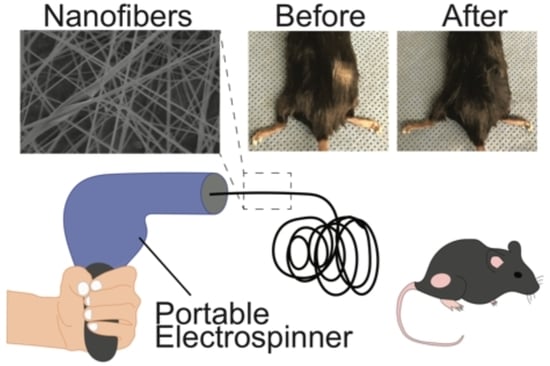
A Portable Electrospinner for Nanofiber Synthesis and Its Application for Cosmetic Treatment of Alopecia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
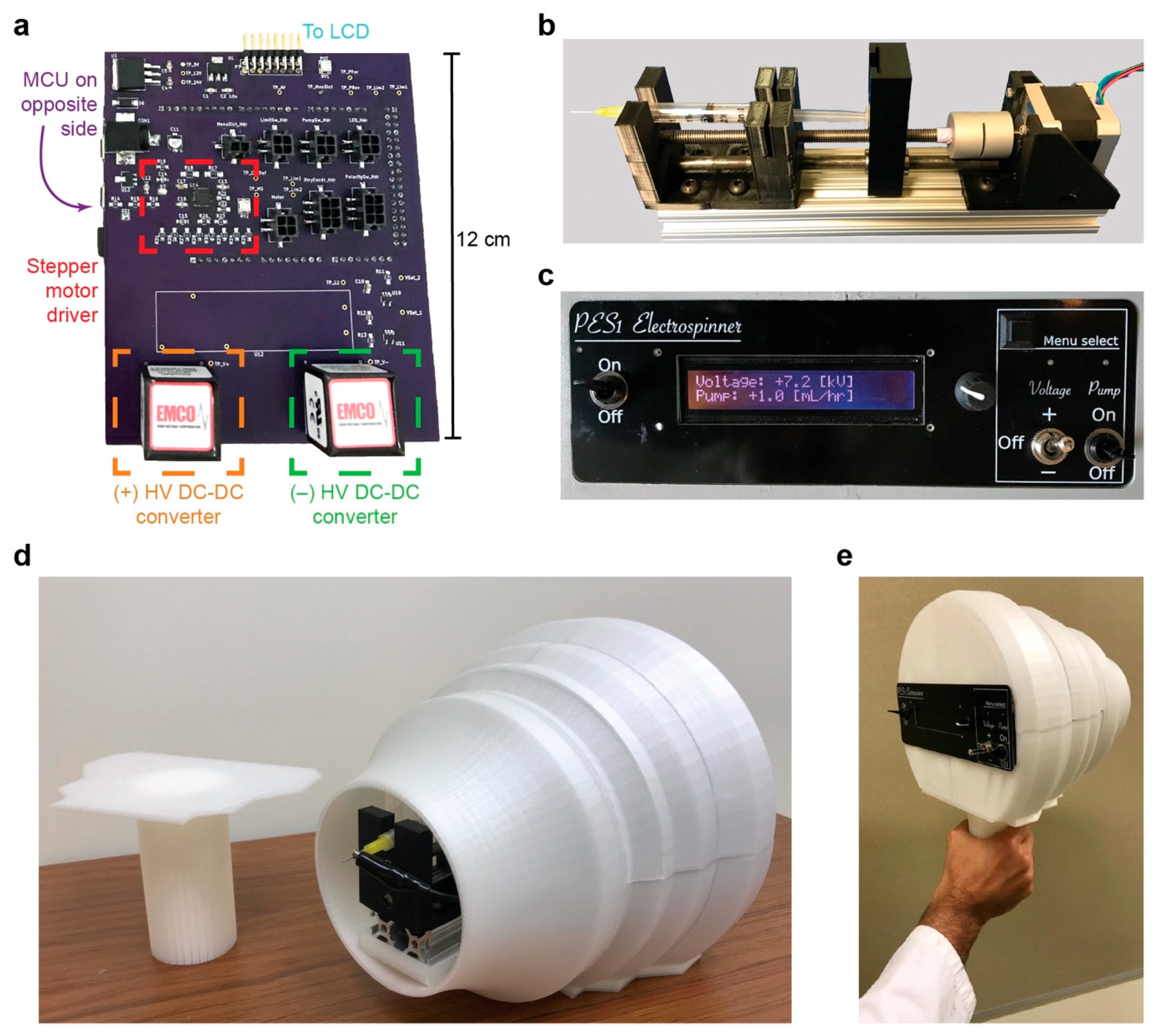
2.1. Electrospinner Components and Fabrication
2.2. Polymer Solutions
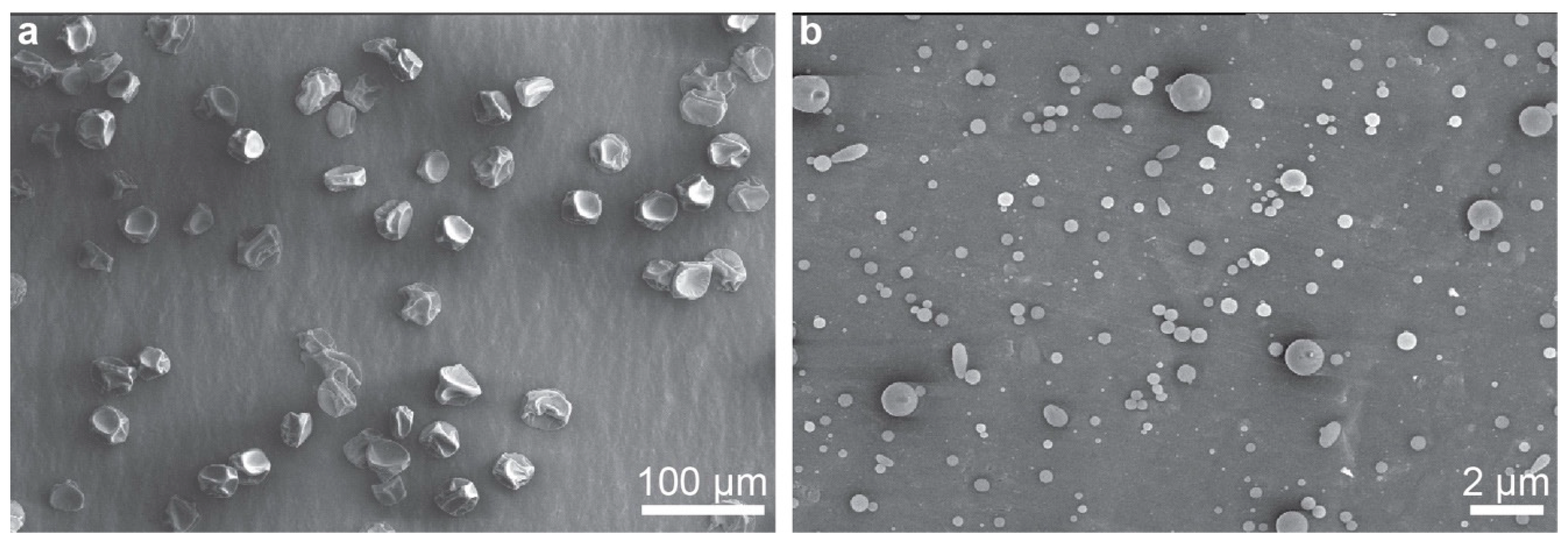
2.3. Electrospinning and Electrospraying
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.5. Determination of Solution Viscosity
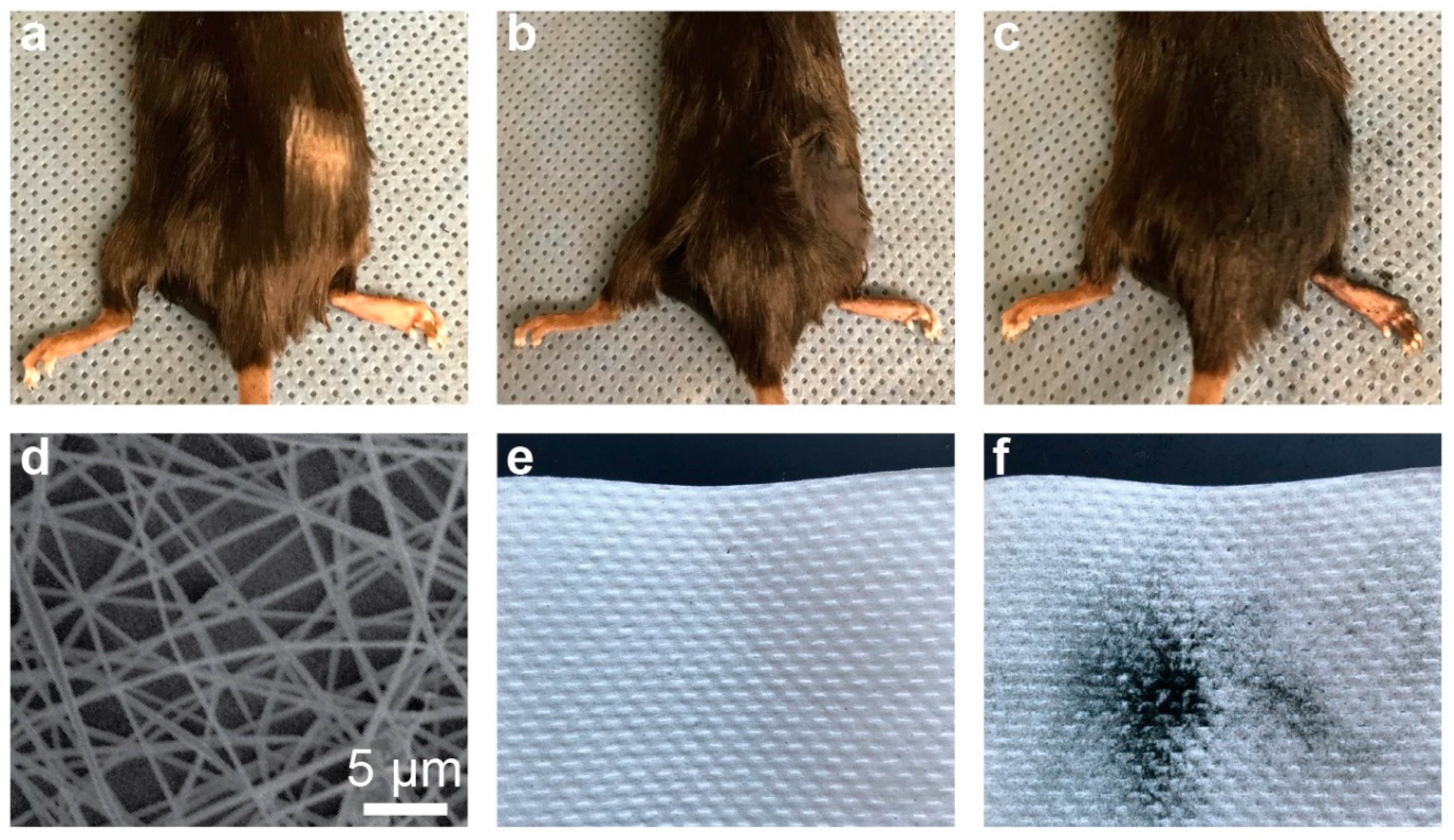
2.6. Hair Thickening
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Electrospinner Design
3.2. Nanofiber Synthesis and Characterization
3.3. Biological and Cosmetic Applications
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ding, Y.; Xu, W.; Wang, W.; Fong, H.; Zhu, Z. Scalable and facile preparation of highly stretchable electrospun PEDOT:PSS@PU fibrous nonwovens toward wearable conductive textile applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 30014–30023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.S.; Shim, J.; Park, M.; Kim, H.Y.; Son, D.I. Transparent nanofiber textiles with intercalated ZnO@graphene QD LEDs for wearable electronics. Compos. Part B: Eng. 2017, 130, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-C.; Lu, Y.-T.; Chien, Y.-A.; Wang, J.-A.; You, T.-H.; Wang, Y.-S.; Lin, C.-W.; Ma, C.-C.M.; Hu, C.-C. Asymmetric supercapacitors based on functional electrospun carbon nanofiber/manganese oxide electrodes with high power density and energy density. J. Power Sources 2017, 362, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, A.; Mehebub Alam, M.; Sadhukhan, P.; Ghorai, U.K.; Das, S.; Middya, T.R.; Mandal, D. Organo-lead halide perovskite regulated green light emitting poly(vinylidene fluoride) electrospun nanofiber mat and its potential utility for ambient mechanical energy harvesting application. Nano Energy 2018, 49, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazhamalai, P.; Krishnamoorthy, K.; Mariappan, V.K.; Sahoo, S.; Manoharan, S.; Kim, S.J. A high efficacy self-charging MoSe2 solid-state supercapacitor using electrospun nanofibrous piezoelectric separator with ionogel electrolyte. