Hybrid Technologies Combining Solid-State Sensors and Paper/Fabric Fluidics for Wearable Analytical Devices
Abstract
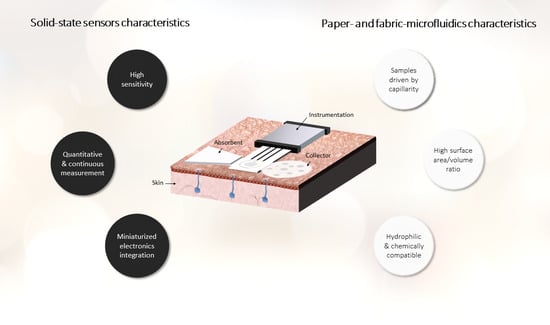
:1. Introduction
1.1. Microfluidic Elements
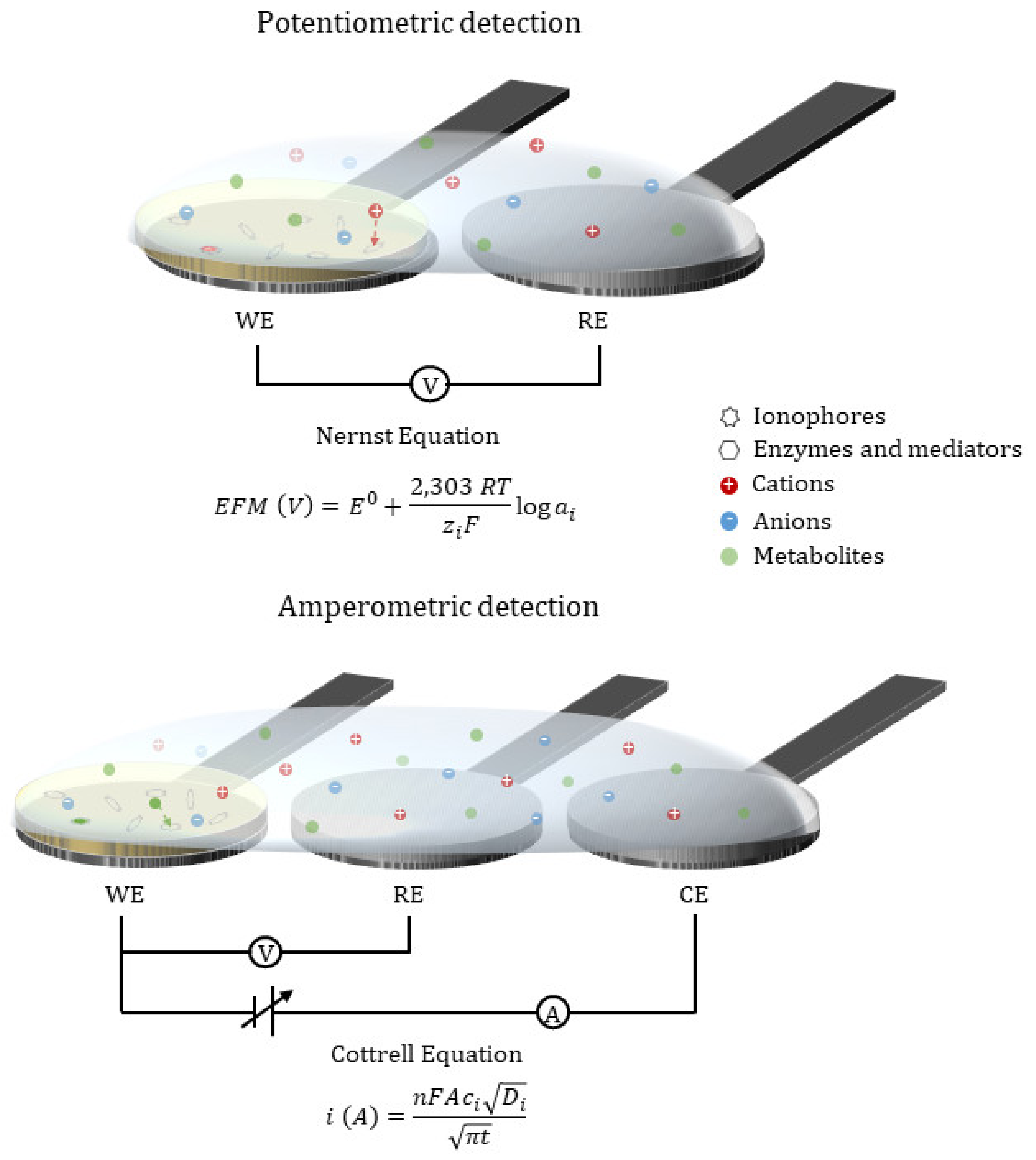
1.2. Sensor Types
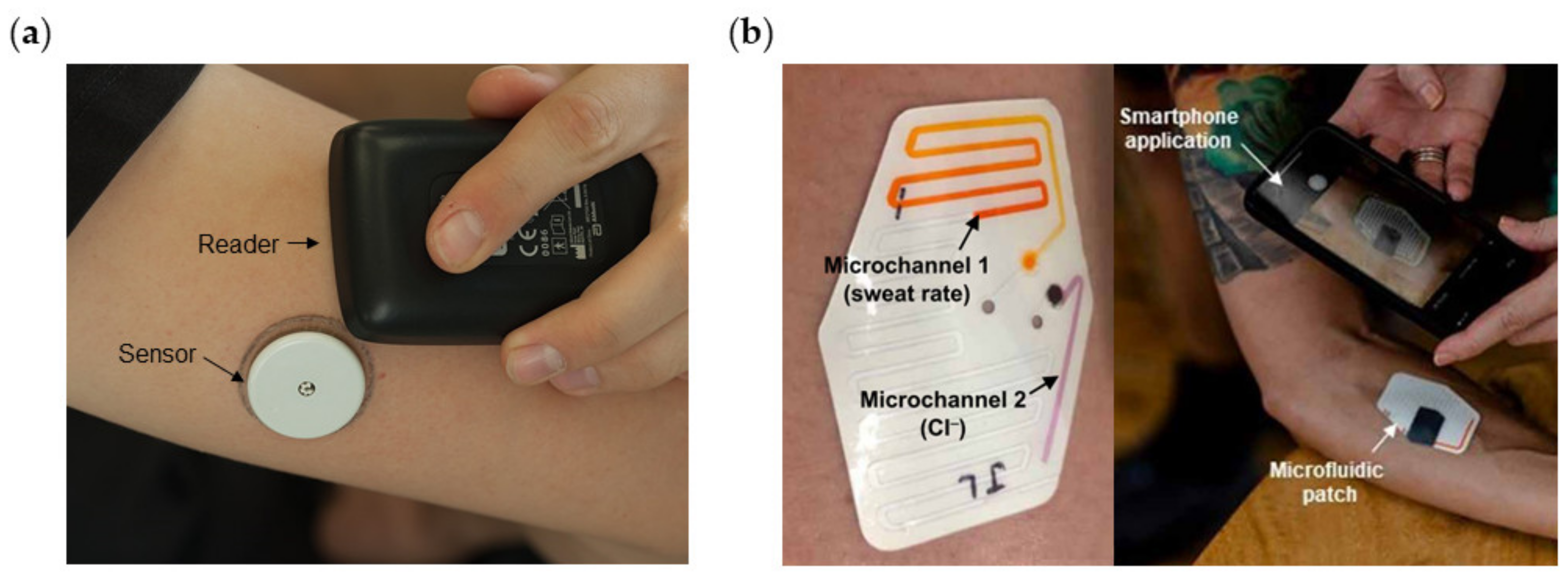
