Distinguishing Amyloid β-Protein in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease by Label-Free Vibrational Imaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
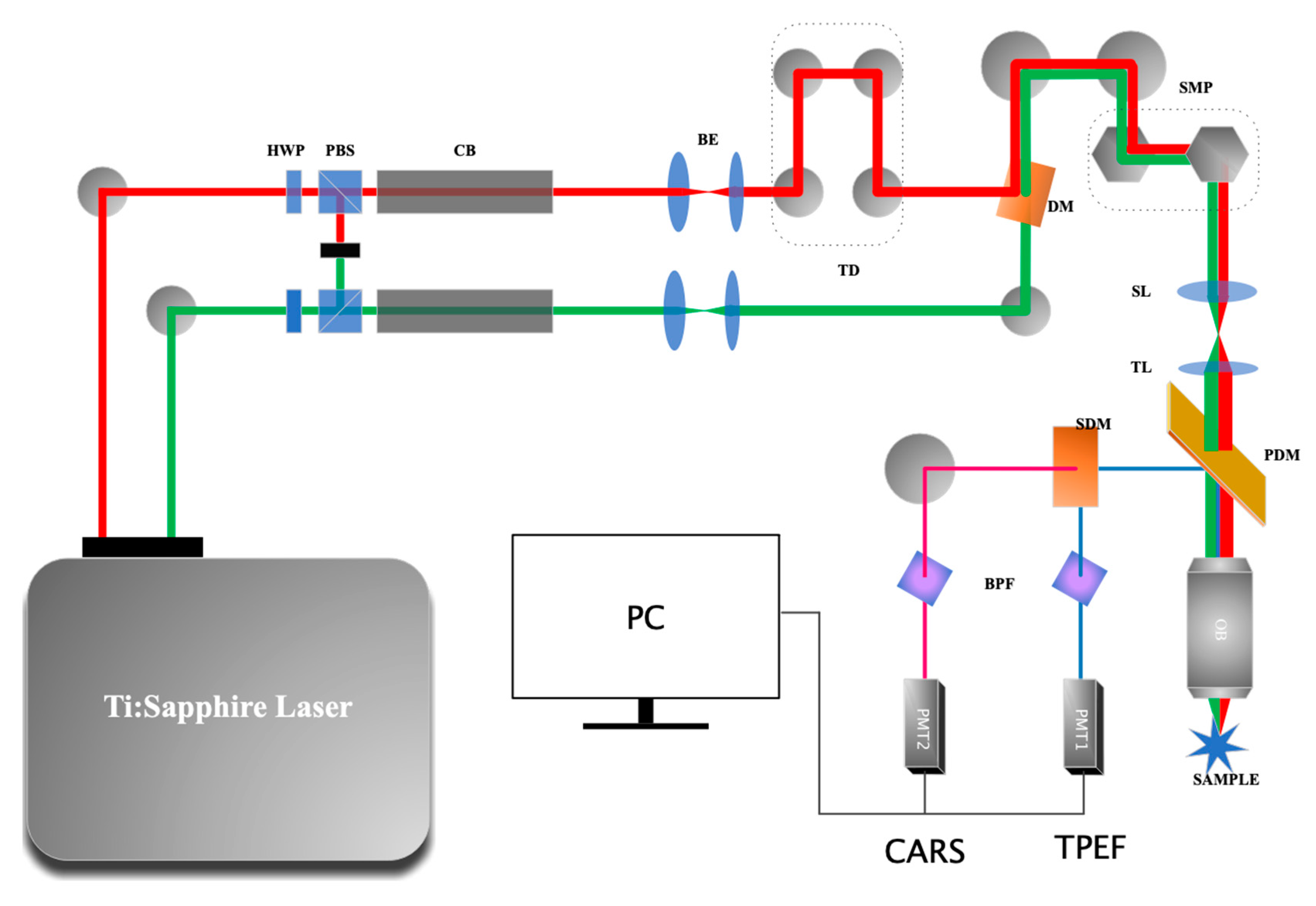
2.1. The CARS Microscope
2.2. Sample Preparation
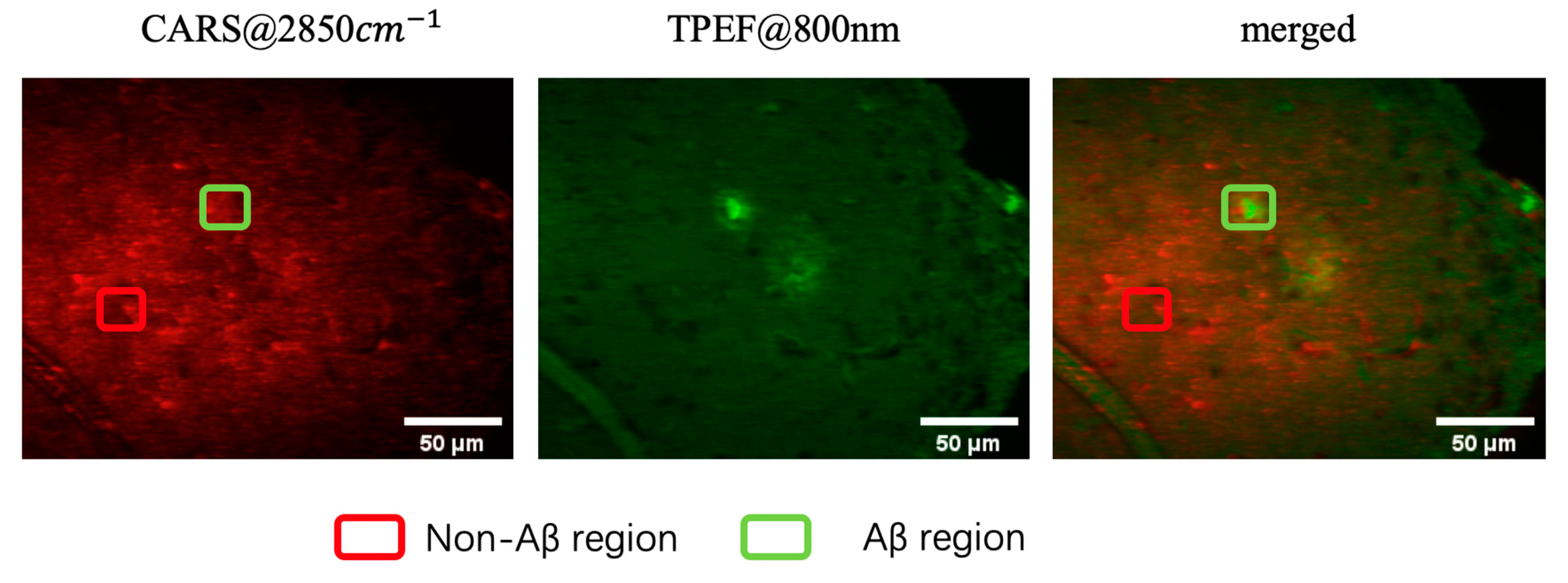
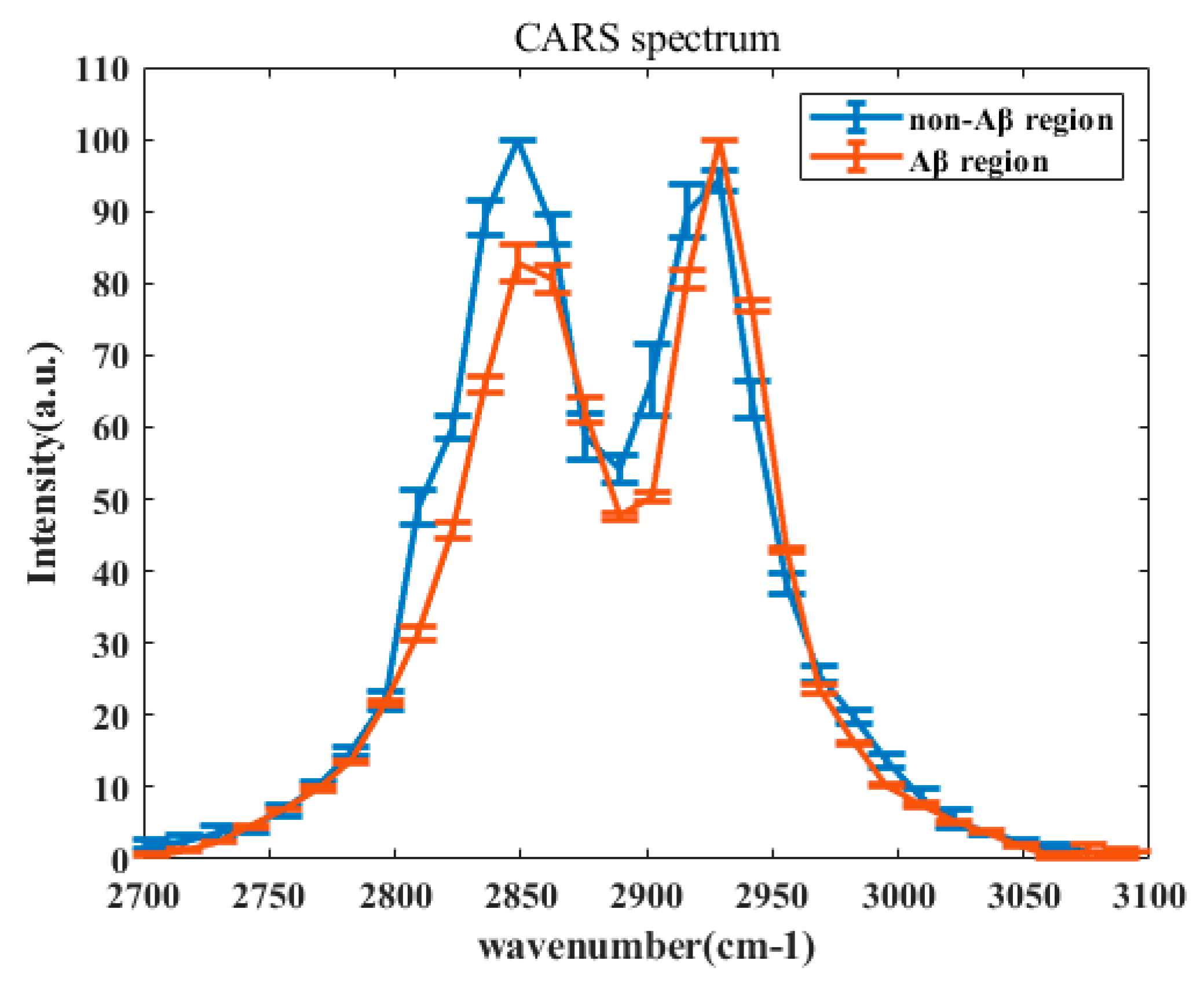
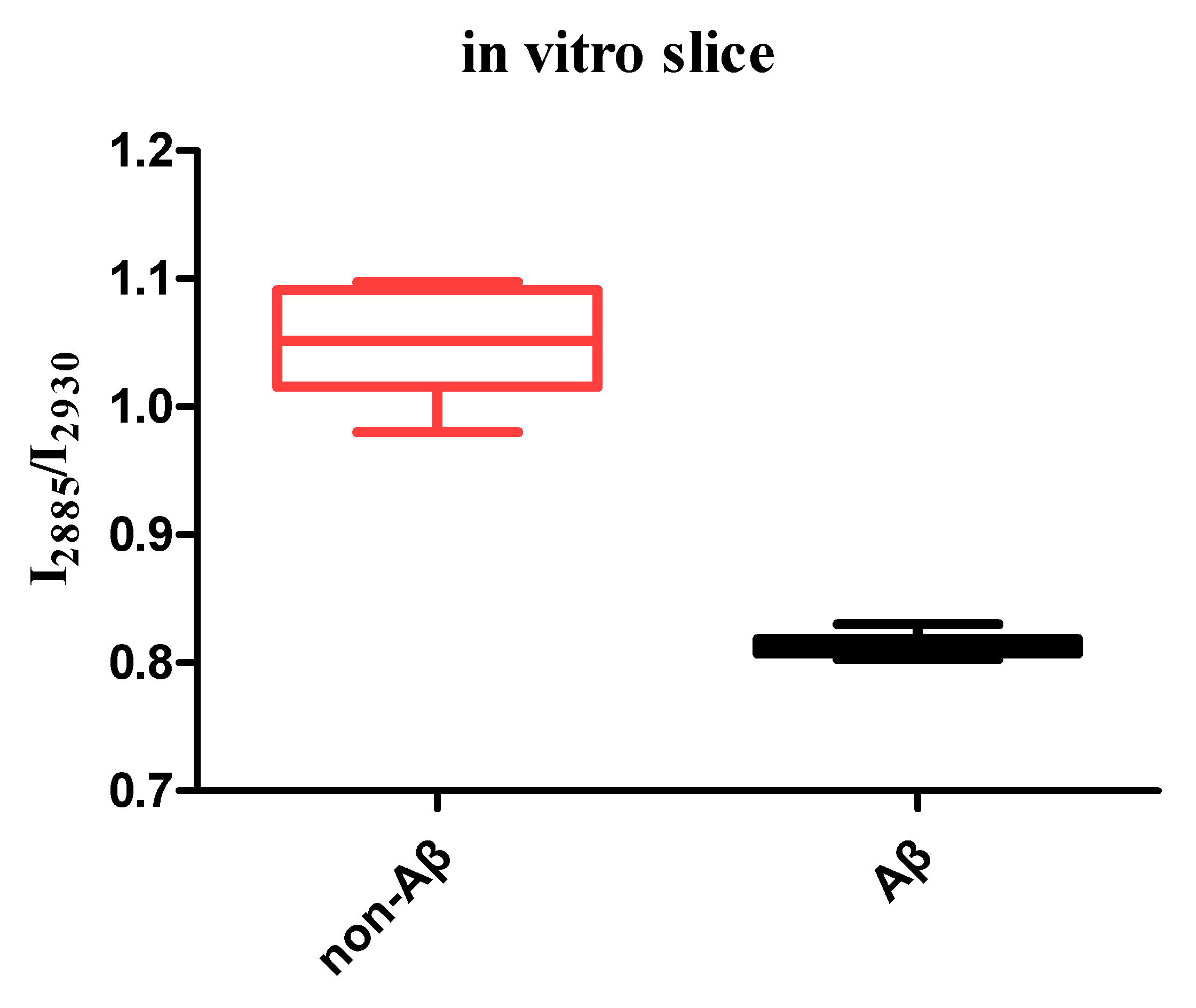
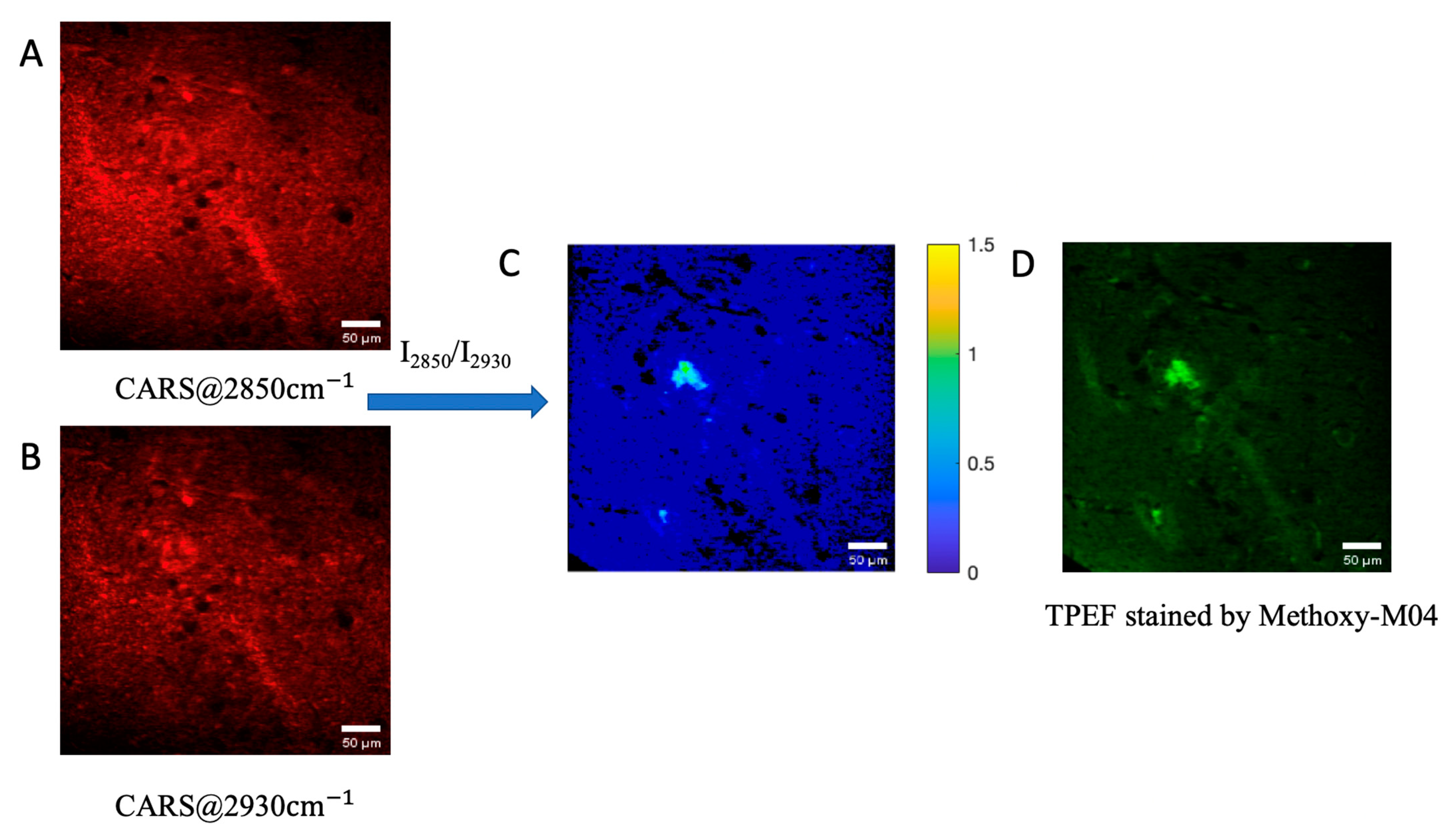
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Small, S.A.; Duff, K. Linking Aβ and Tau in Late-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease: A Dual Pathway Hypothesis. Neuron 2008, 60, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, J.; Selkoe, D.J. The Amyloid Hypothesis of Alzheimer’s Disease: Progress and Problems on the Road to Therapeutics. Science 2002, 297, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, J.A.; Higgins, G.A. Alzheimer’s Disease: The Amyloid Cascade Hypothesis. Science 1992, 256, 184–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, J.; Allsop, D. Amyloid Deposition as the Central Event in the Aetiology of Alzheimer’s Disease. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1991, 12, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtzman, D.M.; Morris, J.C.; Goate, A.M. Alzheimer’s Disease: The Challenge of the Second Century. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 77sr1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordberg, A. PET Imaging of Amyloid in Alzheimer’s Disease. Lancet Neurol. 2004, 3, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klunk, W.E.; Engler, H.; Nordberg, A.; Wang, Y.; Blomqvist, G.; Holt, D.P.; Långström, B.; Bergström, M.; Savitcheva, I.; Huang, G.F.; et al. Imaging Brain Amyloid in Alzheimer’s Disease with Pittsburgh Compound-B. Ann. Neurol. Off. J. Am. Neurol. Assoc. Child Neurol. Soc. 2004, 55, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabuurs, R.J.; Natté, R.; de Ronde, F.M.; Hegeman-Kleinn, I.; Dijkstra, J.; van Duinen, S.G.; Webb, A.G.; Rozemuller, A.J.; van Buchem, M.A.; van der Weerd, L. MR Microscopy of Human Amyloid-β Deposits: Characterization of Parenchymal Amyloid, Diffuse Plaques, and Vascular Amyloid. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2013, 34, 1037–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, J. Lipid metabolism in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Bull. 2014, 30, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch-Reinshagen, V.; Burgess, B.L.; Wellington, C.L. Why lipids are important for Alzheimer disease? Mol. Cell Biochem. 2009, 326, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, Y.; Yi, R.; Liu, L.; Qu, J. Coherent Anti-Stokes Raman Scattering Microscopy and Its Applications. Front. Phys. 2020, 8, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, I.I.; Steuwe, C.; Reichelt, S.; Mahajan, S. Coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering for label-free biomedical imaging. J. Opt. 2013, 15, 094006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Evans, C.L.; Xu, X.; Kesari, S.; Xie, X.S.; Wong, S.T.; Young, G.S. Chemically-selective imaging of brain structures with CARS microscopy. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 12076–12087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.-X.; Xie, X.S. Coherent Anti-Stokes Raman Scattering Microscopy: Instrumentation, Theory, and Applications. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 827–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.X.; Jia, Y.K.; Zheng, G.; Xie, X.S. Laser-scanning coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering microscopy and applications to cell biology. Biophys. J. 2002, 83, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkmer, A.; Cheng, J.-X.; Sunney Xie, X. Vibrational Imaging with High Sensitivity via Epidetected Coherent Anti-Stokes Raman Scattering Microscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 023901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumbusch, A.; Holtom, G.R.; Xie, X.S. Three-Dimensional Vibrational Imaging by Coherent Anti-Stokes Raman Scattering. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 82, 4142–4145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Liang, Z.; Zhou, B.; Li, X.; Lui, C.; Ip, N.Y.; Qu, J.Y. In Vivo Near-Infrared Two-Photon Imaging of Amyloid Plaques in Deep Brain of Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 3128–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lin, B.; Lin, G.; Sun, C.; Lin, R.; Huang, J.; Tao, J.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Chen, L.; et al. Label-free multiphoton imaging of beta-amyloid plaques in Alzheimer’s disease mouse models. Neurophotonics 2019, 6, 045008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, P.K.; Koelsch, P. Label-free imaging of amyloids using their intrinsic linear and nonlinear optical properties. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 743–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koronyo-Hamaoui, M.; Koronyo, Y.; Ljubimov, A.V.; Miller, C.A.; Ko, M.K.; Black, K.L.; Schwartz, M.; Farkas, D.L. Identification of amyloid plaques in retinas from Alzheimer’s patients and noninvasive in vivo optical imaging of retinal plaques in a mouse model. Neuroimage 2011, 54, S204–S217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, K.A.; Klymenko, Y.; Feist, P.E.; Hummon, A.B.; Stack, M.S.; Schultz, Z.D. Chemical Analysis of Morphological Changes in Lysophosphatidic Acid-Treated Ovarian Cancer Cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, T.; Chemnitz, M.; Baumgartl, M.; Gottschall, T.; Pascher, T.; Matthäus, C.; Romeike, B.F.; Brehm, B.R.; Limpert, J.; Tünnermann, A.; et al. Expanding Multimodal Microscopy by High Spectral Resolution Coherent Anti-Stokes Raman Scattering Imaging for Clinical Disease Diagnostics. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 6703–6715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M.; Poljak, A.; Braidy, N.; Crawford, J.; Sachdev, P. Blood fatty acids in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Ageing Res. Rev. 2020, 60, 101043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonteh, A.N.; Cipolla, M.; Chiang, A.J.; Edminster, S.P.; Arakaki, X.; Harrington, M.G. Polyunsaturated fatty acid composition of cerebrospinal fluid fractions shows their contribution to cognitive resilience of a pre-symptomatic Alzheimer’s disease cohort. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, H.; Solomon, V.A.; Fonteh, A.N. Involvement of Lipids in Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology and Potential Therapies. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safieh, M.; Korczyn, A.D.; Michaelson, D.M. ApoE4: An emerging therapeutic target for Alzheimer’s disease. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonteh, A.N.; Cipolla, M.; Chiang, J.; Arakaki, X.; Harrington, M.G. Human cerebrospinal fluid fatty acid levels differ between supernatant fluid and brain-derived nanoparticle fractions, and are altered in Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saido, T.C. Metabolism of amyloid β peptide and pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2013, 89, 321–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakkour, A.; Morris, J.C.; Wolk, D.A.; Dickerson, B.C. The effects of aging and Alzheimer’s disease on cerebral cortical anatomy: Specificity and differential relationships with cognition. Neuroimage 2013, 76, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinser, E.G.; Hartmann, T.; Grimm, M.O.W. Amyloid beta-protein and lipid metabolism. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2007, 1768, 1991–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolozin, B. Cholesterol and the Biology of Alzheimer’s Disease. Neuron 2004, 41, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.B.; Arbel, M.; Zhang, L.; Freudiger, C.W.; Hou, S.S.; Lin, D.; Yang, X.; Bacskai, B.J.; Xie, X.S. Label-free imaging of amyloid plaques in Alzheimer’s disease with stimulated Raman scattering microscopy. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaat7715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, D.H.; Song, W.K.; Oh, M.K.; Ko, D.K. Label-free imaging and quantitative chemical analysis of Alzheimer’s disease brain samples with multimodal multiphoton nonlinear optical microspectroscopy. J. Biomed. Opt. 2015, 20, 56013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enejder, A.; Kiskis, J.; Fink, H.; Nyberg, L.; Thyr, J.; Li, J.Y. CARS microscopy of Alzheimer’s diseased brain tissue, in Multiphoton Microscopy in the Biomedical Sciences XIV. Int. Soc. Opt. Photonics 2014, 8948, 89480U. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, R.; Xu, H.; Zhou, T.; Liu, L.; Qu, J. Distinguishing Amyloid β-Protein in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease by Label-Free Vibrational Imaging. Biosensors 2021, 11, 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11100365
Li S, Luo Z, Zhang R, Xu H, Zhou T, Liu L, Qu J. Distinguishing Amyloid β-Protein in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease by Label-Free Vibrational Imaging. Biosensors. 2021; 11(10):365. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11100365
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shaowei, Ziyi Luo, Renlong Zhang, Hao Xu, Ting Zhou, Liwei Liu, and Junle Qu. 2021. "Distinguishing Amyloid β-Protein in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease by Label-Free Vibrational Imaging" Biosensors 11, no. 10: 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11100365
APA StyleLi, S., Luo, Z., Zhang, R., Xu, H., Zhou, T., Liu, L., & Qu, J. (2021). Distinguishing Amyloid β-Protein in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease by Label-Free Vibrational Imaging. Biosensors, 11(10), 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11100365





