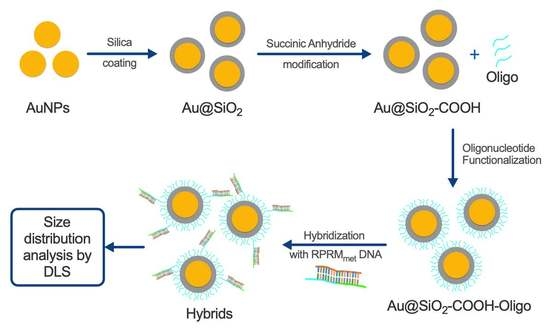
Gold@Silica Nanoparticles Functionalized with Oligonucleotides: A Prominent Tool for the Detection of the Methylated Reprimo Gene in Gastric Cancer by Dynamic Light Scattering
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines
2.2. Reagents
2.3. Oligonucleotides
2.4. Synthesis of AuNPs
2.5. Synthesis of Core–Shell Au@SiO2–COOH
2.6. Functionalization of Au@SiO2–COOH with Oligonucleotides
2.7. DNA Samples
2.8. DNAmet-RPRM Captured by Hybridization and PCR Assay
2.9. Hybridization Assay
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Gold Nanoparticles
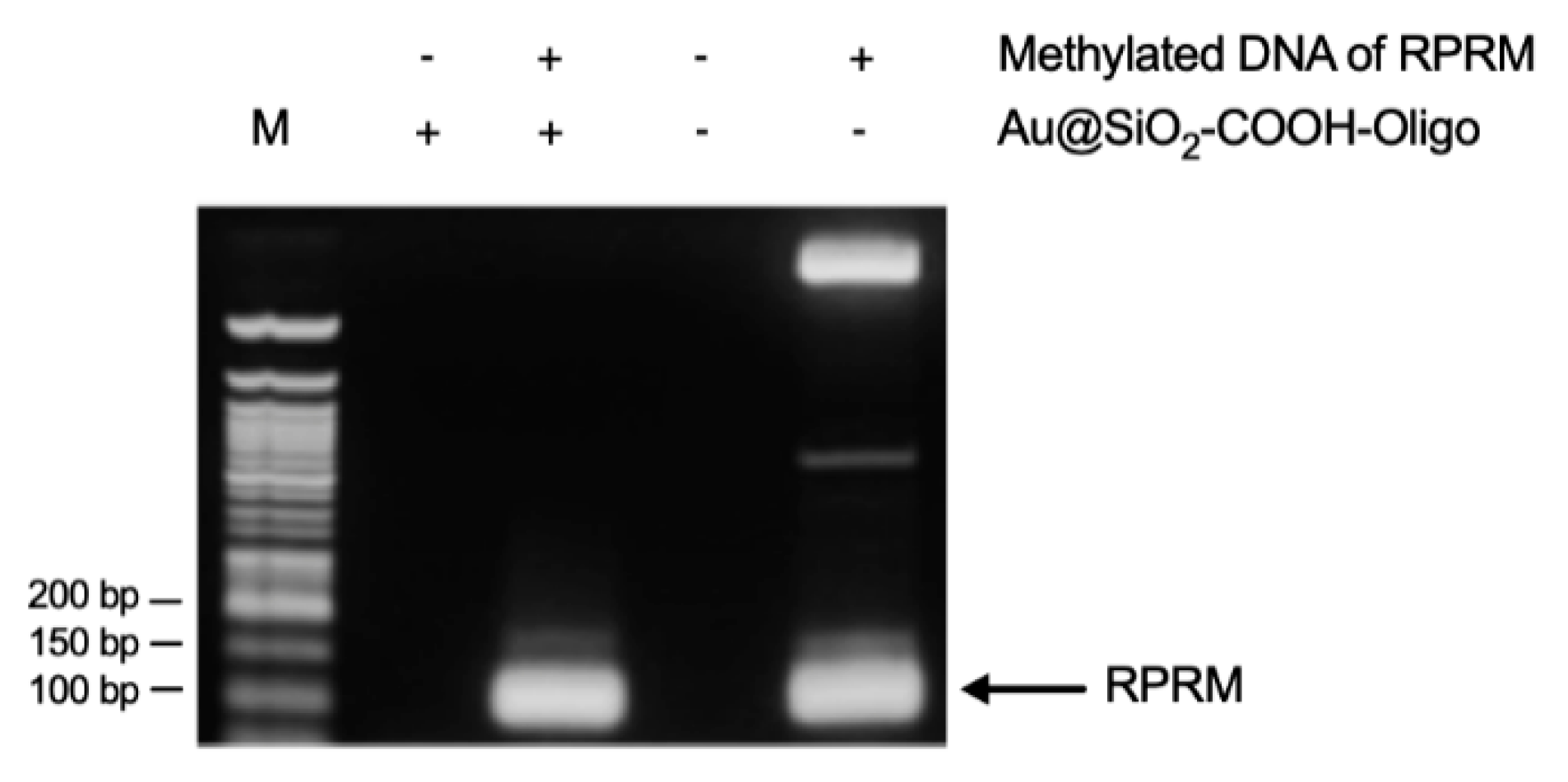
3.2. Capture Assay and Functionality of Au@SiO2–COOH-Oligo
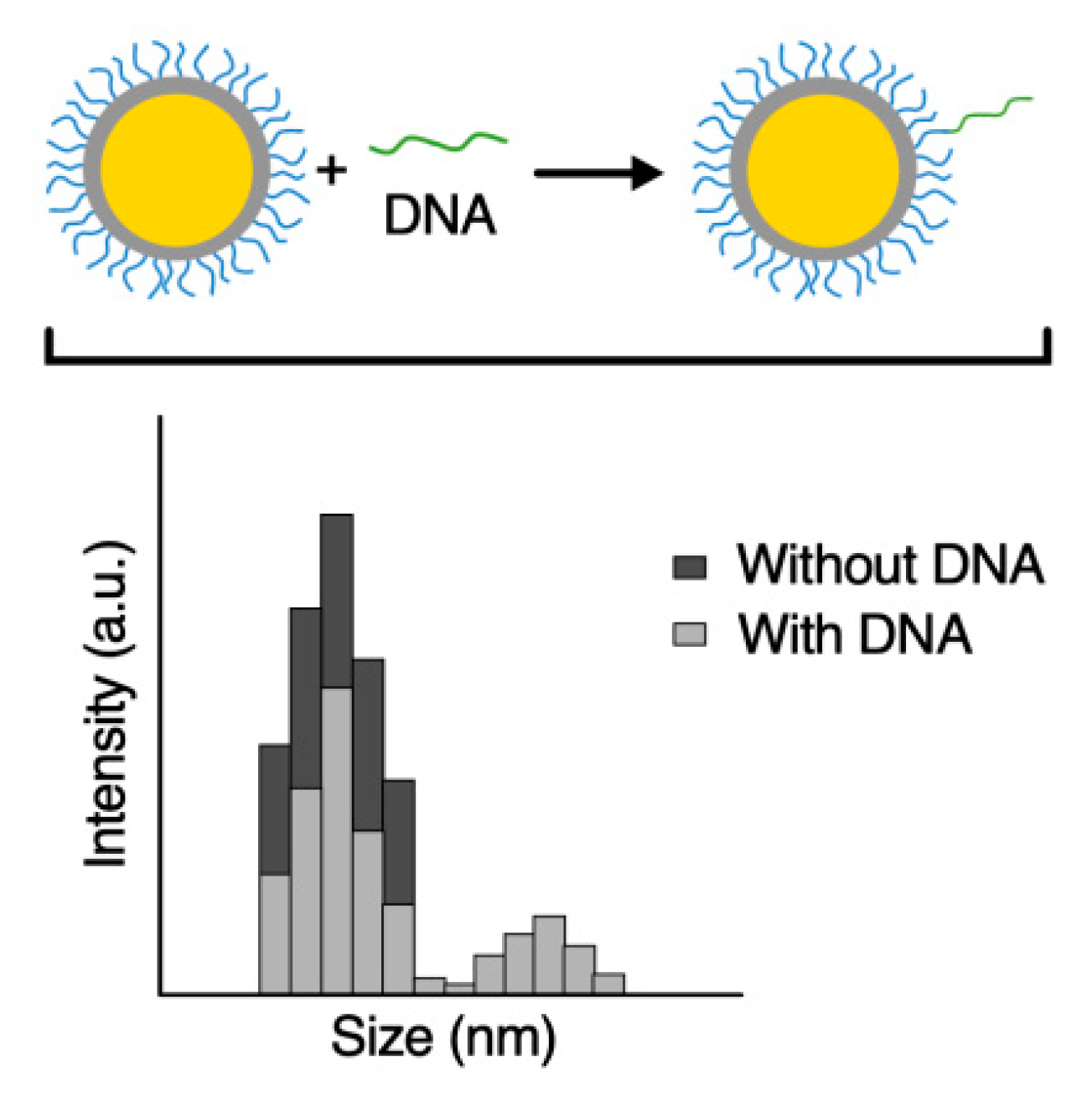
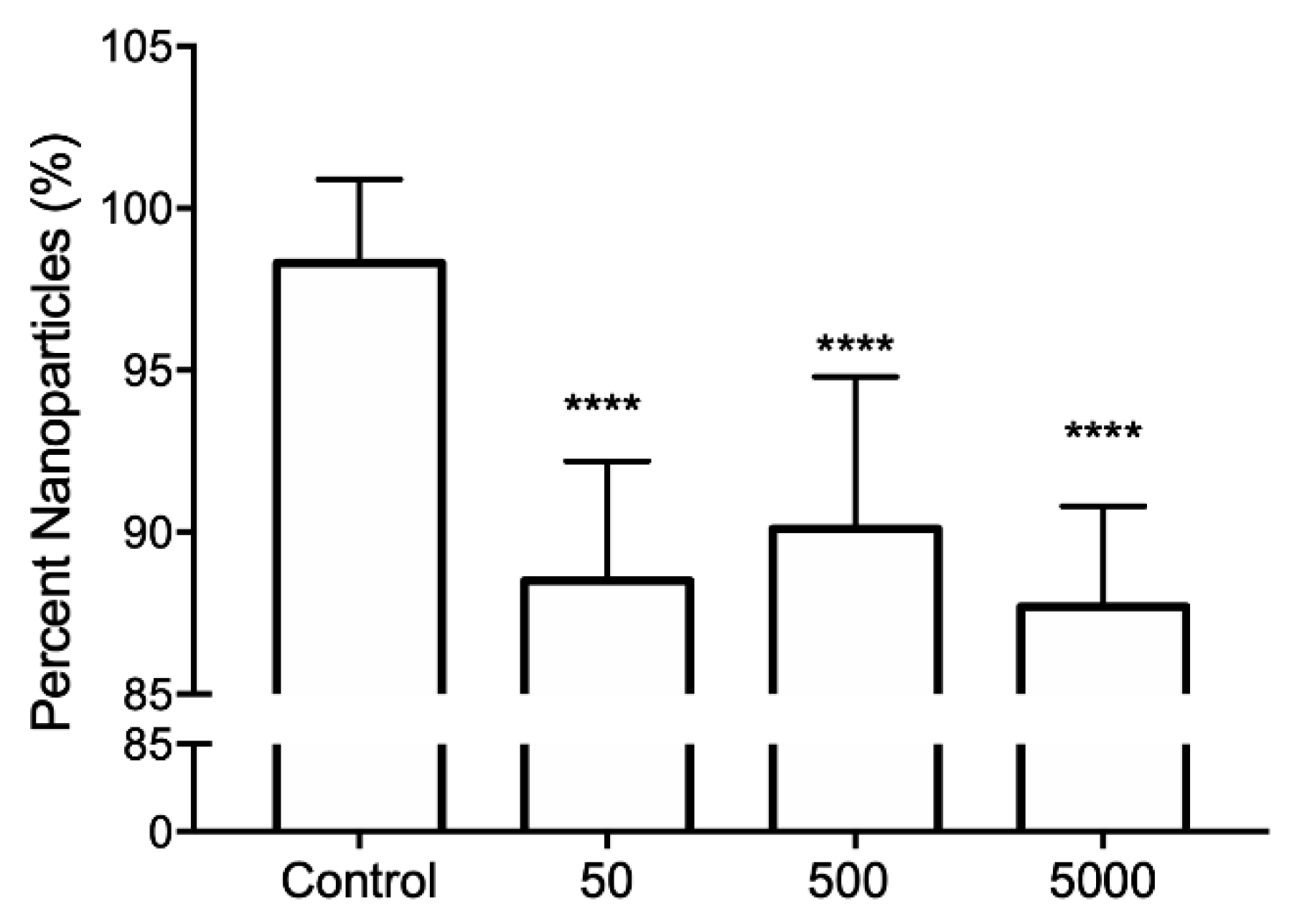
3.3. Hybridization Assay of Au@SiO2–COOH-Oligo with a Synthetic Fragment of RPRM-DNA Analyzed by DLS
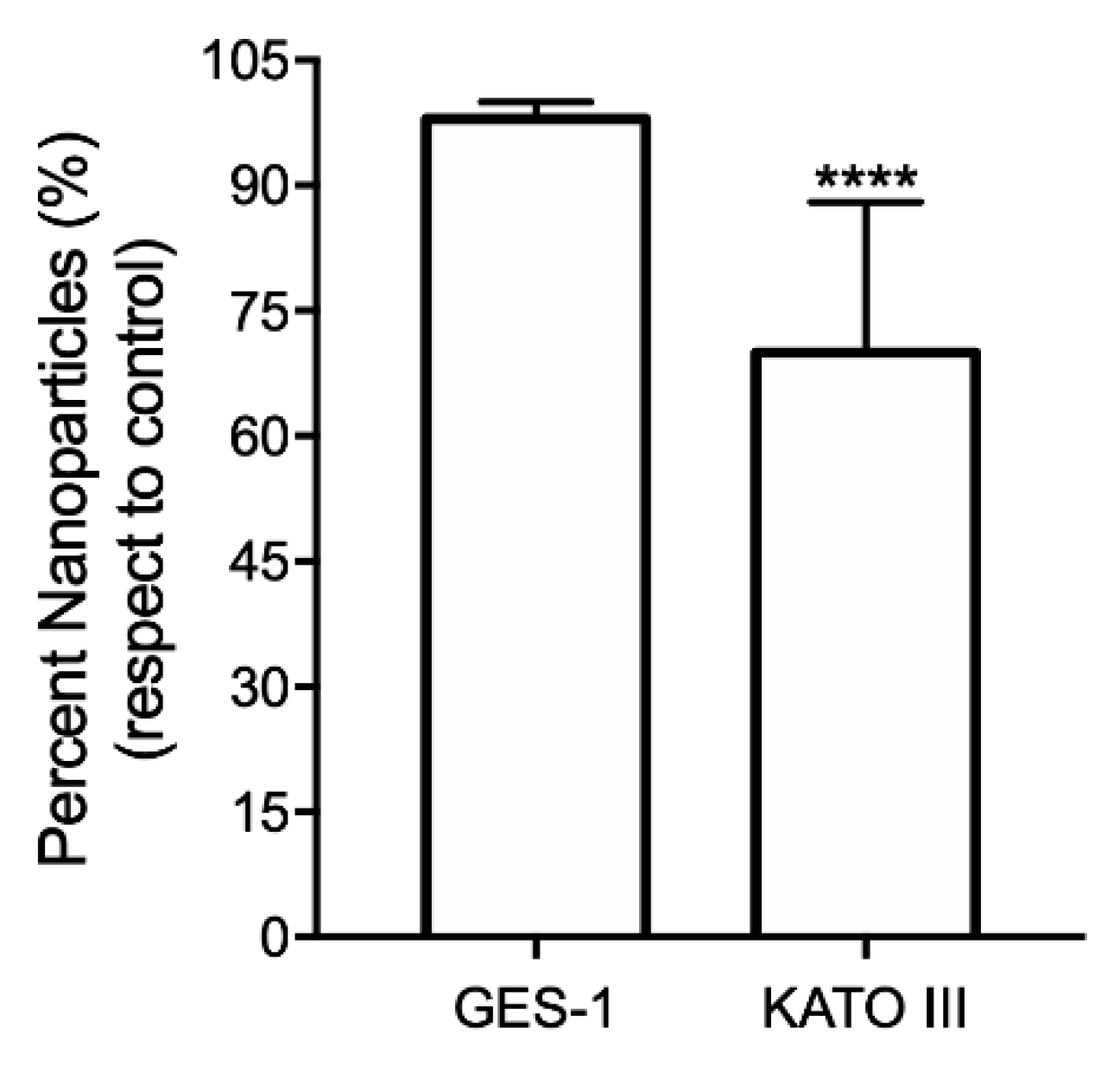
3.4. Hybridization Assay of Au@SiO2–COOH-Oligo with DNA from Cell Lines Analyzed by DLS
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, G.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, P.; Wang, L.; Huang, Y.; Li, K. Global patterns and trends in stomach cancer incidence: Age, period and birth cohort analysis. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 141, 1333–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abbas, M.; Habib, M.; Naveed, M.; Karthik, K.; Dhama, K.; Shi, M.; Dingding, C. The relevance of gastric cancer biomarkers in prognosis and pre-and post-chemotherapy in clinical practice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 95, 1082–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohki, R.; Nemoto, J.; Murasawa, H.; Oda, E.; Inazawa, J.; Tanaka, N.; Taniguchi, T. Reprimo, a new candidate mediator of the p53-mediated cell cycle arrest at the G2 phase. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 22627–22630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernal, C.; Aguayo, F.; Villarroel, C.; Vargas, M.; Díaz, I.; Ossandon, F.J.; Santibañez, E.; Palma, M.; Aravena, E.; Barrientos, C.; et al. Reprimo as a potential biomarker for early detection in gastric cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 6264–6269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, J.; Wang, H.; Luo, Q.; Huang, S.; Lin, S.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, Q. The relationship between DNA methylation and Reprimo gene expression in gastric cancer cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 108610–108623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Yang, X. Implication of Reprimo and hMLH1 gene methylation in early diagnosis of gastric carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 14977. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.Q.; Xu, X.; Bertrand, N.; Pridgen, E.; Swami, A.; Farokhzad, O.C. Interactions of nanomaterials and biological systems: Implications to personalized nanomedicine. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 1363–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, M.I.; Bhatti, H.N.; Nawaz, H.; Kashif, M. Nanobiotechnology: Applications of Nanomaterials in Biological Research. In Integrating Green Chemistry and Sustainable Engineering; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 581–615. [Google Scholar]
- Petryayeva, E.; Krull, U.J. Localized surface plasmon resonance: Nanostructures, bioassays and biosensing; A Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 706, 8–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, K.M.; Hafner, J.H. Localized surface plasmon resonance sensors. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 3828–3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Jackman, J.A.; Yang, H.H.; Chen, P.; Cho, N.J.; Kim, D.H. Strategies for enhancing the sensitivity of plasmonic