Ni0.5Cu0.5Co2O4 Nanocomposites, Morphology, Controlled Synthesis, and Catalytic Performance in the Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane for Hydrogen Production
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Synthesis of Catalysts
2.2. Characterizations
2.3. Catalytic Tests
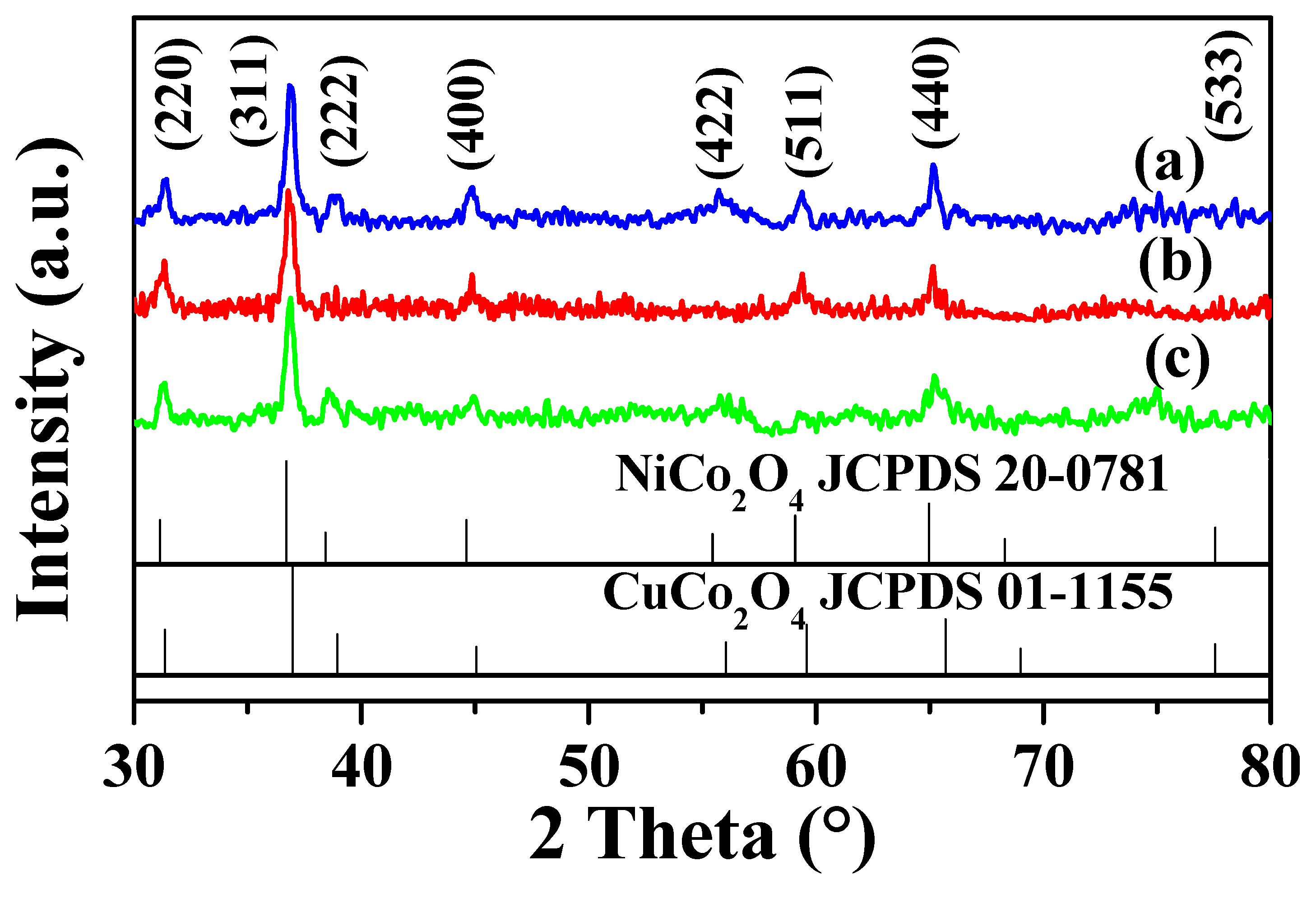
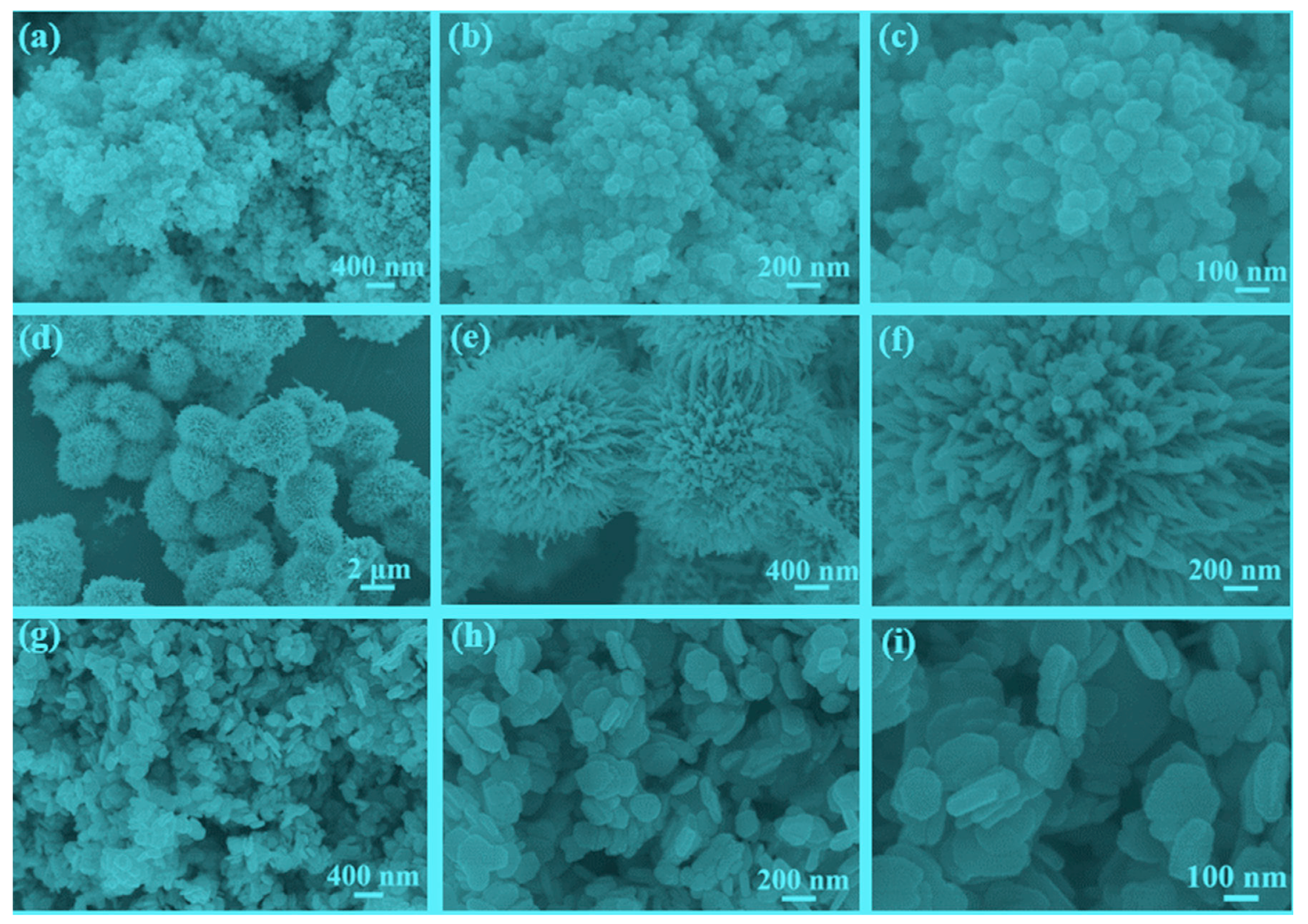
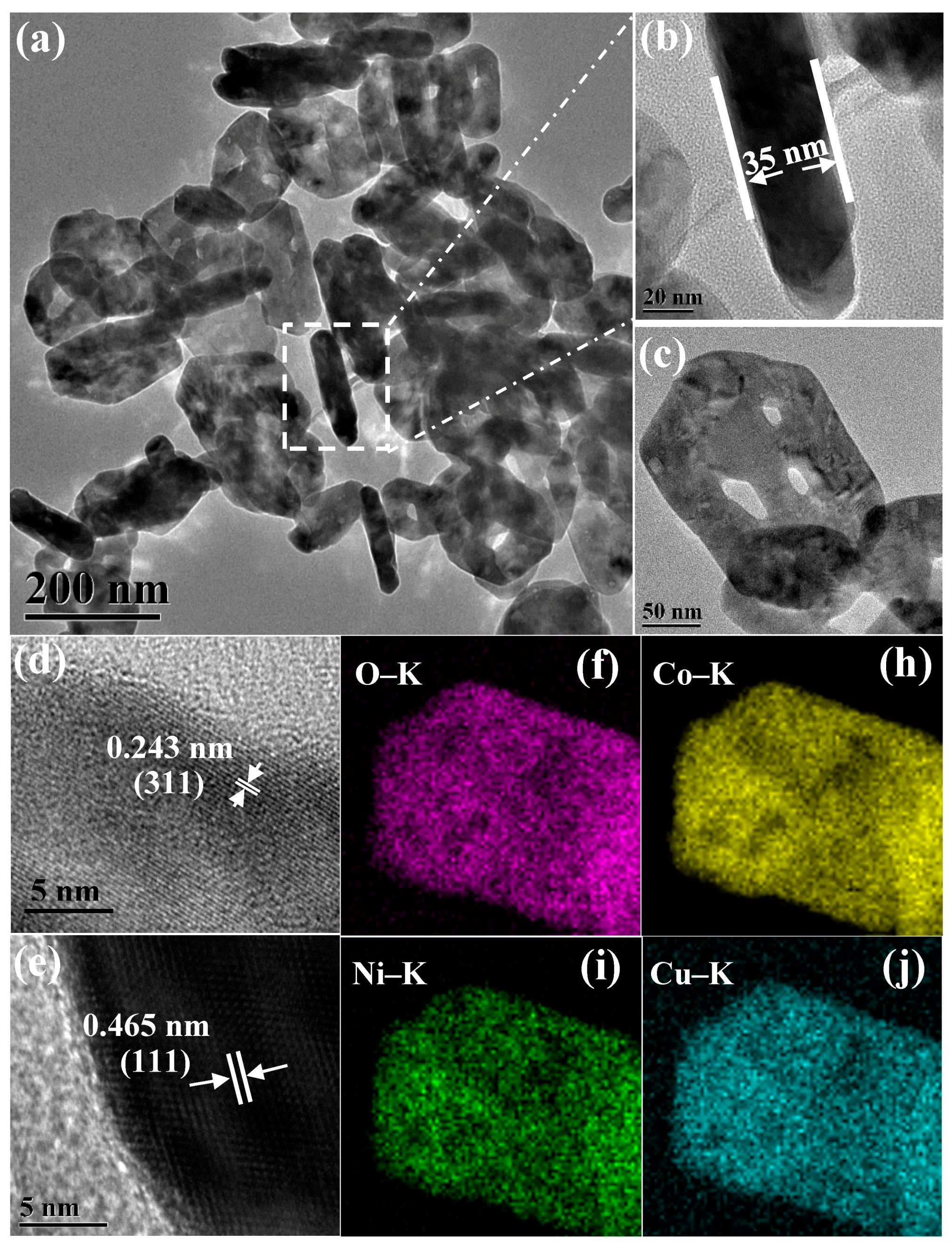
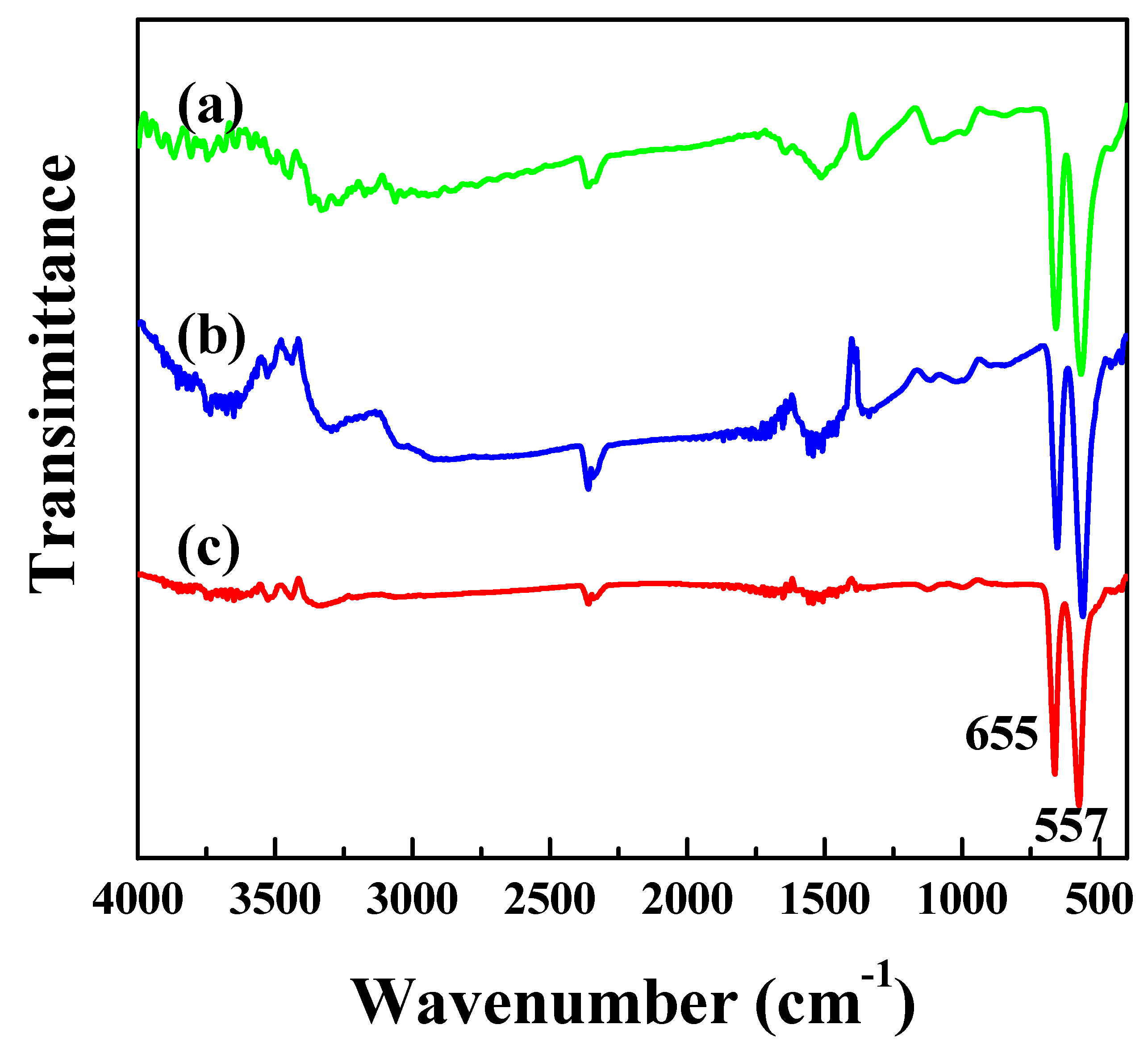
3. Results and Discussion
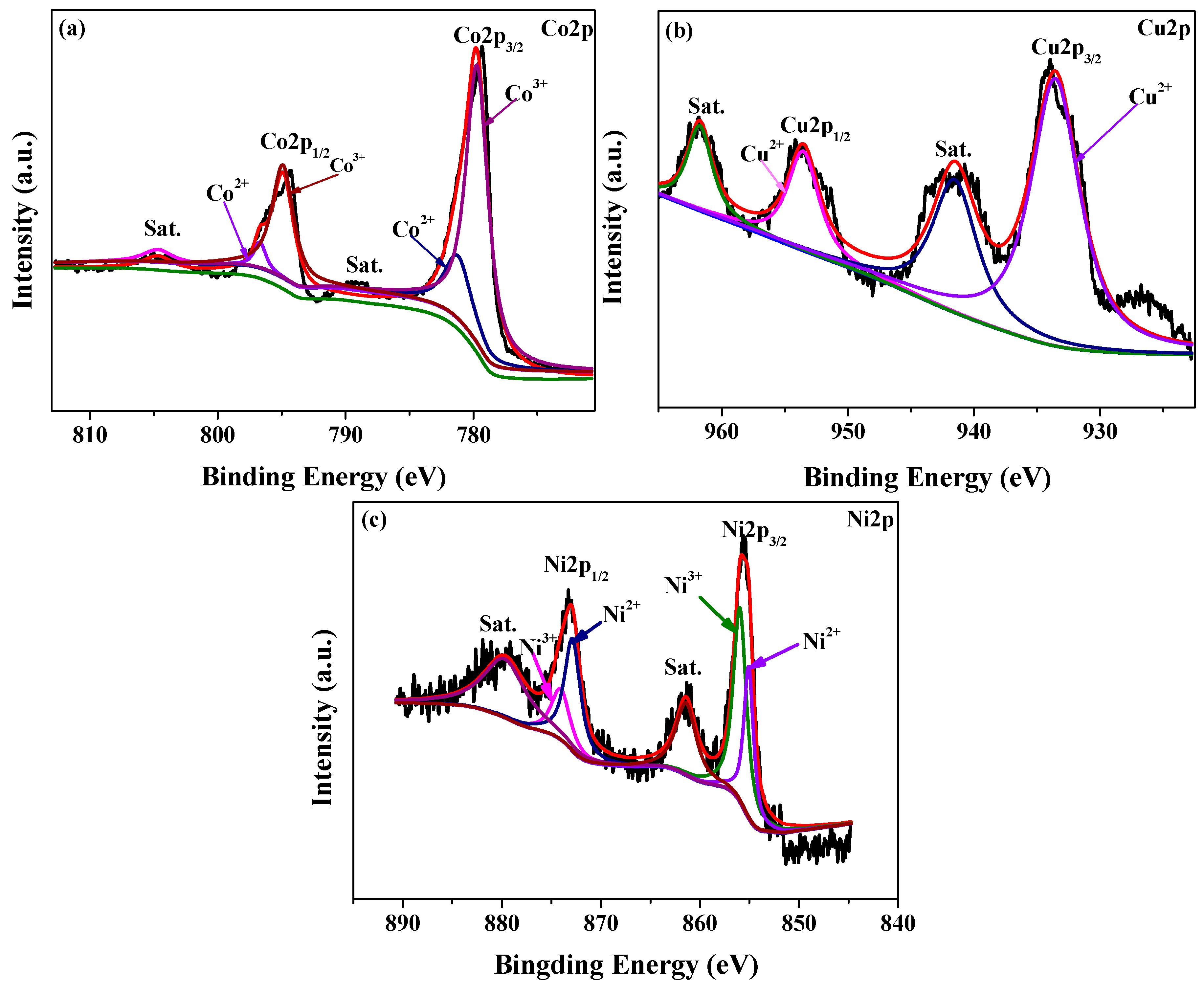
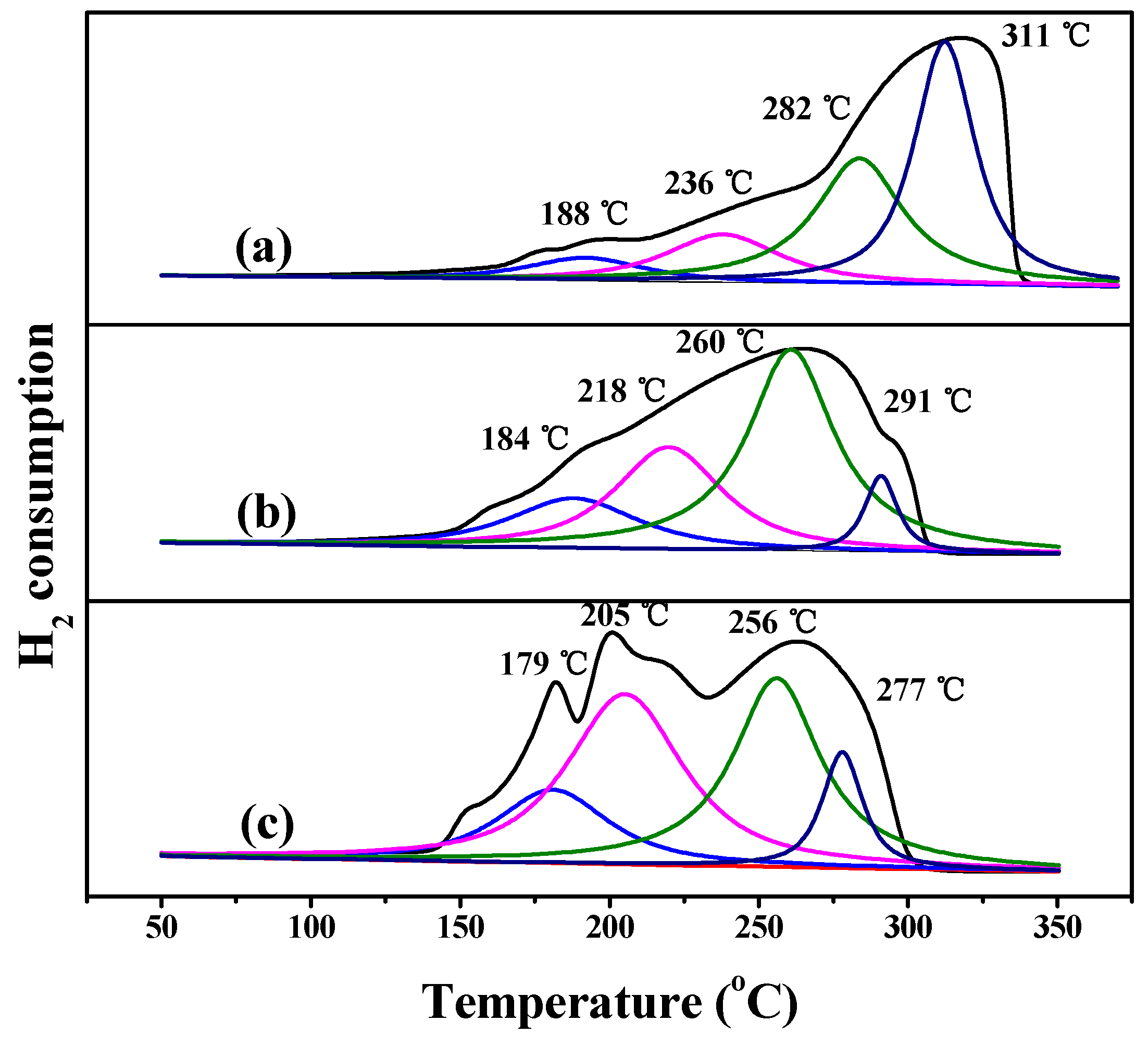
3.1. Characterization of the Catalysts
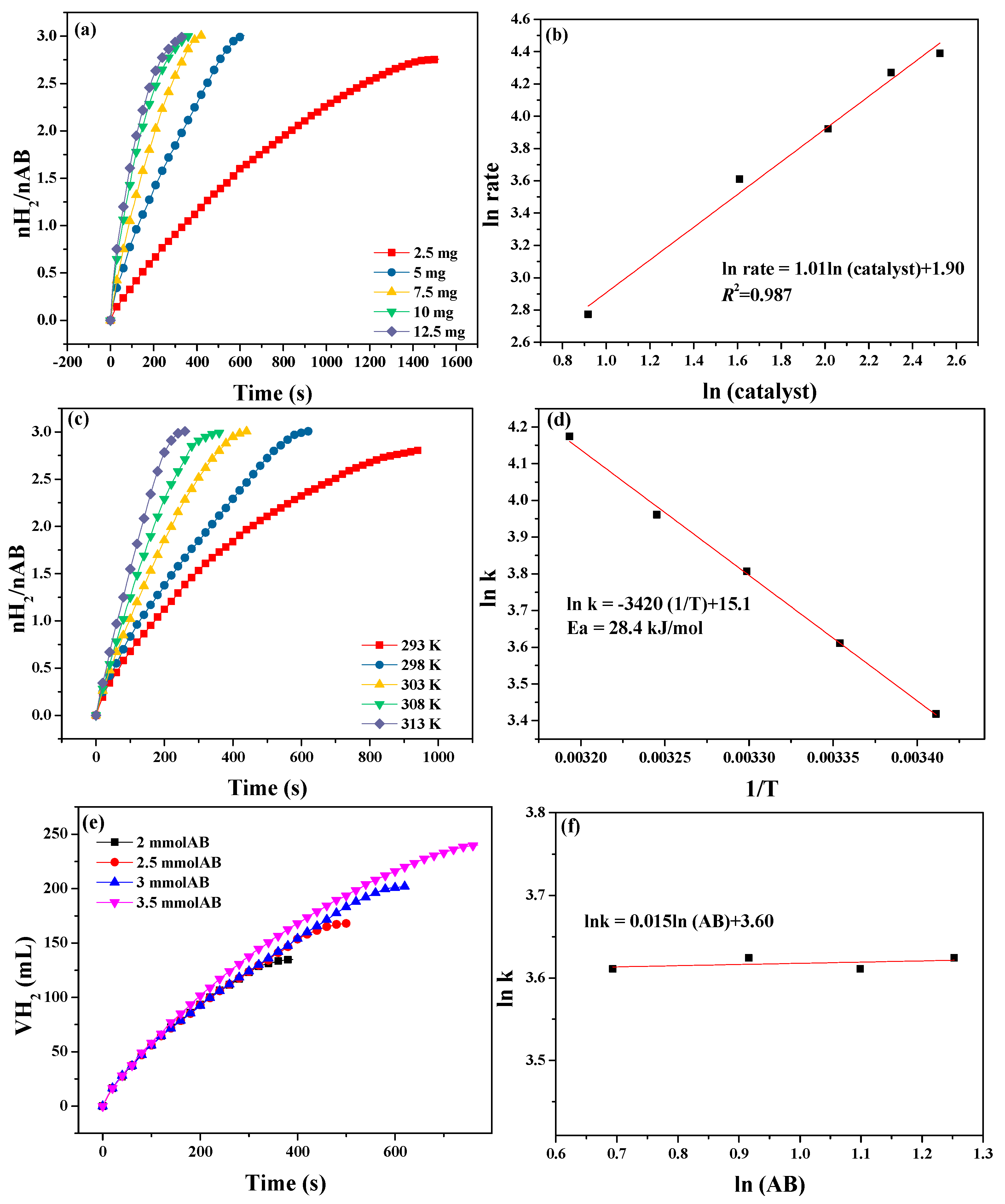
3.2. Catalytic Tests
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, P.; Xu, C.; Yin, H.; Gao, X.; Qu, L. Shock induced conversion of carbon dioxide to few layer graphene. Carbon 2017, 115, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyar, T.; Beşkci, D. Integration of hydrogen energy systems into renewable energy systems for better design of 100% renewable energy communities. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 2453–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edalati, K.; Uehiro, R.; Ikeda, Y.; Li, H.-W.; Emami, H.; Filinchuk, Y.; Arita, M.; Saucage, X.; Tanaka, I.; Akiba, E.; et al. Design and synthesis of a magnesium alloy for room temperature hydrogen storage. Acta Mater. 2018, 149, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.L.; Lu, Z.H.; Huang, W.; Chen, X.; Zhu, J. High Pt-like activity of the Ni–Mo/graphene catalyst for hydrogen evolution from hydrolysis of ammonia borane. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 8579–8583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbayrak, S.; Özkar, S. Ammonia borane as hydrogen storage materials. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 18592–18606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Wang, C.; Wang, Q.; Martinez-Villacorta, A.; Escobar, A.; Chong, H.; Wang, X.; Moya, S.; Salmon, L.; Fouquet, E.; et al. Highly selective and sharp volcano-type synergistic Ni2Pt@ZIF-8-catalyzed hydrogen evolution from ammonia borane hydrolysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 10034–10042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, M.; Xu, Q. A high-performance hydrogen generation system: Transition metal-catalyzed dissociation and hydrolysis of ammonia–borane. J. Power Sources 