A Self-Powered Six-Axis Tactile Sensor by Using Triboelectric Mechanism
Abstract
1. Introduction
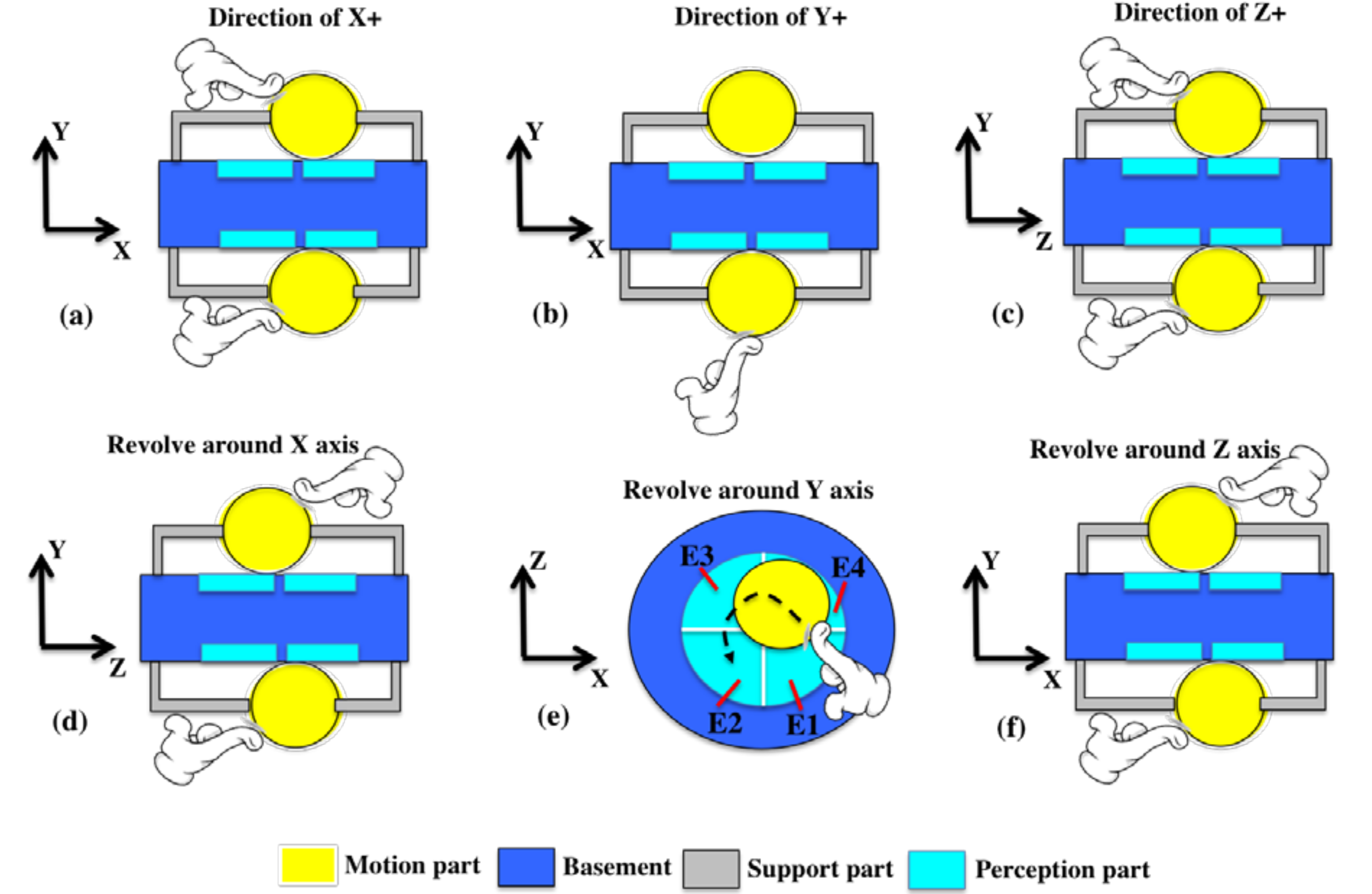
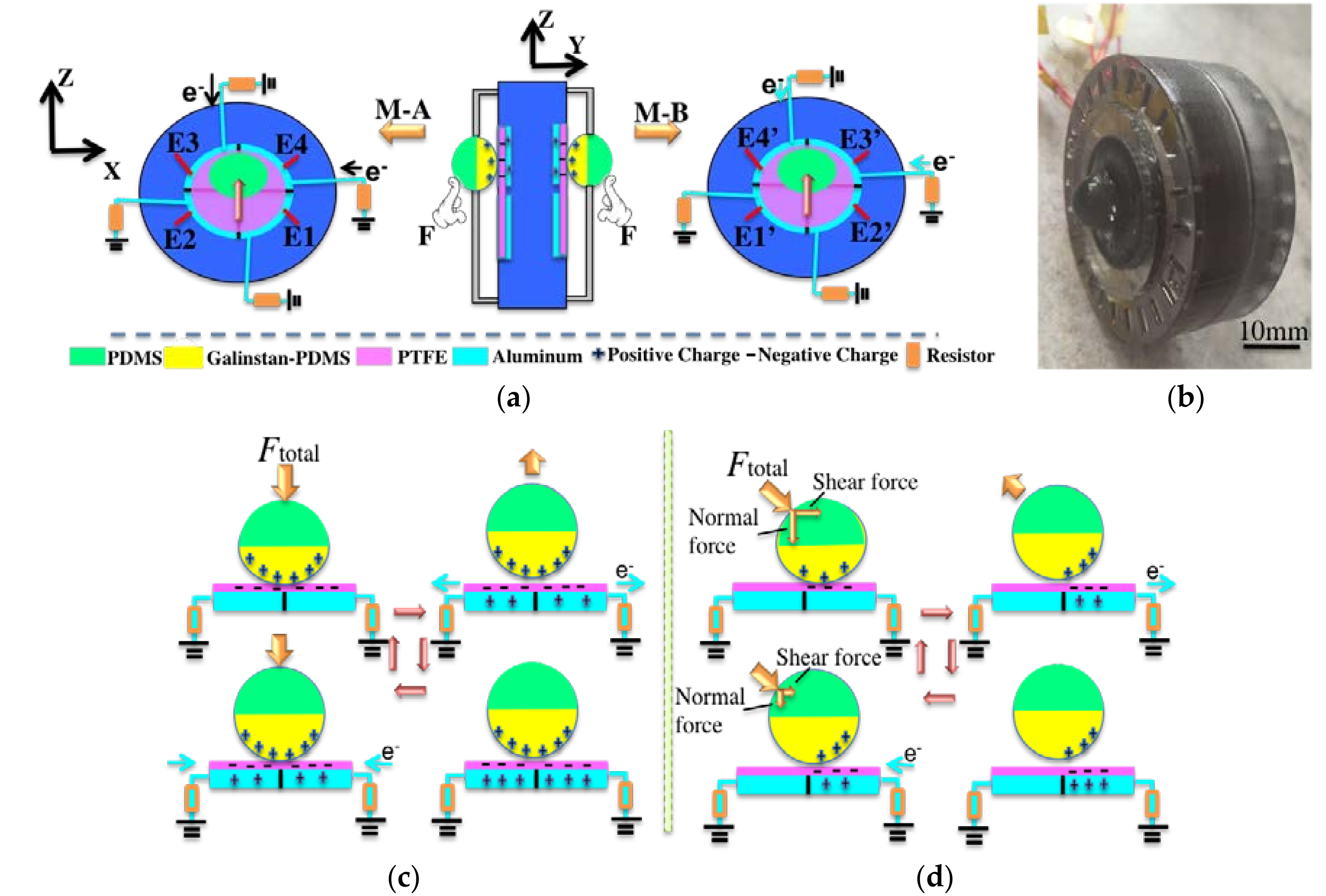
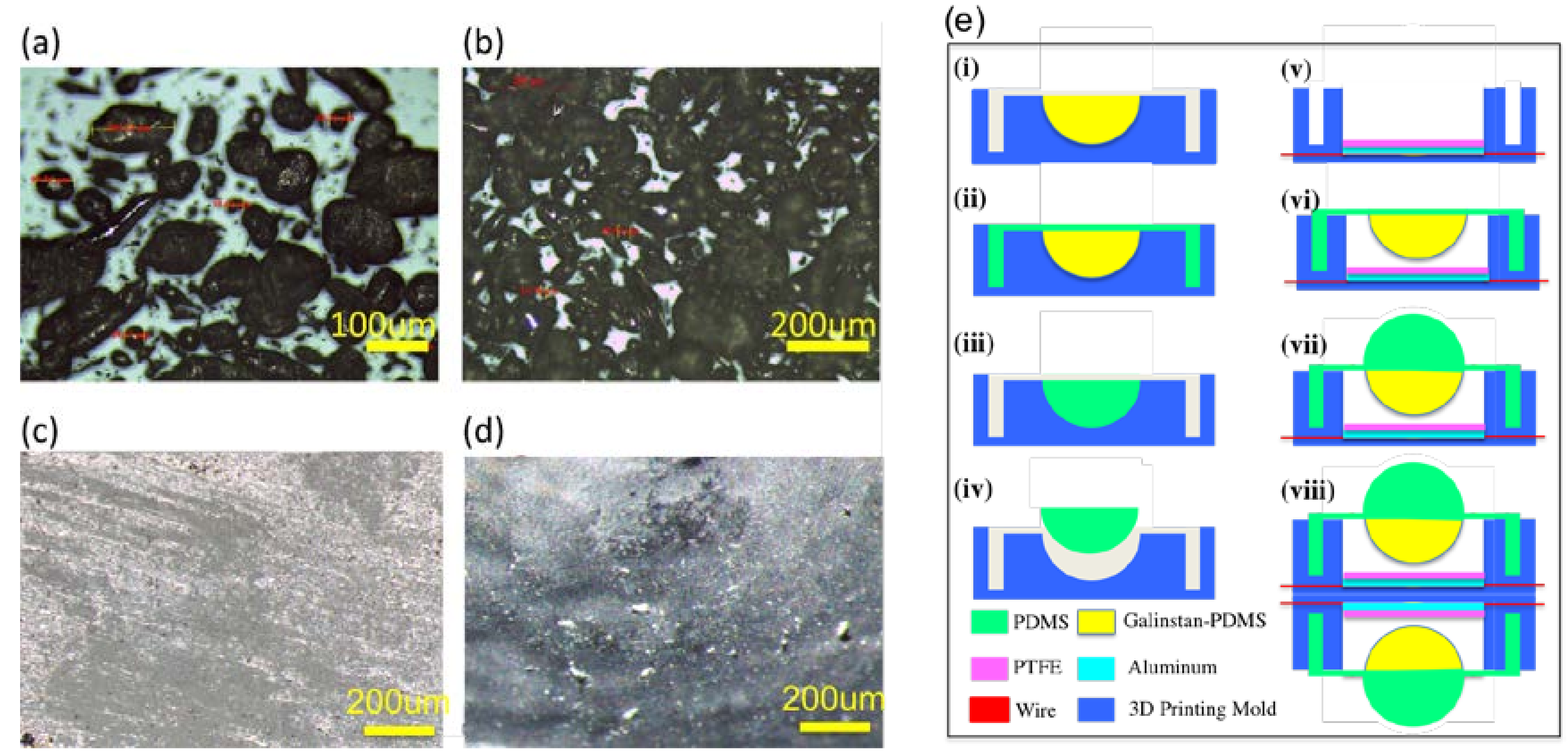
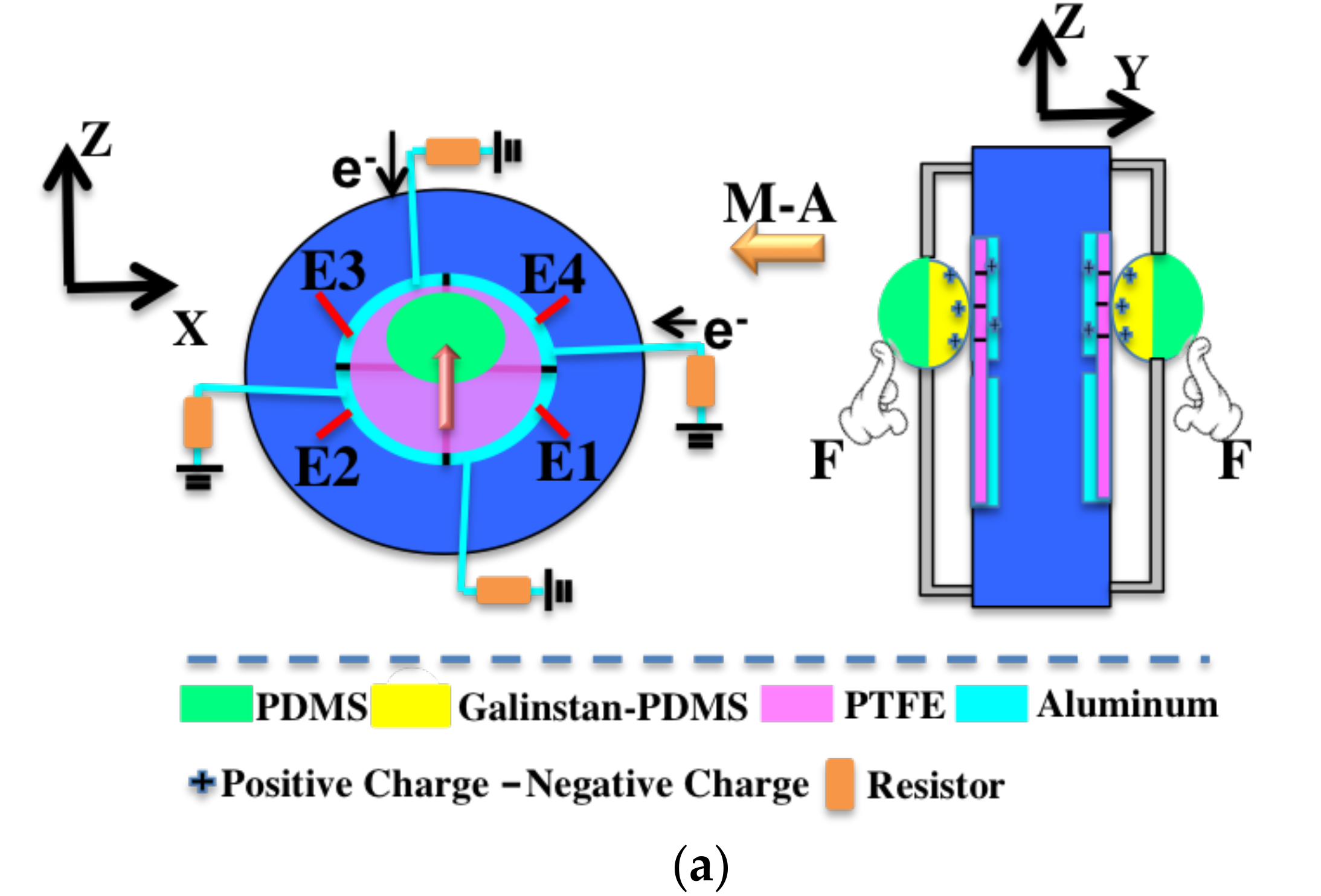
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussions
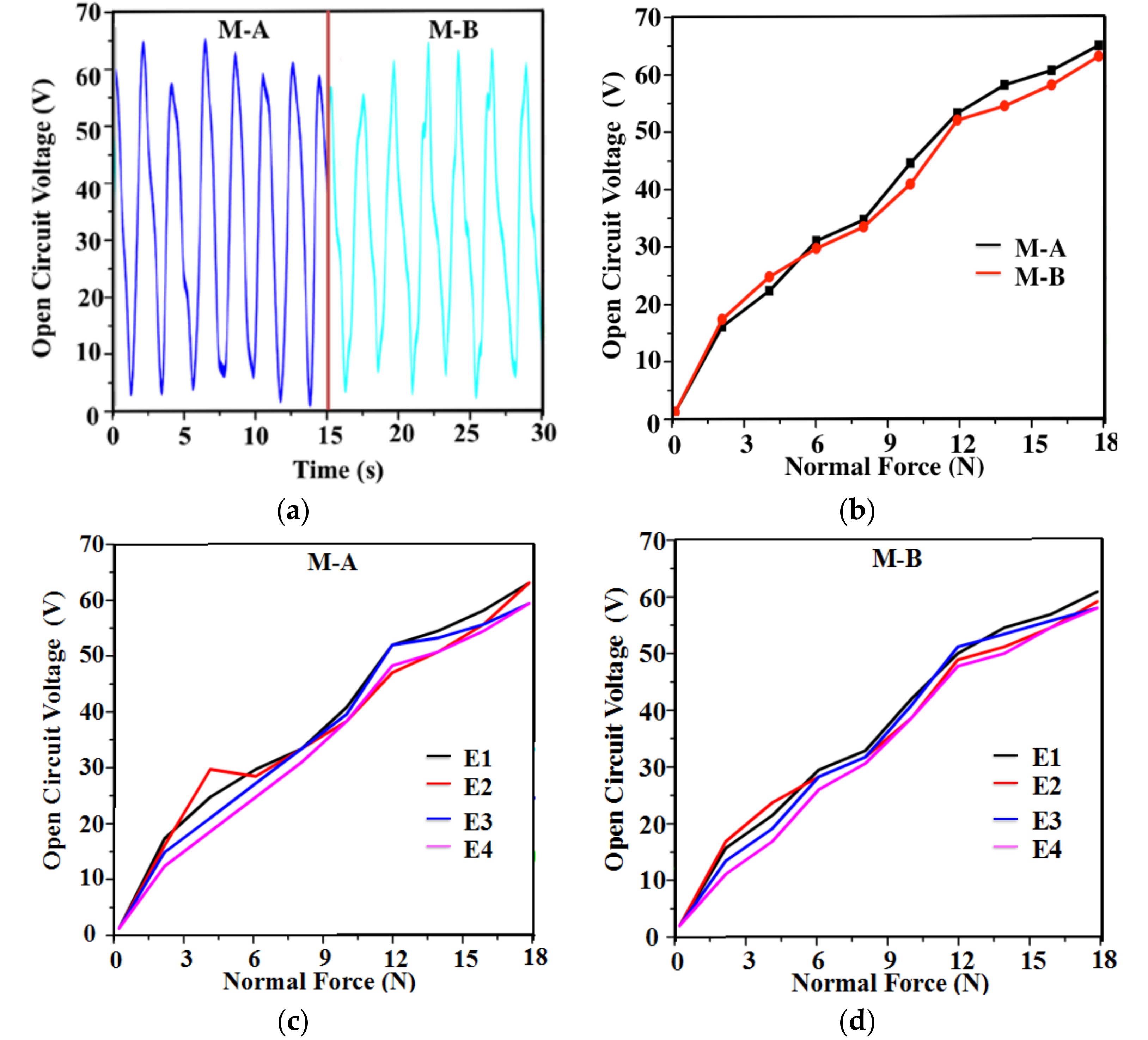
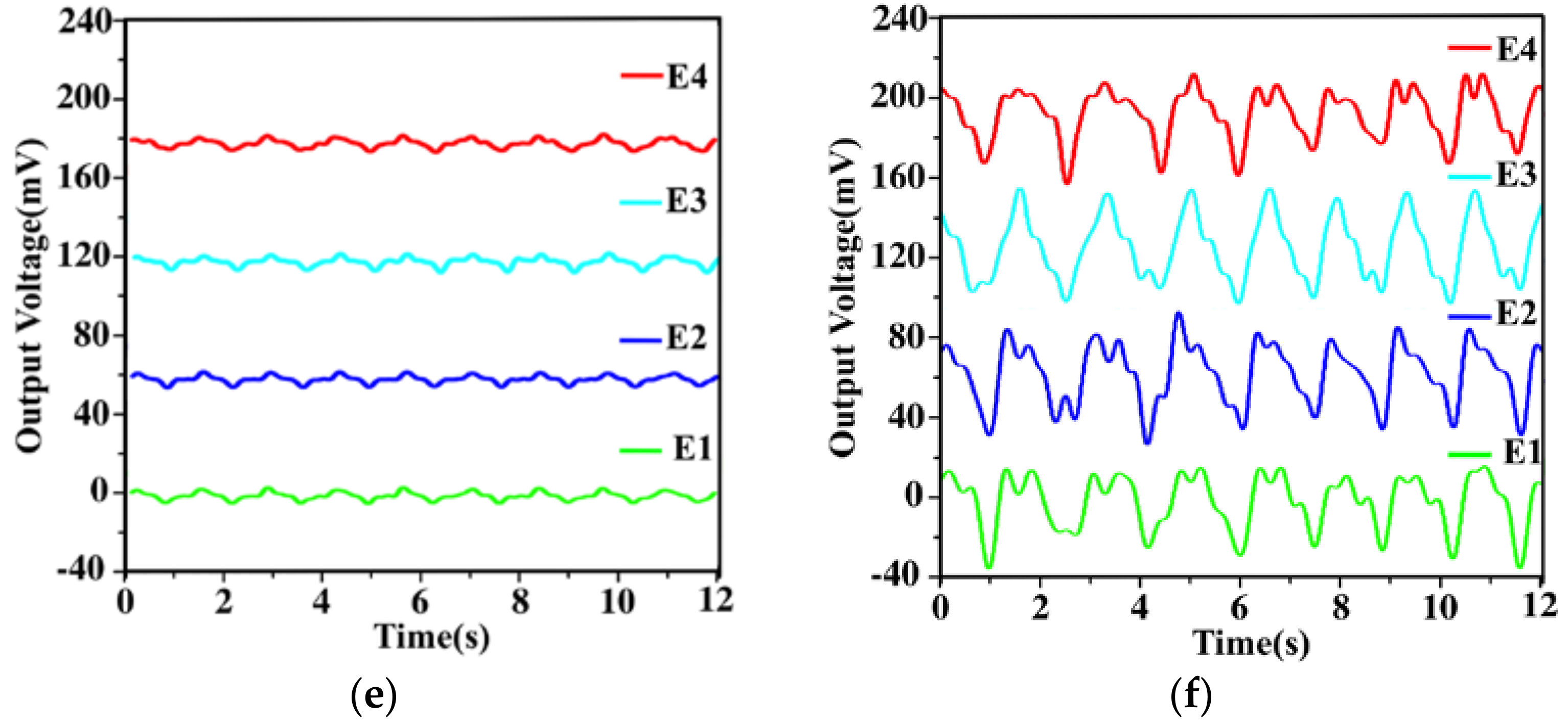
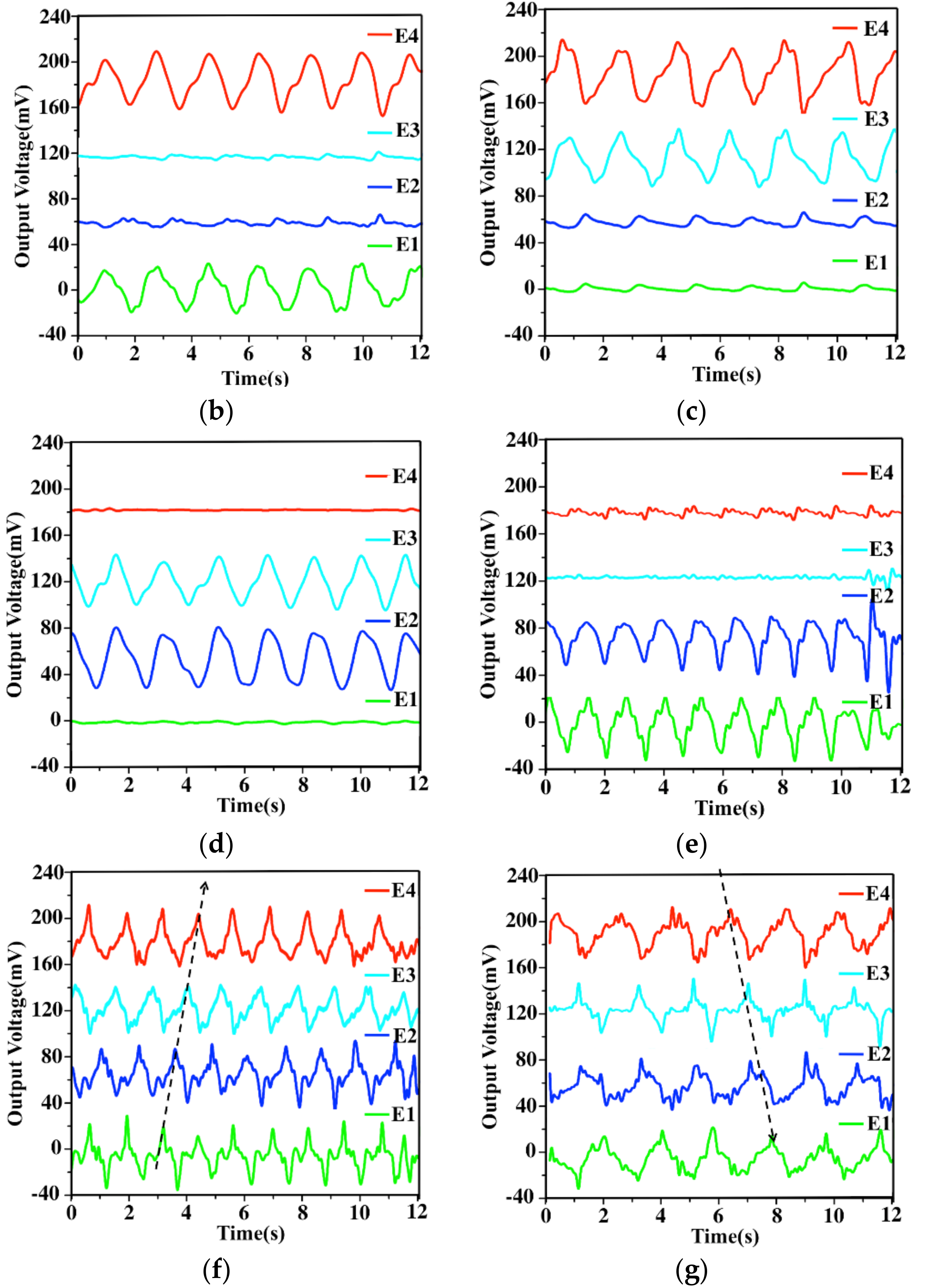
3.1. Detection of Normal Force
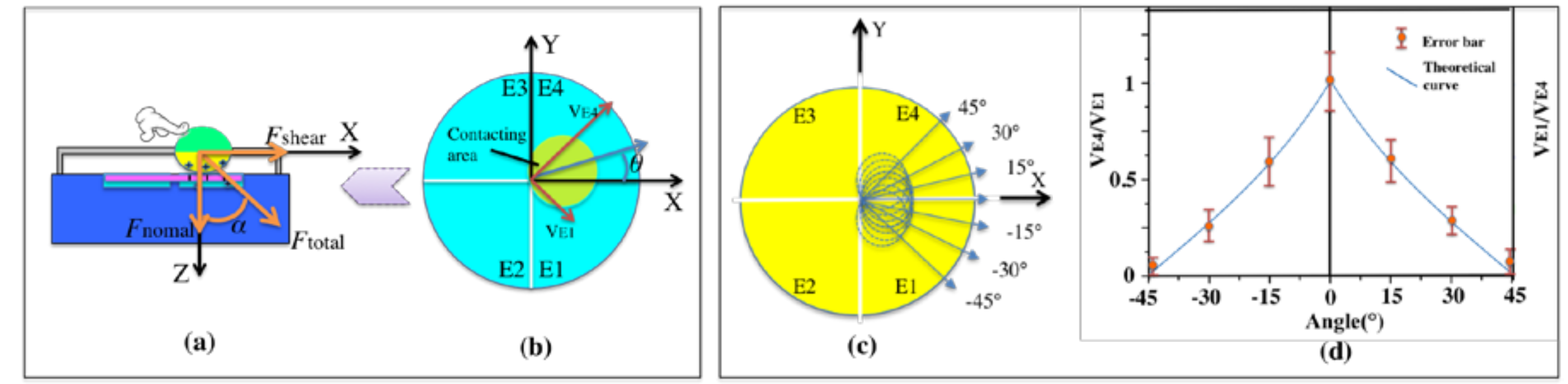
3.2. Detection of Shear Force
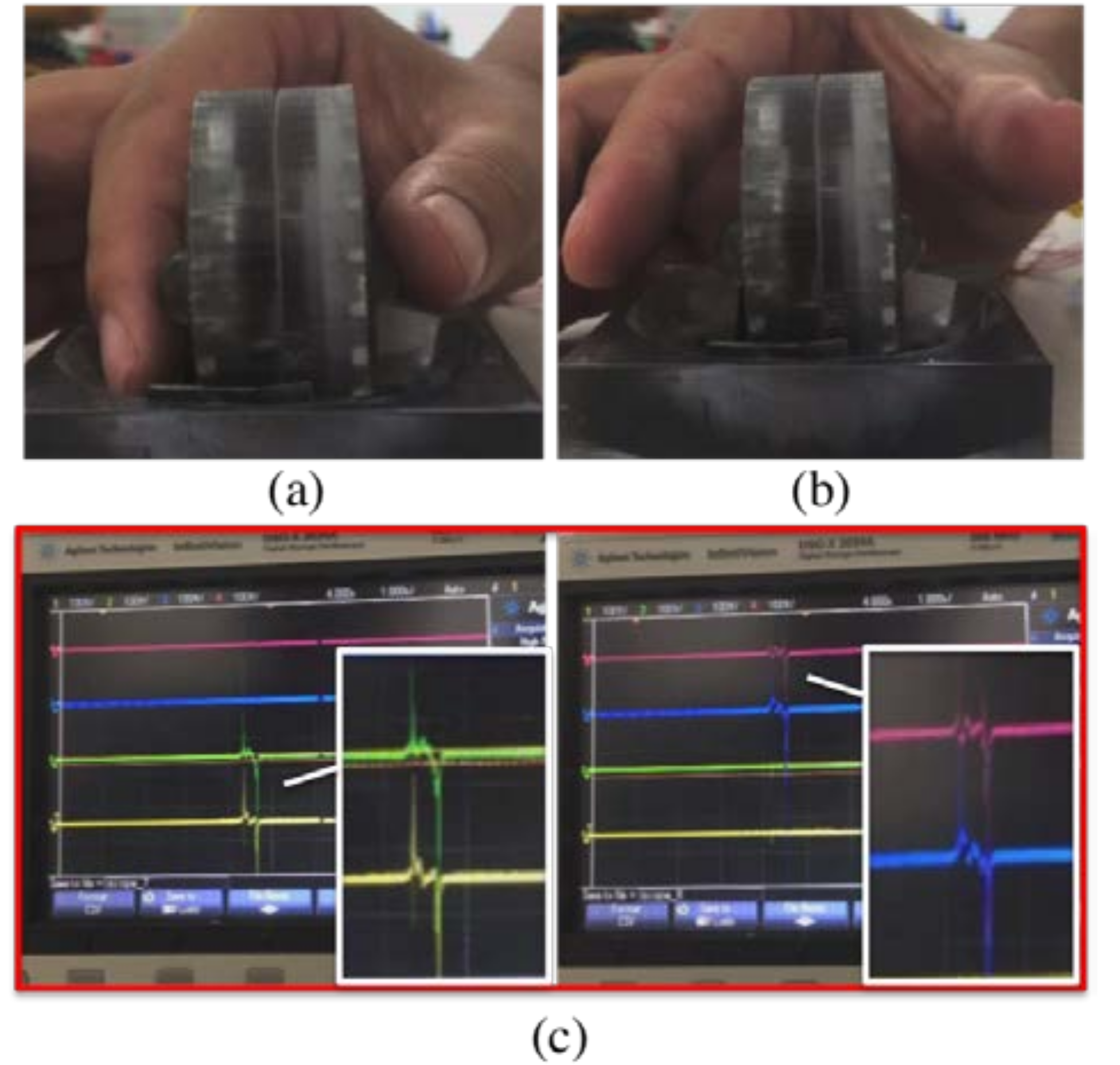
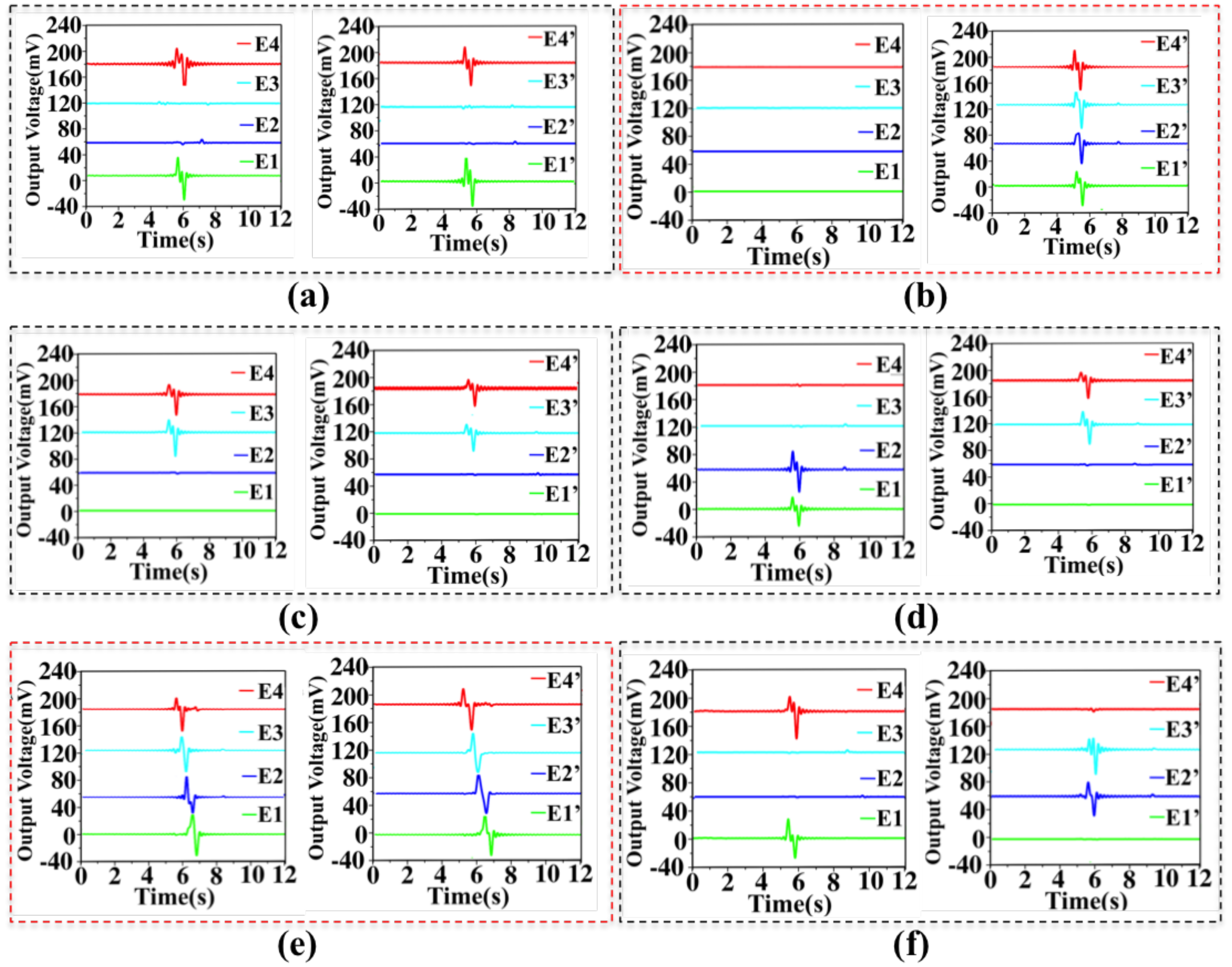
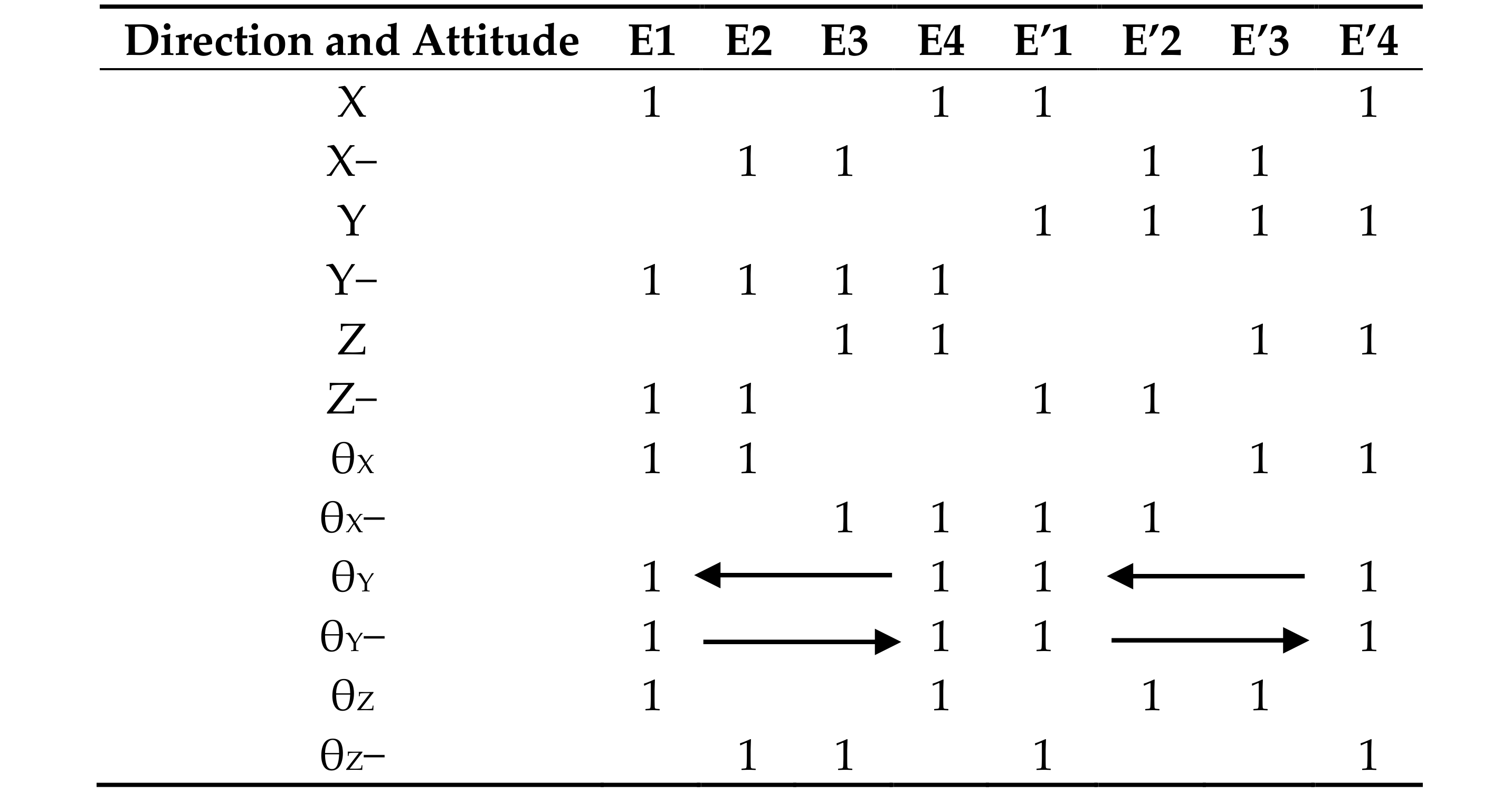
3.3. Characterization of Six-Axis Attitude Detecting
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baytekin, H.T.; Patashinski, A.Z.; Branicki, M.; Baytekin, B.; Soh, S.; Grzybowski, B.A. The mosaic of surface charge in contact electrification. Science 2011, 333, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schein, L.B. Applied physics. Recent progress and continuing puzzles in electrostatics. Science 2006, 316, 1572–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgo, T.A.L.; Ducati, T.R.D.; Francisco, K.R.; Clinckspoor, K.J.; Galembeck, F.; Galembeck, S.E. Triboelectricity: Macroscopic charge patterns formed by self-arraying ions on polymer surfaces. Langmuir 2012, 28, 7407–7416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzybowski, B.A.; Winkleman, A.; Wiles, J.A.; Brumer, Y.; Whitesides, G.M. Electrostatic self-assembly of macroscopic crystals using contact electrification. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Ji, Z.; Xu, H.; Sun, M.; Chen, T.; Sun, L.; Chen, G.; Wang, Z. Large-Scale and Flexible Self-Powered Triboelectric Tactile Sensing Array for Sensitive Robot Skin. Polymers 2017, 9, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.R.; Lin, L.; Zhu, G.; Wu, W.Z.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Z.L. Transparent triboelectric nanogenerators and self-powered pressure sensors based on micropatterned plastic films. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 3109–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lin, Z.H.; Zhou, Y.S.; Jing, Q.; Su, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Hu, C.; Wang, Z.L. Human skin based triboelectric nanogenerators for harvesting biomechanical energy and as self-powered active tactile sensor system. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 9213–9222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Miao, L.; Song, Y.; Su, Z.; Chen, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H. High Efficiency Energy Management and Charge Boosting Strategy for a Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2017, 38, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Su, Z.; Song, Y.; Cheng, X.; Meng, B.; Song, Z.; Chen, D.; Zhang, H. Omnidirectional Bending & Pressure Sensor based on Stretchable CNT-PU sponge. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 27, 1604434. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.H.; Sheshadri, S.; Xiang, Z.; Martinez, I.D.; Xue, N.; Sun, T.; Thakor, N.V.; Yen, S.C.; Lee, C. Selective stimulation and neural recording on peripheral nerves using flexible split ring electrodes. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 242, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Shi, Q.; Cheng, S.; Thakor, N.V.; Lee, C. Battery-Free Neuromodulator for Peripheral Nerve Direct Stimulation. Nano Energy 2018, 50, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Pan, C.F.; Guo, W.X.; Chen, C.; Zhou, Y.S.; Yu, R.M.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric-generator-driven pulse electrodeposition for micropatterning. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 4960–4965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Koh, K.H.; Lee, C. Ultra-wide frequency broadening mechanism for micro-scale electromagnetic energy harvester. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, R175–R195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.W.; Zhang, Q.; Fan, F.R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.H.; Hu, B.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhou, J. Finger typing driven triboelectric nanogenerator and its use for instantaneously lighting up LEDs. Nano Energy 2012, 2, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Wang, H.; Shi, Q.; Dhakar, L.; Wang, J.; Thakor, N.V.; Yen, S.C.; Lee, C. Development of battery-free neural interface and modulated control of tibialis anterior muscle via common peroneal nerve based on triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs). Nano Energy 2017, 33, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, F.A.; Mogan, R.P.; Gammad, G.G.L.; Wang, H.; Yen, S.C.; Thakor, N.V.; Lee, C. Toward a Self-Control System for a Neurogenic Underactive Bladder—A Triboelectric Nanogenerator Sensor Integrated with a Bi-Stable Micro-Actuator. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 3487–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Tao, C.; Fan, X.; Chen, J. Progress in triboelectric nanogenerators as self-powered smart sensors. J. Mater. Res. 2017, 32, 1628–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Chen, J.; Lin, L. Progress in triboelectric nanogenerators as a new energy technology and self-powered sensors. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 2250–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, L.; Sun, H.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X.; Luo, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, T. Porous Ionic Membrane Based Flexible Humidity Sensor and its Multifunctional Applications. Adv. Sci. 2017, 4, 1600404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wu, H.; Hasan, D.; He, T.; Shi, Q.; Lee, C. Self-Powered Dual-Mode Amenity Sensor Based on the Water-Air Triboelectric Nanogenerator. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 10337–10346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhong, X.; Yi, F.; Yu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Electret film-enhanced triboelectric nanogenerator matrix for self-powered instantaneous tactile imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 3680–3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, D. The Internet of Things: How the Next Evolution of the Internet Is Changing Everything; CISCO White Paper; CISCO Internet Business Solutions Group (IBSG): San Jose, CA, USA, 2011; p. 11. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.; Xie, Y.; Wang, S.; Wu, W.; Niu, S.; Wen, X.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric active sensor array for self-powered static and dynamic pressure detection and tactile imaging. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 8266–8274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.S.; Zhu, G.; Niu, S.; Liu, Y.; Bai, P.; Jing, Q.; Wang, Z.L. Nanometer resolution self-powered static and dynamic motion sensor based on micro-grated triboelectrification. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 1719–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, Q.; Zhu, G.; Wu, W.; Bai, P.; Xie, Y.; Han, R.P.; Wang, Z.L. Self-powered triboelectric velocity sensor for dual-mode sensing of rectified linear and rotary motions. Nano Energy 2014, 10, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Xia, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, H.; Sun, L.; Lee, C. A Hybrid Flapping-Blade Wind Energy Harvester Based on Vortex Shedding Effect. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2016, 25, 845–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Wang, S.; Niu, S.; Liu, C.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Noncontact free-rotating disk triboelectric nanogenerator as a sustainable energy harvester and self-powered mechanical sensor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 3031–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.S.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Lee, S.; Wang, Z.L. A single-electrode based triboelectric nanogenerator as self-powered tracking system. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 6594–6601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Yang, W.Q.; Zhang, T.; Jing, Q.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.S.; Bai, P.; Wang, Z.L. Self-powered, ultrasensitive, flexible tactile sensors based on contact electrification. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 3208–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Q.; Wang, H.; Wu, H.; Lee, C. Self-powered triboelectric nanogenerator buoy ball for applications ranging from environment monitoring to water wave energy farm. Nano Energy 2017, 40, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Li, T.; Gu, Y.; Luo, H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, T. Fingerprint-Inspired Flexible Tactile Sensor for Accurately Discerning Surface Texture. Small 2018, 14, 1703902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Liu, L.; Wu, G.; Chen, W.; Qin, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, T. Self-Powered UV–Near Infrared Photodetector Based on Reduced Graphene Oxide/n-Si Vertical Heterojunction. Small 2016, 12, 5019–5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, F.; Lin, L.; Niu, S.; Yang, J.; Wu, W.; Wang, S.; Liao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Self-Powered Trajectory, Velocity, and Acceleration Tracking of a Moving Object/Body using a Triboelectric Sensor. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 7488–7494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, T.; Lee, C. Self-powered liquid triboelectric microfluidic sensor for pressure sensing and finger motion monitoring applications. Nano Energy 2016, 30, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, B.; Tang, W.; Too, Z.H.; Zhang, X.; Han, M.; Liu, W.; Zhang, H. A transparent single-friction-surface triboelectric generator and self-powered touch sensor. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 3235–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, J.; Guo, H.; Fan, X.; Wen, Z.; Yeh, M.H.; Yu, C.; Cao, X.