nanosensors. Nano Today 2015, 10, 213–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stetefeld, J.; McKenna, S.A.; Patel, T.R. Dynamic light scattering: a practical guide and applications in biomedical sciences. Biophys. Rev. 2016, 8, 409–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qadami, F.; Molaeirad, A.; Alijanianzadeh, M.; Azizi, A.; Kamali, N. Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance (LSPR)-Based Nanobiosensor for Methamphetamin Measurement. Plasmonics 2018, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seow, N.; Tan, Y.N.; Yung, L.Y.L.; Su, X. DNA-directed assembly of nanogold dimers: a unique dynamic light scattering sensing probe for transcription factor detection. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turkevich, J.; Stevenson, P.C.; Hillier, J. A study of the nucleation and growth processes in the synthesis of colloidal gold. Discuss. Faraday Soc. 1951, 11, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liz-Marzán, L.M.; Giersig, M.; Mulvaney, P. Synthesis of nanosized gold-silica core-shell particles. Langmuir 1996, 12, 4329–4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; He, Y. Effect of surface charge of PDDA-protected gold nanoparticles on the specificity and efficiency of DNA polymerase chain reaction. Analyst 2013, 138, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanzha, E.; Pylaev, T.; Khanadeev, V.; Konnova, S.; Fedorova, V.; Khlebtsov, N. Gold nanoparticle-assisted polymerase chain reaction: effects of surface ligands, nanoparticle shape and material. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 10146–110154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Li, X.; Sun, J.; Shao, Z. Enhanced PCR amplification of GC-rich DNA templates by gold nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 11520–11524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seow, N.; Tan, Y.N.; Yung, L.Y.L. Gold nanoparticle–dynamic light scattering tandem for the rapid and quantitative detection of the let7 microRNA family. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2014, 31, 1260–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutariya, P.G.; Pandya, A.; Lodha, A.; Menon, S.K. A simple and rapid creatinine sensing via DLS selectivity, using calix[4]arene thiol functionalized gold nanoparticles. Talanta 2016, 147, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saavedra, K.; Valbuena, J.; Olivares, W.; Marchant, M.J.; Rodríguez, A.; Torres-Estay, V.; Carrasco-Avino, G.; Guzman, L.; Aguayo, F.; Roa, J.C.; et al. Loss of expression of reprimo, a p53-induced cell cycle arrest gene, correlates with invasive stage of tumor progression and p73 expression in gastric cancer. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Q.; Liu, X.; Coutts, J.; Austin, L.; Huo, Q. A one-step highly sensitive method for DNA detection using dynamic light scattering. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 8138–8139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
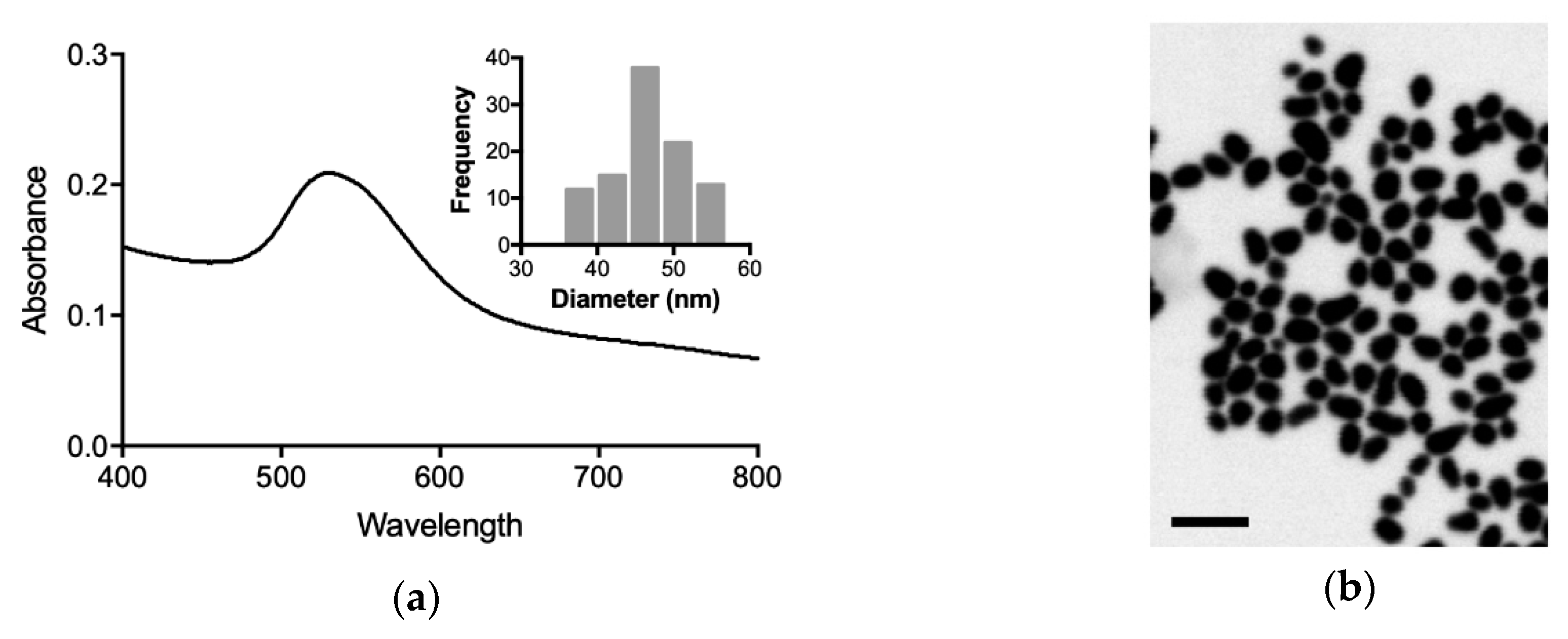
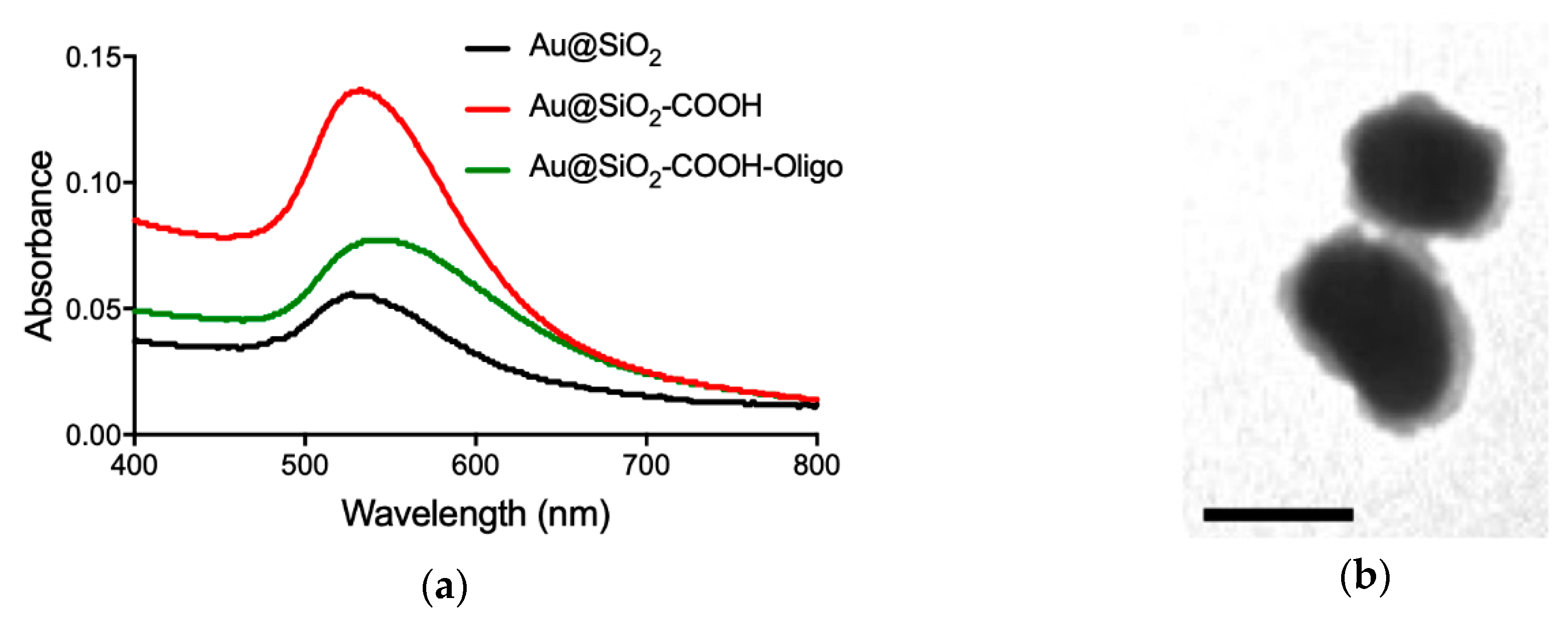
| AuNP | λmax (nm) | Size a,b (nm) | Zeta Potential a (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Au | 528 | 46 ± 7 | −62 ± 3 c |
| Au@SiO2 | 530 | 71 ± 2 | −26 ± 1 c |
| Au@SiO2–COOH | 533 | 73 ± 1 | −44 ± 1 c |
| Au@SiO2–COOH-Oligo | 536 | 93 ± 2 | −29 ± 1 d |
| Reaction | Size (nm) a | Percentage of NPs a |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 151 ± 11 | 98 ± 3 |
| 50 | 142 ± 11 | 88 ± 4 b |
| 500 | 149 ± 18 | 90 ± 5 b |
| 5000 | 150 ± 9 | 88 ± 3 b |
| GES-1 | 236 ± 77 | 98 ± 2 b |
| KATO III | 240 ± 98 | 70 ± 18 b |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marchant, M.J.; Guzmán, L.; Corvalán, A.H.; Kogan, M.J. Gold@Silica Nanoparticles Functionalized with Oligonucleotides: A Prominent Tool for the Detection of the Methylated Reprimo Gene in Gastric Cancer by Dynamic Light Scattering. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1333. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9091333
Marchant MJ, Guzmán L, Corvalán AH, Kogan MJ. Gold@Silica Nanoparticles Functionalized with Oligonucleotides: A Prominent Tool for the Detection of the Methylated Reprimo Gene in Gastric Cancer by Dynamic Light Scattering. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(9):1333. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9091333
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarchant, María José, Leda Guzmán, Alejandro H. Corvalán, and Marcelo J. Kogan. 2019. "Gold@Silica Nanoparticles Functionalized with Oligonucleotides: A Prominent Tool for the Detection of the Methylated Reprimo Gene in Gastric Cancer by Dynamic Light Scattering" Nanomaterials 9, no. 9: 1333. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9091333
APA StyleMarchant, M. J., Guzmán, L., Corvalán, A. H., & Kogan, M. J. (2019). Gold@Silica Nanoparticles Functionalized with Oligonucleotides: A Prominent Tool for the Detection of the Methylated Reprimo Gene in Gastric Cancer by Dynamic Light Scattering. Nanomaterials, 9(9), 1333. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9091333