2006, 156, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluhm, M.; Bradley, M.; Butterick, R.; Kusari, U.; Sneddon, L. Amineborane-based chemical hydrogen storage: Enhanced ammonia borane dehydrogenation in ionic liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 7748–7749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heldebrant, D.; Karkamkar, A.; Hess, N.; Bowden, M.; Rassat, S.; Zheng, F.; Rappe, K.; Autrey, T. The effects of chemical additives on the induction phase in solid-state thermal decomposition of ammonia borane. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 5332–5336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.J.; Wang, H.L.; Yan, J.M.; Jiang, Q. Oleylamine-stabilized Cu0.9Ni0.1 nanoparticles as efficient catalyst for ammonia borane dehydrogenation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 25251–25257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakap, M.; Kalu, E.; Özkar, S. Hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of ammonia-borane using Pd-PVB-TiO2 and Co-Ni-P/Pd-TiO2 under stirred conditions. J. Power Sources 2012, 210, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, N.-Z.; Feng, C.; Gao, S.-T.; Wang, C. Ag/Pd nanoparticles supported on amine-functionalized metal–organic framework for catalytic hydrolysis of ammonia borane. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 944–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.D.; Tian, X.K.; Yang, C.; Zhou, Z.X.; Liu, X.W.; Li, Y. Active 3D Pd/graphene aerogel catalyst for hydrogen generation from the hydrolysis of ammonia-borane. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 15225–15235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göksu, H.; Yıldız, Y.; Çelik, B.; Yazıcı, M.; Kılbas, B.; Şen, F. Highly efficient and monodisperse graphene oxide furnished Ru/Pd nanoparticles for the dehalogenation of aryl halides via ammonia borane. ChemistrySelect 2016, 1, 953–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-K.; Kim, T.-J.; Kim, T.-Y.; Lee, G.; Park, J.; Nam, S.; Kang, S. Tetraglyme-mediated synthesis of Pd nanoparticles for dehydrogenation of ammonia borane. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 2021–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.M.; Zhang, X.B.; Han, S.; Shioyama, H.; Xu, Q. Synthesis of longtime water/air-stable Ni nanoparticles and their high catalytic activity for hydrolysis of ammonia− borane for hydrogen generation. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 48, 7389–7393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakap, M.; Özkar, S. Hydrogen generation from the hydrolysis of ammonia-borane using intrazeolite cobalt (0) nanoclusters catalyst. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 3341–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Lu, Z.-H.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.; Lan, Y. One-pot synthesis of core-shell Cu@SiO2 nanospheres and their catalysis for hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane and hydrazine borane. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7597–7604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Lu, Z.-H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Feng, G. Synergetic catalysis of non-noble bimetallic Cu-Co nanoparticles embedded in SiO2 nanospheres in hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 14167–14174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Liao, J.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, R. Magnetic field induced synthesis of amorphous CoB alloy nanowires as a highly active catalyst for hydrogen generation from ammonia borane. Catal. Commun. 2016, 84, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, Y.; Yano, K.; Fukuzumi, S. Catalytic application of shape-controlled Cu2O particles protected by Co3O4 nanoparticles for hydrogen evolution from ammonia borane. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 5356–5363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, H.; Kleitz, F. High-performance solid catalysts for H2 generation from ammonia borane: Progress through synergetic Cu–Ni interactions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 14790–14796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Zhong, J.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, H.; Xu, L.; Sun, X.; Lee, S.T. CuxCo1−xO nanoparticles on graphene oxide as a synergistic catalyst for high-efficiency hydrolysis of ammonia–borane. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 11950–11954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Shen, W. Morphology-dependent nanocatalysts: Rod-shaped oxides. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 1543–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, Y.; Yano, K.; Xu, Q.; Fukuzumi, S. Cu/Co3O4 nanoparticles as catalysts for hydrogen evolution from ammonia borane by hydrolysis. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 16456–16462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Huang, M.; Lu, Z.-H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Yang, Z. Methanolysis of ammonia borane by shape-controlled mesoporous copper nanostructures for hydrogen generation. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 1070–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Feng, K.; Shang, Y.; Kang, Z.; Sun, X.; Zhong, J. Cube-like CuCoO nanostructures on reduced graphene oxide for H2 generation from ammonia borane. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2018, 5, 1180–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugavani, A.; Selvan, R. Improved electrochemical performances of CuCo2O4/CuO nanocomposites for asymmetric supercapacitors. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 188, 852–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Shen, X.; Ji, Z.; Cai, X.; Zhu, G.; Chen, K. Porous NiCo2O4 nanosheets/reduced graphene oxide composite: Facile synthesis and excellent capacitive performance for supercapacitors. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2015, 440, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Pu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Jing, M.; Chen, Q.; Jia, X.; Ji, X. Uniform porous spinel NiCo2O4 with enhanced electrochemical performances. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 632, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y. Synthesis and electrochemical characterization of uniformly-dispersed high loading Pt nanoparticles on sonochemically-treated carbon nanotubes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 19255–19259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filiz, B.; Figen, A.; Pişkin, S. The remarkable role of metal promoters on the catalytic activity of Co-Cu based nanoparticles for boosting hydrogen evolution: Ammonia borane hydrolysis. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2018, 238, 365–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Liao, J.; Zhong, S.; Leng, Y.; Ji, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, R.; Li, H. Cu0.6Ni0.4Co2O4 nanowires, a novel noble-metal-free catalyst with ultrahigh catalytic activity towards the hydrolysis of ammonia borane for hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 5541–5550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, L.; Gao, H.; Dong, W.; Yang, M.; Wang, G. Hierarchically nanostructured MnCo2O4 as active catalysts for the synthesis of N-benzylideneaniline from benzyl alcohol and aniline. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, S.; Liao, J.; Feng, K.; Zheng, Y.; Polletc, B.; Li, H. CuCo2O4 nanoplate film as a low-cost, highly active and durable catalyst towards the hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane for hydrogen production. J. Power Sources 2017, 355, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Feng, K.; Yao, Y. Fabrication of a Ti-supported NiCo2O4 nanosheet array and its superior catalytic performance in the hydrolysis of ammonia borane for hydrogen generation. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 3893–3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Ji, J.; Feng, X.; Duan, X.; Qian, G.; Li, P.; Zhou, X.; Chen, D.; Yuan, W. Mechanistic insight into size-dependent activity and durability in Pt/CNT catalyzed hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 16736–16739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.; Lu, D.; Diao, G.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, M.; Li, H. Co0.8Cu0.2MoO4 microspheres composed of nanoplatelets as a robust catalyst for the hydrolysis of ammonia borane. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5843–5851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaura, H.; Hirao, S.; Yanaguchi, S.; Yahiro, H. Investigation on reduction behaviors of SnO2 and SnO2-supported CuO sensor materials by temperature-programmed reduction method combined with resistance measurement. Sens. Mater. 2016, 28, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar]
- Trivedi, S.; Prasad, R. Selection of cobaltite and effect of preparation method of NiCo2O4 for catalytic oxidation of CO-CH4 mixture. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 12, 440–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Yang, L.; Cao, N.; Du, C.; Dai, H.; Luo, W.; Chen, G. In situ facile synthesis of bimetallic CoNi catalyst supported on graphene for hydrolytic dehydrogenation of amine borane. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 3371–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Jiang, R.; Li, Q.; Zeng, F.; Zheng, X.; Xu, Z.; Chen, C.; Peng, J. The hydrolysis of ammonia borane catalyzed by NiCoP/OPC-300 nanocatalysts: high selectivity and efficiency, and mechanism. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 850–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Tuninetti, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Ciganda, R.; Salmon, L.; Moya, S.; Ruiz, J.; Astruc, D. Hydrolysis of ammonia-borane over Ni/ZIF-8 nanocatalyst: High efficiency, mechanism, and controlled hydrogen release. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 11610–11615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.; Li, J.; Lin, C.; Liao, J.; Feng, Y.; Ding, Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, Q.; Li, H. A simple and scalable route to synthesize CoxCu1−xCo2O4@CoyCu1−yCo2O4 yolk-shell microspheres, a high-performance catalyst to hydrolyze ammonia borane for hydrogen production. Small 2019, 15, 1805460–1805468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.; Feng, Y.; Wu, S.; Ye, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Xie, F.; Li, H. Hexagonal CuCo2O4 nanoplatelets, a highly active catalyst for the hydrolysis of ammonia borane for hydrogen production. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.; Kang, L.; Cao, S.; Chen, Y.; Lin, Z.S.; Fu, W.F. Nanostructured Ni2P as a robust catalyst for the hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia–borane. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2015, 54, 15725–15729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, M.; Zhou, X.; Lu, H. Amine-capped Co nanoparticles for highly efficient dehydrogenation of ammonia borane. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2014, 6, 13191–13200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Feng, Y.; Ding, Z.; Liao, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.-R.; Li, H. MoO3-doped MnCo2O4 microspheres consisting of nanosheets: An inexpensive nanostructured catalyst to hydrolyze ammonia borane for hydrogen generation. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Li, S.; Xia, B.; Yang, L.; Cao, N.; Su, J.; He, M.; Luo, W.; Cheng, G. Decoration of graphene with tetrametallic Cu@FeCoNi core-shell nanoparticles for catalytic hydrolysis of amine boranes. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 32817–32825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhu, Q.; Xu, Q. Non-noble bimetallic CuCo nanoparticles encapsulated in the pores of metal-organic frameworks: Synergetic catalysis in the hydrolysis of ammonia borane for hydrogen generation. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Dai, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Huang, B. Covalently-terminated germanane GeH and GeCH3 for hydrogen generation from catalytic hydrolysis of ammonia borane under visible light irradiation. Catal. Commun. 2019, 118, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.-H.; Li, J.; Zhu, A.; Yao, Q.; Huang, W.; Zhou, R.; Zhou, R.; Chen, X. Catalytic hydrolysis of ammonia borane via magnetically recyclable copper iron nanoparticles for chemical hydrogen storage. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 5330–5337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metin, Ö.; Özkar, S.; Sun, S. Monodisperse nickel nanoparticles supported on SiO2 as an effective catalyst for the hydrolysis of ammonia-borane. Nano Res. 2010, 3, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, F.; Dai, Y.; Li, L.; Xu, C.; Huang, Y.; Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; Jiao, L.; Yuan, H. Synthesis of Cu@ FeCo core-shell nanoparticles for the catalytic hydrolysis of ammonia borane. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metin, Ö.; Özkar, S. Water soluble nickel(0) and cobalt(0) nanoclusters stabilized by poly(4-styrenesulfonic acid-co-maleic acid): Highly active, durable and cost effective catalysts in hydrogen generation from the hydrolysis of ammonia borane. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 1424–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Q. Rapid and energy-efficient synthesis of a graphene-CuCo hybrid as a high performance catalyst. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 10990–10993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; He, J.; Liu, G.; Qi, S.; Cheng, L.; Chen, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, J. Efficient hydrogen evolution from the hydrolysis of ammonia borane using bilateral-like WO3−x nanorods coupled with Ni2P nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 6188–6191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Catalysts | TOF (molhydrogen·min−1·mol−1cat) | Ea (kJ·mol−1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5% Pt/C | 194.2 | 19.1 | This Work |
| Cu0.6Ni0.4Co2O4 nanowires | 119.5 | 33.91 | [33] |
