Origin of Room-Temperature Ferromagnetism in Hydrogenated Epitaxial Graphene on Silicon Carbide
Abstract
1. Introduction
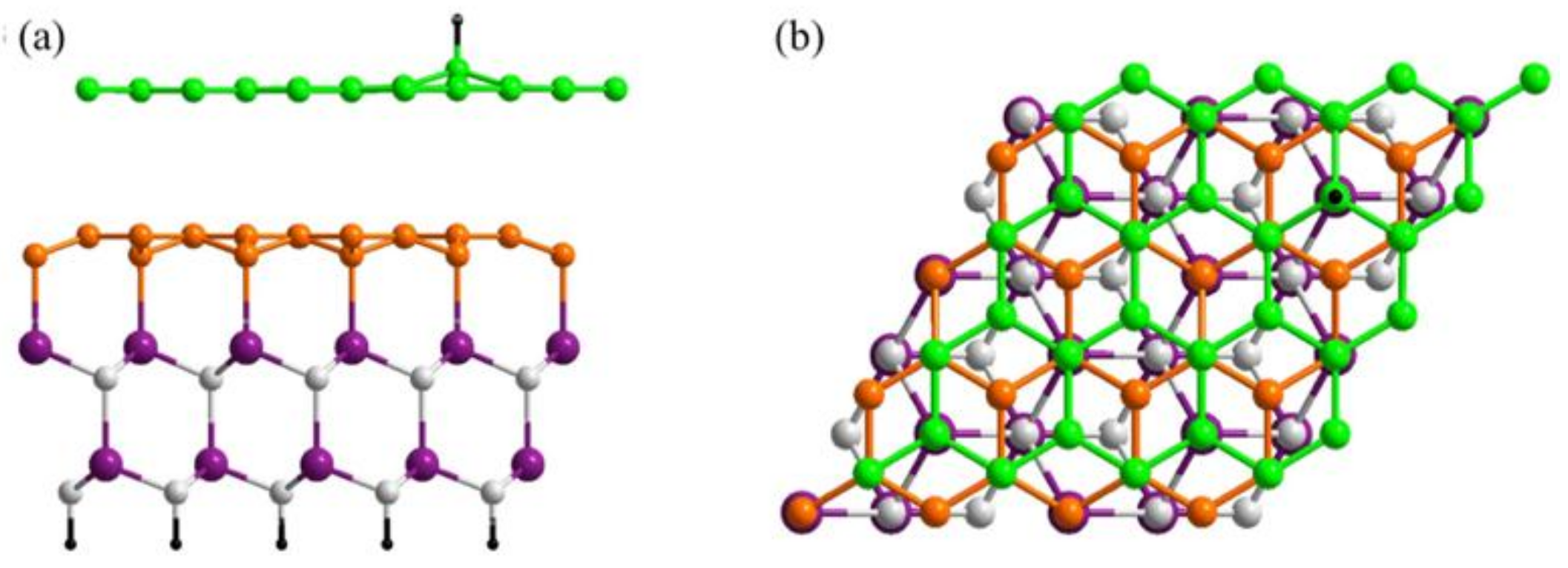
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
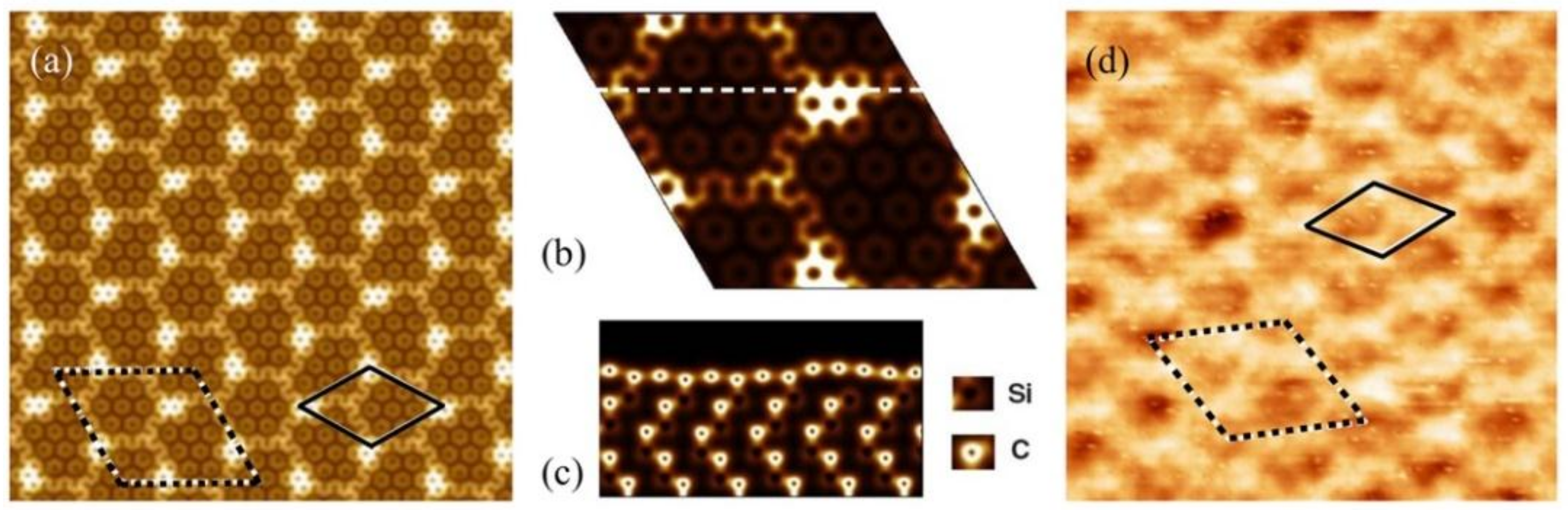
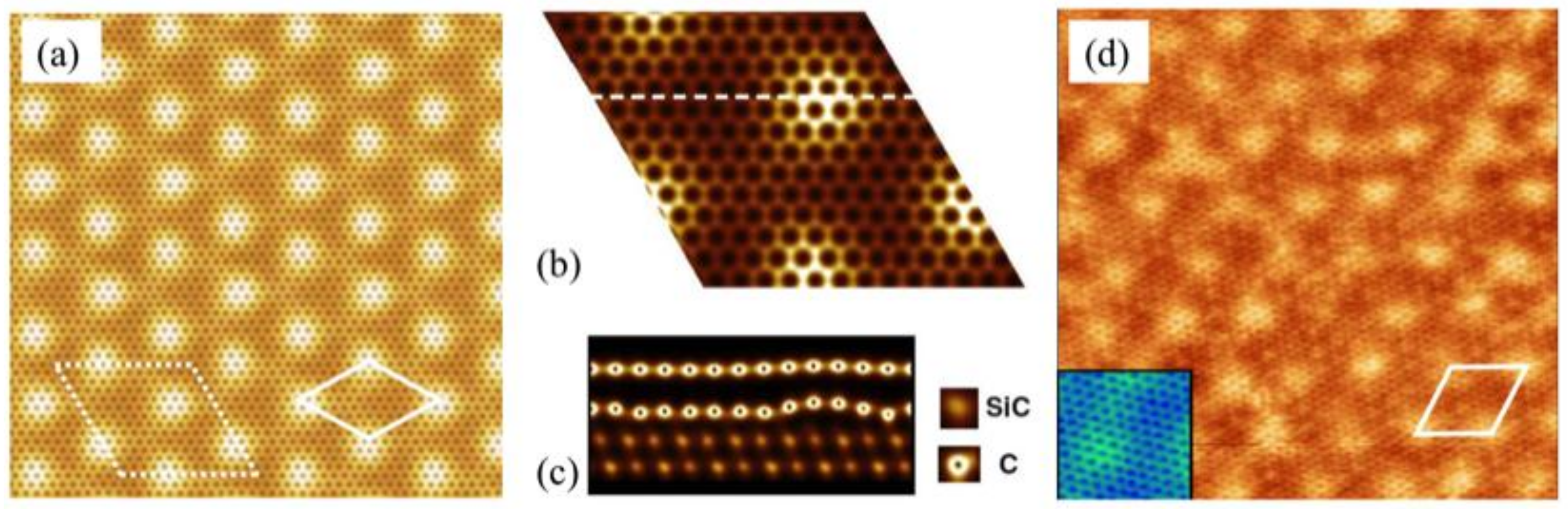
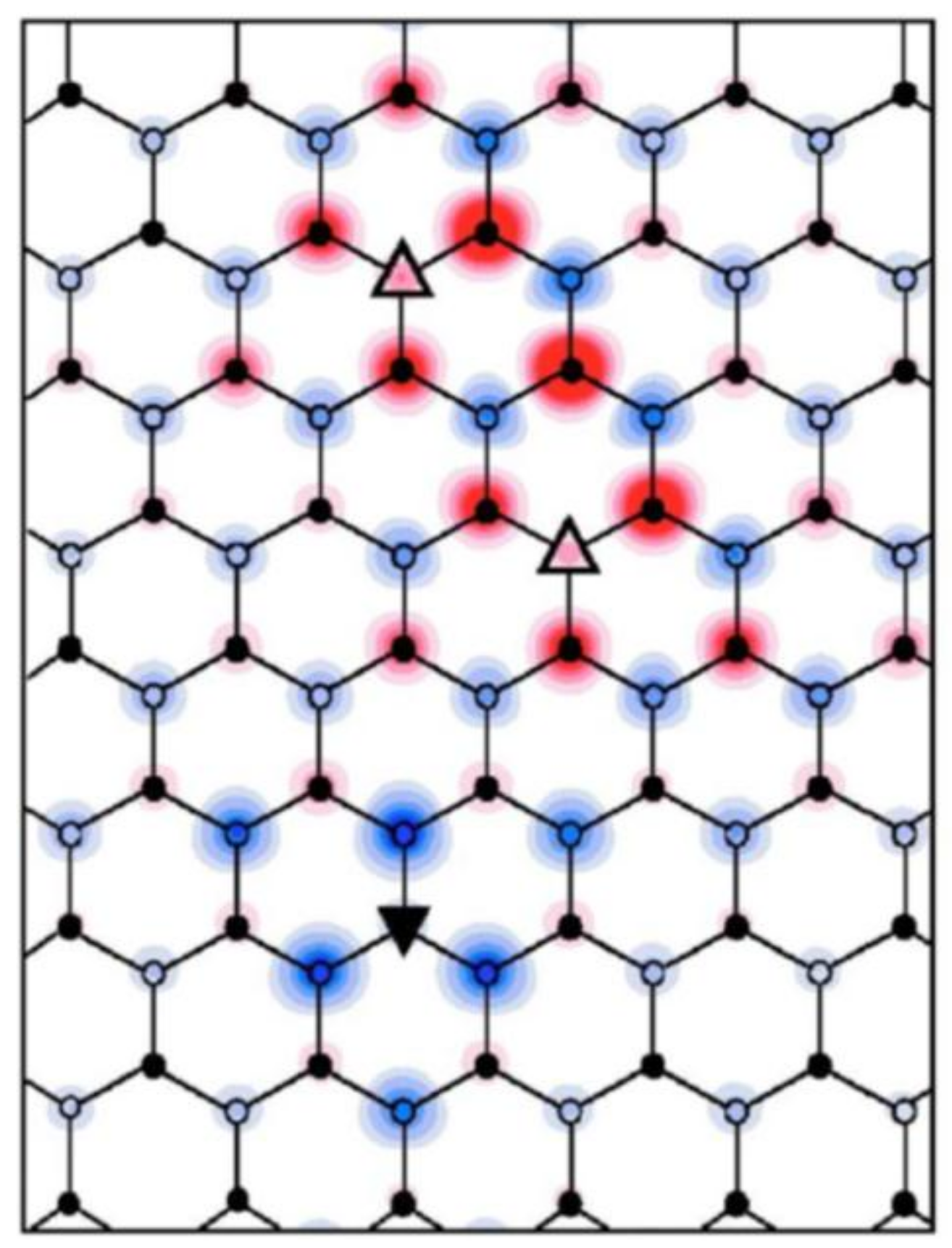
3.1. Preferential Hydrogen Adsorption Sites in Epitaxial Graphene on SiC(0001)
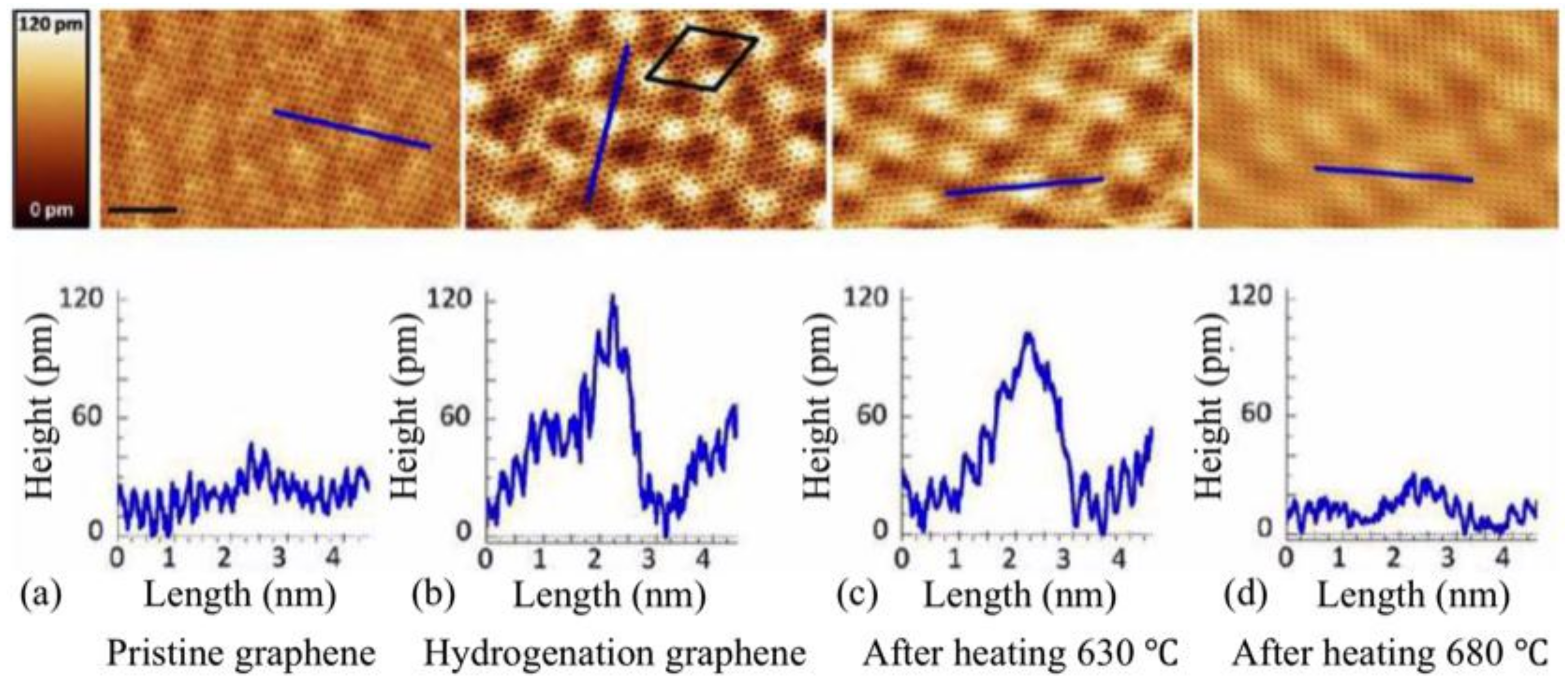
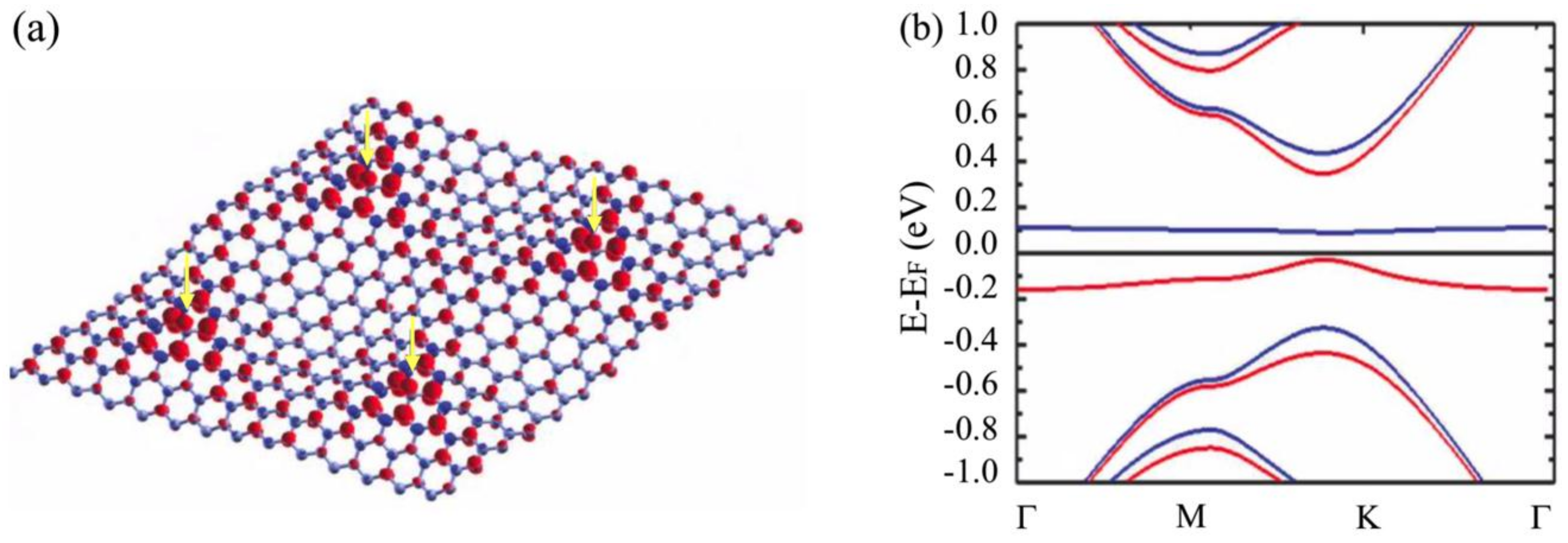
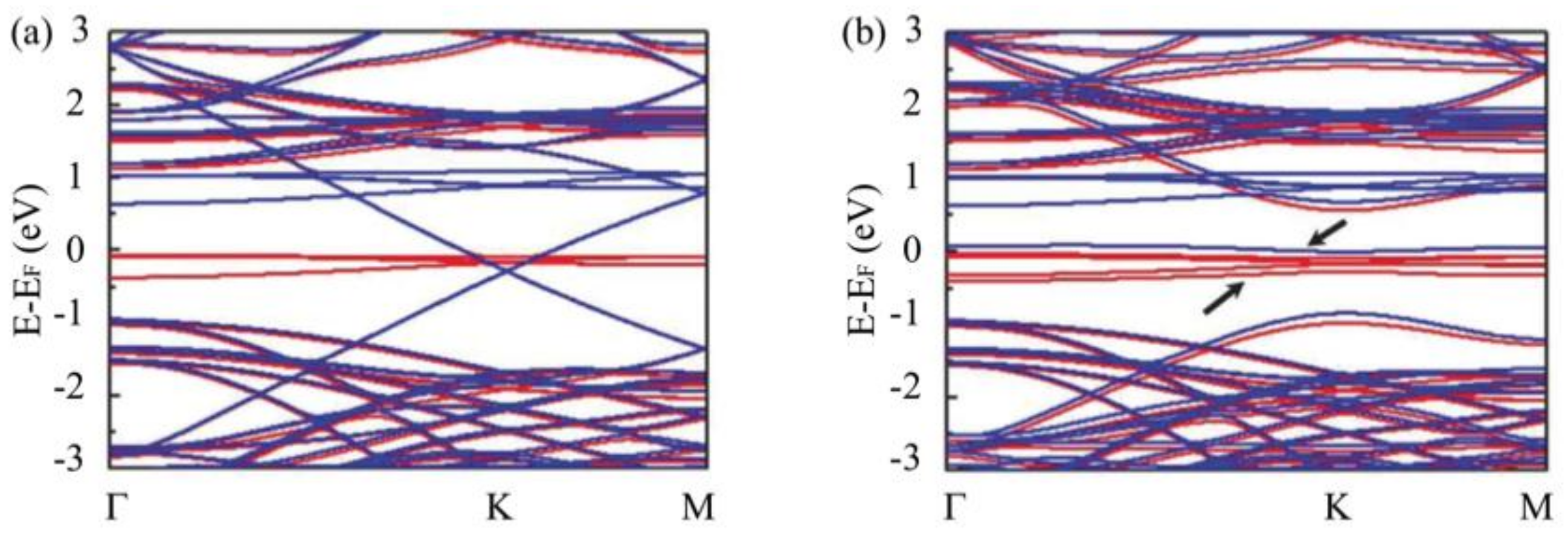
3.2. Room-Temperature Ferromagnetism in Hydrogenated Epitaxial Graphene on SiC(0001)
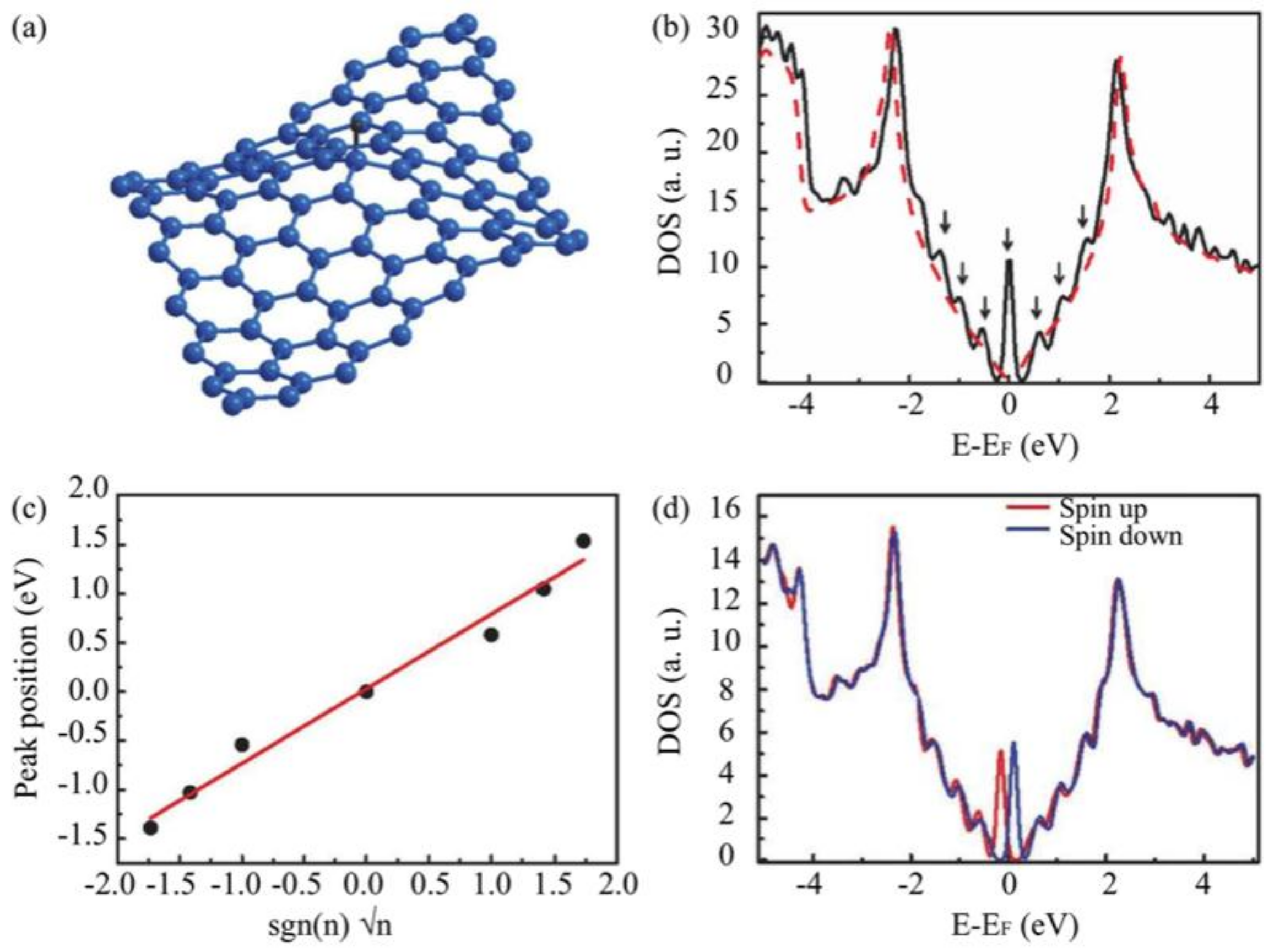
3.3. Substrate Effect on the Electronic Properties of Hydrogenated Epitaxial Graphene
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deng, W.Q.; Xu, X.; Goddard, W.A. New alkali doped pillared carbon materials designed to achieve practical reversible hydrogen storage for transportation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 166103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, V.M.; Guinea, F.; Lopes dos Santos, J.M.B.; Peres, N.M.R.; Castro Neto, A.H. Disorder induced localized states in graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 96, 036801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunlycke, D.; Li, J.; Mintmire, J.W.; White, C.T. Altering low-bias transport in zigzag-edge graphene nanostrips with edge chemistry. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 112108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazyev, O.V.; Helm, L. Defect-induced magnetism in graphene. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 75, 125408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, R.N.C.; Farias, G.A.; Peeters, F.M. Graphene ribbons with a line of impurities: Opening of a gap. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 76, 193409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, E.J.; Li, Z.; Yang, J.; Hou, J.G. Half-metallicity in edge-modified zigzag graphene nanoribbons. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 4224–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, J.P.; Schomerus, H.; Oroszlány, L.; Fal’ko, V.I. Adsorbate-limited conductivity of graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 196803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanella, I.; Guerini, S.; Fagan, S.B.; Filho, J.M.; Filho, A.G.S. Chemical doping-induced gap opening and spin polarization in graphene, Phys. Rev. B 2008, 77, 073404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukhvalov, D.W.; Katsnelson, M.I. Chemical functionalization of graphene with defects. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 4373–4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes-Sodi, F.; Csányi, G.; Piscanec, S.; Ferrari, A.C. Edge-functionalized and substitutionally doped graphene nanoribbons: Electronic and spin properties. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 77, 165427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.T.; Neaton, J.B.; Cohen, M.L. First-principles study of metal adatom adsorption on graphene. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 77, 235430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukhvalov, D.W.; Katsnelson, M.I.; Lichtenstein, A.I. Hydrogen on graphene: Electronic structure, total energy, structural distortions and magnetism from first-principles calculations. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 77, 035427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Ding, F.; Yakobson, B.I. Hydrogen storage by spillover on graphene as a phase nucleation process. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 78, 041402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miwa, R.H.; Martins, T.B.; Fazzio, A. Hydrogen adsorption on boron doped graphene: An ab initio study. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 155708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Liu, F.; Wu, J.; Gu, B.L.; Duan, W. Suppression of spin polarization in graphene nanoribbons by edge defects and impurities, Phys. Rev. B 2008, 77, 153411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marconcini, P.; Cresti, A.; Triozon, F.; Fiori, G.; Biel, B.; Niquet, Y.-M.; Macucci, M.; Roche, S. Atomistic boron-doped graphene field-effect transistors: A route toward unipolar characteristics. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 7942–7947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boukhvalov, D.W.; Katsnelson, M.I. Tuning the gap in bilayer graphene using chemical functionalization: Density functional calculations. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 78, 085413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Q.; Chen, X.S.; Kawazoe, Y.; Jena, P. Ferromagnetism in Semihydrogenated Graphene Sheet. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 3867–3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, D.C.; Nair, R.R.; Mohiuddin, T.M.G.; Morozov, S.V.; Blake, P.; Halsall, M.P.; Ferrari, A.C.; Boukhvalov, D.W.; Katsnelson, M.I.; Geim, A.K.; et al. Control of graphene’s properties by reversible hydrogenation: evidence for graphane. Science 2009, 323, 610–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostwick, A.; McChesney, J.L.; Emtsev, K.V.; Seyller, T.; Horn, K.; Kevan, S.D.; Rotenberg, E. Quasiparticle transformation during a metal-insulator transition in graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 103, 056404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostwick, A.; Ohta, T.; McChesney, J.L.; Emtsev, K.V.; Speck, F.; Seyller, T.; Horn, K.; Kevan, S.D.; Rotenberg, E. The interaction of quasi-particles in graphene with chemical dopants. New J. Phys. 2010, 12, 125014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tang, N.; Wan, X.; Feng, Q.; Li, M.; Xu, Q.; Liu, F.; Du, Y. Realization of ferromagnetic graphene oxide with high magnetization by doping graphene oxide with nitrogen. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Daukiya, L.; Haldar, S.; Lindblad, A.; Sanyal, B.; Eriksson, O.; Aubel, D.; Hajjar-Garreau, S.; Simon, L.; Leifer, K. Site-selective local fluorination of graphene induced by focused ion beam irradiation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazyev, O.V. Magnetism in disordered graphene and irradiated graphite. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 037203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesbers, A.J.M.; Uhlírová, K.; Konečny, M.; Peters, E.C.; Burghard, M.; Aarts, J.; Flipse, C.F.J. Interface-induced room-temperature ferromagnetism in hydrogenated epitaxial graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 111, 166101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goler, S.; Coletti, C.; Tozzini, V.; Piazza, V.; Mashoff, T.; Beltram, F.; Pellegrini, V.; Heun, S. Influence of graphene curvature on hydrogen adsorption: toward hydrogen storage devices. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 11506–11513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler, J.M.; Artacho, E.; Gale, J.D.; García, A.; Junquera, J.; Ordejón, P.; Sánchez-Portal, D. The SIESTA method for ab initio order-N materials simulation. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2002, 14, 2745–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troullier, N.; Martins, J.L. Efficient pseudopotentials for plane-wave calculations. Phys. Rev. B 1993, 43, 1993–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monkhorst, H.J.; Pack, J.D. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B 1976, 13, 5188–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridene, M.; Kha, C.S.; Flipse, C.F.J. Role of silicon dangling bonds in the electronic properties of epitaxial graphene on silicon carbide. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 125705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudarev, S.L.; Botton, G.A.; Savrasov, S.Y.; Humphreys, C.J.; Sutton, A.P. Electron-energy-loss spectra and the structural stability of nickel oxide: An LSDA+U study. Phys. Rev. B 1998, 57, 1505–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- First, P.N.; de Heer, W.A.; Seyller, T.; Berger, C.; Stroscio, J.A.; Moon, J.-S. Epitaxial graphene on silicon carbide. MRS Bull. 2010, 35, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedl, C.; Coletti, C.; Iwasaki, T.; Zakharov, A.A.; Starke, U. Quasi-free-standing epitaxial graphene on SiC obtained by hydrogen intercalation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 103, 246804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varchon, F.; Mallet, P.; Veuillen, J.-Y.; Magaud, L. Ripples in epitaxial graphene on the Si-terminated SiC(0001) surface. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 77, 235412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moaied, M.; Alvarez, J.V.; Palacios, J.J. Hydrogenation-induced ferromagnetism on graphite surfaces. Phys. Rev. B 2014, 90, 115441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieb, E.H. Two theorems on the Hubbard model. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1989, 62, 1201–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, N.; Burke, S.A.; Meaker, K.L.; Panlasigui, M.; Zettl, A.; Guinea, F.; Neto, A.H.C.; Crommie, M.F. Strain-induced pseudo–magnetic fields greater than 300 tesla in graphene nanobubbles. Science 2010, 329, 544–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinea, F.; Katsnelson, M.I.; Geim, A.K. Energy gaps and a zero-field quantum Hall effect in graphene by strain engineering. Nat. Phys. 2010, 6, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinea, F.; Katsnelson, M.I.; Vozmediano, M.A.H. Midgap states and charge inhomogeneities in corrugated graphene. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 77, 075422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehling, T.O.; Balatsky, A.V.; Tsvelik, A.M.; Katsnelson, M.I.; Lichtenstein, A.I. Midgap states in corrugated graphene: Ab initio calculations and effective field theory. EPL 2008, 84, 17003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Anna, L.; de Martino, A. Multiple magnetic barriers in graphene. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 045420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Y.; Liang, J.; Chen, Y. Room-temperature ferromagnetism of graphene. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, D.M.; Katsnelson, M.I. High-temperature ferromagnetism of sp electrons in narrow impurity bands: application to CaB6. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2006, 18, 7209–7725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattausch, A.; Pankratov, O. Ab Initio study of graphene on SiC. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 076802–1-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varchon, F.; Feng, R.; Hass, J.; Li, X.; Nguyen, B.N.; Naud, C.; Mallet, P.; Veuillen, J.-Y.; Berger, C.; Conrad, E.H.; Magaud, L. Electronic structure of epitaxial graphene layers on SiC: effect of the substrate. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 126805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Cao, T.; Cellini, F.; Berger, C.; de Heer, W.A.; Tosatti, E.; Riedo, E.; Bongiorno, A. Ultrahard carbon film from epitaxial graphene. Nature Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ridene, M.; Najafi, A.; Flipse, K. Origin of Room-Temperature Ferromagnetism in Hydrogenated Epitaxial Graphene on Silicon Carbide. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020228
Ridene M, Najafi A, Flipse K. Origin of Room-Temperature Ferromagnetism in Hydrogenated Epitaxial Graphene on Silicon Carbide. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(2):228. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020228
Chicago/Turabian StyleRidene, Mohamed, Ameneh Najafi, and Kees Flipse. 2019. "Origin of Room-Temperature Ferromagnetism in Hydrogenated Epitaxial Graphene on Silicon Carbide" Nanomaterials 9, no. 2: 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020228
APA StyleRidene, M., Najafi, A., & Flipse, K. (2019). Origin of Room-Temperature Ferromagnetism in Hydrogenated Epitaxial Graphene on Silicon Carbide. Nanomaterials, 9(2), 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020228