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 5, 1800055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, H.-Y.; Jing, X.; Zheng, Q.; Fang, L.; Huang, H.-X.; Turng, L.-S.; Gong, S. High-performance flexible triboelectric nanogenerator based on porous aerogels and electrospun nanofibers for energy harvesting and sensitive self-powered sensing. Nano Energy 2018, 48, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Kai, D.; Ye, H.; Tian, L.; Ding, X.; Ramakrishna, S.; Loh, X.J. Electrospinning of poly(glycerol sebacate)-based nanofibers for nerve tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng.: C 2017, 70, 1089–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Miszuk, J.M.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, H.; Fong, H. Electrospun polycaprolactone 3D nanofibrous scaffold with interconnected and hierarchically structured pores for bone tissue engineering. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2015, 4, 2238–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Jin, L.; Li, C.; Kuddannayai, S.; Zhang, Y. The effect of electrical stimulation on cortical cells in 3D nanofibrous scaffolds. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 11027–11035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unnithan, A.R.; Sasikala, A.R.K.; Thomas, S.S.; Nejad, A.G.; Cha, Y.S.; Park, C.H.; Kim, C.S. Strategic design and fabrication of biomimetic 3D scaffolds: Unique architectures of extracellular matrices for enhanced adipogenesis and soft tissue reconstruction. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wróblewska-Krepsztul, J.; Rydzkowski, T.; Michalska-Pożoga, I.; Thakur, K.V. Biopolymers for Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Applications: Recent Advances and Overview of Alginate Electrospinning. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.-S.; Kim, M.H.; Shin, J.Y.; Park, S.R.; Jung, J.-Y.; Park, W.H. Electrospinning and wound healing activity of β-chitin extracted from cuttlefish bone. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 193, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böhm, G.; Groll, J.; Heffels, K.