1.3. Applications in Healthcare
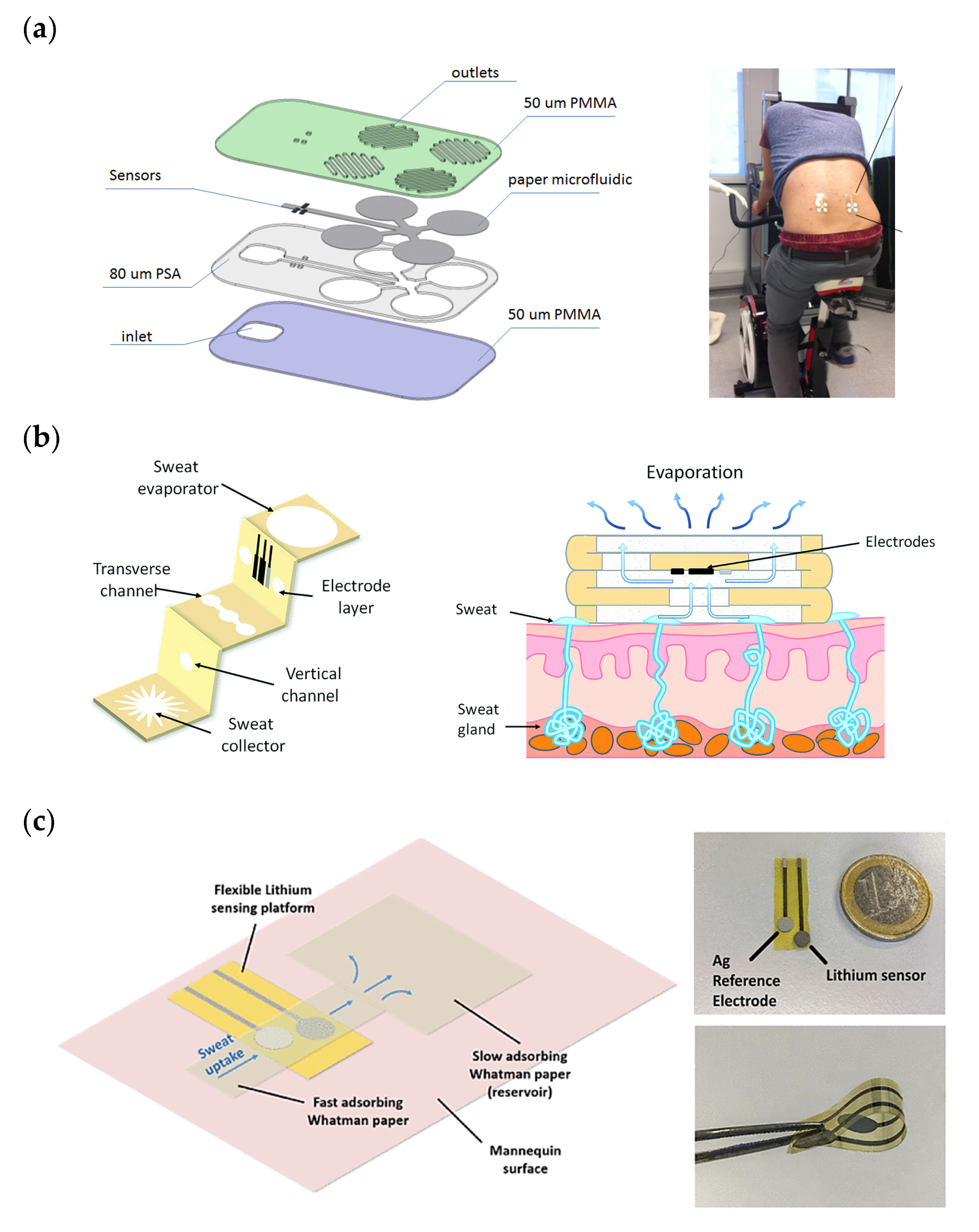
2. Paper-Based Microfluidics for Wearable Devices
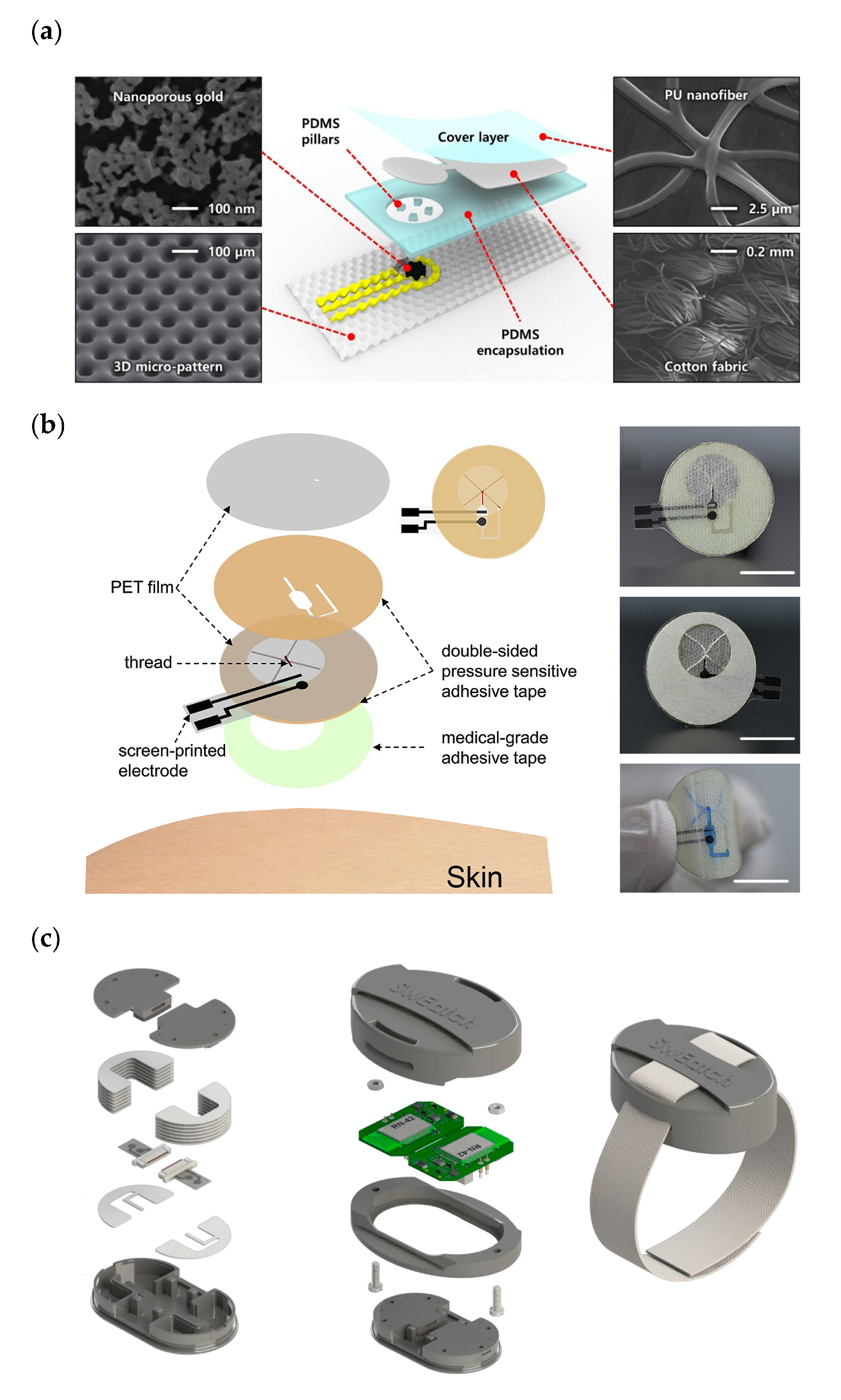
3. Fabric-Based Microfluidics for Wearable Devices
4. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eltzov, E.; Guttel, S.; Kei, A.L.Y.; Sinawang, P.D.; Ionescu, R.E.; Marks, R.S. Lateral Flow Immunoassays – from Paper Strip to Smartphone Technology. Electroanalysis 2015, 27, 2116–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisgrab, G.; Ovsianikov, A.; Costa, P.F. Functional 3D Printing for Microfluidic Chips. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1900275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abbot An Easy, Integrated Point-of-Care Testing (POCT) Solution for a Broad Range of Clinical Settings. Available online: https://www.pointofcare.abbott/int/en/offerings/istat (accessed on 30 July 2021).