| NiCoP/OPC-300 | 95.2 | 38.9 | [42] |
| Ni-ZIF8 | 85.7 | 28.0 | [43] |
| CoxCu1−xCo2O4@ CoyCu1−yCo2O4 yolk–shell microspheres | 81.8 | 24.97 | [44] |
| Ni0.5Cu0.5Co2O4 nanoplatelets | 80.2 | 28.4 | This work |
| CuCo2O4 | 73.4 | / a | [45] |
| Cu0.8Co0.2O-GO | 70.0 | 45.53 | [23] |
| Ni0.5Cu0.5Co2O4 microspheres | 65.1 | 29.5 | This work |
| Co0.8Cu0.2MoO4 microspheres | 55.0 | 39.6 | [38] |
| Ni0.5Cu0.5Co2O4 nanoparticles | 45.5 | 43.2 | This work |
| Ni2P NPs | 40.4 | 44.6 | [46] |
| Co/PEI-GO | 39.9 | 28.2 | [47] |
| MoO3-doped MnCo2O4 | 26.4 | 34.24 | [48] |
| Cu@FeCoNi/graphene | 20.93 | 31.82 | [49] |
| CuCo@MIL-101 | 19.6 | / | [50] |
| GeCH3 | 18.1 | / | [51] |
| Cu0.33Fe0.67 | 13.9 | 43.2 | [52] |
| Ni/SiO2 | 13.2 | 34 ± 2 | [53] |
| Cu0.3@Fe0.1Co0.6 core-shell nanoparticles | 10.5 | 38.75 | [54] |
| PSMA-Ni | 10.1 | 32 ± 2 | [55] |
| CuCo/rGO | 9.1 | / | [56] |
| Ni2P | 8.1 | / | [57] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ye, H.; Li, L.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, H. Ni0.5Cu0.5Co2O4 Nanocomposites, Morphology, Controlled Synthesis, and Catalytic Performance in the Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane for Hydrogen Production. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9091334
Feng Y, Zhang J, Ye H, Li L, Wang H, Li X, Zhang X, Li H. Ni0.5Cu0.5Co2O4 Nanocomposites, Morphology, Controlled Synthesis, and Catalytic Performance in the Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane for Hydrogen Production. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(9):1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9091334
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Yufa, Jin Zhang, Huilong Ye, Liling Li, Huize Wang, Xian Li, Xibin Zhang, and Hao Li. 2019. "Ni0.5Cu0.5Co2O4 Nanocomposites, Morphology, Controlled Synthesis, and Catalytic Performance in the Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane for Hydrogen Production" Nanomaterials 9, no. 9: 1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9091334
APA StyleFeng, Y., Zhang, J., Ye, H., Li, L., Wang, H., Li, X., Zhang, X., & Li, H. (2019). Ni0.5Cu0.5Co2O4 Nanocomposites, Morphology, Controlled Synthesis, and Catalytic Performance in the Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane for Hydrogen Production. Nanomaterials, 9(9), 1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9091334