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectrification-Enabled Self-Powered Detection and Removal of Heavy Metal Ions in Wastewater. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 2983–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, W.; Yu, R.; He, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Theoretical Study of Triboelectric-Potential Gated/Driven Metal–Oxide–Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 4395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Duan, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Dong, G.; Wang, Z.L. Flexible Organic Tribotronic Transistor Memory for a Visible and Wearable Touch Monitoring System. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Q.; Wu, H.; Wang, H.; Wu, H.C.; Lee, C. Self-Powered Gyroscope Ball Using Triboelectric Mechanism. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1701300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric nanogenerators as new energy technology and self-powered sensors—Principles, problems and perspectives. Faraday Discuss. 2015, 176, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Zi, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhang, S.L.; Wang, J.; Ding, W.; Zou, H.; Zhang, W.; Lu, C.; Wang, Z.L. An ultrathin paper-based self-powered system for portable electronics and wireless human-machine interaction. Nano Energy 2017, 39, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jiang, R.; Li, G.; Chen, Y.; Tang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, H.; Zhi, C. Flexible Dual-Mode Tactile Sensor Derived from Three-Dimensional Porous Carbon Architecture. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 22685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhou, F. Solid-liquid triboelectrification in smart U-tube for multifunctional sensors. Nano Energy 2017, 40, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassler, A.; Majidi, C. Liquid-phase metal inclusions for a conductive polymer composite. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 1928–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameter Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Radius of sphere | 5 × 10−3 m |
| Radius of electrodes | 10 × 10−3 m |
| Gap between electrodes | 1 × 10−3 m |
| Spacing between PTFE and sphere | 2 × 10−3 m |
| Diameter of integral sensor | 50 × 10−3 m |
| Thickness of integral sensor | 32 × 10−3 m |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, T.; Shi, Q.; Yang, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Sun, L.; Lee, C. A Self-Powered Six-Axis Tactile Sensor by Using Triboelectric Mechanism. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8070503
Chen T, Shi Q, Yang Z, Liu J, Liu H, Sun L, Lee C. A Self-Powered Six-Axis Tactile Sensor by Using Triboelectric Mechanism. Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(7):503. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8070503
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Tao, Qiongfeng Shi, Zhan Yang, Jinchang Liu, Huicong Liu, Lining Sun, and Chengkuo Lee. 2018. "A Self-Powered Six-Axis Tactile Sensor by Using Triboelectric Mechanism" Nanomaterials 8, no. 7: 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8070503
APA StyleChen, T., Shi, Q., Yang, Z., Liu, J., Liu, H., Sun, L., & Lee, C. (2018). A Self-Powered Six-Axis Tactile Sensor by Using Triboelectric Mechanism. Nanomaterials, 8(7), 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8070503