-H.; Heussen, N.; Ink, P.; Alizai, H.P.; Neumann, U.P.; Schnabel, R.; Mirastschijski, U. Influence of MMP inhibitor GM6001 loading of fibre coated polypropylene meshes on wound healing: Implications for hernia repair. J. Biomater. Appl. 2018, 32, 1343–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarhan, W.A.; Azzazy, H.M.E.; El-Sherbiny, I.M. Honey/chitosan nanofiber wound dressing enriched with Allium sativum and Cleome droserifolia: Enhanced antimicrobial and wound healing activity. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 6379–6390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, N.; Gao, P.-L.; Wang, K.; Wang, J.-Y.; Zhong, Y.; Luo, Y. Fibrous scaffolds potentiate the paracrine function of mesenchymal stem cells: A new dimension in cell-material interaction. Biomaterials 2017, 141, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roque-Ruiz, J.H.; Cabrera-Ontiveros, E.A.; Torres-Pérez, J.; Reyes-López, S.Y. Preparation of PCL/clay and PVA/clay electrospun fibers for cadmium (Cd+2), chromium (Cr+3), copper (Cu+2) and lead (Pb+2) removal from water. Waterairsoil Pollut. 2016, 227, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi-Azarbayjani, A.; Qun, L.; Chan, Y.W.; Chan, S.Y. Novel vitamin and gold-loaded nanofiber facial mask for topical delivery. Aaps Pharmscitech 2010, 11, 1164–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.; Dong, L.; Zhang, X.; Lei, T.; Ehrenhauser, F.; Song, K.; Li, M.; Sun, X.; Wu, Q. Electrospun Nanofibers Made of Silver Nanoparticles, Cellulose Nanocrystals, and Polyacrylonitrile as Substrates for Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Materials 2017, 10, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Zhou, L.; Li, M.-C.; Wu, Q.; Kojima, Y.; Zhou, D. Preparation and Properties of Electrospun Poly (Vinyl Pyrrolidone)/Cellulose Nanocrystal/Silver Nanoparticle Composite Fibers. Materials 2016, 9, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfian, S.; Giraudmaillet, C.; Yoosefinejad, A.; Thakur, V.K.; Nezhad, H.Y. Electrospun Piezoelectric Polymer Nanofiber Layers for Enabling in Situ Measurement in High-Performance Composite Laminates. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 8891–8902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feltz, K.P.; Kalaf, E.A.G.; Chen, C.; Martin, R.S.; Sell, S.A. A review of electrospinning manipulation techniques to direct fiber deposition and maximize pore size. Electrospinning 2017, 1, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Maurer, T.; Mirmirani, P. Understanding and addressing hair disorders in transgender individuals. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2018, 19, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirmirani, P. Age-related hair changes in men: Mechanisms and management of alopecia and graying. Maturitas 2015, 80, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norwood, O.T. Incidence of female androgenetic alopecia (female pattern alopecia). Dermatol. Surg. 2001, 27, 53–54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.-M.; Chiou, H.-G.; Lin, S.-L.; Lin, J.-M. Effects of electrostatic polarity and the types of electrical charging on electrospinning behavior. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 126, E89–E97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terada, D.; Kobayashi, H.; Zhang, K.; Tiwari, A.; Yoshikawa, C.; Hanagata, N. Transient charge-masking effect of applied voltage on electrospinning of pure chitosan nanofibers from aqueous solutions. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2012, 13, 015003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mit-uppatham, C.; Nithitanakul, M.; Supaphol, P. Effects of solution concentration, emitting electrode polarity, solvent type, and salt addition on electrospun polyamide-6 fibers: A preliminary report. Macromol. Symp. 2004, 216, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachewicz, U.; Stone, C.A.; Willis, C.R.; Barber, A.H. Charge assisted tailoring of chemical functionality at electrospun nanofiber surfaces. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 22935–22941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, L.B.; Cartelli, L.; Graham, N. A Complete Electrical Shock Hazard Classification System and Its Application. Ieee Trans. Ind. Appl. 2018, 54, 6554–6565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; You, M.-H.; Lou, T.; Yu, M.; Zhang, J.-C.; Gong, M.-G.; Lv, F.-Y.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Long, Y.