- Gutiérrez-Capitán, M.; Baldi, A.; Fernández-Sánchez, C. Electrochemical paper-based biosensor devices for rapid detection of biomarkers. Sensors 2020, 20, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tseng, C.-C.; Kung, C.-T.; Chen, R.-F.; Tsai, M.-H.; Chao, H.-R.; Wang, Y.-N.; Fu, L.-M. Recent advances in microfluidic paper-based assay devices for diagnosis of human diseases using saliva, tears and sweat samples. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elizalde, E.; Urteaga, R.; Berli, C.L.A. Rational design of capillary-driven flows for paper-based microfluidics. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 2173–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimeski, G.; Jones, B.W.; Tilley, V.; Greenslade, M.N.; Russell, A.W. Glucose meters: Evaluation of the new formulation measuring strips from Roche (Accu-Chek) and Abbott (MediSense). Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2010, 47, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Shi, D.; Wan, N.; Yang, X.; Liu, H.; Gao, H.; Zhang, M.; Bai, Z.; Li, D.; Dai, E.; et al. Development of spike protein-based fluorescence lateral flow assay for the simultaneous detection of SARS-CoV-2 specific IgM and IgG. Analyst 2021, 146, 3908–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Tian, J.; Shen, W. Thread as a versatile material for low-cost microfluidic diagnostics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhandari, P.; Narahari, T.; Dendukuri, D. Fab-Chips: A versatile, fabric-based platform for low-cost, rapid and multiplexed diagnostics. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 2493–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatamie, A.; Angizi, S.; Kumar, S.; Pandey, C.M.; Simchi, A.; Willander, M.; Malhotra, B.D. Review - Textile Based Chemical and Physical Sensors for Healthcare Monitoring. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cate, D.M.; Adkins, J.A.; Mettakoonpitak, J.; Henry, C.S. Recent Developments in Paper-Based Microfluidic Devices. Anal. Chem. 2014, 87, 19–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nery, E.W.; Kubota, L.T. Sensing approaches on paper-based devices: A review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 7573–7595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Promphet, N.; Rattanawaleedirojn, P.; Siralertmukul, K.; Soatthiyanon, N.; Potiyaraj, P.; Thanawattano, C.; Hinestroza, J.P.; Rodthongkum, N. Non-invasive textile based colorimetric sensor for the simultaneous detection of sweat pH and lactate. Talanta 2019, 192, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noviana, E.; McCord, C.P.; Clark, K.M.; Jang, I.; Henry, C.S. Electrochemical paper-based devices: Sensing approaches and progress toward practical applications. Lab Chip 2019, 20, 9–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Li, L.; Song, Y. Inkjet printing wearable electronic devices. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 2971–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demuru, S.; Kunnel, B.P.; Briand, D. Real-Time Multi-Ion Detection in the Sweat Concentration Range Enabled by Flexible, Printed, and Microfluidics-Integrated Organic Transistor Arrays. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, S.; Arie, T.; Akita, S.; Takei, K. Wearable, Flexible, and Multifunctional Healthcare Device with an ISFET Chemical Sensor for Simultaneous Sweat pH and Skin Temperature Monitoring. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Rupakula, M.; Bellando, F.; Garcia Cordero, E.; Longo, J.; Wildhaber, F.; Herment, G.; Guérin, H.; Ionescu, A.M. Sweat Biomarker Sensor Incorporating Picowatt, Three-Dimensional Extended Metal Gate Ion Sensitive Field Effect Transistors. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 2039–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Cordero, E.; Bellando, F.; Zhang, J.; Wildhaber, F.; Longo, J.; Guérin, H.; Ionescu, A.M. Three-Dimensional Integrated Ultra-Low-Volume Passive Microfluidics with Ion-Sensitive Field-Effect Transistors for Multiparameter Wearable Sweat Analyzers. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 12646–12656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, D. Wiley: Principles of Chemical and Biological Sensors. 1998. Available online: https://www.wiley.com/en-us/Principles+of+Chemical+and+Biological+Sensors-p-9780471546191 (accessed on 25 August 2021).
- Abbott FreeStyle Libre. Available online: https://www.freestyle.abbott/us-en/home.html (accessed on 23 August 2021).
- Bunn, J.A.; Navalta, J.W.; Fountaine, C.J.; Reece, J.D. Current State of Commercial Wearable Technology in Physical Activity Monitoring 2015–2017. Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2018, 11, 503. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baker, L.B.; Model, J.B.; Barnes, K.A.; Anderson, M.L.; Lee, S.P.; Lee, K.A.; Brown, S.D.; Reimel, A.J.; Roberts, T.J.; Nuccio, R.P.; et al. Skin-interfaced microfluidic system with personalized sweating rate and sweat chloride analytics for sports science applications. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabe3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirunavukkarasye-Raveendran Blutzuckermessgerät FreeStyle Libre Mit Auslesegerät, Am Oberarm Befestigt. Available online: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:FreeStyle_libre_am_Oberarm_und_Auslesegerät-5.JPG#globalusage (accessed on 26 August 2021).
