection | χ2 = 0.000076 | Not done |
| R2 = 0.91 | ||
| Kd = 0.43 ± 0.17 µg/mL | ||
| LoD = 70 ng/mL a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soroush, M.; Ait Mammar, W.; Wilson, A.; Ghourchian, H.; Salmain, M.; Boujday, S. Design and Optimization of A Magneto-Plasmonic Sandwich Biosensor for Integration within Microfluidic Devices. Biosensors 2022, 12, 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12100799
Soroush M, Ait Mammar W, Wilson A, Ghourchian H, Salmain M, Boujday S. Design and Optimization of A Magneto-Plasmonic Sandwich Biosensor for Integration within Microfluidic Devices. Biosensors. 2022; 12(10):799. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12100799
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoroush, Mona, Walid Ait Mammar, Axel Wilson, Hedayatollah Ghourchian, Michèle Salmain, and Souhir Boujday. 2022. "Design and Optimization of A Magneto-Plasmonic Sandwich Biosensor for Integration within Microfluidic Devices" Biosensors 12, no. 10: 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12100799
APA StyleSoroush, M., Ait Mammar, W., Wilson, A., Ghourchian, H., Salmain, M., & Boujday, S. (2022). Design and Optimization of A Magneto-Plasmonic Sandwich Biosensor for Integration within Microfluidic Devices. Biosensors, 12(10), 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12100799