-Z. Colorful hydrophobic poly(vinyl butyral)/cationic dye fibrous membranes via a colored solution electrospinning process. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daneshvar, E.; Tehran, M.A.; Kandi, S.G.; Zeighami, F. Investigating the characteristics of two different methods in nanofiber yarn coloration. J. Text. Inst. 2016, 107, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantini, D.; Costa, L. Dye, fluorophores and pigment coloration of nanofibers produced by electrospinning. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2009, 20, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Polymer | Solvent | Concentration | Voltage | Fiber Diameter | Viscosity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (wt.%) | (kV) | (nm) | (Pa⋅s) | ||
| CA | Acetone/water (4:1 v/v) | 4 | 9 | 600 ± 180 | 3.8 × 10−1 ± 1.4 × 10−1 |
| PVA | THF | 6 | 10 | 85 ± 20 | 2.3 × 10−2 ± 7.6 × 10−2 |
| PAN | DMF | 10 | 7 | 570 ± 75 | 3.2 × 10−1 ± 1 × 10−3 |
| PEO | Water | 6 | 8 | 570 ± 100 | 2.8 × 10−2 ± 8.4 × 10−4 |
| PCL | TFE | 15 | 5 | 320 ± 55 | 2.4 × 101 ± 1.1 |
| PVDF | DMF/acetone (1:1 v/v) | 15 | 10 | 170 ± 45 | 5.8 × 10−2 ± 1.9 × 10−3 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Revia, R.A.; Wagner, B.A.; Zhang, M. A Portable Electrospinner for Nanofiber Synthesis and Its Application for Cosmetic Treatment of Alopecia. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1317. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9091317
Revia RA, Wagner BA, Zhang M. A Portable Electrospinner for Nanofiber Synthesis and Its Application for Cosmetic Treatment of Alopecia. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(9):1317. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9091317
Chicago/Turabian StyleRevia, Richard A., Brandon A. Wagner, and Miqin Zhang. 2019. "A Portable Electrospinner for Nanofiber Synthesis and Its Application for Cosmetic Treatment of Alopecia" Nanomaterials 9, no. 9: 1317. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9091317
APA StyleRevia, R. A., Wagner, B. A., & Zhang, M. (2019). A Portable Electrospinner for Nanofiber Synthesis and Its Application for Cosmetic Treatment of Alopecia. Nanomaterials, 9(9), 1317. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9091317