- Schazmann, B.; Morris, D.; Slater, C.; Beirne, S.; Fay, C.; Reuveny, R.; Moyna, N.; Diamond, D. A wearable electrochemical sensor for the real-time measurement of sweat sodium concentration. Anal. Methods 2010, 2, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Pandey, C.M.; Hatamie, A.; Simchi, A.; Willander, M.; Malhotra, B.D. Nanomaterial-Modified Conducting Paper: Fabrication, Properties, and Emerging Biomedical Applications. Glob. Chall. 2019, 3, 1900041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghahremani Honarvar, M.; Latifi, M. Overview of wearable electronics and smart textiles. J. Text. Inst. 2017, 108, 631–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.; Mohammadifar, M.; Choi, S. A single-use, self-powered, paper-based sensor patch for detection of exercise-induced hypoglycemia. Micromachines 2017, 8, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colozza, N.; Kehe, K.; Dionisi, G.; Popp, T.; Tsoutsoulopoulos, A.; Steinritz, D.; Moscone, D.; Arduini, F. A wearable origami-like paper-based electrochemical biosensor for sulfur mustard detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 129, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Wang, L.; Liu, R.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, G.; Li, Y.; Hou, C.; Wang, H. A highly integrated sensing paper for wearable electrochemical sweat analysis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 174, 112828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.L.; Chuang, M.C.; Lou, S.L.; Wang, J. Thick-film textile-based amperometric sensors and biosensors. Analyst 2010, 135, 1230–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guinovart, T.; Parrilla, M.; Crespo, G.A.; Rius, F.X.; Andrade, F.J. Potentiometric sensors using cotton yarns, carbon nanotubes and polymeric membranes. Analyst 2013, 138, 5208–5215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppedè, N.; Tarabella, G.; Villani, M.; Calestani, D.; Iannotta, S.; Zappettini, A. Human stress monitoring through an organic cotton-fiber biosensor. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 5620–5626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zahed, M.A.; Sharifuzzaman, M.; Yoon, S.; Hui, X.; Barman, S.C.; Sharma, S.; Yoon, H.S.; Park, C.; Park, J.Y. A wearable battery-free wireless and skin-interfaced microfluidics integrated electrochemical sensing patch for on-site biomarkers monitoring in human perspiration. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 175, 112844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curto, V.F.; Fay, C.; Coyle, S.; Byrne, R.; O’Toole, C.; Barry, C.; Hughes, S.; Moyna, N.; Diamond, D.; Benito-Lopez, F. Real-time sweat pH monitoring based on a wearable chemical barcode micro-fluidic platform incorporating ionic liquids. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2012, 171–172, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, D.; Yu, H.; Pu, Z.; Lai, X.; Sun, C.; Wu, H.; Zhang, X. Flexible Microfluidics for Wearable Electronics. Flex. Wearable Electron. Smart Cloth. 2020, 213–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safavieh, R.; Zhou, G.Z.; Juncker, D. Microfluidics made of yarns and knots: From fundamental properties to simple networks and operations. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 2618–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilghaz, A.; Wicaksono, D.H.B.; Gustiono, D.; Majid, F.A.A.; Supriyanto, E.; Kadir, M.R.A. Flexible microfluidic cloth-based analytical devices using a low-cost wax patterning technique. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballerini, D.R.; Li, X.; Shen, W. Patterned paper and alternative materials as substrates for low-cost microfluidic diagnostics. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2012, 13, 769–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilghaz, A.; Ballerini, D.R.; Shen, W. Exploration of microfluidic devices based on multi-filament threads and textiles: A review. Biomicrofluidics 2013, 7, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mabey, D.; Peeling, R.W.; Ustianowski, A.; Perkins, M.D. Diagnostics for the developing world. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyazi, T.; Basabe-Desmonts, L.; Benito-Lopez, F. Review on microfluidic paper-based analytical devices towards commercialisation. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1001, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, T.; Chu, J.; Gao, B.; He, B. Modern evolution of paper-based analytical devices for wearable use: From disorder to order. Analyst 2020, 145, 5388–5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, Y. Test Paper. US Patent US2129754, 13 September 1938. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, R.H.; Clegg, D.L. Automatic Paper Chromatography. Anal. Chem. 1949, 21, 1123–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Sánchez, C.; McNeil, C.J.; Rawson, K.; Nilsson, O. Disposable noncompetitive immunosensor for free and total prostate-specific antigen based on capacitance measurement. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 5649–5656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, A.W.; Phillips, S.T.; Butte, M.J.; Whitesides, G.M. Patterned Paper as a Platform for Inexpensive, Low-Volume, Portable Bioassays. Angew. Chem. 2007, 119, 1340–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salentijn, G.I.J.; Grajewski, M.; Verpoorte, E. Reinventing (Bio)chemical Analysis with Paper. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 13815–13825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarrón, J.M. Screen-printed electrodes: Promising paper and wearable transducers for (bio)sensing. Biosensors 2020, 10, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, D.P.; Ratterman, M.E.; Griffin, D.K.; Hou, L.; Kelley-Loughnane, N.; Naik, R.R.; Hagen, J.A.; Papautsky, I.; Heikenfeld, J.C. Adhesive RFID sensor patch for monitoring of sweat electrolytes. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 62, 1457–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastasova, S.; Crewther, B.; Bembnowicz, P.; Curto, V.; Ip, H.M.; Rosa, B.; Yang, G.Z. A wearable multisensing patch for continuous sweat monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 93, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokus, M.A.; Saha, T.; Fang, J.; Dickey, M.D.; Velev, O.D.; Daniele, M.A. Towards Wearable Electrochemical Lactate Sensing using Osmotic-Capillary Microfluidic Pumping. Proc. IEEE Sensors 2019, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shay, T.; Dickey, M.D.; Velev, O.D. Hydrogel-enabled osmotic pumping for microfluidics: Towards wearable human-device interfaces. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Q.; Liang, B.; Tu, T.; Wei, J.; Fang, L.; Ye, X. Three-dimensional paper-based microfluidic electrochemical integrated devices (3D-PMED) for wearable electrochemical glucose detection. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 5674–5681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, B.; Cao, Q.; Mao, X.; Pan, W.; Tu, T.; Fang, L.; Ye, X. An Integrated Paper-Based Microfluidic Device for Real-Time Sweat Potassium Monitoring. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 9642–9648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokus, M.A.; Agcayazi, T.; Traenkle, M.; Bozkurt, A.; Daniele, M.A. Wearable Sweat Rate Sensors. Proc. IEEE Sens. 2020, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criscuolo, F.; Cantu, F.; Taurino, I.; Carrara, S.; De Micheli, G. A Wearable Electrochemical Sensing System for Non-Invasive Monitoring of Lithium Drug in Bipolar Disorder. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 9649–9656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criscuolo, F.; Hanitra, I.N.; Aiassa, S.; Taurino, I.; Oliva, N.; Carrara, S.; De Micheli, G. Wearable multifunctional sweat-sensing system for efficient healthcare monitoring. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Su, Y.; Liang, Y.; Lai, W. Microfluidic Cloth-Based Analytical Devices: Emerging Technologies and Applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 168, 112391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; He, J.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, F.; Xia, Q.; Wang, X.; Yu, L.; Lu, Z.; Li, C.-M. Facile and Low-Cost Fabrication of a Thread/Paper-Based Wearable System for Simultaneous Detection of Lactate and pH in Human Sweat. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2020, 2, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, S.; Jiang, J.; Pan, T. Interfacial microfluidic transport on micropatterned superhydrophobic textile. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 1937–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, W.; Powles, E.; Zhang, L.; Shen, W. Go with the capillary flow. Simple thread-based microfluidics. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 334, 129670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, C.W.; Toi, P.T.; Kim, B.Y.; Lee, W.I.; Lee, H.B.; Hanif, A.; Lee, E.H.; Lee, N.E. Fully Stretchable Capillary Microfluidics-Integrated Nanoporous Gold Electrochemical Sensor for Wearable Continuous Glucose Monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 14567–14575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, B.; Chi, J.; Xu, C.; Ni, Y.; Zhao, C.; Liu, H. Wearable capillary microfluidics for continuous perspiration sensing. Talanta 2020, 212, 120786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirovano, P.; Dorrian, M.; Shinde, A.; Donohoe, A.; Brady, A.J.; Moyna, N.M.; Wallace, G.; Diamond, D.; McCaul, M. A wearable sensor for the detection of sodium and potassium in human sweat during exercise. Talanta 2020, 219, 121145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glennon, T.; O’Quigley, C.; McCaul, M.; Matzeu, G.; Beirne, S.; Wallace, G.G.; Stroiescu, F.; O’Mahoney, N.; White, P.; Diamond, D. ‘SWEATCH’: A Wearable Platform for Harvesting and Analysing Sweat Sodium Content. Electroanalysis 2016, 28, 1283–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Integration of Substrate, Sensors and Microfluidics | Detection Technique | Sensor Technique/Type | Marker | Response Time * | Sensitivity (Linear Range) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paper microfluidics | ||||||
| Paper microfluidics + ISE and RE on flexible Kapton substrate | Pot | Pd and Ag electrodeposited on patterned Cu electrodes for WE and RE | Sodium | 30 s | 0.3 mV/mM (10–90 mM) | [51] |
| PMMA layers and paper microfluidics + 6 electrodes placed inside a paper channel | Pot/Amp | Pt and Ag flexible microneedles for 3 WE, 2 RE and CE; pH IrOx membrane; Na WE coated with PEDOT; lactate LOx in BSA/PU + SPEES/PES | pH/ Sodium/ Lactate | 10 s | pH: 71.9 mV/dec Na: 56 mV/dec | [52] |
| A hydrogel and paper microfluidics + WE, RE and CE on PI substrate | Amp | SP WE with Prussian Blue/carbon ink, RE with Ag/AgCl ink and CE with carbon ink; LOx and Nafion drop-casted in WE | Lactate | 16–20 min | 0.03 µA/(mM·mm2) (5–20 mM) LOD: 6 mM | [53] |
| 3D wax-printed paper microfluidics + WE, RE and CE on PET substrate | Amp | SP WE and CE with Prussian Blue/graphite ink and RE with Ag/AgCl ink; GOx drop-casted in WE | Glucose | - | 35.7 µA/(mM·cm2) (0–1.9 mM) LOD: 5 µM | [55] |
| 3D wax-printed paper microfluidics + WE and RE on PET substrate | Pot | SP WE and RE with Ag/AgCl and carbon inks; WE coated with PEDOT:PSS | Potassium | 5 s | 61.8 mV/dec (1–32 mM) | [56] |
| Paper microfluidics + electrode on PI film | Imp | SP electrode with carbon ink | Sweat rate | 30 min | - | [57] |
| Paper microfluidics + ISE and RE on a flexible PI substrate | Pot | WE (ISE) and RE by photolithography patterning | Lithium | - | 56.8 mV/dec (2 mM–1 M) LOD: 1.7 mM | [58] |
| Fabric microfluidics | ||||||
| Cotton fabric and PU nanofiber cover + WE, RE and CE on flexible PDMS substrate | Amp | Nanoporous Au WE and CE vacuum-deposited and Ag/AgCl RE | Glucose | 16.15 min | 57.6 μA/(mM·cm2) | [64] |
| Thread + ISE and RE on PET film | Pot | SP ISE and RE with graphite and Ag/AgCl inks resp.; ISE and RE coated with PEDOT and PVB resp. | Sodium | 8–10 min | 56.7 mV/dec | [65] |
| 3D printed platform containing thread microfluidics and ISEs on PET substrate | Pot | Pt CE, Ag pseudoRE and ISEs SP with carbon ink; ISEs and REs coated with PEDOT and POT | Sodium/ Potassium | 8 min | Na: 52.4 and 56.4 mV/dec for PEDOT and POT resp. K: 45.7 and 54.3 mV/dec for PEDOT and POT resp. | [66] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rovira, M.; Fernández-Sánchez, C.; Jiménez-Jorquera, C. Hybrid Technologies Combining Solid-State Sensors and Paper/Fabric Fluidics for Wearable Analytical Devices. Biosensors 2021, 11, 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11090303
Rovira M, Fernández-Sánchez C, Jiménez-Jorquera C. Hybrid Technologies Combining Solid-State Sensors and Paper/Fabric Fluidics for Wearable Analytical Devices. Biosensors. 2021; 11(9):303. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11090303
Chicago/Turabian StyleRovira, Meritxell, César Fernández-Sánchez, and Cecilia Jiménez-Jorquera. 2021. "Hybrid Technologies Combining Solid-State Sensors and Paper/Fabric Fluidics for Wearable Analytical Devices" Biosensors 11, no. 9: 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11090303
APA StyleRovira, M., Fernández-Sánchez, C., & Jiménez-Jorquera, C. (2021). Hybrid Technologies Combining Solid-State Sensors and Paper/Fabric Fluidics for Wearable Analytical Devices. Biosensors, 11(9), 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11090303